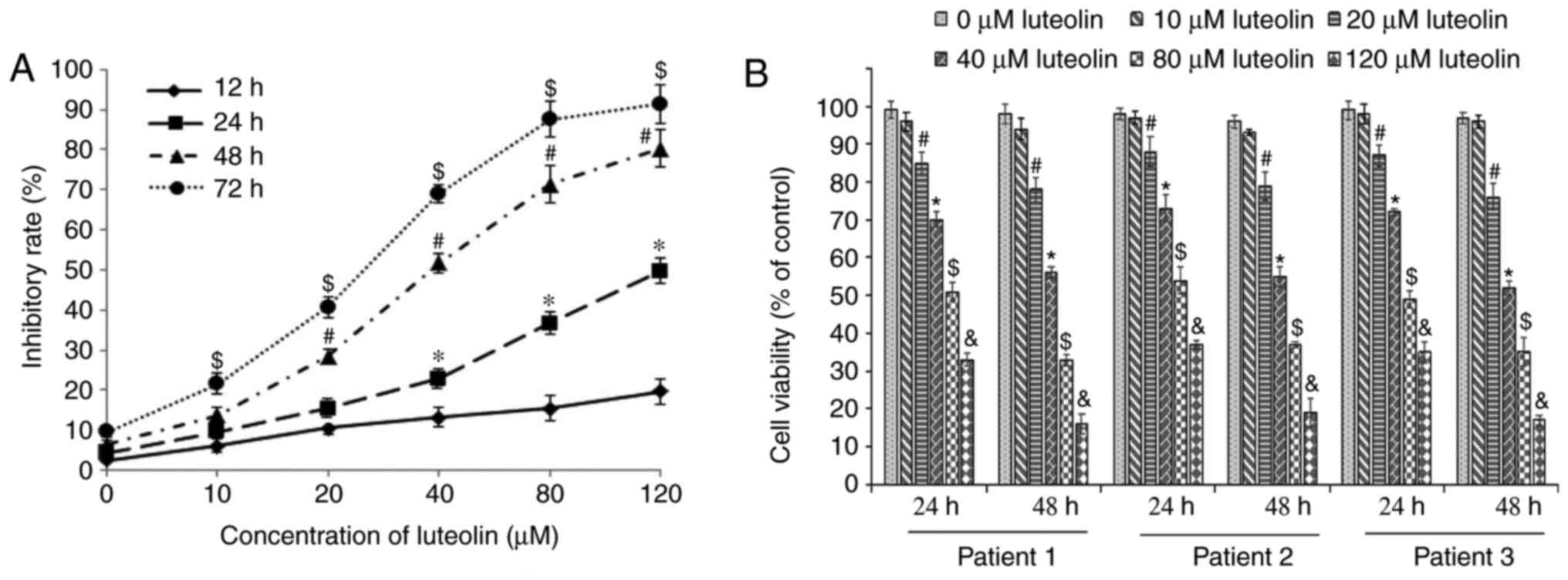
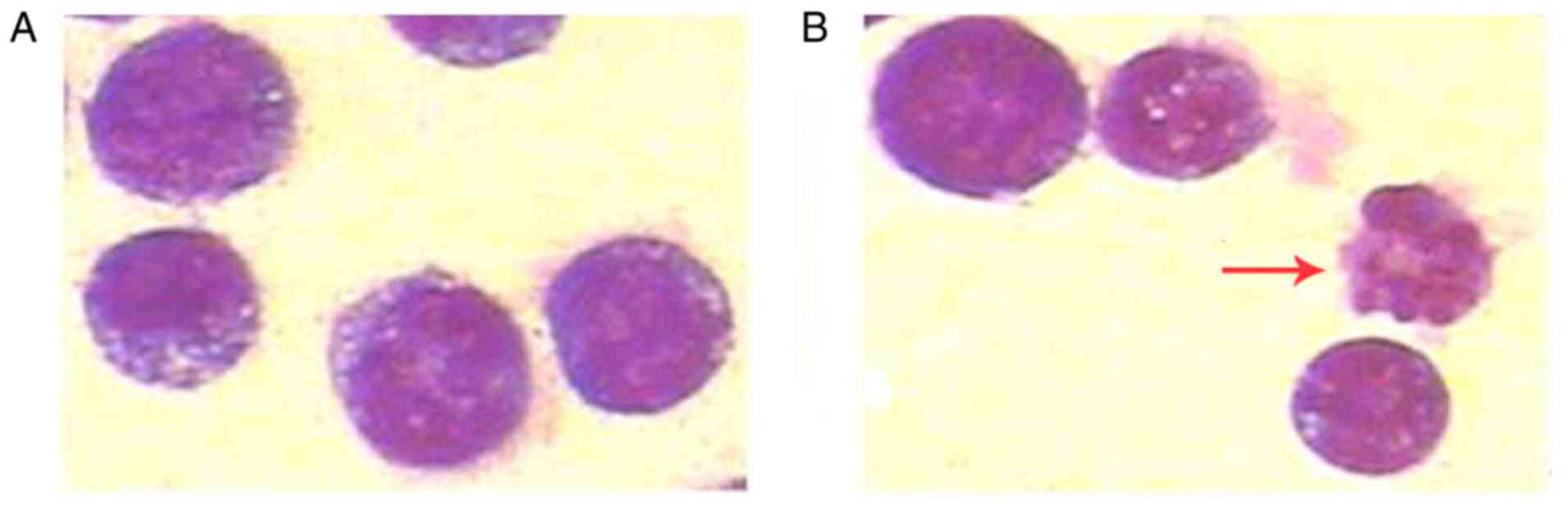
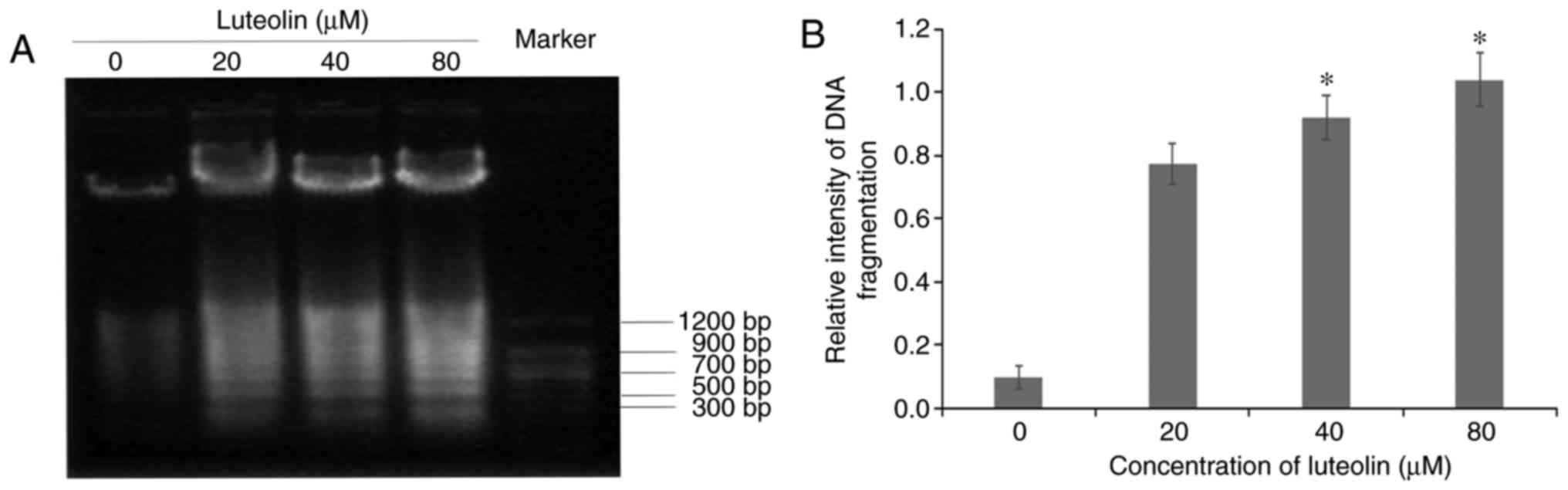
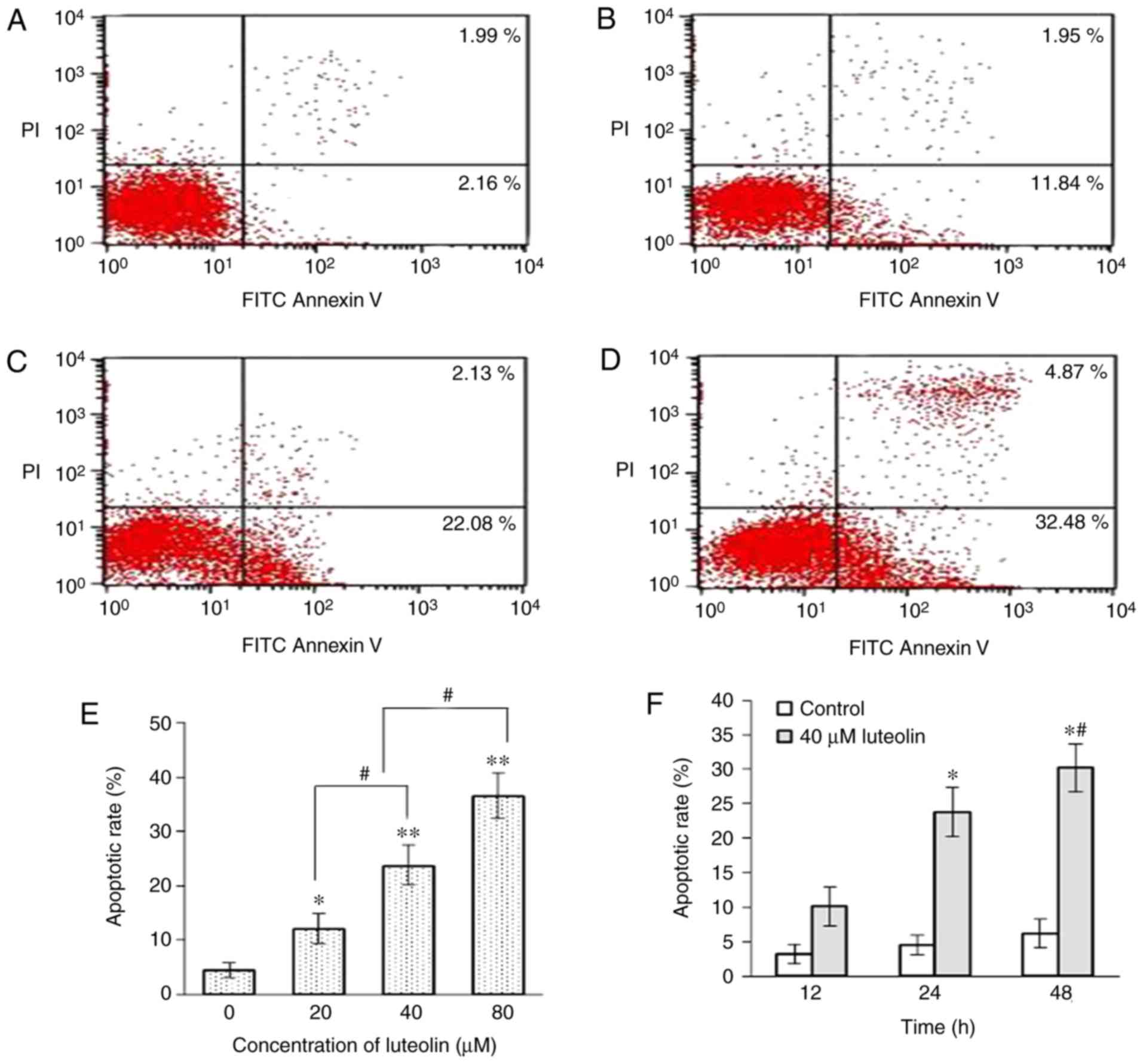
|
1
|
Sekeres MA and Cutler C: How we treat
higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 123:829–836. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ferrero D, Crisà E, Marmont F, Audisio E,
Frairia C, Giai V, Gatti T, Festuccia M, Bruno B, Riera L, et al:
Survival improvement of poor-prognosis AML/MDS patients by
maintenance treatment with low-dose chemotherapy and
differentiating agents. Ann Hematol. 93:1391–1400. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Smith SM, Le Beau MM, Huo D, Karrison T,
Sobecks RM, Anastasi J, Vardiman JW, Rowley JD and Larson RA:
Clinical-cytogenetic associations in 306 patients with
therapy-related myelodysplasia and myeloid leukemia: The University
of Chicago series. Blood. 102:43–52. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khan N, Afaq F, Syed DN and Mukhtar H:
Fisetin, a novel dietary flavonoid, causes apoptosis and cell cycle
arrest in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells. Carcinogenesis.
29:1049–1056. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang SX, Cao M, Xu SH, Zhang JM, Wang ZG,
Mao XD, Yao XM and Liu C: Effect of luteolin on inflammatory
responses in RAW264.7 macrophages activated with LPS and IFN-γ. J
Funct Foods. 32:123–130. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang YC, Gan FF, Shelar SB, Ng KY and
Chew EH: Antioxidant and Nrf2 inducing activities of luteolin, a
flavonoid constituent in Ixeris sonchifolia Hance, provide
neuroprotective effects against ischemia-induced cellular injury.
Food Chem Toxicol. 59:272–280. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lu J, Li G, He K and Jiang W: Luteolin
exerts a marked antitumor effect in cMet-overexpressing
patient-derived tumor xenograft models of gastric cancer. J Transl
Med. 13:422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suh KS, Chon S and Choi EM: Luteolin
alleviates methylglyoxal-induced cytotoxicity in osteoblastic
MC3T3-E1 cells. Cytotechnology. 68:2539–2552. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen P, Zhang JY, Sha BB, Ma YE, Hu T, Ma
YC, Sun H, Shi JX, Dong ZM and Li P: Luteolin inhibits cell
proliferation and induces cell apoptosis via down-regulation of
mitochondrial membrane potential in esophageal carcinoma cells EC1
and KYSE450. Oncotarget. 8:27471–27480. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lim W, Yang C, Bazer FW and Song G:
Luteolin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human
placental choriocarcinoma cells by blocking the PI3K/AKT pathway
and regulating sterol regulatory element binding protein activity.
Biol Reprod. 95:822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Park SH, Ham S, Kwon TH, Kim MS, Lee DH,
Kang JW, Oh SR and Yoon DY: Luteolin induces cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis through extrinsic and intrinsic signaling pathways in
MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol.
33:219–231. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pandurangan AK, Dharmalingam P, Sadagopan
SK and Ganapasam S: Luteolin inhibits matrix metalloproteinase 9
and 2 in azoxymethane-induced colon carcinogenesis. Hum Exp
Toxicol. 33:1176–1185. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tsai PH, Cheng CH, Lin CY, Huang YT, Lee
LT, Kandaswami CC, Lin YC, Lee KP, Hung CC, Hwang JJ, et al:
Dietary flavonoids luteolin and quercetin suppressed cancer stem
cell properties and metastatic potential of isolated prostate
cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 36:6367–6380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Deng L, Jiang L, Lin X, Tseng KF, Lu Z and
Wang X: Luteolin, a novel p90 ribosomal S6 kinase inhibitor,
suppresses proliferation and migration in leukemia cells. Oncol
Lett. 13:1370–1378. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen HM, Tang XX, Zhou B, Zhou Z, Xu N and
Wang Y: A ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway and Nrf2 pathway
activation are involved in BDE-47 induced apoptosis in Neuro-2a
cells. Chemosphere. 184:679–686. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang W, Zhao FI, Zhang J and Gao D:
Luteolin induces apoptosis in mouse liver cancer cells through ROS
mediated pathway: A mechanistic investigation. Biomed Res.
28:839–845. 2017.
|
|
17
|
Kittiratphatthana N, Kukongviriyapan V,
Prawan A and Senggunprai L: Luteolin induces cholangiocarcinoma
cell apoptosis through the mitochondrial-dependent pathway mediated
by reactive oxygen species. J Pharm Pharmacol. 68:1184–1192. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gerl R and Vaux DL: Apoptosis in the
development and treatment of cancer. Carcinogenesis. 26:263–270.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ju W, Wang X, Shi H, Chen W, Belinsky SA
and Lin Y: A critical role of luteolin-induced reactive oxygen
species in blockage of tumor necrosis factor-activated nuclear
factor-kappa B pathway and sensitization of apoptosis in lung
cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. 71:1381–1388. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ding GL, Zhao JQ and Jiang DM: Allicin
inhibits oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and
apoptosis by promoting PI3K/AKT and CREB/ERK signaling in
osteoblast cells. Exp Ther Med. 11:2553–2560. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu BX, Zhou JY, Li Y, Zou X, Wu J, Gu JF,
Yuan JR, Zhao BJ, Feng L, Jia XB and Wang RP: Hederagenin from the
leaves of ivy (Hedera helix L.) induces apoptosis in human LoVo
colon cells through the mitochondrial pathway. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 14:4122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nakagawa T, Matozaki S, Murayama T,
Nishimura R, Tsutsumi M, Kawaguchi R, Yokoyama Y, Hikiji K, Isobe T
and Chihara K: Establishment of a leukaemic cell line from a
patient with acquisition of chromosomal abnormalities during
disease progression in myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol.
85:469–761. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xia G, Chen B, Ding J, Gao C, Lu H, Shao
Z, Gao F and Wang X: Effect of magnetic Fe3O4
nanoparticles with 2-methoxyestradiol on the cell-cycle progression
and apoptosis of myelodysplastic syndrome cells. Int J
Nanomedicine. 6:1921–1927. 2011.
|
|
24
|
Kim SY, Lee YM and Cho JS: Korean red
ginseng extract exhibits neuroprotective effects through inhibition
of apoptotic cell death. Biol Pharm Bull. 37:938–946. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu H, Gao F, Shu G, Xia G, Shao Z, Lu H
and Cheng K: Wogonin inhibits the proliferation of myelodysplastic
syndrome cells through the induction of cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 12:7285–7292. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jing Y, Shen X, Mei Q and Han W: Spotlight
on decitabine for myelodysplastic syndromes in Chinese patients.
Onco Targets Ther. 8:2783–2790. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim YS, Kim SH, Shin J, Harikishore A, Lim
JK, Jung Y, Lyu HN, Baek NI, Choi KY, Yoon HS and Kim KT: Luteolin
suppresses cancer cell proliferation by targeting vaccinia-related
kinase 1. PLoS One. 9:e1096552014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Abdel Hadi L, Di Vito C, Marfia G,
Ferraretto A, Tringali C, Viani P and Riboni L: Sphingosine kinase
2 and ceramide transport as key targets of the natural flavonoid
luteolin to induce apoptosis in colon cancer cells. PloS One.
10:e01433842015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Devi PS, Kumar MS and Das SM: Evaluation
of antiproliferative activity of red sorghum bran anthocyanin on a
human breast cancer cell line (mcf-7). Int J Breast Cancer.
2011:8914812011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Cheng AC, Huang TC, Lai CS and Pan MH:
Induction of apoptosis by luteolin through cleavage of Bcl-2 family
in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 509:1–10. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ko WG, Kang TH, Lee SJ, Kim YC and Lee BH:
Effects of luteolin on the inhibition of proliferation and
induction of apoptosis in human myeloid leukaemia cells. Phytother
Res. 16:295–298. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sak K, Kasemaa K and Everaus H:
Potentiation of luteolin cytotoxicity by flavonols fisetin and
quercetin in human chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell lines. Food
Funct. 7:3815–3824. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fiandalo MV and Kyprianou N: Caspase
control: Protagonists of cancer cell apoptosis. Exp Oncol.
34:165–175. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schwartz JT, Barker JH, Kaufman J, Fayram
DC, McCracken JM and Allen LA: Francisella tularensis inhibits the
intrinsic and extrinsic pathways to delay constitutive apoptosis
and prolong human neutrophil lifespan. J Immunol. 188:3351–3363.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Marchi S, Giorgi C, Suski JM, Agnoletto C,
Bononi A, Bonora M, De Marchi E, Missiroli S, Patergnani S, Poletti
F, et al: Mitochondriaros crosstalk in the control of cell death
and aging. J Signal Transduct. 2012:3296352012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Rao PS, Satelli A, Moridani M, Jenkins M
and Rao US: Luteolin induces apoptosis in multidrug resistant
cancer cells without affecting the drug transporter function:
Involvement of cell line-specific apoptotic mechanisms. Int J
Cancer. 130:2703–2714. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Shelton LM, Park BK and Copple IM: Role of
Nrf2 in protection against acute kidney injury. Kidney Int.
84:1090–1095. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu R, Meng F, Zhang L, Liu A, Qin H, Lan
X, Li L and Du G: Luteolin isolated from the medicinal plant
Elsholtzia rugulosa (Labiatae) prevents copper-mediated toxicity in
β-amyloid precursor protein Swedish mutation overexpressing SH-SY5Y
cells. Molecules. 16:2084–2096. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang Q, Wang H, Jia Y, Pan H and Ding H:
Luteolin induces apoptosis by ROS/ER stress and mitochondrial
dysfunction in gliomablastoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
79:1031–1041. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Choi IY, Lee SJ, Ju C, Nam W, Kim HC, Ko
KH and Kim WK: Protection by a manganese porphyrin of endogenous
peroxynitrite-induced death of glial cells via inhibition of
mitochondrial transmembrane potential decrease. Glia. 31:155–164.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lin Y, Xu JP, Liao HH, Li L and Pan L:
Piperine induces apoptosis of lung cancer A549 cells via
p53-dependent mitochondrial signaling pathway. Tumor Biol.
35:3305–3310. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yee SB, Choi HJ, Chung SW, Park DH, Sung
B, Chung HY and Kim ND: Growth inhibition of luteolin on HepG2
cells is induced via p53 and Fas/Fas-ligand besides the TGF-β
pathway. Int J Oncol. 47:747–754. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ham S, Kim KH, Kwon TH, Bak Y, Lee DH,
Song YS, Park SH, Park YS, Kim MS, Kang JW, et al: Luteolin induces
intrinsic apoptosis via inhibition of E6/E7 oncogenes and
activation of extrinsic and intrinsic signaling pathways in
HPV-18-associated cells. Oncol Rep. 31:2683–2691. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lim DY, Jeong Y, Tyner AL and Park JH:
Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HT-29 human colon
cancer cells by the dietary compound luteolin. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 292:G66–G75. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hytti M, Szabó D, Piippo N, Korhonen E,
Honkakoski P, Kaarniranta K, Petrovski G and Kauppinen A: Two
dietary poly-phenols, fisetin and luteolin, reduce inflammation but
augment DNA damage-induced toxicity in human RPE cells. J Nutr
Biochem. 42:37–42. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ge Q, Wang C, Ruan Y, Chen Z, Liu J and Ye
Z: Overexpression of p53 activated by small activating RNA
suppresses the growth of human prostate cancer cells. Onco Targets
Ther. 9:231–241. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang C, Ge Q, Zhang Q, Chen Z, Hu J, Li F
and Ye Z: Targeted p53 activation by saRNA suppresses human bladder
cancer cells growth and metastasis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
35:532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Macip S, Igarashi M, Berggren P, Yu J, Lee
SW and Aaronson SA: Influence of induced reactive oxygen species in
p53-mediated cell fate decisions. Mol Cell Biol. 23:8576–8585.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang YH, Kong DL, Wang XW, Dong X, Tao Y
and Gong H: Molecular mechanisms of luteolin induced growth
inhibition and apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cells. Iran J Pharm
Res. 14:531–538. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chen Q, Liu S, Chen J, Zhang Q, Lin S,
Chen Z and Jiang J: Luteolin induces mitochondria-dependent
apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cell. Nat Prod Commun.
7:29–32. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kilbride SM and Prehn JH: Central roles of
apoptotic proteins in mitochondrial function. Oncogene.
32:2703–2711. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Bao Q, Lu W, Rabinowitz JD and Shi Y:
Calcium blocks formation of apoptosome by preventing nucleotide
exchange in Apaf-1. Mol Cell. 25:181–192. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ding S, Hu A, Hu Y, Ma J, Weng P and Dai
J: Anti-hepatoma cells function of luteolin through inducing
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Tumour Biol. 35:3053–3060. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Kobayashi T, Masumoto J, Tada T, Nomiyama
T, Hongo K and Nakayama J: Prognostic significance of the
immunohistochemical staining of cleaved caspase-3, an activated
form of caspase-3, in gliomas. Clin Cancer Res. 13:3868–3874. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|