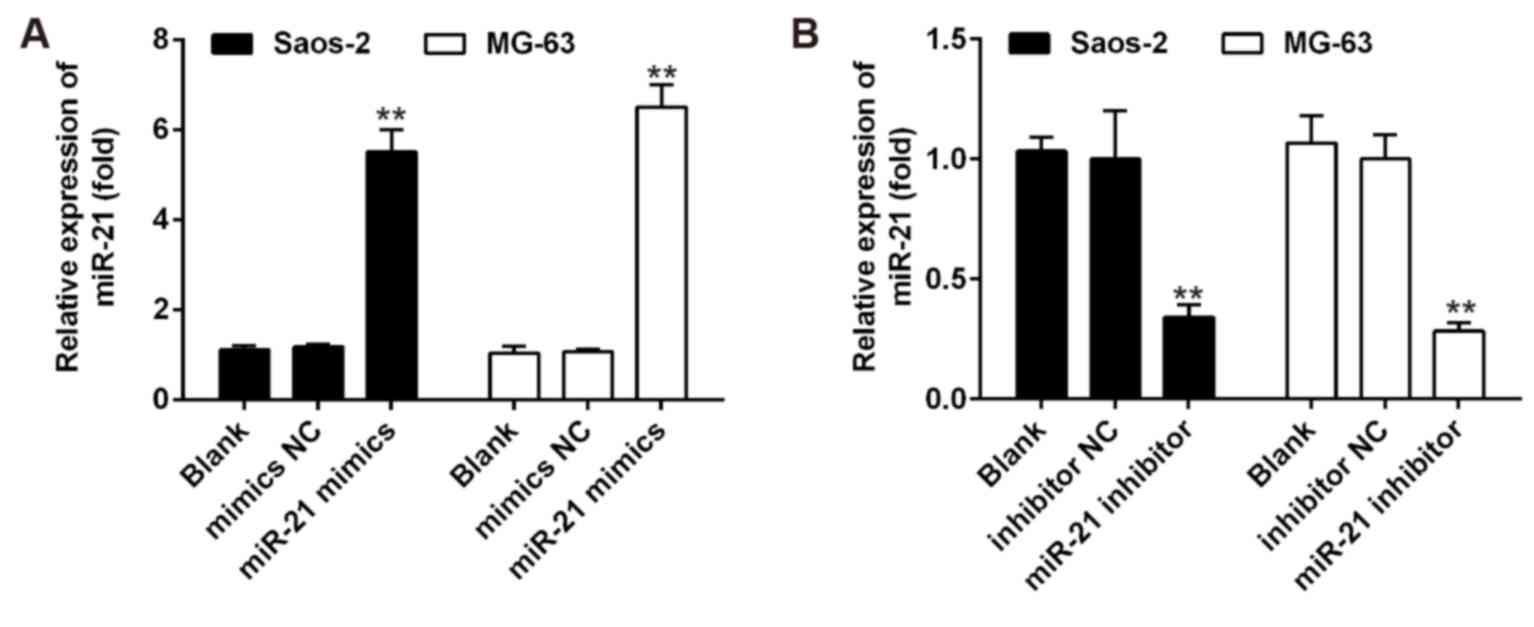
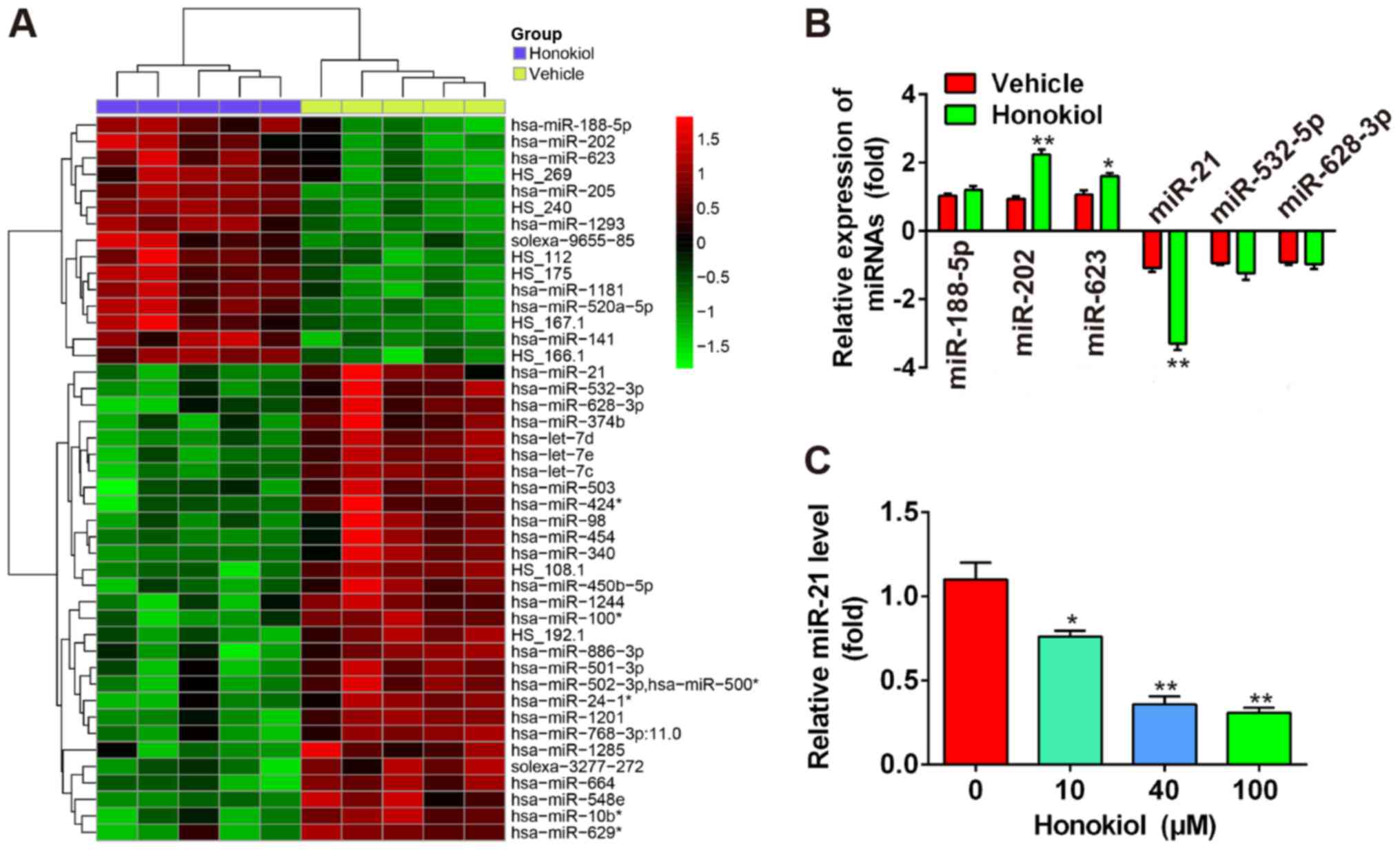
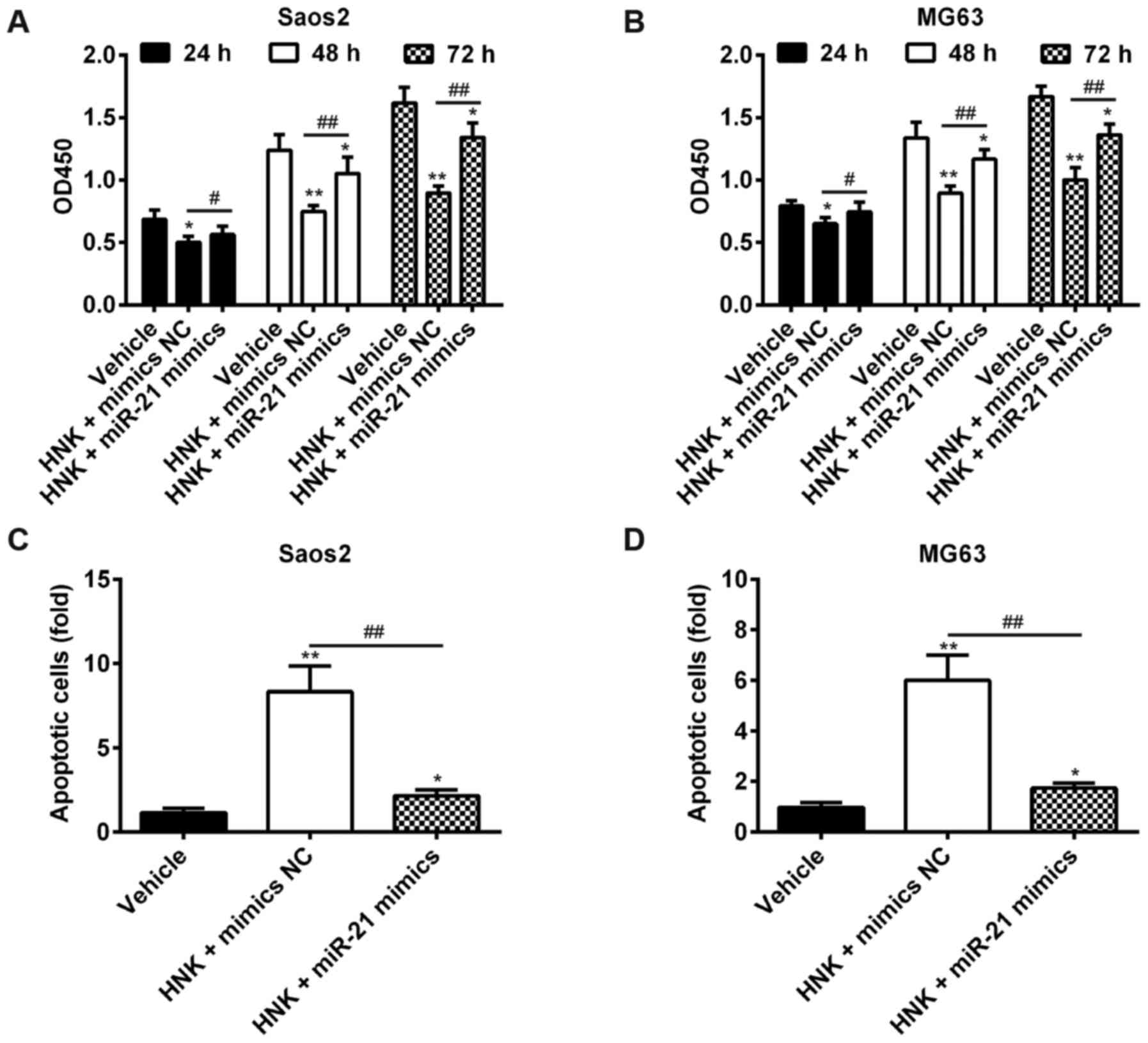
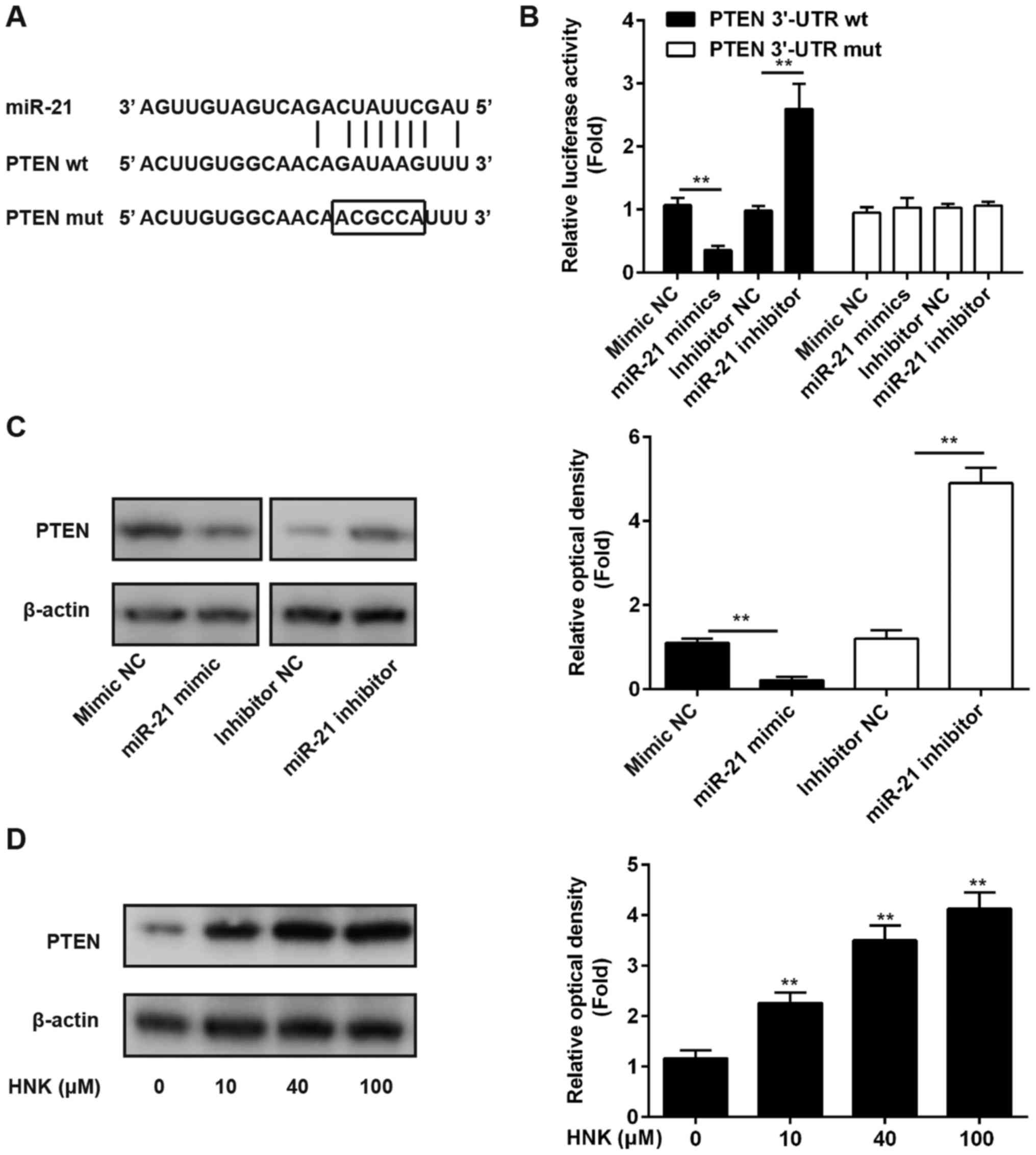
|
1
|
Hung GY, Horng JL, Yen HJ, Yen CC, Chen
WM, Chen PC, Wu HT and Chiou HJ: Incidence patterns of primary bone
cancer in taiwan (2003–2010) A population-based study. Ann Surg
Oncol. 21:2490–2498. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
He H, Ni J and Huang J: Molecular
mechanisms of chemoresistance in osteosarcoma (Review). Oncol Lett.
7:1352–1362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Longhi A, Errani C, De Paolis M, Mercuri M
and Bacci G: Primary bone osteosarcoma in the pediatric age: State
of the art. Cancer Treat Rev. 32:423–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marina N, Gebhardt M, Teot L and Gorlick
R: Biology and therapeutic advances for pediatric osteosarcoma.
Oncologist. 9:422–441. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Steinmann P, Walters DK, Arlt MJ, Banke
IJ, Ziegler U, Langsam B, Arbiser J, Muff R, Born W and Fuchs B:
Antimetastatic activity of honokiol in osteosarcoma. Cancer.
118:2117–2127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ho KY, Tsai CC, Chen CP, Huang JS and Lin
CC: Antimicrobial activity of honokiol and magnolol isolated fro
Magnolia officinalis. Phytother Res. 15:139–141. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ou HC, Chou FP, Lin TM, Yang CH and Sheu
WH: Protective effects of honokiol against oxidized LDL-induced
cytotoxicity and adhesion molecule expression in endothelial cells.
Chem Biol Interact. 161:1–13. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bai X, Cerimele F, Ushio-Fukai M, Waqas M,
Campbell PM, Govindarajan B, Der CJ, Battle T, Frank DA, Ye K, et
al: Honokiol, a small molecular weight natural product, inhibits
angiogenesis in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. J Biol Chem.
278:35501–35507. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ishitsuka K, Hideshima T, Hamasaki M, Raje
N, Kumar S, Hideshima H, Shiraishi N, Yasui H, Roccaro AM,
Richardson P, et al: Honokiol overcomes conventional drug
resistance in human multiple myeloma by induction of
caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis. Blood. 106:1794–1800.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen F, Wang T, Wu Y-F, Gu Y, Xu X-L,
Zheng S and Hu X: Honokiol: A potent chemotherapy candidate for
human colorectal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 10:3459–3463.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Avtanski DB, Nagalingam A, Kuppusamy P,
Bonner MY, Arbiser JL, Saxena NK and Sharma D: Honokiol abrogates
leptin-induced tumor progression by inhibiting Wnt1-MTA1-β-catenin
signaling axis in a microRNA-34a dependent manner. Oncotarget.
6:16396–16410. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sheu ML, Liu SH and Lan KH: Honokiol
induces calpain-mediated glucose-regulated protein-94 cleavage and
apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells and reduces tumor growth.
PLoS One. 2:e10962007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen YJ, Wu CL, Liu JF, Fong YC, Hsu SF,
Li TM, Su YC, Liu SH and Tang CH: Honokiol induces cell apoptosis
in human chondrosarcoma cells through mitochondrial dysfunction and
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cancer Lett. 291:20–30. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hahm ER and Singh SV: Honokiol causes
G0-G1 phase cell cycle arrest in human prostate cancer cells in
association with suppression of retinoblastoma protein
level/phosphorylation and inhibition of E2F1 transcriptional
activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:2686–2695. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Crane C, Panner A, Pieper RO, Arbiser J
and Parsa AT: Honokiol mediated inhibition of PI3K/mTOR pathway: A
potential strategy to overcome immunoresistance in glioma, breast
and prostate carcinoma without impacting T cell function. J
Immunother. 32:585–592. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zamani M, Sadeghizadeh M, Behmanesh M and
Najafi F: Dendrosomal curcumin increases expression of the long
non-coding RNA gene MEG3 via up-regulation of epi-miRs in
hepatocellular cancer. Phytomedicine. 22:961–967. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu S, Fang Y, Shen H, Xu W and Li H:
Berberine sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin through
miR-21/PDCD4 axis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 45:756–762.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hong M, Wang N, Tan HY, Tsao SW and Feng
Y: MicroRNAs and Chinese Medicinal Herbs: New possibilities in
cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel). 7:1643–1657. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang Q, Zhao W, Ye C, Zhuang J, Chang C,
Li Y, Huang X, Shen L, Li Y, Cui Y, et al: Honokiol inhibits
bladder tumor growth by suppressing EZH2/miR-143 axis. Oncotarget.
6:37335–37348. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lai YJ, Lin CI, Wang CL and Chao JI:
Expression of survivin and p53 modulates honokiol-induced apoptosis
in colorectal cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 115:1888–1899.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Battle TE, Arbiser J and Frank DA: The
natural product honokiol induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells. Blood.
106:690–697. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal
K, Jacob ST and Patel T: MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer.
Gastroenterology. 133:647–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu YR, Qi HJ, Deng DF, Luo YY and Yang SL:
MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and resistance
to apoptosis through PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in esophageal
cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:12061–12070. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu ZL, Wang H, Liu J and Wang ZX:
MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) expression promotes growth, metastasis, and
chemo- or radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by
targeting PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem. 372:35–45. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Guo H, German P, Bai S, Barnes S, Guo W,
Qi X, Lou H, Liang J, Jonasch E, Mills GB, et al: The PI3K/AKT
pathway and renal cell carcinoma. J Genet Genomics. 42:343–353.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fang Y, Xue JL, Shen Q, Chen J and Tian L:
MicroRNA-7 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting the
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 55:1852–1862. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ayoub N, Singab AN, El-Naggar M and
Lindequist U: Investigation of phenolic leaf extract of Heimia
myrtifolia (Lythraceae): Pharmacological properties (stimulation of
mineralization of SaOS-2 osteosarcoma cells) and identification of
polyphenols. Drug Discov Ther. 4:341–348. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sumiyoshi M, Taniguchi M, Baba K and
Kimura Y: Antitumor and antimetastatic actions of xanthoangelol and
4-hydroxyderricin isolated from Angelica keiskei roots through the
inhibited activation and differentiation of M2 macrophages.
Phytomedicine. 22:759–767. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xia YZ, Ni K, Guo C, Zhang C, Geng YD,
Wang ZD, Yang L and Kong LY: Alopecurone B reverses
doxorubicin-resistant human osteosarcoma cell line by inhibiting
P-glycoprotein and NF-kappa B signaling. Phytomedicine. 22:344–351.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang T, Gong X, Jiang R, Li H, Du W and
Kuang G: Ferulic acid inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis
via blockage of PI3K/Akt pathway in osteosarcoma cell. Am J Transl
Res. 8:968–980. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Er S and Dikmen M: Camellia sinensis
increased apoptosis on U2OS osteosarcoma cells and wound
healing potential on NIH3T3 fibroblast cells.
Cytotechnology. May 16–2017.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Steinmann P, Walters DK, Arlt MJ, Banke
IJ, Ziegler U, Langsam B, Arbiser J, Muff R, Born W and Fuchs B:
Antimetastatic activity of honokiol in osteosarcoma. Cancer.
118:2117–2127. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Raja SM, Chen S, Yue P, Acker TM, Lefkove
B, Arbiser JL, Khuri FR and Sun SY: The natural product honokiol
preferentially inhibits cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein and
augments death receptor-induced apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:2212–2223. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zeng CW, Zhang XJ, Lin KY, Ye H, Feng SY,
Zhang H and Chen YQ: Camptothecin induces apoptosis in cancer cells
via microRNA-125b-mediated mitochondrial pathways. Mol Pharmacol.
81:578–586. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Novello C, Pazzaglia L, Conti A, Quattrini
I, Pollino S, Perego P, Picci P and Benassi MS: p53-dependent
activation of microRNA-34a in response to etoposide-induced DNA
damage in osteosarcoma cell lines not impaired by dominant negative
p53 expression. PLoS One. 9:e1147572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao Y, Tu MJ, Yu YF, Wang WP, Chen QX,
Qiu JX, Yu AX and Yu AM: Combination therapy with bioengineered
miR-34a prodrug and doxorubicin synergistically suppresses
osteosarcoma growth. Biochem Pharmacol. 98:602–613. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lin CJ, Chang YA, Lin YL, Liu SH, Chang CK
and Chen RM: Preclinical effects of honokiol on treating
glioblastoma multiforme via G1 phase arrest and cell apoptosis.
Phytomedicine. 23:517–527. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Luo LX, Li Y, Liu ZQ, Fan XX, Duan FG, Li
RZ, Yao XJ, Leung EL and Liu L: Honokiol induces apoptosis, G1
arrest, and autophagy in KRAS mutant lung cancer cells. Front
Pharmacol. 8:1992017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen HC, Hsu HT, Weng JW, Chang YF, Hsia
CY, Lee HC and Chi CW: Combined effect of honokiol and
rosiglitazone on cell growth inhibition through enhanced G0/G1
phase arrest in hepatoma cells. J Chin Med Assoc. 79:415–421. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Benhamouche-Trouillet S and Postic C:
Emerging role of miR-21 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut.
65:1781–1783. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xu B, Xia H, Cao J, Wang Z, Yang Y and Lin
Y: MicroRNA-21 inhibits the apoptosis of osteosarcoma cell line
SAOS-2 via targeting caspase-8. Oncol Res. Jan 20–2017.Epub ahead
of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wu YR, Qi HJ, Deng DF, Luo YY and Yang SL:
MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and resistance
to apoptosis through PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in esophageal
cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:12061–12070. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lv C, Hao Y and Tu G: MicroRNA-21 promotes
proliferation, invasion and suppresses apoptosis in human
osteosarcoma line MG63 through PTEN/Akt pathway. Tumour Biol.
37:9333–9342. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang Z, Fang S, Di Y, Ying W, Tan Y and Gu
W: Modulation of NF-κB/miR-21/PTEN pathway sensitizes non-small
cell lung cancer to cisplatin. PLoS One. 10:e01215472015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Xu LF, Wu ZP, Chen Y, Zhu QS, Hamidi S and
Navab R: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) regulates cellular proliferation,
invasion, migration, and apoptosis by targeting PTEN, RECK and
Bcl-2 in lung squamous carcinoma, Gejiu City, China. PLoS One.
9:e1036982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Datta SR, Brunet A and Greenberg ME:
Cellular survival: A play in three Akts. Genes Dev. 13:2905–2927.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Di Cristofano A and Pandolfi PP: The
multiple roles of PTEN in tumor suppression. Cell. 100:387–390.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bai YN, Yu ZY, Luo LX, Yi J, Xia QJ and
Zeng Y: MicroRNA-21 accelerates hepatocyte proliferation in vitro
via PI3K/Akt signaling by targeting PTEN. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 443:802–807. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|