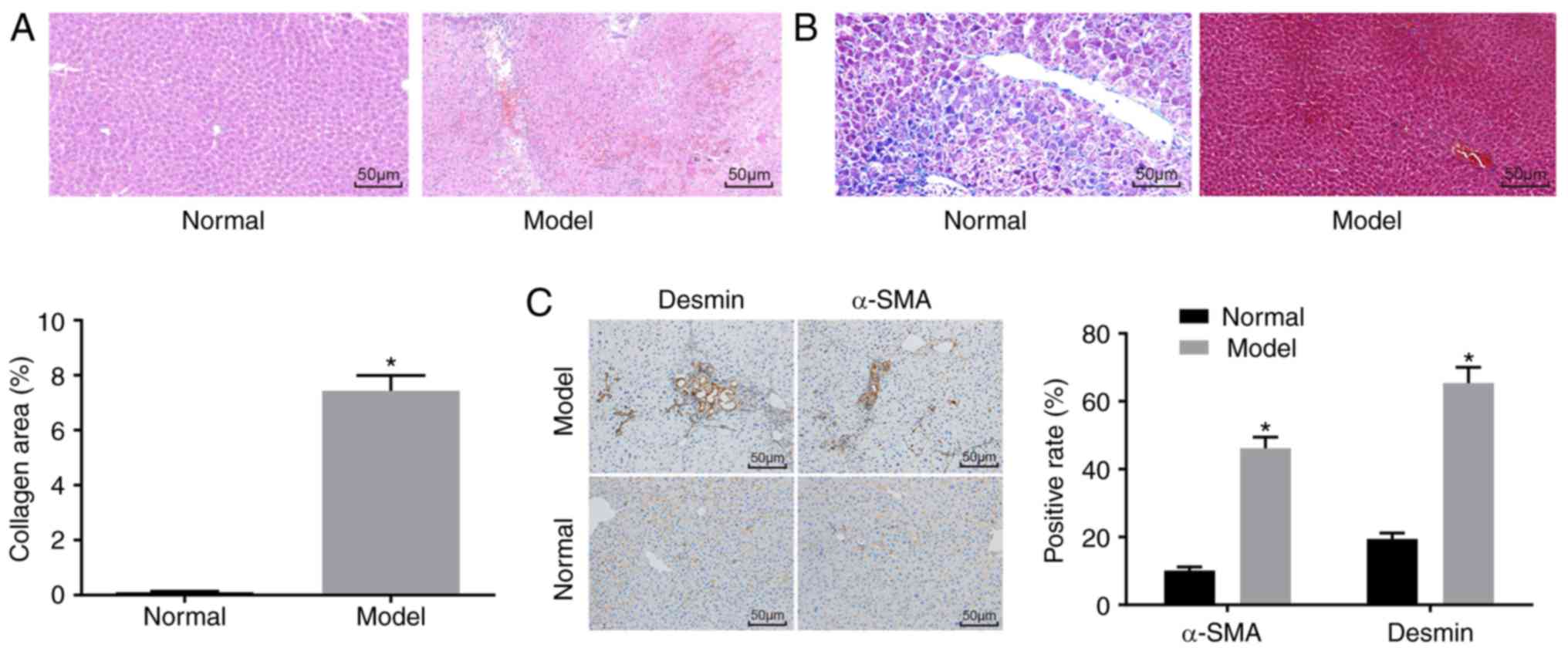
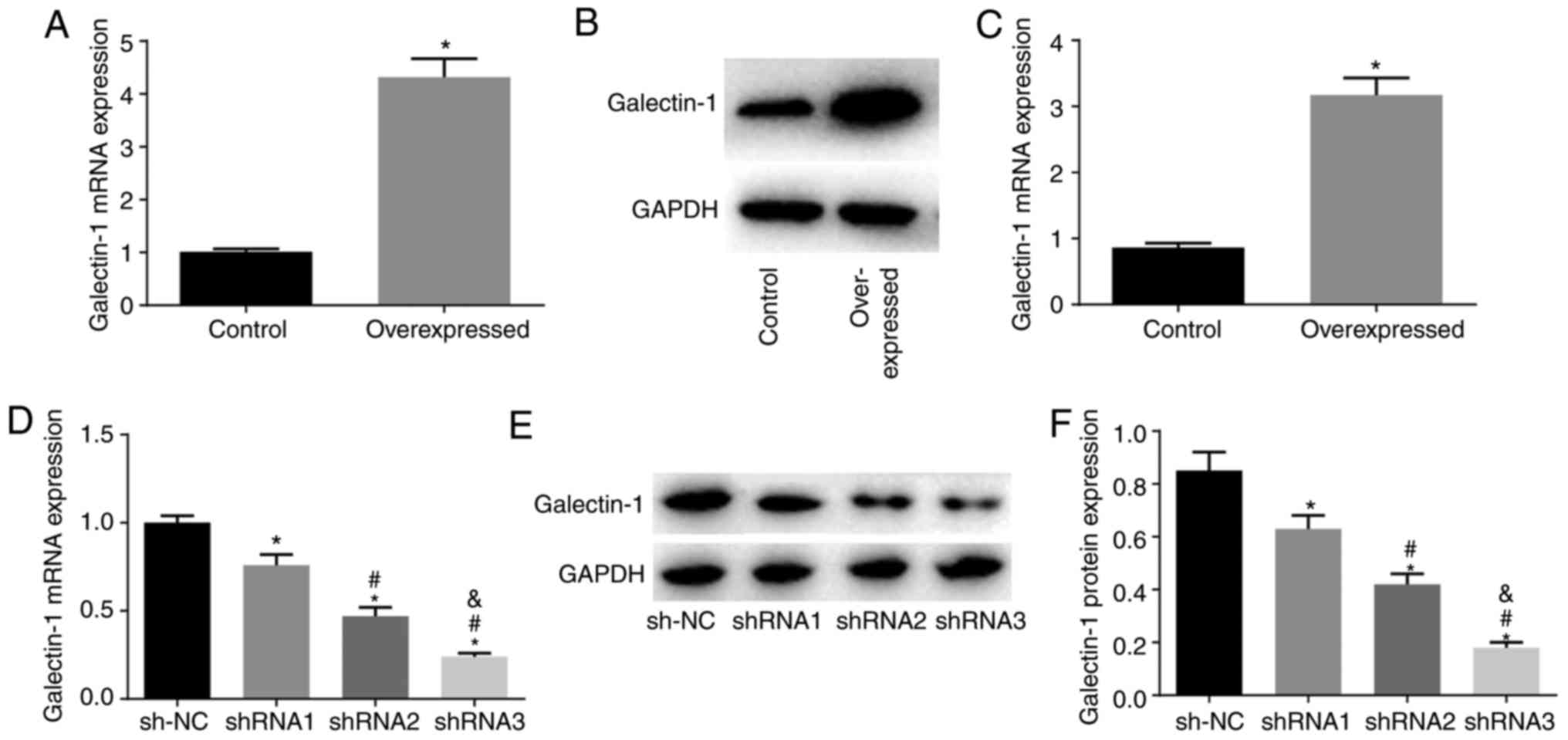
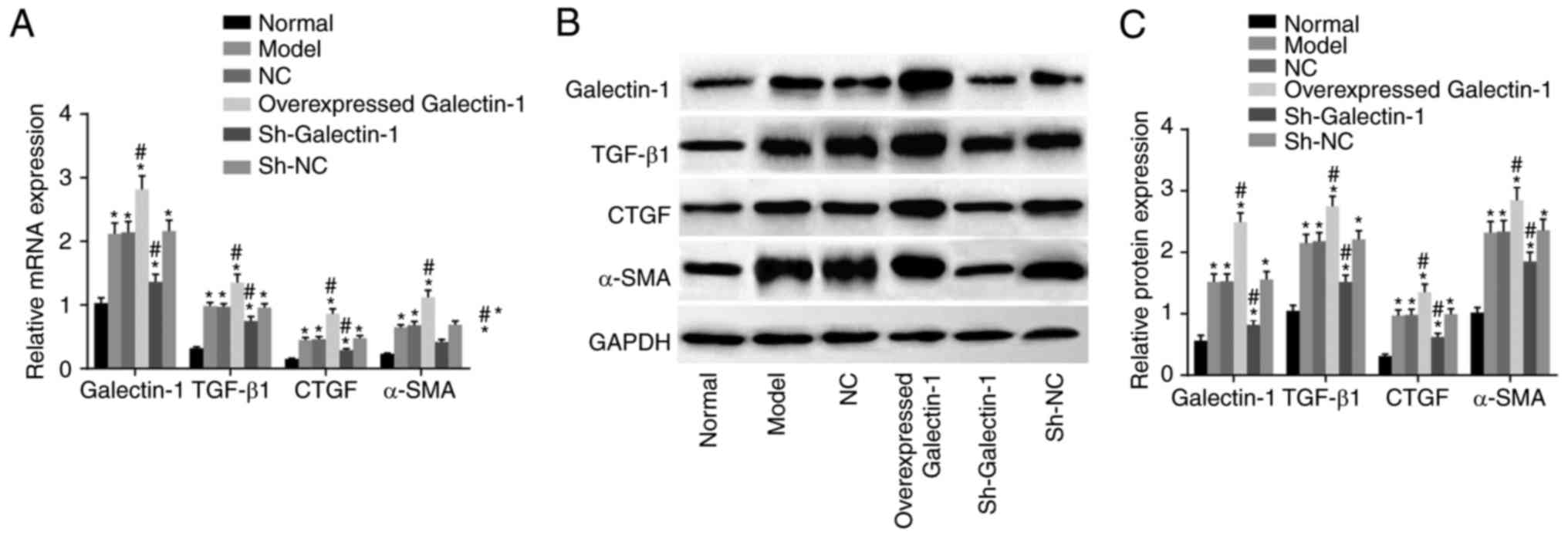
|
1
|
Moran-Salvador E and Mann J: Epigenetics
and liver fibrosis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 4:125–134.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hyun J and Jung Y: MicroRNAs in liver
fibrosis: Focusing on the interaction with hedgehog signaling.
World J Gastroenterol. 22:6652–6662. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ellis EL and Mann DA: Clinical evidence
for the regression of liver fibrosis. J Hepatol. 56:1171–1180.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kisseleva T, Cong M, Paik Y, Scholten D,
Jiang C, Benner C, Iwaisako K, Moore-Morris T, Scott B, Tsukamoto
H, et al: Myofibroblasts revert to an inactive phenotype during
regression of liver fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci US. 109:9448–9453.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lee UE and Friedman SL: Mechanisms of
hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
25:195–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Troeger JS, Mederacke I, Gwak GY, Dapito
DH, Mu X, Hsu CC, Pradere JP, Friedman RA and Schwabe RF:
Deactivation of hepatic stellate cells during liver fibrosis
resolution in mice. Gastroenterology. 143:1073–1083.e22. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Krizhanovsky V, Yon M, Dickins RA, Hearn
S, Simon J, Miething C, Yee H, Zender L and Lowe SW: Senescence of
activated stellate cells limits liver fibrosis. Cell. 134:657–667.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Friedman SL: Hepatic stellate cells:
Protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol
Rev. 88:125–172. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yin C, Evason KJ, Asahina K and Stainier
DY: Hepatic stellate cells in liver development, regeneration, and
cancer. J Clin Invest. 123:1902–1910. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moreira RK: Hepatic stellate cells and
liver fibrosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 131:1728–1734. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
You Y, Tan JX, Dai HS, Chen HW, Xu XJ,
Yang AG, Zhang YJ, Bai LH and Bie P: MiRNA-22 inhibits oncogene
galectin-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:57099–57116.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cousin JM and Cloninger MJ: The role of
galectin-1 in cancer progression, and synthetic multivalent systems
for the study of galectin-1. Int J Mol Sci. 17:E15662016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang YJ, Shiau AL, Chen SY, Chen YL, Wang
CR, Tsai CY, Chang MY, Li YT, Leu CH and Wu CL: Multivalent
structure of galectin-1-nanogold complex serves as potential
therapeutics for rheumatoid arthritis by enhancing receptor
clustering. Eur Cell Mater. 23:170–181. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
D’Haene N, Sauvage S, Maris C, Adanja I,
Le Mercier M, Decaestecker C, Baum L and Salmon I: VEGFR1 and
VEGFR2 involvement in extracellular galectin-1- and
galectin-3-induced angiogenesis. PLoS One. 8:e670292013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Belardi B, O’Donoghue GP, Smith AW, Groves
JT and Bertozzi CR: Investigating cell surface galectin-mediated
cross-linking on glycoengineered cells. J Am Chem Soc.
134:9549–9552. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hernandez JD, Nguyen JT, He J, Wang W,
Ardman B, Green JM, Fukuda M and Baum LG: Galectin-1 binds
different CD43 glycoforms to cluster CD43 and regulate T cell
death. J Immunol. 177:5328–5336. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Laderach DJ, Gentilini LD, Giribaldi L,
Delgado VC, Nugnes L, Croci DO, Al Nakouzi N, Sacca P, Casas G,
Mazza O, et al: A unique galectin signature in human prostate
cancer progression suggests galectin-1 as a key target for
treatment of advanced disease. Cancer Res. 73:86–96. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu FT and Rabinovich GA: Galectins as
modulators of tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:29–41. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Elola MT, Wolfenstein-Todel C, Troncoso
MF, Vasta GR and Rabinovich GA: Galectins: Matricellular
glycan-binding proteins linking cell adhesion, migration, and
survival. Cell Mol Life Sci. 64:1679–1700. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Maeda N, Kawada N, Seki S, Arakawa T,
Ikeda K, Iwao H, Okuyama H, Hirabayashi J, Kasai K and Yoshizato K:
Stimulation of proliferation of rat hepatic stellate cells by
galectin-1 and galectin-3 through different intracellular signaling
pathways. J Biol Chem. 278:18938–18944. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lim MJ, Ahn J, Yi JY, Kim MH, Son AR, Lee
SL, Lim DS, Kim SS, Kang MA, Han Y and Song JY: Induction of
galectin-1 by TGF-β1 accelerates fibrosis through enhancing nuclear
retention of Smad2. Exp Cell Res. 326:125–135. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Brown RS and Wahl RL: Overexpression of
Glut-1 glucose transporter in human breast cancer. An
immunohistochemical study Cancer. 72:2979–2985. 1993.
|
|
23
|
Tuo YL, Li XM and Luo J: Long noncoding
RNA UCA1 modulates breast cancer cell growth and apoptosis through
decreasing tumor suppressive miR-143. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
19:3403–3411. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Friedman SL and Roll FJ: Isolation and
culture of hepatic lipocytes, Kupffer cells, and sinusoidal
endothelial cells by density gradient centrifugation with Stractan.
Anal Biochem. 161:207–218. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang QL, Wang JM, Jiang S, Wen LM and
Zhou H: Large-scale real-time titration of
green-fluorescence-protein-marked recombinant retrovirus:
Comparison with standard titration method. Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue
Bao. 23:1101–1103. 2003.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu J, Hao G, Wang D, Liu J, Dong X, Sun Y,
Pan Q, Li Y, Shi X, Li L and Cao H: Therapeutic effect and location
of GFP-labeled placental mesenchymal stem cells on hepatic fibrosis
in rats. Stem Cells Int. 2017.1798260:2017.
|
|
27
|
Pais R, Barritt AS IV, Calmus Y, Scatton
O, Runge T, Lebray P, Poynard T, Ratziu V and Conti F: NAFLD and
liver transplantation: Current burden and expected challenges. J
Hepatol. 65:1245–1257. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Addolorato G, Mirijello A, Barrio P and
Gual A: Treatment of alcohol use disorders in patients with
alcoholic liver disease. J Hepatol. 65:618–630. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bacigalupo ML, Manzi M, Rabinovich GA and
Troncoso MF: Hierarchical and selective roles of galectins in
hepatocarcinogenesis, liver fibrosis and inflammation of
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 19:8831–8849.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Liu FT and Rabinovich GA: Galectins:
Regulators of acute and chronic inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1183:158–182. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Carobene A, Braga F, Roraas T, Sandberg S
and Bartlett WA: A systematic review of data on biological
variation for alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase
and gamma-glutamyl transferase. Clin Chem Lab Med. 51:1997–2007.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tai DI, Lin SM, Sheen IS, Chu CM, Lin DY
and Liaw YF: Long-term outcome of hepatitis B e antigen-negative
hepatitis B surface antigen carriers in relation to changes of
alanine amino-transferase levels over time. Hepatology.
49:1859–1867. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ceriotti F, Henny J, Queraltó J, Ziyu S,
Özarda Y, Chen B, Boyd JC and Panteghini M: IFCC Committee on
Reference Intervalsand Decision Limits (C-RIDL); Committee on
Reference Systems for Enzymes (C-RSE): Common reference intervals
for aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase
(ALT) and γ-glutamyl transferase (GGT) in serum: Results from an
IFCC multicenter study. Clin Chem Lab Med. 48:1593–1601. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moreno-Otero R, Trapero-Marugan M and
Mendoza J: Liver fibrosis assessment by transient elastography in
hepatitis C patients with normal alanine aminotransferase. Gut.
55:1055–1056. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liang CC, Liu CH, Chung CS, Lin CK, Su TH,
Yang HC, Liu CJ, Chen PJ, Chen DS and Kao JH: Advanced hepatic
fibrosis and steatosis are associated with persistent alanine
aminotransferase elevation in chronic hepatitis C patients negative
for hepatitis C virus RNA during pegylated interferon plus
ribavirin therapy. J Infect Dis. 211:1429–1436. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wang T, Zhao LJ, Li P, Jiang H, Lu GC,
Zhang WD, Li HL and Yuan BJ: Hepatoprotective effects and
mechanisms of dehydrocavidine in rats with carbon
tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis. J Ethnopharmacol.
138:76–84. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mangus RS, O’Connor MG, Tector AJ, Lim JD
and Vianna RM: Use of the aspartate aminotransferase to platelet
ratio index to follow liver fibrosis progression in infants with
short gut. J Pediatr Surg. 45:1266–1273. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Petersen JR, Stevenson HL, Kasturi KS,
Naniwadekar A, Parkes J, Cross R, Rosenberg WM, Xiao SY and Snyder
N: Evaluation of the aspartate aminotransferase/platelet ratio
index and enhanced liver fibrosis tests to detect significant
fibrosis due to chronic hepatitis C. J Clin Gastroenterol.
48:370–376. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Blomme B, Van Steenkiste C, Vanhuysse J,
Colle I, Callewaert N and Van Vlierberghe H: Impact of elevation of
total bilirubin level and etiology of the liver disease on serum
N-glycosylation patterns in mice and humans. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 298:G615–G624. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Spinella R, Sawhney R and Jalan R: Albumin
in chronic liver disease: Structure, functions and therapeutic
implications. Hepatol Int. 10:124–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lee H, Jeong H, Park S, Yoo W, Choi S,
Choi K, Lee MG, Lee M, Cha D, Kim YS, et al: Fusion protein of
retinol-binding protein and albumin domain III reduces liver
fibrosis. EMBO Mol Med. 7:819–830. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tang D, Yuan Z, Xue X, Lu Z, Zhang Y, Wang
H, Chen M, An Y, Wei J, Zhu Y, et al: High expression of Galectin-1
in pancreatic stellate cells plays a role in the development and
maintenance of an immunosuppressive microenvironment in pancreatic
cancer. Int J Cancer. 130:2337–2348. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Masamune A, Satoh M, Hirabayashi J, Kasai
K, Satoh K and Shimosegawa T: Galectin-1 induces chemokine
production and proliferation in pancreatic stellate cells. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 290:G729–G736. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tang D, Zhang J, Yuan Z, Gao J, Wang S, Ye
N, Li P, Gao S, Miao Y, Wang D and Jiang K: Pancreatic satellite
cells derived galectin-1 increase the progression and less survival
of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e904762014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Spano D, Russo R, Di Maso V, Rosso N,
Terracciano LM, Roncalli M, Tornillo L, Capasso M, Tiribelli C and
Iolascon A: Galectin-1 and its involvement in hepatocellular
carcinoma aggressiveness. Mol Med. 16:102–115. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Satelli A and Rao US: Galectin-1 is
silenced by promoter hyper-methylation and its re-expression
induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
301:38–46. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Bektas S, Bahadir B, Ucan BH and Ozdamar
SO: CD24 and galectin-1 expressions in gastric adenocarcinoma and
clinicopathologic significance. Pathol Oncol Res. 16:569–577. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tang D, Wu Q, Zhang J, Zhang H, Yuan Z, Xu
J, Chong Y, Huang Y, Xiong Q, Wang S, et al: Galectin-1 expression
in activated pancreatic satellite cells promotes fibrosis in
chronic pancreatitis/pancreatic cancer via the TGF-β1/Smad pathway.
Oncol Rep. 39:1347–1355. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Prunotto M, Bruschi M, Gunning P, Gabbiani
G, Weibel F, Ghiggeri GM, Petretto A, Scaloni A, Bonello T,
Schevzov G, et al: Stable incorporation of α-smooth muscle actin
into stress fibers is dependent on specific tropomyosin isoforms.
Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 72:257–267. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wu MH, Hong HC, Hong TM, Chiang WF, Jin YT
and Chen YL: Targeting galectin-1 in carcinoma-associated
fibroblasts inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis by
downregulating MCP-1/CCL2 expression. Clin Cancer Res.
17:1306–1316. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Le Mercier M, Mathieu V, Haibe-Kains B,
Bontempi G, Mijatovic T, Decaestecker C, Kiss R and Lefranc F:
Knocking down galectin 1 in human hs683 glioblastoma cells impairs
both angiogenesis and endoplasmic reticulum stress responses. J
Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 67:456–469. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Park S, Choi S, Lee MG, Lim C and Oh J:
Retinol binding protein-albumin domain III fusion protein
deactivates hepatic stellate cells. Mol Cells. 34:517–522. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lefranc F, Mathieu V and Kiss R:
Galectin-1-mediated biochemical controls of melanoma and glioma
aggressive behavior. World J Biol Chem. 2:193–201. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chung LY, Tang SJ, Sun GH, Chou TY, Yeh
TS, Yu SL and Sun KH: Galectin-1 promotes lung cancer progression
and chemoresistance by upregulating p38 MAPK, ERK, and
cyclo-oxygenase-2. Clin Cancer Res. 18:4037–4047. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Verschuere T, Van Woensel M, Fieuws S,
Lefranc F, Mathieu V, Kiss R, Van Gool SW and De Vleeschouwer S:
Altered galectin-1 serum levels in patients diagnosed with
high-grade glioma. J Neurooncol. 115:9–17. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dalotto-Moreno T, Croci DO, Cerliani JP,
Martinez-Allo VC, Dergan-Dylon S, Méndez-Huergo SP, Stupirski JC,
Mazal D, Osinaga E, Toscano MA, et al: Targeting galectin-1
overcomes breast cancer-associated immunosuppression and prevents
metastatic disease. Cancer Res. 73:1107–1117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Kim HJ, Do IG, Jeon HK, Cho YJ, Park YA,
Choi JJ, Sung CO, Lee YY, Choi CH, Kim TJ, et al: Galectin 1
expression is associated with tumor invasion and metastasis in
stage IB to IIA cervical cancer. Hum Pathol. 44:62–68. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Hsu YL, Wu CY, Hung JY, Lin YS, Huang MS
and Kuo PL: Galectin-1 promotes lung cancer tumor metastasis by
potentiating integrin α6β4 and Notch1/Jagged2 signaling pathway.
Carcinogenesis. 34:1370–1381. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Cimmino F, Schulte JH, Zollo M, Koster J,
Versteeg R, Iolascon A, Eggert A and Schramm A: Galectin-1 is a
major effector of TrkB-mediated neuroblastoma aggressiveness.
Oncogene. 28:2015–2023. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Jung EJ, Moon HG, Cho BI, Jeong CY, Joo
YT, Lee YJ, Hong SC, Choi SK, Ha WS, Kim JW, et al: Galectin-1
expression in cancer-associated stromal cells correlates tumor
invasiveness and tumor progression in breast cancer. Int J Cancer.
120:2331–2338. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wu MH, Hong TM, Cheng HW, Pan SH, Liang
YR, Hong HC, Chiang WF, Wong TY, Shieh DB, Shiau AL, et al:
Galectin-1-mediated tumor invasion and metastasis, up-regulated
matrix metalloproteinase expression, and reorganized actin
cytoskeletons. Mol Cancer Res. 7:311–318. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Cvejic D, Savin S, Petrovic I, Selemetjev
S, Paunovic I, Tatic S and Havelka M: Galectin-3 and proliferating
cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) expression in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Exp Oncol. 27:210–214. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Juríková M, Danihel Ľ, Polák Š and Varga
I: Ki67, PCNA, and MCM proteins: Markers of proliferation in the
diagnosis of breast cancer. Acta Histochem. 118:544–552. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yang M, Zhai X, Xia B, Wang Y and Lou G:
Long noncoding RNA CCHE1 promotes cervical cancer cell
proliferation via upregulating PCNA. Tumour Biol. 36:7615–7622.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Strzalka W and Ziemienowicz A:
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA): A key factor in DNA
replication and cell cycle regulation. Ann Bot. 107:1127–1140.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
66
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Tabrizi SJ, Niiro H, Masui M, Yoshimoto G,
Iino T, Kikushige Y, Wakasaki T, Baba E, Shimoda S, Miyamoto T, et
al: T cell leukemia/lymphoma 1 and galectin-1 regulate
survival/cell death pathways in human naive and IgM+
memory B cells through altering balances in Bcl-2 family proteins.
J Immunol. 182:1490–1499. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
González-Puertos VY, Hernández-Pérez E,
Nuño-Lámbarri N, Ventura-Gallegos JL, López-Diázguerrero NE,
Robles-Díaz G, Gutiérrez-Ruiz MC and Konigsberg M: Bcl-2
overexpression in hepatic stellate cell line CFSC-2G, induces a
pro-fibrotic state. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 25:1306–1314. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang D, Wang NY, Yang CB, Fang GX, Liu W,
Wen J and Luo C: The clinical value of serum connective tissue
growth factor in the assessment of liver fibrosis. Dig Dis Sci.
55:767–774. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Guo-Qiu W, Nai-Feng L, Xiao-Bo V, Linxian
L, Chen Z, Lixia G and Zhao L: The level of connective tissue
growth factor in sera of patients with hepatitis B virus strongly
correlates with stage of hepatic fibrosis. Viral Immunol. 23:71–78.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Trebicka J, Hennenberg M, Odenthal M, Shir
K, Klein S, Granzow M, Vogt A, Dienes HP, Lammert F, Reichen J, et
al: Atorvastatin attenuates hepatic fibrosis in rats after bile
duct ligation via decreased turnover of hepatic stellate cells. J
Hepatol. 53:702–712. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|