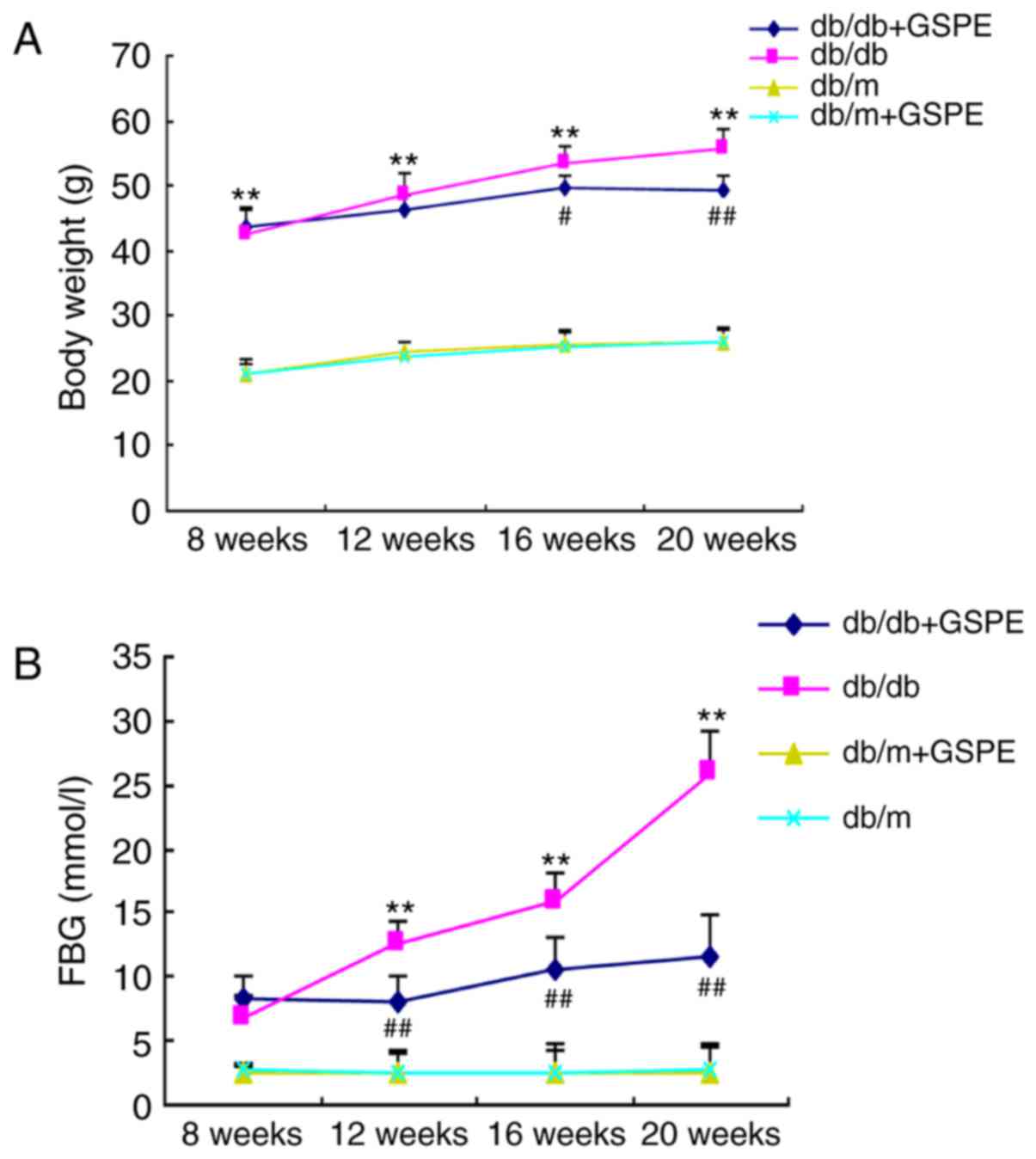
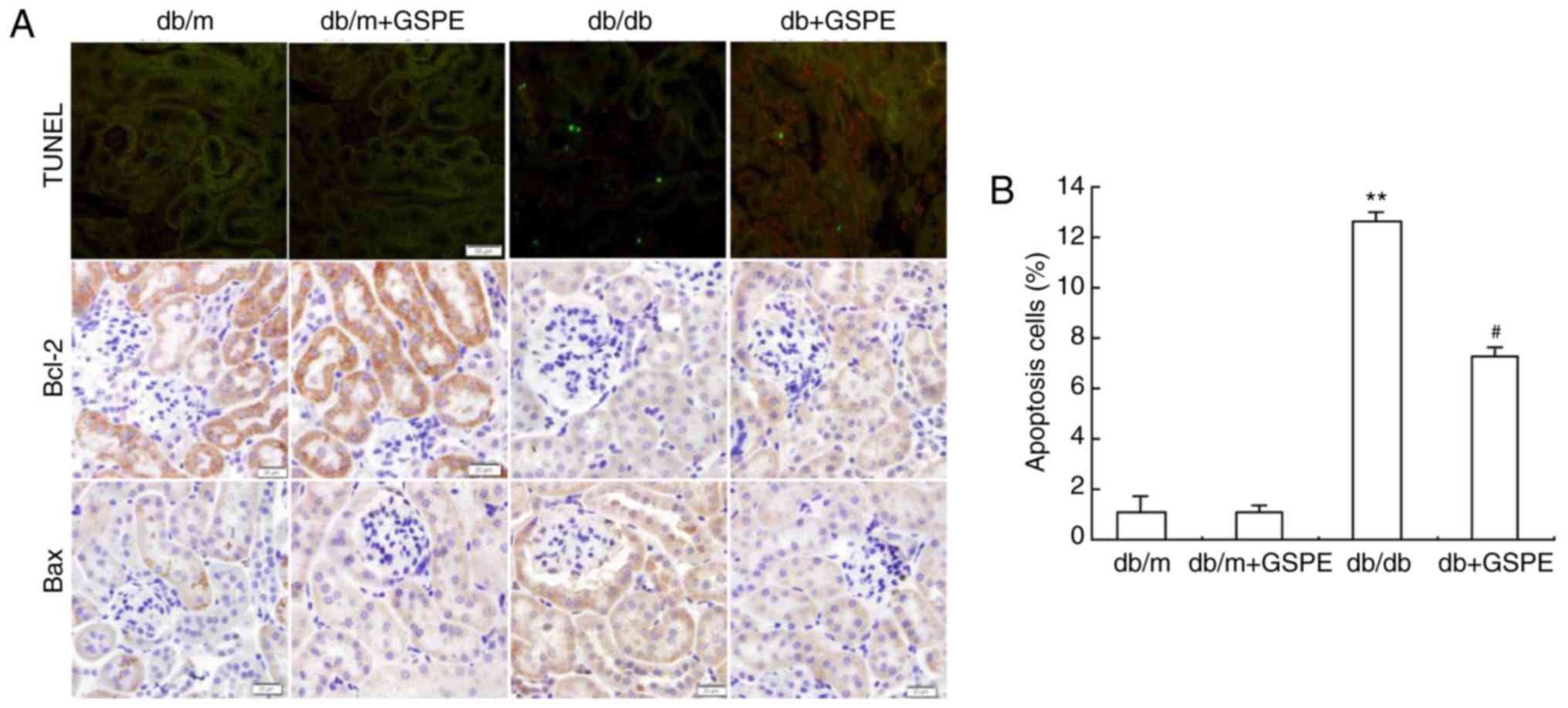
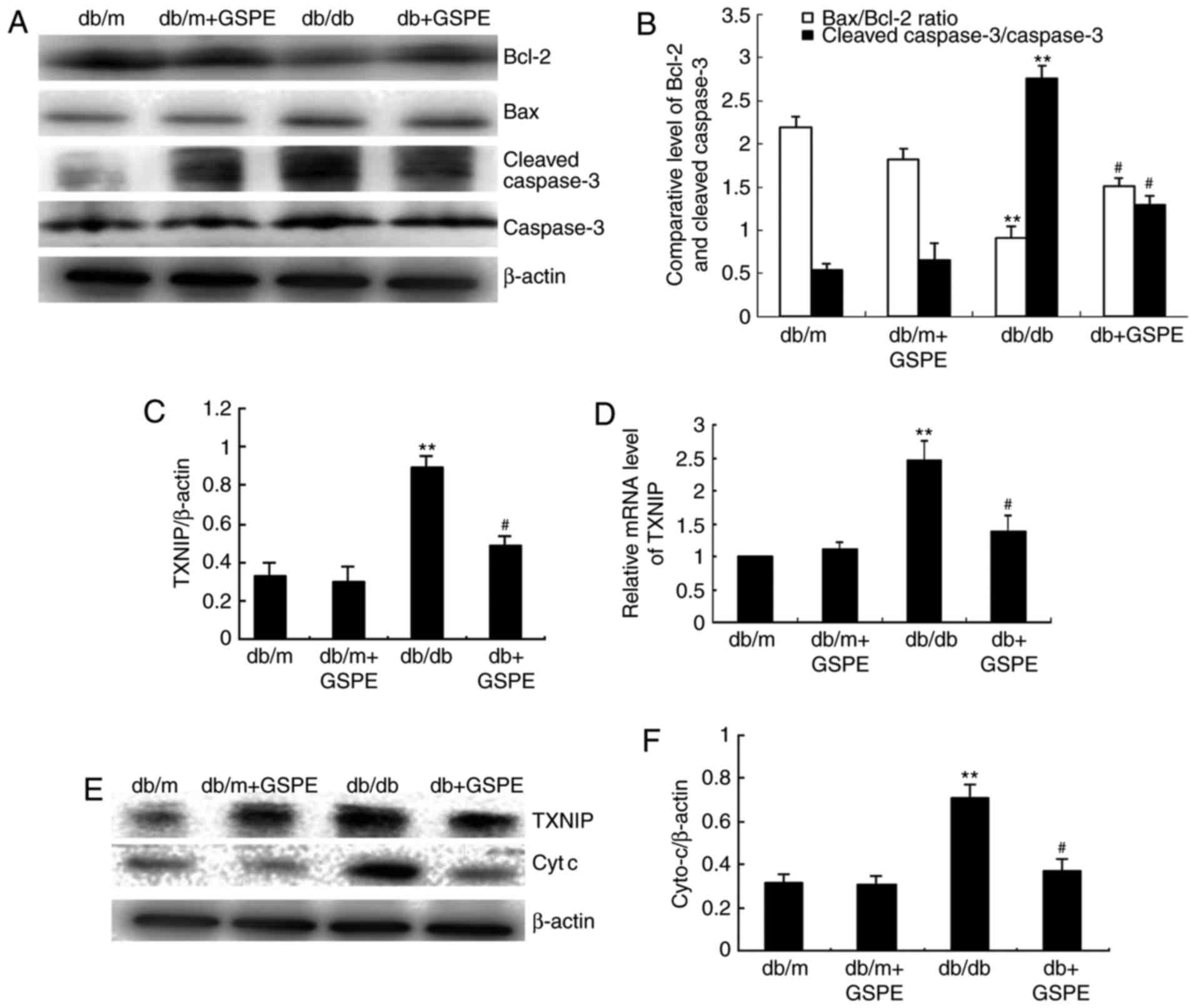
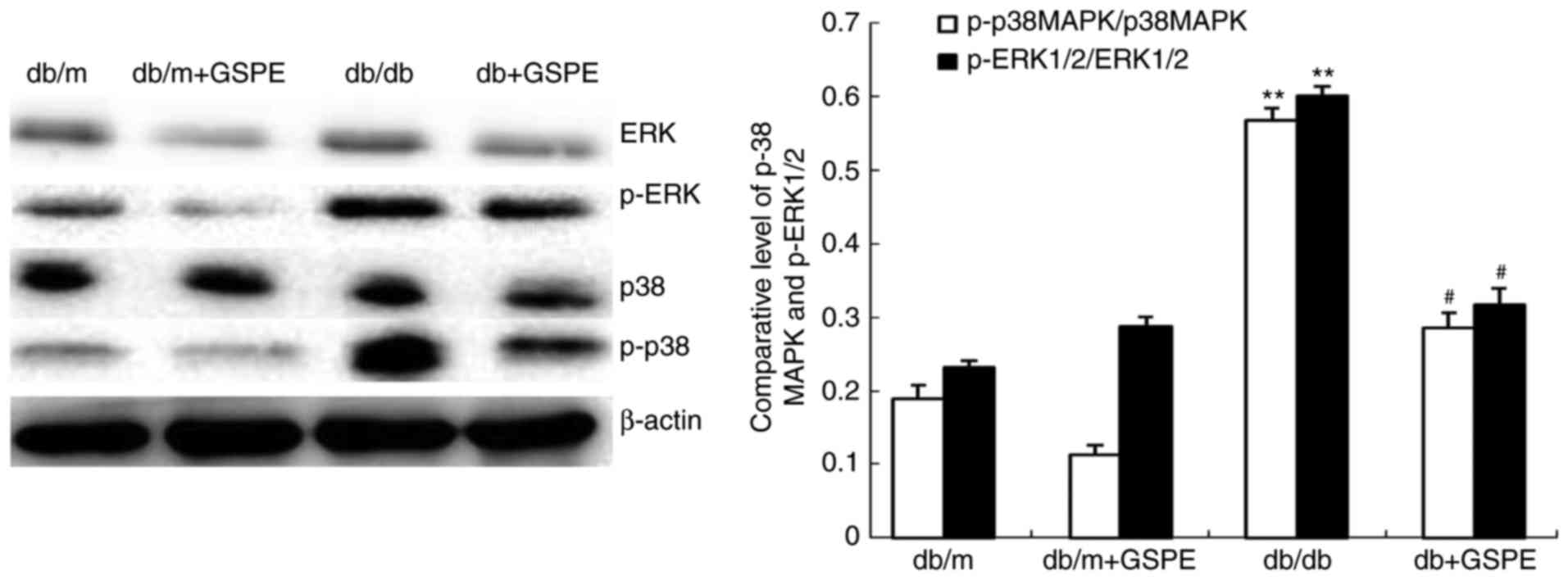
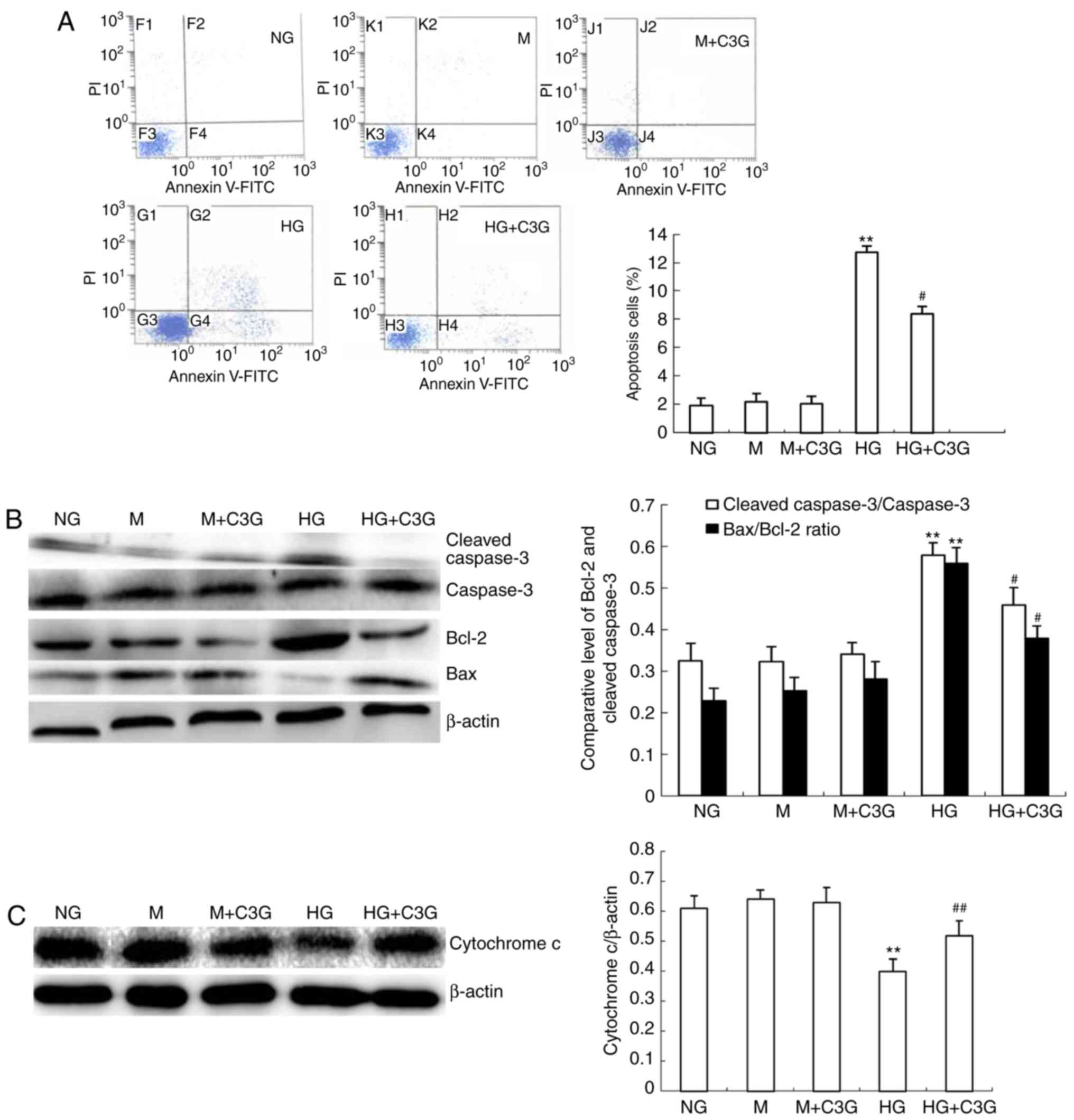
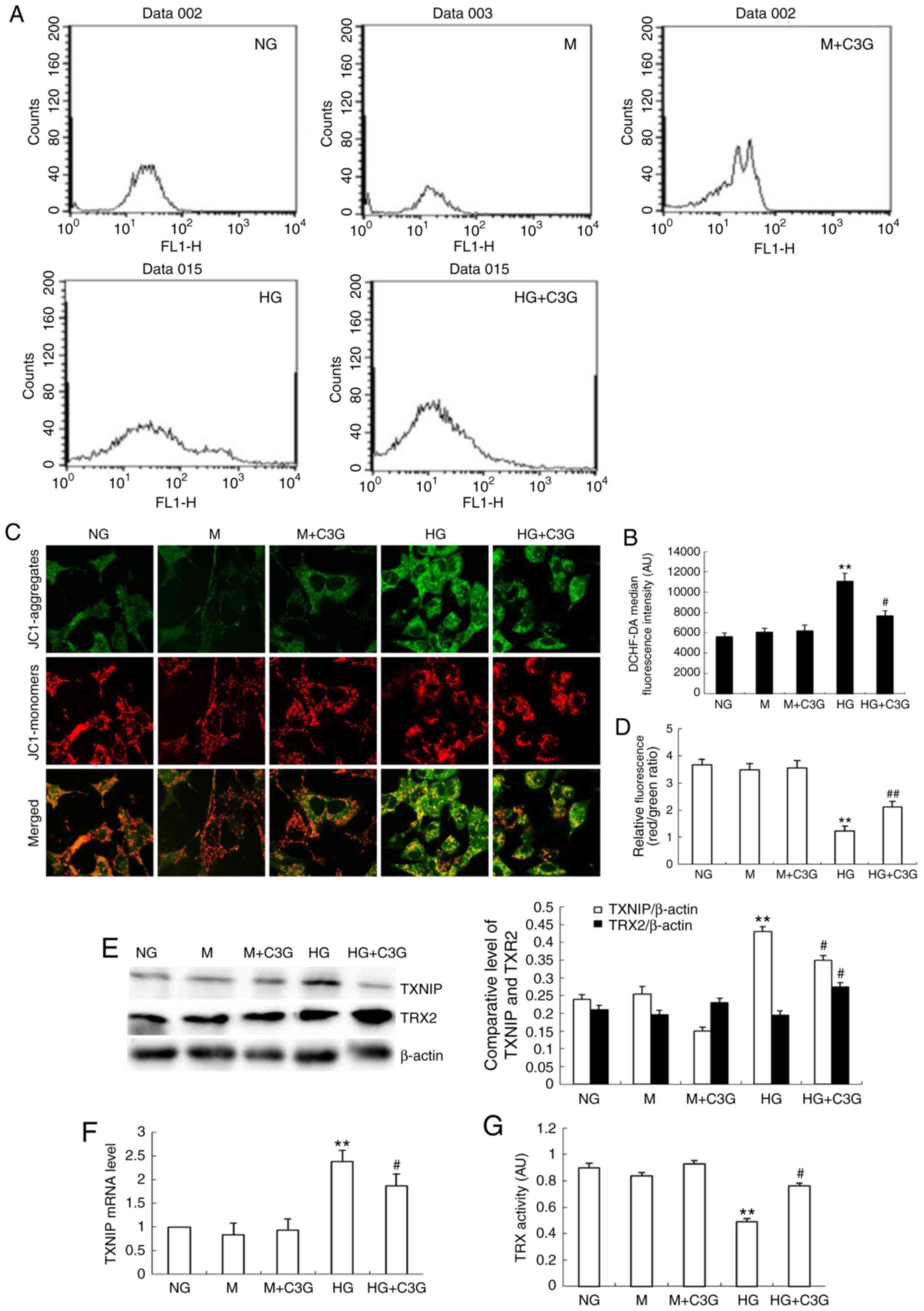
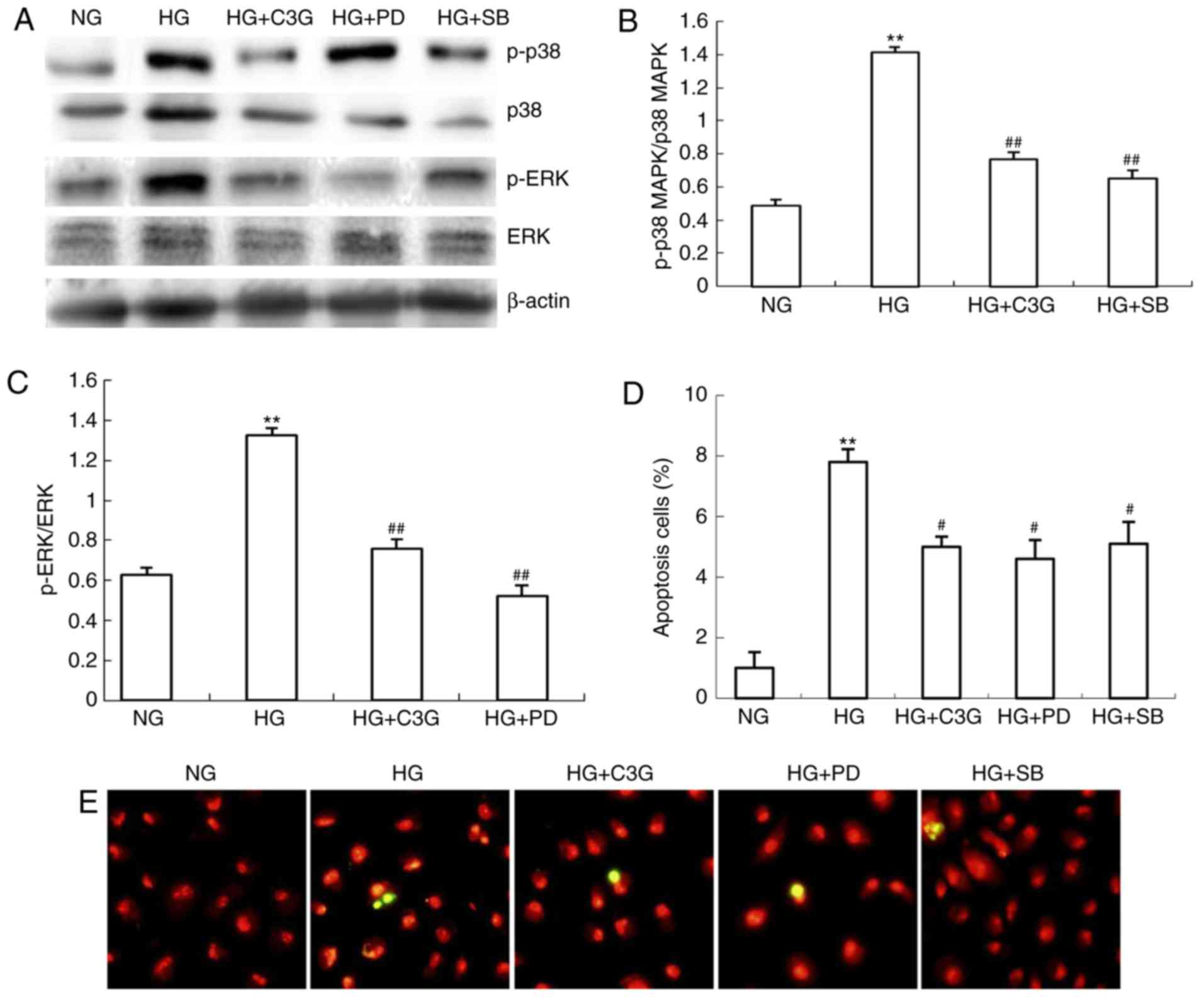
|
1
|
Miranda-Díaz AG, Pazarín-Villaseñor L,
Yanowsky-Escatell FG and Andrade-Sierra J: Oxidative stress in
diabetic nephropathy with early chronic kidney disease. J Diabetes
Res. 2016:70472382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pesce C, Menini S, Pricci F, Favre A, Leto
G, DiMario U and Pugliese G: Glomerular cell replication and cell
loss through apoptosis in experimental diabetes mellitus. Nephron.
90:484–488. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Devine PJ, Perreault SD and Luderer U:
Roles of reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in ovarian
toxicity. Biol Reprod. 86:272012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Fujii J, Iuchi Y and Okada F: Fundamental
roles of reactive oxygen species and protective mechanisms in the
female reproductive system. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 3:432005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sena LA and Chandel NS: Physiological
roles of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Mol Cell.
48:158–167. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu H, Shi Y, Deng X, Su Y, Du C, Wei J,
Ren Y, Wu M, Hou Y and Duan H: Inhibition of c-Src/p38 MAPK pathway
ameliorates renal tubular epithelial cells apoptosis in db/db mice.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 417:27–35. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kanwar YS, Wada J, Sun L, Xie P, Wallner
EI, Chen S, Chugh S and Danesh FR: Diabetic nephropathy: Mechanisms
of renal disease progression. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 233:4–11.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sun L, Dutta RK, Xie P and Kanwar YS:
Myoinositol oxygenase overexpression accentuates generation of
reactive oxygen species and exacerbates cellular injury following
high glucose ambience: A new mechanism relevant to the pathogenesis
of diabetic nephropathy. J Biol Chem. 291:5688–5707. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mishra R, Emancipator SN, Kern T and
Simonson MS: High glucose evokes an intrinsic proapoptotic
signaling pathway in mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 67:82–93. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wei J, Shi Y, Yan J, Ren Y, Du C, Zhang L,
Li Y and Duan H: Knockdown of thioredoxin-interacting protein
ameliorates high glucose-induced epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in renal tubular epithelial cells. Cell Signal.
25:2788–2796. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Punithavathi VR, Stanely Mainzen Prince P,
Kumar MR and Selvakumari CJ: Protective effects of gallic acid on
hepatic lipid peroxide metabolism, glycoprotein components and
lipids in streptozotocin-induced type II diabetic Wistar rats. J
Biochem Mol Toxicol. 25:68–76. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takikawa M, Inoue S, Horio F and Tsuda T:
Dietary anthocyanin-rich bilberry extract ameliorates hyperglycemia
and insulin sensitivity via activation of AMP-activated protein
kinase in diabetic mice. J Nutr. 140:527–533. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kang MK, Li J, Kim JL, Gong JH, Kwak SN,
Park JH, Lee JY, Lim SS and Kang YH: Purple corn anthocyanins
inhibit diabetes-associated glomerular monocyte activation and
macrophage infiltration. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
303:F1060–F1069. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Du C, Shi Y, Ren Y, Wu H, Yao F, Wei J, Wu
M, Hou Y and Duan H: Anthocyanins inhibit high-glucose-induced
cholesterol accumulation and inflammation by activating LXRα
pathway in HK-2 cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:5099–5113. 2015.
|
|
15
|
Rota C, Chignell CF and Mason RP: Evidence
for free radical formation during the oxidation of
2′-7′-dichlorofluorescin to the fluorescent dye
2′-7′-dichlorofluorescein by horseradish peroxidase: Possible
implications for oxidative stress measurements. Free Radic Biol
Med. 27:873–881. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Holmgren A and Björnstedt M: Thioredoxin
and thioredoxin reductase. Methods Enzymol. 252:199–208. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shi Y, Ren Y, Zhao L, Du C, Wang Y, Zhang
Y, Li Y, Zhao S and Duan H: Knockdown of thioredoxin interacting
protein attenuates high glucose-induced apoptosis and activation of
ASK1 in mouse mesangial cells. FEBS Lett. 585:1789–1795. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bocanegra V, Gil Lorenzo AF, Cacciamani V,
Benardón ME, Costantino VV and Vallés PG: RhoA and MAPK signal
transduction pathways regulate NHE1-dependent proximal tubule cell
apoptosis after mechanical stretch. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
307:F881–F889. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hammes HP: Pathophysiological mechanisms
of diabetic angiopathy. J Diabetes Complications. 17(Suppl 2):
S16–S19. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Suganya N, Bhakkiyalakshmi E, Sarada DV
and Ramkumar KM: Reversibility of endothelial dysfunction in
diabetes: Role of polyphenols. Br J Nutr. 116:223–246. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ha H, Hwang IA, Park JH and Lee HB: Role
of reactive oxygen species in the pathogenesis of diabetic
nephropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 82(Suppl 1): S42–S45. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Speciale A, Canali R, Chirafisi J, Saija
A, Virgili F and Cimino F: Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside protection
against TNF-α-induced endothelial dysfunction: Involvement of
nuclear factor-κB signaling. J Agric Food Chem. 58:12048–12054.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sivasinprasasn S, Pantan R, Thummayot S,
Tocharus J, Suksamrarn A and Tocharus C: Cyanidin-3-glucoside
attenuates angiotensin II-induced oxidative stress and inflammation
in vascular endothelial cells. Chem Biol Interact:. Oct
28–2016.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sun J, Xu W, Zhu C, Hu Y, Jiang X, Ou S,
Su Z, Huang Y, Jiao R and Bai W: Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside protects
against 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol-induced reduction of progesterone
by Up-regulation of Steroidogenic Enzymes and cAMP level in leydig
cells. Front Pharmacol. 7:3992016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Zhou Y, Li BY, Li XL, Wang YJ, Zhang Z,
Pei F, Wang QZ, Zhang J, Cai YW, Cheng M and Gao HQ: Restoration of
Mimecan expression by grape seed procyanidin B2 through regulation
of nuclear Factor-kappaB in mice with diabetic nephropathy. Iran J
Kidney Dis. 10:325–331. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang JQ, Gao BW, Wang J, Ren QL, Chen JF,
Ma Q, Zhang ZJ and Xing BS: Critical role of FoxO1 in granulosa
cell apoptosis caused by oxidative stress and protective effects of
grape seed procyanidin B2. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:61473452016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tyagi A, Raina K, Shrestha SP, Miller B,
Thompson JA, Wempe MF, Agarwal R and Agarwal C: Procyanidin B2
3,3′-di-O-gallate, a biologically active constituent of grape seed
extract, induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells via
targeting NF-κB, Stat3 and AP1 transcription factors. Nutr Cancer.
66:736–746. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li BY, Li XL, Cai Q, Cao HQ, Cheng M,
Zhang JH, Wang JF, Yu F and Zhou RH: Induction of lactadherin
mediates the apoptosis of endothelial cells in response to advanced
glycation end products and protective effects of grape seed
procyanidin B2 and resveratrol. Apoptosis. 16:732–745. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sanchez-Niño MD, Sanz AB, Lorz C, Gnirke
A, Rastaldi MP, Nair V, Egido J, Ruiz-Ortega M, Kretzler M and
Ortiz A: BASP1 promotes apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 21:610–621. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu Y, Zhang M, Liu R and Zhao C: Oxidative
Stress-activated NHE1 is involved in high Glucose-induced apoptosis
in renal tubular epithelial cells. Yonsei Med J. 57:1252–1259.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Havasi A and Dong Z: Autophagy and tubular
cell death in the kidney. Semin Nephrol. 36:174–188. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhu W, Jia Q, Wang Y, Zhang Y and Xia M:
The anthocyanin cyanidin-3-O-β-glucoside, a flavonoid, increases
hepatic glutathione synthesis and protects hepatocytes against
reactive oxygen species during hyperglycemia: Involvement of a
cAMP-PKA-dependent signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med.
52:314–327. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ren Y, Shi Y, Wang Y, Li Y, Wu S, Li H,
Zhang Y and Duan H: p38 MAPK pathway is involved in high
glucose-induced thioredoxin interacting protein induction in mouse
mesangial cells. FEBS Lett. 584:3480–3485. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yoshihara E, Masaki S, Matsuo Y, Chen Z,
Tian H and Yodoi J: Thioredoxin/Txnip: Redoxisome, as a redoxs
witch for the pathogenesis of diseases. Front Immunol. 4:5142014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sakai N, Wada T, Furuichi K, Iwata Y,
Yoshimoto K, Kitagawa K, Kokubo S, Kobayashi M, Hara A, Yamahana J,
et al: Involvement of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38
in human diabetic nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 45:54–65. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou X, Liu R, Duan S, Huang G, Ye Y and
Kong Y: High glucose enhances oxLDL-induced apoptosis in human
renal proximal tubular epithelial cells largely via inducing
Lectin-Like ox-LDL receptor-1. Pharmacology. 98:20–28. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang Z, Li BY, Li XL, Cheng M, Yu F, Lu
WD, Cai Q, Wang JF, Zhou RH, Gao HQ and Shen L: Proteomic analysis
of kidney and protective effects of grape seed procyanidin B2 in
db/db mice indicate MFG-E8 as a key molecule in the development of
diabetic nephropathy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832:805–816. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Takami Y, Uto H, Takeshita M, Kai H,
Akamatsu E, Moriuchi A, Hasegawa S, Oketani M, Ido A, Kataoka H and
Tsubouchi H: Proanthocyanidin derived from the leaves of Vaccinium
virgatum suppresses platelet-derived growth factor-induced
proliferation of the human hepatic stellate cell line LI90. Hepatol
Res. 40:337–345. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|