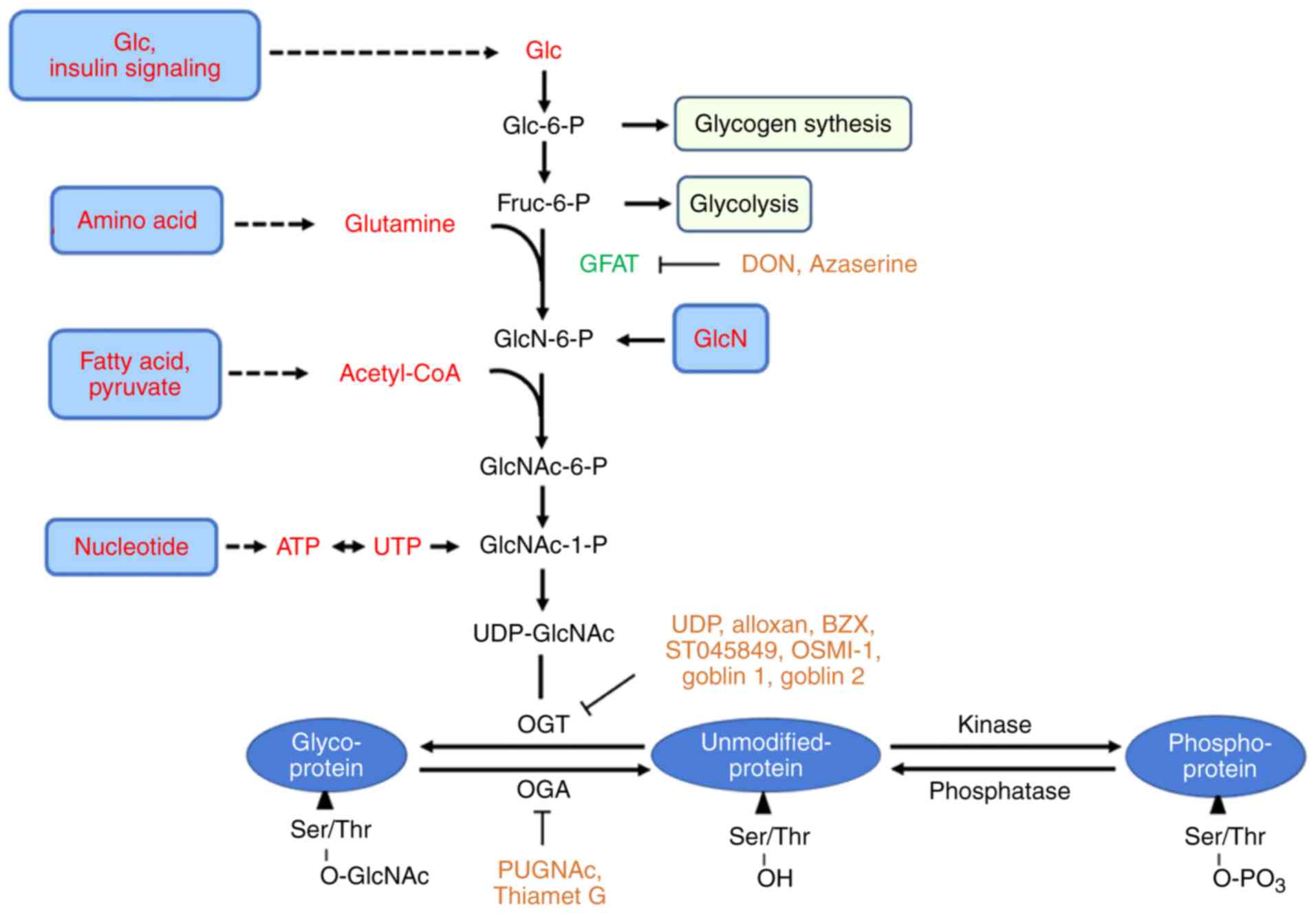
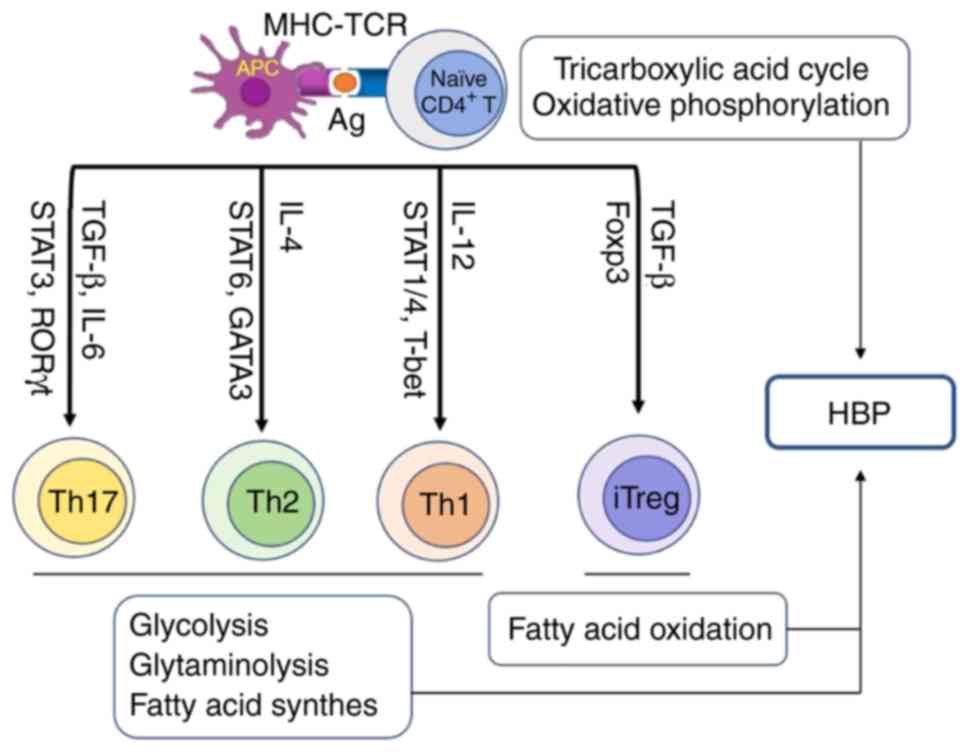
|
1
|
Ong Q, Han W and Yang) X: O-GlcNAc as an
integrator of signaling pathways. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
9:5992018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
D'Hondt C, Iyyathurai J, Vinken M, Rogiers
V, Leybaert L, Himpens B and Bultynck G: Regulation of connexin-
and pannexin-based channels by post-translational modifications.
Biol Cell. 105:373–398. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xie Y, Kang R, Sun X, Zhong M, Huang J,
Klionsky DJ and Tang D: Posttranslational modification of
autophagy-related proteins in macroautophagy. Autophagy. 11:28–45.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Schedin-Weiss S, Winblad B and Tjernberg
LO: The role of protein glycosylation in Alzheimer disease. FEBS J.
281:46–62. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gurel Z and Sheibani N: O-Linked
β-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) modification: A new pathway to
decode pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Clin Sci (Lond).
132:185–198. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hurtado-Guerrero R, Dorfmueller HC and van
Aalten DM: Molecular mechanisms of O-GlcNAcylation. Curr Opin
Struct Biol. 18:551–557. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang X and Qian K: Protein
O-GlcNAcylation: Emerging mechanisms and functions. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 18:452–465. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Myslicki JP, Belke DD and Shearer J: Role
of O-GlcNAcylation in nutritional sensing, insulin resistance and
in mediating the benefits of exercise. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab.
39:1205–1213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Levine ZG and Walker S: The biochemistry
of O-GlcNAc transferase: Which functions make it essential in
mammalian cells? Annu Rev Biochem. 85:631–657. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Aquino-Gil M, Pierce A, Perez-Cervera Y,
Zenteno E and Lefebvre T: OGT: A short overview of an enzyme
standing out from usual glycosyltransferases. Biochem Soc Trans.
45:365–370. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ogawa M, Furukawa K and Okajima T:
Extracellular O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine: Its biology and
relationship to human disease. World J Biol Chem. 5:224–230.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Varshney S and Stanley P: EOGT and
O-GlcNAc on secreted and membrane proteins. Biochem Soc Trans.
45:401–408. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ruan HB, Nie Y and Yang X: Regulation of
protein degradation by O-GlcNAcylation: Crosstalk with
ubiquitination. Mol Cell Proteomics. 12:3489–3497. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu Y, Liu TW, Cecioni S, Eskandari R,
Zandberg WF and Vocadlo DJ: O-GlcNAc occurs cotranslationally to
stabilize nascent polypeptide chains. Nat Chem Biol. 11:319–325.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sayat R, Leber B, Grubac V, Wiltshire L
and Persad S: O-GlcNAc-glycosylation of beta-catenin regulates its
nuclear localization and transcriptional activity. Exp Cell Res.
314:2774–2787. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Skorobogatko Y, Landicho A, Chalkley RJ,
Kossenkov AV, Gallo G and Vosseller K: O-linked
β-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) site thr-87 regulates synapsin I
localization to synapses and size of the reserve pool of synaptic
vesicles. J Biol Chem. 289:3602–3612. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Butkinaree C, Park K and Hart GW: O-linked
beta-N-acetylglu-cosamine (O-GlcNAc): Extensive crosstalk with
phosphorylation to regulate signaling and transcription in response
to nutrients and stress. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1800:96–106. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Levine ZG, Fan C, Melicher MS, Orman M,
Benjamin T and Walker S: O-GlcNAc transferase recognizes protein
substrates using an asparagine ladder in the tetratricopeptide
repeat (TPR) superhelix. J Am Chem Soc. 140:3510–3513. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rafie K, Raimi O, Ferenbach AT, Borodkin
VS, Kapuria V and van Aalten DMF: Recognition of a glycosylation
substrate by the O-GlcNAc transferase TPR repeats. Open Biol.
7:1700782017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma X, Liu P, Yan H, Sun H, Liu X, Zhou F,
Li L, Chen Y, Muthana MM, Chen X, et al: Substrate specificity
provides insights into the sugar donor recognition mechanism of
O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT). PLoS One. 8:e634522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nagel AK and Ball LE: O-GlcNAc transferase
and O-GlcNAcase: Achieving target substrate specificity. Amino
Acids. 46:2305–2316. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bullen JW, Balsbaugh JL, Chanda D,
Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Neumann D and Hart GW: Cross-talk between
two essential nutrient-sensitive enzymes: O-GlcNAc transferase
(OGT) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). J Biol Chem.
289:10592–10606. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Watson LJ, Long BW, DeMartino AM, Brittian
KR, Readnower RD, Brainard RE, Cummins TD, Annamalai L, Hill BG and
Jones SP: Cardiomyocyte Ogt is essential for postnatal viability.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 306:H142–H153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Ortiz-Meoz RF, Jiang J, Lazarus MB, Orman
M, Janetzko J, Fan C, Duveau DY, Tan ZW, Thomas CJ and Walker S: A
small molecule that inhibits OGT activity in cells. ACS Chem Biol.
10:1392–1397. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gross BJ, Kraybill BC and Walker S:
Discovery of O-GlcNAc transferase inhibitors. J Am Chem Soc.
127:14588–14589. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang J, Lazarus MB, Pasquina L, Sliz P
and Walker S: A neutral diphosphate mimic crosslinks the active
site of human O-GlcNAc transferase. Nat Chem Biol. 8:72–77. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Borodkin VS, Schimpl M, Gundogdu M, Rafie
K, Dorfmueller HC, Robinson DA and van Aalten DM: Bisubstrate
UDP-peptide conjugates as human O-GlcNAc transferase inhibitors.
Biochem J. 457:497–502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Trapannone R, Rafie K and van Aalten DM:
O-GlcNAc transferase inhibitors: Current tools and future
challenges. Biochem Soc Trans. 44:88–93. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ruan HB, Singh JP, Li MD, Wu J and Yang X:
Cracking the O-GlcNAc code in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
24:301–309. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hanover JA, Krause MW and Love DC:
Bittersweet memories: Linking metabolism to epigenetics through
O-GlcNAcylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:312–321. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
He Y, Roth C, Turkenburg JP and Davies GJ:
Three-dimensional structure of a Streptomyces sviceus GNAT
acetyltransferase with similarity to the C-terminal domain of the
human GH84 O-GlcNAcase. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr.
70:186–195. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Elsen NL, Patel SB, Ford RE, Hall DL, Hess
F, Kandula H, Kornienko M, Reid J, Selnick H, Shipman JM, et al:
Insights into activity and inhibition from the crystal structure of
human O-GlcNAcase. Nat Chem Biol. 13:613–615. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Keembiyehetty CN, Krzeslak A, Love DC and
Hanover JA: A lipid-droplet-targeted O-GlcNAcase isoform is a key
regulator of the proteasome. J Cell Sci. 124:2851–2860. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Khidekel N, Ficarro SB, Clark PM, Bryan
MC, Swaney DL, Rexach JE, Sun YE, Coon JJ, Peters EC and
Hsieh-Wilson LC: Probing the dynamics of O-GlcNAc glycosylation in
the brain using quantitative proteomics. Nat Chem Biol. 3:339–348.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Crotty S: Follicular helper CD4 T cells
(TFH). Annu Rev Immunol. 29:621–663. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang R, Dillon CP, Shi LZ, Milasta S,
Carter R, Finkelstein D, McCormick LL, Fitzgerald P, Chi H, Munger
J and Green DR: The transcription factor Myc controls metabolic
reprogramming upon T lymphocyte activation. Immunity. 35:871–882.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
MacIver NJ, Michalek RD and Rathmell JC:
Metabolic regulation of T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol.
31:259–283. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Machacek M, Slawson C and Fields PE:
O-GlcNAc: A novel regulator of immunometabolism. J Bioenerg
Biomembr. 50:223–229. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Woo CM, Lund PJ, Huang AC, Davis MM,
Bertozzi CR and Pitteri SJ: Mapping and quantification of over
2,000 O-linked glycopeptides in activated human T cells with
isotope-targeted glycoproteomics (IsoTaG). Mol Cell Proteomics.
17:764–775. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lund PJ, Elias JE and Davis MM: Global
analysis of O-GlcNAc glycoproteins in activated human T cells. J
Immunol. 197:3086–3098. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Swamy M, Pathak S, Grzes KM, Damerow S,
Sinclair LV, van Aalten DM and Cantrell DA: Glucose and glutamine
fuel protein O-GlcNAcylation to control T cell self-renewal and
malignancy. Nat Immunol. 17:712–720. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hao X, Li Y, Wang J, Ma J, Zhao S, Ye X,
He L, Yang J, Gao M, Xiao F and Wei H: Deficient O-GlcNAc
glycosylation impairs regulatory T cell differentiation and notch
signaling in autoimmune hepatitis. Front Immunol. 9:20892018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ghosh S, May MJ and Kopp EB: NF-kappa B
and Rel proteins: Evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune
responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 16:225–260. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Karin M and Ben-Neriah Y: Phosphorylation
meets ubiquitination: The control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 18:621–663. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lecoq L, Raiola L, Chabot PR, Cyr N,
Arseneault G, Legault P and Omichinski JG: Structural
characterization of interactions between transactivation domain 1
of the p65 subunit of NF-κB and transcription regulatory factors.
Nucleic Acids Res. 45:5564–5576. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yi H, Peng R, Zhang LY, Sun Y, Peng HM,
Liu HD, Yu LJ, Li AL, Zhang YJ, Jiang WH and Zhang Z:
LincRNA-Gm4419 knockdown ameliorates NF-κB/NLRP3
inflammasome-mediated inflammation in diabetic nephropathy. Cell
Death Dis. 8:e25832017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Grundy SM: Overnutrition, ectopic lipid
and the metabolic syndrome. J Investig Med. 64:1082–1086. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang Q, Lenardo MJ and Baltimore D: 30
years of NF-κB: A blossoming of relevance to human pathobiology.
Cell. 168:37–57. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Baker RG, Hayden MS and Ghosh S: NF-κB,
inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 13:11–22. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hayes JB, Sircy LM, Heusinkveld LE, Ding
W, Leander RN, McClelland EE and Nelson DE: Modulation of
macrophage inflammatory nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling by
intracellular cryptococcus neoformans. J Biol Chem.
291:15614–15627. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Esser N, Paquot N and Scheen AJ:
Anti-inflammatory agents to treat or prevent type 2 diabetes,
metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Expert Opin Investig
Drugs. 24:283–307. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Golks A, Tran TT, Goetschy JF and Guerini
D: Requirement for O-linked N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase in
lymphocytes activation. EMBO J. 26:4368–4379. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bunting K, Rao S, Hardy K, Woltring D,
Denyer GS, Wang J, Gerondakis S and Shannon MF: Genome-wide
analysis of gene expression in T cells to identify targets of the
NF-kappa B transcription factor c-Rel. J Immunol. 178:7097–7109.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ramakrishnan P, Clark PM, Mason DE, Peters
EC, Hsieh- Wilson LC and Baltimore D: Activation of the
transcriptional function of the NF-κB protein c-Rel by O-GlcNAc
glycosylation. Sci Signal. 6:ra752013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Baudoin L and Issad) T: O-GlcNacylation
and inflammation: A vast territory to explore. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 5:2352014.
|
|
56
|
Wu JL, Chiang MF, Hsu PH, Tsai DY, Hung
KH, Wang YH, Angata T and Lin KI: O-GlcNAcylation is required for B
cell homeostasis and antibody responses. Nat Commun. 8:18542017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zanni MV, Burdo TH, Makimura H, Williams
KC and Grinspoon SK: Relationship between monocyte/macrophage
activation marker soluble CD163 and insulin resistance in obese and
normal-weight subjects. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 77:385–390. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Nagareddy PR, Kraakman M, Masters SL,
Stirzaker RA, Gorman DJ, Grant RW, Dragoljevic D, Hong ES,
Abdel-Latif A, Smyth SS, et al: Adipose tissue macrophages promote
myelopoi-esis and monocytosis in obesity. Cell Metab. 19:821–835.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mauldin JP, Nagelin MH, Wojcik AJ,
Srinivasan S, Skaflen MD, Ayers CR, McNamara CA and Hedrick CC:
Reduced expression of ATP-binding cassette transporter G1 increases
cholesterol accumulation in macrophages of patients with type 2
diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 117:2785–2792. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Westerbacka J, Kolak M, Kiviluoto T,
Arkkila P, Sirén J, Hamsten A, Fisher RM and Yki-Järvinen H: Genes
involved in fatty acid partitioning and binding, lipolysis,
monocyte/macrophage recruitment, and inflammation are overexpressed
in the human fatty liver of insulin-resistant subjects. Diabetes.
56:2759–2765. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Vasamsetti SB, Karnewar S, Kanugula AK,
Thatipalli AR, Kumar JM and Kotamraju S: Metformin inhibits
monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation via AMPK-mediated inhibition
of STAT3 activation: Potential role in atherosclerosis. Diabetes.
64:2028–2041. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hwang JS, Kwon MY, Kim KH, Lee Y, Lyoo IK,
Kim JE, Oh ES and Han IO: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated iNOS
induction is increased by glucosamine under normal glucose
conditions but is inhibited by glucosamine under high glucose
conditions in macrophage cells. J Biol Chem. 292:1724–1736. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
63
|
Ryu IH and Do SI: Denitrosylation of
S-nitrosylated OGT is triggered in LPS-stimulated innate immune
response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 408:52–57. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hwang SY, Shin JH, Hwang JS, Kim SY, Shin
JA, Oh ES, Oh S, Kim JB, Lee JK and Han IO: Glucosamine exerts a
neuro-protective effect via suppression of inflammation in rat
brain ischemia/reperfusion injury. Glia. 58:1881–1892. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hwang JS, Hwang SY and Han IO: Basal
transcription is regulated by lipopolysaccharide and glucosamine
via the regulation of DNA binding of RNA polymerase II in RAW264.7
cells. Life Sci. 110:93–98. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kneass ZT and Marchase RB: Protein
O-GlcNAc modulates motility-associated signaling intermediates in
neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 280:14579–14585. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kneass ZT and Marchase RB: Neutrophils
exhibit rapid agonist-induced increases in protein-associated
O-GlcNAc. J Biol Chem. 279:45759–45765. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Madsen-Bouterse SA, Xu Y, Petty HR and
Romero R: Quantification of O-GlcNAc protein modification in
neutrophils by flow cytometry. Cytometry A. 73:667–672. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hart GW, Slawson C, Ramirez-Correa G and
Lagerlof O: Cross talk between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation:
Roles in signaling, transcription, and chronic disease. Annu Rev
Biochem. 80:825–858. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ma J and Hart GW: O-GlcNAc profiling: From
proteins to proteomes. Clin Proteomics. 11:82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Krick S, Helton ES, Hutcheson SB, Blumhof
S, Garth JM, Denson RS, Zaharias RS, Wickham H and Barnes JW: FGF23
Induction of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine regulates IL-6 secretion
in human bronchial epithelial cells. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
9:7082018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Guo X, Shang J, Deng Y, Yuan X, Zhu D and
Liu H: Alterations in left ventricular function during intermittent
hypoxia: Possible involvement of O-GlcNAc protein and MAPK
signaling. Int J Mol Med. 36:150–158. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
James LR, Tang D, Ingram A, Ly H, Thai K,
Cai L and Scholey JW: Flux through the hexosamine pathway is a
determinant of nuclear factor kappaB- dependent promoter
activation. Diabetes. 51:1146–1156. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Dela Justina V, Goncalves JS, de Freitas
RA, Fonseca AD, Volpato GT, Tostes RC, Carneiro FS, Lima VV and
Giachini FR: Increased O-linked N-acetylglucosamine modification of
NF-κB and augmented cytokine production in the placentas from
hyperglycemic rats. Inflammation. 40:1773–1781. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhang D, Cai Y, Chen M, Gao L, Shen Y and
Huang Z: OGT-mediated O-GlcNAcylation promotes NF-κB activation and
inflammation in acute pancreatitis. Inflamm Res. 64:943–952. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Li Y, Liu H, Xu QS, Du YG and Xu J:
Chitosan oligosaccharides block LPS-induced O-GlcNAcylation of
NF-κB and endothelial inflammatory response. Carbohydr Polym.
99:568–578. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Yang WH, Park SY, Nam HW, Kim DH, Kang JG,
Kang ES, Kim YS, Lee HC, Kim KS and Cho JW: NFkappaB activation is
associated with its O-GlcNAcylation state under hyperglycemic
conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:17345–17350. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Allison DF, Wamsley JJ, Kumar M, Li D,
Gray LG, Hart GW, Jones DR and Mayo MW: Modification of RelA by
O-linked N-acetylglucosamine links glucose metabolism to NF-κB
acetylation and transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:16888–16893. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Ma Z, Chalkley RJ and Vosseller K:
Hyper-O-GlcNAcylation activates nuclear factor
κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling
through interplay with phosphorylation and acetylation. J Biol
Chem. 292:9150–9163. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kawauchi K, Araki K, Tobiume K and Tanaka
N: Loss of p53 enhances catalytic activity of IKKbeta through
O-linked beta-N-acetyl glucosamine modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 106:3431–3436. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Donovan K, Alekseev O, Qi X, Cho W and
Azizkhan-Clifford J: O-GlcNAc modification of transcription factor
Sp1 mediates hyperglycemia-induced VEGF-A upregulation in retinal
cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 55:7862–7873. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhang Y, Qu Y, Niu T, Wang H and Liu K:
O-GlcNAc modification of Sp1 mediates hyperglycaemia-induced ICAM-1
up-regulation in endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
484:79–84. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
O'Shea JJ and Plenge R: JAK and STAT
signaling molecules in immunoregulation and immune-mediated
disease. Immunity. 36:542–550. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Li X, Zhang Z, Li L, Gong W, Lazenby AJ,
Swanson BJ, Herring LE, Asara JM, Singer JD and Wen H:
Myeloid-derived cullin 3 promotes STAT3 phosphorylation by
inhibiting OGT expression and protects against intestinal
inflammation. J Exp Med. 214:1093–1109. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Pathak S, Borodkin VS, Albarbarawi O,
Campbell DG, Ibrahim A and van Aalten DM: O-GlcNAcylation of TAB1
modulates TAK1-mediated cytokine release. EMBO J. 31:1394–1404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Hirata Y, Takahashi M, Morishita T,
Noguchi T and Matsuzawa A: Post-translational modifications of the
TAK1-TAB complex. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E2052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhang D, Xu Z, Tao T, Liu X, Sun X, Ji Y,
Han L, Qiu H, Zhu G, Shen Y, et al: Modification of TAK1 by
O-linked N-acetylglucosamine facilitates TAK1 activation and
promotes M1 macrophage polarization. Cell Signal. 28:1742–1752.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Hou CW, Mohanan V, Zachara NE and Grimes
CL: Identification and biological consequences of the O-GlcNAc
modification of the human innate immune receptor, Nod2.
Glycobiology. 26:13–18. 2016.
|
|
89
|
Xing D, Feng W, Not LG, Miller AP, Zhang
Y, Chen YF, Majid-Hassan E, Chatham JC and Oparil S: Increased
protein O-GlcNAc modification inhibits inflammatory and neointimal
responses to acute endoluminal arterial injury. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 295:H335–H342. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Hilgers RH, Xing D, Gong K, Chen YF,
Chatham JC and Oparil S: Acute O-GlcNAcylation prevents
inflammation-induced vascular dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 303:H513–H522. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zou L, Yang S, Hu S, Chaudry IH, Marchase
RB and Chatham JC: The protective effects of PUGNAc on cardiac
function after trauma-hemorrhage are mediated via increased protein
O-GlcNAc levels. Shock. 27:402–408. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zou L, Yang S, Champattanachai V, Hu S,
Chaudry IH, Marchase RB and Chatham JC: Glucosamine improves
cardiac function following trauma-hemorrhage by increased protein
O-GlcNAcylation and attenuation of NF-{kappa}B signaling. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 296:H515–H523. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Yamamoto Y and Gaynor RB: IkappaB kinases:
Key regulators of the NF-kappaB pathway. Trends Biochem Sci.
29:72–79. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Meirow Y and Baniyash M: Immune biomarkers
for chronic inflammation related complications in non-cancerous and
cancerous diseases. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 66:1089–1101. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Holmdahl R, Sareila O, Olsson LM, Backdahl
L and Wing K: Ncf1 polymorphism reveals oxidative regulation of
autoimmune chronic inflammation. Immunol Rev. 269:228–247. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Pietropaolo M, Barinas-Mitchell E and
Kuller LH: The heterogeneity of diabetes: Unraveling a dispute: Is
systemic inflammation related to islet autoimmunity? Diabetes.
56:1189–1197. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Vaidyanathan K and Wells L: Multiple
tissue-specific roles for the O-GlcNAc post-translational
modification in the induction of and complications arising from
type II diabetes. J Biol Chem. 289:34466–34471. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Xing D, Gong K, Feng W, Nozell SE, Chen
YF, Chatham JC and Oparil S: O-GlcNAc modification of NFκB p65
inhibits TNF-α-induced inflammatory mediator expression in rat
aortic smooth muscle cells. PLoS One. 6:e240212011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Hirata Y, Nakagawa T, Moriwaki K,
Koubayashi E, Kakimoto K, Takeuchi T, Inoue T, Higuchi K and Asahi
M: Augmented O-GlcNAcylation alleviates inflammation-mediated colon
carcinogenesis via suppression of acute inflammation. J Clin
Biochem Nutr. 62:221–229. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Hwang SY, Hwang JS, Kim SY and Han IO:
O-GlcNAcylation and p50/p105 binding of c-Rel are dynamically
regulated by LPS and glucosamine in BV2 microglia cells. Br J
Pharmacol. 169:1551–1560. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Zheng GM, Yu C and Yang Z: Puerarin
suppresses production of nitric oxide and inducible nitric oxide
synthase in lipopolysac-charide-induced N9 microglial cells through
regulating MAPK phosphorylation, O-GlcNAcylation and NF-κB
translocation. Int J Oncol. 40:1610–1618. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Hwang SY, Hwang JS, Kim SY and Han IO:
O-GlcNAc transferase inhibits LPS-mediated expression of inducible
nitric oxide synthase through an increased interaction with mSin3A
in RAW264.7 cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 305:C601–C608. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
He Y, Ma X, Li D and Hao J: Thiamet G
mediates neuroprotection in experimental stroke by modulating
microglia/macrophage polarization and inhibiting NF-κB p65
signaling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 37:2938–2951. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Lim K and Chang HI: O-GlcNAc inhibits
interaction between Sp1 and Elf-1 transcription factors. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 380:569–574. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Lim K and Chang HI: O-GlcNAcylation of Sp1
interrupts Sp1 interaction with NF-Y. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
382:593–597. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Jokela TA, Makkonen KM, Oikari S, Kärnä R,
Koli E, Hart GW, Tammi RH, Carlberg C and Tammi MI: Cellular
content of UDP-N-acetylhexosamines controls hyaluronan synthase 2
expression and correlates with O-linked N-acetylglucosamine
modification of transcription factors YY1 and SP1. J Biol Chem.
286:33632–33640. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Lim K and Chang HI: O-GlcNAc inhibits
interaction between Sp1 and sterol regulatory element binding
protein 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 393:314–318. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Suh HN, Lee YJ, Kim MO, Ryu JM and Han HJ:
Glucosamine- induced Sp1 O-GlcNAcylation ameliorates
hypoxia-induced SGLT dysfunction in primary cultured renal proximal
tubule cells. J Cell Physiol. 229:1557–1568. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Lee HJ, Ryu JM, Jung YH, Lee KH, Kim DI
and Han HJ: Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase-1 upregulation by
O-GlcNAcylation of Sp1 protects against hypoxia-induced mouse
embryonic stem cell apoptosis via mTOR activation. Cell Death Dis.
7:e21582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Coornaert B, Carpentier I and Beyaert R:
A20: Central gatekeeper in inflammation and immunity. J Biol Chem.
284:8217–8221. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
111
|
Yao D, Xu L, Xu O, Li R, Chen M, Shen H,
Zhu H, Zhang F, Yao D, Chen YF, et al: O-Linked
β-N-acetylglucosamine modification of A20 enhances the inhibition
of NF-κB (nuclear factor-κB) activation and elicits vascular
protection after acute endoluminal arterial injury. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 38:1309–1320. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Yang WH, Park SY, Ji S, Kang JG, Kim JE,
Song H, Mook-Jung I, Choe KM and Cho JW: O-GlcNAcylation regulates
hyperglycemia-induced GPX1 activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
391:756–761. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Olivier-Van Stichelen S and Hanover JA:
You are what you eat: O-linked N-acetylglucosamine in disease,
development and epigenetics. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care.
18:339–345. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Someya A, Ikegami T, Sakamoto K and
Nagaoka I: Glucosamine downregulates the IL-1β-induced expression
of proinflammatory cytokine genes in human synovial MH7A cells by
O-GlcNAc modification-dependent and -independent mechanisms. PLoS
One. 11:e01651582016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Chehimi M, Vidal H and Eljaafari A:
Pathogenic role of IL-17-producing immune cells in obesity, and
related inflammatory diseases. J Clin Med. 6:E682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Ridker PM, Everett BM, Thuren T, MacFadyen
JG, Chang WH, Ballantyne C, Fonseca F, Nicolau J, Koenig W, Anker
SD, et al: Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for
atherosclerotic disease. N Engl J Med. 377:1119–1131. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Carbo A, Hontecillas R, Kronsteiner B,
Viladomiu M, Pedragosa M, Lu P, Philipson CW, Hoops S, Marathe M,
Eubank S, et al: Systems modeling of molecular mechanisms
controlling cytokine-driven CD4+ T cell differentiation
and phenotype plasticity. PLoS Comput Biol. 9:e10030272013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Hewagama A, Gorelik G, Patel D,
Liyanarachchi P, McCune WJ, Somers E, Gonzalez-Rivera T, Michigan
Lupus Cohort, Strickland F and Richardson B: Overexpression of
X-linked genes in T cells from women with lupus. J Autoimmun.
41:60–71. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Liu R, Ma X, Chen L, Yang Y, Zeng Y, Gao
J, Jiang W, Zhang F, Li D, Han B, et al: MicroRNA-15b suppresses
Th17 differentiation and is associated with pathogenesis of
multiple sclerosis by targeting O-GlcNAc transferase. J Immunol.
198:2626–2639. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|