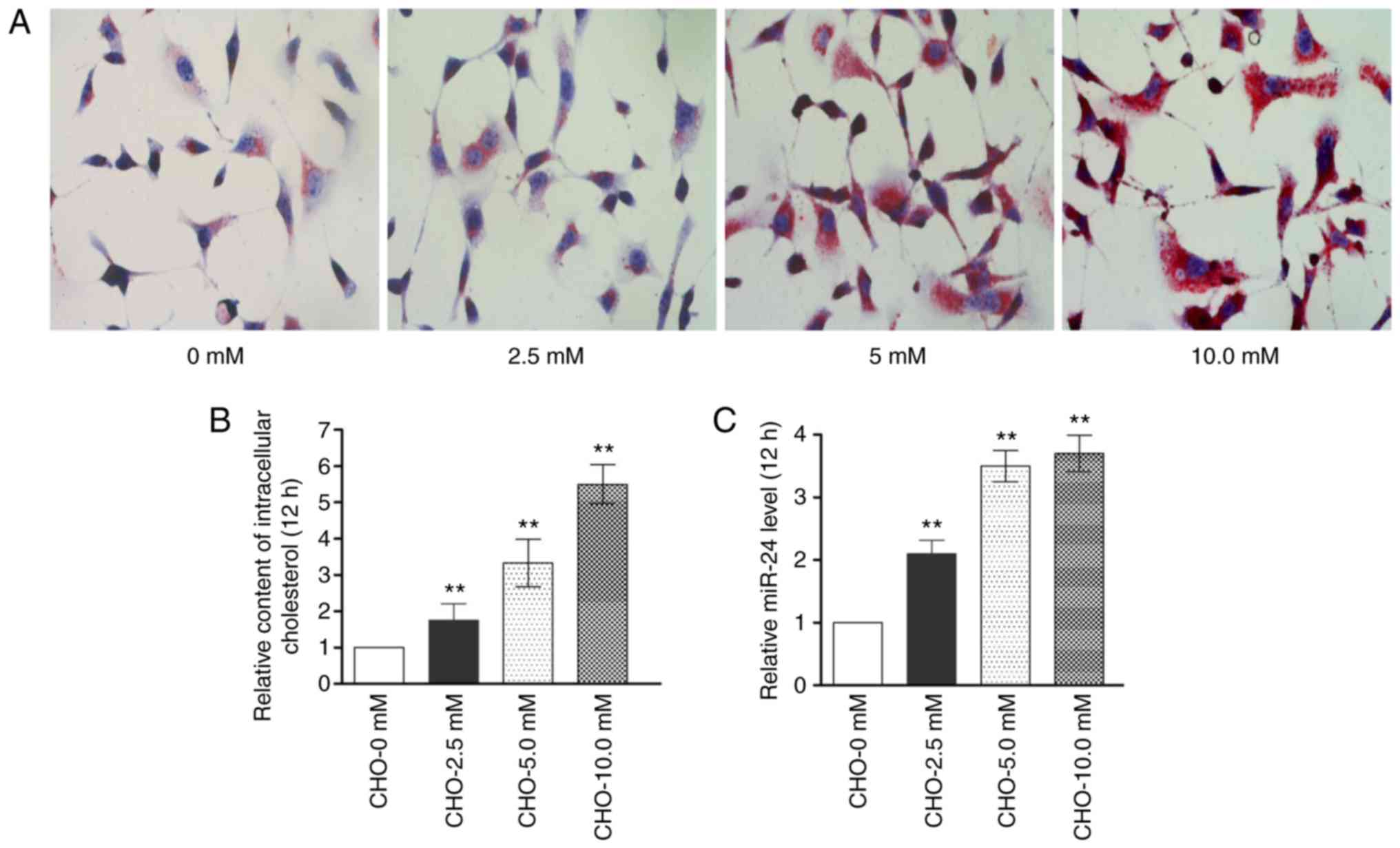
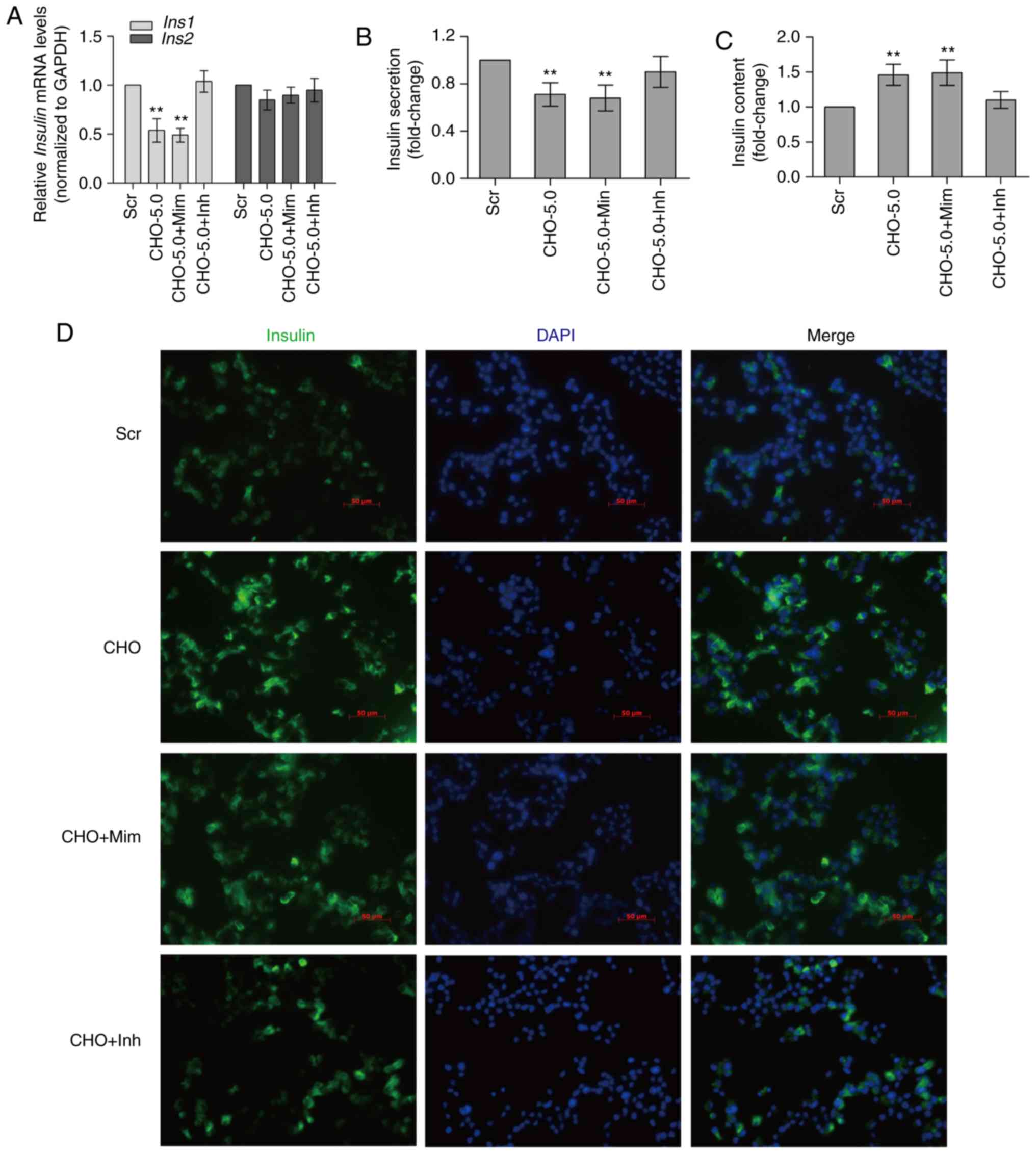
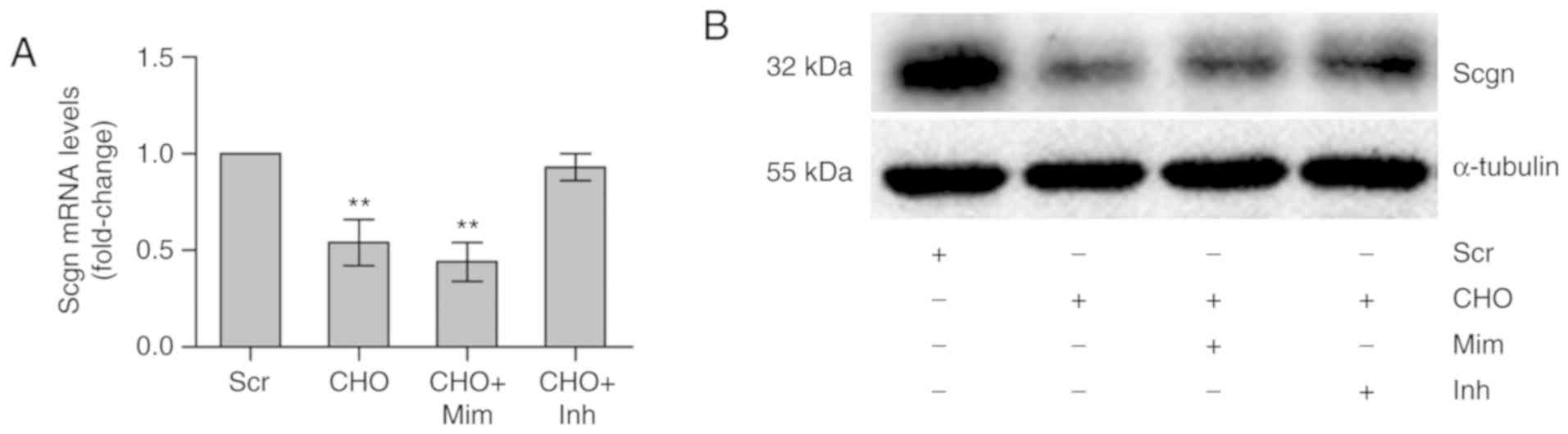
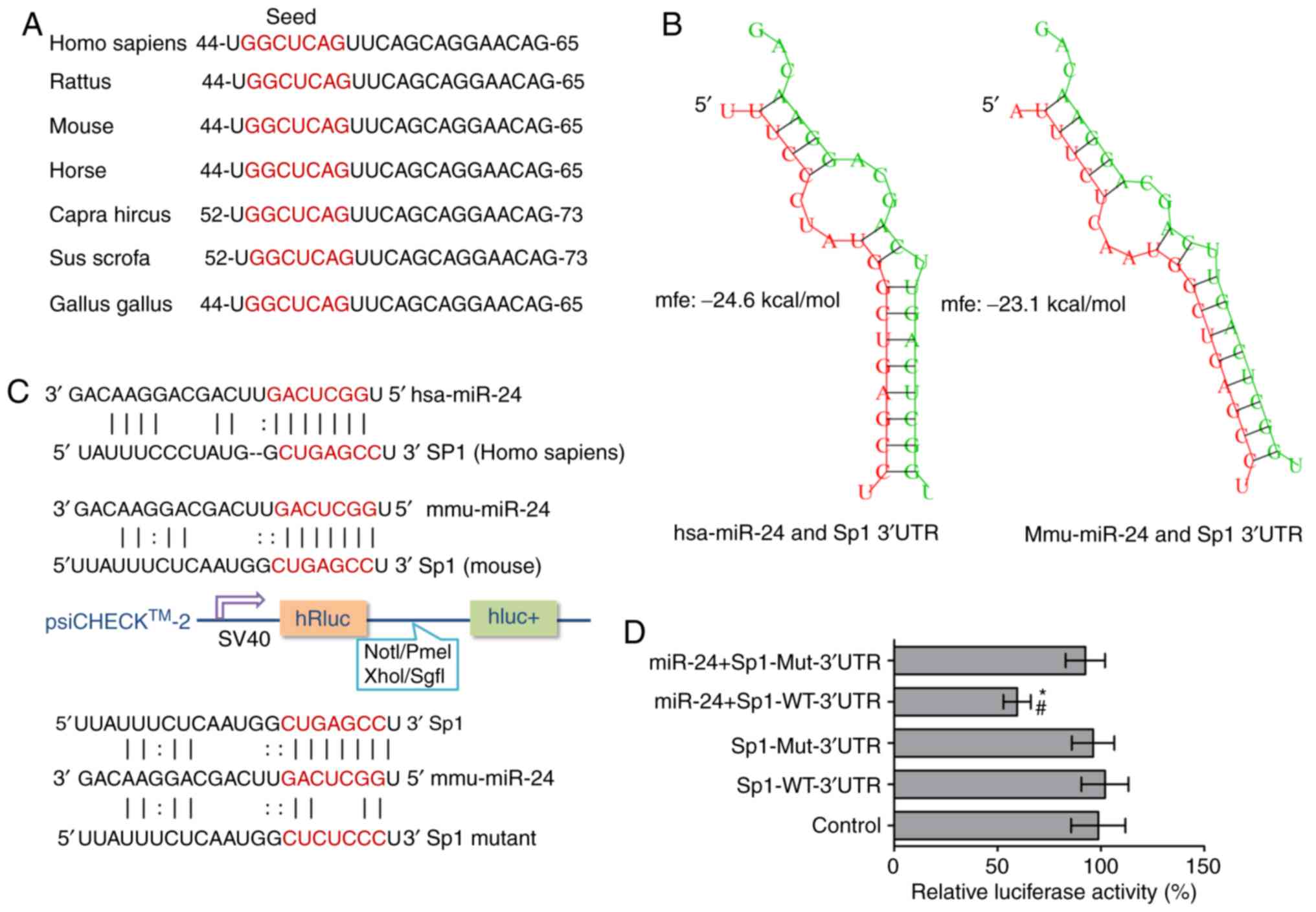
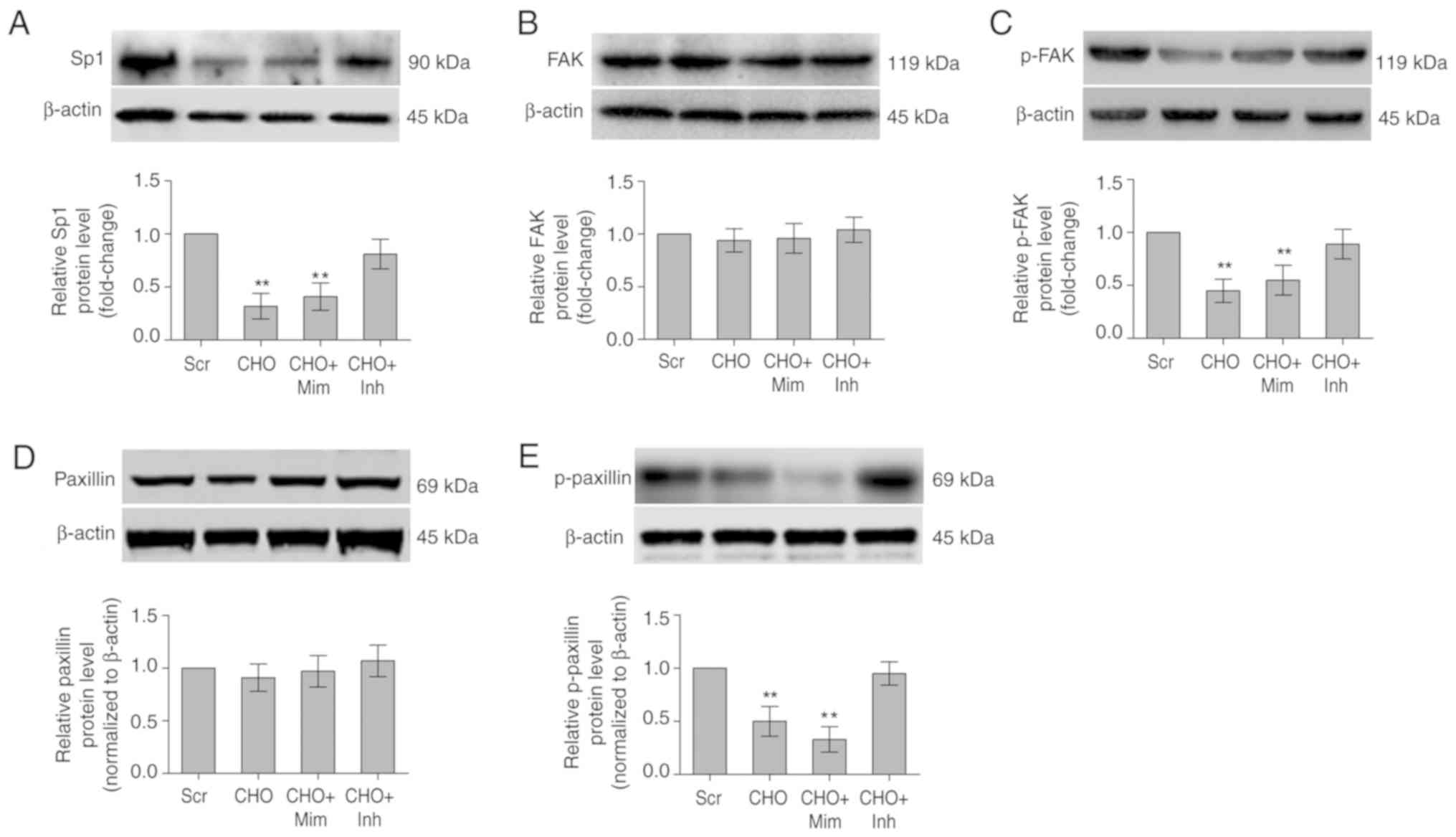
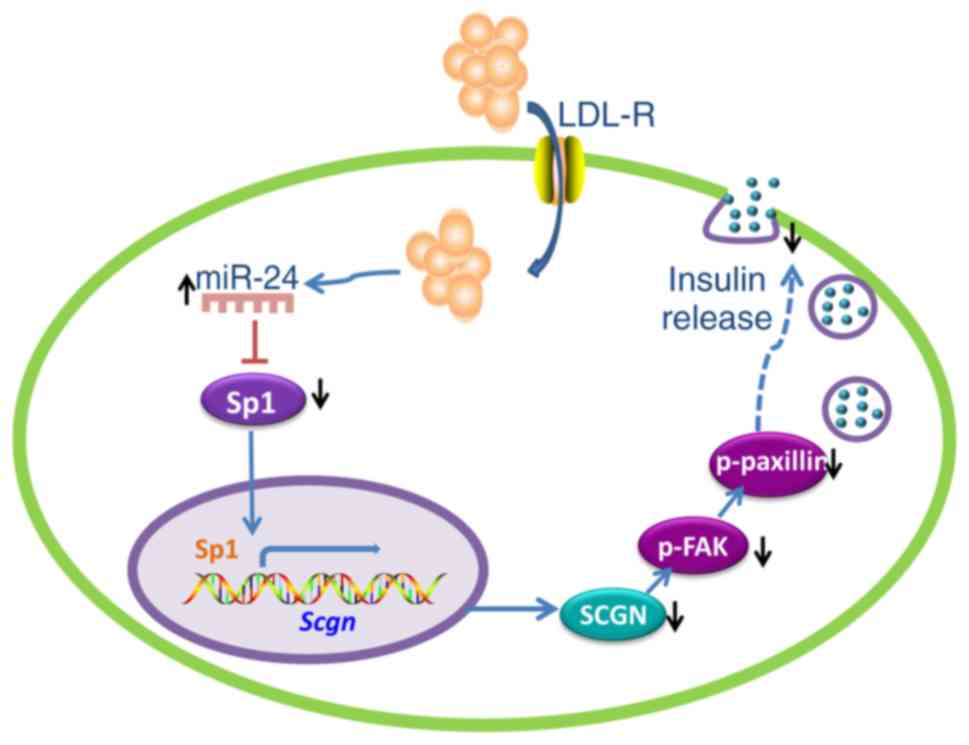
|
1
|
Brunham LR, Kruit JK, Verchere CB and
Hayden MR: Cholesterol in islet dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. J
Clin Invest. 118:403–408. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hao M, Head WS, Gunawardana SC, Hasty AH
and Piston DW: Direct effect of cholesterol on insulin secretion: A
novel mechanism for pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. Diabetes.
56:2328–2338. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu Y, Toomre DK, Bogan JS and Hao M:
Excess cholesterol inhibits glucose-stimulated fusion pore dynamics
in insulin exocytosis. J Cell Mol Med. 21:2950–2962. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bogan JS, Xu Y and Hao M: Cholesterol
accumulation increases insulin granule size and impairs membrane
trafficking. Traffic. 13:1466–1480. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kruit JK, Kremer PH, Dai L, Tang R, Ruddle
P, de Haan W, Brunham LR, Verchere CB and Hayden MR: Cholesterol
efflux via ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) and
cholesterol uptake via the LDL receptor influences
cholesterol-induced impairment of beta cell function in mice.
Diabetologia. 53:1110–1119. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Poy MN, Eliasson L, Krutzfeldt J, Kuwajima
S, Ma X, Macdonald PE, Pfeffer S, Tuschl T, Rajewsky N, Rorsman P
and Stoffel M: A pancreatic islet-specific microRNA regulates
insulin secretion. Nature. 432:226–230. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Osmai M, Osmai Y, Bang-Berthelsen CH,
Pallesen EM, Vestergaard AL, Novotny GW, Pociot F and
Mandrup-Poulsen T: MicroRNAs as regulators of beta-cell function
and dysfunction. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 32:334–349. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li Y, Luo T, Wang L, Wu J and Guo S:
MicroRNA-19a-3p enhances the proliferation and insulin secretion,
while it inhibits the apoptosis of pancreatic cells via the
inhibition of SOCS3. Int J Mol Med. 38:1515–1524. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tugay K, Guay C, Marques AC, Allagnat F,
Locke JM, Harries LW, Rutter GA and Regazzi R: Role of microRNAs in
the age-associated decline of pancreatic beta cell function in rat
islets. Diabetologia. 59:161–169. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhu Y, You W, Wang H, Li Y, Qiao N, Shi Y,
Zhang C, Bleich D and Han X: MicroRNA-24/MODY gene regulatory
pathway mediates pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. Diabetes.
62:3194–3206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Malenczyk K, Girach F, Szodorai E, Storm
P, Segerstolpe A, Tortoriello G, Schnell R, Mulder J, Romanov RA,
Borok E, et al: A TRPV1-to-secretagogin regulatory axis controls
pancreatic beta-cell survival by modulating protein turnover. EMBO
J. 36:2107–2125. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wagner L, Oliyarnyk O, Gartner W, Nowotny
P, Groeger M, Kaserer K, Waldhausl W and Pasternack MS: Cloning and
expression of secretagogin, a novel neuroendocrine- and pancreatic
islet of langerhans-specific Ca2+-binding protein. J Biol Chem.
275:24740–24751. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang SY, Lee JJ, Lee JH, Lee K, Oh SH, Lim
YM, Lee MS and Lee KJ: Secretagogin affects insulin secretion in
pancreatic beta-cells by regulating actin dynamics and focal
adhesion. Biochem J. 473:1791–1803. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lv YC, Tang YY, Peng J, Zhao GJ, Yang J,
Yao F, Ouyang XP, He PP, Xie W, Tan YL, et al: MicroRNA-19b
promotes macrophage cholesterol accumulation and aortic
atherosclerosis by targeting ATP-binding cassette transporter A1.
Atherosclerosis. 236:215–226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Staaf J, Ubhayasekera SJ, Sargsyan E,
Chowdhury A, Kristinsson H, Manell H, Bergquist J, Forslund A and
Bergsten P: Initial hyperinsulinemia and subsequent beta-cell
dysfunction is associated with elevated palmitate levels. Pediatr
Res. 80:267–274. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Barlow J, Jensen VH, Jastroch M and
Affourtit C: Palmitate-induced impairment of glucose-stimulated
insulin secretion precedes mitochondrial dysfunction in mouse
pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 473:487–496. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Tiwari J, Gupta G, de Jesus Andreoli Pinto
T, Sharma R, Pabreja K, Matta Y, Arora N, Mishra A, Sharma R and
Dua K: Role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in the pathophysiology of
diabetes mellitus. Panminerva Med. 60:25–28. 2018.
|
|
19
|
Hashimoto N and Tanaka T: Role of miRNAs
in the pathogenesis and susceptibility of diabetes mellitus. J Hum
Genet. 62:141–150. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Calderari S, Diawara MR, Garaud A and
Gauguier D: Biological roles of microRNAs in the control of insulin
secretion and action. Physiol Genomics. 49:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Gu C, Stein GH, Pan N, Goebbels S,
Hornberg H, Nave KA, Herrera P, White P, Kaestner KH, Sussel L and
Lee JE: Pancreatic beta cells require NeuroD to achieve and
maintain functional maturity. Cell Metab. 11:298–310. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang ZW, Zhang LQ, Ding L, Wang F, Sun
YJ, An Y, Zhao Y, Li YH and Teng CB: MicroRNA-19b downregulates
insulin 1 through targeting transcription factor neuroD1. FEBS
Lett. 585:2592–2598. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee JJ, Yang SY, Park J, Ferrell JE Jr,
Shin DH and Lee KJ: Calcium ion induced structural changes promote
dimerization of secretagogin, which is required for its insulin
secretory function. Sci Rep. 7:69762017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kobayashi M, Yamato E, Tanabe K, Tashiro
F, Miyazaki S and Miyazaki J: Functional analysis of novel
candidate regulators of insulin secretion in the MIN6 mouse
pancreatic beta cell line. PLoS One. 11:e01519272016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bazwinsky-Wutschke I, Wolgast S, Muhlbauer
E and Peschke E: Distribution patterns of calcium-binding proteins
in pancreatic tissue of non-diabetic as well as type 2 diabetic
rats and in rat insulinoma beta-cells (INS-1). Histochem Cell Biol.
134:115–127. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Segerstolpe A, Palasantza A, Eliasson P,
Andersson EM, Andreasson AC, Sun X, Picelli S, Sabirsh A, Clausen
M, Bjursell MK, et al: Single-cell transcriptome profiling of human
pancreatic islets in health and Type 2 diabetes. Cell Metabo.
24:593–607. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hansson SF, Zhou AX, Vachet P, Eriksson
JW, Pereira MJ, Skrtic S, Jongsm Wallin H, Ericsson-Dahistrand A,
Karlsson D, Ahnmark A, et al: Secretagogin is increased in plasma
from type 2 diabetes patients and potentially reflects stress and
islet dysfunction. PLoS One. 13:e01966012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rorsman P and Renstrom E: Insulin granule
dynamics in pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia. 46:1029–1045.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Heaslip AT, Nelson SR, Lombardo AT, Beck
Previs S, Armstrong J and Warshaw DM: Cytoskeletal dependence of
insulin granule movement dynamics in INS-1 beta-cells in response
to glucose. PLoS One. 9. pp. e1090822014, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Rondas D, Tomas A and Halban PA: Focal
adhesion remodeling is crucial for glucose-stimulated insulin
secretion and involves activation of focal adhesion kinase and
paxillin. Diabetes. 60:1146–1157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|