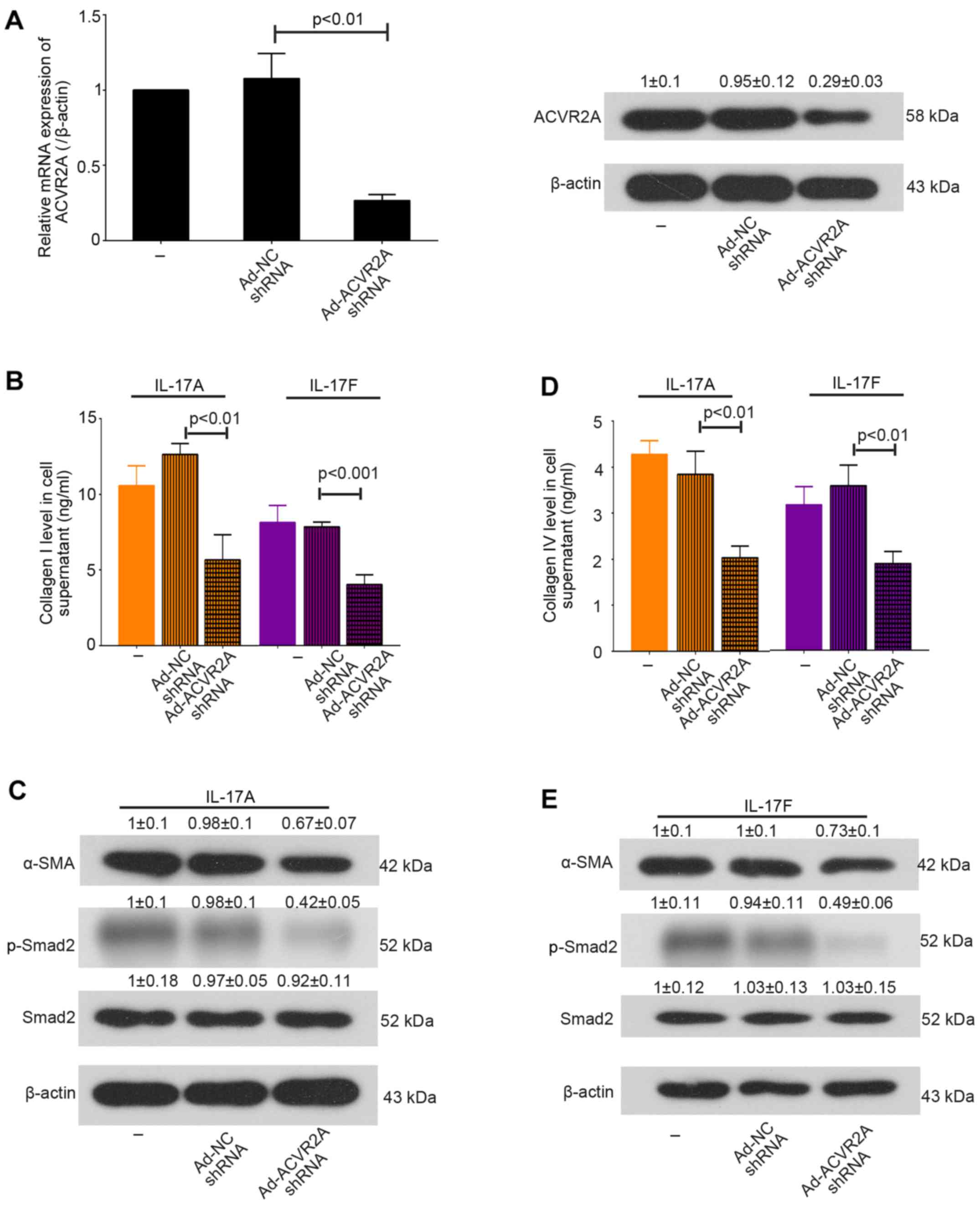
|
1
|
Pellicoro A, Ramachandran P, Iredale JP
and Fallowfield JA: Liver fibrosis and repair: Immune regulation of
wound healing in a solid organ. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:181–194. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nanthakumar CB, Hatley RJ, Lemma S,
Gauldie J, Marshall RP and Macdonald SJ: Dissecting fibrosis:
Therapeutic insights from the small-molecule toolbox. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 14:693–720. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee YA, Wallace MC and Friedman SL:
Pathobiology of liver fibrosis: A translational success story. Gut.
64:830–841. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mederacke I, Hsu CC, Troeger JS, Huebener
P, Mu X, Dapito DH, Pradere JP and Schwabe RF: Fate tracing reveals
hepatic stellate cells as dominant contributors to liver fibrosis
independent of its aetiology. Nat Commun. 4:28232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen RJ, Wu HH and Wang YJ: Strategies to
prevent and reverse liver fibrosis in humans and laboratory
animals. Arch Toxicol. 89:1727–1750. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Seki E and Schwabe RF: Hepatic
inflammation and fibrosis: Functional links and key pathways.
Hepatology. 61:1066–1079. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Bissell DM, Roulot D and George J:
Transforming growth factor beta and the liver. Hepatology.
34:859–867. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nakamura T, Sakata R, Ueno T, Sata M and
Ueno H: Inhibition of transforming growth factor beta prevents
progression of liver fibrosis and enhances hepatocyte regeneration
in dimethylnitrosamine-treated rats. Hepatology. 32:247–255. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qi Z, Atsuchi N, Ooshima A, Takeshita A
and Ueno H: Blockade of type beta transforming growth factor
signaling prevents liver fibrosis and dysfunction in the rat. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:2345–2349. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Weiss A and Attisano L: The TGFbeta
superfamily signaling pathway. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol.
2:47–63. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kreidl E, Oztürk D, Metzner T, Berger W
and Grusch M: Activins and follistatins: Emerging roles in liver
physiology and cancer. World J Hepatol. 1:17–27. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sugiyama M, Ichida T, Sato T, Ishikawa T,
Matsuda Y and Asakura H: Expression of activin A is increased in
cirrhotic and fibrotic rat livers. Gastroenterology. 114:550–558.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gold EJ, Francis RJ, Zimmermann A, Mellor
SL, Cranfield M, Risbridger GP, Groome NP, Wheatley AM and Fleming
JS: Changes in activin and activin receptor subunit expression in
rat liver during the development of CCl4-induced
cirrhosis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 201:143–153. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fujita T, Soontrapa K, Ito Y, Iwaisako K,
Moniaga CS, Asagiri M, Majima M and Narumiya S: Hepatic stellate
cells relay inflammation signaling from sinusoids to parenchyma in
mouse models of immune-mediated hepatitis. Hepatology.
63:1325–1339. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Louis H, Le Moine A, Quertinmont E, Peny
MO, Geerts A, Goldman M, Le Moine O and Devière J: Repeated
concanavalin A challenge in mice induces an interleukin
10-producing phenotype and liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 31:381–390.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tu CT, Li J, Wang FP, Li L, Wang JY and
Jiang W: Glycyrrhizin regulates CD4+ T cell response during liver
fibrogenesis via JNK, ERK and PI3K/AKT pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 14:410–421. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Meng F, Wang K, Aoyama T, Grivennikov SI,
Paik Y, Scholten D, Cong M, Iwaisako K, Liu X, Zhang M, et al:
Interleukin-17 signaling in inflammatory, Kupffer cells, and
hepatic stellate cells exacerbates liver fibrosis in mice.
Gastroenterology. 143:765–76. e1–3. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Song E, Lee SK, Wang J, Ince N, Ouyang N,
Min J, Chen J, Shankar P and Lieberman J: RNA interference
targeting Fas protects mice from fulminant hepatitis. Nat Med.
9:347–351. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu PB, Beppu H, Kawai N, Li E and Bloch
KD: Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type II receptor deletion
reveals BMP ligand-specific gain of signaling in pulmonary artery
smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 280:24443–24450. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu WH, Hu HG, Tian Y, Wang SZ, Li J, Li
JZ, Deng X, Qian H, Qiu L, Hu ZL, et al: Bioactive compound reveals
a novel function for ribosomal protein S5 in hepatic stellate cell
activation and hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology. 60:648–660. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tan Z, Qian X, Jiang R, Liu Q, Wang Y,
Chen C, Wang X, Ryffel B and Sun B: IL-17A plays a critical role in
the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis through hepatic stellate cell
activation. J Immunol. 191:1835–1844. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li Y, Kim BG, Qian S, Letterio JJ, Fung
JJ, Lu L and Lin F: Hepatic stellate cells inhibit T cells through
active TGF-β1 from a cell surface-bound latent TGF-β1/GARP complex.
J Immunol. 195:2648–2656. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu MC, Chen CH, Liang X, Wang L, Gandhi
CR, Fung JJ, Lu L and Qian S: Inhibition of T-cell responses by
hepatic stellate cells via B7-H1-mediated T-cell apoptosis in mice.
Hepatology. 40:1312–1321. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Weiskirchen S, Tag CG, Sauer-Lehnen S,
Tacke F and Weiskirchen R: Isolation and culture of primary murine
hepatic stellate cells. Methods Mol Biol. 1627:165–191. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chang J, Lan T, Li C, Ji X, Zheng L, Gou
H, Ou Y, Wu T, Qi C, Zhang Q, et al: Activation of Slit2-Robo1
signaling promotes liver fibrosis. J Hepatol. 63:1413–1420. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Patella S, Phillips DJ, Tchongue J, de
Kretser DM and Sievert W: Follistatin attenuates early liver
fibrosis: Effects on hepatic stellate cell activation and
hepatocyte apoptosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
290:G137–G144. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Patella S, Phillips DJ, de Kretser DM,
Evans LW, Groome NP and Sievert W: Characterization of serum
activin-A and follistatin and their relation to virological and
histological determinants in chronic viral hepatitis. J Hepatol.
34:576–583. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang DH, Wang YN, Ge JY, Liu HY, Zhang HJ,
Qi Y, Liu ZH and Cui XL: Role of activin A in carbon
tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury. World J Gastroenterol.
19:3802–3809. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
George J, Roulot D, Koteliansky VE and
Bissell DM: In vivo inhibition of rat stellate cell activation by
soluble transforming growth factor beta type II receptor: A
potential new therapy for hepatic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:12719–12724. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fenoglio D, Bernuzzi F, Battaglia F,
Parodi A, Kalli F, Negrini S, De Palma R, Invernizzi P and Filaci
G: Th17 and regulatory T lymphocytes in primary biliary cirrhosis
and systemic sclerosis as models of autoimmune fibrotic diseases.
Autoimmun Rev. 12:300–304. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen Y, Peng H, Chen Y, Wei H, Sun R and
Tian Z: CD49a promotes T-cell-mediated hepatitis by driving T
helper 1 cytokine and interleukin-17 production. Immunology.
141:388–400. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Kolls JK and Lindén A: Interleukin-17
family members and inflammation. Immunity. 21:467–476. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Q, Zhou J, Zhang B, Tian Z, Tang J,
Zheng Y, Huang Z, Tian Y, Jia Z, Tang Y, et al: Hepatitis B virus
induces IL-23 production in antigen presenting cells and causes
liver damage via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. PLoS Pathog. 9:e10034102013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Seeger P, Bosisio D, Parolini S, Badolato
R, Gismondi A, Santoni A and Sozzani S: Activin A as a mediator of
NK-dendritic cell functional interactions. J Immunol.
192:1241–1248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
González-Domínguez É, Domínguez-Soto Á,
Nieto C, Flores-Sevilla JL, Pacheco-Blanco M, Campos-Peña V,
Meraz-Ríos MA, Vega MA, Corbí ÁL and Sánchez-Torres C: Atypical
activin A and IL-10 production impairs human CD16+ monocyte
differentiation into anti-inflammatory macrophages. J Immunol.
196:1327–1337. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wada W, Kuwano H, Hasegawa Y and Kojima I:
The dependence of transforming growth factor-beta-induced collagen
production on autocrine factor activin A in hepatic stellate cells.
Endocrinology. 145:2753–2759. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Macias MJ, Martin-Malpartida P and
Massagué J: Structural determinants of Smad function in TGF-β
signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 40:296–308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen L, Zhang W, Liang HF, Zhou QF, Ding
ZY, Yang HQ, Liu WB, Wu YH, Man Q, Zhang BX, et al: Activin A
induces growth arrest through a SMAD- dependent pathway in hepatic
progenitor cells. Cell Commun Signal. 12:182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yoshida K, Murata M, Yamaguchi T,
Matsuzaki K and Okazaki K: Reversible human TGF-β signal shifting
between tumor suppression and fibro-carcinogenesis: Implications of
Smad phospho-isoforms for hepatic epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions. J Clin Med. 5:52016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Souchelnytskyi S, Tamaki K, Engström U,
Wernstedt C, ten Dijke P and Heldin CH: Phosphorylation of Ser465
and Ser467 in the C terminus of Smad2 mediates interaction with
Smad4 and is required for transforming growth factor-beta
signaling. J Biol Chem. 272:28107–28115. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wynn TA: Fibrotic disease and the
T(H)1/T(H)2 paradigm. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:583–594. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ,
Locksley RM and Stockinger B: TGFbeta in the context of an
inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of
IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity. 24:179–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kang JO, Lee JB and Chang J: Cholera toxin
promotes Th17 cell differentiation by modulating expression of
polarizing cytokines and the antigen-presenting potential of
dendritic cells. PLoS One. 11:e01570152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ihn HJ, Kim DH, Oh SS, Moon C, Chung JW,
Song H and Kim KD: Identification of Acvr2a as a Th17 cell-specific
gene induced during Th17 differentiation. Biosci Biotechnol
Biochem. 75:2138–2141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|