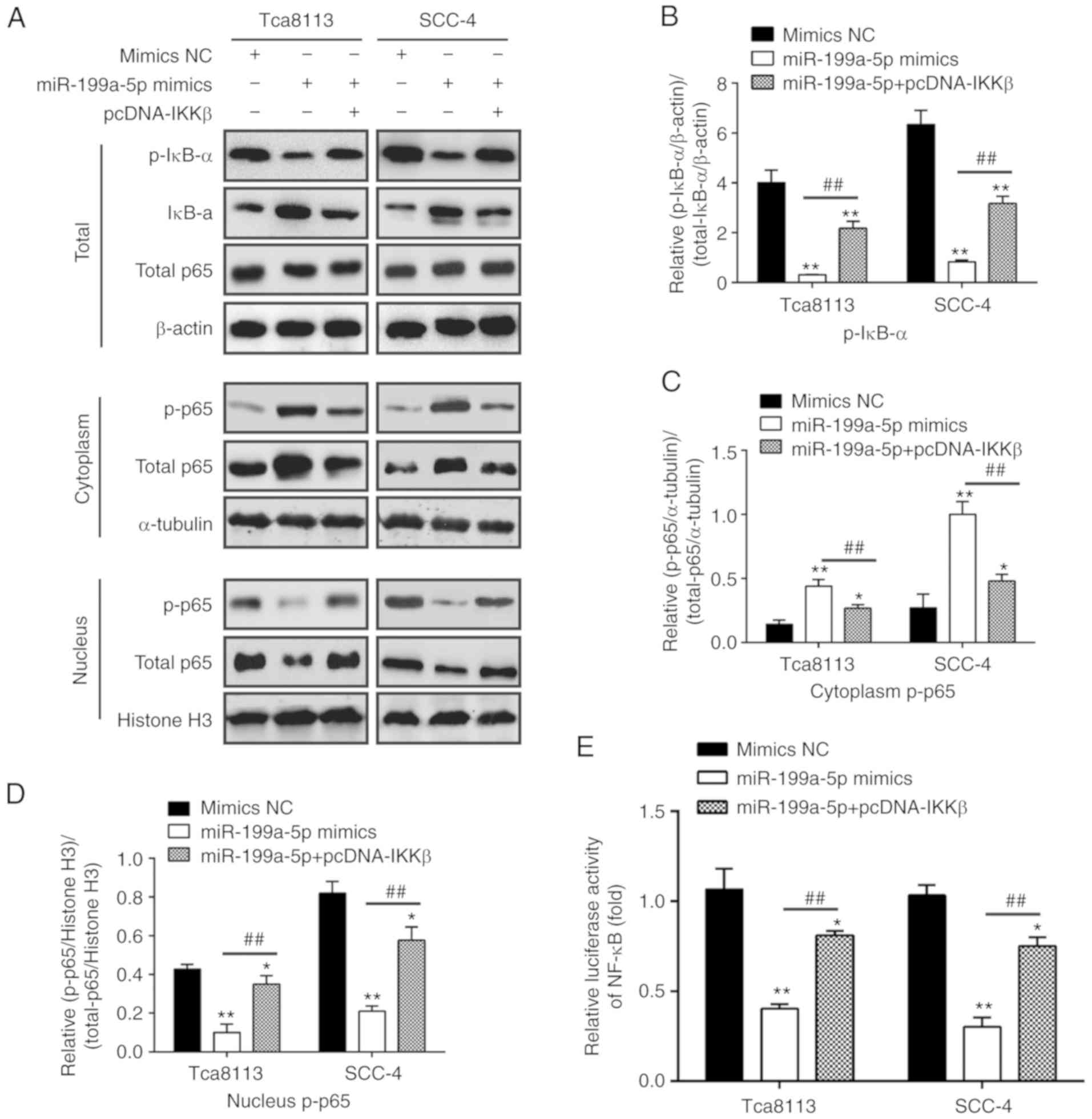
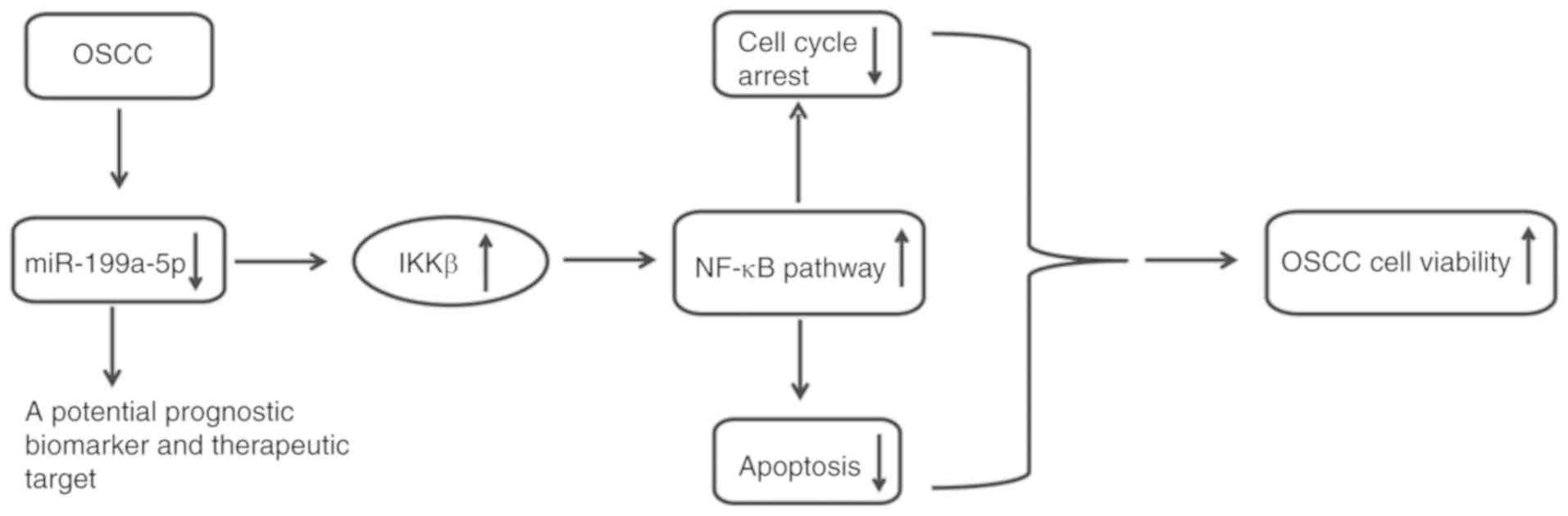
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J,
Murray T and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2008. CA. Cancer J Clin.
58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Silverman S Jr: Demographics and
occurrence of oral and pharyngeal cancers. The outcomes, the
trends, the challenge. J Am Dent Assoc. 132(Suppl 132): S7–S11.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Su L, Wang Y, Xiao M, Lin Y and Yu L:
Up-regulation of survivin in oral squamous cell carcinoma
correlates with poor prognosis and chemoresistance. Oral Surg Oral
Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 110:484–491. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Genden EM, Ferlito A, Bradley PJ, Rinaldo
A and Scully C: Neck disease and distant metastases. Oral Oncol.
39:207–212. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Menssen A, Häupl T, Sittinger M, Delorme
B, Charbord P and Ringe J: Differential gene expression profiling
of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells during
adipogenic development. BMC Genomics. 12:4612011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Perkins ND: Integrating cell-signalling
pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
8:49–62. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pan MH, Lin-Shiau SY and Lin JK:
Comparative studies on the suppression of nitric oxide synthase by
curcumin and its hydrogenated metabolites through downregulation of
IkappaB kinase and NFkappaB activation in macrophages. Biochem
Pharmacol. 60:1665–1676. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tanaka T, Nakayama H, Yoshitake Y, Irie A,
Nagata M, Kawahara K, Takamune Y, Yoshida R, Nakagawa Y, Ogi H, et
al: Selective inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB by nuclear
factor-kappaB essential modulator-binding domain peptide suppresses
the metastasis of highly metastatic oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancer Sci. 103:455–463. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Aggarwal BB and Sung B: NF-κB in cancer: A
matter of life and death. Cancer Discov. 1:469–471. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Nakayama H, Ikebe T, Beppu M and Shirasuna
K: High expression levels of nuclear factor kappaB, IkappaB kinase
alpha and Akt kinase in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity.
Cancer. 92:3037–3044. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Julien S, Puig I, Caretti E, Bonaventure
J, Nelles L, van Roy F, Dargemont C, de Herreros AG, Bellacosa A
and Larue L: Activation of NF-kappaB by Akt upregulates Snail
expression and induces epithelium mesenchyme transition. Oncogene.
26:7445–7456. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Furuta H, Osawa K, Shin M, Ishikawa A,
Matsuo K, Khan M, Aoki K, Ohya K, Okamoto M, Tominaga K, et al:
Selective inhibition of NF-kappaB suppresses bone invasion by oral
squamous cell carcinoma in vivo. Int J Cancer. 131:E625–E635. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Johnson J, Shi Z, Liu Y and Stack MS:
Inhibitors of NF-kappaB reverse cellular invasion and target gene
upregulation in an experimental model of aggressive oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 50:468–477. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Barwari T, Joshi A and Mayr M: MicroRNAs
in cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 68:2577–2584. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Alipoor SD, Adcock IM, Garssen J, Mortaz
E, Varahram M, Mirsaeidi M and Velayati A: The roles of miRNAs as
potential biomarkers in lung diseases. Eur J Pharmacol.
791:395–404. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McManus MT: MicroRNAs and cancer. Semin
Cancer Biol. 13:253–258. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang B, Li Y, Hou D, Shi Q, Yang S and Li
Q: MicroRNA-375 inhibits growth and enhances radiosensitivity in
oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting insulin like growth
factor 1 receptor. Cell Physiol Biochem. 42:2105–2117. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Feng X, Luo Q, Wang H, Zhang H and Chen F:
MicroRNA-22 suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion
in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting NLRP3. J Cell Physiol.
233:6705–6713. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔC T method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Rasola A and Geuna M: A flow cytometry
assay simultaneously detects independent apoptotic parameters.
Cytometry. 45:151–157. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Price LC, Caramori G, Perros F, Meng C,
Gambaryan N, Dorfmuller P, Montani D, Casolari P, Zhu J, Dimopoulos
K, et al: Nuclear factor κ-B is activated in the pulmonary vessels
of patients with end-stage idiopathic pulmonary arterial
hypertension. PLoS One. 8:e754152013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yu T, Wang XY, Gong RG, Li A, Yang S, Cao
YT, Wen YM, Wang CM and Yi XZ: The expression profile of microRNAs
in a model of 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthrance-induced oral
carcinogenesis in Syrian hamster. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:642009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
He J, Jing Y, Li W, Qian X, Xu Q, Li FS,
Liu LZ, Jiang BH and Jiang Y: Roles and mechanism of miR-199a and
miR-125b in tumor angiogenesis. PLoS One. 8:e566472013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cheng W, Liu T, Wan X, Gao Y and Wang H:
MicroRNA-199a targets CD44 to suppress the tumorigenicity and
multidrug resistance of ovarian cancer-initiating cells. FEBS J.
279:2047–2059. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tsukigi M, Bilim V, Yuuki K, Ugolkov A,
Naito S, Nagaoka A, Kato T, Motoyama T and Tomita Y: Re-expression
of miR-199a suppresses renal cancer cell proliferation and survival
by targeting GSK-3beta. Cancer Lett. 315:189–197. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Jia XQ, Cheng HQ, Qian X, Bian CX, Shi ZM,
Zhang JP, Jiang BH and Feng ZQ: Lentivirus-mediated overexpression
of microRNA-199a inhibits cell proliferation of human
hepatocel-lular carcinoma. Cell Biochem Biophys. 62:237–244. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Huang L, Lin JX, Yu YH, Zhang MY, Wang HY
and Zheng M: Downregulation of six microRNAs is associated with
advanced stage, lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in small
cell carcinoma of the cervix. PLoS One. 7:e337622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen R, Alvero AB, Silasi DA, Kelly MG,
Fest S, Visintin I, Leiser A, Schwartz PE, Rutherford T and Mor G:
Regulation of IKKbeta by miR-199a affects NF-kappaB activity in
ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene. 27:4712–4723. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsuchiya Y, Osaki K, Kanamoto M, Nakao Y,
Takahashi E, Higuchi T and Kamata H: Distinct B subunits of PP2A
regulate the NF-kappaB signalling pathway through dephosphorylation
of IKKβ, IkappaBα and RelA. FEBS Lett. 591:4083–4094. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fang R, Wang C, Jiang Q, Lv M, Gao P, Yu
X, Mu P, Zhang R, Bi S, Feng JM and Jiang Z: NEMO-IKKβ are
essential for IRF3 and NF-κB activation in the cGAS-STING pathway.
J Immunol. 199:3222–3233. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li ZW, Chu W, Hu Y, Delhase M, Deerinck T,
Ellisman M, Johnson R and Karin M: The IKKbeta subunit of IkappaB
kinase (IKK) is essential for nuclear factor kappaB activation and
prevention of apoptosis. J Exp Med. 189:1839–1845. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ma XF, Zhang J, Shuai HL, Guan BZ, Luo X
and Yan RL: IKKbeta/NF-kappaB mediated the low doses of bisphenol A
induced migration of cervical cancer cells. Arch Biochem Biophys.
573:52–58. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
He G, Yu GY, Temkin V, Ogata H, Kuntzen C,
Sakurai T, Sieghart W, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Leffert HL and Karin
M: Hepatocyte IKKbeta/NF-kappaB inhibits tumor promotion and
progression by preventing oxidative stress-driven STAT3 activation.
Cancer Cell. 17:286–297. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lu M, Wang C, Chen W, Mao C and Wang J:
miR-654-5p targets GRAP to promote proliferation, metastasis, and
chemoresistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma through Ras/MAPK
signaling. DNA Cell Biol. 37:381–388. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shiah SG, Hsiao JR, Chang WM, Chen YW, Jin
YT, Wong TY, Huang JS, Tsai ST, Hsu YM, Chou ST, et al:
Downregulated miR329 and miR410 promote the proliferation and
invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting Wnt-7b.
Cancer Res. 74:7560–7572. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang K, Jin J, Ma T and Zhai H: MiR-139-5p
inhibits the tumorigenesis and progression of oral squamous
carcinoma cells by targeting HOXA9. J Cell Mol Med. 21:3730–3740.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Murakami Y, Yasuda T, Saigo K, Urashima T,
Toyoda H, Okanoue T and Shimotohno K: Comprehensive analysis of
microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and
non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene. 25:2537–2545. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Jiang J, Gusev Y, Aderca I, Mettler TA,
Nagorney DM, Brackett DJ, Roberts LR and Schmittgen TD: Association
of MicroRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis
infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clin Cancer Res.
14:419–427. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shen Q, Cicinnati VR, Zhang X, Iacob S,
Weber F, Sotiropoulos GC, Radtke A, Lu M, Paul A, Gerken G and
Beckebaum S: Role of microRNA-199a-5p and discoidin domain receptor
1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma invasion. Mol Cancer.
9:2272010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Su SF, Chang YW, Andreu-Vieyra C, Fang JY,
Yang Z, Han B, Lee AS and Liang G: miR-30d, miR-181a and
miR-199a-5p cooperatively suppress the endoplasmic reticulum
chaperone and signaling regulator GRP78 in cancer. Oncogene.
32:4694–4701. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Xu N, Zhang J, Shen C, Luo Y, Xia L, Xue F
and Xia Q: Cisplatin-induced downregulation of miR-199a-5p
increases drug resistance by activating autophagy in HCC cell.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 423:826–831. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun D, Han S, Liu C, Zhou R, Sun W, Zhang
Z and Qu J: Microrna-199a-5p functions as a tumor suppressor via
suppressing connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) in follicular
thyroid carcinoma. Med Sci Monit. 22:1210–1217. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dai L, Gu L and Di W: MiR-199a attenuates
endometrial stromal cell invasiveness through suppression of the
IKKβ/NF-κB pathway and reduced interleukin-8 expression. Mol Hum
Reprod. 18:136–145. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Jing H and Lee S: NF-κB in cellular
senescence and cancer treatment. Mol Cells. 37:189–195. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang J, Kantrow S, Sai J, Hawkins OE,
Boothby M, Ayers GD, Young ED, Demicco EG, Lazar AJ, Lev D and
Richmond A: INK4a/ARF [corrected] inactivation with activation of
the NF-kappaB/IL-6 pathway is sufficient to drive the development
and growth of angiosarcoma. Cancer Res. 72:4682–4695. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, Park JM,
Li ZW, Egan LJ, Kagnoff MF and Karin M: IKKbeta links inflammation
and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer.
Cell. 118:285–296. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang Y, Lapidus RG, Liu P, Choi EY,
Adediran S, Hussain A, Wang X, Liu X and Dan HC: Targeting IκB
kinase β/NF-κB signaling in human prostate cancer by a novel IκB
kinase β inhibitor CmpdA. Mol Cancer Ther. 15:1504–1514. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fan JY, Fan YJ, Wang XL, Xie H, Gao HJ,
Zhang Y, Liu M and Tang H: miR-429 is involved in regulation of
NF-κB activity by targeting IKKβ and suppresses oncogenic activity
in cervical cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 591:118–128. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Kong XJ, Duan LJ, Qian XQ, Xu D, Liu HL,
Zhu YJ and Qi J: Tumor-suppressive microRNA-497 targets IKKβ to
regulate NF-κB signaling pathway in human prostate cancer cells. Am
J Cancer Res. 5:1795–1804. 2015.
|
|
52
|
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR and Li ZW:
NF-kappaB in cancer: From innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat
Rev Cancer. 2:301–310. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu Z, Diep C, Mao T, Huang L, Merrill R,
Zhang Z and Peng Y: MicroRNA-92b promotes tumor growth and
activation of NF-κB signaling via regulation of NLK in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 34:2961–2968. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|