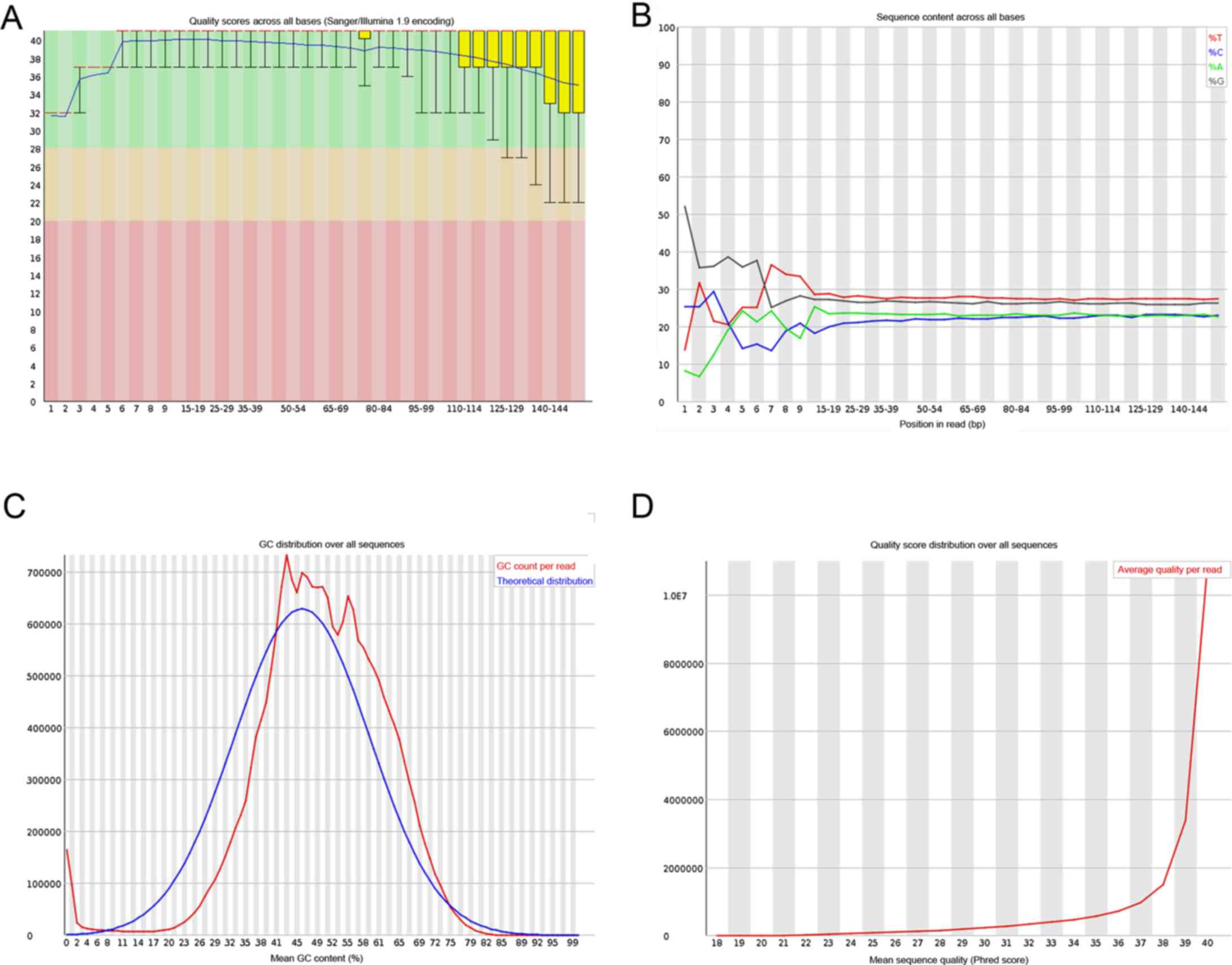
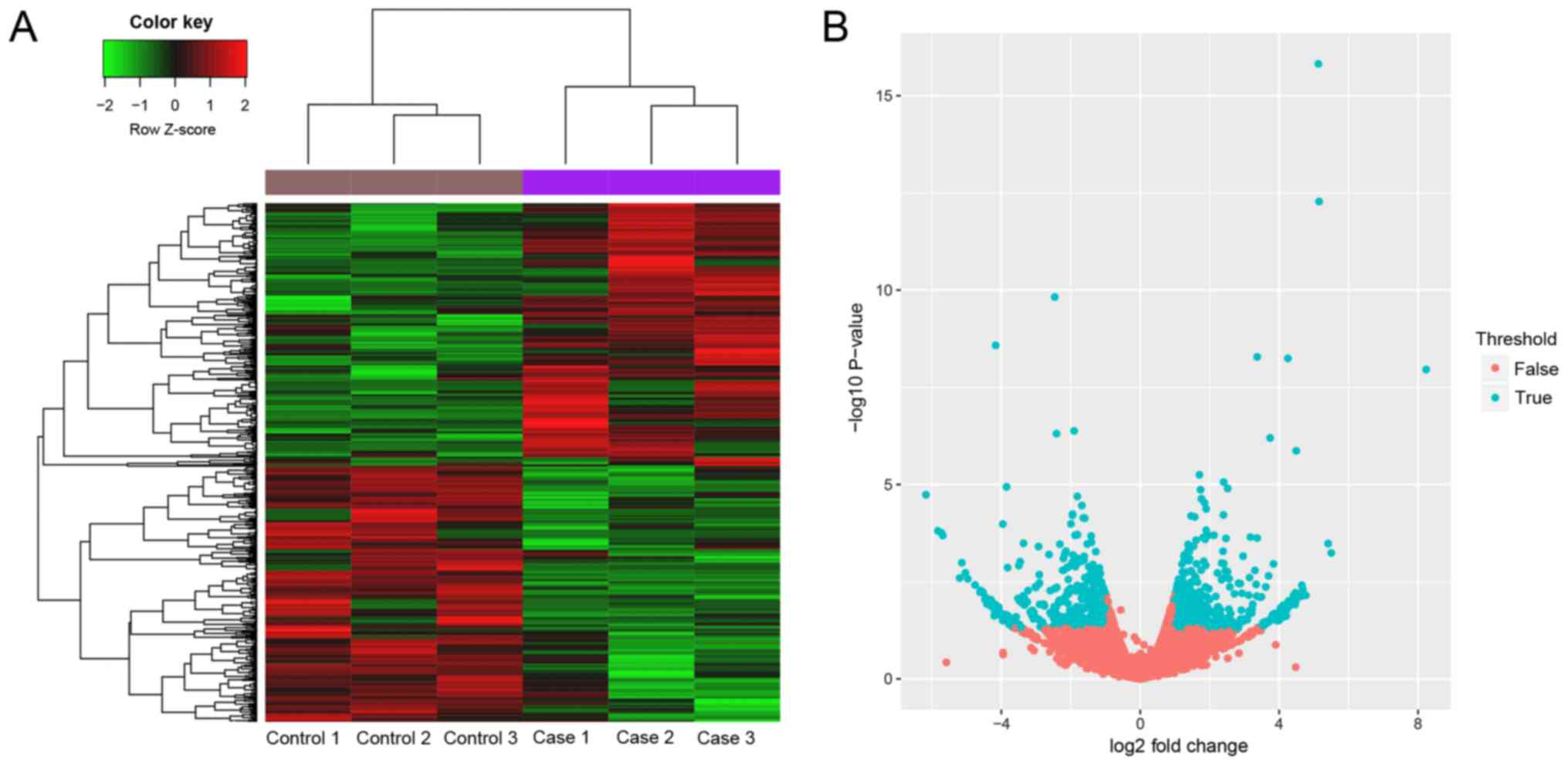
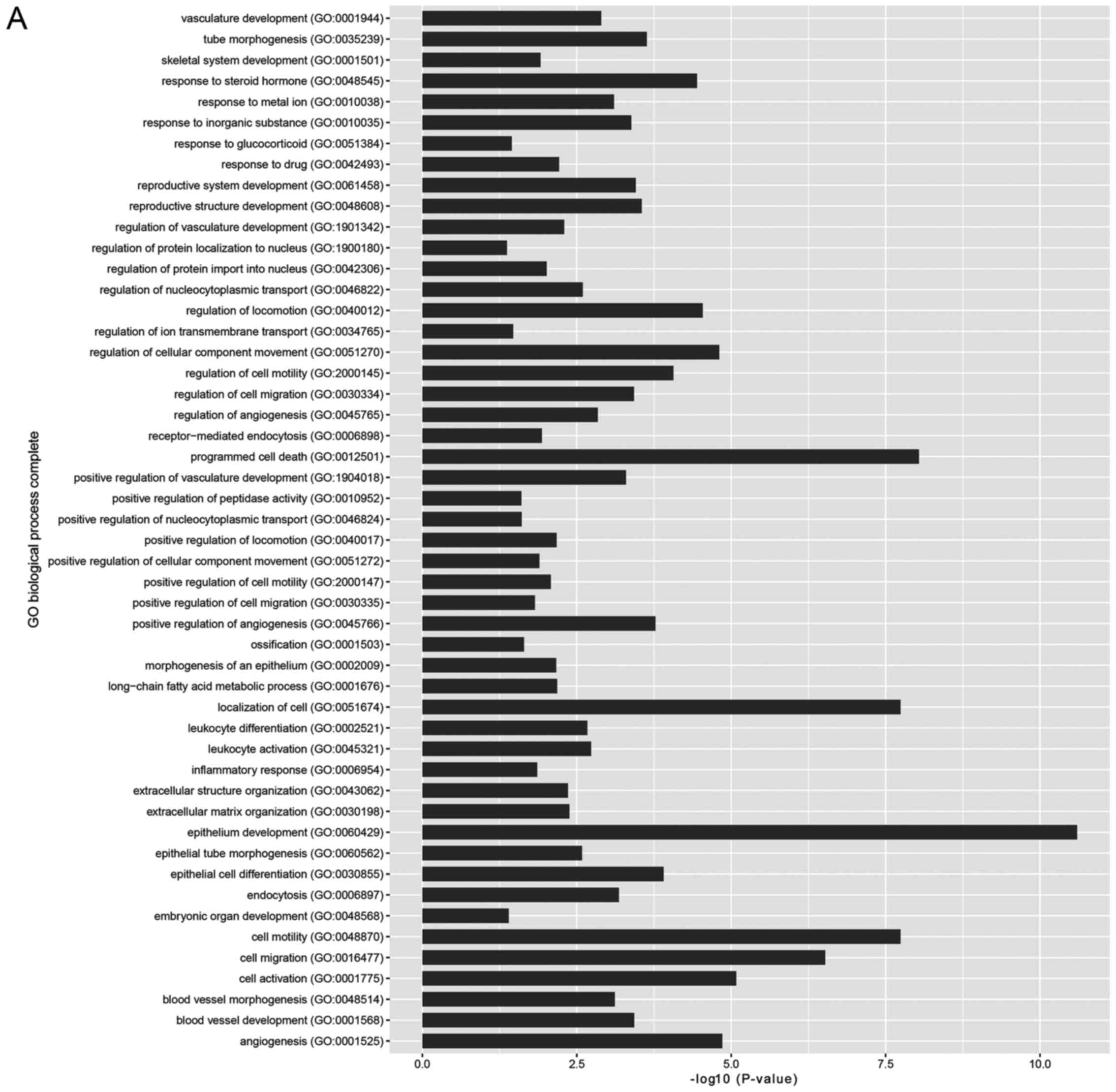
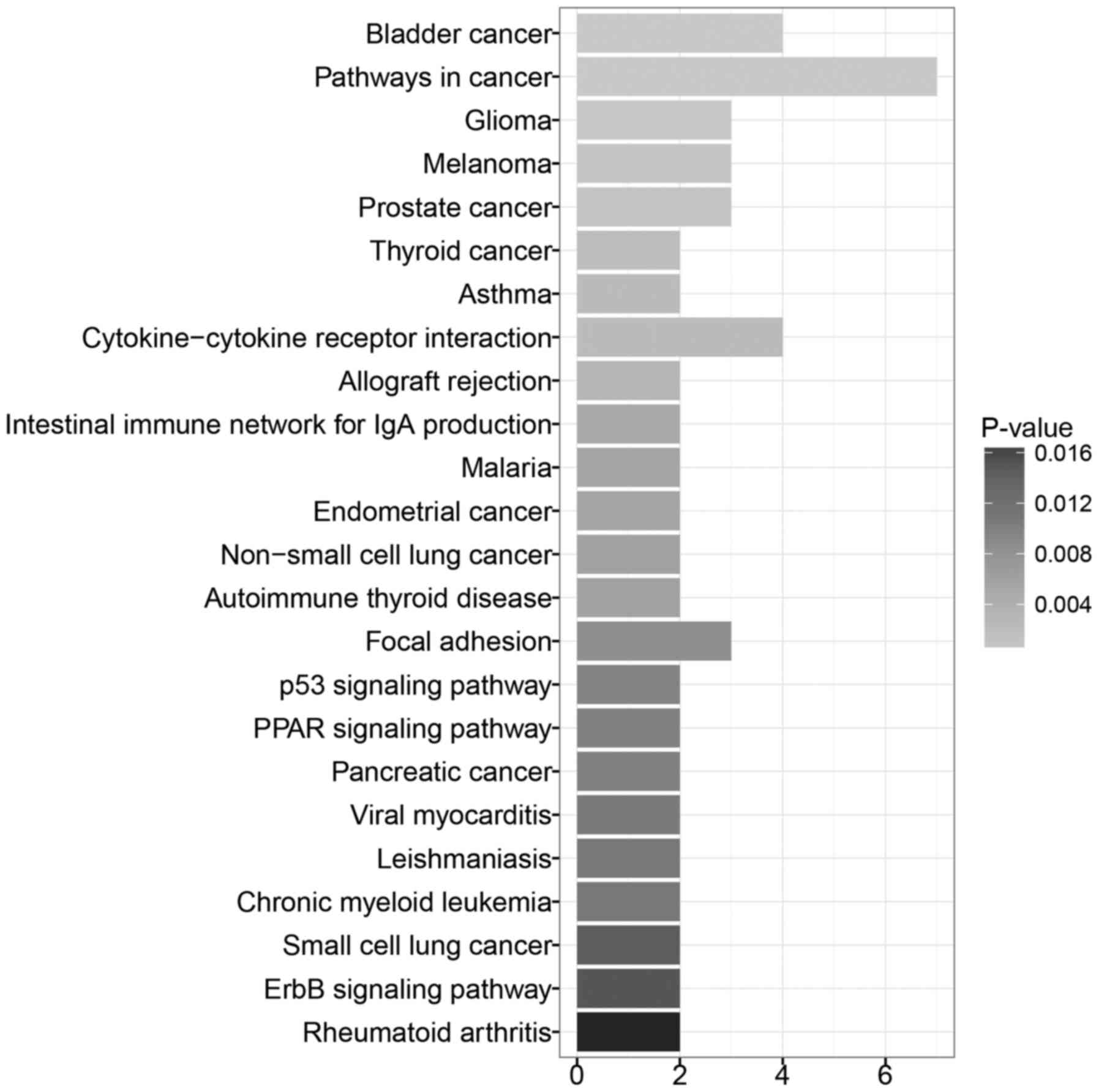
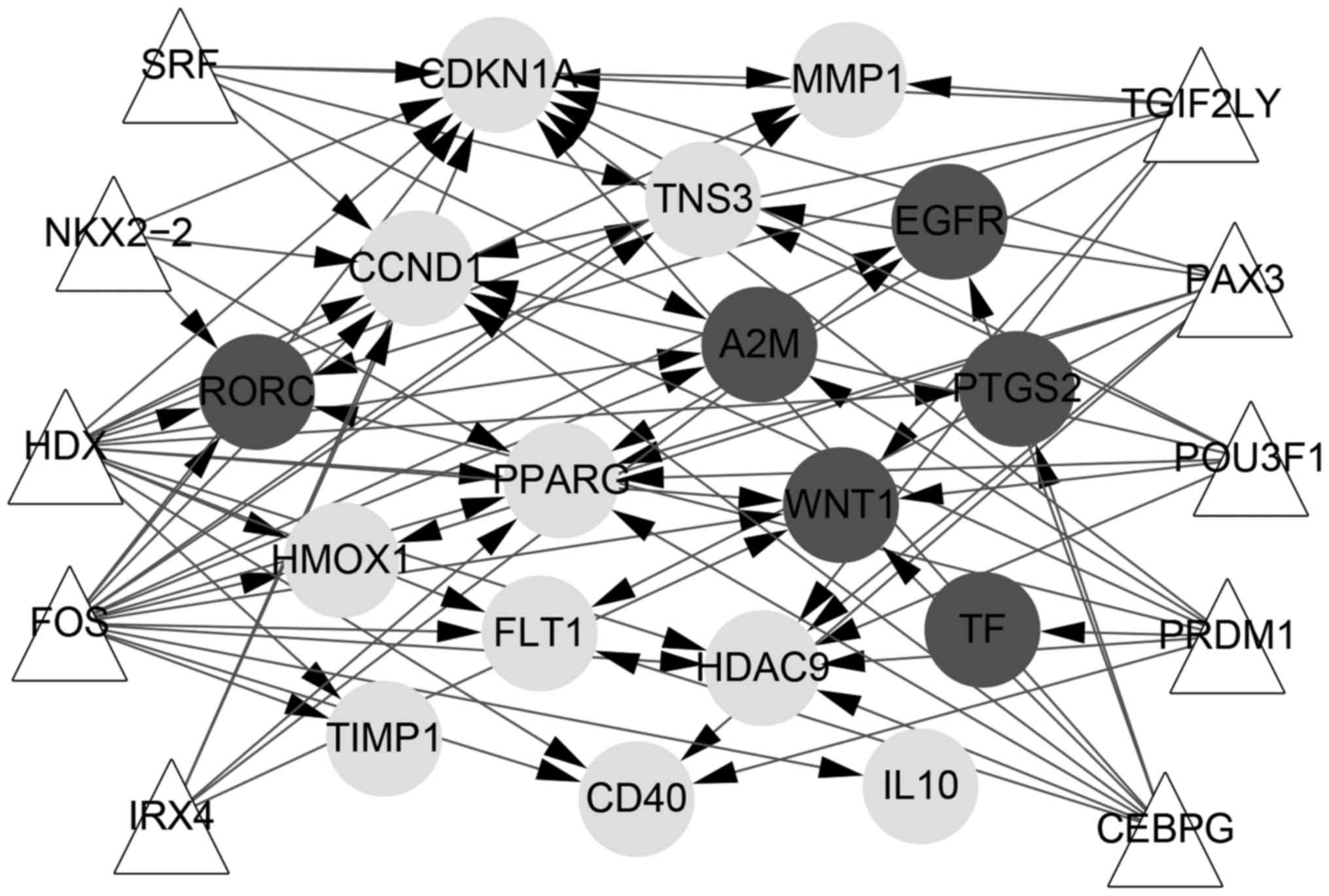
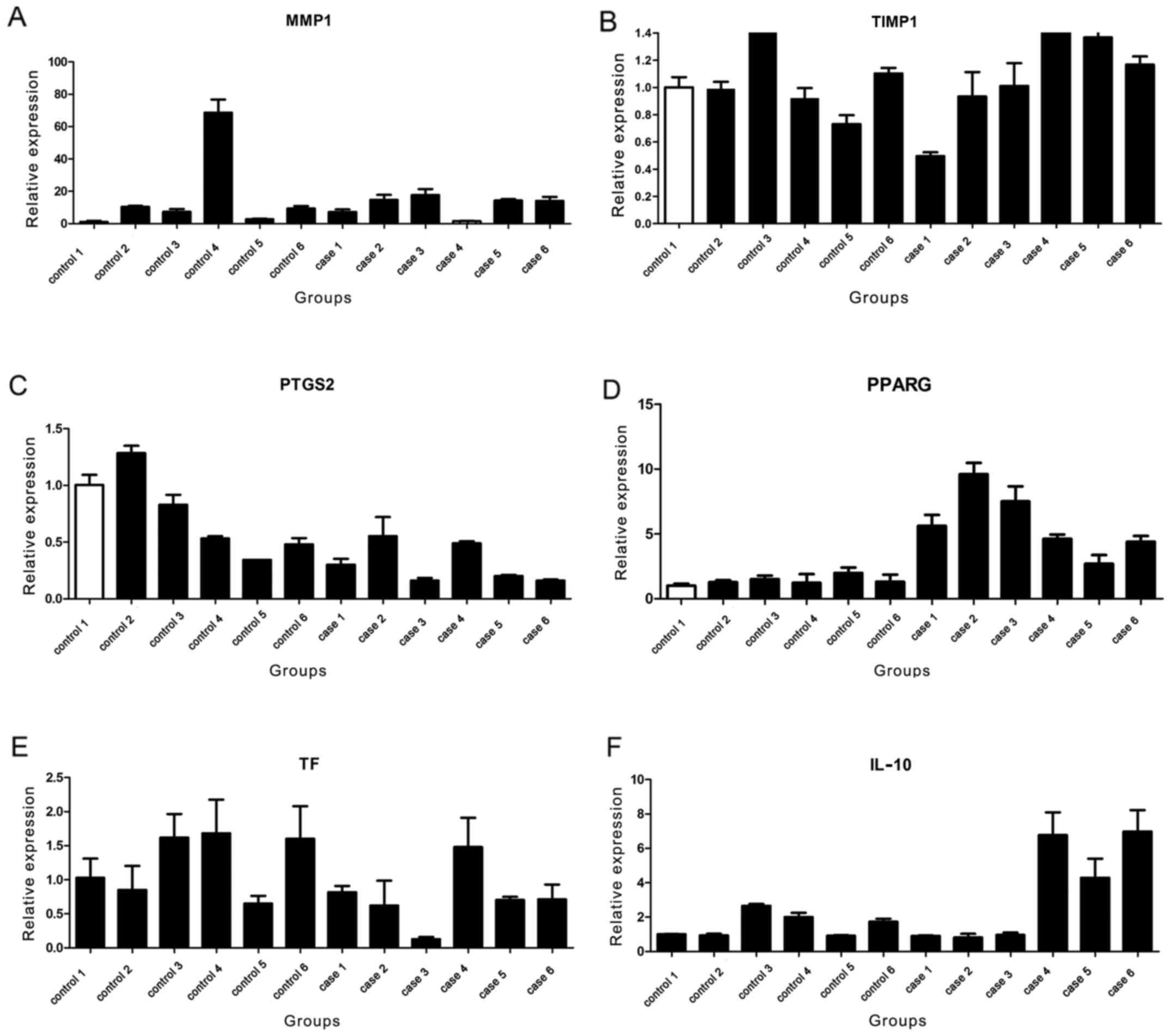
|
1
|
Principi N, Esposito S, Cavagna R, Bosis
S, Droghetti R, Faelli N, Tosi S and Begliatti E; Snoopy Study
Group: Recurrent respiratory tract infections in pediatric age: a
population-based survey of the therapeutic role of macrolides. J
Chemother. 15:53–59. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Martino M and Ballotti S: The child
with recurrent respiratory infections: normal or not? Pediatr
Allergy Immunol. 18(Suppl 18): 13–18. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
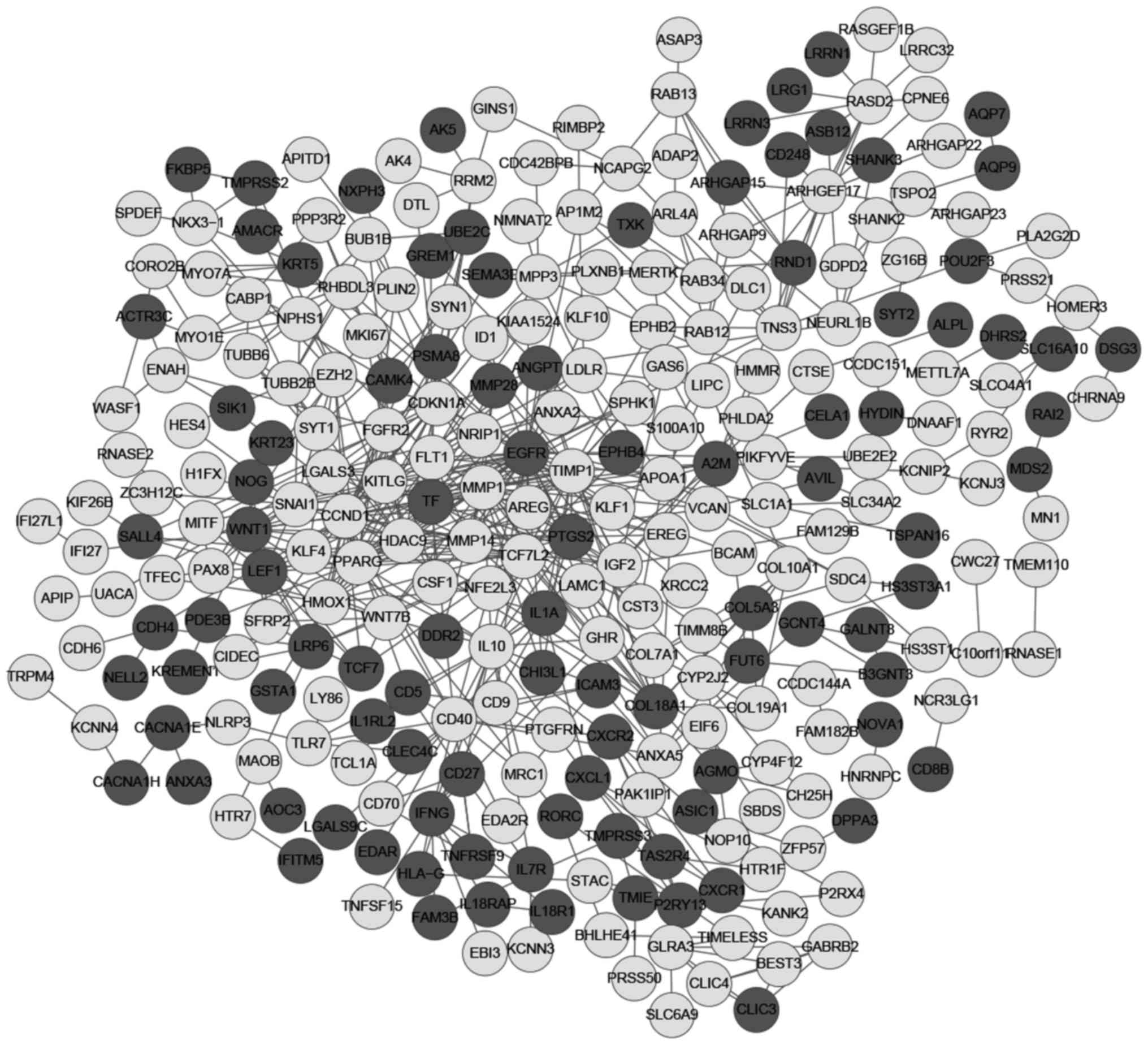
|
3
|
Bellanti JA: Recurrent respiratory tract
infections in paediatric patients. Drugs. 54(Suppl 1): 1–4. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khasawneh FA and Jou-Tindo AJ: A
30-year-old woman with recurrent lower respiratory tract
infections. Chest. 143:1500–1503. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
De Benedetto F and Sevieri G: Prevention
of respiratory tract infections with bacterial lysate OM-85
bronchomunal in children and adults: a state of the art.
Multidiscip Respir Med. 8:332013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bergman P, Norlin A-C, Hansen S, Rekha RS,
Agerberth B, Björkhem-Bergman L, Ekström L, Lindh JD and Andersson
J: Vitamin D3 supplementation in patients with frequent
respiratory tract infections: a randomised and double-blind
intervention study. BMJ Open. 2:e0016632012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jesenak M, Hrubisko M, Majtan J, Rennerova
Z and Banovcin P: Anti-allergic effect of Pleuran (β-glucan from
Pleurotus ostreatus) in children with recurrent respiratory tract
infections. Phytother Res. 28:471–474. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Maldonado J, Cañabate F, Sempere L, Vela
F, Sánchez AR, Narbona E, López-Huertas E, Geerlings A, Valero AD,
Olivares M, et al: Human milk probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum
CECT5716 reduces the incidence of gastrointestinal and upper
respiratory tract infections in infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol
Nutr. 54:55–61. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Orlowsky EW and Kraus VB: The role of
innate immunity in osteoarthritis: when our first line of defense
goes on the offensive. J Rheumatol. 42:363–371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Martin M: Cutadapt removes adapter
sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. 17:10–12.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: Limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Smyth GK: LIMMA: linear models for
microarray data. Statistics for Biology and Health: Bioinformatics
and Computational Biology Solutions Using R and Bioconductor.
Springer; New York: pp. 397–420. 2005, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Law CW, Chen Y, Shi W and Smyth GK: voom:
Precision weights unlock linear model analysis tools for RNA-seq
read counts. Genome Biol. 15:R292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Warnes GR, Bolker B, Bonebakker L,
Gentleman R, Liaw A, Lumley T, Maechler M, Magnusson A, Moeller S,
Schwartz M, et al: gplots: Various R programming tools for plotting
data. R package version 2. 2009.
|
|
15
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al The Gene Ontology Consortium: Gene ontology: tool for the
unification of biology. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: a
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Opsahl T, Agneessens F and Skvoretz J:
Node centrality in weighted networks: generalizing degree and
shortest paths. Soc Networks. 32:245–251. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang H, Hernandez JM and Van Mieghem P:
Betweenness centrality in a weighted network. Phys Rev E Stat
Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 77:0461052008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Estrada E and Rodríguez-Velázquez JA:
Subgraph centrality in complex networks. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin
Soft Matter Phys. 71:0561032005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Okamoto K, Chen W and Li XY: Ranking of
closeness centrality for large-scale social networks. Frontiers in
Algorithmics. Springer; Berlin: pp. 186–195. 2008, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tang Y, Li M, Wang J, Pan Y and Wu FX:
CytoNCA: a cytoscape plugin for centrality analysis and evaluation
of protein interaction networks. Biosystems. 127:67–72. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ferreira JA: The Benjamini-Hochberg method
in the case of discrete test statistics. Int J Biostat. 3:112007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Janky R, Verfaillie A, Imrichová H, Van de
Sande B, Standaert L, Christiaens V, Hulselmans G, Herten K, Naval
Sanchez M, Potier D, et al: iRegulon: from a gene list to a gene
regulatory network using large motif and track collections. PLOS
Comput Biol. 10:e1003731. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luan H, Zhang Q, Wang L, Wang C, Zhang M,
Xu X, Zhou H, Li X, Xu Q, He F, et al: OM85-BV induced the
productions of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α via TLR4- and TLR2-mediated
ERK1/2/NF-κB pathway in RAW264.7 cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
34:526–536. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bhattacharjee S, Bhattacharjee A, Majumder
S, Majumdar SB and Majumdar S: Glycyrrhizic acid suppresses
Cox-2-mediated anti-inflammatory responses during Leishmania
donovani infection. J Antimicrob Chemother. 67:1905–1914. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun L, Cornell TT, LeVine A, Berlin AA,
Hinkovska-Galcheva V, Fleszar AJ, Lukacs NW and Shanley TP: Dual
role of interleukin-10 in the regulation of respiratory syncitial
virus (RSV)-induced lung inflammation. Clin Exp Immunol.
172:263–279. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Moon CM, Kwon JH, Kim JS, Oh SH, Jin Lee
K, Park JJ, Pil Hong S, Cheon JH, Kim TI and Kim WH: Nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs suppress cancer stem cells via inhibiting
PTGS2 (cyclooxygenase 2) and NOTCH/HES1 and activating PPARG in
colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 134:519–529. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bank S, Skytt Andersen P, Burisch J,
Pedersen N, Roug S, Galsgaard J, Ydegaard Turino S, Brodersen JB,
Rashid S, Kaiser Rasmussen B, et al: Polymorphisms in the
inflammatory pathway genes TLR2, TLR4, TLR9, LY96, NFKBIA, NFKB1,
TNFA, TNFRSF1A, IL6R, IL10, IL23R, PTPN22, and PPARG are associated
with susceptibility of inflammatory bowel disease in a Danish
cohort. PLoS One. 9:e98815. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huizar I, Malur A, Patel J, McPeek M,
Dobbs L, Wingard C, Barna BP and Thomassen MJ: The role of PPARγ in
carbon nanotube-elicited granulomatous lung inflammation. Respir
Res. 14:72013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Crichton RR and Charloteaux-Wauters M:
Iron transport and storage. Eur J Biochem. 164:485–506. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ritchie RF, Palomaki GE, Neveux LM,
Navolotskaia O, Ledue TB and Craig WY: Reference distributions for
the negative acute-phase serum proteins, albumin, transferrin and
transthyretin: a practical, simple and clinically relevant approach
in a large cohort. J Clin Lab Anal. 13:273–279. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wang Q and Bai Q: Influence of injection
with coenzyme A on IL-8, C-reaction protein, transferrin in the
elderly with acute upper respiratory tract infections. Chinese J
Nosocomiol. 15:0092013.In Chinese.
|
|
35
|
Gleeson M, Bishop N, Oliveira M, McCauley
T, Tauler P and Muhamad AS: Respiratory infection risk in athletes:
association with antigen-stimulated IL-10 production and salivary
IgA secretion. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 22:410–417. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Bont L, Heijnen CJ, Kavelaars A, van
Aalderen WM, Brus F, Draaisma JT, Geelen SM and Kimpen JL: Monocyte
IL-10 production during respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis
is associated with recurrent wheezing in a one-year follow-up
study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 161:1518–1523. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tryggvason K, Höyhtyä M and Salo T:
Proteolytic degradation of extracellular matrix in tumor invasion.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 907:191–217. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Karelina TV, Hruza GJ, Goldberg GI and
Eisen AZ: Localization of 92-kDa type IV collagenase in human skin
tumors: comparison with normal human fetal and adult skin. J Invest
Dermatol. 100:159–165. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Woessner JF Jr: Matrix metalloproteinases
and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J.
5:2145–2154. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|