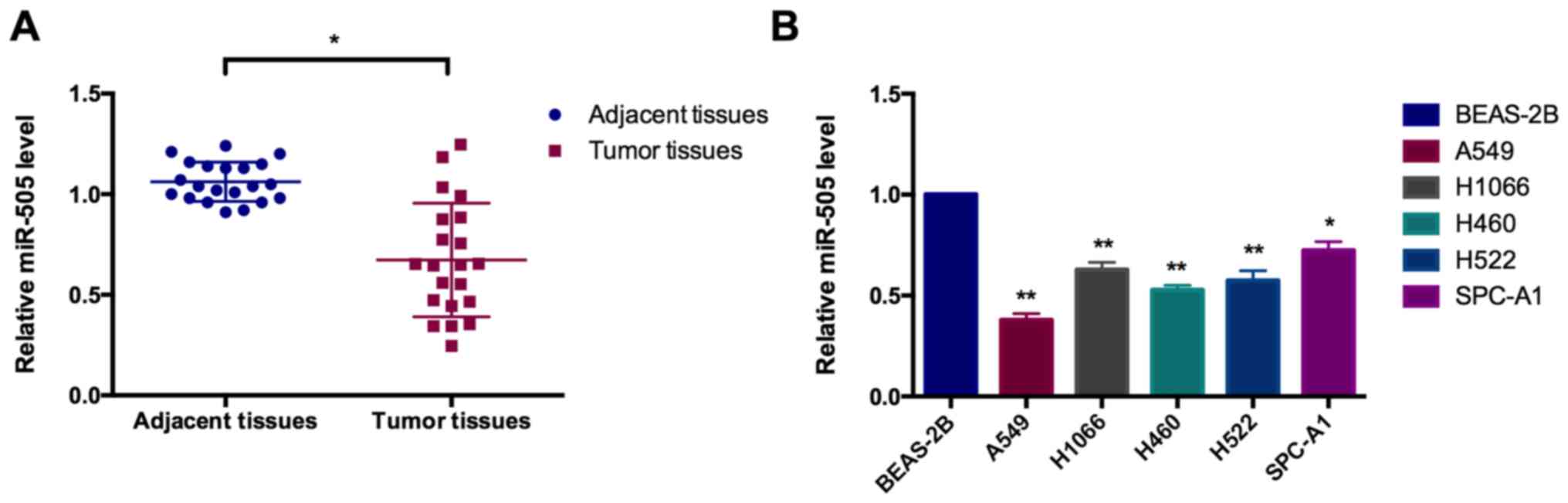
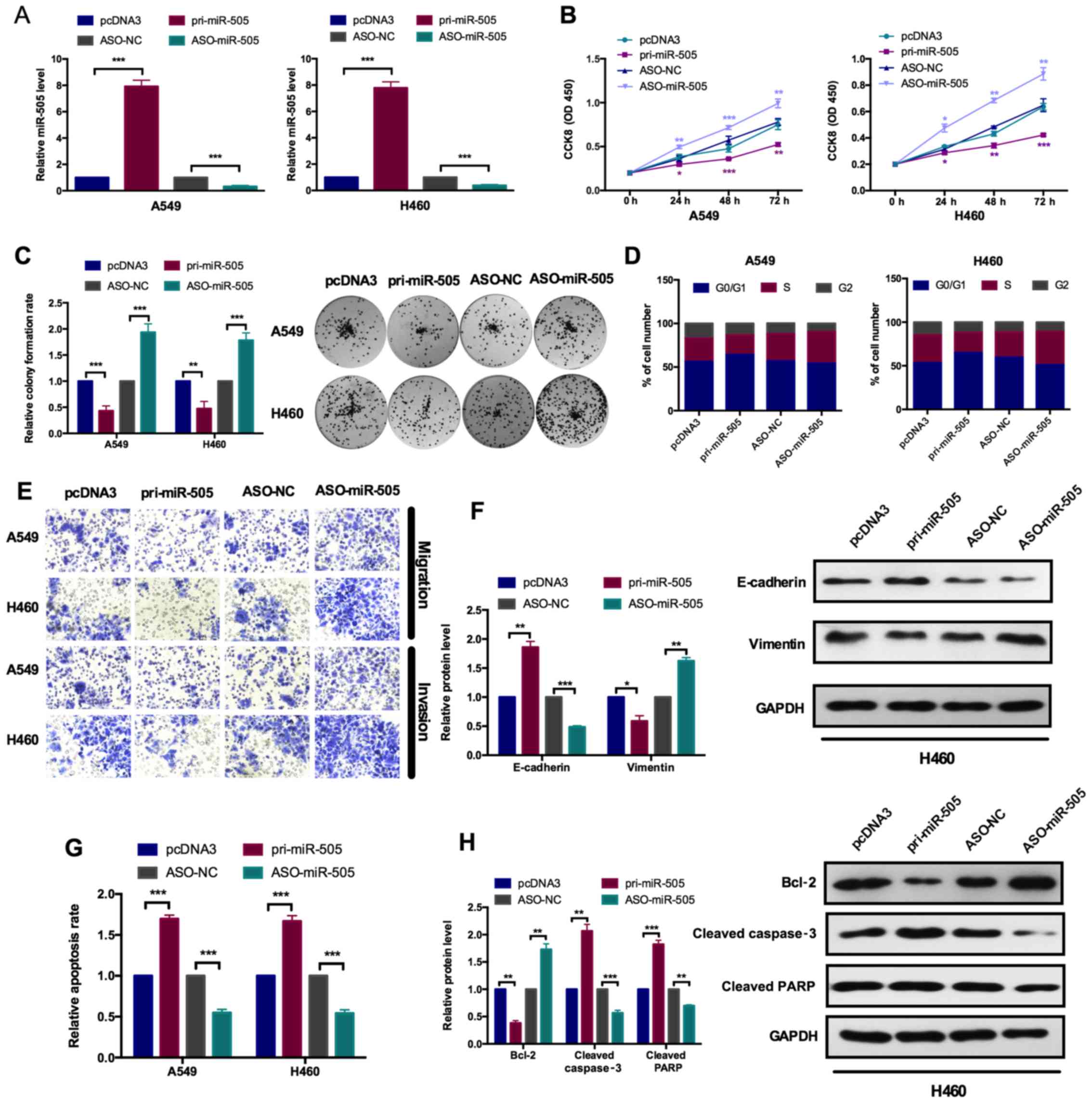
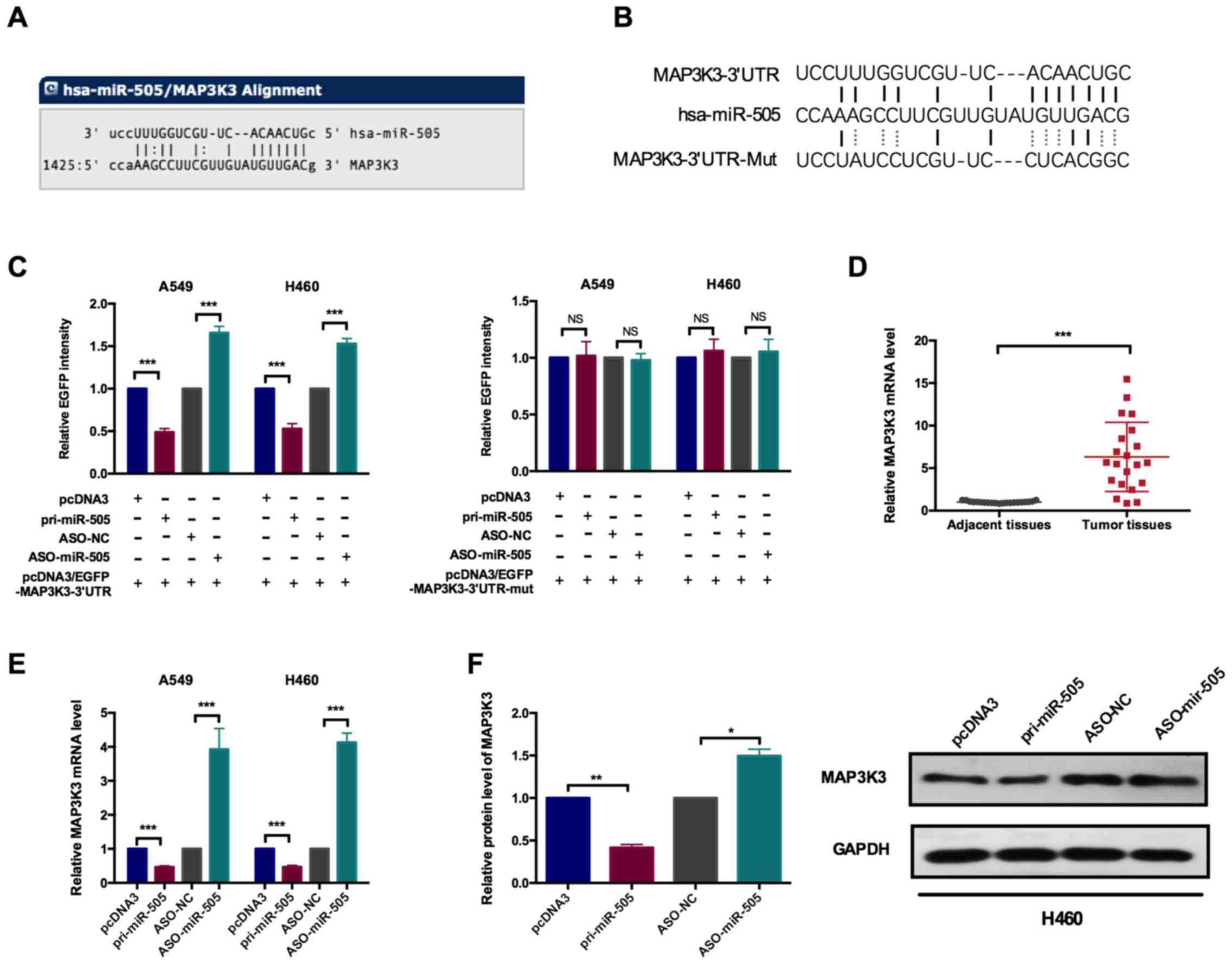
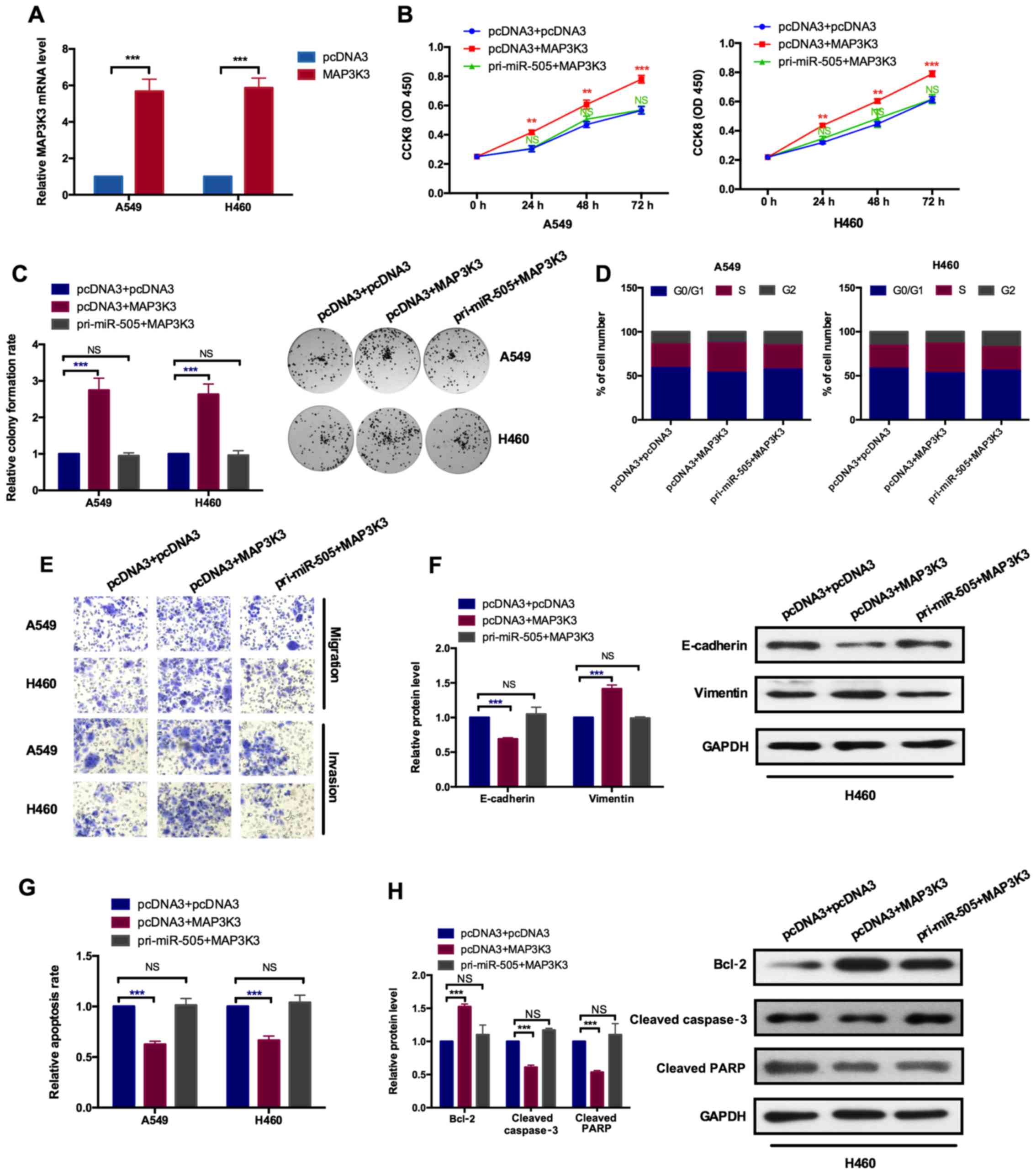
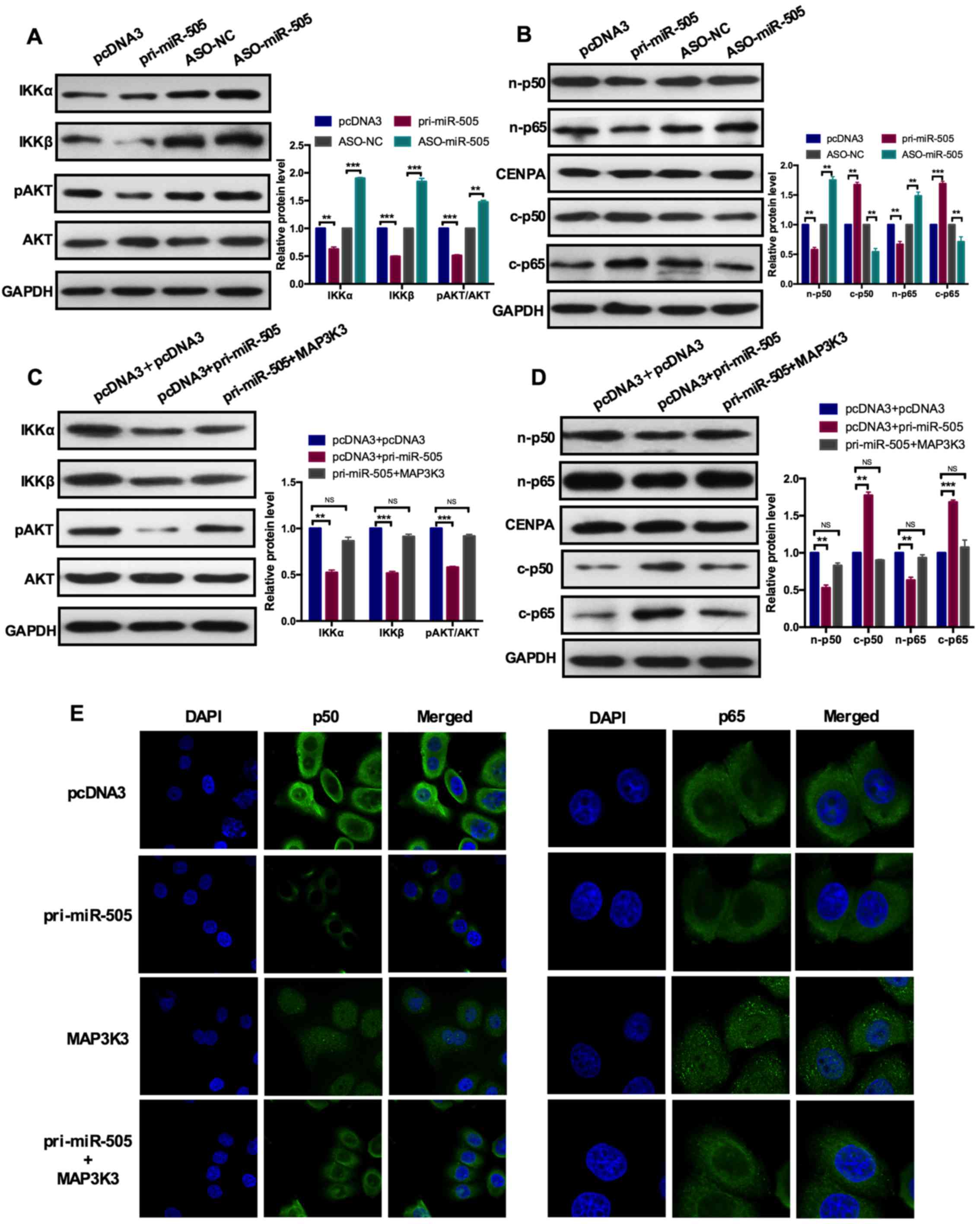
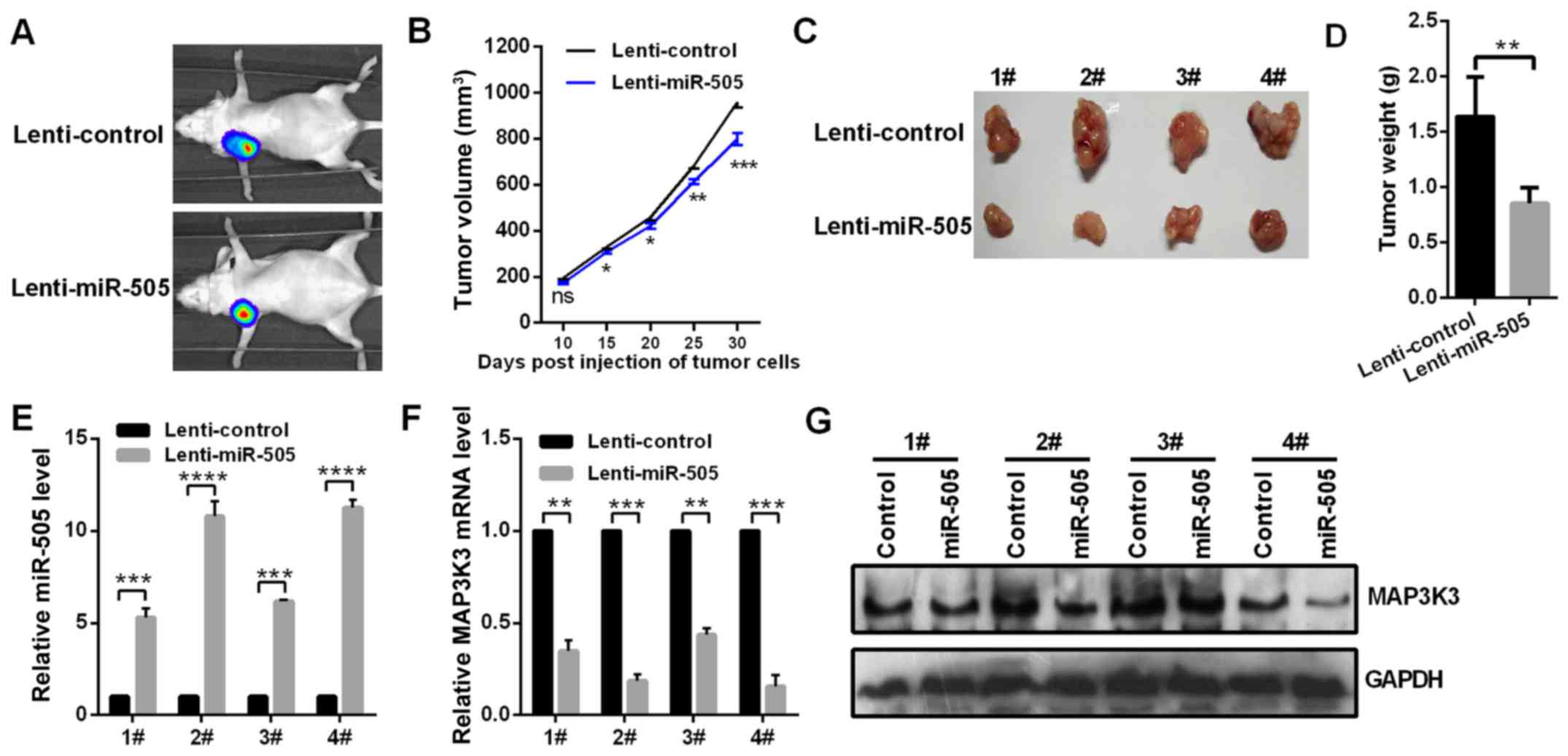
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Herbst RS, Heymach JV and Lippman SM: Lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:1367–1380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abbosh C, Birkbak NJ and Swanton C: Early
stage NSCLC - challenges to implementing ctDNA-based screening and
MRD detection. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 15:577–586. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Frega S, Bonanno L, Guarneri V, Conte P
and Pasello G: Therapeutic perspectives for brain metastases in
non-oncogene addicted non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Towards a
less dismal future? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 128:19–29. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tsiara A, Liontos M, Kaparelou M,
Zakopoulou R, Bamias A and Dimopoulos MA: Implementation of
immunotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC). Ann Transl Med. 6:1442018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Economopoulou P and Mountzios G: The
emerging treatment landscape of advanced non-small cell lung
cancer. Ann Transl Med. 6:1382018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNAs in
cancer: Small molecules with a huge impact. J Clin Oncol.
27:5848–5856. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yuan HL, Wang T and Zhang KH: MicroRNAs as
potential biomarkers for diagnosis, therapy and prognosis of
gastric cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 11:3891–3900. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Han Y and Li H: miRNAs as biomarkers and
for the early detection of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J
Thorac Dis. 10:3119–3131. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lekka E and Hall J: Noncoding RNAs in
disease. FEBS Lett. 592:2884–2900. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA-cancer
connection: The beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 66:7390–7394.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Farazi TA, Hoell JI, Morozov P and Tuschl
T: MicroRNAs in human cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 774:1–20. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang W, Wan S, Yang Z, Teschendorff AE and
Zou Q: Tumor origin detection with tissue-specific miRNA and DNA
methylation markers. Bioinformatics. 34:398–406. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yamamoto Y, Yoshioka Y, Minoura K,
Takahashi RU, Takeshita F, Taya T, Horii R, Fukuoka Y, Kato T,
Kosaka N, et al: An integrative genomic analysis revealed the
relevance of microRNA and gene expression for drug-resistance in
human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 10:1352011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang Q, Jia C, Wang P, Xiong M, Cui J, Li
L, Wang W, Wu Q, Chen Y and Zhang T: MicroRNA-505 identified from
patients with essential hypertension impairs endothelial cell
migration and tube formation. Int J Cardiol. 177:925–934. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Escate R, Mata P, Cepeda JM, Padró T and
Badimon L: miR-505-3p controls chemokine receptor up-regulation in
macrophages: Role in familial hypercholesterolemia. FASEB J.
32:601–612. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu YJ, Li W, Chang F, Liu JN, Lin JX and
Chen DX: MicroRNA-505 is downregulated in human osteosarcoma and
regulates cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Oncol Rep.
39:491–500. 2018.
|
|
20
|
Lu L, Qiu C, Li D, Bai G, Liang J and Yang
Q: MicroRNA-505 suppresses proliferation and invasion in hepatoma
cells by directly targeting high-mobility group box 1. Life Sci.
157:12–18. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma C, Xu B, Husaiyin S, Wang L,
Wusainahong K, Ma J, Zhu K and Niyazi M: MicroRNA-505 predicts
prognosis and acts as tumor inhibitor in cervical carcinoma with
inverse association with FZD4. Biomed Pharmacother. 92:586–594.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen S, Sun KX, Liu BL, Zong ZH and Zhao
Y: MicroRNA-505 functions as a tumor suppressor in endometrial
cancer by targeting TGF-α. Mol Cancer. 15:112016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Paner GP, Stadler WM, Hansel DE, Montironi
R, Lin DW and Amin MB: Updates in the Eighth Edition of the
Tumor-Node-Metastasis Staging Classification for Urologic Cancers.
Eur Urol. 73:560–569. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-ΔΔC(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yang Z, Wang XL, Bai R, Liu WY, Li X, Liu
M and Tang H: miR-23a promotes IKKα expression but suppresses ST7L
expression to contribute to the malignancy of epithelial ovarian
cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 115:731–740. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Samanta AK, Huang HJ, Le XF, Mao W, Lu KH,
Bast RC Jr and Liao WS: MEKK3 expression correlates with nuclear
factor kappa B activity and with expression of antiapoptotic genes
in serous ovarian carcinoma. Cancer. 115:3897–3908. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Landi MT, Zhao Y, Rotunno M, Koshiol J,
Liu H, Bergen AW, Rubagotti M, Goldstein AM, Linnoila I, Marincola
FM, et al: MicroRNA expression differentiates histology and
predicts survival of lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:430–441.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Du X, Zhang J, Wang J, Lin X and Ding F:
Role of miRNA in lung cancer-potential biomarkers and therapies.
Curr Pharm Des. 23:5997–6010. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yang CL, Zheng XL, Ye K, Ge H, Sun YN, Lu
YF and Fan QX: MicroRNA-183 acts as a tumor suppressor in human
non-small cell lung cancer by down-regulating MTA1. Cell. Physiol
Biochem. 46:93–106. 2018.
|
|
30
|
Qi Z, Zhang B, Zhang J, Hu Q, Xu F, Chen B
and Zhu C: MicroRNA-30b inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell
growth by targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor.
Neoplasma. 65:192–200. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang RS, Zheng YL, Li C, Ding C, Xu C and
Zhao J: MicroRNA-485-5p suppresses growth and metastasis in
non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting IGF2BP2. Life Sci.
199:104–111. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu D, Liu J, Chen J, He H, Ma H and Lv X:
MiR-449a suppresses tumor growth, migration and invasion in
non-small cell lung cancer by targeting HMGB1-mediated NF-κB
signaling way. Oncol Res. Mar 21–2018.Epub ahead of print.
|
|
33
|
Liu M, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Cai H, Zhang C,
Yang Z, Niu Y, Wang H, Wei X, Wang W, et al: MicroRNA-1253
suppresses cell proliferation and invasion of non-small-cell lung
carcinoma by targeting WNT5A. Cell Death Dis. 9:1892018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu J, Jia Y, Jia L, Li T, Yang L and
Zhang G: MicroRNA-615-3p inhibits the tumor growth and metastasis
of NSCLC via inhibiting IGF2. Oncol Res. Mar 21–2018.Epub ahead of
print.
|
|
35
|
Ding X, Zhong T, Jiang L, Huang J, Xia Y
and Hu R: miR-25 enhances cell migration and invasion in
non-small-cell lung cancer cells via ERK signaling pathway by
inhibiting KLF4. Mol Med Rep. 17:7005–7016. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chang L and Karin M: Mammalian MAP kinase
signalling cascades. Nature. 410:37–40. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang J, Lin Y, Guo Z, Cheng J, Huang J,
Deng L, Liao W, Chen Z, Liu Z and Su B: The essential role of MEKK3
in TNF-induced NF-kappaB activation. Nat Immunol. 2:620–624. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hasan R, Sharma R, Saraya A, Chattopadhyay
TK, DattaGupta S, Walfish PG, Chauhan SS and Ralhan R: Mitogen
activated protein kinase kinase kinase 3 (MAP3K3/MEKK3)
overexpression is an early event in esophageal tumorigenesis and is
a predictor of poor disease prognosis. BMC Cancer. 14:1–7. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Fan Y, Ge N, Wang X, Sun W, Mao R, Bu W,
Creighton CJ, Zheng P, Vasudevan S, An L, et al: Amplification and
over-expression of MAP3K3 gene in human breast cancer promotes
formation and survival of breast cancer cells. J Pathol. 232:75–86.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Jia W, Dong Y, Tao L, Pang L, Ren Y, Liang
W, Jiang J, Cheng G, Zhang WJ, Yuan X, et al: MAP3K3 overexpression
is associated with poor survival in ovarian carcinoma. Hum Pathol.
50:162–169. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
He Y, Wang L, Liu W, Zhong J, Bai S, Wang
Z, Thomas DG, Lin J, Reddy RM, Ramnath N, et al: MAP3K3 expression
in tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is correlated
with favorable patient survival in lung cancer. Sci Rep.
5:114712015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Iqbal MA, Arora S, Prakasam G, Calin GA
and Syed MA: MicroRNA in lung cancer: Role, mechanisms, pathways
and therapeutic relevance. Mol Aspects Med. 18:30065–30067.
2018.
|
|
44
|
Yao L, Ye Y, Mao H, Lu F, He X, Lu G and
Zhang S: MicroRNA-124 regulates the expression of MEKK3 in the
inflammatory pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. J
Neuroinflammation. 15:132018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zheng Y, Liu H and Kong Y: miR-188
promotes senescence of lineage-negative bone marrow cells by
targeting MAP3K3 expression. FEBS Lett. 591:2290–2298. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhao L, Ni X, Zhao L, Zhang Y, Jin D, Yin
W, Wang D and Zhang W: MiroRNA-188 acts as tumor suppressor in
non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting MAP3K3. Mol Pharm.
15:1682–1689. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|