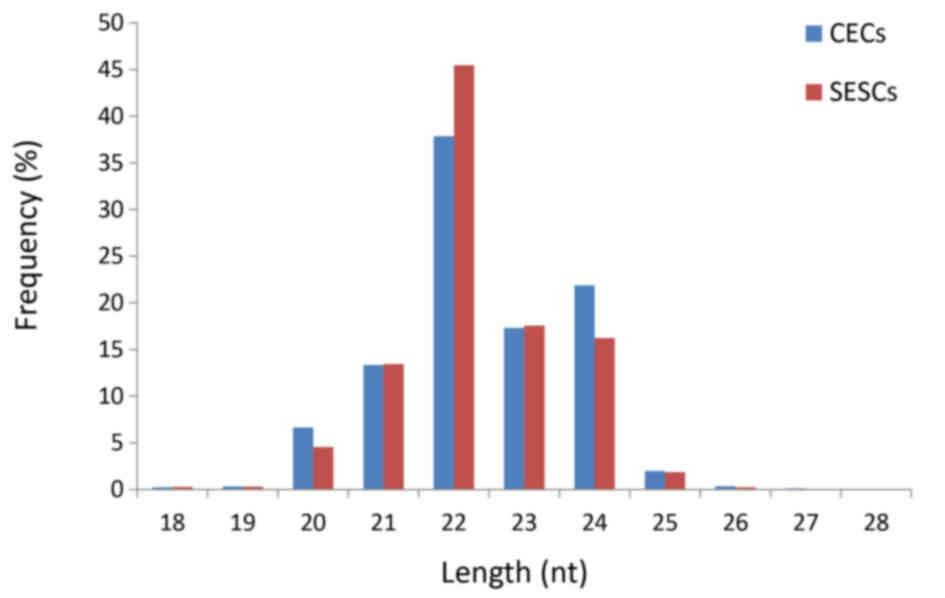
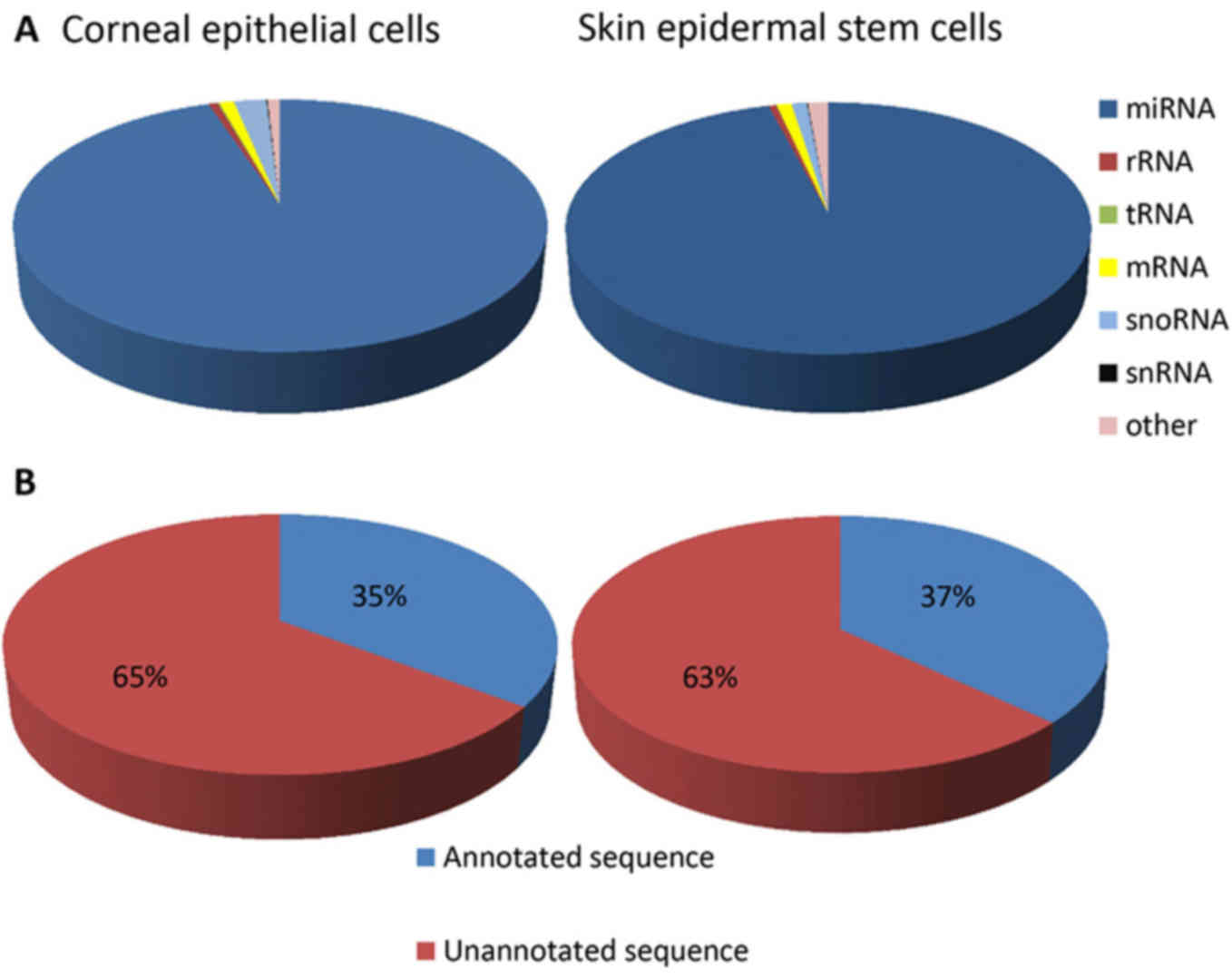
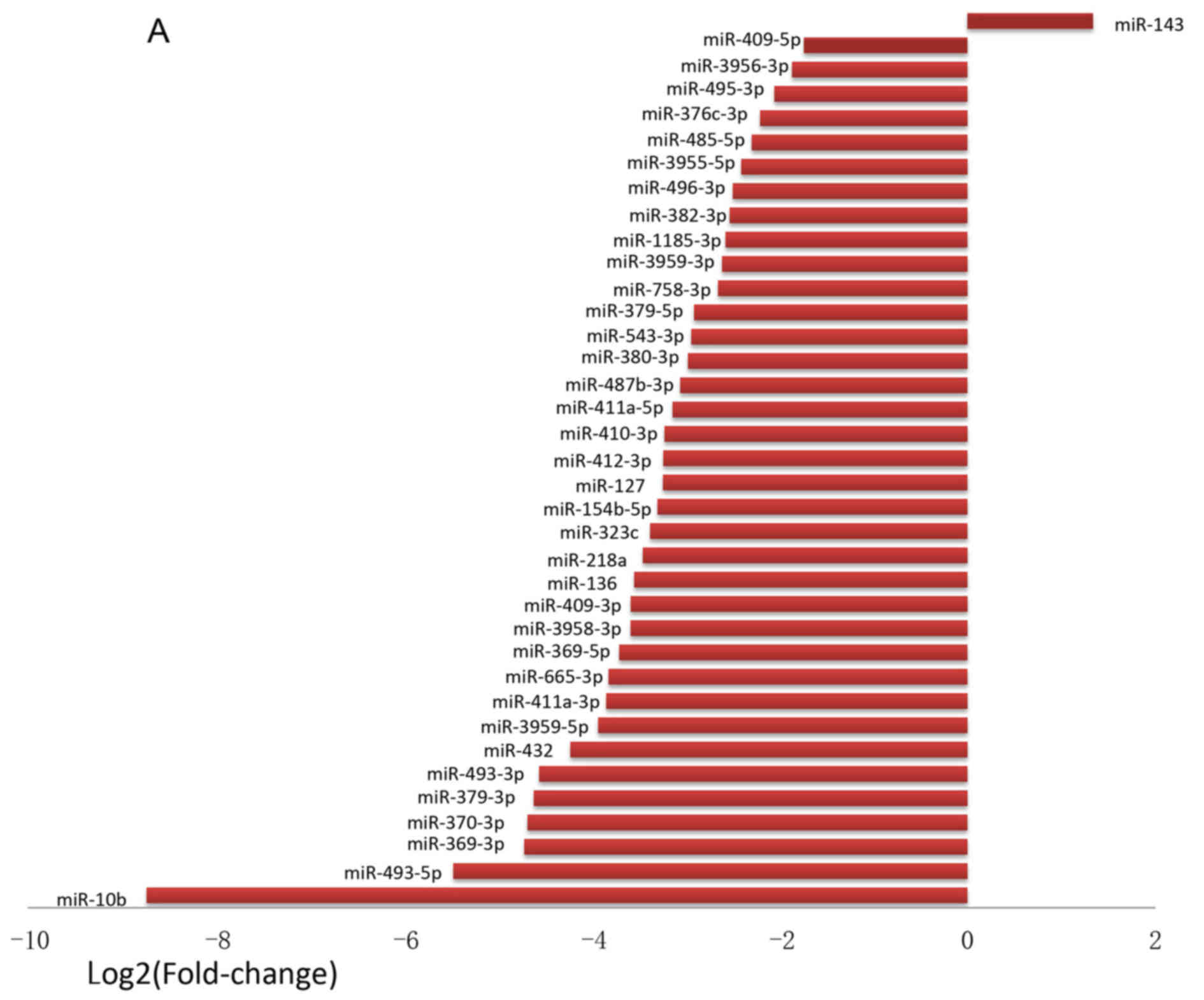
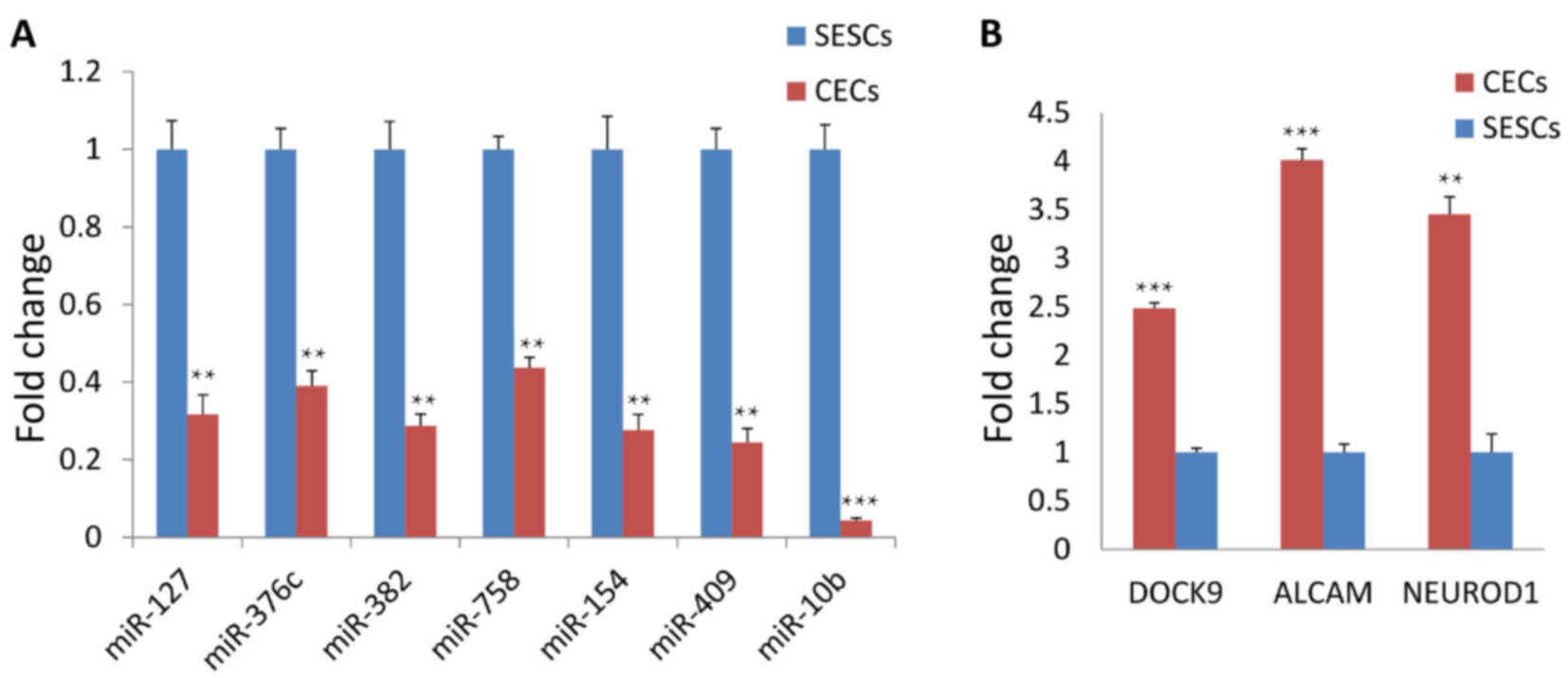
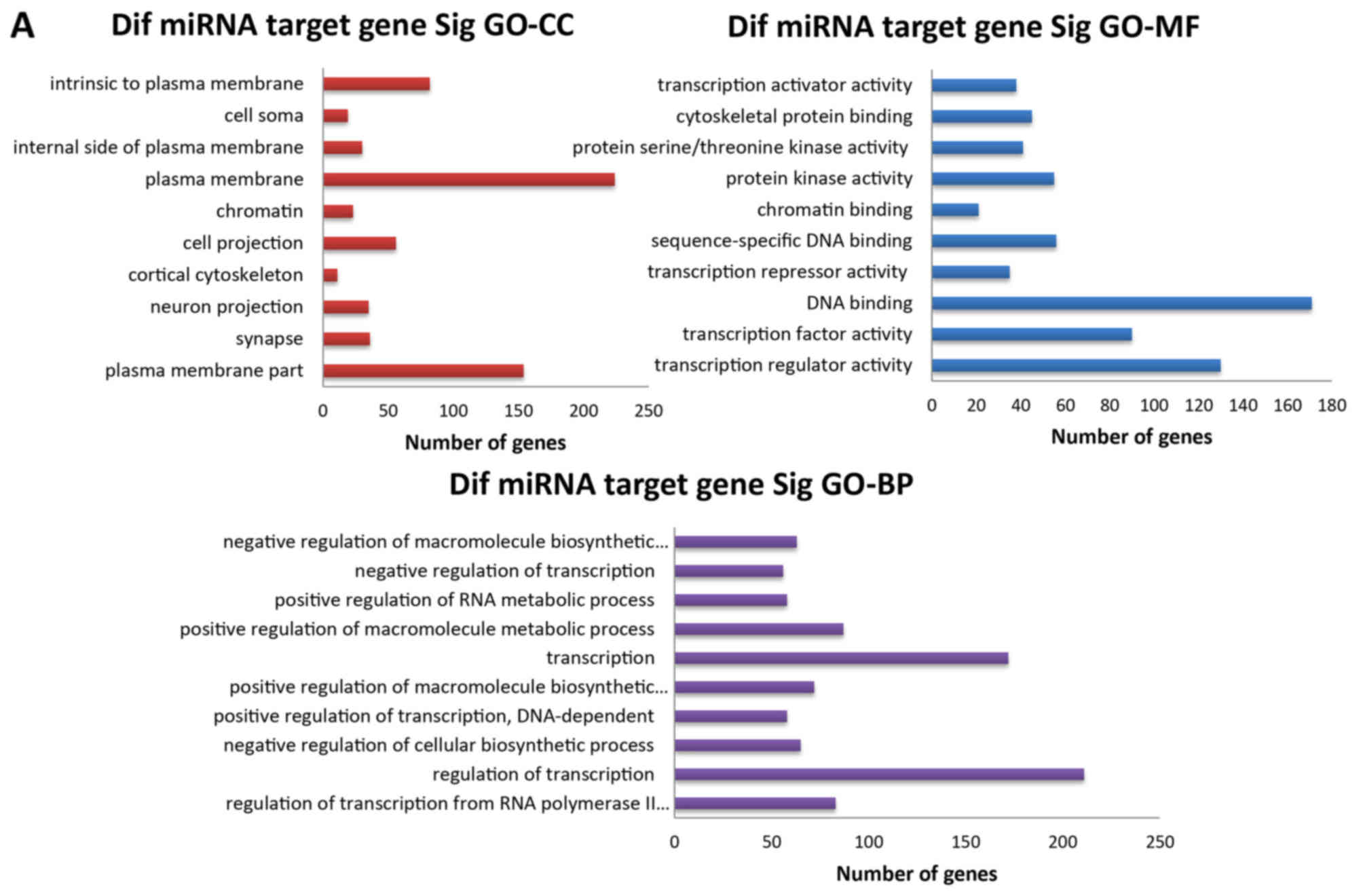
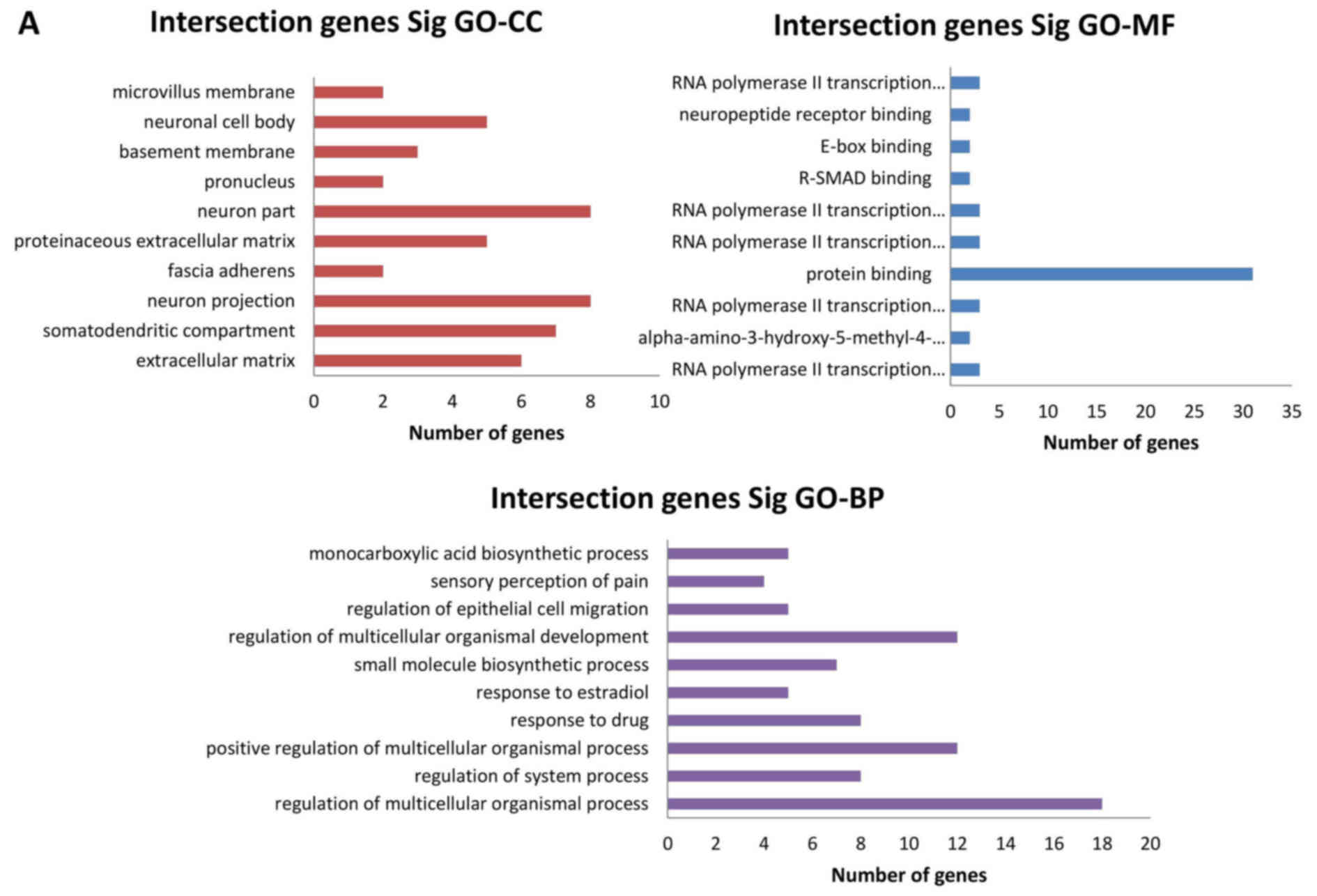
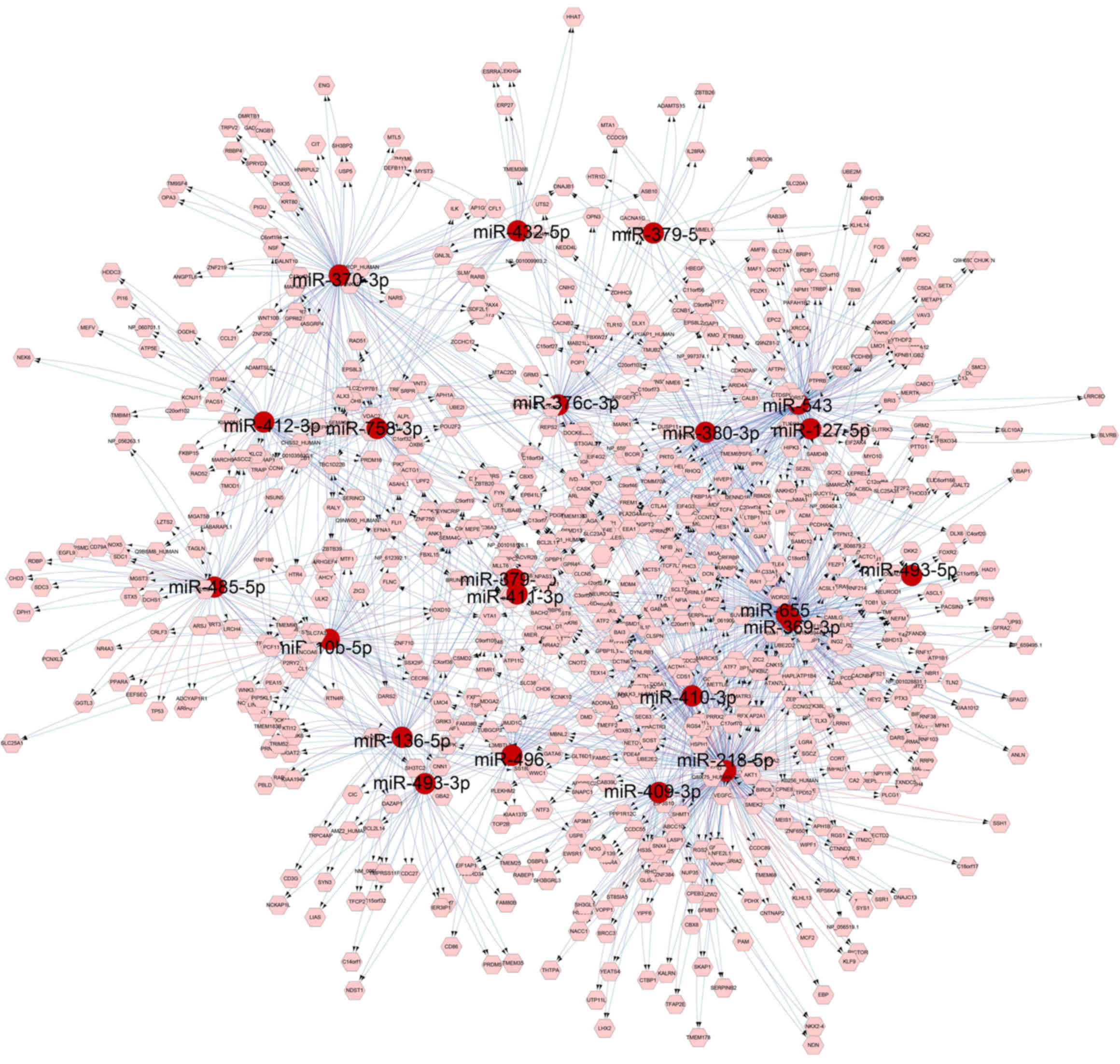
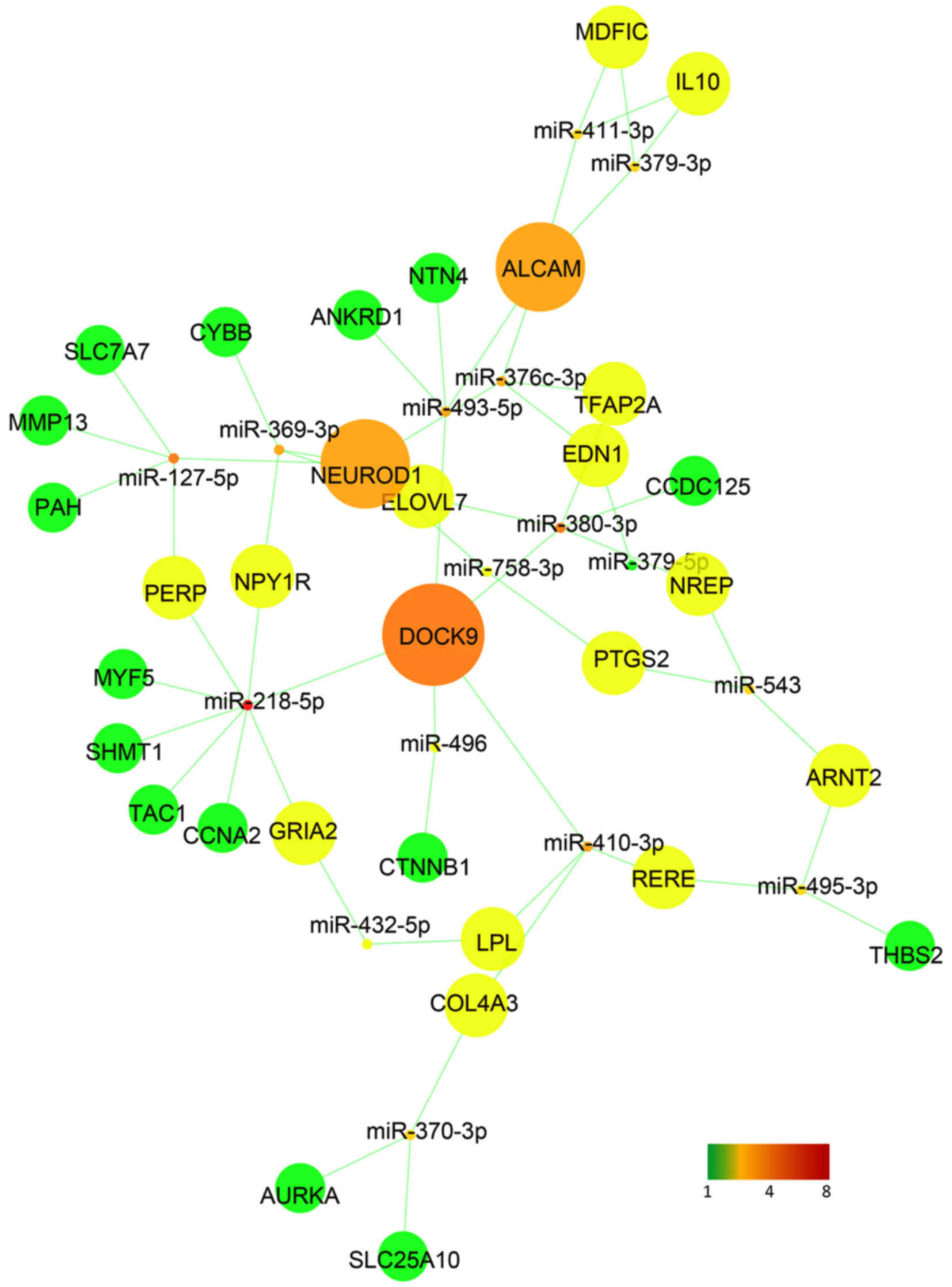
|
1
|
Pellegrini G, Traverso CE, Franzi AT,
Zingirian M, Cancedda R and De Luca M: Long-term restoration of
damaged corneal surfaces with autologous cultivated corneal
epithelium. Lancet. 349:990–993. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ouyang H, Xue Y, Lin Y, Zhang X, Xi L,
Patel S, Cai H, Luo J, Zhang M, Zhang M, et al: WNT7A and PAX6
define corneal epithelium homeostasis and pathogenesis. Nature.
511:358–361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li W, Chen YT, Hayashida Y, Blanco G,
Kheirkah A, He H, Chen SY, Liu CY and Tseng SC: Down-regulation of
Pax6 is associated with abnormal differentiation of corneal
epithelial cells in severe ocular surface diseases. J Pathol.
214:114–122. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lamm V, Hara H, Mammen A, Dhaliwal D and
Cooper DK: Corneal blindness and xenotransplantation.
Xenotransplantation. 21:99–114. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang X, Moldovan I, Zhao Q, Mi S, Zhou Z,
Chen D, Gao Z, Tong D and Dou Z: Reconstruction of damaged cornea
by autologous transplantation of epidermal adult stem cells. Mol
Vis. 14:1064–1070. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shortt AJ, Secker GA, Notara MD, Limb GA,
Khaw PT, Tuft SJ and Daniels JT: Transplantation of ex vivo
cultured limbal epithelial stem cells: A review of techniques and
clinical results. Surv Ophthalmol. 52:483–502. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tseng SC, Prabhasawat P, Barton K, Gray T
and Meller D: Amniotic membrane transplantation with or without
limbal allografts for corneal surface reconstruction in patients
with limbal stem cell deficiency. Arch Ophthalmol. 116:431–441.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nakamura T and Kinoshita S: Ocular surface
reconstruction using cultivated mucosal epithelial stem cells.
Cornea. 22(Suppl 7): S75–S80. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Utheim TP, Utheim OA, Khan QE and Sehic A:
Culture of oral mucosal epithelial cells for the purpose of
treating limbal stem cell deficiency. J Funct Biomater. 7:52016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Nishida K, Yamato M, Hayashida Y, Watanabe
K, Yamamoto K, Adachi E, Nagai S, Kikuchi A, Maeda N, Watanabe H,
et al: Corneal reconstruction with tissue-engineered cell sheets
composed of autologous oral mucosal epithelium. N Engl J Med.
351:1187–1196. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Katikireddy KR, Dana R and Jurkunas UV:
Differentiation potential of limbal fibroblasts and bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells to corneal epithelial cells. Stem Cells.
32:717–729. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gu S, Xing C, Han J, Tso MO and Hong J:
Differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into
corneal epithelial cells in vivo and ex vivo. Mol Vis. 15:99–107.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ahmad S, Stewart R, Yung S, Kolli S,
Armstrong L, Stojkovic M, Figueiredo F and Lako M: Differentiation
of human embryonic stem cells into corneal epithelial-like cells by
in vitro replication of the corneal epithelial stem cell niche.
Stem Cells. 25:1145–1155. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gomes JA, Geraldes Monteiro B, Melo GB,
Smith RL, Cavenaghi Pereira da Silva M, Lizier NF, Kerkis A,
Cerruti H and Kerkis I: Corneal reconstruction with
tissue-engineered cell sheets composed of human immature dental
pulp stem cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 51:1408–1414. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Toma JG, Akhavan M, Fernandes KJ,
Barnabé-Heider F, Sadikot A, Kaplan DR and Miller FD: Isolation of
multipotent adult stem cells from the dermis of mammalian skin. Nat
Cell Biol. 3:778–784. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dyce PW, Wen L and Li J: In vitro germline
potential of stem cells derived from fetal porcine skin. Nat Cell
Biol. 8:384–390. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chee KY, Kicic A and Wiffen SJ: Limbal
stem cells: The search for a marker. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol.
34:64–73. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lavker RM and Sun TT: Epidermal stem
cells: Properties, markers, and location. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:13473–13475. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bose A, Teh MT, Mackenzie IC and Waseem A:
Keratin k15 as a biomarker of epidermal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci.
14:19385–19398. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Forni MF, Trombetta-Lima M and Sogayar MC:
Stem cells in embryonic skin development. Biol Res. 45:215–222.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ghadially R: 25 years of epidermal stem
cell research. J Invest Dermatol. 132:797–810. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Blazejewska EA, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U,
Zenkel M, Bachmann B, Chankiewitz E, Jacobi C and Kruse FE: Corneal
limbal microenvironment can induce transdifferentiation of hair
follicle stem cells into corneal epithelial-like cells. Stem Cells.
27:642–652. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Saichanma S, Bunyaratvej A and Sila-Asna
M: In vitro trans-differentiation of corneal epithelial-like cells
from human skin-derived precursor cells. Int J Ophthalmol.
5:158–163. 2012.
|
|
24
|
Araki K, Ohashi Y, Sasabe T, Kinoshita S,
Hayashi K, Yang XZ, Hosaka Y, Aizawa S and Handa H: Immortalization
of rabbit corneal epithelial cells by a recombinant SV40-adenovirus
vector. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 34:2665–2671. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang X, Qu L, Wang X, Zhao M, Li W, Hua J,
Shi M, Moldovan N, Wang H and Dou Z: Plasticity of epidermal adult
stem cells derived from adult goat ear skin. Mol Reprod Dev.
74:386–396. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Shukla GC, Singh J and Barik S: MicroRNAs:
Processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory
functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 3:83–92. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Baffa R, Fassan M, Volinia S, O'Hara B,
Liu CG, Palazzo JP, Gardiman M, Rugge M, Gomella LG, Croce CM, et
al: MicroRNA expression profiling of human metastatic cancers
identifies cancer gene targets. J Pathol. 219:214–221. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J and Weinberg RA:
Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast
cancer. Nature. 449:682–688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F,
Volinia S, Alder H, Hagan JP, Liu CG, Bhatt D, Taccioli C and Croce
CM: MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic
adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA.
297:1901–1908. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tian Y, Luo A, Cai Y, Su Q, Ding F, Chen H
and Liu Z: MicroRNA-10b promotes migration and invasion through
KLF4 in human esophageal cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem.
285:7986–7994. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ciafrè SA, Galardi S, Mangiola A, Ferracin
M, Liu CG, Sabatino G, Negrini M, Maira G, Croce CM and Farace MG:
Extensive modulation of a set of microRNAs in primary glioblastoma.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 334:1351–1358. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ma L, Reinhardt F, Pan E, Soutschek J,
Bhat B, Marcusson EG, Teruya-Feldstein J, Bell GW and Weinberg RA:
Therapeutic silencing of miR-10b inhibits metastasis in a mouse
mammary tumor model. Nat Biotechnol. 28:341–347. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chai G, Liu N, Ma J, Li H, Oblinger JL,
Prahalad AK, Gong M, Chang LS, Wallace M, Muir D, et al:
MicroRNA-10b regulates tumorigenesis in neurofibromatosis type 1.
Cancer Sci. 101:1997–2004. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin J, Teo S, Lam DH, Jeyaseelan K and
Wang S: MicroRNA-10b pleiotropically regulates invasion,
angiogenicity and apoptosis of tumor cells resembling mesenchymal
subtype of glioblastoma multiforme. Cell Death Dis. 3:e3982012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Widelitz RB: Wnt signaling in skin
organogenesis. Organogenesis. 4:123–133. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lim X and Nusse R: Wnt signaling in skin
development, homeostasis, and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 5:52013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Pearton DJ, Yang Y and Dhouailly D:
Transdifferentiation of corneal epithelium into epidermis occurs by
means of a multistep process triggered by dermal developmental
signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:3714–3719. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mukhopadhyay M, Gorivodsky M, Shtrom S,
Grinberg A, Niehrs C, Morasso MI and Westphal H: Dkk2 plays an
essential role in the corneal fate of the ocular surface
epithelium. Development. 133:2149–2154. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kwofie MA and Skowronski J: Specific
recognition of Rac2 and Cdc42 by DOCK2 and DOCK9 guanine nucleotide
exchange factors. J Biol Chem. 283:3088–3096. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Czugala M, Karolak JA, Nowak DM,
Polakowski P, Pitarque J, Molinari A, Rydzanicz M, Bejjani BA, Yue
BY, Szaflik JP, et al: Novel mutation and three other sequence
variants segregating with phenotype at keratoconus 13q32
susceptibility locus. Eur J Hum Genet. 20:389–397. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Caspi E and Rosin-Arbesfeld R: A novel
functional screen in human cells identifies MOCA as a negative
regulator of Wnt signaling. Mol Biol Cell. 19:4660–4674. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Poulin G, Turgeon B and Drouin J:
NeuroD1/beta2 contributes to cell-specific transcription of the
proopiomelanocortin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 17:6673–6682. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Marsich E, Vetere A, Di Piazza M, Tell G
and Paoletti S: The PAX6 gene is activated by the basic
helix-loop-helix transcription factor NeuroD/BETA2. Biochem J.
376:707–715. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fujiwara K, Ohuchida K, Sada M, Horioka K,
Ulrich CD III, Shindo K, Ohtsuka T, Takahata S, Mizumoto K, Oda Y,
et al: CD166/ALCAM expression is characteristic of tumorigenicity
and invasive and migratory activities of pancreatic cancer cells.
PLoS One. 9:e1072472014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Park GB, Kim D, Kim YS, Kim S, Lee HK,
Yang JW and Hur DY: The Epstein-Barr virus causes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human corneal epithelial cells
via Syk/src and Akt/Erk signaling pathways. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 55:1770–1779. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|