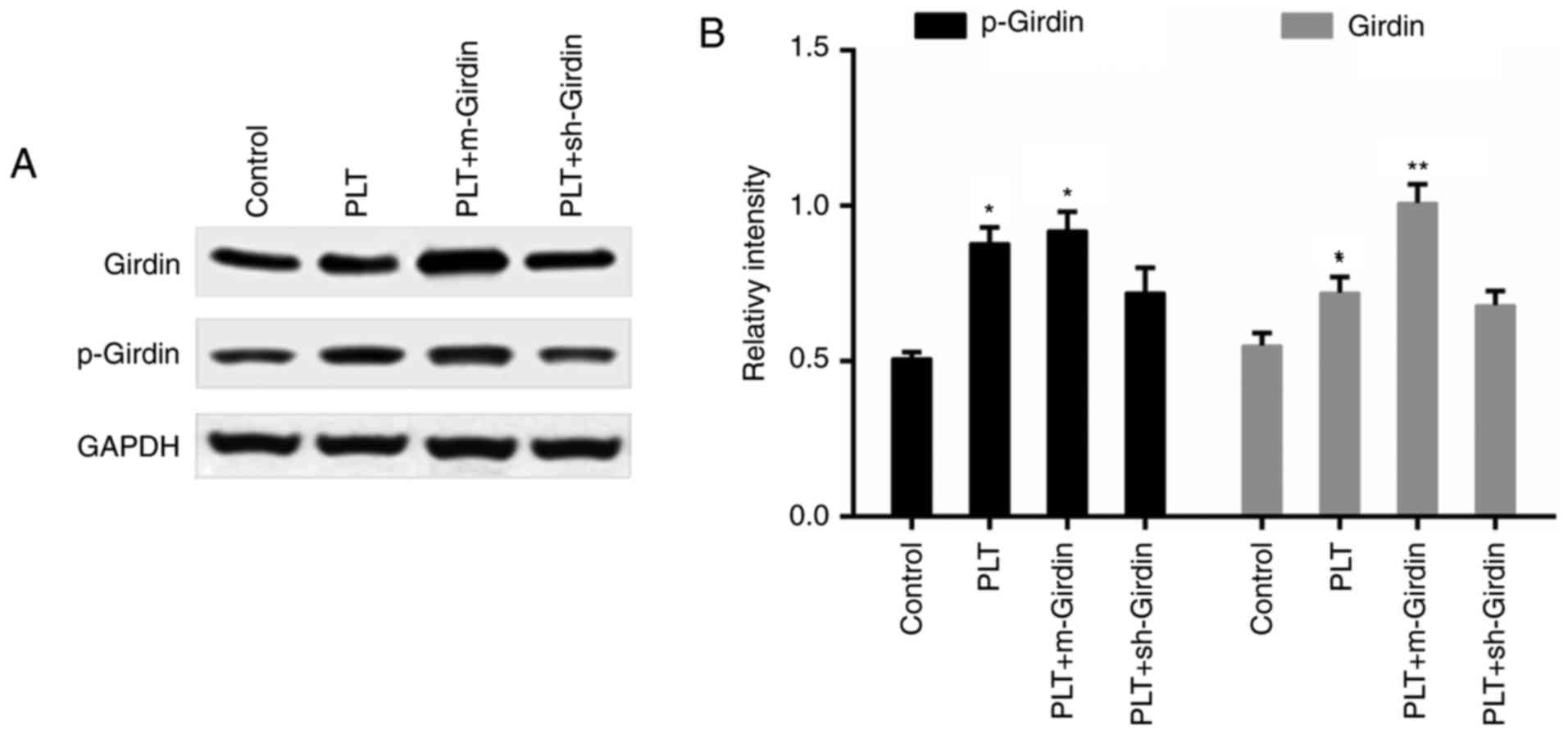
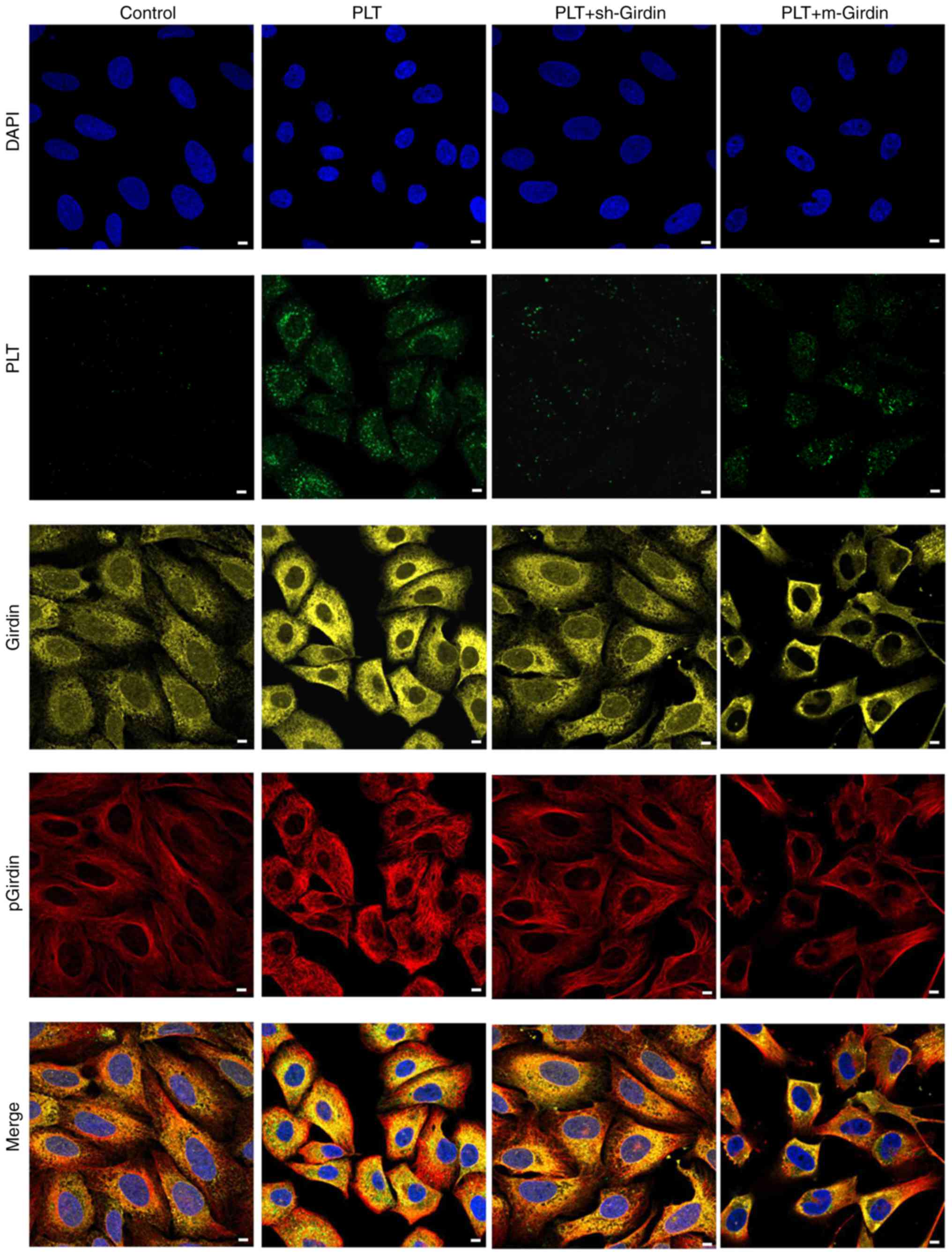
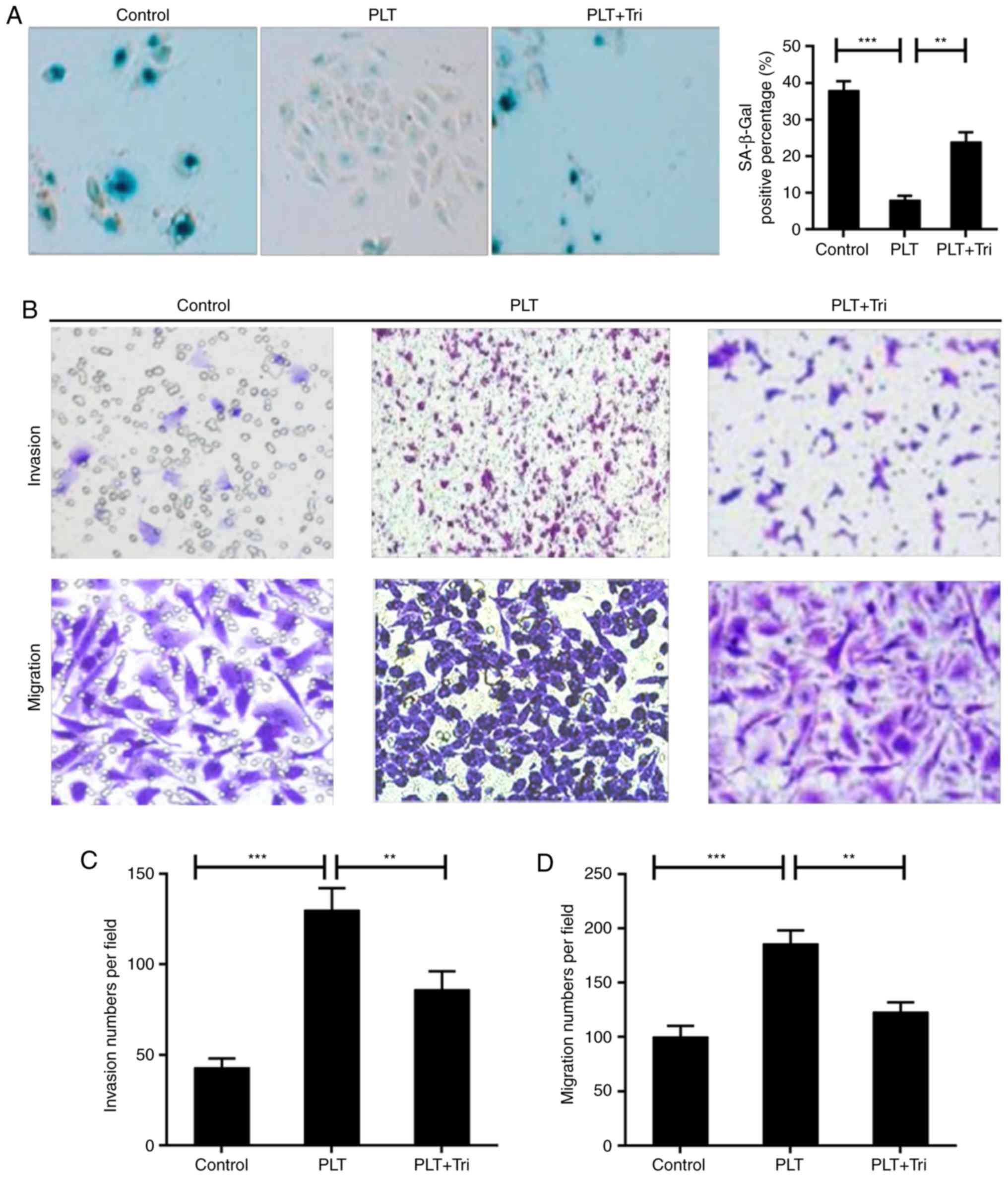
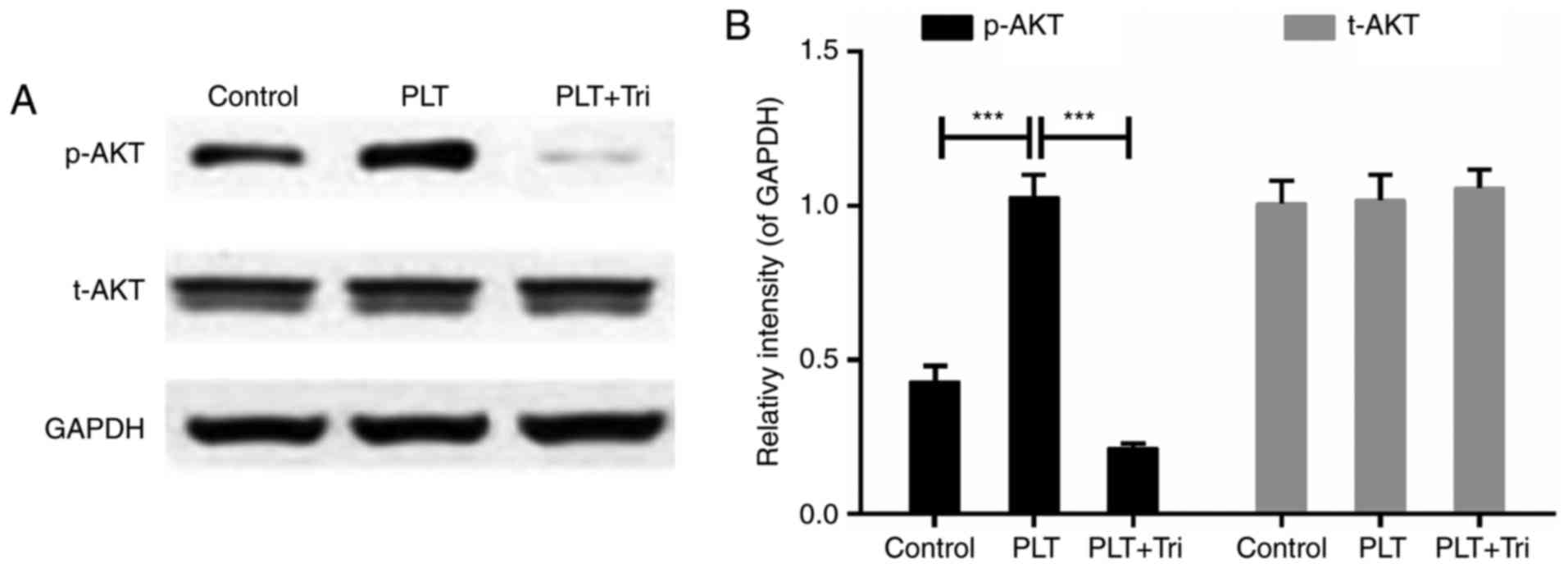
|
1
|
Yang Y and Rosenberg GA: Blood-brain
barrier breakdown in acute and chronic cerebrovascular disease.
Stroke. 42:3323–3328. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee SW, Kim WJ, Choi YK, Song HS, Son MJ,
Gelman IH, Kim YJ and Kim KW: SSeCKS regulates angiogenesis and
tight junction formation in blood-brain barrier. Nat Med.
9:900–906. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lahteenvuo J and Rosenzweig A: Effects of
aging on angiogenesis. Circ Res. 110:1252–1264. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Capettini LS, Cortes SF, Silva JF,
Alvarez-Leite JI and Lemos VS: Decreased production of neuronal
NOS-derived hydrogen peroxide contributes to endothelial
dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Br J Pharmacol. 164:1738–1748.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pelham CJ, Keen HL, Lentz SR and Sigmund
CD: Dominant negative PPARgamma promotes atherosclerosis, vascular
dysfunction, and hypertension through distinct effects in
endothelium and vascular muscle. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp
Physiol. 304:R690–R701. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Erusalimsky JD and Skene C: Mechanisms of
endothelial senescence. Exp Physiol. 94:299–304. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rivard A, Fabre JE, Silver M, Chen D,
Murohara T, Kearney M, Magner M, Asahara T and Isner JM:
Age-dependent impairment of angiogenesis. Circulation. 99:111–120.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fujio Y and Walsh K: Akt mediates
cytoprotection of endothelial cells by vascular endothelial growth
factor in an anchorage-dependent manner. J Biol Chem.
274:16349–16354. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shiojima I and Walsh K: Role of Akt
signaling in vascular homeostasis and angiogenesis. Circ Res.
90:1243–1250. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sata M, Maejima Y, Adachi F, Fukino K,
Saiura A, Sugiura S, Aoyagi T, Imai Y, Kurihara H, Kimura K, et al:
A mouse model of vascular injury that induces rapid onset of medial
cell apop-tosis followed by reproducible neointimal hyperplasia. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 32:2097–2104. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Enomoto A, Murakami H, Asai N, Morone N,
Watanabe T, Kawai K, Murakumo Y, Usukura J, Kaibuchi K and
Takahashi M: Akt/PKB regulates actin organization and cell motility
via Girdin/APE. Dev Cell. 9:389–402. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kitamura T, Asai N, Enomoto A, Maeda K,
Kato T, Ishida M, Jiang P, Watanabe T, Usukura J, Kondo T, et al:
Regulation of VEGF-mediated angiogenesis by the Akt/PKB substrate
Girdin. Nat Cell Biol. 10:329–337. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Angiolillo DJ, Ferreiro JL, Price MJ,
Kirtane AJ and Stone GW: Platelet function and genetic testing. J
Am Coll Cardiol. 62(Suppl 17): S21–S31. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
de Groot PG, Urbanus RT and Roest M:
Platelet interaction with the vessel wall. Handb Exp Pharmacol.
210:87–110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sopova K, Tatsidou P and Stellos K:
Platelets and platelet interaction with progenitor cells in
vascular homeostasis and inflammation. Curr Vasc Pharmacol.
10:555–562. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sharma D, Brummel-Ziedins KE, Bouchard BA
and Holmes CE: Platelets in tumor progression: A host factor that
offers multiple potential targets in the treatment of cancer. J
Cell Physiol. 229:1005–1015. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Radziwon-Balicka A, Moncada de la Rosa C
and Jurasz P: Platelet-associated angiogenesis regulating factors:
A pharmacological perspective. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 90:679–688.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Andrae J, Gallini R and Betsholtz C: Role
of platelet-derived growth factors in physiology and medicine.
Genes Dev. 22:1276–1312. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Andia I, Zumstein MA,
Zhang CQ, Pinto NR and Bielecki T: Classification of platelet
concentrates (Platelet-Rich Plasma-PRP, Platelet-Rich Fibrin-PRF)
for topical and infiltrative use in orthopedic and sports medicine:
Current consensus, clinical implications and perspectives. Muscles
Ligaments Tendons J. 4:3–9. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kakudo N, Morimoto N, Kushida S, Ogawa T
and Kusumoto K: Platelet-rich plasma releasate promotes
angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Med Mol Morphol. 47:83–89. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Marx RE: Platelet-rich plasma: Evidence to
support its use. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 62:489–496. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hayon Y, Dashevsky O, Shai E, Brill A,
Varon D and Leker RR: Platelet microparticles induce angiogenesis
and neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia. Curr Neurovasc Res.
9:185–192. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ohtsuka M, Sasaki K, Ueno T, Seki R,
Nakayoshi T, Koiwaya H, Toyama Y, Yokoyama S, Mitsutake Y, Chibana
H, et al: Platelet-derived microparticles augment the adhesion and
neovascularization capacities of circulating angiogenic cells
obtained from atherosclerotic patients. Atherosclerosis.
227:275–282. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kuckleburg CJ, McClenahan DJ and
Czuprynski CJ: Platelet activation by histophilus somni and its
lipooligosaccharide induces endothelial cell proinflammatory
responses and platelet internalization. Shock. 29:189–196.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deli MA, Abraham CS, Kataoka Y and Niwa M:
Permeability studies on in vitro blood-brain barrier models:
Physiology, pathology, and pharmacology. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
25:59–127. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bachmeier C, Mullan M and Paris D:
Characterization and use of human brain microvascular endothelial
cells to examine β-amyloid exchange in the blood-brain barrier.
Cytotechnology. 62:519–529. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Helms HC, Abbott NJ, Burek M, Cecchelli R,
Couraud PO, Deli MA, Förster C, Galla HJ, Romero IA, Shusta EV, et
al: In vitro models of the blood-brain barrier: An overview of
commonly used brain endothelial cell culture models and guidelines
for their use. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 36:862–890. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gloesenkamp CR, Nitzsche B, Ocker M, Di
Fazio P, Quint K, Hoffmann B, Scherubl H and Hopfner M: AKT
inhibition by triciribine alone or as combination therapy for
growth control of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Int
J Oncol. 40:876–888. 2012.
|
|
29
|
Jiang P, Ren YL, Lan Y, Li JL, Luo J, Li J
and Cai JP: Phagocytosis of platelets enhances endothelial cell
survival under serum deprivation. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
240:876–883. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
van Moorselaar RJ and Voest EE:
Angiogenesis in prostate cancer: Its role in disease progression
and possible therapeutic approaches. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
197:239–250. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Luster AD, Alon R and von Andrian UH:
Immune cell migration in inflammation: Present and future
therapeutic targets. Nat Immunol. 6:1182–1190. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Garrett CR, Coppola D, Wenham RM, Cubitt
CL, Neuger AM, Frost TJ, Lush RM, Sullivan DM, Cheng JQ and Sebti
SM: Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of
triciri-bine phosphate monohydrate, a small-molecule inhibitor of
AKT phosphorylation, in adult subjects with solid tumors containing
activated AKT. Invest New Drugs. 29:1381–1389. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Risau W and Wolburg H: Development of the
blood-brain barrier. Trends Neurosci. 13:174–178. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Plate KH: Mechanisms of angiogenesis in
the brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 58:313–320. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Porter AG and Janicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Johnson SA, Balboa RS, Dessel BH, Monto
RW, Siegesmund KA and Greenwalt TJ: The mechanism of the
endothelial supporting function of intact platelets. Exp Mol
Pathol. 3:115–127. 1964. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lang D, Dohle F, Terstesse M, Bangen P,
August C, Pauels HG and Heidenreich S: Down-regulation of monocyte
apoptosis by phagocytosis of platelets: Involvement of a caspase-9,
caspase-3, and heat shock protein 70-dependent pathway. J Immunol.
168:6152–6158. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shin WS, Maeng YS, Jung JW, Min JK, Kwon
YG and Lee ST: Soluble PTK7 inhibits tube formation, migration, and
invasion of endothelial cells and angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 371:793–798. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Moussa M, Lajeunesse D, Hilal G, El Atat
O, Haykal G, Serhal R, Chalhoub A, Khalil C and Alaaeddine N:
Platelet rich plasma (PRP) induces chondroprotection via increasing
autophagy, anti-inflammatory markers, and decreasing apoptosis in
human osteoarthritic cartilage. Exp Cell Res. 352:146–156. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Luzak B, Golanski J, Rozalski M, Krajewska
U, Olas B and Watala C: Extract from Aronia melanocarpa fruits
potentiates the inhibition of platelet aggregation in the presence
of endothelial cells. Arch Med Sci. 6:141–144. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Metzig C, Grabowska E, Eckert K, Rehse K
and Maurer HR: Bromelain proteases reduce human platelet
aggregation in vitro, adhesion to bovine endothelial cells and
thrombus formation in rat vessels in vivo. In Vivo. 13:7–12.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wen H, Lu Y, Yao H and Buch S: Morphine
induces expression of platelet-derived growth factor in human brain
microvascular endothelial cells: Implication for vascular
permeability. PLoS One. 6:e217072011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rauch BH, Millette E, Kenagy RD, Daum G,
Fischer JW and Clowes AW: Syndecan-4 is required for
thrombin-induced migration and proliferation in human vascular
smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 280:17507–17511. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Enomoto A, Ping J and Takahashi M: Girdin,
a novel actin-binding protein, and its family of proteins possess
versatile functions in the Akt and Wnt signaling pathways. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1086:169–184. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Skurk C, Maatz H, Kim HS, Yang J, Abid MR,
Aird WC and Walsh K: The Akt-regulated forkhead transcription
factor FOXO3a controls endothelial cell viability through
modulation of the caspase-8 inhibitor FLIP. J Biol Chem.
279:1513–1525. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yang JY, Michod D, Walicki J and Widmann
C: Surviving the kiss of death. Biochem Pharmacol. 68:1027–1031.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Curry JM, Eubank TD, Roberts RD, Wang Y,
Pore N, Maity A and Marsh CB: M-CSF signals through the MAPK/ERK
pathway via Sp1 to induce VEGF production and induces angiogenesis
in vivo. PLoS One. 3:e34052008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jehle AW, Gardai SJ, Li S, Linsel-Nitschke
P, Morimoto K, Janssen WJ, Vandivier RW, Wang N, Greenberg S, Dale
BM, et al: ATP-binding cassette transporter A7 enhances
phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and associated ERK signaling in
macrophages. J Cell Biol. 174:547–556. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|