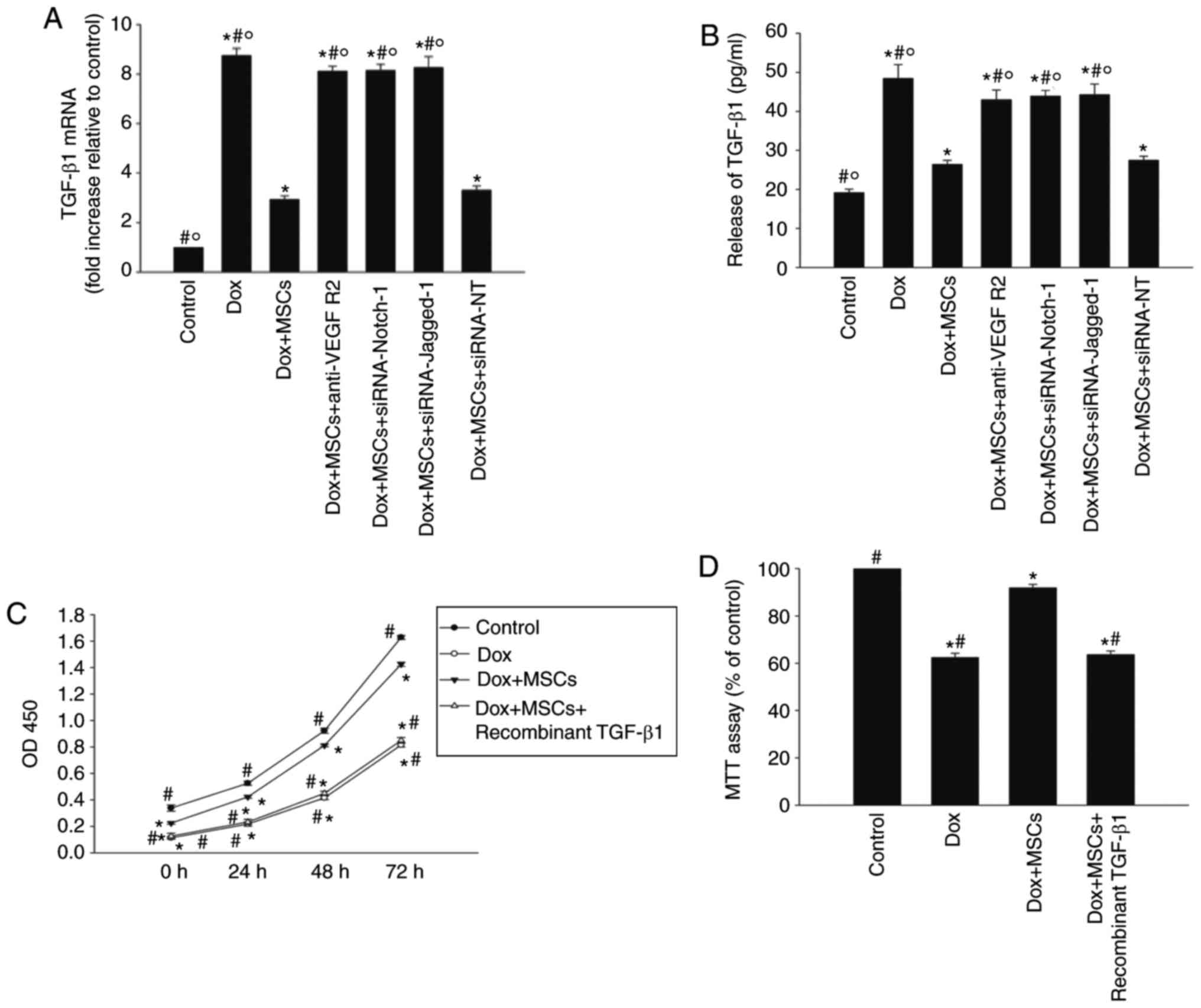
|
1
|
Octavia Y, Tocchetti CG, Gabrielson KL,
Janssens S, Crijns HJ and Moens AL: Doxorubicin-induced
cardiomyopathy: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic
strategies. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 52:1213–1225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carvalho C, Santos RX, Cardoso S, Correia
S, Oliveira PJ, Santos MS and Moreira PI: Doxorubicin: The good,
the bad and the ugly effect. Curr Med Chem. 16:3267–3285. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stěrba M, Popelová O, Vávrová A, Jirkovský
E, Kovaříková P, Geršl V and Simůnek T: Oxidative stress, redox
signaling, and metal chelation in anthracycline cardiotoxicity and
pharmacological cardioprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal.
18:899–929. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Singh P, Sharma R, McElhanon K, Allen CD,
Megyesi JK, Beneš H and Singh SP: Sulforaphane protects the heart
from doxorubicin-induced toxicity. Free Radic Biol Med. 86:90–101.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guarita-Souza LC, Teixeira de Carvalho KA,
Francisco JC, Simeoni R and Faria-Neto JR: Cellular transplantation
for the treatment of non-ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathies. Eur
Heart J Suppl. 10:K7–K10. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mohammadi Gorji S, Karimpor Malekshah AA,
Hashemi-Soteh MB, Rafiei A, Parivar K and Aghdami N: Effect of
mesenchymal stem cells on doxorubicin-induced fibrosis. Cell J.
14:142–151. 2012.
|
|
7
|
Ezquer F, Gutiérrez J, Ezquer M, Caglevic
C, Salgado HC and Calligaris SD: Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for
doxorubicin cardiomyopathy: Hopes and fears. Stem Cell Res Ther.
6:1162015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Garbade J, Dhein S, Lipinski C, Aupperle
H, Arsalan M, Borger MA, Barten MJ, Lehmann S, Walther T and Mohr
FW: Bone marrow-derived stem cells attenuate impaired contractility
and enhance capillary density in a rabbit model of
doxorubicin-induced failing hearts. J Card Surg. 24:591–599. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tian Y, Xu Y, Xue T, Chen L, Shi B, Shu B,
Xie C, Max Morandi M, Jaeblon T, Marymont JV and Dong Y: Notch
activation enhances mesenchymal stem cell sheet osteogenic
potential by inhibition of cellular senescence. Cell Death Dis.
8:e25952017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iglesias-Bartolome R and Gutkind JS:
Signaling circuitries controlling stem cell fate: To be or not to
be. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 23:716–723. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Towbin JA, Lorts A and Jefferies JL: Left
ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy. Lancet. 386:813–825.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gude N, Joyo E, Toko H, Quijada P,
Villanueva M, Hariharan N, Sacchi V, Truffa S, Joyo A, Voelkers M,
et al: Notch activation enhances lineage commitment and protective
signaling in cardiac progenitor cells. Basic Res Cardiol.
110:292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ieronimakis N, Hays AL, Janebodin K,
Mahoney WM Jr, Duffield JS, Majesky MW and Reyes M: Coronary
adventitial cells are linked to perivascular cardiac fibrosis via
TGFβ1 signaling in the mdx mouse model of duchenne muscular
dystrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 63:122–134. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Castañares C, Redondo-Horcajo M,
Magán-Marchal N, Ten Dijke P, Lamas S and Rodríguez-Pascual F:
Signaling by ALK5 mediates TGF-beta-induced ET-1 expression in
endothelial cells: A role for migration and proliferation. J Cell
Sci. 120:1256–1266. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Konorev EA, Vanamala S and Kalyanaraman B:
Differences in doxorubicin-induced apoptotic signaling in adult and
immature cardiomyocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 45:1723–1728. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hou J, Wang L, Hou J, Guo T, Xing Y, Zheng
S, Zhou C, Huang H, Long H, Zhong T, et al: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma promotes mesenchymal stem
cells to express connexin43 via the inhibition of tgf-β1/smads
signaling in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Rev.
11:885–899. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Witek P, Korga A, Burdan F, Ostrowska M,
Nosowska B, Iwan M and Dudka J: The effect of a number of H9C2 rat
cardiomyocytes passage on repeatability of cytotoxicity study
results. Cytotechnology. 68:2407–2415. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xia W, Zhang F, Xie C, Jiang M and Hou M:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor confers resistance to
senescence through cd74-dependent ampk-foxo3a signaling in
mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 6:822015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hou M, Liu J, Liu F, Liu K and Yu B: C1q
tumor necrosis factor-related protein-3 protects mesenchymal stem
cells against hypoxia- and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis
through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med.
33:97–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Piegari E, Russo R, Cappetta D, Esposito
G, Urbanek K, Dell’Aversana C, Altucci L, Berrino L, Rossi F and De
Angelis A: MicroRNA-34a regulates doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity in rat. Oncotarget. 7:62312–62326. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-(Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Xia W and Hou M: Macrophage migration
inhibitory factor rescues mesenchymal stem cells from
doxorubicin-induced senescence though the PI3K-Akt signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 41:1127–1137. 2018.
|
|
23
|
Kourembanas S: Exosomes: Vehicles of
intercellular signaling, biomarkers, and vectors of cell therapy.
Annu Rev Physiol. 77:13–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xu LL, Fu HX, Zhang JM, Feng FE, Wang QM,
Zhu XL, Xue J, Wang CC, Chen Q, Liu X, et al: Impaired function of
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from immune thrombocytopenia
patients in inducing regulatory dendritic cell differentiation
through the Notch-1/Jagged-1 signaling pathway. Stem Cell Dev.
26:1648–1661. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cardinale D, Colombo A, Bacchiani G,
Tedeschi I, Meroni CA, Veglia F, Civelli M, Lamantia G, Colombo N,
Curigliano G, et al: Early detection of anthracycline
cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy.
Circulation. 131:1981–1988. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Carver JR, Shapiro CL, Ng A, Jacobs L,
Schwartz C, Virgo KS, Hagerty KL, Somerfield MR and Vaughn DJ; ASCO
Cancer Survivorship Expert Panel: American society of clinical
oncology clinical evidence review on the ongoing care of adult
cancer survivors: Cardiac and pulmonary late effects. J Clin Oncol.
25:3991–4008. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Du WW, Yang W, Chen Y, Wu ZK, Foster FS,
Yang Z, Li X and Yang BB: Foxo3 circular RNA promotes cardiac
senescence by modulating multiple factors associated with stress
and senescence responses. Eur Heart J. 38:1402–1412. 2017.
|
|
28
|
Jackson JG, Pant V, Li Q, Chang LL,
Quintás-Cardama A, Garza D, Tavana O, Yang P, Manshouri T, Li Y, et
al: p53-mediated senescence impairs the apoptotic response to
chemotherapy and clinical outcome in breast cancer. Cancer Cell.
21:793–806. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baar MP, Brandt RMC, Putavet DA, Klein
JDD, Derks KWJ, Bourgeois BRM, Stryeck S, Rijksen Y, van
Willigenburg H, Feijtel DA, et al: Targeted apoptosis of senescent
cells restores tissue homeostasis in response to chemotoxicity and
aging. Cell. 169:132–147. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mao C, Hou X, Wang B, Chi J, Jiang Y,
Zhang C and Li Z: Intramuscular injection of human umbilical
cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves cardiac function in
dilated cardiomyopathy rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 8:182017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bollini S, Cheung KK, Riegler J, Dong X,
Smart N, Ghionzoli M, Loukogeorgakis SP, Maghsoudlou P, Dubé KN,
Riley PR, et al: amniotic fluid stem cells are cardioprotective
following acute myocardial infarction. Stem Cells Dev.
20:1985–1994. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lazzarini E, Balbi C, Altieri P, Pfeffer
U, Gambini E, Canepa M, Varesio L, Bosco MC, Coviello D, Pompilio
G, et al: The human amniotic fluid stem cell secretome effectively
counteracts doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Sci Rep.
6:299942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou N, Fu Y, Wang Y, Chen P, Meng H, Guo
S, Zhang M, Yang Z and Ge Y: p27kip1 haplo-insufficiency improves
cardiac function in early-stages of myocardial infarction by
protecting myocardium and increasing angiogenesis by promoting IKK
activation. Sci Rep. 4:59782014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Rios C, D’Ippolito G, Curtis KM, Delcroix
GJ, Gomez LA, El Hokayem J, Rieger M, Parrondo R, de Las Pozas A,
Perez-Stable C, et al: Low oxygen modulates multiple signaling
pathways increasing self-renewal while decreasing differentiation,
senescence and apoptosis in stromal miami cells. Stem Cells Dev.
25:848–460. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Packard RRS, Baek KI, Beebe T, Jen N, Ding
Y, Shi F, Fei P, Kang BJ, Chen PH, Gau J, et al: Automated
segmentation of light-sheet fluorescent imaging to characterize
experimental doxorubicin-induced cardiac injury and repair. Sci
Rep. 7:86032017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chua S, Lee FY, Chiang HJ, Chen KH, Lu HI,
Chen YT, Yang CC, Lin KC, Chen YL, Kao GS, et al: The
cardioprotective effect of melatonin and exendin-4 treatment in a
rat model of cardiorenal syndrome. J Pineal Res. 61:438–456. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sun Z, Schriewer J, Tang M, Marlin J,
Taylor F, Shohet RV and Konorev EA: The TGF-β pathway mediates
doxorubicin effects on cardiac endothelial cells. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 90:129–138. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cappetta D, Esposito G, Piegari E, Russo
R, Ciuffreda LP, Rivellino A, Berrino L, Rossi F, De Angelis A and
Urbanek K: SIRT1 activation attenuates diastolic dysfunction by
reducing cardiac fibrosis in a model of anthracycline
cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol. 205:99–110. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li H, Xu D, Toh BH and Liu JP: TGF-beta
and cancer: Is Smad3 a repressor of hTERT gene? Cell Res.
16:169–173. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen P, Wu R, Zhu W, Jiang Z, Xu Y, Chen
H, Zhang Z, Chen H, Zhang L, Yu H, et al: Hypoxia preconditioned
mesenchymal stem cells prevent cardiac fibroblast activation and
collagen production via leptin. PloS one. 9:e1035872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|