|
1
|
Al-Khindi T, Macdonald RL and Schweizer
TA: Cognitive and functional outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Stroke. 41:e519–e536. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cahill J, Calvert JW and Zhang JH:
Mechanisms of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 26:1341–1353. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ayer R, Chen W, Sugawara T, Suzuki H and
Zhang JH: Role of gap junctions in early brain injury following
subarachnoid hemorrhage. Brain Res. 1315:150–158. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Fujii M, Yan J, Rolland WB, Soejima Y,
Caner B and Zhang JH: Early brain injury, an evolving frontier in
subarachnoid hemorrhage research. Transl Stroke Res. 4:432–446.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
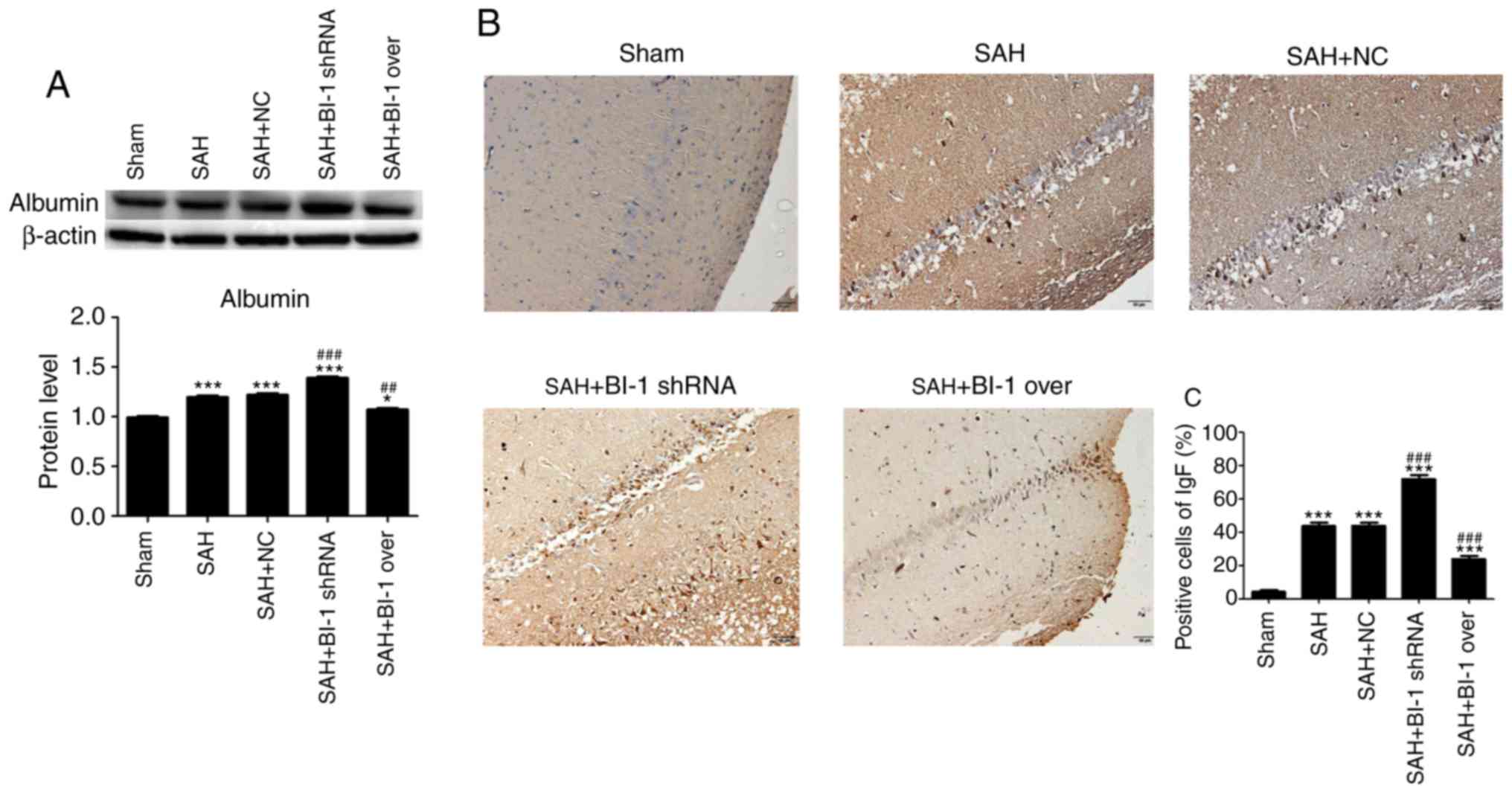
|
Ayer R and Zhang J: Connecting the early
brain injury of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage to clinical
practice. Turk Neurosurg. 20:159–166. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
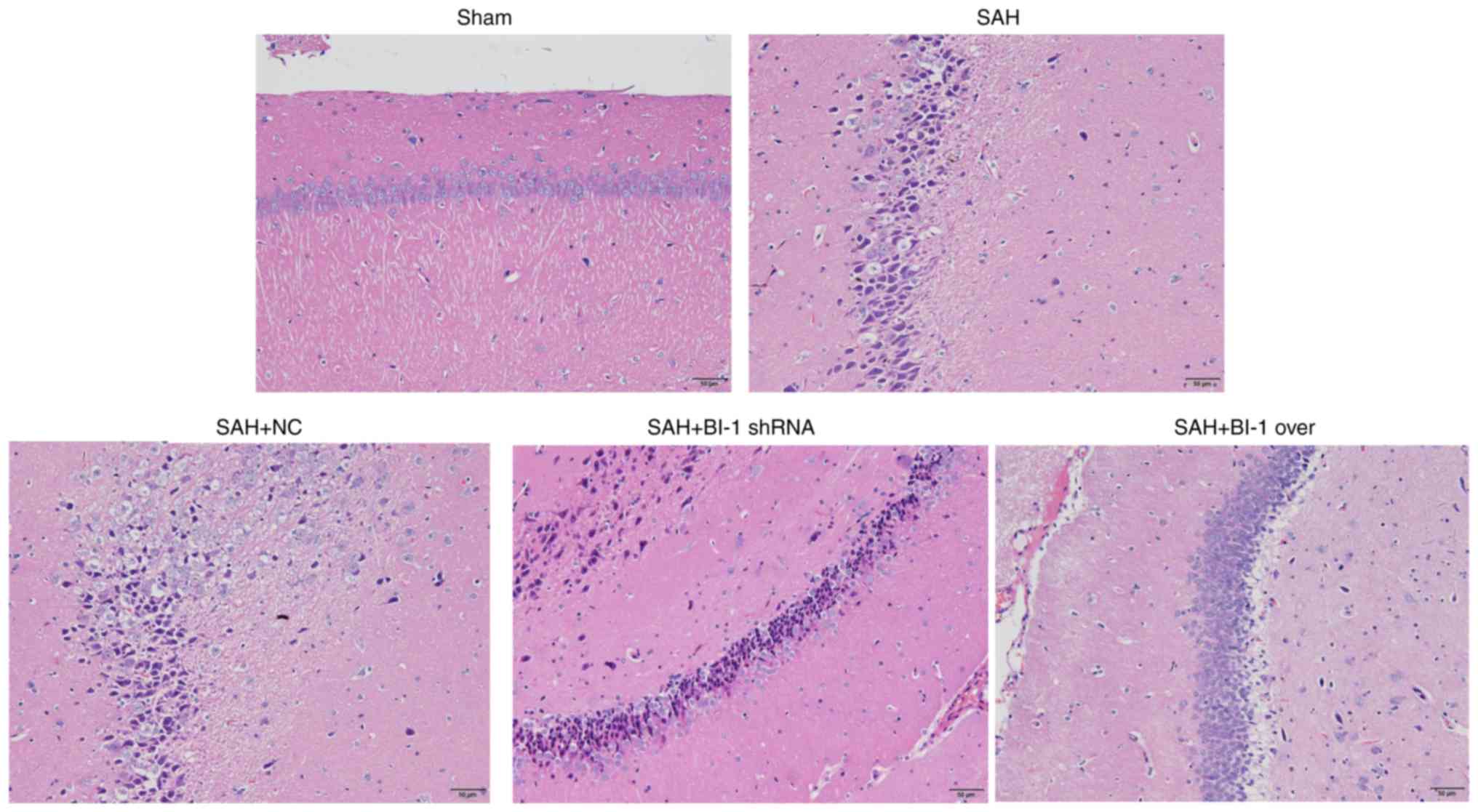
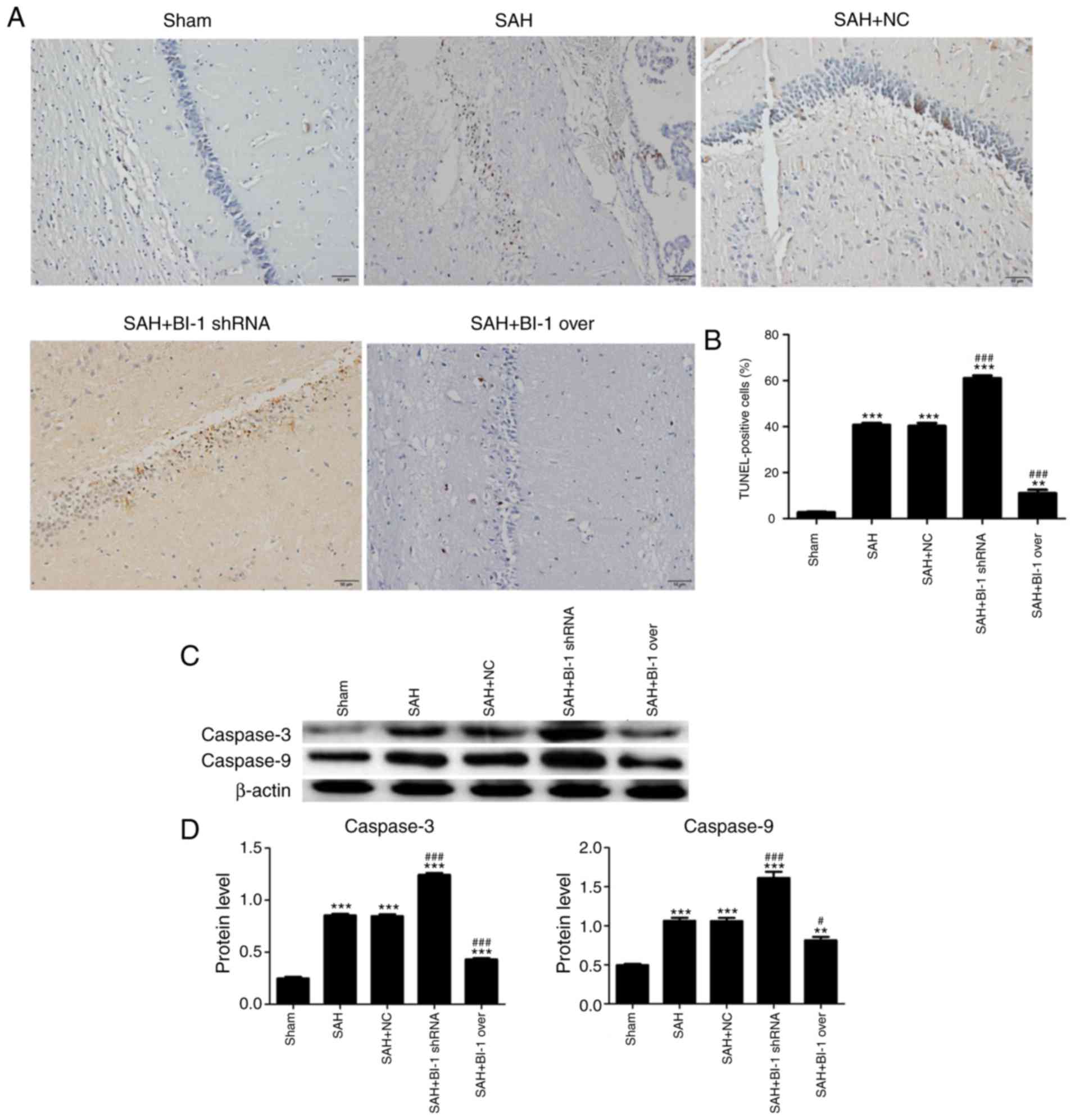
Yuksel S, Tosun YB, Cahill J and Solaroglu
I: Early brain injury following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage:
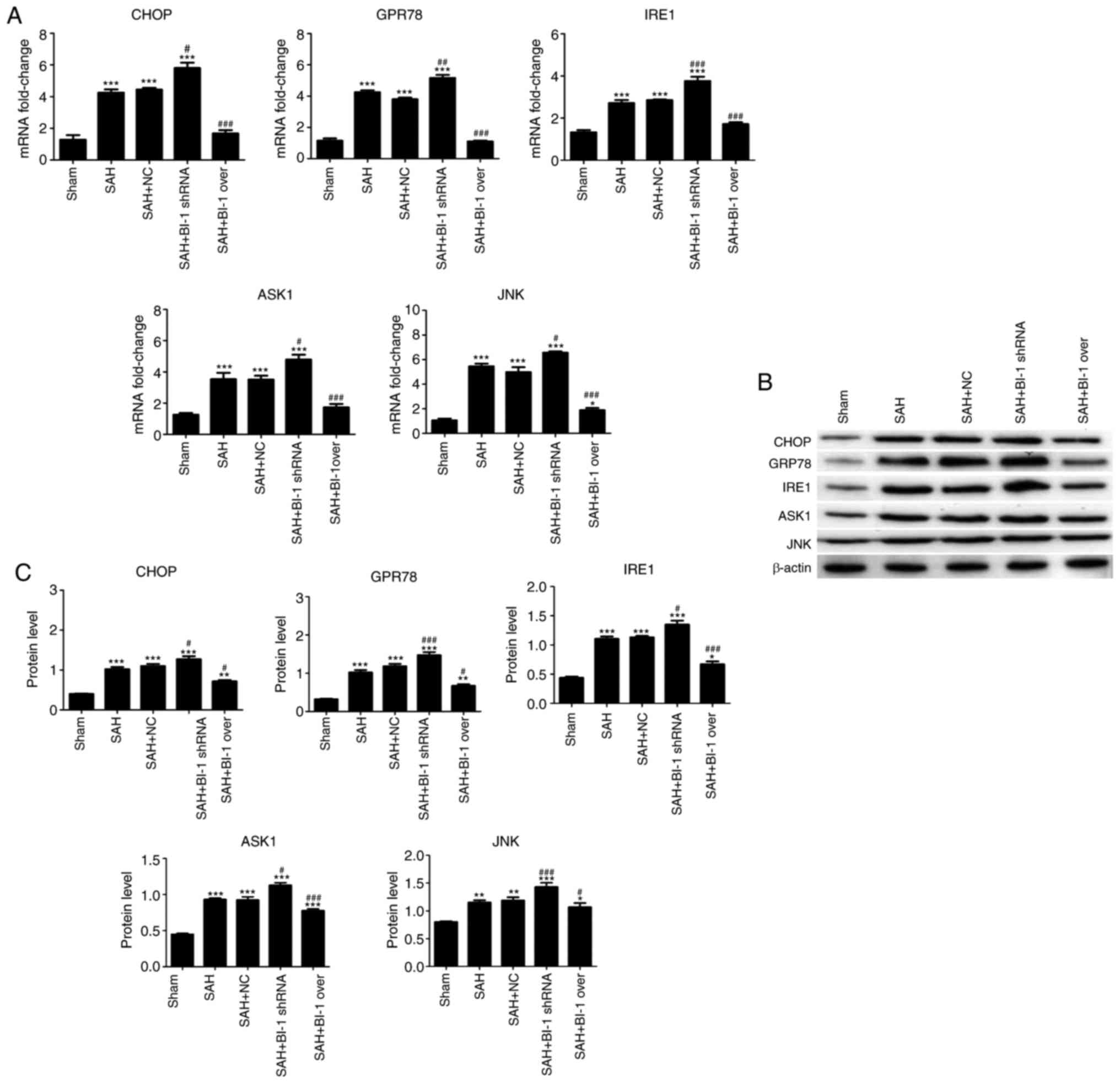
Emphasis on cellular apoptosis. Turk Neurosurg. 22:529–533.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hasegawa Y, Suzuki H, Sozen T, Altay O and
Zhang JH: Apoptotic mechanisms for neuronal cells in early brain
injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl.
110:43–48. 2011.
|
|
8
|
Cheng G, Chunlei W, Pei W, Zhen L and
Xiangzhen L: Simvastatin activates Akt/glycogen synthase
kinase-3beta signal and inhibits caspase-3 activation after
experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Vascul Pharmacol. 52:77–83.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kusaka G, Ishikawa M, Nanda A, Granger DN
and Zhang JH: Signaling pathways for early brain injury after
subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 24:916–925.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Endo H, Nito C, Kamada H, Yu F and Chan
PH: Akt/GSK3beta survival signaling is involved in acute brain
injury after subarach-noid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke.
37:2140–2146. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu Q and Reed JC: Bax inhibitor-1, a
mammalian apoptosis suppressor identified by functional screening
in yeast. Mol Cell. 1:337–346. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chae HJ, Kim HR, Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B,
Krajewska M, Krajewski S, Banares S, Cui J, Digicaylioglu M, Ke N,
et al: BI-1 regulates an apoptosis pathway linked to endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Mol Cell. 15:355–366. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bredesen DE, Rao RV and Mehlen P: Cell
death in the nervous system. Nature. 443:796–802. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim I, Xu W and Reed JC: Cell death and
endoplasmic reticulum stress: Disease relevance and therapeutic
opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:1013–1030. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Patil C and Walter P: Intracellular
signaling from the endoplasmic reticulum to the nucleus: The
unfolded protein response in yeast and mammals. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 13:349–355. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hetz C, Bernasconi P, Fisher J, Lee AH,
Bassik MC, Antonsson B, Brandt GS, Iwakoshi NN, Schinzel A,
Glimcher LH and Korsmeyer SJ: Proapoptotic BAX and BAK modulate the
unfolded protein response by a direct interaction with IRE1alpha.
Science. 312:572–576. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM and Samali
A: Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis.
EMBO Rep. 7:880–885. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nishitoh H, Matsuzawa A, Tobiume K,
Saegusa K, Takeda K, Inoue K, Hori S, Kakizuka A and Ichijo H: ASK1
is essential for endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal cell
death triggered by expanded polyglutamine repeats. Genes Dev.
16:1345–1355. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lei K and Davis RJ: JNK phosphorylation of
Bim-related members of the Bcl2 family induces Bax-dependent
apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:2432–2437. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Krajewska M, Xu L, Xu W, Krajewski S,
Kress CL, Cui J, Yang L, Irie F, Yamaguchi Y, Lipton SA and Reed
JC: Endoplasmic reticulum protein BI-1 modulates unfolded protein
response signaling and protects against stroke and traumatic brain
injury. Brain Res. 1370:227–237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Bailly-Maitre B, Fondevila C, Kaldas F,
Droin N, Luciano F, Ricci JE, Croxton R, Krajewska M, Zapata JM,
Kupiec-Weglinski JW, et al: Cytoprotective gene bi-1 is required
for intrinsic protection from endoplasmic reticulum stress and
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2809–2814.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu B, Li Y, Li H, Zhang Y, Xu J, Ren L, Fu
S and Zhou Y: Bax inhibitor-1 is overexpressed in non-small cell
lung cancer and promotes its progression and metastasis. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:1411–1418. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grzmil M, Thelen P, Hemmerlein B, Schweyer
S, Voigt S, Mury D and Burfeind P: Bax inhibitor-1 is overexpressed
in prostate cancer and its specific down-regulation by RNA
interference leads to cell death in human prostate carcinoma cells.
Am J Pathol. 163:543–552. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bailly-Maitre B, Bard-Chapeau E, Luciano
F, Droin N, Bruey JM, Faustin B, Kress C, Zapata JM and Reed JC:
Mice lacking bi-1 gene show accelerated liver regeneration. Cancer
Res. 67:1442–1450. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bailly-Maitre B, Belgardt BF, Jordan SD,
Coornaert B, von Freyend MJ, Kleinridders A, Mauer J, Cuddy M,
Kress CL, Willmes D, et al: Hepatic Bax inhibitor-1 inhibits
IRE1alpha and protects from obesity-associated insulin resistance
and glucose intolerance. J Biol Chem. 285:6198–6207. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jeon K, Lim H, Kim JH, Han D, Lee ER, Yang
GM, Song MK, Kim JH and Cho SG: Bax inhibitor-1 enhances survival
and neuronal differentiation of embryonic stem cells via
differential regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases
activities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1823:2190–2200. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dohm CP, Siedenberg S, Liman J, Esposito
A, Wouters FS, Reed JC, Bähr M and Kermer P: Bax inhibitor-1
protects neurons from oxygen-glucose deprivation. J Mol Neurosci.
29:1–8. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Prunell GF, Mathiesen T and Svendgaard NA:
A new experimental model in rats for study of the pathophysiology
of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neuroreport. 13:2553–2556. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sugawara T, Ayer R, Jadhav V and Zhang JH:
A new grading system evaluating bleeding scale in filament
perforation subarachnoid hemorrhage rat model. J Neurosci Methods.
167:327–334. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Alafuzoff I, Adolfsson R, Bucht G and
Winblad B: Albumin and immunoglobulin in plasma and cerebrospinal
fluid, and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier function in patients
with dementia of Alzheimer type and multi-infarct dementia. J
Neurol Sci. 60:465–472. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sorjonen DC: Total protein, albumin quota,
and electrophoretic patterns in cerebrospinal fluid of dogs with
central nervous system disorders. Am J Vet Res. 48:301–305.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kumar A, Mittal R, Khanna HD and Basu S:
Free radical injury and blood-brain barrier permeability in
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 122:e722–e727. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schmidt-Kastner R, Szymas J and Hossmann
KA: Immunohistochemical study of glial reaction and serum-protein
extravasation in relation to neuronal damage in rat hippocampus
after ischemia. Neuroscience. 38:527–540. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Suzuki H: What is early brain injury?
Transl Stroke Res. 6:1–3. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sehba FA, Hou J, Pluta RM and Zhang JH:
The importance of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Prog Neurobiol. 97:14–37. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hosaka K and Hoh BL: Inflammation and
cerebral aneurysms. Transl Stroke Res. 5:190–198. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Chen S, Yang Q, Chen G and Zhang JH: An
update on inflammation in the acute phase of intracerebral
hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res. 6:4–8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sabri M, Kawashima A, Ai J and Macdonald
RL: Neuronal and astrocytic apoptosis after subarachnoid
hemorrhage: A possible cause for poor prognosis. Brain Res.
1238:163–171. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Matz PG, Fujimura M and Chan PH:
Subarachnoid hemolysate produces DNA fragmentation in a pattern
similar to apoptosis in mouse brain. Brain Res. 858:312–319. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lindholm D, Wootz H and Korhonen L: ER
stress and neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Death Differ.
13:385–392. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
He Z, Ostrowski RP, Sun X, Ma Q, Huang B,
Zhan Y and Zhang JH: CHOP silencing reduces acute brain injury in
the rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 43:484–490. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Roussel BD, Kruppa AJ, Miranda E, Crowther
DC, Lomas DA and Marciniak SJ: Endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction in
neurological disease. Lancet Neurol. 12:105–118. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Placido AI, Pereira CM, Duarte AI,
Candeias E, Correia SC, Carvalho C, Cardoso S, Oliveira CR and
Moreira PI: Modulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress: An
opportunity to prevent neurodegeneration? CNS Neurol Disord Drug
Targets. 14:518–533. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Stefani IC, Wright D, Polizzi KM and
Kontoravdi C: The role of ER stress-induced apoptosis in
neurodegeneration. Curr Alzheimer Res. 9:373–387. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
McManus MJ, Murphy MP and Franklin JL:
Mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species mediate
caspase-dependent and-independent neuronal deaths. Mol Cell
Neurosci. 63:13–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Winklhofer KF and Haass C: Mitochondrial
dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1802:29–44. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Itoh K, Nakamura K, Iijima M and Sesaki H:
Mitochondrial dynamics in neurodegeneration. Trends Cell Biol.
23:64–71. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Chen J, Wang L, Wu C, Hu Q, Gu C, Yan F,
Li J, Yan W and Chen G: Melatonin-enhanced autophagy protects
against neural apoptosis via a mitochondrial pathway in early brain
injury following a subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Pineal Res. 56:12–19.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Liang Y, Che X, Zhao Q, Darwazeh R, Zhang
H, Jiang D, Zhao J, Xiang X, Qin W, Liu L and He Z:
Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates mitochondrion-dependent
apoptosis in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Mol
Cell Biochem. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|