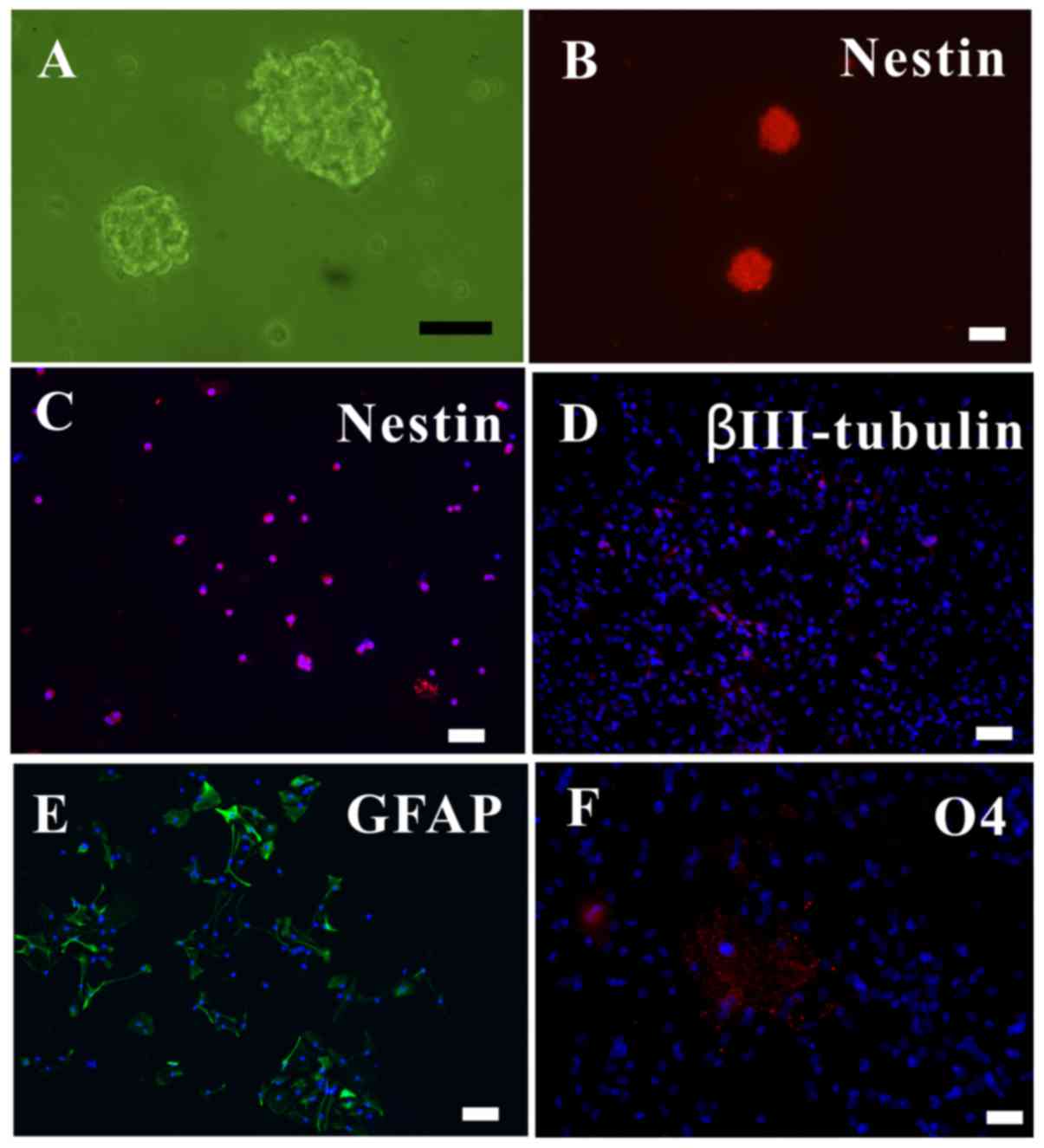
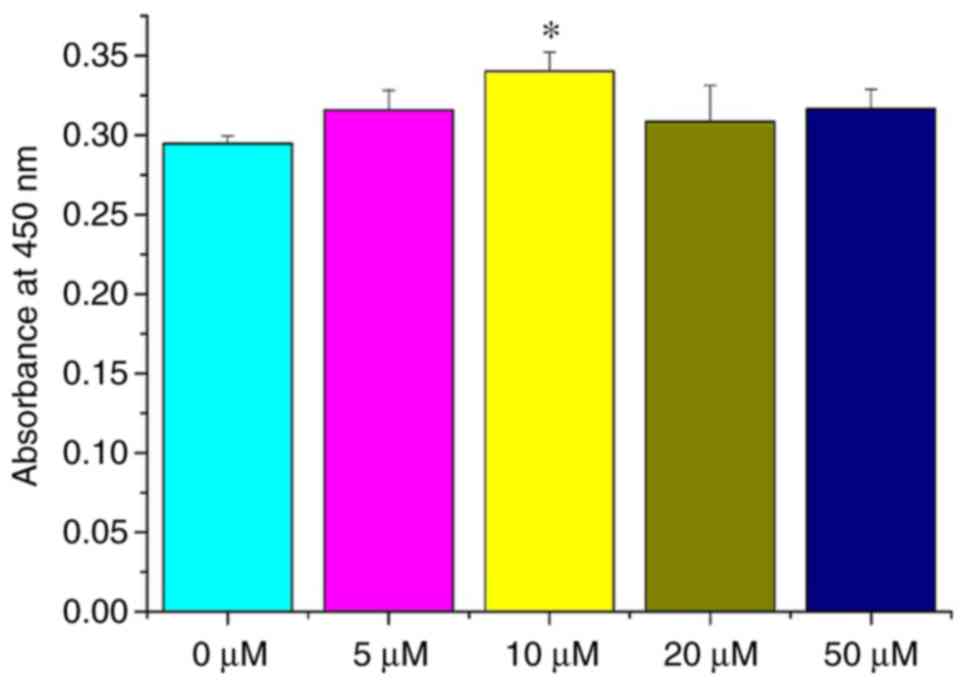
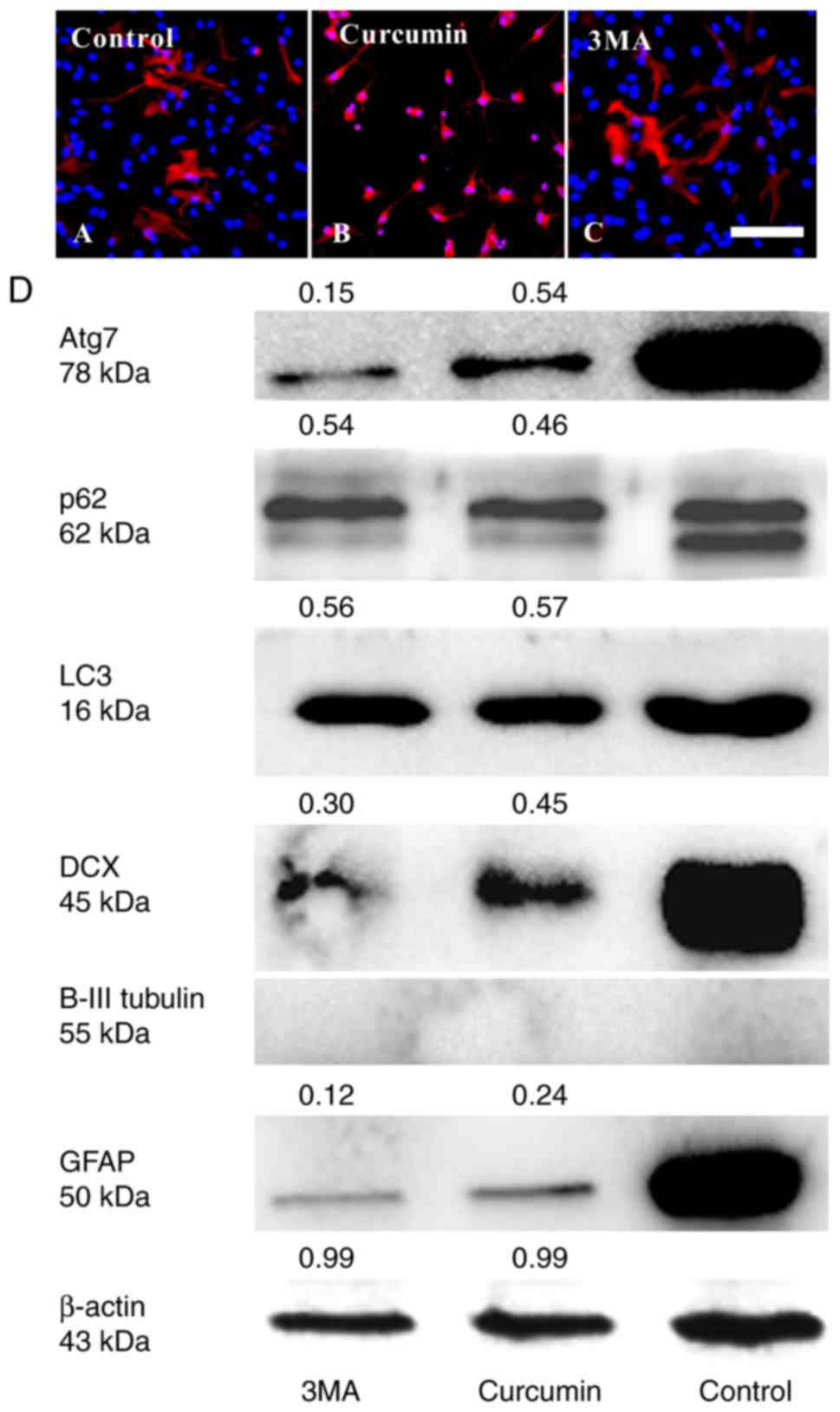
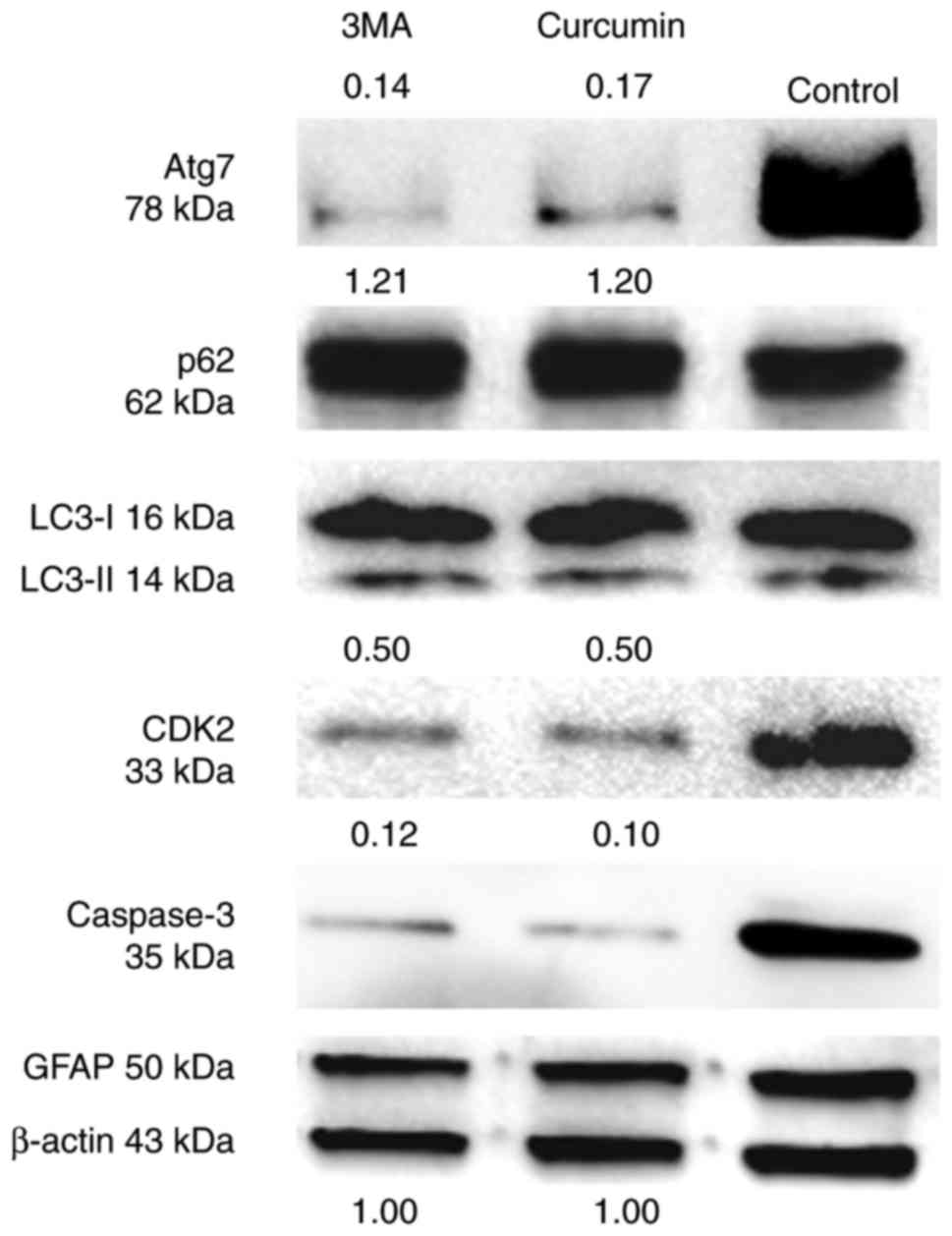
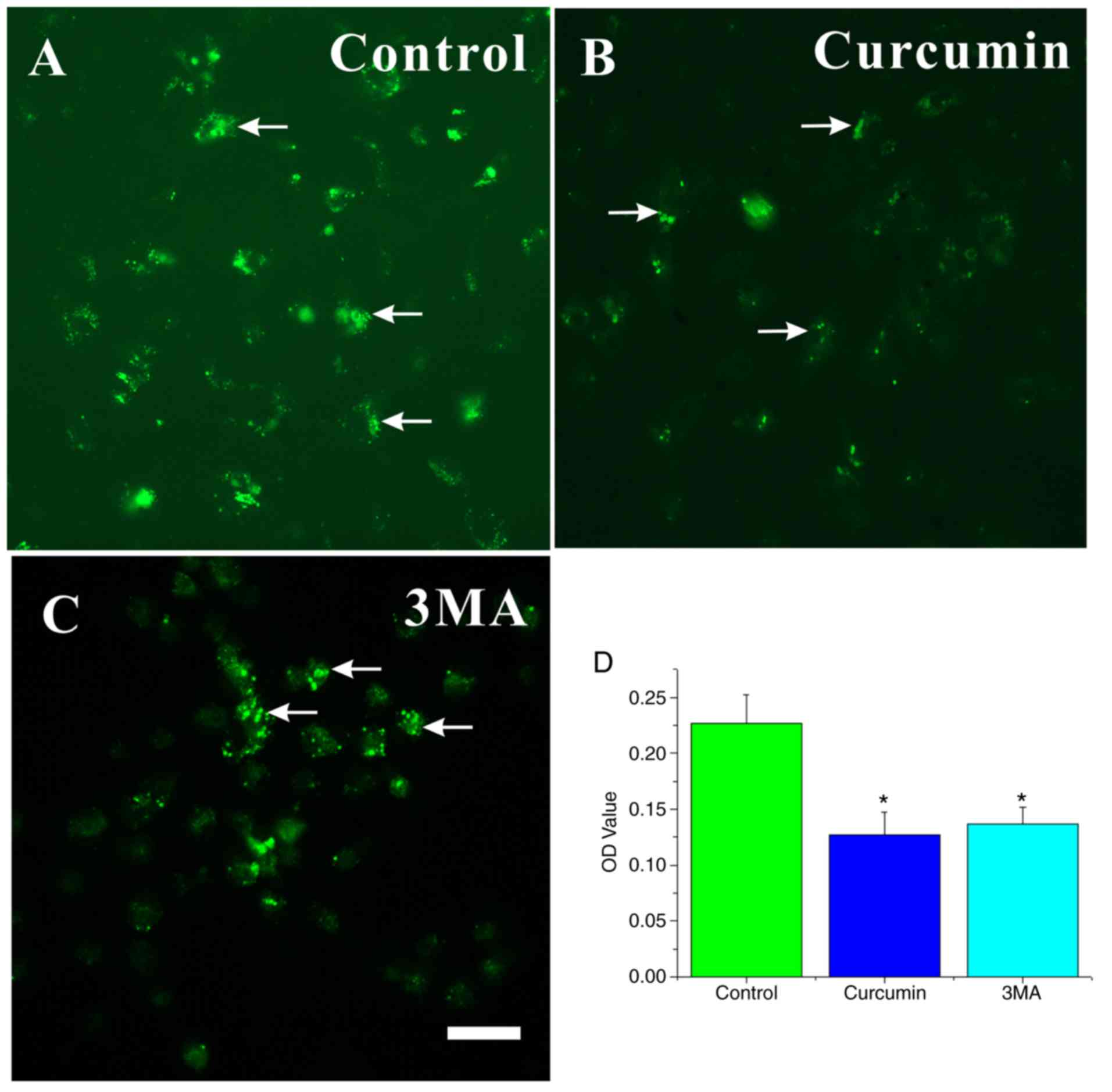
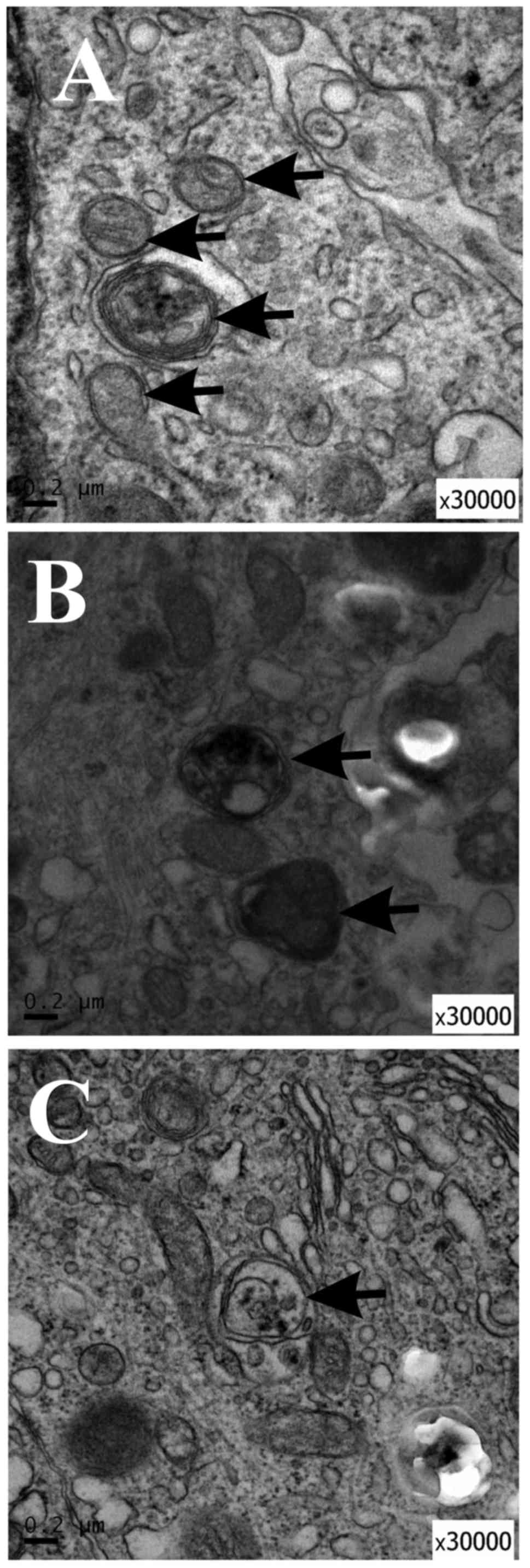
|
1
|
Aoki H, Takada Y, Kondo S, Sawaya R,
Aggarwal BB and Kondo Y: Evidence that curcumin suppresses the
growth of malignant gliomas in vitro and in vivo through induction
of autophagy: Role of Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase
signaling pathways. Mol Pharmacol. 72:29–39. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang R, Li Y, Li Y, Xu Y, Wu H and Li X:
Curcumin protects against glutamate excitotoxicity in rat cerebral
cortical neurons by increasing brain-derived neurotrophic factor
level and activating. TrkB Brain Res. 1210:84–91. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ramadan G, Al-Kahtani MA and El-Sayed WM:
Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties of curcuma longa
(turmeric) versus zingiber officinale (ginger) rhizomes in rat
adjuvant-induced arthritis. Inflammation. 34:291–301. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kang SK, Cha SH and Jeon HG:
Curcumin-induced histone hypoacetylation enhances
caspase-3-dependent glioma cell death and neurogenesis of neural
progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev. 15:165–174. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim SJ, Son TG, Park HR, Park M, Kim MS,
Kim HS, Chung HY, Mattson MP and Lee J: Curcumin stimulates
proliferation of embryonic neural progenitor cells and neurogenesis
in the adult hippocampus. J Biol Chem. 283:14497–14505. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Long DX, Hu D, Wang P and Wu YJ: Induction
of autophagy in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells by
tri-ortho-cresyl phosphate. Mol Cell Biochem. 396:33–40. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shi R, Weng J, Zhao L, Li XM, Gao TM and
Kong J: Excessive autophagy contributes to neuron death in cerebral
ischemia. CNS Neurosci Ther. 18:250–260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kroemer G, Mariño G and Levine B:
Autophagy and the integrated stress response. Mol Cell. 40:280–293.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gomez-Puerto MC, Folkerts H, Wierenga ATJ,
Schepers K, Schuringa JJ, Coffer PJ and Vellenga E: Autophagy
proteins ATG5 and ATG7 are essential for the maintenance of human
CD34+ hematopoietic stem-progenitor cells. Stem Cells.
34:1651–1663. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ouyang L, Zhang L, Zhang S, Yao D, Zhao Y,
Wang G, Fu L, Lei P and Liu B: Small-molecule activator of
UNC-51-like kinase 1 (ULK1) that induces cytoprotective autophagy
for Parkinson's disease treatment. J Med Chem. 61:2776–2792. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Karabiyik C, Lee MJ and Rubinsztein DC:
Autophagy impairment in Parkinson's disease. Essays Biochem.
61:711–720. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kabuta T, Suzuki Y and Wada K: Degradation
of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked mutant Cu, Zn-superoxide
dismutase proteins by macroautophagy and the proteasome. J Biol
Chem. 281:30524–30533. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fornai F, Longone P, Ferrucci M, Lenzi P,
Isidoro C, Ruggieri S and Paparelli A: Autophagy and amyotrophic
lateral sclerosis: The multiple roles of lithium. Autophagy.
4:527–530. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nixon RA, Wegiel J, Kumar A, Yu WH,
Peterhoff C, Cataldo A and Cuervo AM: Extensive involvement of
autophagy in Alzheimer disease: An immunoelectron microscopy study.
J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 64:113–122. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cianfanelli V and Cecconi F: AMBRA1: When
autophagy meets cell proliferation. Autophagy. 11:1705–1707. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Revuelta M and Matheu A: Autophagy in stem
cell aging. Aging Cell. 16:912–915. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Codogno P and Meijer AJ: Autophagy and
signaling: Their role in cell survival and cell death. Cell Death
Differ. 2(Suppl 12): S1509–S1518. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang C, Wu JM, Liao M, Wang JL and Xu CJ:
The ROCK/GGtase pathway are essential to the proliferation and
differentiation of neural stem cells mediated by simvastatin. J Mol
Neurosci. 60:474–485. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu CJ, Xu L, Huang LD, Li Y, Yu PP, Hang
Q, Xu XM and Lu PH: Combined NgR vaccination and neural stem cell
transplantation promote functional recovery after spinal cord
injury in adult rats. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 37:135–155. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Peng ZW, Xue F, Wang HN, Zhang RG, Chen
YC, Wang Y, Zhang LY, Fan J and Tan QR: Paroxetine up-regulates
neurogenesis in hippocampus-derived neural stem cell from fetal
rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 375:105–113. 2013.
|
|
21
|
Vázquez CL and Colombo MI: Chapter 6
assays to assess autophagy induction and fusion of autophagic
vacuoles with a degradative compartment, using monodansylcadaverine
(MDC) and DQ-BSA. Methods Enzymol. 452:85–95. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mizushima N and Yoshimori T: How to
interpret LC3 immunoblotting. Autophagy. 3:542–545. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Ueno T, Iwata J,
Murata S, Tanida I, Ezaki J, Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y, Uchiyama Y, et
al: Impairment of starvation-induced and constitutive autophagy in
Atg7-deficient mice. J Cell Biol. 169:425–434. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bjørkøy G, Lamark T, Brech A, Outzen H,
Perander M, Overvatn A, Stenmark H and Johansen T: p62/SQSTM1 forms
protein aggregates degraded by autophagy and has a protective
effect on huntingtin-induced cell death. J Cell Biol. 171:603–614.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bjørkøy G, Lamark T, Pankiv S, Øvervatn A,
Brech A and Johansen T: Monitoring autophagic degradation of
p62/SQSTM1. Methods Enzymol. 452:181–197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hamzehzadeh L, Atkin SL, Majeed M, Butler
AE and Sahebkar A: The versatile role of curcumin in cancer
prevention and treatment: A focus on PI3K/AKT pathway. J Cell
Physiol. 233:6530–6537. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu X and Zhu R: Curcumin suppresses the
progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma through the
upregulation of miR-145 and inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR
pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 11:3521–3531. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ahmed AI, Shtaya AB, Zaben MJ, Owens EV,
Kiecker C and Gray WP: Endogenous GFAP-positive neural
stem/progenitor cells in the postnatal mouse cortex are activated
following traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 29:828–842. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Vermeulen K, Van Bockstaele DR and
Berneman ZN: The cell cycle: A review of regulation, deregulation
and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 36:131–149. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Munafó DB and Colombo MI: A novel assay to
study autophagy: Regulation of autophagosome vacuole size by amino
acid deprivation. J Cell Sci. 114:3619–3629. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gukovskaya AS and Gukovsky I: Autophagy
and pancreatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
303:G993–G1003. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhuang W, Long L, Zheng B, Ji W, Yang N,
Zhang Q and Liang Z: Curcumin promotes differentiation of
glioma-initiating cells by inducing autophagy. Cancer Sci.
103:684–690. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shi L, Wang Z and Sun G: Curcumin induces
glioma stem-like cell formation. Neuroreport. 26:167–172. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Méndez J: Cell proliferation without
cyclin E-CDK2. Cell. 114:398–399. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tetsu O and Mccormick F: Proliferation of
cancer cells despite CDK2 inhibition. Cancer Cell. 3:233–245. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kelly TJ and Brown GW: Regulation of
chromosome replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 69:829–880. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tasdemir E, Maiuri MC, Tajeddine N, Vitale
I, Criollo A, Vicencio JM, Hickman JA, Geneste O and Kroemer G:
Cell cycle-dependent induction of autophagy, mitophagy and
reticulophagy. Cell Cycle. 6:2263–2267. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee IH, Kawai Y, Fergusson MM, Rovira II,
Bishop AJ, Motoyama N, Cao L and Finkel T: Atg7 modulates p53
activity to regulate cell cycle and survival during metabolic
stress. Science. 336:225–228. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhu J, Yang L, Tian Z, Hua X, Gu J, Li J,
Liu C, Jin H, Wang Y, Jiang G, et al: ATG7 overexpression is
crucial for tumorigenic growth of bladder cancer in vitro and in
vivo by targeting the ETS2/miRNA196b/FOXO1/p27 axis. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 7:299–313. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ojha R, Ishaq M and Singh SK:
Caspase-mediated crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis: Mutual
adjustment or matter of dominance. J Cancer Res Ther. 11:514–524.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Oral O, Oz-Arslan D, Itah Z, Naghavi A,
Deveci R, Karacali S and Gozuacik D: Cleavage of Atg3 protein by
caspase-8 regulates autophagy during receptor-activated cell death.
Apoptosis. 17:810–820. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Han J, Hou W, Goldstein LA, Stolz DB,
Watkins SC and Rabinowich H: A complex between atg7 and caspase-9:
A novel mechanism of cross-regulation between autophagy and
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 289:6485–6497. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Chang JL, Chow JM, Chang JH, Wen YC, Lin
YW, Yang SF, Lee WJ and Chien MH: Quercetin simultaneously induces
G0/G1-phase arrest and caspase-mediated crosstalk between apoptosis
and autophagy in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Environ Toxicol.
32:1857–1868. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rubinstein AD, Eisenstein M, Ber Y, Bialik
S and Kimchi A: The autophagy protein atg12 associates with
antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members to promote mitochondrial
apoptosis. Mol Cell. 44:698–709. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang C, Chen S, Yeo S, Karsli-Uzunbas G,
White E, Mizushima N, Virgin HW and Guan JL: Elevated p62/SQSTM1
determines the fate of autophagy-deficient neural stem cells by
increasing superoxide. J Cell Biol. 212:545–560. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Taniguchi K, Yamachika S, He F and Karin
M: p62/SQSTM1-Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde that prevents oxidative
stress but promotes liver cancer. FEBS Lett. 590:2375–2397. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang L, Cano M and Handa JT: p62 provides
dual cytoprotection against oxidative stress in the retinal pigment
epithelium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843:1248–1258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Carroll B, Otten EG, Manni D, Stefanatos
R, Menzies FM, Smith GR, Jurk D, Kenneth N, Wilkinson S, Passos JF,
et al: Oxidation of SQSTM1/p62 mediates the link between redox
state and protein homeostasis. Nat Commun. 9:2562018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Perez Estrada C, Covacu R, Sankavaram SR,
Svensson M and Brundin L: Oxidative stress increases neurogenesis
and oligodendrogenesis in adult neural progenitor cells. Stem Cells
Dev. 23:2311–2327. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Panchal HD, Vranizan K, Lee CY, Ho J, Ngai
J and Timiras PS: Early anti-oxidative and anti-proliferative
curcumin effects on neuroglioma cells suggest therapeutic targets.
Neurochem Res. 33:1701–1710. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mizushima N: Autophagy: Process and
function. Genes Dev. 21:2861–2873. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mizushima N: Methods for monitoring
autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:2491–2502. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yasuda T and Adams DJ: Physiological roles
of ion channels in adult neural stem cells and their progeny. J
Neurochem. 114:946–959. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang X, Chen Q, Wang Y, Peng W and Cai H:
Effects of curcumin on ion channels and transporters. Front
Physiol. 5:942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nalli M, Ortar G, Schiano Moriello A, Di
Marzo V and De Petrocellis L: Effects of curcumin and curcumin
analogues on TRP channels. Fitoterapia. 122:126–131. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|