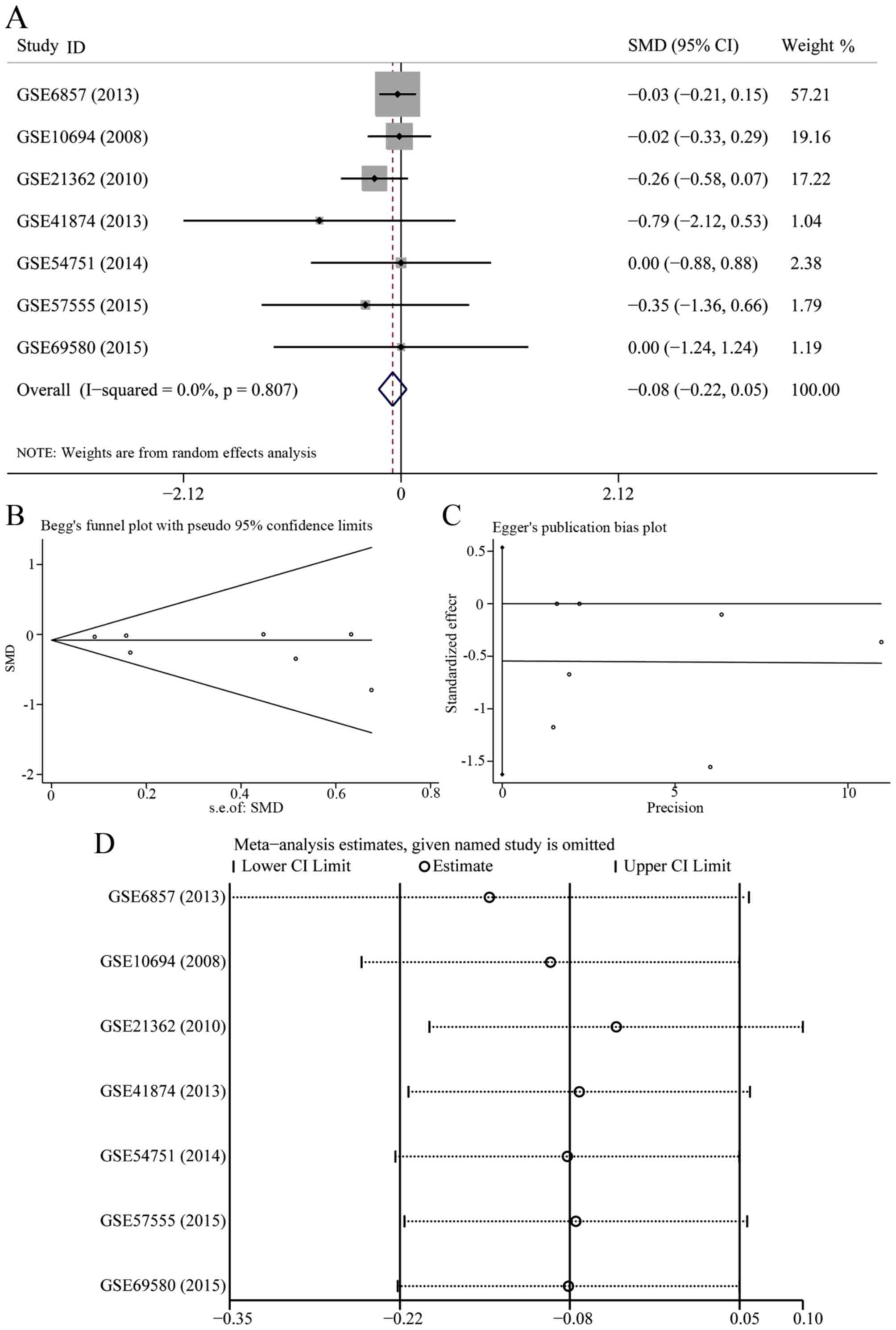
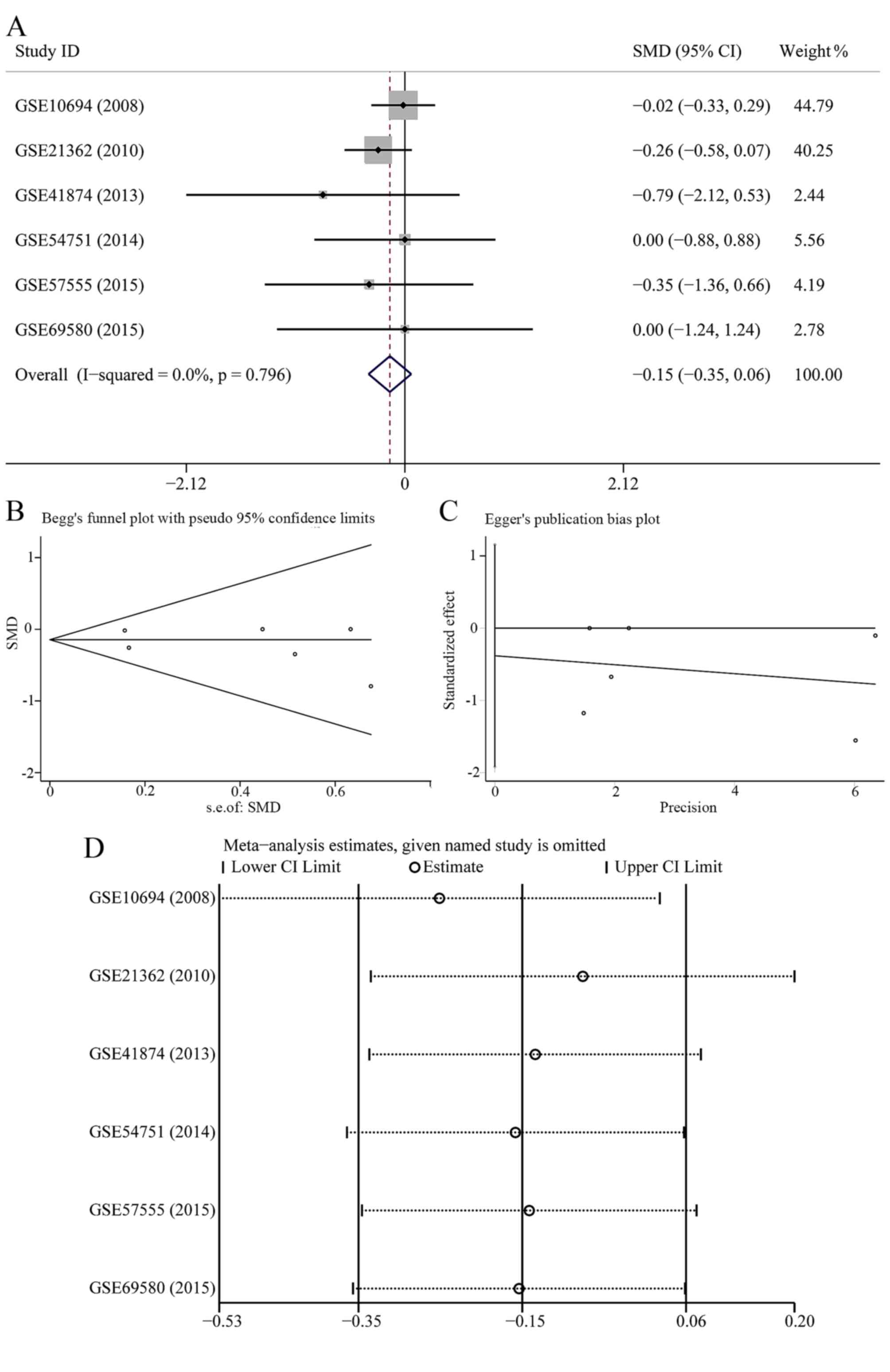
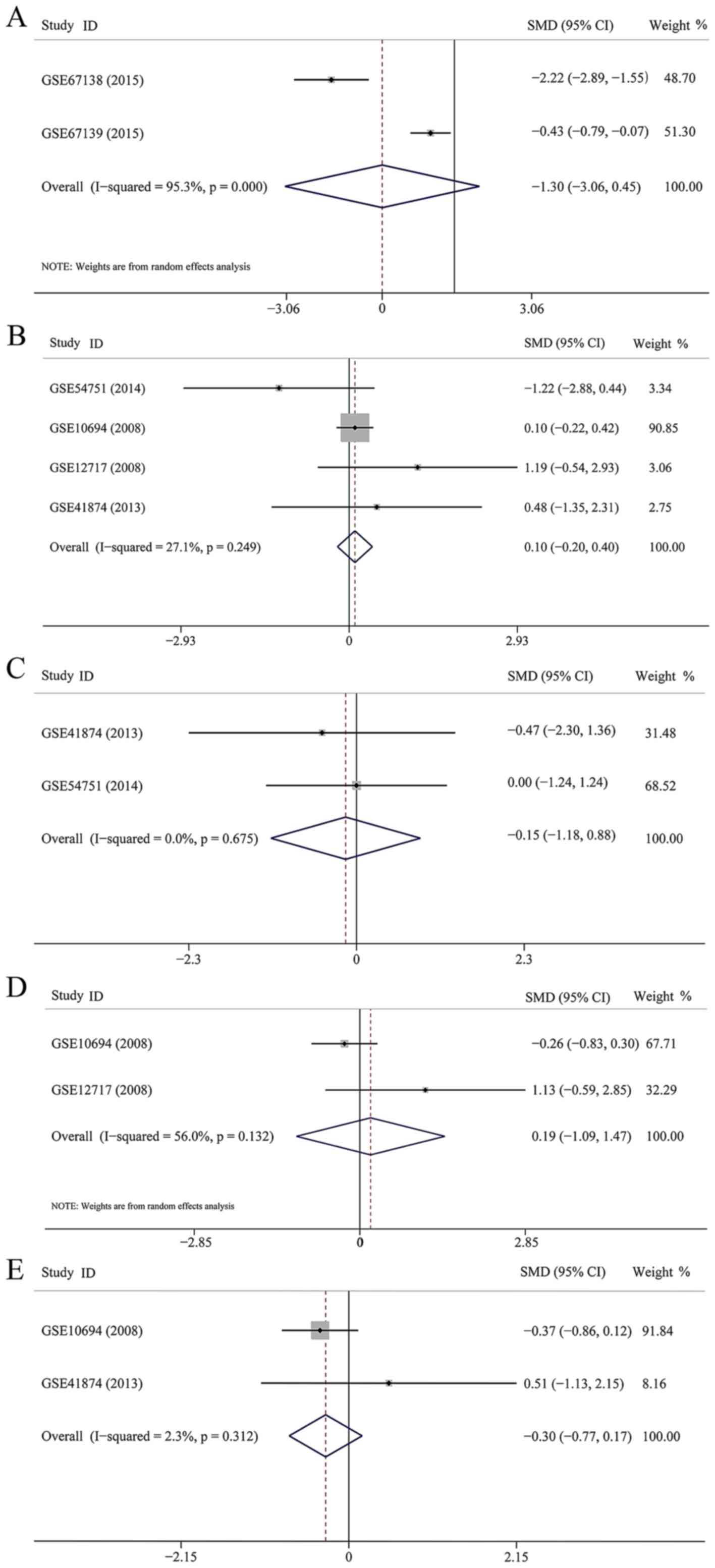
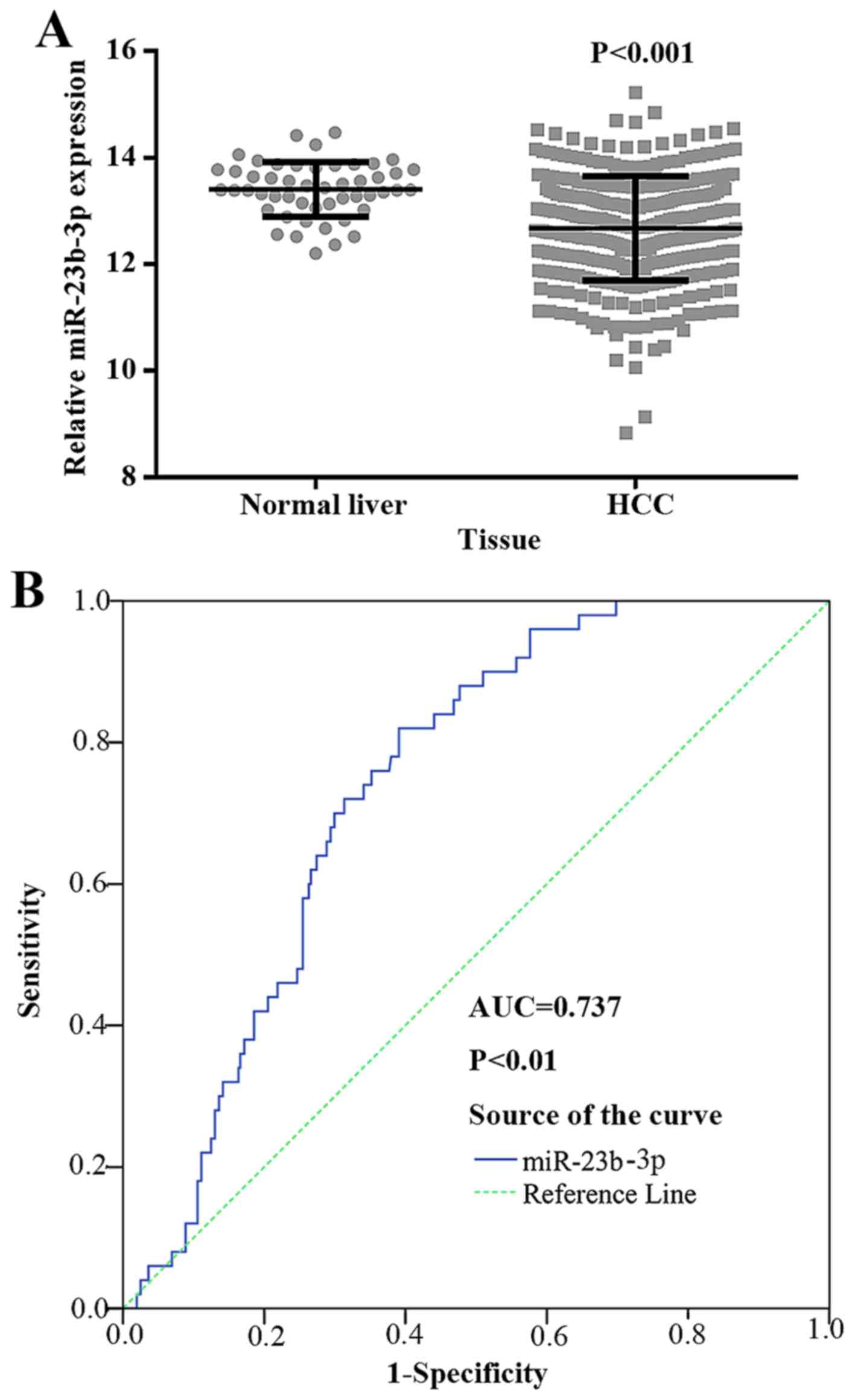
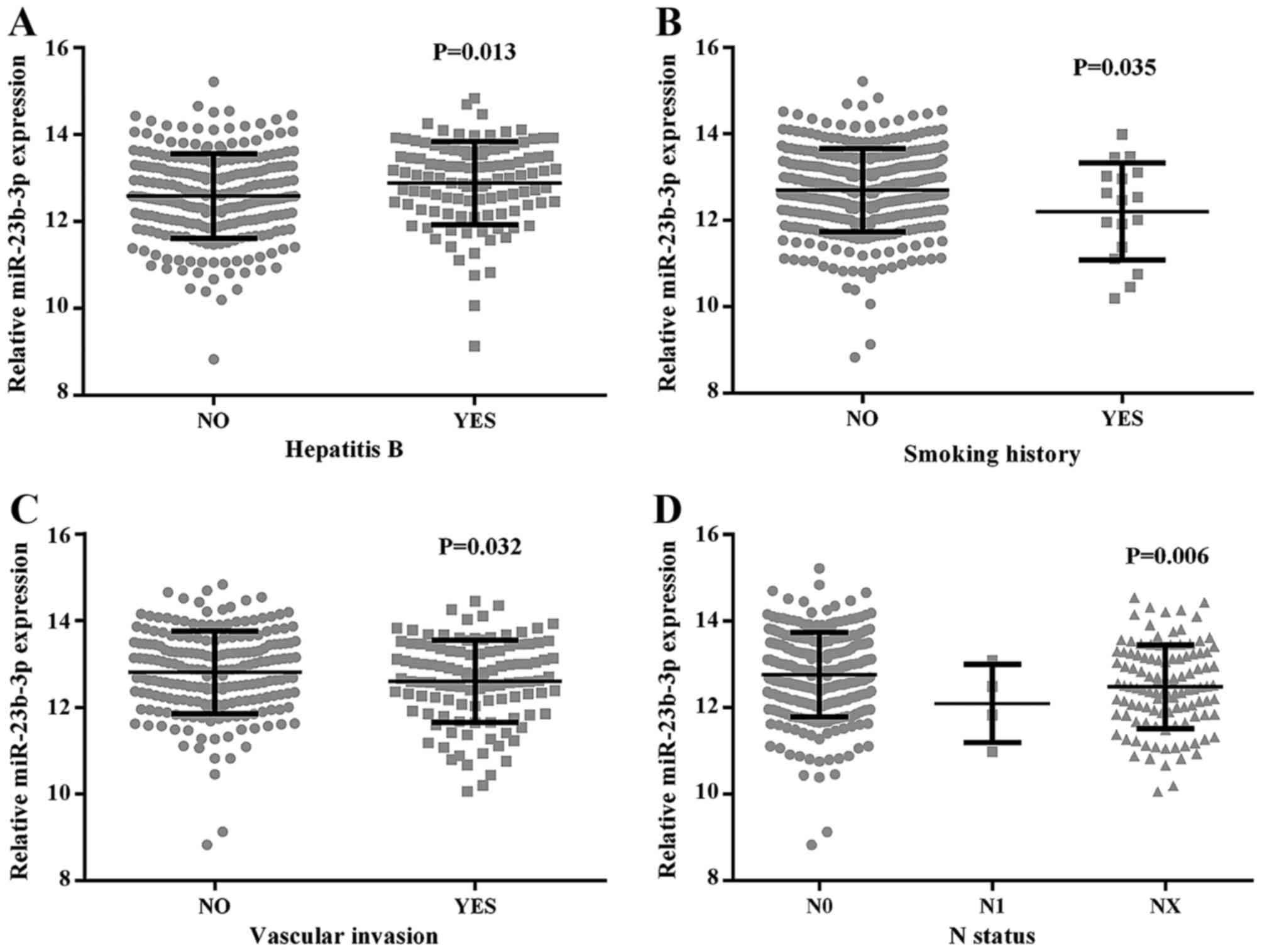
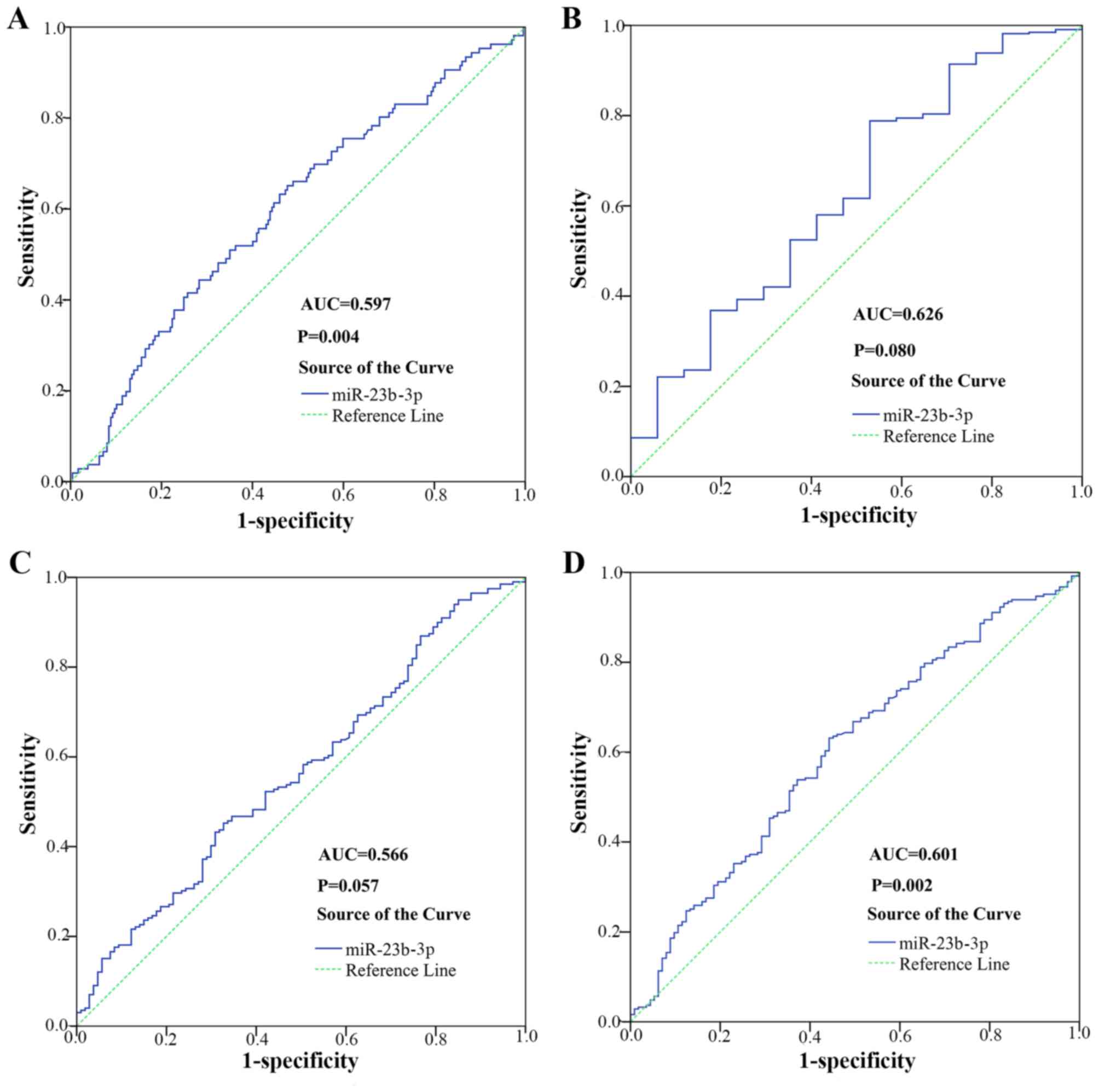
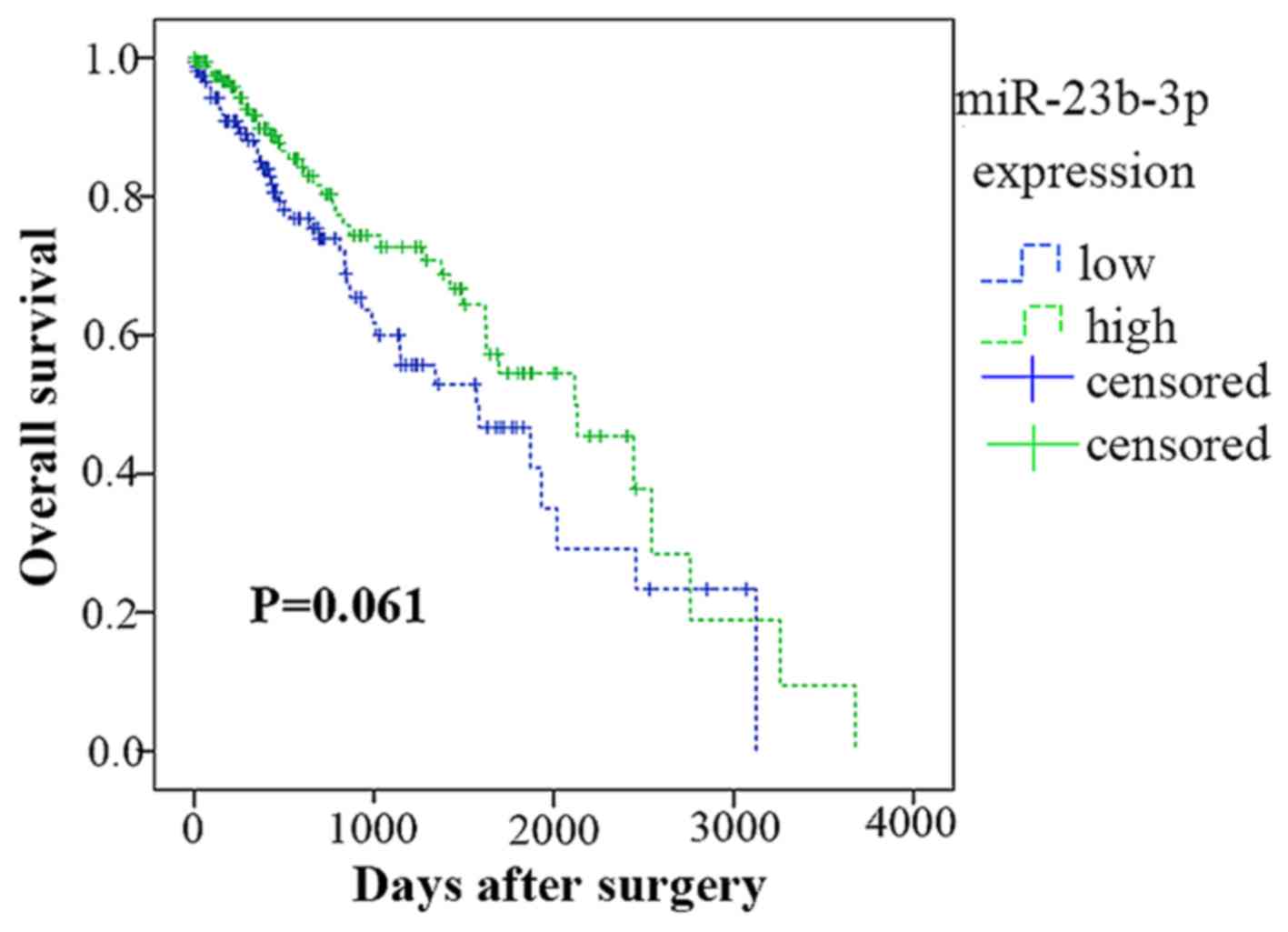
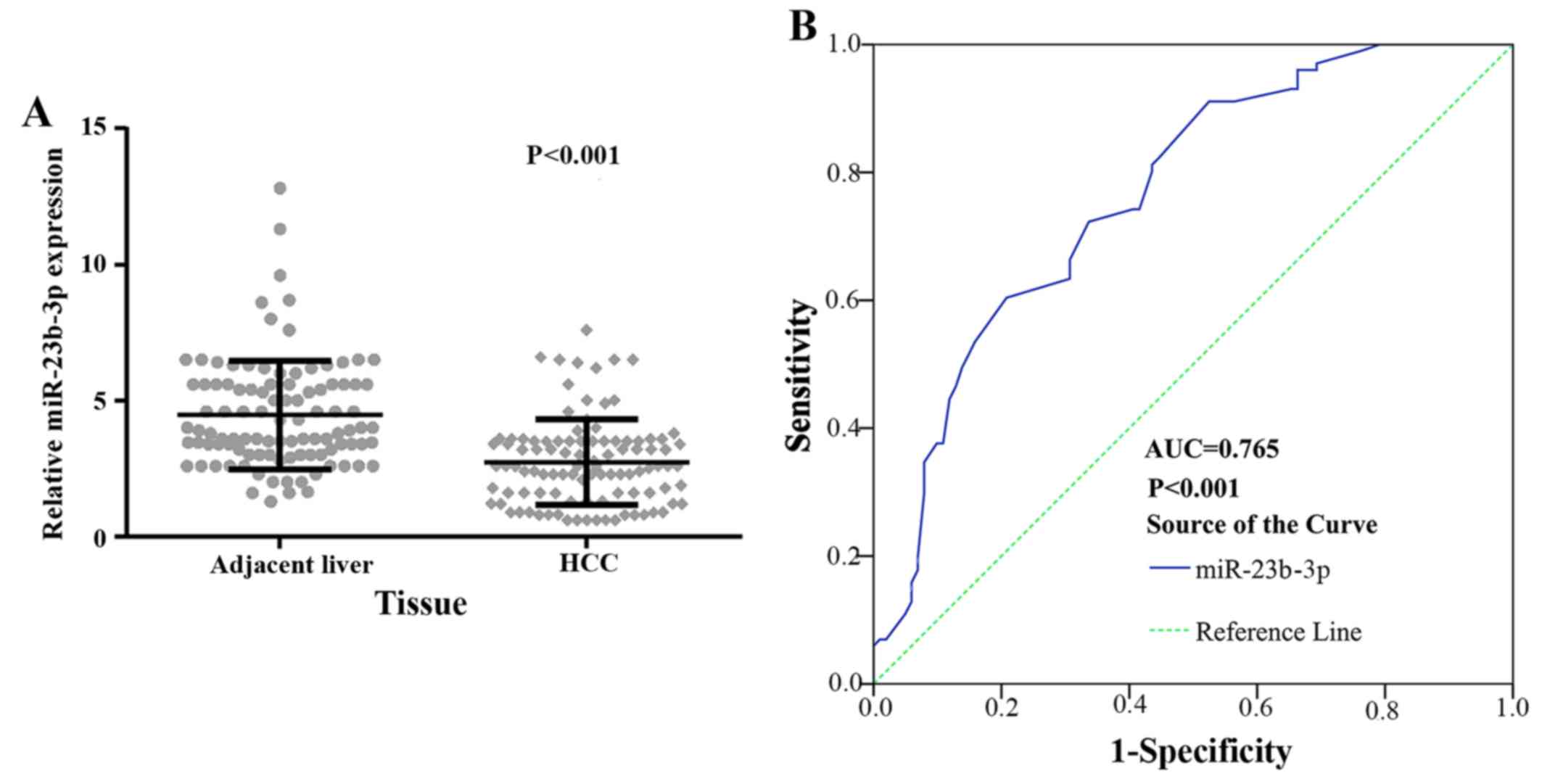
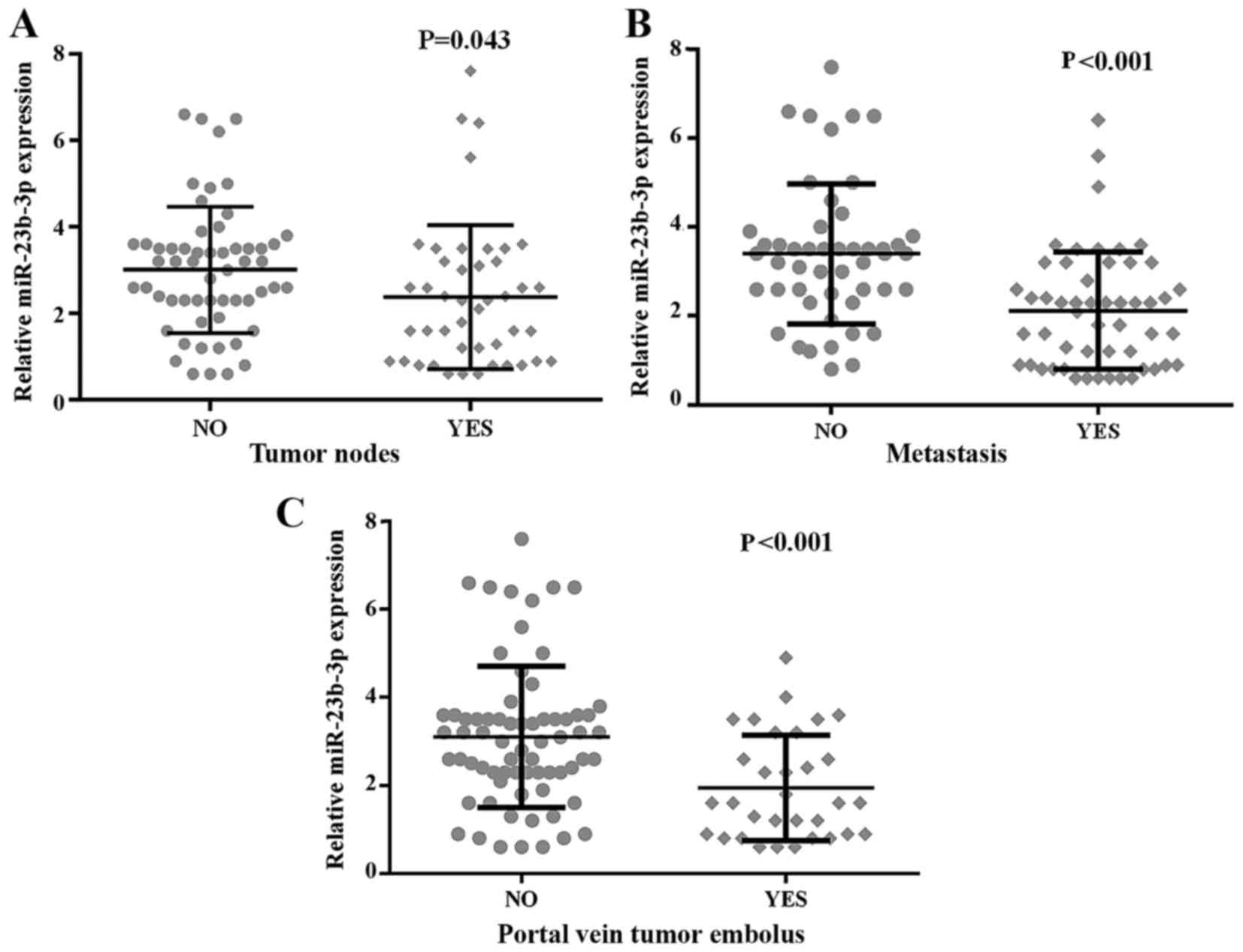
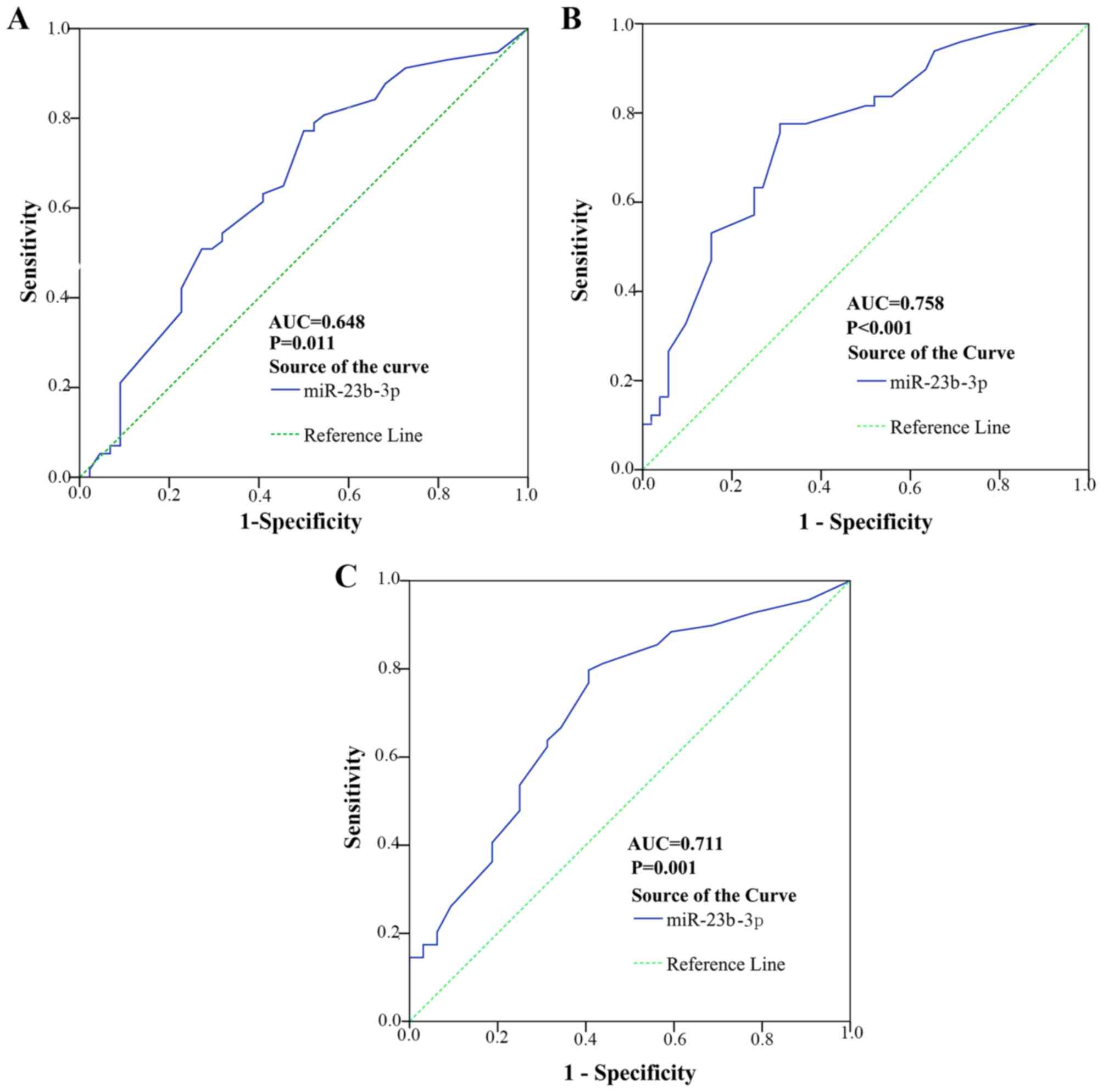
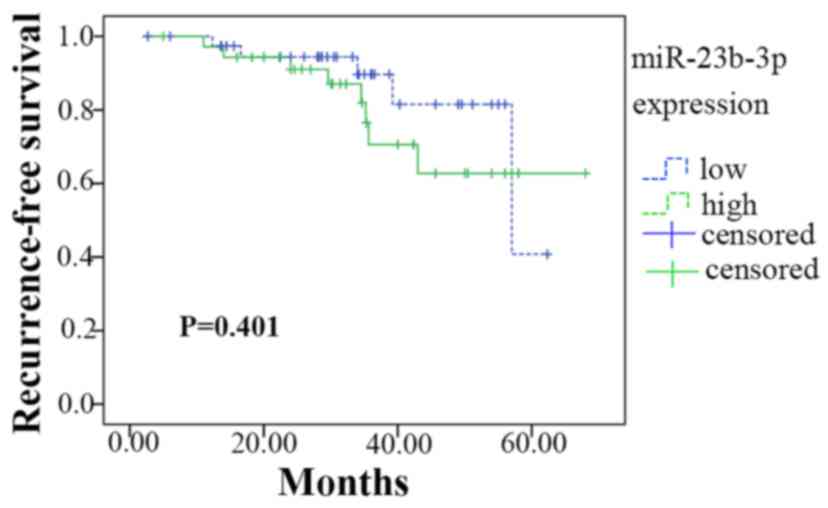
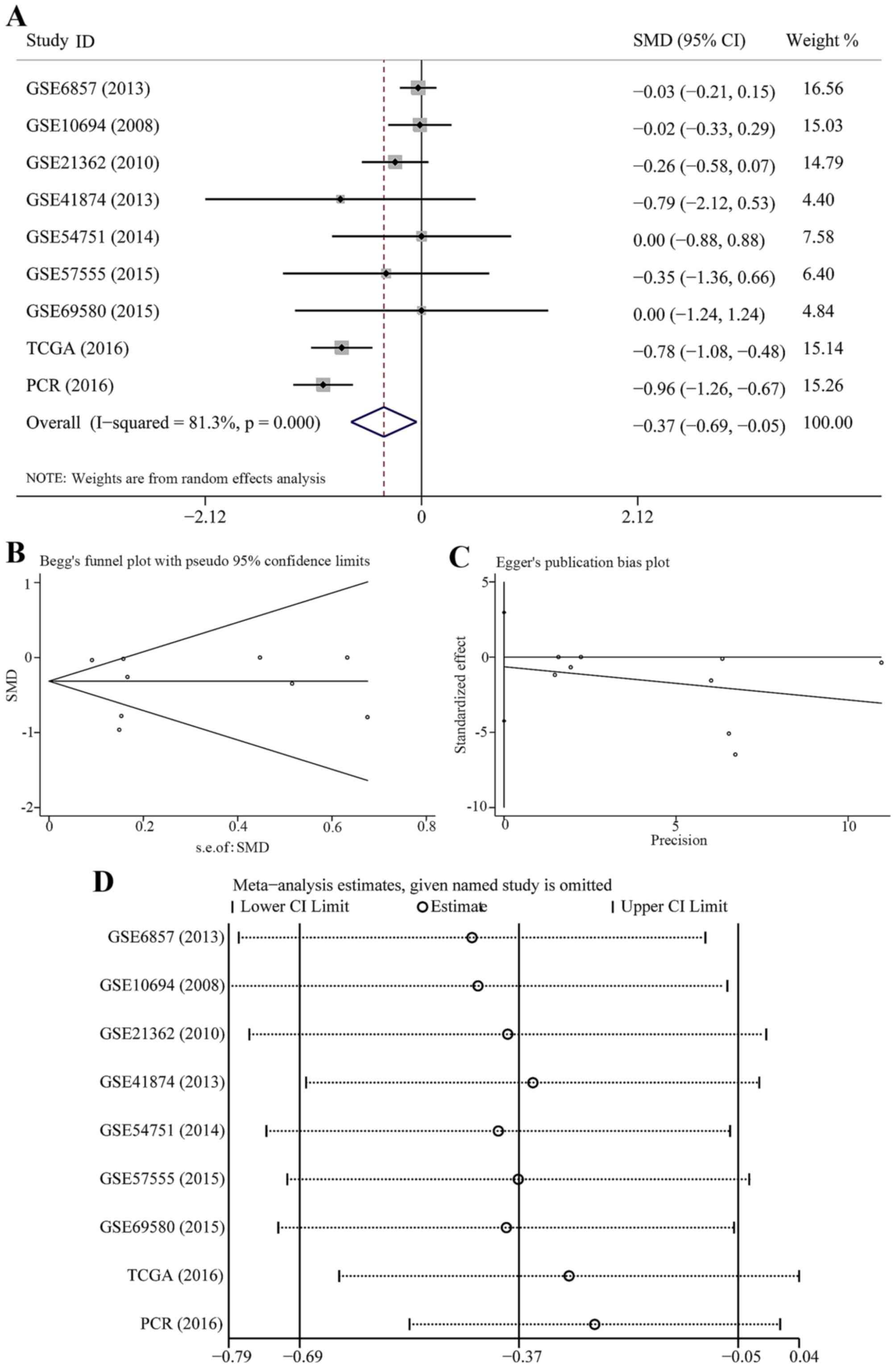
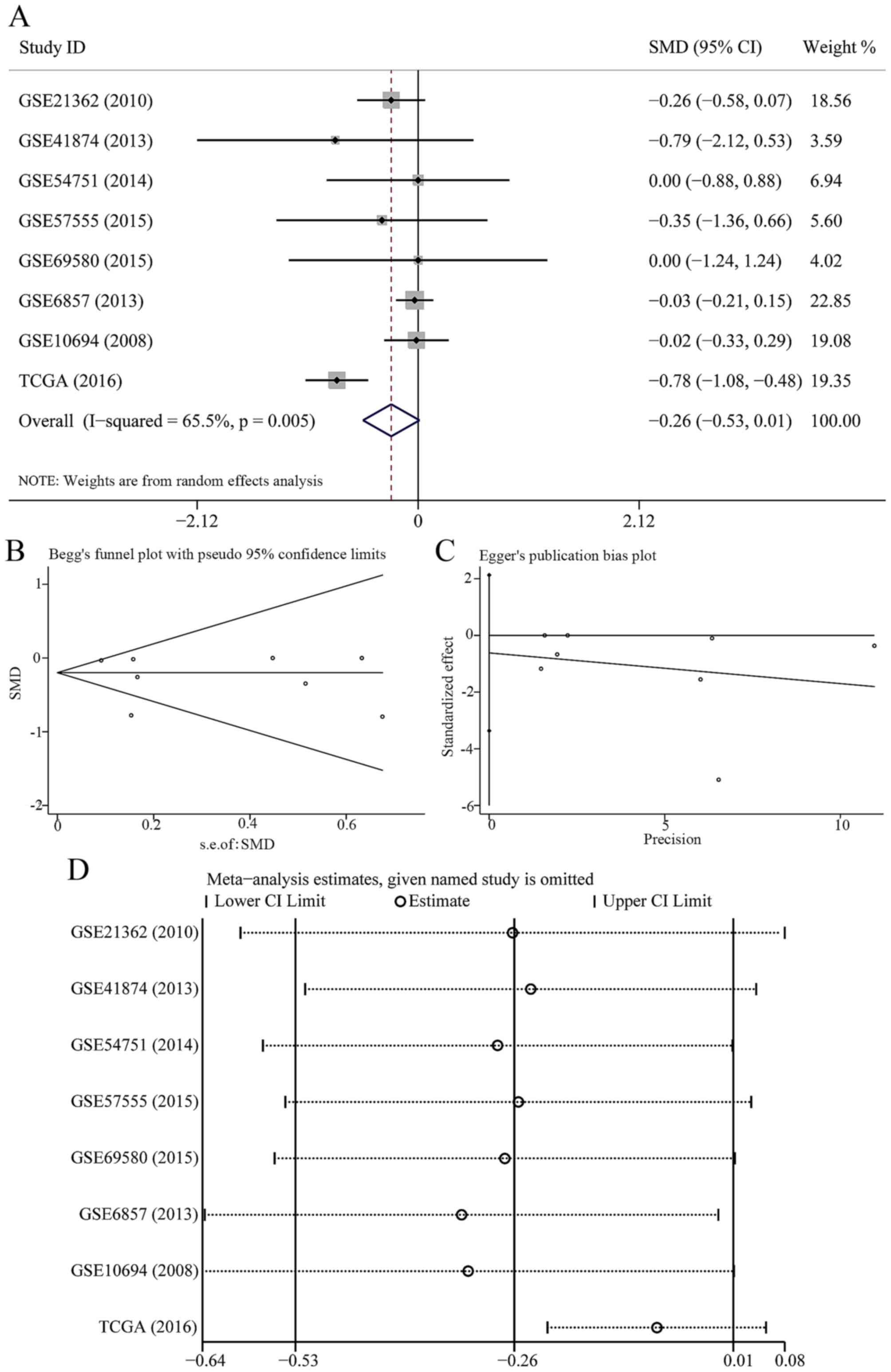
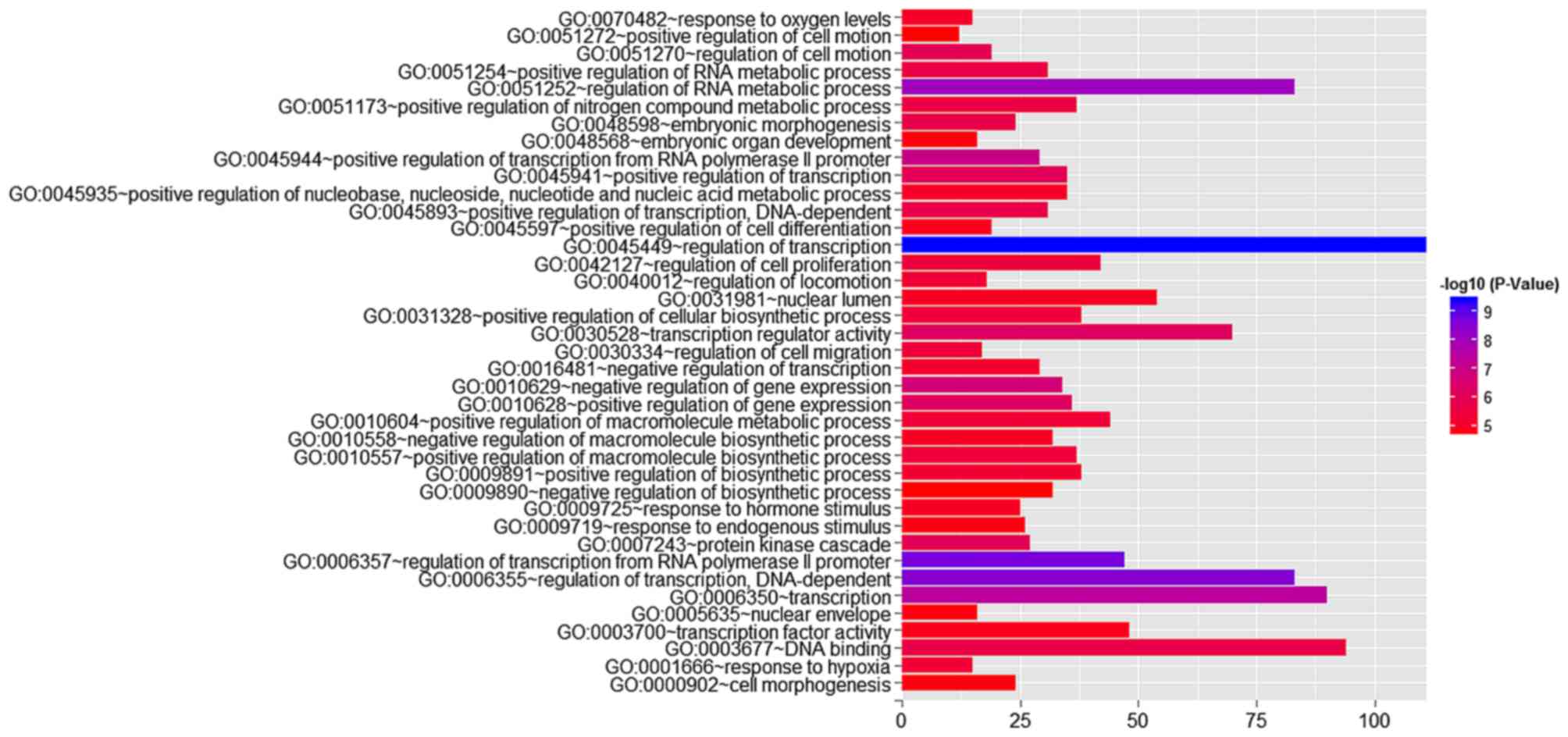
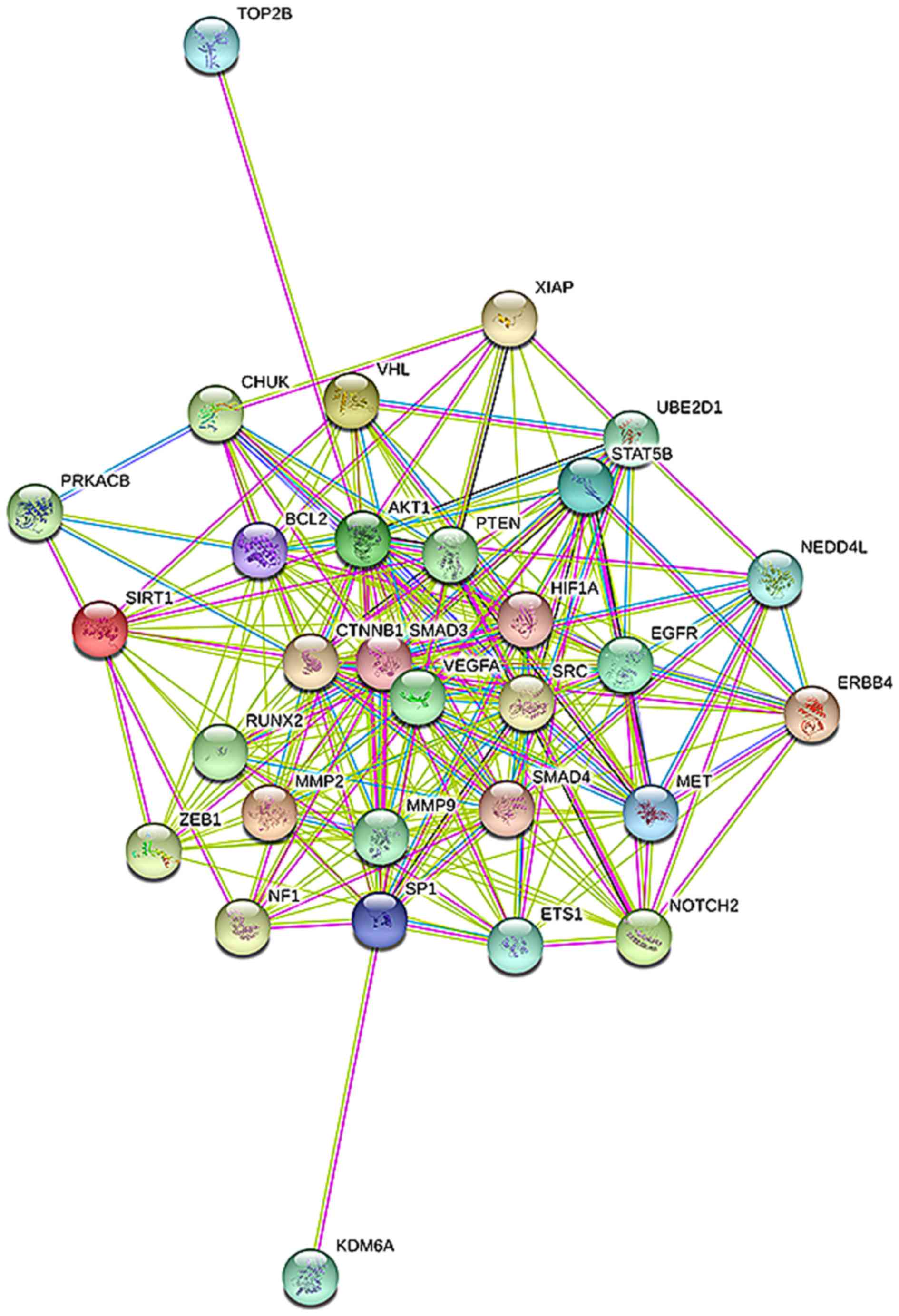
|
1
|
de Martel C, Maucort-Boulch D, Plummer M
and Franceschi S: World-wide relative contribution of hepatitis B
and C viruses in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
62:1190–1200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yun EH, Lim MK, Oh JK, Park JH, Shin A,
Sung J and Park EC: Combined effect of socioeconomic status, viral
hepatitis, and lifestyles on hepatocelluar carcinoma risk in Korea.
Br J Cancer. 103:741–746. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
M'Bengue AK, Doumbia M, Denoman SR,
Ouattara DN, Adoubi I and Pineau P: A major shift of viral and
nutritional risk factors affects the hepatocellular carcinoma risk
among Ivorian patients: A preliminary report. Infect Agent Cancer.
10:182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
O'Hara SP, Mott JL, Splinter PL, Gores GJ
and LaRusso NF: MicroRNAs: Key modulators of posttranscriptional
gene expression. Gastroenterology. 136:17–25. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Francis P, Moon SY, Bilke S, Zhu YJ and
Meltzer PS: Role of the microRNA-23 27 24 clusters in osteosarcoma.
Cancer Res. 72(Suppl 8): 11132012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Kojima S, Sakamoto S,
Kawamura K, Imamoto T, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Kinoshita T, Naya Y,
et al: The functional significance and its regulated molecular
targets of microrna-23b/27b/24-1 cluster in prostate cancer. J
Urol. 191:e456–e457. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ishihara T, Chiyomaru T, Inoguchi S,
Enokida H, Seki N and Nakagawa M: The clustered microRNA-23b/27b
function as tumor suppressors and useful prognostic markers in
renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 191:e2432014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jiang W, Min J, Sui X, Qian Y, Liu Y, Liu
Z, Zhou H, Li X and Gong Y: MicroRNA-26a-5p and microRNA-23b-3p
up-regulate peroxiredoxin III in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk
Lymphoma. 56:460–471. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Han L, Chen L, Zhang K, Shi Z, Zhang J,
Zhang A, Wang Y, Song Y, Zheng Y, Jiang T, et al: MicroRNA-23b
expression is regulated by VHL and effects on glioma cell survival
and invasion. Cancer Res. 72:82012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Jin L, Wessely O, Marcusson EG, Ivan C,
Calin GA and Alahari SK: Prooncogenic factors miR-23b and miR-27b
are regulated by Her2/Neu, EGF, and TNF-α in breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 73:2884–2896. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma G, Dai W, Sang A, Yang X and Gao C:
Upregulation of microRNA-23a/b promotes tumor progression and
confers poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:8833–8840. 2014.
|
|
14
|
Rogler CE, Levoci L, Ader T, Massimi A,
Tchaikovskaya T and Norel R: MicroRNA-23b cluster microRNAs
regulate transforming growth factor-beta/bone morphogenetic protein
signaling and liver stem cell differentiation by targeting Smads.
Hepatology. 50:575–584. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yuan B, Dong R, Shi D, Zhou Y, Zhao Y,
Miao M and Jiao B: Down-regulation of miR-23b may contribute to
activation of the TGF-β1/Smad3 signalling pathway during the
termination stage of liver regeneration. FEBS Lett. 585:927–934.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Salvi A, Sabelli C, Moncini S, Venturin M,
Arici B, Riva P, Portolani N, Giulini SM, De Petro G and Barlati S:
MicroRNA-23b mediates urokinase and c-met downmodulation and a
decreased migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. FEBS
J. 276:2966–2982. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lau J, Ioannidis JP and Schmid CH:
Quantitative synthesis in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med.
127:820–826. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zamora J, Abraira V, Muriel A, Khan K and
Coomarasamy A: Meta-DiSc: A software for meta-analysis of test
accuracy data. BMC Med Res Methodol. 6:312006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Khan N: Meta-analysis: A quantitative
approach of data pooling. Pak Oral Dental J. 20:214–221. 2000.
|
|
21
|
Budhu A, Roessler S, Zhao X, Yu Z, Forgues
M, Ji J, Karoly E, Qin LX, Ye QH, Jia HL, et al: Integrated
metabolite and gene expression profiles identify lipid biomarkers
associated with progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and patient
outcomes. Gastroenterology. 144:1066–1075.e1. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li W, Xie L, He X, Li J, Tu K, Wei L, Wu
J, Guo Y, Ma X, Zhang P, et al: Diagnostic and prognostic
implications of microRNAs in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 123:1616–1622. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sato F, Hatano E, Kitamura K, Myomoto A,
Fujiwara T, Takizawa S, Tsuchiya S, Tsujimoto G, Uemoto S and
Shimizu K: MicroRNA profile predicts recurrence after resection in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan Criteria.
PLoS One. 6:e164352011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Su H, Yang JR, Xu T, Huang J, Xu L, Yuan Y
and Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-101, down-regulated in hepatocellular
carcinoma, promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity. Cancer
Res. 69:1135–1142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shen J, LeFave C, Sirosh I, Siegel AB,
Tycko B and Santella RM: Integrative epigenomic and genomic
filtering for methylation markers in hepatocellular carcinomas. BMC
Med Genomics. 8:282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Murakami Y, Kubo S, Tamori A, Itami S,
Kawamura E, Iwaisako K, Ikeda K, Kawada N, Ochiya T and Taguchi YH:
Comprehensive analysis of transcriptome and metabolome analysis in
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci
Rep. 5:162942015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang H, Hao Y, Yang J, Zhou Y, Li J, Yin
S, Sun C, Ma M, Huang Y and Xi JJ: Genome-wide functional screening
of miR-23b as a pleiotropic modulator suppressing cancer
metastasis. Nat Commun. 2:5542011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Salvi A, Sabelli C, Moncini S, Venturin M,
Arici B, Riva P, Portolani N, Giulini SM, De Petro G and Barlati S:
MicroRNA-23b mediates urokinase and c-met downmodulation and a
decreased migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. FEBS
J. 276:2966–2982. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dehm SM and Bonham K: SRC gene expression
in human cancer: The role of transcriptional activation. Biochem
Cell Biol. 82:263–274. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Finn RS: Targeting Src in breast cancer.
Ann Oncol. 19:1379–1386. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao Y, Scott A, Zhang P, Hao Y, Feng X,
Somasundaram S, Khalil AM, Willis J and Wang Z: Regulation of
paxillin-p130-PI3K-AKT signaling axis by Src and PTPRT impacts
colon tumorigenesis. Oncotarget. 8:48782–48793. 2017.
|
|
32
|
Sun L, Wang D, Li X, Zhang L, Zhang H and
Zhang Y: Extracellular matrix protein ITGBL1 promotes ovarian
cancer cell migration and adhesion through Wnt/PCP signaling and
FAK/SRC pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 81:145–151. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xiong J, Wu JS, Mao SS, Yu XN and Huang
XX: Effect of saracatinib on pulmonary metastases from
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 36:1483–1490. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shor AC, Keschman EA, Lee FY, Muro-Cacho
C, Letson GD, Trent JC, Pledger WJ and Jove R: Dasatinib inhibits
migration and invasion in diverse human sarcoma cell lines and
induces apoptosis in bone sarcoma cells dependent on SRC kinase for
survival. Cancer Res. 67:2800–2808. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vojtechová M, Turecková J, Kucerová D,
Sloncová E, Vachtenheim J and Tuhácková Z: Regulation of mTORC1
signaling by Src kinase activity is Akt1-independent in
RSV-transformed cells. Neoplasia. 10:99–107. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Park S, Kim D, Kaneko S, Szewczyk KM,
Nicosia SV, Yu H, Jove R and Cheng JQ: Molecular cloning and
characterization of the human AKT1 promoter uncovers its
up-regulation by the Src/Stat3 pathway. J Biol Chem.
280:38932–38941. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li B, Sun M, Gao F, Liu W, Yang Y, Liu H,
Cheng Y, Liu C and Cai J: Up-regulated expression of miR-23a/b
targeted the pro-apoptotic Fas in radiation-induced thymic
lymphoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 32:1729–1740. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Majid S, Dar AA, Saini S, Arora S,
Shahryari V, Zaman MS, Chang I, Yamamura S, Tanaka Y, Deng G, et
al: miR-23b represses proto-oncogene Src kinase and functions as
methylation-silenced tumor suppressor with diagnostic and
prognostic significance in prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
72:6435–6446. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Majid S, Dar AA, Saini S, Deng G, Chang I,
Greene K, Tanaka Y, Dahiya R and Yamamura S: MicroRNA-23b functions
as a tumor suppressor by regulating Zeb1 in bladder cancer. PLoS
One. 8:e676862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bisio A, De Sanctis V, Del Vescovo V,
Denti MA, Jegga AG, Inga A and Ciribilli Y: Identification of new
p53 target microRNAs by bioinformatics and functional analysis. BMC
Cancer. 13:5522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen L, Han L, Zhang K, Shi Z, Zhang J,
Zhang A, Wang Y, Song Y, Li Y, Jiang T, et al: VHL regulates the
effects of miR-23b on glioma survival and invasion via suppression
of HIF-1α/VEGF and β-catenin/Tcf-4 signaling. Neuro Oncol.
14:1026–1036. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen Y, Li L, Zhou Z, Wang N, Zhang CY and
Zen K: A pilot study of serum microRNA signatures as a novel
biomarker for occult hepatitis B virus infection. Med Microbiol
Immunol. 201:389–395. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|