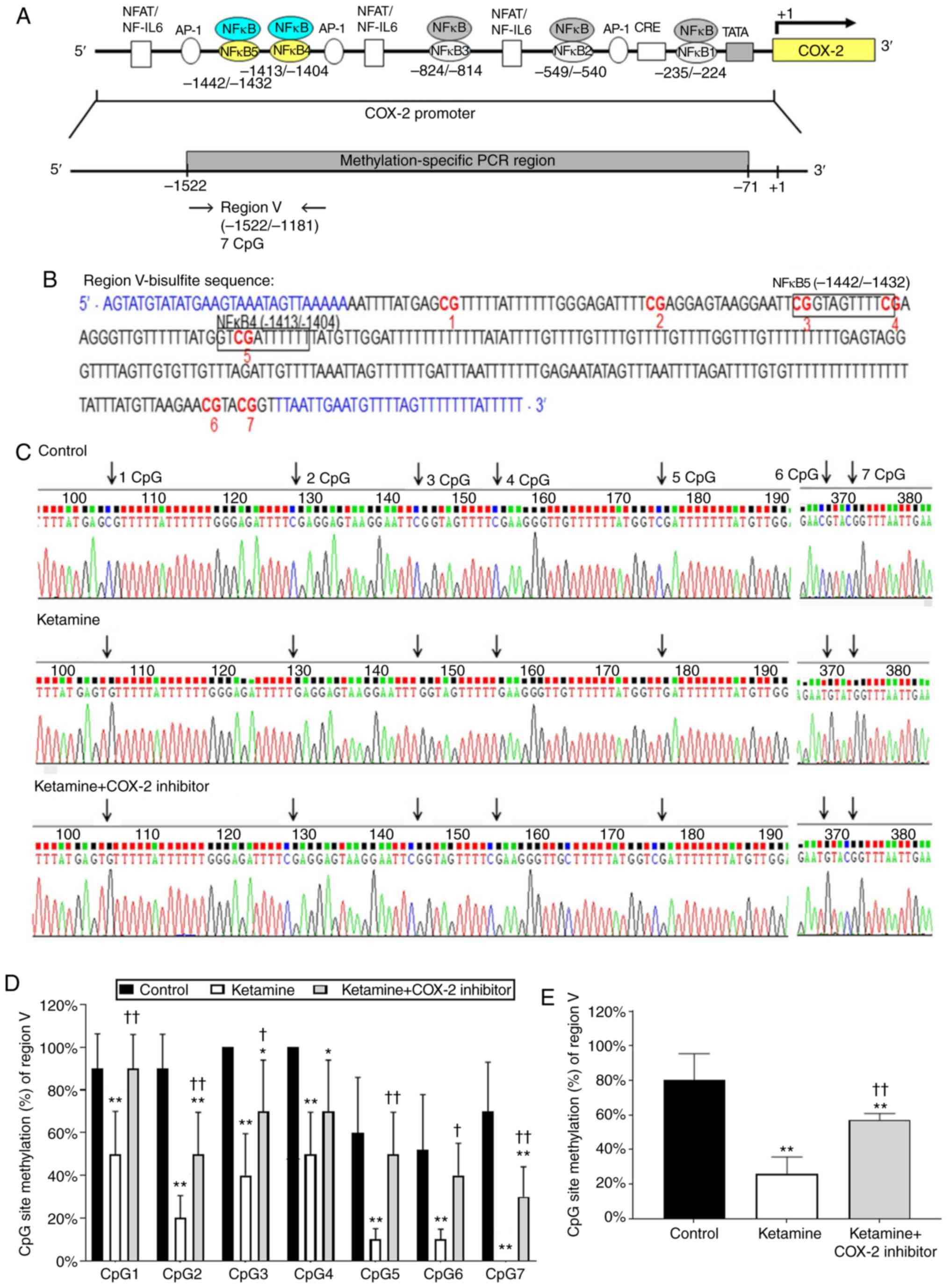
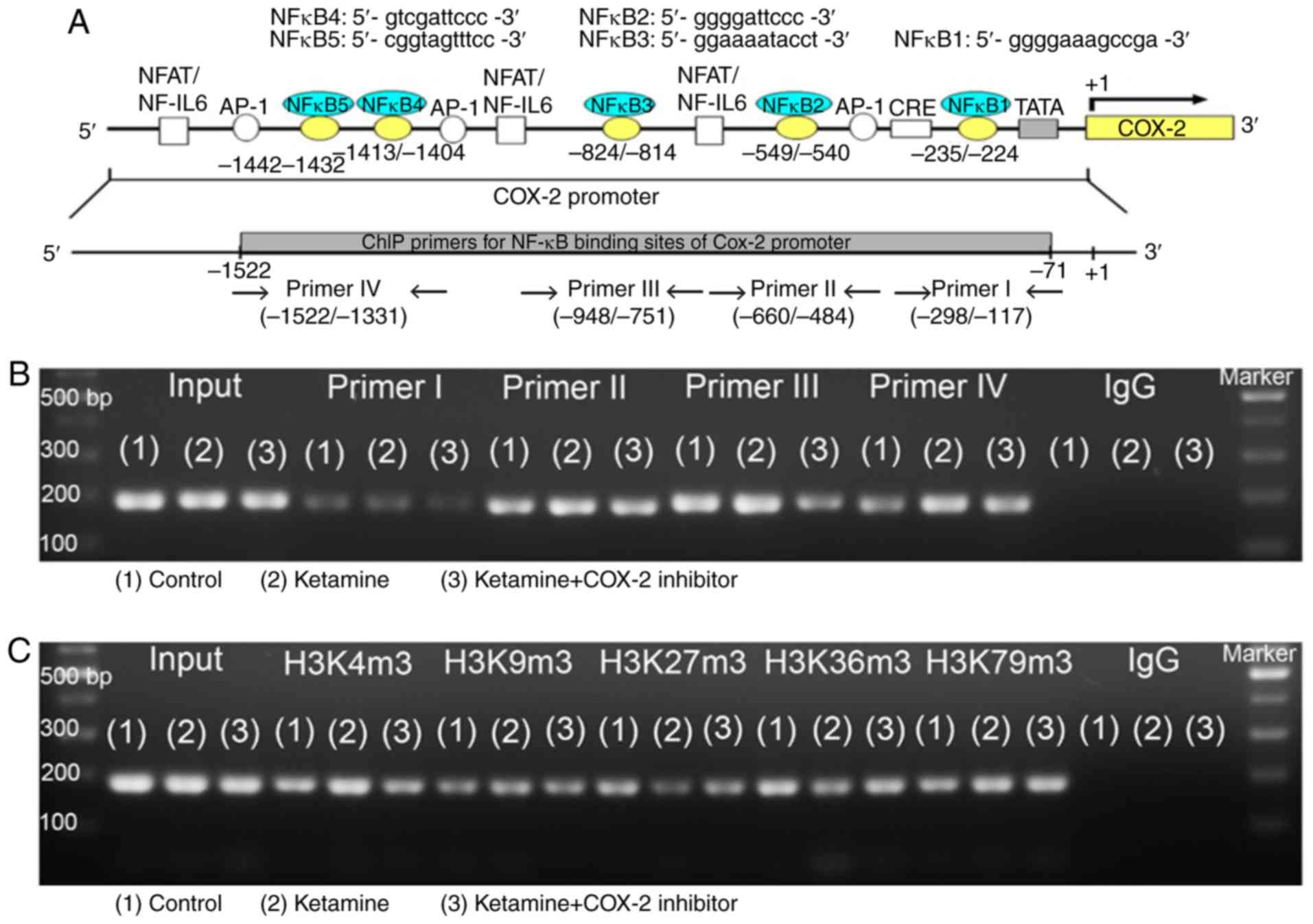
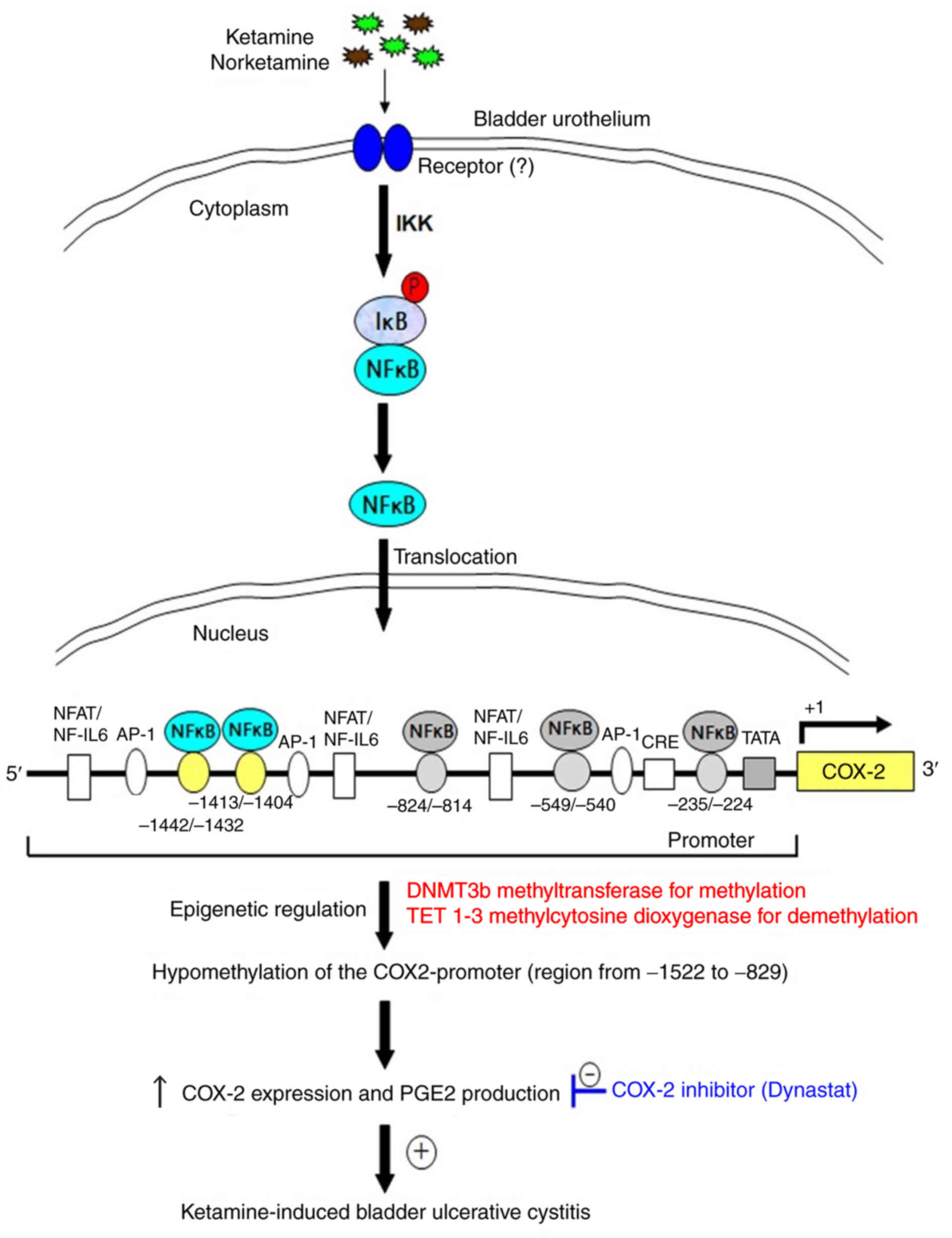
|
1
|
Lee YL, Lin KL, Chuang SM, Lee YC, Lu MC,
Wu BN, Wu WJ, Yuan SF, Ho WT and Juan YS: Elucidating mechanisms of
bladder repair after hyaluronan instillation in ketamine-induced
ulcerative cystitis in animal model. Am J Pathol. 187:1945–1959.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shahani R, Streutker C, Dickson B and
Stewart RJ: Ketamine-associated ulcerative cystitis: A new clinical
entity. Urology. 69:810–812. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Middela S and Pearce I: Ketamine-induced
vesicopathy: A literature review. Int J Clin Pract. 65:27–30. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chuang SM, Liu KM, Li YL, Jang MY, Lee HH,
Wu WJ, Chang WC, Levin RM and Juan YS: Dual involvements of
cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthase expressions in
ketamine-induced ulcerative cystitis in rat bladder. Neurourol
Urodyn. 32:1137–1143. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu KM, Chuang SM, Long CY, Lee YL, Wang
CC, Lu MC, Lin RJ, Lu JH, Jang MY, Wu WJ, et al: Ketamine-induced
ulcerative cystitis and bladder apoptosis involve oxidative stress
mediated by mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 309:F318–331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
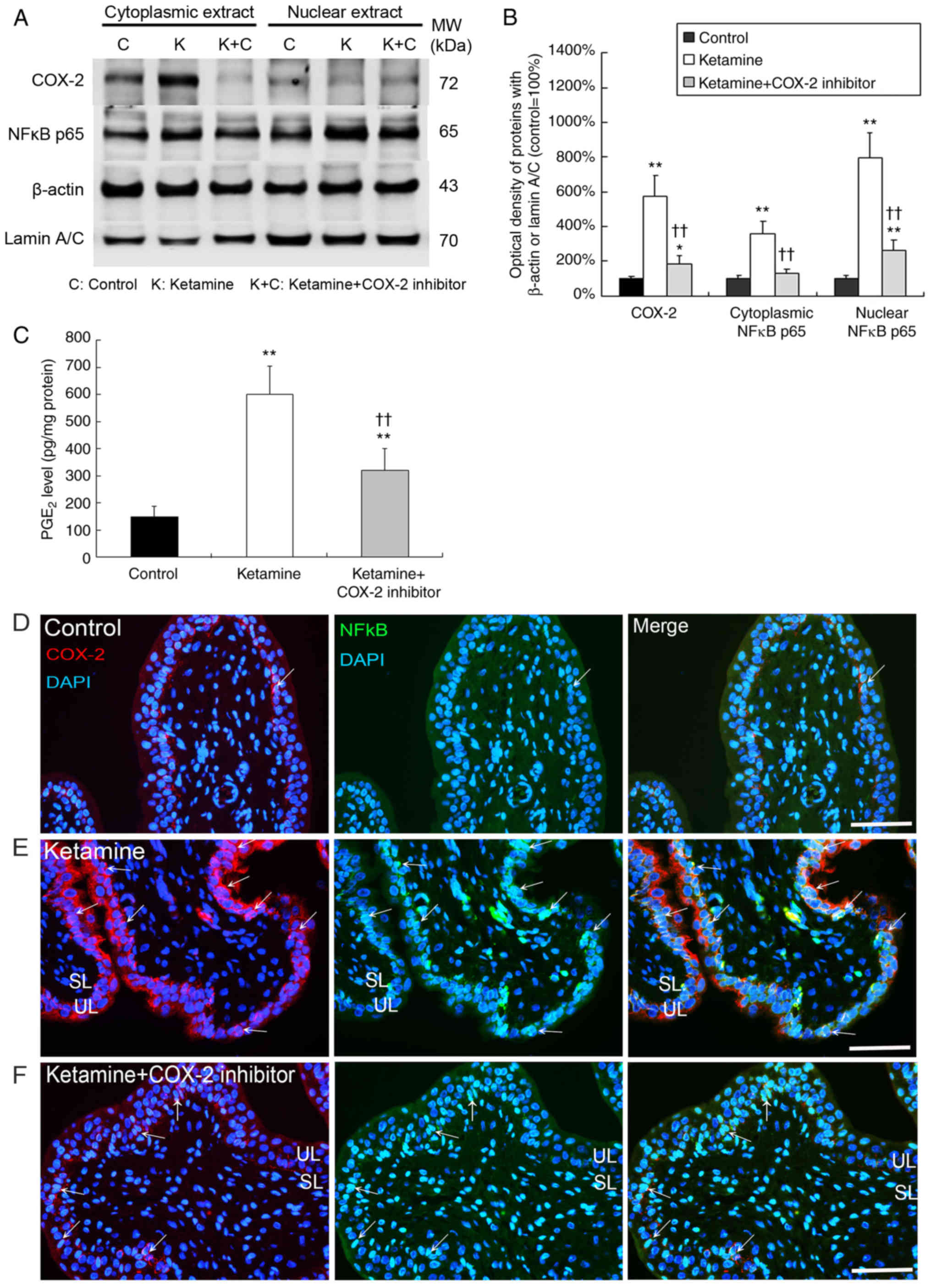
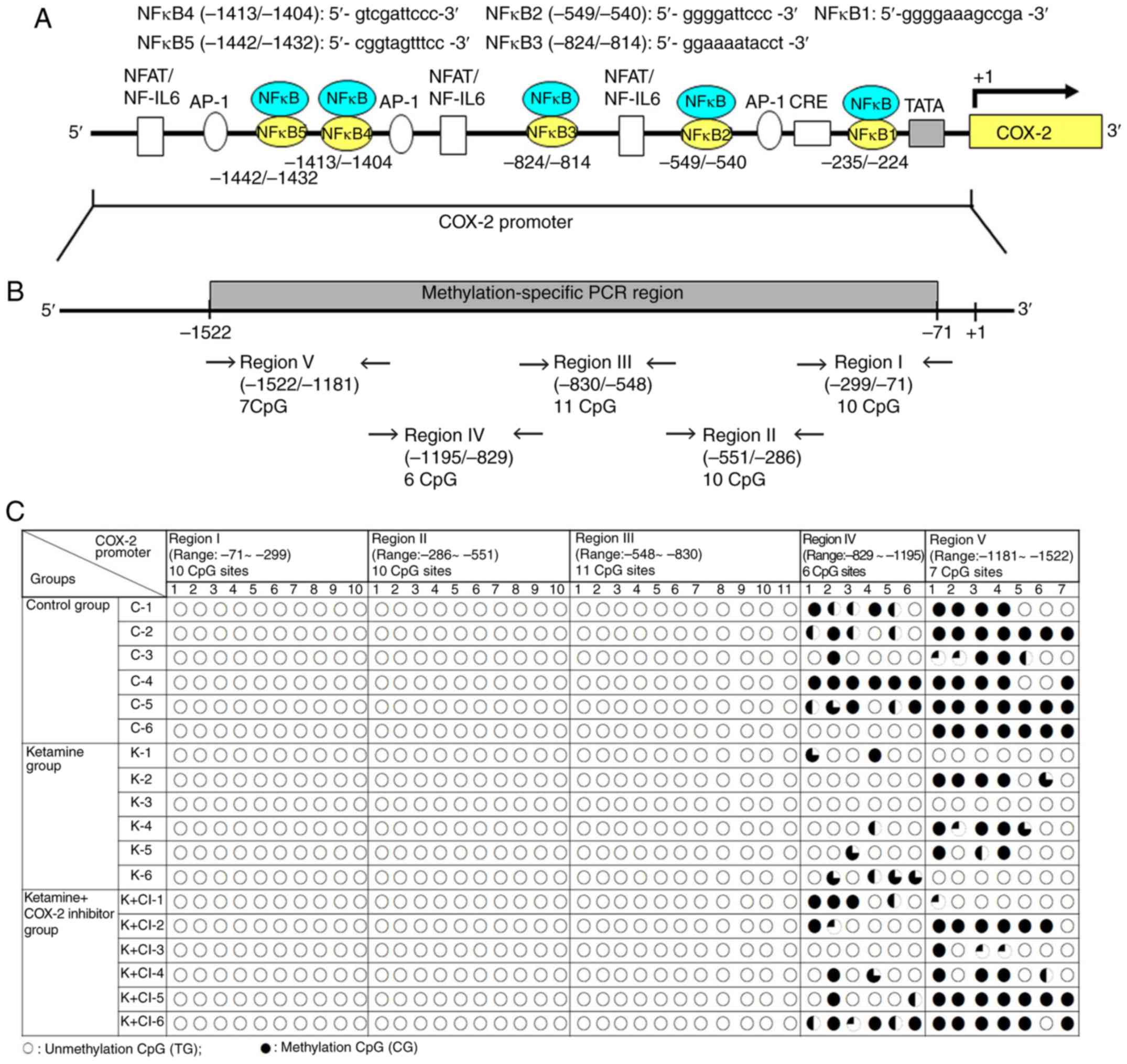
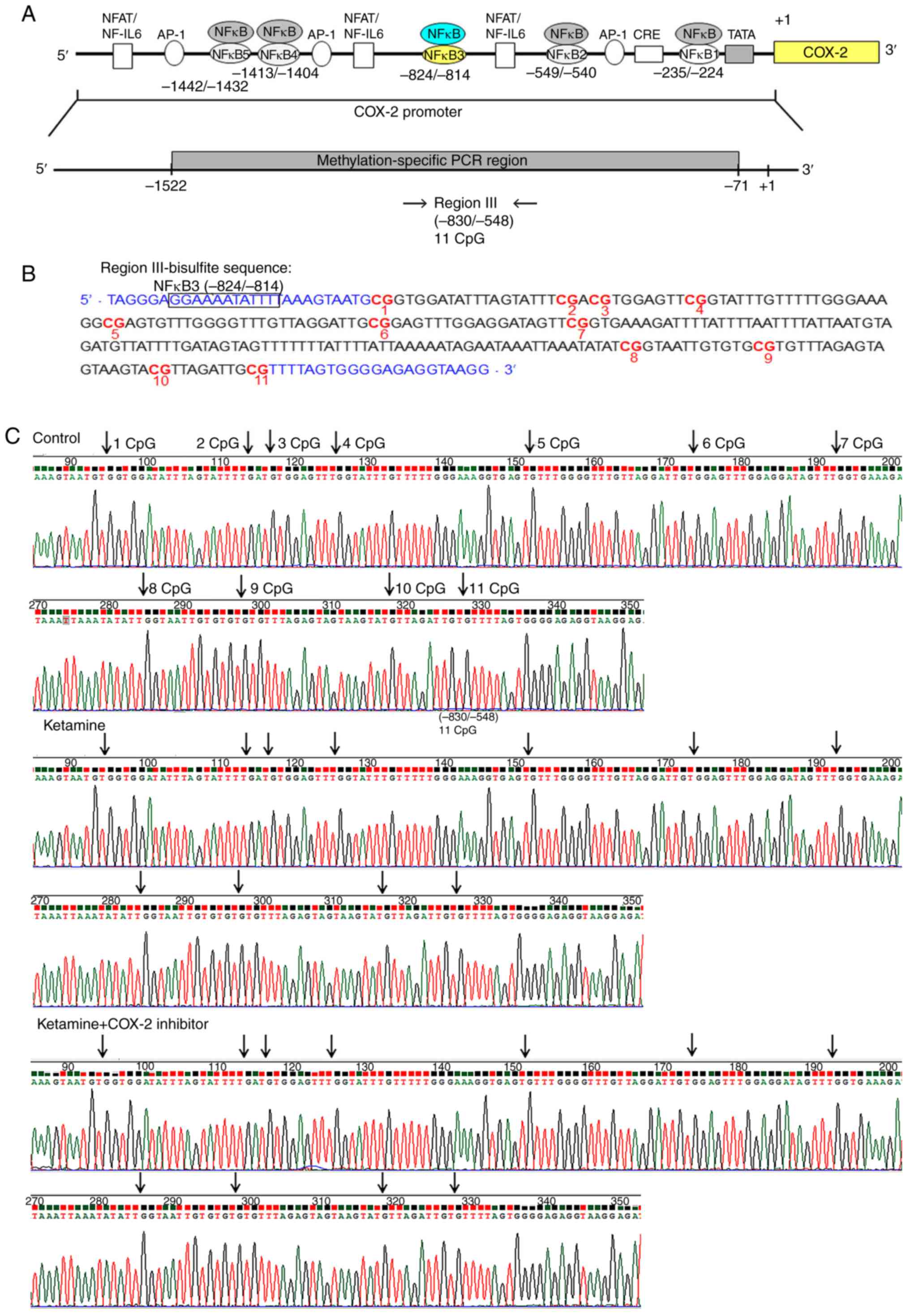
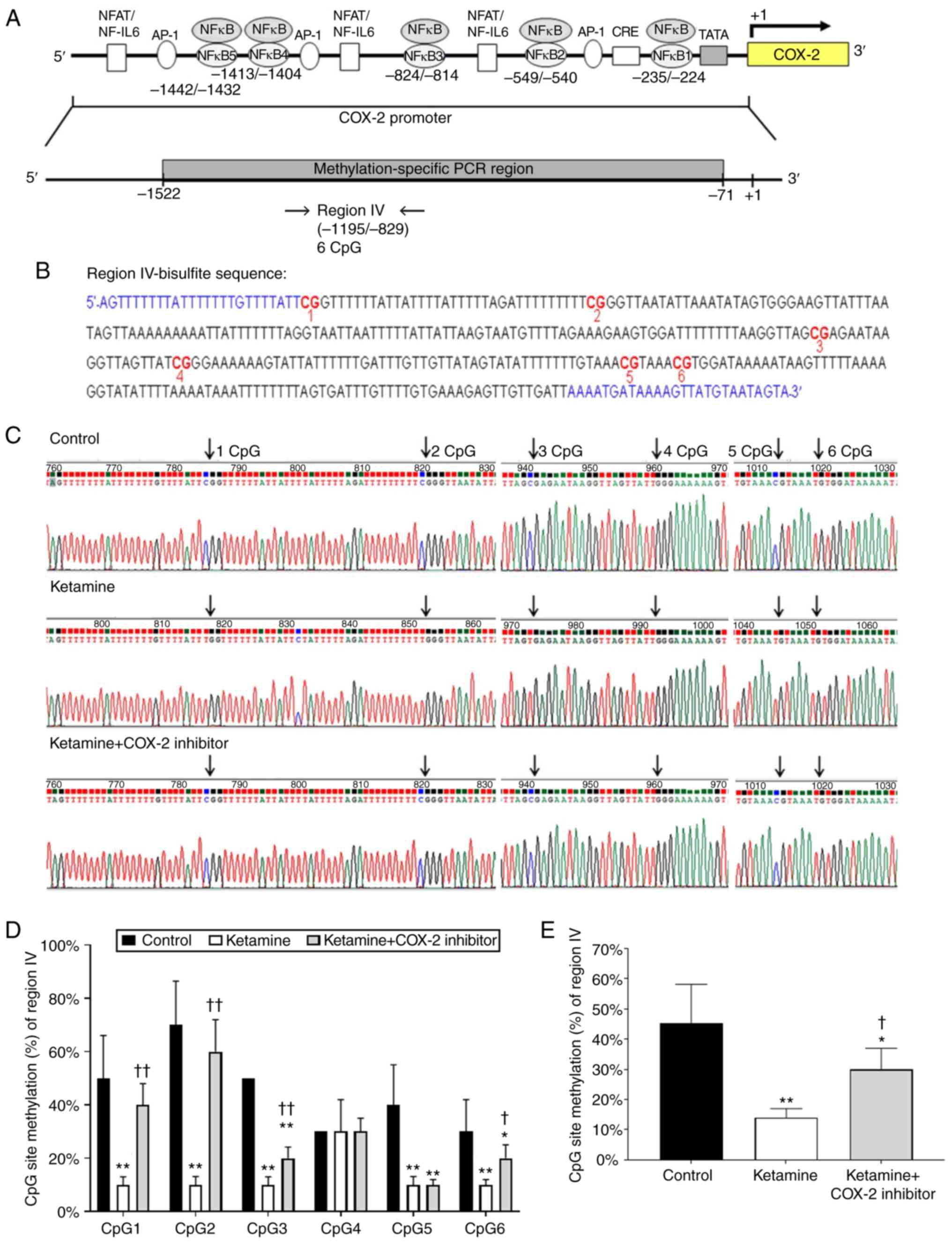
Juan YS, Lee YL, Long CY, Wong JH, Jang
MY, Lu JH, Wu WJ, Huang YS, Chang WC and Chuang SM: Translocation
of NF-κB and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 are enhanced by
ketamine-induced ulcerative cystitis in rat bladder. Am J Pathol.
185:2269–2285. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jhang JF, Hsu YH, Jiang YH and Kuo HC:
Elevated serum IgE may be associated with development of ketamine
cystitis. J Urol. 192:1249–1256. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee CL, Jiang YH and Kuo HC: Increased
apoptosis and suburothelial inflammation in patients with
ketamine-related cystitis: A comparison with non-ulcerative
interstitial cystitis and controls. BJU Int. 112:1156–1162. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jones PL and Wolffe AP: Relationships
between chromatin organization and DNA methylation in determining
gene expression. Semin Cancer Biol. 9:339–347. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jenuwein T and Allis CD: Translating the
histone code. Science. 293:1074–1080. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kelavkar UP, Harya NS, Hutzley J, Bacich
DJ, Monzon FA, Chandran U, Dhir R and O'Keefe DS: DNA methylation
paradigm shift: 15-lipoxygenase-1 upregulation in prostatic
intraepithelial neoplasia and prostate cancer by atypical promoter
hypermethylation. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 82:185–197.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Curradi M, Izzo A, Badaracco G and
Landsberger N: Molecular mechanisms of gene silencing mediated by
DNA methylation. Mol Cell Biol. 22:3157–3173. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Urnov FD and Wolffe AP: Chromatin
remodeling and transcriptional activation: The cast (in order of
appearance). Oncogene. 20:2991–3006. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dantas Machado AC, Zhou T, Rao S, Goel P,
Rastogi C, Lazarovici A, Bussemaker HJ and Rohs R: Evolving
insights on how cytosine methylation affects protein-DNA binding.
Brief Funct Genomics. 14:61–73. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jin B and Robertson KD: DNA
methyltransferases, DNA damage repair, and cancer. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 754:3–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Deneberg S, Guardiola P, Lennartsson A, Qu
Y, Gaidzik V, Blanchet O, Karimi M, Bengtzén S, Nahi H, Uggla B, et
al: Prognostic DNA methylation patterns in cytogenetically normal
acute myeloid leukemia are predefined by stem cell chromatin marks.
Blood. 118:5573–5582. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kouzarides T: Chromatin modifications and
their function. Cell. 128:693–705. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Völkel P and Angrand PO: The control of
histone lysine methylation in epigenetic regulation. Biochimie.
89:1–20. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sims RJ III and Reinberg D: Histone H3 Lys
4 methylation: Caught in a bind? Genes Dev. 20:2779–2786. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang S, Barros SP, Niculescu MD, Moretti
AJ, Preisser JS and Offenbacher S: Alteration of PTGS2 promoter
methylation in chronic periodontitis. J Dent Res. 89:133–137. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Loo WT, Jin L, Cheung MN, Wang M and Chow
LW: Epigenetic change in E-cadherin and COX-2 to predict chronic
periodontitis. J Transl Med. 8:1102010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pedre X, Mastronardi F, Bruck W,
Lopez-Rodas G, Kuhlmann T and Casaccia P: Changed histone
acetylation patterns in normal-appearing white matter and early
multiple sclerosis lesions. J Neurosci. 31:3435–3445. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Toyota M, Shen L, Ohe-Toyota M, Hamilton
SR, Sinicrope FA and Issa JP: Aberrant methylation of the
Cyclooxygenase 2 CpG island in colorectal tumors. Cancer Res.
60:4044–4048. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kikuchi T, Itoh F, Toyota M, Suzuki H,
Yamamoto H, Fujita M, Hosokawa M and Imai K: Aberrant methylation
and histone deacetylation of cyclooxygenase 2 in gastric cancer.
Int J Cancer. 97:272–277. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma X, Yang Q, Wilson KT, Kundu N, Meltzer
SJ and Fulton AM: Promoter methylation regulates cyclooxygenase
expression in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 6:R316–R321. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Feinberg AP and Vogelstein B:
Hypomethylation distinguishes genes of some human cancers from
their normal counterparts. Nature. 301:89–92. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jones PA and Laird PW: Cancer epigenetics
comes of age. Nat Genet. 21:163–167. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chell S, Kaidi A, Williams AC and
Paraskeva C: Mediators of PGE2 synthesis and signalling downstream
of COX-2 represent potential targets for the prevention/treatment
of colorectal cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1766:104–119.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou Y and Hu Z: Genome-wide demethylation
by 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine alters the cell fate of stem/progenitor
cells. Stem Cell Rev. 11:87–95. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Murata H, Tsuji S, Tsujii M, Sakaguchi Y,
Fu HY, Kawano S and Hori M: Promoter hypermethylation silences
cyclooxygenase-2 (Cox-2) and regulates growth of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Lab Invest. 84:1050–1059. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liou JT, Chen ZY, Ho LJ, Yang SP, Chang
DM, Liang CC and Lai JH: Differential effects of triptolide and
tetrandrine on activation of COX-2, NF-kappaB, and AP-1 and virus
production in dengue virus-infected human lung cells. Eur J
Pharmacol. 589:288–298. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Poligone B and Baldwin AS: Positive and
negative regulation of NF-kappaB by COX-2: Roles of different
prostaglandins. J Biol Chem. 276:38658–38664. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Glinghammar B and Rafter J: Colonic
luminal contents induce cyclooxygenase 2 transcription in human
colon carcinoma cells. Gastroenterology. 120:401–410. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu VY, Malley S, Dattilio A, Folsom JB,
Zvara P and Vizzard MA: COX-2 and prostanoid expression in
micturition pathways after cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis in the
rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 284:R574–R585. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li LC and Dahiya R: MethPrimer: Designing
primers for methylation PCRs. Bioinformatics. 18:1427–1431. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Aoki T, Nishimura M, Matsuoka T, Yamamoto
K, Furuyashiki T, Kataoka H, Kitaoka S, Ishibashi R, Ishibazawa A,
Miyamoto S, et al: PGE(2) -EP(2) signalling in endothelium is
activated by haemodynamic stress and induces cerebral aneurysm
through an amplifying loop via NF-κB. Br J Pharmacol.
163:1237–1249. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Paul AG, Chandran B and Sharma-Walia N:
Cyclooxygenase-2-prostaglandin E2-eicosanoid receptor inflammatory
axis: A key player in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus
associated malignancies. Transl Res. 162:77–92. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rundhaug JE, Simper MS, Surh I and Fischer
SM: The role of the EP receptors for prostaglandin E2 in skin and
skin cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 30:465–480. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Müller N: COX-2 inhibitors as
antidepressants and antipsychotics: Clinical evidence. Curr Opin
Investig Drugs. 11:31–42. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ackerman WE IV, Summerfield TL, Vandre DD,
Robinson JM and Kniss DA: Nuclear factor-kappa B regulates
inducible pros-taglandin E synthase expression in human amnion
mesenchymal cells. Biol Reprod. 78:68–76. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Rossi A, Kapahi P, Natoli G, Takahashi T,
Chen Y, Karin M and Santoro MG: Anti-inflammatory cyclopentenone
prostaglandins are direct inhibitors of IkappaB kinase. Nature.
403:103–108. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen H, Cai W, Chu ESH, Tang J, Wong CC,
Wong SH, Sun W, Liang Q, Fang J, Sun Z and Yu J: Hepatic
cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression induced spontaneous hepatocellular
carcinoma formation in mice. Oncogene. 36:4415–4426. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Akhtar M, Cheng Y, Magno RM, Ashktorab H,
Smoot DT, Meltzer SJ and Wilson KT: Promoter methylation regulates
Helicobacter pylori-stimulated cyclooxygenase-2 expression in
gastric epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 61:2399–2403. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Clark SJ, Harrison J and Molloy PL: Sp1
binding is inhibited by (m)Cp(m)CpG methylation. Gene. 195:67–71.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pabo CO and Sauer RT: Protein-DNA
recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 53:293–321. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li E and Zhang Y: DNA methylation in
mammals. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 6:pp. a0191332014,
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chuang TJ and Chen FC: DNA methylation is
associated with an increased level of conservation at nondegenerate
nucleotides in mammals. Mol Biol Evol. 31:387–396. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Kass SU, Pruss D and Wolffe AP: How does
DNA methylation repress transcription? Trends Genet. 13:444–449.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Bestor TH: Gene silencing. Methylation
meets acetylation. Nature. 393:311–312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Davies NM, Longstreth J and Jamali F:
Misoprostol therapeutics revisited. Pharmacotherapy. 21:60–73.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gobejishvili L, Ghare S, Khan R, Cambon A,
Barker DF, Barve S, McClain C and Hill D: Misoprostol modulates
cytokine expression through a cAMP pathway: Potential therapeutic
implication for liver disease. Clin Immunol. 161:291–299. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|