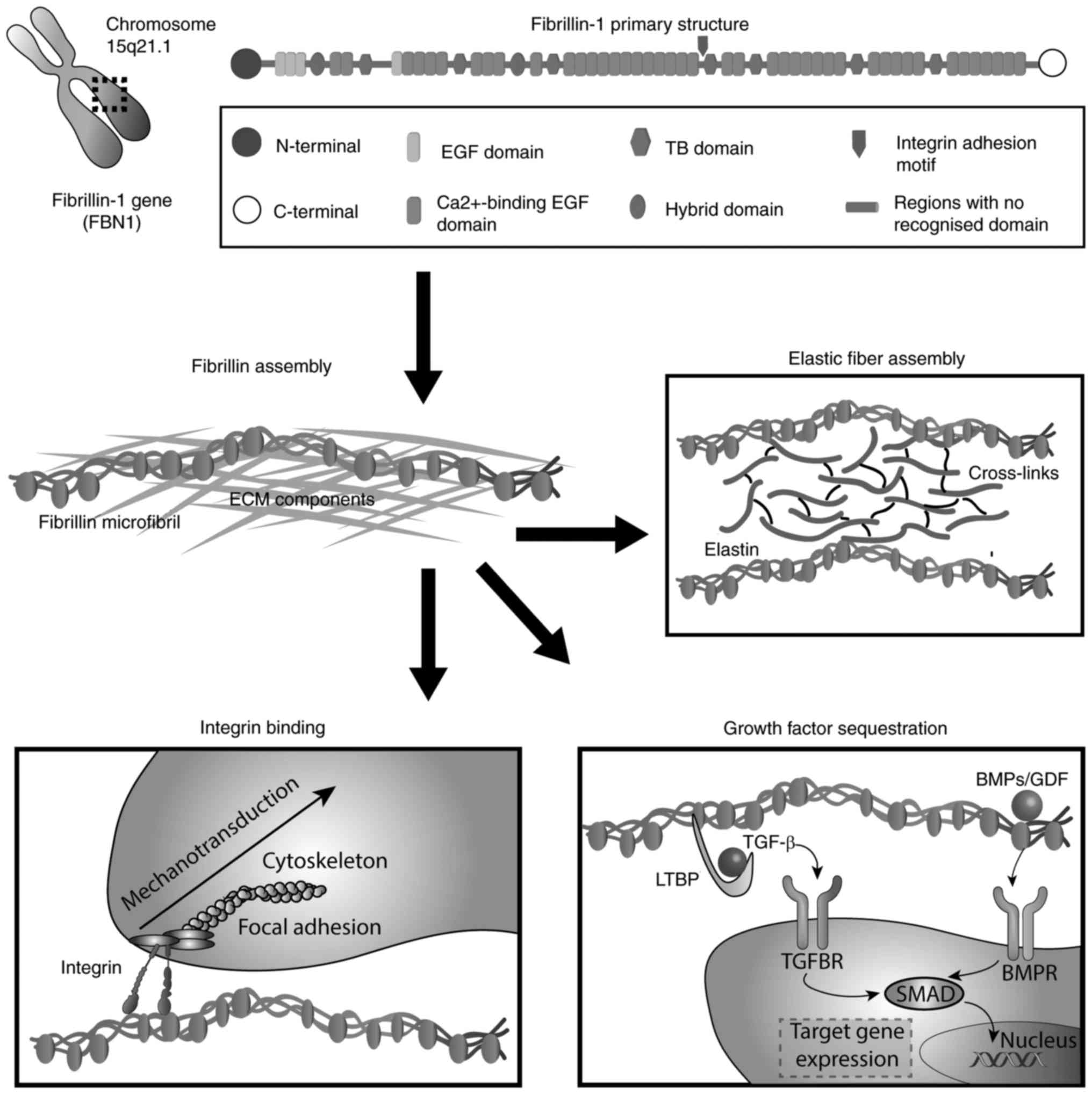
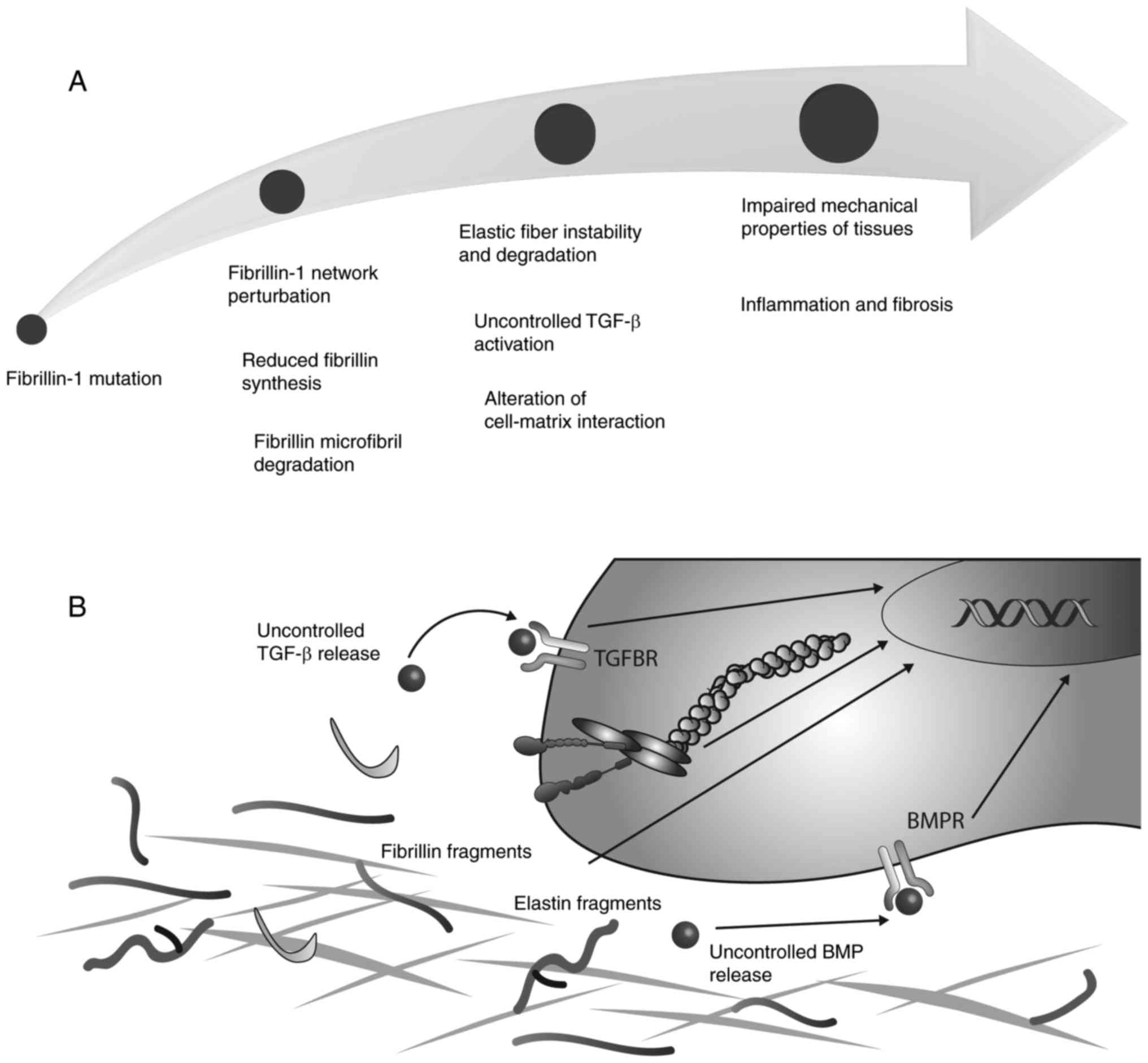
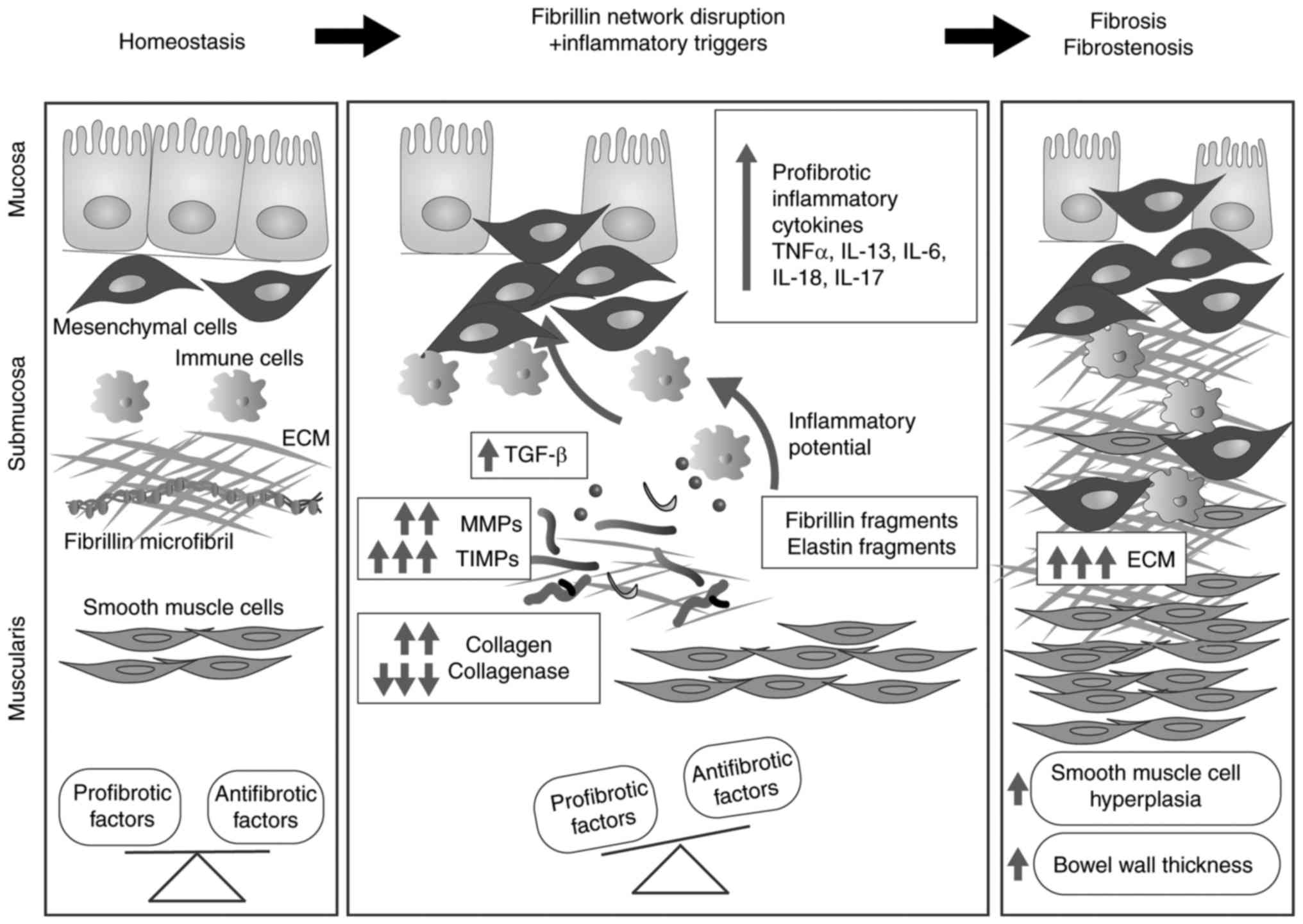
|
1
|
Biery NJ, Eldadah ZA, Moore CS, Stetten G,
Spencer F and Dietz HC: Revised genomic organization of FBN1 and
significance for regulated gene expression. Genomics. 56:70–77.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kainulainen K, Pulkkinen L, Savolainen A,
Kaitila I and Peltonen L: Location on chromosome 15 of the gene
defect causing Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 323:935–939. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Robertson I, Jensen S and Handford P: TB
domain proteins: Evolutionary insights into the multifaceted roles
of fibrillins and LTBPs. Biochem J. 433:263–276. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Corson GM, Chalberg SC, Dietz HC,
Charbonneau NL and Sakai LY: Fibrillin binds calcium and is coded
by cDNAs that reveal a multidomain structure and alternatively
spliced exons at the 5′end. Genomics. 17:476–484. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maslen CL, Corson GM, Maddox BK, Glanville
RW and Sakai LY: Partial sequence of a candidate gene for the
Marfan syndrome. Nature. 352:334–337. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Handford PA, Mayhew M and Brownlee GG:
Calcium binding to fibrillin? Nature. 353:3951991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Werner JM, Knott V, Handford PA, Campbell
ID and Downing AK: Backbone dynamics of a cbEGF domain pair in the
presence of calcium. J Mol Biol. 296:1065–1078. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Downing AK, Knott V, Werner JM, Cardy CM,
Campbell ID and Handford PA: Solution structure of a pair of
calcium-binding epidermal growth factor-like domains: Implications
for the Marfan syndrome and other genetic disorders. Cell.
85:597–605. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Smallridge RS, Whiteman P, Werner JM,
Campbell ID, Handford PA and Downing AK: Solution structure and
dynamics of a calcium binding epidermal growth factor-like domain
pair from the neonatal region of human fibrillin-1. J Biol Chem.
278:12199–12206. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Reinhardt DP, Mechling DE, Boswell BA,
Keene DR, Sakai LY and Bächinger HP: Calcium determines the shape
of fibrillin. J Biol Chem. 272:7368–7373. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Reinhardt DP, Ono RN and Sakai LY: Calcium
stabilizes fibrillin-1 against proteolytic degradation. J Biol
Chem. 272:1231–1236. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin G, Tiedemann K, Vollbrandt T, Peters
H, Batge B, Brinckmann J and Reinhardt DP: Homo- and heterotypic
fibrillin-1 and -2 interactions constitute the basis for the
assembly of microfibrils. J Biol Chem. 277:50795–50804. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Marson A, Rock MJ, Cain SA, Freeman LJ,
Morgan A, Mellody K, Shuttleworth CA, Baldock C and Kielty CM:
Homotypic fibrillin-1 interactions in microfibril assembly. J Biol
Chem. 280:5013–5021. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Reinhardt DP, Sasaki T, Dzamba BJ, Keene
DR, Chu ML, Göhring W, Timpl R and Sakai LY: Fibrillin-1 and
fibulin-2 interact and are colocalized in some tissues. J Biol
Chem. 271:19489–19496. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jensen SA, Reinhardt DP, Gibson MA and
Weiss AS: Protein interaction studies of MAGP-1 with tropoelastin
and fibrillin-1. J Biol Chem. 276:39661–39666. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Isogai Z, Ono RN, Ushiro S, Keene DR, Chen
Y, Mazzieri R, Charbonneau NL, Reinhardt DP, Rifkin DB and Sakai
LY: Latent transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 1
interacts with fibrillin and is a microfibril-associated protein. J
Biol Chem. 278:2750–2757. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Rock MJ, Cain SA, Freeman LJ, Morgan A,
Mellody K, Marson A, Shuttleworth CA, Weiss AS and Kielty CM:
Molecular basis of elastic fiber formation. Critical interactions
and a tropoelastin-fibrillin-1 cross-link. J Biol Chem.
279:23748–23758. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Robertson IB, Horiguchi M, Zilberberg L,
Dabovic B, Hadjiolova K and Rifkin DB: Latent TGF-β-binding
proteins. Matrix Biol. 47:44–53. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jovanovic J, Takagi J, Choulier L,
Abrescia NG, Stuart DI, van der Merwe PA, Mardon HJ and Handford
PA: alphaVbeta6 is a novel receptor for human fibrillin-1.
Comparative studies of molecular determinants underlying
integrin-rgd affinity and specificity. J Biol Chem. 282:6743–6751.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jensen SA, Iqbal S, Lowe ED, Redfield C
and Handford PA: Structure and interdomain interactions of a hybrid
domain: A disulphide-rich module of the fibrillin/LTBP superfamily
of matrix proteins. Structure. 17:759–768. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lönnqvist L, Reinhardt D, Sakai L and
Peltonen L: Evidence for furin-type activity-mediated C-terminal
processing of profibrillin-1 and interference in the processing by
certain mutations. Hum Mol Genet. 7:2039–2044. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Raghunath M, Putnam EA, Ritty T, Hamstra
D, Park ES, Tschödrich-Rotter M, Peters R, Rehemtulla A and
Milewicz DM: Carboxy-terminal conversion of profibrillin to
fibrillin at a basic site by PACE/furin-like activity required for
incorporation in the matrix. J Cell Sci. 112:1093–1100.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Trask TM, Ritty TM, Broekelmann T, Tisdale
C and Mecham RP: N-terminal domains of fibrillin 1 and fibrillin 2
direct the formation of homodimers: A possible first step in
microfibril assembly. Biochem J. 340:693–701. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang H, Apfelroth SD, Hu W, Davis EC,
Sanguineti C, Bonadio J, Mecham RP and Ramirez F: Structure and
expression of fibrillin-2, a novel microfibrillar component
preferentially located in elastic matrices. J Cell Biol.
124:855–863. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wallis DD, Putnam EA, Cretoiu JS, Carmical
SG, Cao SN, Thomas G and Milewicz DM: Profibrillin-1 maturation by
human dermal fibroblasts: Proteolytic processing and molecular
chaperones. J Cell Biochem. 90:641–652. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Reinhardt DP, Keene DR, Corson GM, Pöschl
E, Bächinger HP, Gambee JE and Sakai LY: Fibrillin-1: Organization
in microfibrils and structural properties. J Mol Biol. 258:104–116.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Baldock C, Siegler V, Bax DV, Cain SA,
Mellody KT, Marson A, Haston JL, Berry R, Wang MC, Grossmann JG, et
al: Nanostructure of fibrillin-1 reveals compact conformation of
EGF arrays and mechanism for extensibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:11922–11927. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kuo CL, Isogai Z, Keene DR, Hazeki N, Ono
RN, Sengle G, Bächinger HP and Sakai LY: Effects of fibrillin-1
degradation on microfibril ultrastructure. J Biol Chem.
282:4007–4020. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Qian RQ and Glanville RW: Alignment of
fibrillin molecules in elastic microfibrils is defined by
transglutaminase-derived cross-links. Biochemistry. 36:15841–15847.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Keene DR, Maddox BK, Kuo HJ, Sakai LY and
Glanville RW: Extraction of extendable beaded structures and their
identification as fibrillin-containing extracellular matrix
microfibrils. J Histochem Cytochem. 39:441–449. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kielty CM and Shuttleworth CA:
Fibrillin-containing microfibrils: Structure and function in health
and disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 27:747–760. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kewley MA, Williams G and Steven FS:
Studies of elastic tissue formation in the developing bovine
ligamentum nuchae. J Pathol. 124:95–101. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Carta L, Pereira L, Arteaga-Solis E,
Lee-Arteaga SY, Lenart B, Starcher B, Merkel CA, Sukoyan M, Kerkis
A, Hazeki N, et al: Fibrillins 1 and 2 perform partially
overlapping functions during aortic development. J Biol Chem.
281:8016–8023. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yuan X, Werner JM, Lack J, Knott V,
Handford PA, Campbell ID and Downing AK: Effects of the N2144S
mutation on backbone dynamics of a TB-cbEGF domain pair from human
fibrillin-1. J Mol Biol. 316:113–125. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yadin DA, Robertson IB, McNaught-Davis J,
Evans P, Stoddart D, Handford PA, Jensen SA and Redfield C:
Structure of the fibrillin-1 N-terminal domains suggests that
heparan sulfate regulates the early stages of microfibril assembly.
Structure. 21:1743–1756. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sabatier L, Chen D, Fagotto-Kaufmann C,
Hubmacher D, McKee MD, Annis DS, Mosher DF and Reinhardt DP:
Fibrillin assembly requires fibronectin. Mol Biol Cell. 20:846–858.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kinsey R, Williamson MR, Chaudhry S,
Mellody KT, McGovern A, Takahashi S, Shuttleworth CA and Kielty CM:
Fibrillin-1 microfibril deposition is dependent on fibronectin
assembly. J Cell Sci. 121:2696–2704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sabatier L, Djokic J, Fagotto-Kaufmann C,
Chen M, Annis DS, Mosher DF and Reinhardt DP: Complex contributions
of fibronectin to initiation and maturation of microfibrils.
Biochem J. 456:283–295. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Baldwin AK, Cain SA, Lennon R, Godwin A,
Merry CL and Kielty CM: Epithelial-mesenchymal status influences
how cells deposit fibrillin microfibrils. J Cell Sci. 127:158–171.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Gibson MA, Kumaratilake JS and Cleary EG:
The protein components of the 12-nanometer microfibrils of elastic
and nonelastic tissues. J Biol Chem. 264:4590–4598. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Trask BC, Trask TM, Broekelmann T and
Mecham RP: The microfibrillar proteins MAGP-1 and fibrillin-1 form
a ternary complex with the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan
decorin. Mol Biol Cell. 11:1499–1507. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mecham RP and Gibson MA: The
microfibril-associated glycoproteins (MAGPs) and the microfibrillar
niche. Matrix Biol. 47:13–33. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kostka G, Giltay R, Bloch W, Addicks K,
Timpl R, Fässler R and Chu ML: Perinatal lethality and endothelial
cell abnormalities in several vessel compartments of
fibulin-1-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biol. 21:7025–7034. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Freeman LJ, Lomas A, Hodson N, Sherratt
MJ, Mellody KT, Weiss AS, Shuttleworth A and Kielty CM: Fibulin-5
interacts with fibrillin-1 molecules and microfibrils. Biochem J.
388:1–5. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yanagisawa H, Davis EC, Starcher BC, Ouchi
T, Yanagisawa M, Richardson JA and Olson EN: Fibulin-5 is an
elastin-binding protein essential for elastic fibre development in
vivo. Nature. 415:168–171. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hirai M, Ohbayashi T, Horiguchi M, Okawa
K, Hagiwara A, Chien KR, Kita T and Nakamura T: Fibulin-5/DANCE has
an elastogenic organizer activity that is abrogated by proteolytic
cleavage in vivo. J Cell Biol. 176:1061–1071. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gabriel LA, Wang LW, Bader H, Ho JC,
Majors AK, Hollyfield JG, Traboulsi EI and Apte SS: ADAMTSL4, a
secreted glycoprotein widely distributed in the eye, binds
fibrillin-1 microfibrils and accelerates microfibril biogenesis.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:461–469. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Tsutsui K, Manabe R, Yamada T, Nakano I,
Oguri Y, Keene DR, Sengle G, Sakai LY and Sekiguchi K: ADAMTSL-6 is
a novel extracellular matrix protein that binds to fibrillin-1 and
promotes fibrillin-1 fibril formation. J Biol Chem. 285:4870–4882.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Kutz WE, Wang LW, Bader HL, Majors AK,
Iwata K, Traboulsi EI, Sakai LY, Keene DR and Apte SS: ADAMTS10
protein interacts with fibrillin-1 and promotes its deposition in
extracellular matrix of cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem.
286:17156–17167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hubmacher D and Apte SS: ADAMTS proteins
as modulators of microfibril formation and function. Matrix Biol.
47:34–43. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Iozzo RV: Basement membrane proteoglycans:
From cellar to ceiling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:646–656. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Murdoch AD, Liu B, Schwarting R, Tuan RS
and Iozzo RV: Widespread expression of perlecan proteoglycan in
basement membranes and extracellular matrices of human tissues as
detected by a novel monoclonal antibody against domain III and by
in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 42:239–249. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Reinboth B, Hanssen E, Cleary EG and
Gibson MA: Molecular interactions of biglycan and decorin with
elastic fiber components: Biglycan forms a ternary complex with
tropoelastin and microfibril-associated glycoprotein 1. J Biol
Chem. 277:3950–3957. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Raghunath M, Superti-Furga A, Godfrey M
and Steinmann B: Decreased extracellular deposition of fibrillin
and decorin in neonatal Marfan syndrome fibroblasts. Hum Genet.
90:511–515. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Superti-Furga A, Raghunath M and Willems
PJ: Deficiencies of fibrillin and decorin in fibroblast cultures of
a patient with neonatal Marfan syndrome. J Med Genet. 29:875–878.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hayes AJ, Lord MS, Smith SM, Smith MM,
Whitelock JM, Weiss AS and Melrose J: Colocalization in vivo and
association in vitro of perlecan and elastin. Histochem Cell Biol.
136:437–454. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tiedemann K, Sasaki T, Gustafsson E,
Göhring W, Bätge B, Notbohm H, Timpl R, Wedel T,
Schlötzer-Schrehardt U and Reinhardt DP: Microfibrils at basement
membrane zones interact with perlecan via fibrillin-1. J Biol Chem.
280:11404–11412. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Whitelock JM, Melrose J and Iozzo RV:
Diverse cell signaling events modulated by perlecan. Biochemistry.
47:11174–11183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kerever A, Mercier F, Nonaka R, de Vega S,
Oda Y, Zalc B, Okada Y, Hattori N, Yamada Y and Arikawa-Hirasawa E:
Perlecan is required for FGF-2 signaling in the neural stem cell
niche. Stem Cell Res. 12:492–505. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Thisse B and Thisse C: Functions and
regulations of fibroblast growth factor signaling during embryonic
development. Dev Biol. 287:390–402. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Murasawa Y, Watanabe K, Yoneda M, Zako M,
Kimata K, Sakai LY and Isogai Z: Homotypic versican G1 domain
interactions enhance hyaluronan incorporation into fibrillin
microfibrils. J Biol Chem. 288:29170–29181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wight TN and Merrilees MJ: Proteoglycans
in atherosclerosis and restenosis: Key roles for versican. Circ
Res. 94:1158–1167. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wu YJ, La Pierre DP, Wu J, Yee AJ and Yang
BB: The interaction of versican with its binding partners. Cell
Res. 15:483–494. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zheng PS, Vais D, Lapierre D, Liang YY,
Lee V, Yang BL and Yang BB: PG-M/versican binds to P-selectin
glycoprotein ligand-1 and mediates leukocyte aggregation. J Cell
Sci. 117:5887–5895. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Grässel S, Unsöld C, Schäcke H,
Bruckner-Tuderman L and Bruckner P: Collagen XVI is expressed by
human dermal fibroblasts and keratinocytes and is associated with
the microfibrillar apparatus in the upper papillary dermis. Matrix
Biol. 18:309–317. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Hubert T, Grimal S, Ratzinger S, Mechaly
I, Grassel S and Fichard-Carroll A: Collagen XVI is a neural
component of the developing and regenerating dorsal root ganglia
extracellular matrix. Matrix Biol. 26:206–210. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Ono RN, Sengle G, Charbonneau NL, Carlberg
V, Bächinger HP, Sasaki T, Lee-Arteaga S, Zilberberg L, Rifkin DB,
Ramirez F, et al: Latent transforming growth factor beta-binding
proteins and fibulins compete for fibrillin-1 and exhibit exquisite
specificities in binding sites. J Biol Chem. 284:16872–16881. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Dallas SL, Sivakumar P, Jones CJ, Chen Q,
Peters DM, Mosher DF, Humphries MJ and Kielty CM: Fibronectin
regulates latent transforming growth factor-beta (TGF beta) by
controlling matrix assembly of latent TGF-beta binding protein-1. J
Biol Chem. 280:18871–18880. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Fontana L, Chen Y, Prijatelj P, Sakai T,
Fässler R, Sakai LY and Rifkin DB: Fibronectin is required for
integrin alphavbeta6-mediated activation of latent TGF-beta
complexes containing LTBP-1. FASEB J. 19:1798–1808. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kantola AK, Keski-Oja J and Koli K:
Fibronectin and heparin binding domains of latent TGF-beta binding
protein (LTBP)-4 mediate matrix targeting and cell adhesion. Exp
Cell Res. 314:2488–2500. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Saharinen J, Hyytiäinen M, Taipale J and
Keski-Oja J: Latent transforming growth factor-beta binding
proteins (LTBPs)-structural extracellular matrix proteins for
targeting TGF-beta action. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 10:99–117.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Gregory KE, Ono RN, Charbonneau NL, Kuo
CL, Keene DR, Bachinger HP and Sakai LY: The prodomain of BMP-7
targets the BMP-7 complex to the extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem.
280:27970–27980. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Sengle G, Charbonneau NL, Ono RN, Sasaki
T, Alvarez J, Keene DR, Bächinger HP and Sakai LY: Targeting of
bone morphogenetic protein growth factor complexes to fibrillin. J
Biol Chem. 283:13874–13888. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Sengle G, Tsutsui K, Keene DR, Tufa SF,
Carlson EJ, Charbonneau NL, Ono RN, Sasaki T, Wirtz MK, Samples JR,
et al: Microenvironmental regulation by fibrillin-1. PLoS Genet.
8:e10024252012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wohl AP, Troilo H, Collins RF, Baldock C
and Sengle G: Extracellular regulation of bone morphogenetic
protein activity by the microfibril component fibrillin-1. J Biol
Chem. 291:12732–12746. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Charbonneau NL, Ono RN, Corson GM, Keene
DR and Sakai LY: Fine tuning of growth factor signals depends on
fibrillin microfibril networks. Birth Defects Res Part C Embryo
Today. 72:37–50. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Massagué J and Chen YG: Controlling
TGF-beta signaling. Genes Dev. 14:627–644. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Lawrence DA, Pircher R, Krycève-Martinerie
C and Jullien P: Normal embryo fibroblasts release transforming
growth factors in a latent form. J Cell Physiol. 121:184–188. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Shi M, Zhu J, Wang R, Chen X, Mi L, Walz T
and Springer TA: Latent TGF-β structure and activation. Nature.
474:343–349. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zeyer KA and Reinhardt DP:
Fibrillin-containing microfibrils are key signal relay stations for
cell function. J Cell Commun Signal. 9:309–325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Dubois CM, Laprise MH, Blanchette F,
Gentry LE and Leduc R: Processing of transforming growth factor
beta 1 precursor by human furin convertase. J Biol Chem.
270:10618–10624. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Nunes I, Munger J, Harpel JG, Nagano Y,
Shapiro R, Gleizes PE and Rifkin DB: Structure and activation of
the large latent transforming growth factor-Beta complex. J Am
Optom Assoc. 69:643–648. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Annes JP, Munger JS and Rifkin DB: Making
sense of latent TGFbeta activation. J Cell Sci. 116:217–224. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Hinz B: It has to be the αv: Myofibroblast
integrins activate latent TGF-β1. Nat Med. 19:1567–1568. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Sato Y and Rifkin DB: Inhibition of
endothelial cell movement by pericytes and smooth muscle cells:
Activation of a latent transforming growth factor-beta 1-like
molecule by plasmin during co-culture. J Cell Biol. 109:309–315.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Yu Q and Stamenkovic I: Cell
surface-localized matrix metalloproteinase-9 proteolytically
activates TGF-beta and promotes tumor invasion and angiogenesis.
Genes Dev. 14:163–176. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Jenkins G: The role of proteases in
transforming growth factor-beta activation. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 40:1068–1078. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Lyons RM, Gentry LE, Purchio AF and Moses
HL: Mechanism of activation of latent recombinant transforming
growth factor beta 1 by plasmin. J Cell Biol. 110:1361–1367. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Schultz-Cherry S and Murphy-Ullrich JE:
Thrombospondin causes activation of latent transforming growth
factor-beta secreted by endothelial cells by a novel mechanism. J
Cell Biol. 122:923–932. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Barcellos-Hoff MH, Derynck R, Tsang ML and
Weatherbee JA: Transforming growth factor-beta activation in
irradiated murine mammary gland. J Clin Invest. 93:892–899. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Schmierer B and Hill CS: TGFbeta-SMAD
signal transduction: Molecular specificity and functional
flexibility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:970–982. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Chen X and Xu L: Mechanism and regulation
of nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of smad. Cell Biosci. 1:402011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Tang LY and Zhang YE: Non-degradative
ubiquitination in Smad-dependent TGF-β signaling. Cell Biosci.
1:432011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Feng XH and Derynck R: Specificity and
versatility in tgf-beta signaling through Smads. Annu Rev Cell Dev
Biol. 21:659–693. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Massagué J, Seoane J and Wotton D: Smad
transcription factors. Genes Dev. 19:2783–2810. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Verrecchia F, Chu ML and Mauviel A:
Identification of novel TGF-beta/Smad gene targets in dermal
fibroblasts using a combined cDNA microarray/promoter
transactivation approach. J Biol Chem. 276:17058–17062. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Sengle G, Ono RN, Sasaki T and Sakai LY:
Prodomains of transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta) superfamily
members specify different functions: Biglycan forms a ternary
complex with tropoelastin and microfibril-associated glycoprotein
1. J Biol Chem. 286:5087–5099. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Pereira L, D'Alessio M, Ramirez F, Lynch
JR, Sykes B, Pangilinan T and Bonadio J: Genomic organization of
the sequence coding for fibrillin, the defective gene product in
Marfan syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2:17621993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Bax DV, Bernard SE, Lomas A, Morgan A,
Humphries J, Shuttleworth CA, Humphries MJ and Kielty CM: Cell
adhesion to fibrillin-1 molecules and microfibrils is mediated by
alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha v beta 3 integrins. J Biol Chem.
278:34605–34616. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Marek I, Volkert G, Hilgers KF, Bieritz B,
Rascher W, Reinhardt DP and Hartner A: Fibrillin-1 and alpha8
integrin are co-expressed in the glomerulus and interact to convey
adhesion of mesangial cells. Cell Adh Migr. 8:389–395. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Lee SS, Knott V, Jovanović J, Harlos K,
Grimes JM, Choulier L, Mardon HJ, Stuart DI and Handford PA:
Structure of the integrin binding fragment from fibrillin-1 gives
new insights into microfibril organization. Structure. 12:717–729.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Bouzeghrane F, Reinhardt DP, Reudelhuber
TL and Thibault G: Enhanced expression of fibrillin-1, a
constituent of the myocardial extracellular matrix in fibrosis. Am
J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 289:H982–H991. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Bax DV, Mahalingam Y, Cain S, Mellody K,
Freeman L, Younger K, Shuttleworth CA, Humphries MJ, Couchman JR
and Kielty CM: Cell adhesion to fibrillin-1: Identification of an
Arg-Gly-Asp-dependent synergy region and a heparin-binding site
that regulates focal adhesion formation. J Cell Sci. 120:1383–1392.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Tiedemann K, Bätge B, Müller PK and
Reinhardt DP: Interactions of fibrillin-1 with heparin/heparan
sulfate, implications for microfibrillar assembly. J Biol Chem.
276:36035–36042. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Cain SA, Baldwin AK, Mahalingam Y, Raynal
B, Jowitt TA, Shuttleworth CA, Couchman JR and Kielty CM: Heparan
sulfate regulates fibrillin-1 N- and C-terminal interactions. J
Biol Chem. 283:27017–27027. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Alexopoulou AN, Multhaupt HA and Couchman
JR: Syndecans in wound healing, inflammation and vascular biology.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 39:505–528. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Loeys BL, Gerber EE, Riegert-Johnson D,
Iqbal S, Whiteman P, McConnell V, Chillakuri CR, Macaya D, Coucke
PJ, De Paepe A, et al: Mutations in fibrillin-1 cause congenital
scleroderma: Stiff skin syndrome. Sci Transl Med. 2:23ra202010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Zou Y, Akazawa H, Qin Y, Sano M, Takano H,
Minamino T, Makita N, Iwanaga K, Zhu W, Kudoh S, et al: Mechanical
stress activates angiotensin II type 1 receptor without the
involvement of angiotensin II. Nat Cell Biol. 6:499–506. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Cook JR, Carta L, Bénard L, Chemaly ER,
Chiu E, Rao SK, Hampton TG, Yurchenco P; GenTAC Registry
Consortium; Costa KD, et al: Abnormal muscle mechanosignaling
triggers cardiomyopathy in mice with Marfan syndrome. J Clin
Invest. 124:1329–1339. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Weber E, Rossi A, Solito R, Sacchi G,
Agliano' M and Gerli R: Focal adhesion molecules expression and
fibrillin deposition by lymphatic and blood vessel endothelial
cells in culture. Microvasc Res. 64:47–55. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Dietz HC, Cutting CR, Pyeritz RE, Maslen
CL, Sakai LY, Corson GM, Puffenberger EG, Hamosh A, Nanthakumar EJ,
Curristin SM, et al: Marfan syndrome caused by a recurrent de novo
missense mutation in the fibrillin gene. Nature. 352:337–339. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Collod-Béroud G, Le Bourdelles S, Ades L,
Ala-Kokko L, Booms P, Boxer M, Child A, Comeglio P, De Paepe A,
Hyland JC, et al: Update of the UMD-FBN1 mutation database and
creation of an FBN1 polymorphism database. Hum Mutat. 22:199–208.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Ramirez F and Dietz HC: Marfan syndrome:
From molecular pathogenesis to clinical treatment. Curr Opin Genet
Dev. 17:252–258. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Sakai LY, Keene DR, Renard M and De Backer
J: FBN1: The disease-causing gene for Marfan syndrome and other
genetic disorders. Gene. 591:279–291. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Faivre L, Collod-Beroud G, Loeys BL, Child
A, Binquet C, Gautier E, Callewaert B, Arbustini E, Mayer K,
Arslan-Kirchner M, et al: Effect of mutation type and location on
clinical outcome in 1,013 probands with marfan syndrome or related
phenotypes and fbn1 mutations: An international study. Am J Hum
Genet. 81:454–466. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Booms P, Cisler J, Mathews KR, Godfrey M,
Tiecke F, Kaufmann UC, Vetter U, Hagemeier C and Robinson PN: Novel
exon skipping mutation in the fibrillin-1 gene: Two 'hot spots' for
the neonatal Marfan syndrome. Clin Genet. 55:110–117. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Morse RP, Rockenmacher S, Pyeritz RE,
Sanders SP, Bieber FR, Lin A, MacLeod P, Hall B and Graham JM Jr:
Diagnosis and management of infantile marfan syndrome. Pediatrics.
86:888–895. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Loeys BL, Dietz HC, Braverman AC,
Callewaert BL, De Backer J, Devereux RB, Hilhorst-Hofstee Y,
Jondeau G, Faivre L, Milewicz DM, et al: The revised Ghent nosology
for the Marfan syndrome. J Med Genet. 47:476–485. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Dietz HC and Pyeritz RE: Mutations in the
human gene for fibrillin-1 (FBN1) in the Marfan syndrome and
related disorders. Hum Mol Genet. 4(Spec No): 1799–1809. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Francke U, Berg MA, Tynan K, Brenn T, Liu
W, Aoyama T, Gasner C, Miller DC and Furthmayr H: A Gly1127Ser
mutation in an EGF-like domain of the fibrillin-1 gene is a risk
factor for ascending aortic aneurysm and dissection. Am J Hum
Genet. 56:1287–1296. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Yamawaki T, Nagaoka K, Morishige K,
Sadamatsu K, Tashiro H, Yasunaga H, Morisaki H and Morisaki T:
Familial thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection associated with
Marfan-related gene mutations: Case report of a family with two
gene mutations. Intern Med. 48:555–558. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Sood S, Eldadah ZA, Krause WL, McIntosh I
and Dietz HC: Mutation in fibrillin-1 and the
Marfanoid-craniosynostosis (Shprintzen-Goldberg) syndrome. Nat
Genet. 12:209–211. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Kainulainen K, Karttunen L, Puhakka L,
Sakai L and Peltonen L: Mutations in the fibrillin gene responsible
for dominant ectopia lentis and neonatal Marfan syndrome. Nat
Genet. 6:64–69. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Le Goff C, Mahaut C, Wang LW, Allali S,
Abhyankar A, Jensen S, Zylberberg L, Collod-Beroud G, Bonnet D,
Alanay Y, et al: Mutations in the TGFβ Binding-protein-like domain
5 of FBN1 are responsible for acromicric and geleophysic
dysplasias. Am J Hum Genet. 89:7–14. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Faivre L, Dollfus H, Lyonnet S, Alembik Y,
Mégarbané A, Samples J, Gorlin RJ, Alswaid A, Feingold J, Le Merrer
M, et al: Clinical homogeneity and genetic heterogeneity in
Weill-Marchesani syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 123A:204–207. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Cecchi A, Ogawa N, Martinez HR, Carlson A,
Fan Y, Penny DJ, Guo DC, Eisenberg S, Safi H, Estrera A, et al:
Missense mutations in FBN1 exons 41 and 42 cause Weill-Marchesani
syndrome with thoracic aortic disease and Marfan syndrome. Am J Med
Genet Part A. 161A:2305–2310. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Faivre L, Gorlin RJ, Wirtz MK, Godfrey M,
Dagoneau N, Samples JR, Le Merrer M, Collod-Beroud G, Boileau C,
Munnich A and Cormier-Daire V: In frame fibrillin-1 gene deletion
in autosomal dominant Weill-Marchesani syndrome. J Med Genet.
40:34–36. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Dagoneau N, Benoist-Lasselin C, Huber C,
Faivre L, Mégarbané A, Alswaid A, Dollfus H, Alembik Y, Munnich A,
Legeai-Mallet L and Cormier-Daire V: ADAMTS10 mutations in
autosomal recessive Weill-Marchesani syndrome. Am J Hum Genet.
75:801–806. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Gerber EE, Gallo EM, Fontana SC, Davis EC,
Wigley FM, Huso DL and Dietz HC: Integrin-modulating therapy
prevents fibrosis and autoimmunity in mouse models of scleroderma.
Nature. 503:126–130. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Hollister DW, Godfrey M, Sakai LY and
Pyeritz RE: Immunohistologic abnormalities of the
Microfibrillar-fiber system in the marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med.
323:152–159. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Eldadah ZA, Brenn T, Furthmayr H and Dietz
HC: Expression of a mutant human fibrillin allele upon a normal
human or murine genetic background recapitulates a Marfan cellular
phenotype. J Clin Invest. 95:874–880. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Godfrey M, Raghunath M, Cisler J, Bevins
CL, DePaepe A, Di Rocco M, Gregoritch J, Imaizumi K, Kaplan P,
Kuroki Y, et al: Abnormal morphology of fibrillin microfibrils in
fibroblast cultures from patients with neonatal Marfan syndrome. Am
J Pathol. 146:1414–1421. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Charbonneau NL, Carlson EJ, Tufa S, Sengle
G, Manalo EC, Carlberg VM, Ramirez F, Keene DR and Sakai LY: In
vivo studies of mutant Fibrillin-1 microfibrils. J Biol Chem.
285:24943–24955. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Aoyama T, Tynan K, Dietz HC, Francke U and
Furthmayr H: Missense mutations impair intracellular processing of
fibrillin and microfibril assembly in Marfan syndrome. Hum Mol
Genet. 2:2135–2140. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Judge DP, Biery NJ, Keene DR, Geubtner J,
Myers L, Huso DL, Sakai LY and Dietz HC: Evidence for a critical
contribution of haploinsufficiency in the complex pathogenesis of
Marfan syndrome. J Clin Invest. 114:172–181. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Arbustini E, Grasso M, Ansaldi S, Malattia
C, Pilotto A, Porcu E, Disabella E, Marziliano N, Pisani A,
Lanzarini L, et al: Identification of sixty-two novel and twelve
known FBN1 mutations in eighty-one unrelated probands with Marfan
syndrome and other fibrillinopathies. Hum Mutat. 26:4942005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Reinhardt DP, Ono RN, Notbohm H, Müller
PK, Bächinger HP and Sakai LY: Mutations in calcium-binding
epidermal growth factor modules render fibrillin-1 susceptible to
proteolysis. A potential disease-causing mechanism in Marfan
syndrome. J Biol Chem. 275:12339–12345. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Booms P, Tiecke F, Rosenberg T, Hagemeier
C and Robinson PN: Differential effect of FBN1 mutations on in
vitro proteolysis of recombinant fibrillin-1 fragments. Hum Genet.
107:216–224. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Hindson VJ, Ashworth JL, Rock MJ, Cunliffe
S, Shuttleworth CA and Kielty CM: Fibrillin degradation by matrix
metalloproteinases: Identification of amino- and carboxy-terminal
cleavage sites. FEBS Lett. 452:195–198. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Ikonomidis JS, Jones JA, Barbour JR,
Stroud RE, Clark LL, Kaplan BS, Zeeshan A, Bavaria JE, Gorman JH
III, Spinale FG and Gorman RC: Expression of matrix
metalloproteinases and endogenous inhibitors within ascending
aortic aneurysms of patients with Marfan syndrome. Circulation.
114(Suppl 1): I365–I370. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Segura AM, Luna RE, Horiba K,
Stetler-Stevenson WG, McAllister HA Jr, Willerson JT and Ferrans
VJ: Immunohistochemistry of matrix metalloproteinases and their
inhibitors in thoracic aortic aneurysms and aortic valves of
patients with Marfan's syndrome. Circulation. 98(Suppl 19):
II331–II338. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Fleischer KJ, Nousari HC, Anhalt GJ, Stone
CD and Laschinger JC: Immunohistochemical abnormalities of
fibrillin in cardiovascular tissues in Marfan's syndrome. Ann
Thorac Surg. 63:1012–1017. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Granata A, Serrano F, Bernard WG, McNamara
M, Low L, Sastry P and Sinha S: An iPSC-derived vascular model of
Marfan syndrome identifies key mediators of smooth muscle cell
death. Nat Genet. 49:97–109. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Neptune ER, Frischmeyer PA, Arking DE,
Myers L, Bunton TE, Gayraud B, Ramirez F, Sakai LY and Dietz HC:
Dysregulation of TGF-beta activation contributes to pathogenesis in
Marfan syndrome. Nat Genet. 33:407–411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Ng CM, Cheng A, Myers LA, Martinez-Murillo
F, Jie C, Bedja D, Gabrielson KL, Hausladen JM, Mecham RP, Judge DP
and Dietz HC: TGF-beta-dependent pathogenesis of mitral valve
prolapse in a mouse model of Marfan syndrome. J Clin Invest.
114:1586–1592. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Franken R, den Hartog AW, de Waard V,
Engele L, Radonic T, Lutter R, Timmermans J, Scholte AJ, van den
Berg MP, Zwinderman AH, et al: Circulating transforming growth
factor-β as a prognostic biomarker in Marfan syndrome. Int J
Cardiol. 168:2441–2446. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Pattanaik D, Brown M and Postlethwaite AE:
Vascular involvement in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). J Inflamm
Res. 4:105–125. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Siracusa LD, McGrath R, Ma Q, Moskow JJ,
Manne J, Christner PJ, Buchberg AM and Jimenez SA: A tandem
duplication within the fibrillin 1 gene is associated with the
mouse tight skin mutation. Genome Res. 6:300–313. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Lemaire R, Bayle J and Lafyatis R:
Fibrillin in Marfan syndrome and tight skin mice provides new
insights into transforming growth factor-beta regulation and
systemic sclerosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 18:582–587. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Gayraud B, Keene DR, Sakai LY and Ramirez
F: New insights into the assembly of extracellular microfibrils
from the analysis of the fibrillin 1 mutation in the tight skin
mouse. J Cell Biol. 150:667–680. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Kielty CM, Raghunath M, Siracusa LD,
Sherratt MJ, Peters R, Shuttleworth CA and Jimenez SA: The tight
skin mouse: Demonstration of mutant fibrillin-1 production and
assembly into abnormal microfibrils. J Cell Biol. 140:1159–1166.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Saito S, Nishimura H, Brumeanu TD, Casares
S, Stan AC, Honjo T and Bona CA: Characterization of mutated
protein encoded by partially duplicated fibrillin-1 gene in tight
skin (TSK) mice. Mol Immunol. 36:169–176. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Gardi C, Martorana PA, de Santi MM, van
Even P and Lungarella G: A biochemical and morphological
investigation of the early development of genetic emphysema in
tight-skin mice. Exp Mol Pathol. 50:398–410. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Tan FK, Arnett FC, Antohi S, Saito S,
Mirarchi A, Spiera H, Sasaki T, Shoichi O, Takeuchi K, Pandey JP,
et al: Autoantibodies to the extracellular matrix microfibrillar
protein, fibrillin-1, in patients with scleroderma and other
connective tissue diseases. J Immunol. 163:1066–1072.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Siracusa LD, McGrath R, Fisher JK and
Jimenez SA: The mouse tight skin (Tsk) phenotype is not dependent
on the presence of mature T and B lymphocytes. Mamm Genome.
9:907–909. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Dodig TD, Mack KT, Cassarino DF and Clark
SH: Development of the tight-skin phenotype in immune-deficient
mice. Arthritis Rheum. 44:723–727. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Kissin EY, Lemaire R, Korn JH and Lafyatis
R: Transforming growth factor beta induces fibroblast fibrillin-1
matrix formation. Arthritis Rheum. 46:3000–3009. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Podolsky DK: Inflammatory bowel disease. N
Engl J Med. 347:417–429. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Shimshoni E, Yablecovitch D, Baram L,
Dotan I and Sagi I: ECM remodelling in IBD: Innocent bystander or
partner in crime? The emerging role of extracellular molecular
events in sustaining intestinal inflammation. Gut. 64:367–372.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
160
|
Stumpf M, Cao W, Klinge U, Klosterhalfen
B, Junge K, Krones CJ and Schumpelick V: Reduced expression of
collagen type I and increased expression of matrix
metalloproteinases 1 in patients with Crohn's disease. J Invest
Surg. 18:33–38. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Stumpf M, Cao W, Klinge U, Klosterhalfen
B, Kasperk R and Schumpelick V: Increased distribution of collagen
type III and reduced expression of matrix metalloproteinase 1 in
patients with diverticular disease. Int J Colorectal Dis.
16:271–275. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Stallmach A, Schuppan D, Riese HH, Matthes
H and Riecken EO: Increased collagen type III synthesis by
fibroblasts isolated from strictures of patients with Crohn's
disease. Gastroenterology. 102:1920–1929. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Graham MF, Diegelmann RF, Elson CO,
Lindblad WJ, Gotschalk N, Gay S and Gay R: Collagen content and
types in the intestinal strictures of Crohn's disease.
Gastroenterology. 94:257–265. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Ratzinger S, Eble JA, Pasoldt A, Opolka A,
Rogler G, Grifka J and Grässel S: Collagen XVI induces formation of
focal contacts on intestinal myofibroblasts isolated from the
normal and inflamed intestinal tract. Matrix Biol. 29:177–193.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Koutroubakis IE, Petinaki E, Dimoulios P,
Vardas E, Roussomoustakaki M, Maniatis AN and Kouroumalis EA: Serum
laminin and collagen IV in inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin
Pathol. 56:817–820. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Spenlé C, Lefebvre O, Lacroute J,
Méchine-Neuville A, Barreau F, Blottière HM, Duclos B, Arnold C,
Hussenet T, Hemmerlé J, et al: The laminin response in inflammatory
bowel disease: Protection or malignancy? PLoS One. 9:e1113362014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
de la Motte CA: Hyaluronan in intestinal
homeostasis and inflammation: Implications for fibrosis. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 301:G945–G949. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Sallam H, McNearney TA and Chen JD:
Systematic review: Pathophysiology and management of
gastrointestinal dysmotility in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma).
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 23:691–712. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Sjogren RW: Gastrointestinal motility
disorders in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 37:1265–1282. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Marie I, Ducrotté P, Denis P, Hellot MF
and Levesque H: Outcome of small-bowel motor impairment in systemic
sclerosis-a prospective manometric 5-yr follow-up. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 46:150–153. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Greydanus MP and Camilleri M: Abnormal
postcibal antral and small bowel motility due to neuropathy or
myopathy in systemic sclerosis. Gastroenterology. 96:110–115. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Iovino P, Valentini G, Ciacci C, De Luca
A, Tremolaterra F, Sabbatini F, Tirri E and Mazzacca G: Proximal
stomach function in systemic sclerosis: Relationship with autonomic
nerve function. Dig Dis Sci. 46:723–730. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Ibba-Manneschi L, Del Rosso A, Pacini S,
Tani A, Bechi P and Matucci Cerinic M: Ultrastructural study of the
muscle coat of the gastric wall in a case of systemic sclerosis.
Ann Rheum Dis. 61:754–756. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Manetti M, Neumann E, Milia AF, Tarner IH,
Bechi P, Matucci-Cerinic M, Ibba-Manneschi L and Müller-Ladner U:
Severe fibrosis and increased expression of fibrogenic cytokines in
the gastric wall of systemic sclerosis patients. Arthritis Rheum.
56:3442–3447. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Pedersen J, Gao C, Egekvist H, Bjerring P,
Arendt-Nielsen L, Gregersen H and Drewes AM: Pain and biomechanical
responses to distention of the duodenum in patients with systemic
sclerosis. Gastroenterology. 124:1230–1239. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Latella G, Di Gregorio J, Flati V, Rieder
F and Lawrance IC: Mechanisms of initiation and progression of
intestinal fibrosis in IBD. Scand J Gastroenterol. 50:53–65. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
LeRoy EC, Trojanowska MI and Smith EA:
Cytokines and human fibrosis. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1:215–219.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Babyatsky MW, Rossiter G and Podolsky DK:
Expression of transforming growth factors alpha and beta in colonic
mucosa in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology.
110:975–984. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Kulkarni AB and Karlsson S: Transforming
growth factor-beta 1 knockout mice. A mutation in one cytokine gene
causes a dramatic inflammatory disease. Am J Pathol. 143:3–9.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Gorelik L and Flavell RA: Transforming
growth factor-beta in T-cell biology. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:46–53.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Meijer MJ, Mieremet-Ooms MA, van der Zon
AM, van Duijn W, van Hogezand RA, Sier CF, Hommes DW, Lamers CB and
Verspaget HW: Increased mucosal matrix metalloproteinase-1, -2, -3
and -9 activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and the
relation with Crohn's disease phenotype. Dig Liver Dis. 39:733–739.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Lakatos G, Hritz I, Varga MZ, Juhász M,
Miheller P, Cierny G, Tulassay Z and Herszényi L: The impact of
matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in
inflammatory bowel diseases. Dig Dis. 30:289–295. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Rath T, Roderfeld M, Graf J, Wagner S,
Vehr AK, Dietrich C, Geier A and Roeb E: Enhanced expression of
MMP-7 and MMP-13 in inflammatory bowel disease: A precancerous
potential? Inflamm Bowel Dis. 12:1025–1035. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Booms P, Pregla R, Ney A, Barthel F,
Reinhardt DP, Pletschacher A, Mundlos S and Robinson PN:
RGD-containing fibrillin-1 fragments upregulate matrix
metallopro-teinase expression in cell culture: A potential factor
in the pathogenesis of the Marfan syndrome. Hum Genet. 116:51–61.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
185
|
Booms P, Ney A, Barthel F, Moroy G,
Counsell D, Gille C, Guo G, Pregla R, Mundlos S, Alix AJ and
Robinson PN: A fibrillin-1-fragment containing the
elastin-binding-protein GxxPG consensus sequence upregulates matrix
metallopro-teinase-1: Biochemical and computational analysis. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 40:234–246. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|