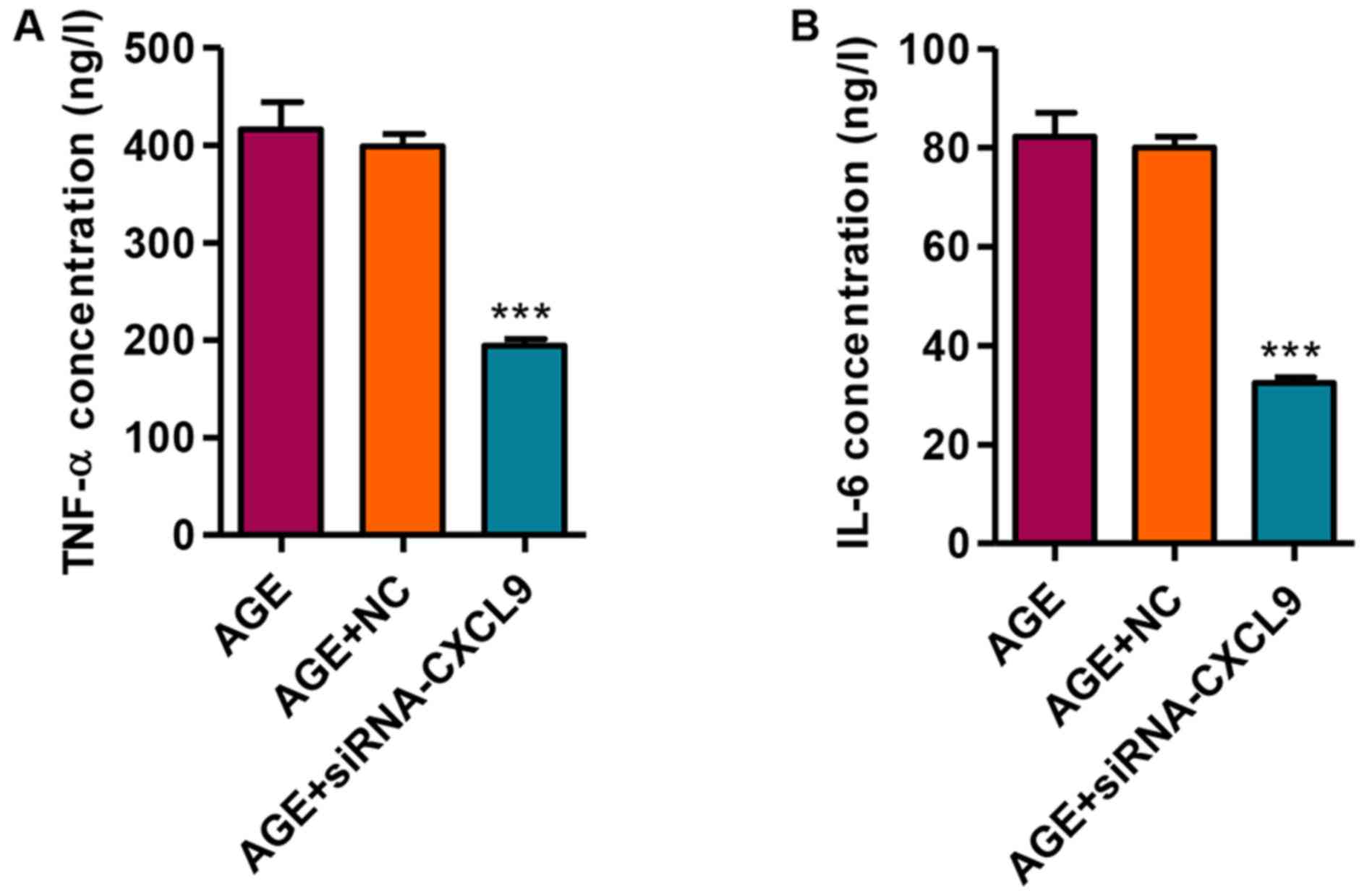
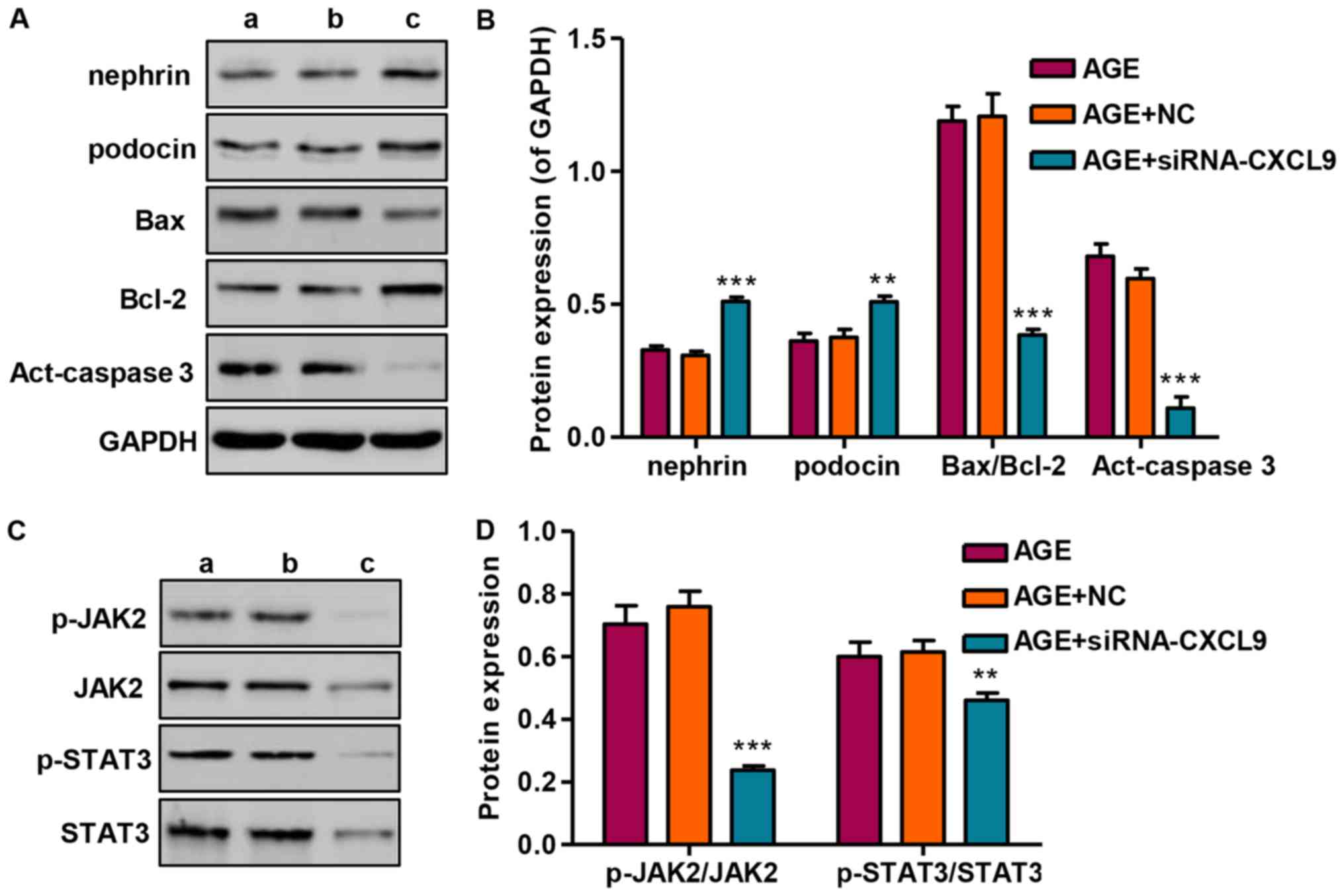
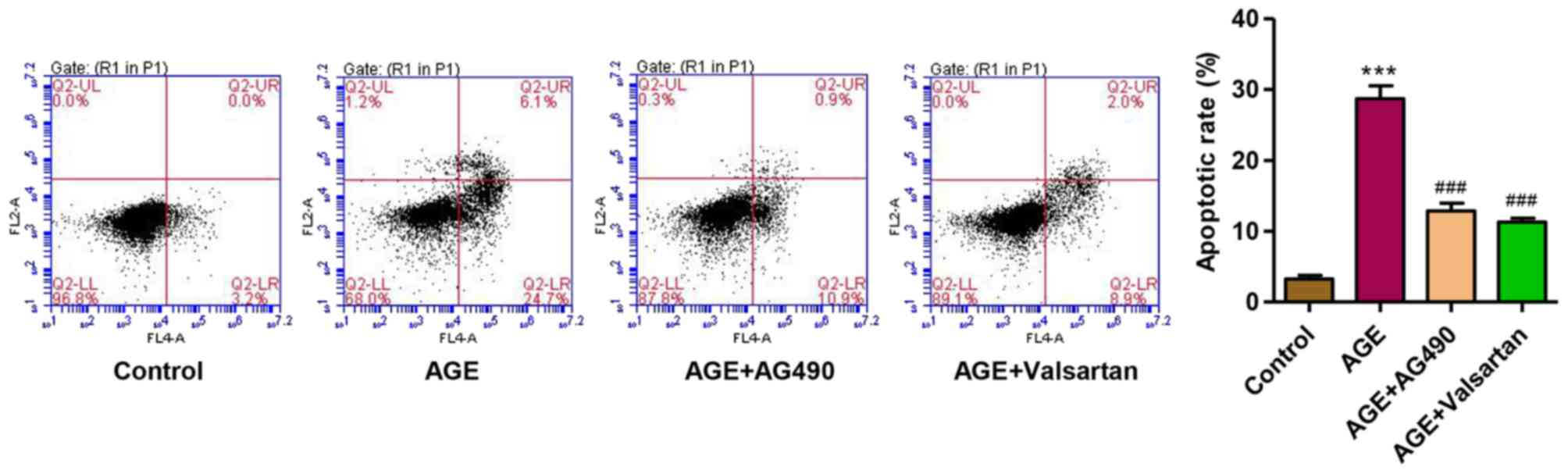
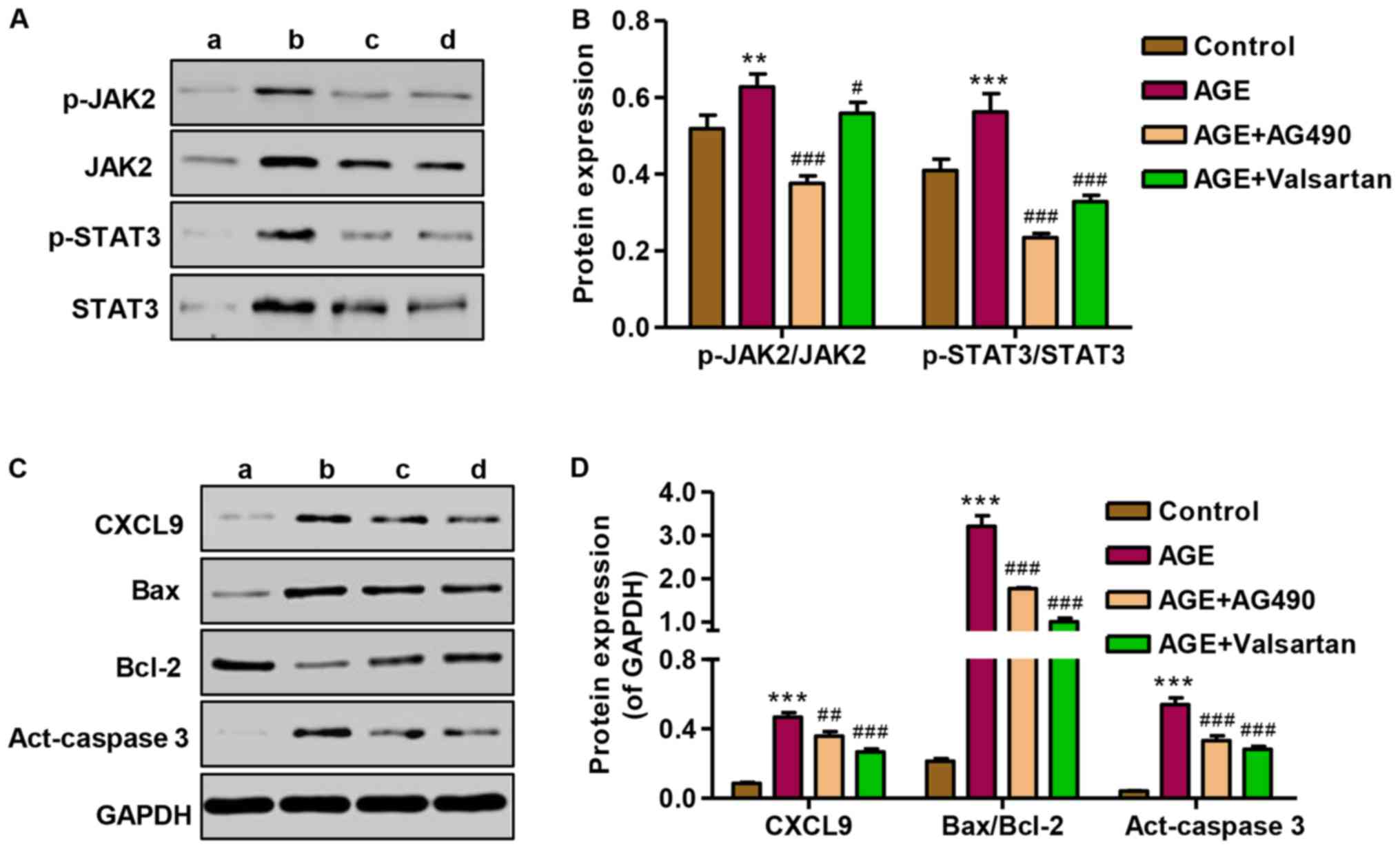
|
1
|
Remuzzi G, Schieppati A and Ruggenenti P:
Clinical practice. Nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. N
Engl J Med. 346:1145–1151. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yamagishi S and Matsui T: Advanced
glycation end products, oxidative stress and diabetic nephropathy.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 3:101–108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Susztak K, Raff AC, Schiffer M and
Böttinger EP: Glucose-induced reactive oxygen species cause
apoptosis of podocytes and podocyte depletion at the onset of
diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 55:225–233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Navarro-González JF, Mora-Fernández C,
Muros de Fuentes M and García-Pérez J: Inflammatory molecules and
pathways in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 7:327–340. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Koike N, Takamura T and Kaneko S:
Induction of reactive oxygen species from isolated rat glomeruli by
protein kinase C activation and TNF-α stimulation, and effects of a
phosphodiesterase inhibitor. Life Sci. 80:1721–1728. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dalla Vestra M, Mussap M, Gallina P,
Bruseghin M, Cernigoi AM, Saller A, Plebani M and Fioretto P:
Acute-phase markers of inflammation and glomerular structure in
patients with type 2 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16(Suppl 1):
S78–S82. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lim AK and Tesch GH: Inflammation in
diabetic nephropathy. Mediators Inflamm. 2012:1461542012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yamagishi S and Imaizumi T: Diabetic
vascular complications: Pathophysiology, biochemical basis and
potential therapeutic strategy. Curr Pharm Des. 11:2279–2299. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bohlender JM, Franke S, Stein G and Wolf
G: Advanced glycation end products and the kidney. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 289:F645–F659. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Busch M, Franke S, Rüster C and Wolf G:
Advanced glycation end-products and the kidney. Eur J Clin Invest.
40:742–755. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cheng C, Zheng Z, Shi C, Liu X, Ye Z and
Lou T: Advanced glycation end-products reduce podocyte adhesion by
activating the renin-angiotensin system and increasing
integrin-linked kinase. Exp Ther Med. 6:1494–1498. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Menke J, Zeller GC, Kikawada E, Means TK,
Huang XR, Lan HY, Lu B, Farber J, Luster AD and Kelley VR: CXCL9,
but not CXCL10, promotes CXCR3-dependent immune-mediated kidney
disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 19:1177–1189. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang K, Wu YG, Su J, Zhang JJ, Zhang P and
Qi XM: Total glucosides of paeony regulates JAK2/STAT3 activation
and macrophage proliferation in diabetic rat kidneys. Am J Chin
Med. 40:521–536. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Banes AK, Shaw S, Jenkins J, Redd H, Amiri
F, Pollock DM and Marrero MB: Angiotensin II blockade prevents
hyperglycemia-induced activation of JAK and STAT proteins in
diabetic rat kidney glomeruli. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
286:F653–F659. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang X, Shaw S, Amiri F, Eaton DC and
Marrero MB: Inhibition of the Jak/STAT signaling pathway prevents
the high glucose-induced increase in tgf-beta and fibronectin
synthesis in mesangial cells. Diabetes. 51:3505–3509. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiao B, Wang YS, Cheng YN, Gao JJ and
Zhang QZ: Valsartan attenuated oxidative stress, decreased MCP-1
and TGF-β1 expression in glomerular mesangial and epithelial cells
induced by high-glucose levels. Biosci Trends. 5:173–181. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chung AC and Lan HY: Chemokines in renal
injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22:802–809. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Higurashi M, Ohya Y, Joh K, Muraguchi M,
Nishimura M, Terawaki H, Yagui K, Hashimoto N, Saito Y and Yamada
K: Increased urinary levels of CXCL5, CXCL8 and CXCL9 in patients
with type 2 diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Complications.
23:178–184. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Galler A, Müller G, Schinzel R, Kratzsch
J, Kiess W and Münch G: Impact of metabolic control and serum
lipids on the concentration of advanced glycation end products in
the serum of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes, as
determined by fluorescence spectroscopy and
nepsilon-(carboxymethyl)lysine ELISA. Diabetes Care. 26:2609–2615.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Genuth S, Sun W, Cleary P, Sell DR, Dahms
W, Malone J, Sivitz W and Monnier VM: Glycation and
carboxymethyllysine levels in skin collagen predict the risk of
future 10-year progression of diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy
in the diabetes control and complications trial and epidemiology of
diabetes interventions and complications participants with type 1
diabetes. Diabetes. 54:3103–3111. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Siu B, Saha J, Smoyer WE, Sullivan KA and
Brosius FC III: Reduction in podocyte density as a pathologic
feature in early diabetic nephropathy in rodents: Prevention by
lipoic acid treatment. BMC Nephrol. 7:62006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dai C, Stolz DB, Kiss LP, Monga SP,
Holzman LB and Liu Y: Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes podocyte
dysfunction and albuminuria. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:1997–2008. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen Y, Liu CP, Xu KF, Mao XD, Lu YB, Fang
L, Yang JW and Liu C: Effect of taurine-conjugated ursodeoxycholic
acid on endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis induced by
advanced glycation end products in cultured mouse podocytes. Am J
Nephrol. 28:1014–1022. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chuang PY, Yu Q, Fang W, Uribarri J and He
JC: Advanced glycation endproducts induce podocyte apoptosis by
activation of the FOXO4 transcription factor. Kidney Int.
72:965–976. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Holdsworth SR and Tipping PG: Leukocytes
in glomerular injury. Semin Immunopathol. 29:355–374. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zychowska M, Rojewska E, Pilat D and Mika
J: The role of some chemokines from the CXC subfamily in a mouse
model of diabetic neuropathy. J Diabetes Res. 2015:7501822015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang JS, Lee YH, Chuang LY, Guh JY and
Hwang JY: Cinnamaldehyde and nitric oxide attenuate advanced
glycation end products - induced the JAK/STAT signaling in human
renal tubular cells. J Cell Biochem. 116:1028–1038. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ho HH and Ivashkiv LB: Role of STAT3 in
type I interferon responses. Negative regulation of STAT1-dependent
inflammatory gene activation. J Biol Chem. 281:14111–14118. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xie M, Mustovich AT, Jiang Y, Trudeau JB,
Ray A, Ray P, Hu H, Holguin F, Freeman B and Wenzel SE: IL-27 and
type 2 immunity in asthmatic patients: Association with severity,
CXCL9, and signal transducer and activator of transcription
signaling. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 135:386–394. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Navarro JF, Mora C, Muros M and García J:
Urinary tumour necrosis factor-α excretion independently correlates
with clinical markers of glomerular and tubulointerstitial injury
in type 2 diabetic patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 21:3428–3434.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Navarro JF, Milena FJ, Mora C, León C and
García J: Renal pro-inflammatory cytokine gene expression in
diabetic nephropathy: Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme
inhibition and pentoxifylline administration. Am J Nephrol.
26:562–570. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Thomson SC, Deng A, Bao D, Satriano J,
Blantz RC and Vallon V: Ornithine decarboxylase, kidney size, and
the tubular hypothesis of glomerular hyperfiltration in
experimental diabetes. J Clin Invest. 107:217–224. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Saleem MA, Ni L, Witherden I, Tryggvason
K, Ruotsalainen V, Mundel P and Mathieson PW: Co-localization of
nephrin, podocin, and the actin cytoskeleton: Evidence for a role
in podocyte foot process formation. Am J Pathol. 161:1459–1466.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Brosius FC III and Alpers CE: New targets
for treatment of diabetic nephropathy: What we have learned from
animal models. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 22:17–25. 2013.
|
|
35
|
Lu TC, Wang ZH, Feng X, Chuang PY, Fang W,
Shen Y, Levy DE, Xiong H, Chen N and He JC: Knockdown of Stat3
activity in vivo prevents diabetic glomerulopathy. Kidney Int.
76:63–71. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Brosius FC III and He JC: JAK inhibition
and progressive kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens.
24:88–95. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Zhang Y, Chen B, Hou XH, Guan GJ, Liu G,
Liu HY and Li XG: Effects of mycophenolate mofetil, valsartan and
their combined therapy on preventing podocyte loss in early stage
of diabetic nephropathy in rats. Chin Med J (Engl). 120:988–995.
2007.
|