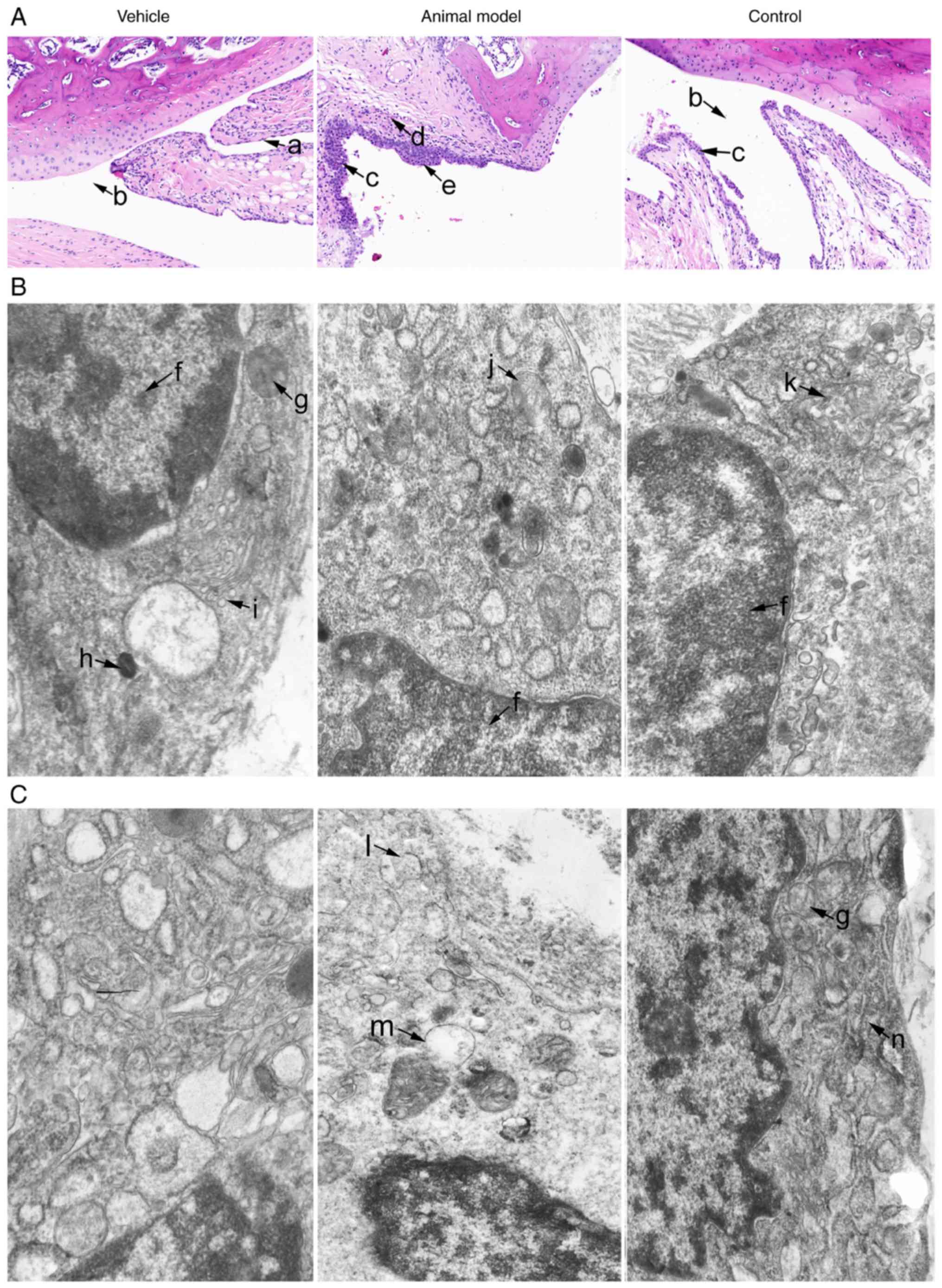
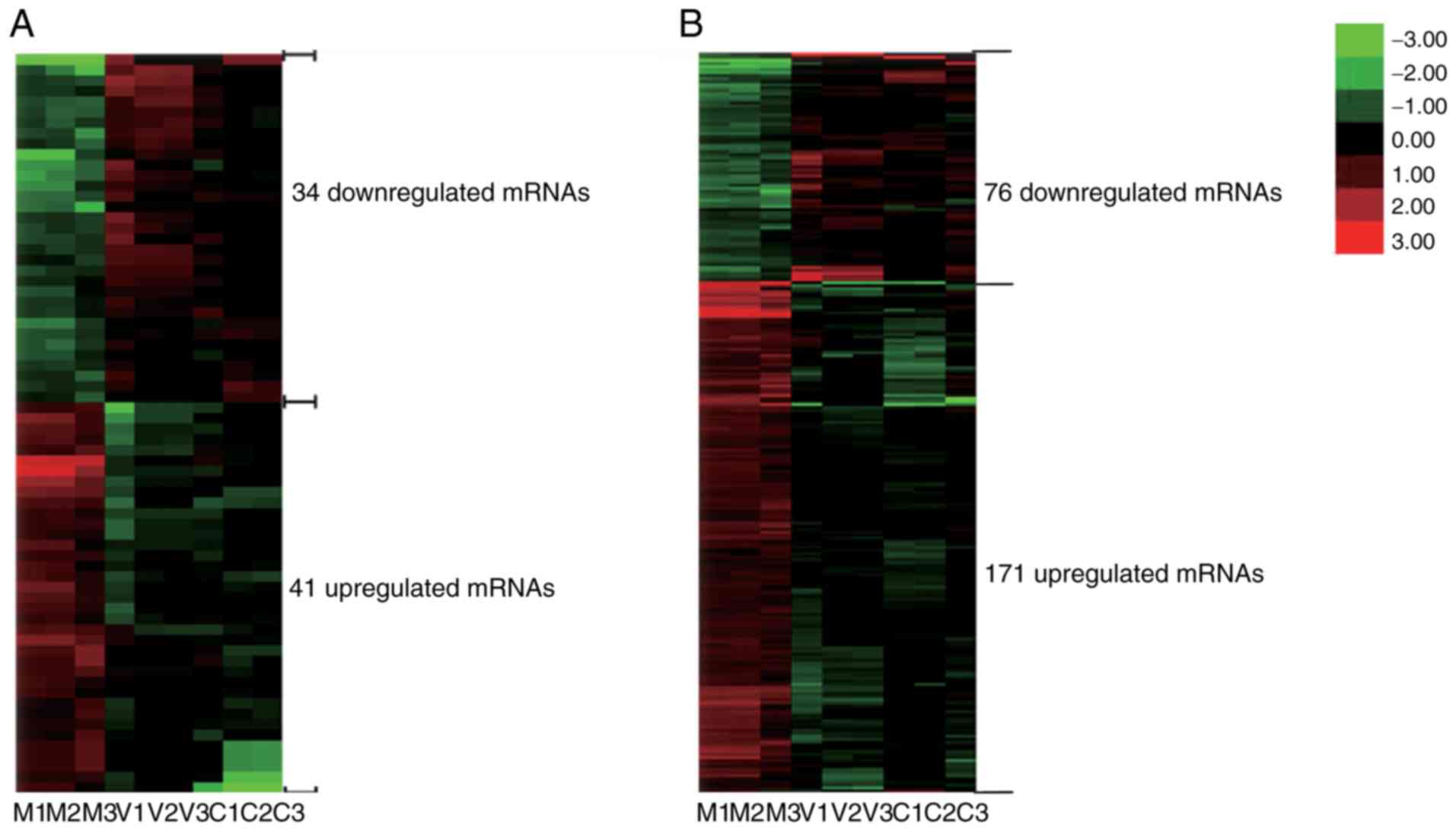
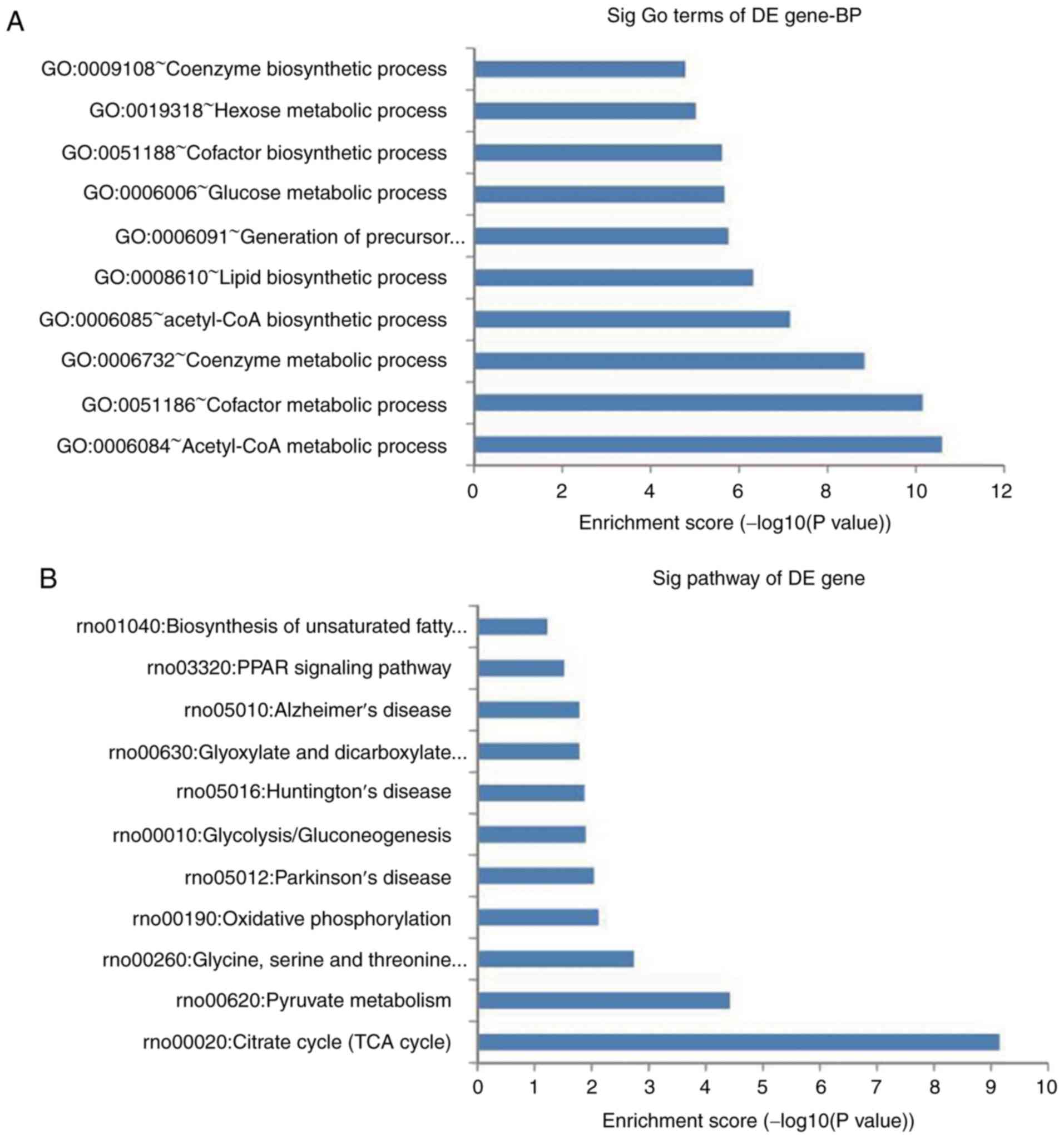
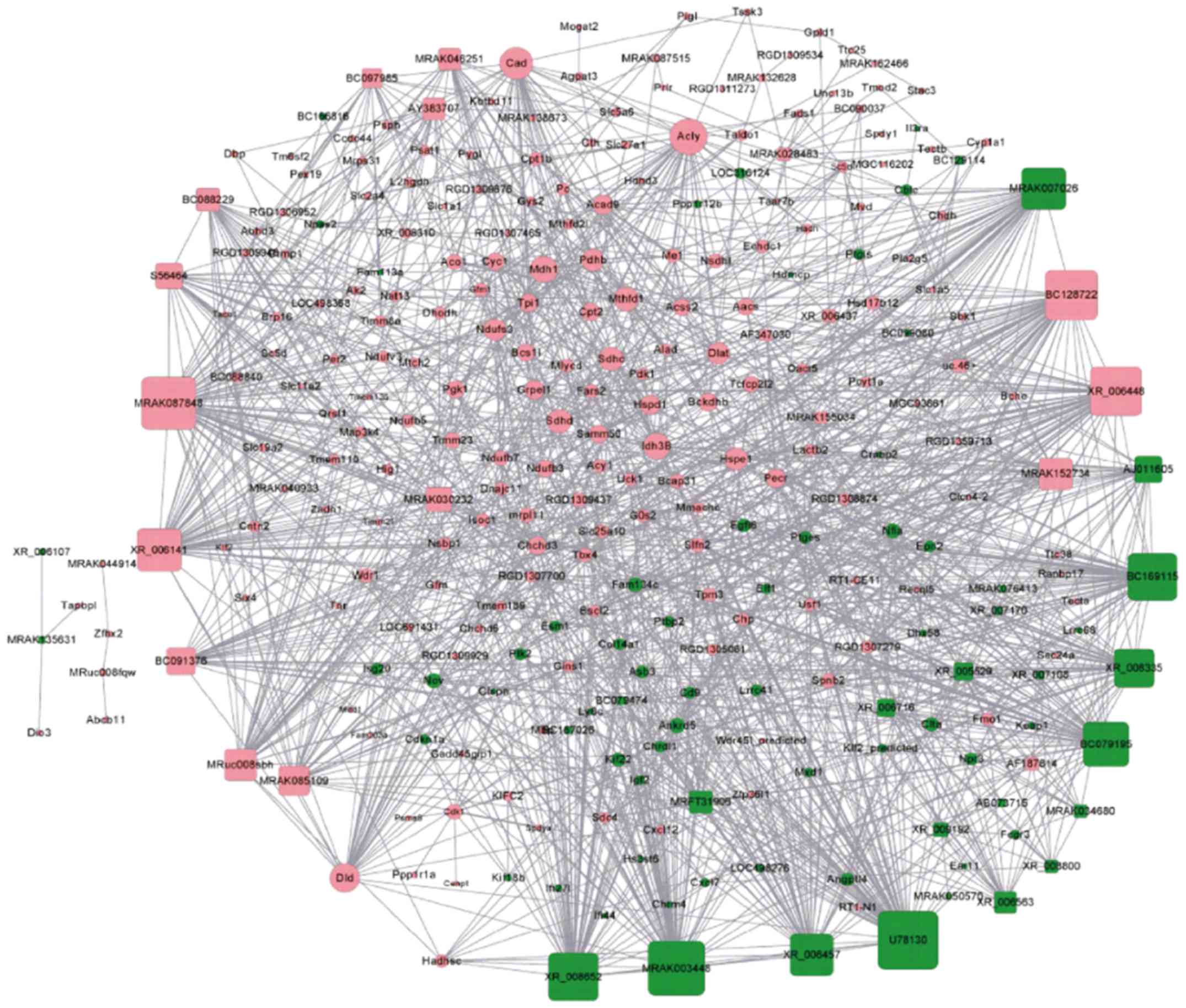
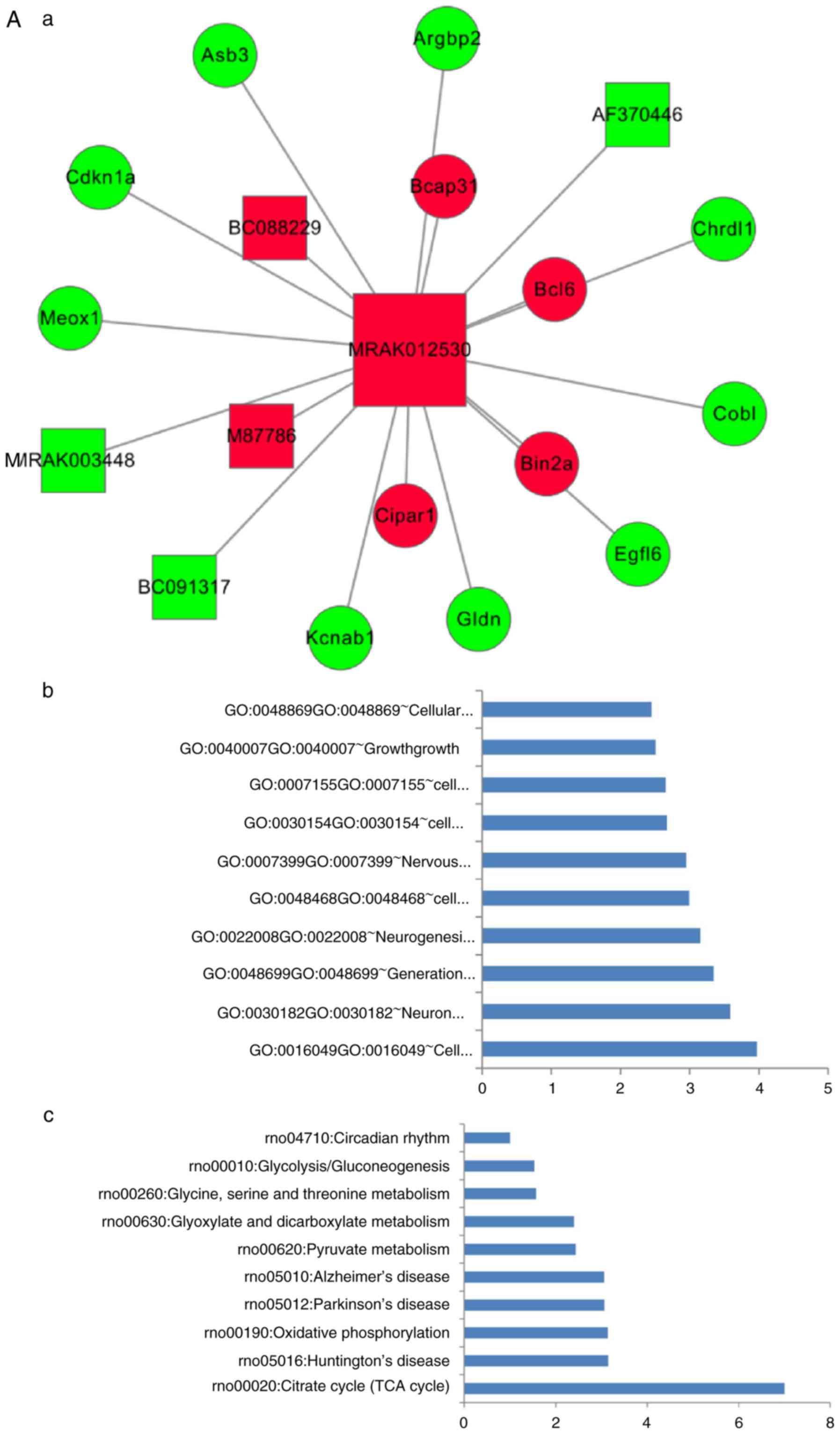
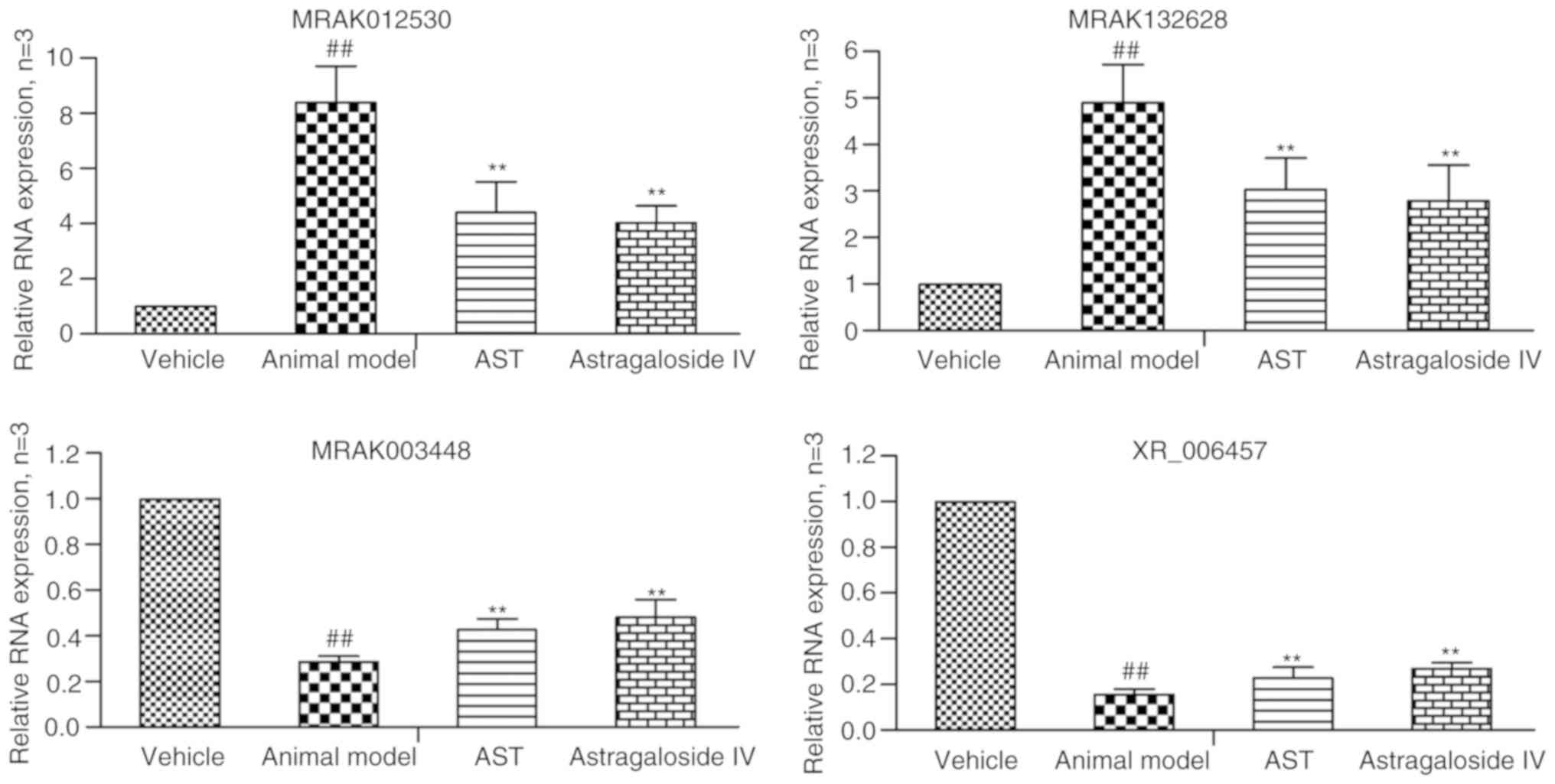
|
1
|
Sarabi ZS, Saeidi MG, Khodashahi M, Rezaie
AE, Hashemzadeh K, Khodashahi R and Heidari H: Evaluation of the
anti-inflammatory effects of atorvastatin on patients with
rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized clinical trial. Electron
Physician. 8:2700–2706. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wechalekar MD, Lester S, Hill CL, Lee A,
Rischmueller M, Smith MD, Walker JG and Proudman SM: Active foot
synovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Unstable remission
status, radiographic progression, and worse functional outcomes in
patients with foot synovitis in apparent remission. Arthritis Care
Res (Hoboken). 68:1616–1623. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang Wu Q, Wang Y, Yu Q, Wang D, Song Y,
Liu L, Ye Z, Xu X, Cao PH, et al: The bispecific antibody aimed at
the vicious circle of IL-1β and IL-17A, is beneficial for the
collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis of mice through NF-κB
signaling pathway. Immunol Lett. 179:68–79. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Burmester GR, Rubbert-Roth A, Cantagrel A,
Hall S, Leszczynski P, Feldman D, Rangaraj MJ, Roane G, Ludivico C,
Bao M, et al: Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous tocilizumab
versus intravenous tocilizumab in combination with traditional
DMARDs in patients with RA at week 97 (SUMMACTA). Ann Rheum Dis.
75:68–74. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Rossi D, Modena V, Sciascia S and
Roccatello D: Rheumatoid arthritis: Biological therapy other than
anti-TNF. Int Immunopharmacol. 27:185–188. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang L, Lv Q, Xie D, Shi T and Wen C:
Deciphering the potential pharmaceutical mechanism of chinese
traditional medicine (Gui-Zhi-Shao-Yao-Zhi-Mu) on rheumatoid
arthritis. Sci Rep. 6:226022016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang Y, Mao X, Guo Q, Bai M, Zhang B, Liu
C, Sun Y, Li S and Lin N: Pathway of PPAR-gamma coactivators in
thermogenesis: A pivotal traditional Chinese medicine-associated
target for individualized treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Oncotarget. 7:15885–15900. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin YC, Chang CW and Wu CR:
Anti-nociceptive, anti-inflammatory and toxicological evaluation of
Fang-Ji-Huang-Qi-Tang in rodents. BMC Complement Altern Med.
15:102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu XY, Xu L, Wang Y, Li JX, Zhang Y,
Zhang C, Wang SS and Zhang XM: Protective effects of total
flavonoids of Astragalus against adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats
by regulating OPG/RANKL/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
44:105–114. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang JB, Qiu JD, Yang LH, He JP, Smith GW
and Li HQ: Therapeutic effects of Astragalus polysaccharides on
inflammation and synovial apoptosis in rats with adjuvant-induced
arthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 13:396–405. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wan L, Liu J, Huang CB, Wang Y, Chen X,
Zhang WD, Wang GZ, Fan HX, Ge Y, Chen RL, et al: Xinfeng capsule
for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients with decreased
pulmonary function -a randomized vehicleled clinical trial. Chin J
Integr Med. 22:168–176. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen X, Wang DD, Wei T, He SM, Zhang GY
and Wei QL: Effects of astragalosides from Radix Astragali on high
glucose-induced proliferation and extracellular matrix accumulation
in glomerular mesangial cells. Exp Ther Med. 11:2561–2566. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu YY, Wu WY, Gong HL, Li WZ and Yin YY:
Astragalosides attenuate learning and memory impairment in rats
following ischemiareperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep. 9:1319–1324.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu JM, Zhang XB, Jiang W, Wang HD and
Zhang YN: Astragalosides promote angiogenesis via vascular
endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in a
rat animal animal model of myocardial infarction. Mol Med Rep.
12:6718–6726. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang Q, Lu JT, Zhou AW, Wang B, He GW and
Chen MZ: Antinociceptive effect of astragalosides and its mechanism
of action. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 22:809–812. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Juan L, Wang G, Radovich M, Schneider BP,
Clare SE, Wang Y and Liu Y: Potential roles of microRNAs in
regulating long intergenic noncoding RNAs. BMC Med Genomics.
6(Suppl 1): S72013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ye N, Rao S, Du T, Hu H, Liu Z, Shen Y and
Xu Q: Intergenic variants may predispose to major depression
disorder through regulation of long non-coding RNA expression.
Gene. 601:21–26. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Szcześniak MW and Makałowska I: lncRNA-RNA
interactions across the human transcriptome. PLoS One.
11:e01503532016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang L, Xu L, Wang Q, Wang M and An G:
Dysregulation of long non-coding RNA profiles in human colorectal
cancer and its association with overall survival. Oncol Lett.
12:4068–4074. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rühle F and Stoll M: Long non-coding RNA
databases in cardiovascular research. Genomics Proteomics
Bioinformatics. 14:191–199. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Messemaker TC, Frank-Bertoncelj M, Marques
RB, Adriaans A, Bakker AM, Daha N, Gay S, Huizinga TW, Toes RE,
Mikkers HM and Kurreeman F: A novel long non-coding RNA in the
rheumatoid arthritis risk locus TRAF1-C5 influences C5 mRNA levels.
Genes Immun. 17:85–92. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li R, Cai L, Hu CM, Wu TN and Li J:
Expression of hedgehog signal pathway in articular cartilage is
associated with the severity of cartilage damage in rats with
adjuvant-induced arthritis. J Inflamm (Lond). 12:242015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hao J, Wu X, Setrerrahmane S, Qian K, Hou
Y, Yu L, Lin C, Wu Q and Xu H: Combination therapy of PEG-HM-3 and
methotrexate retards adjuvant-induced arthritis. Int J Mol Sci.
18:E15382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen Y, Wang QW, Zuo J, Chen JW and Li X:
Anti-arthritic activity of ethanol extract of Claoxylon indicum on
Freund's complete adjuvant-induced arthritis in mice. BMC
complement Altern Med. 17:112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang H, Qin XJ, Li WP, Ma R, Wang T and
Li ZQ: lncRNAs expression in adjuvant-induced arthritis rats
reveals the potential role of lncRNAs contributing to rheumatoid
arthritis pathogenesis. Gene. 593:131–142. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chen D, Liu D, Liu D, He M, Peng A, Xu J,
Lin L, Luo F, Chen L, Huang X, et al: Rheumatoid arthritis
fibroblast-like synoviocyte suppression mediated by PTEN involves
survivin gene silencing. Sci Rep. 7:3672017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang J, Zhao F and Nie J: Anti-rheumatic
effects of Aconitum leucostomum Worosch. on human fibroblast-like
synoviocyte rheumatoid arthritis cells. Exp Ther Med. 14:453–460.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun Y, Pan J, Zhang N, Wei W, Yu S and Ai
L: Knockdown of long non-coding RNA H19 inhibits multiple myeloma
cell growth via NF-κB pathway. Sci Rep. 7:180792017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Xu YZ, Sun N, Liu JH, Chen FF,
Guan XL, Li A, Wang F, Zhao QF, Wang HY, et al: Long noncoding RNA
expression profile in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients
with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 18:2272016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lu MC, Yu HC, Yu CL, Huang HB, Koo M, Tung
CH and Lai NS: Increased expression of long noncoding RNAs
LOC100652951 and LOC100506036 in T cells from patients with
rheumatoid arthritis facilitates the inflammatory responses.
Immunol Res. 64:576–583. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Luo Q, Li X, Xu C, Zeng L, Ye J, Guo Y,
Huang Z and Li J: Integrative analysis of long non-coding RNAs and
messenger RNA expression profiles in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Mol Med Rep. 17:3489–3496. 2018.
|
|
33
|
Cheng B, Zheng H, Wu F, Wu J, Liu X, Tang
C, Lu S, Chen Z, Song F, Ruan J, et al: Metabolomics analysis of
Danggui Sini decoction on treatment of collagen-induced arthritis
in rats. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
1061-1062:282–291. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gu Y, Lu C, Zha Q, Kong H, Lu X, Lu A and
Xu G: Plasma metabonomics study of rheumatoid arthritis and its
Chinese medicine subtypes by using liquid chromatography and gas
chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. Mol Biosyst.
8:1535–1543. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huffman KM, Jessee R, Andonian B, Davis
BN, Narowski R, Huebner JL, Kraus VB, McCracken J, Gilmore BF, Tune
KN, et al: Molecular alterations in skeletal muscle in rheumatoid
arthritis are related to disease activity, physical inactivity, and
disability. Arthritis Res Ther. 19:122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li XF, Sun YY, Bao J, Chen X, Li YH, Yang
Y, Zhang L, Huang C, Wu BM, Meng XM and Li J: Functional role of
PPAR-γ on the proliferation and migration of fibroblast-like
synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep. 7:126712017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lin Y and Luo Z: Aberrant methylation
patterns affect the molecular pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.
Int Immunopharmacol. 46:141–145. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang A, Zhang J, Kaipainen A, Lucas JM
and Yang H: Long non-coding RNA: A newly deciphered 'code' in
prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 375:323–330. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Széll M, Danis J, Bata-Csörgő Z and Kemény
L: PRINS, a primate-specific long non-coding RNA, plays a role in
the keratinocyte stress response and psoriasis pathogenesis.
Pflugers Arch. 468:935–943. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ye S, Yang L, Zhao X, Song W, Wang W and
Zheng S: Bioinformatics method to predict two regulation mechanism:
TF-miRNA-mRNA and lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA in pancreatic cancer. Cell
Biochem Biophys. 70:1849–1858. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen R, Li WX, Sun Y, Duan Y, Li Q, Zhang
AX, Hu JL, Wang YM and Gao YD: Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA and
mRNA expression profiles in lung cancer. Clin Lab. 63:313–320.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang S, Ning Q, Zhang G, Sun H, Wang Z and
Li Y: Construction of differential mRNA-lncRNA crosstalk networks
based on ceRNA hypothesis uncover key roles of lncRNAs implicated
in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:85728–85740.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Song C, Zhang J, Liu Y, Pan H, Qi HP, Cao
YG, Zhao JM, Li S, Guo J, Sun HL and Li CQ: Construction and
analysis of cardiac hypertrophy-associated lncRNA-mRNA network
based on competitive endogenous RNA reveal functional lncRNAs in
cardiac hypertrophy. Oncotarget. 7:10827–10840. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Molina-Pinelo S, Salinas A, Moreno-Mata N,
Ferrer I, Suarez R, Andrés-León E, Rodríguez-Paredes M, Gutekunst
J, Jantus-Lewintre E, Camps C, et al: Impact of DLK1-DIO3 imprinted
cluster hypomethylation in smoker patients with lung cancer.
Oncotarget. 9:4395–4410. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Moon JS, Nakahira K, Chung KP, DeNicola
GM, Koo MJ, Pabón MA, Rooney KT, Yoon JH, Ryter SW, Stout-Delgado H
and Choi AM: NOX4-dependent fatty acid oxidation promotes NLRP3
inflammasome activation in macrophages. Nat Med. 22:1002–1012.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jiang H, Liu J, Wang T, Gao JR, Sun Y,
Huang CB, Meng M and Qin XJ: Urinary metabolite profiling provides
potential differentiation to explore the mechanisms of
adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Biomed Chromatogr.
30:1397–1405. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jiang H, Liu J, Wang T, Gao JR, Sun Y,
Huang CB, Meng M and Qin XJ: Mechanism of xinfeng capsule on
adjuvant-induced arthritis via analysis of urinary metabolomic
profiles. Autoimmune Dis. 2016:56909352016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Smagris E, Gilyard S, BasuRay S, Cohen JC
and Hobbs HH: Inactivation of Tm6sf2, a gene defective in fatty
liver disease, impairs lipidation but not secretion of very low
density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 291:10659–10676. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sookoian S and Pirola CJ: Meta-analysis of
the influence of TM6SF2 E167K variant on plasma concentration of
aminotransferases across different populations and diverse liver
phenotypes. Sci Rep. 6:277182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ko R and Lee SY: Glycogen synthase kinase
3β in Toll-like receptor signaling. BMB Rep. 49:305–310. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Malaver-Ortega LF, Sumer H, Liu J and
Verma PJ: Inhibition of JAK-STAT ERK/MAPK and glycogen synthase
kinase-3 induces a change in gene expression profile of bovine
induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2016:51279842016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sekeli R, Abdullah JO, Namasivayam P, Muda
P, Abu Bakar UK, Yeong WC and Pillai V: RNA interference of
1-aminocyclo-propane-1-carboxylic acid oxidase (ACO1 and ACO2)
genes expression prolongs the shelf life of Eksotika (Carica papaya
L.) papaya fruit. Molecules. 19:8350–8362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhu X, Wang A, Zhu S and Zhang L:
Expression of ACO1, ERS1 and ERF1 genes in harvested bananas in
relation to heat-induced defense against Colletotrichum musae. J
Plant Physiol. 168:1634–1640. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang R, Zhong L, Zhou J and Peng Y:
Complement-C1q TNF-related protein 3 alleviates mesangial cell
activation and inflammatory response stimulated by secretory IgA.
Am J Nephrol. 43:460–468. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ruderman EM: Rheumatoid arthritis: IL-6
inhibition in RA-déjà vu all over again? Nat Rev Rheumatol.
11:321–322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sapan HB, Paturusi I, Jusuf I, Patellongi
I, Massi MN, Pusponegoro AD, Arief SK, Labeda I, Islam AA, Rendy L
and Hatta M: Pattern of cytokine (IL-6 and IL-10) level as
inflammation and anti-inflammation mediator of multiple organ
dysfunction syndrome (MODS) in polytrauma. Int J Burns Trauma.
6:37–43. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Li XY, Han CM, Wang Y, Liu HZ, Wu ZF, Gao
QH and Zhao SH: Expression patterns and association analysis of the
porcine DHX58 gene. Anim Genet. 41:537–540. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Aranaz P, Hurtado C, Erquiaga I, Miguéliz
I, Ormazábal C, Cristobal I, García-Delgado M, Novo FJ and Vizmanos
JL: CBL mutations in myeloproliferative neoplasms are also found in
the gene's prolinerich domain and in patients with the V617FJAK2.
Haematologica. 97:1234–1241. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Huang F and Gu H: Negative regulation of
lymphocyte development and function by the Cbl family of proteins.
Immunol Rev. 224:229–238. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sakaguchi S, Benham H, Cope AP and Thomas
R: T-cell receptor signaling and the pathogenesis of autoimmune
arthritis: Insights from mouse and man. Immunol Cell Biol.
90:277–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Olasz K, Boldizsar F, Kis-Toth K, Tarjanyi
O, Hegyi A, van Eden W, Rauch TA, Mikecz K and Glant TT: T cell
receptor (TCR) signal strength vehicles arthritis severity in
proteo-glycan-specific TCR transgenic mice. Clin Exp Immunol.
167:346–355. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yang Y, Dong Q and Li R: Matrine induces
the apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes derived from rats
with collagen-induced arthritis by suppressing the activation of
the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 39:307–316. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
63
|
Isomäki P, Junttila I, Vidqvist KL,
Korpela M and Silvennoinen O: The activity of JAK-STAT pathways in
rheumatoid arthritis: Constitutive activation of STAT3 correlates
with interleukin 6 levels. Rheumatology (Oxford). 54:1103–1113.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Ohshima S, Mima T, Sasai M, Nishioka K,
Shimizu M, Murata N, Yoshikawa H, Nakanishi K, Suemura M, McCloskey
RV, et al: Tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) interferes with
Fas-mediated apoptotic cell death on rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
synovial cells: A possible mechanism of rheumatoid synovial
hyperplasia and a clinical benefit of anti-TNF-alpha therapy for
RA. Cytokine. 12:281–288. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sakurai N, Kuroiwa T, Ikeuchi H, Hiramatsu
N, Maeshima A, Kaneko Y, Hiromura K and Nojima Y: Expression of
IL-19 and its receptors in RA: Potential role for synovial
hyperplasia formation. Rheumatology (Oxford). 47:815–820. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Ma N, Ma Y, Nakashima A, Kikkawa U and
Furuyashiki T: The loss of Lam2 and Npr2-Npr3 diminishes the
vacuolar localization of Gtr1-Gtr2 and disinhibits TORC1 activity
in fission yeast. PLoS One. 11:e01562392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|