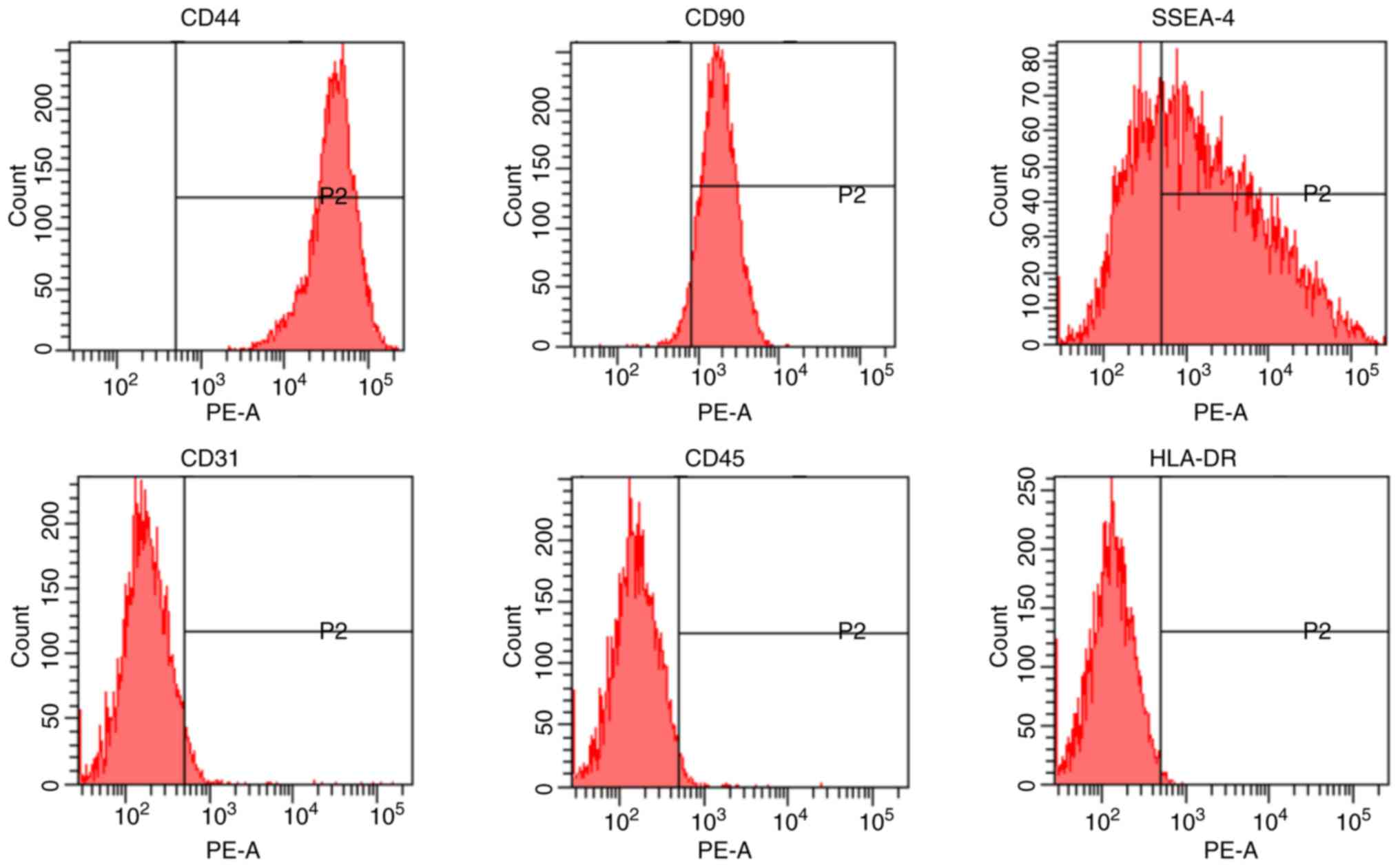
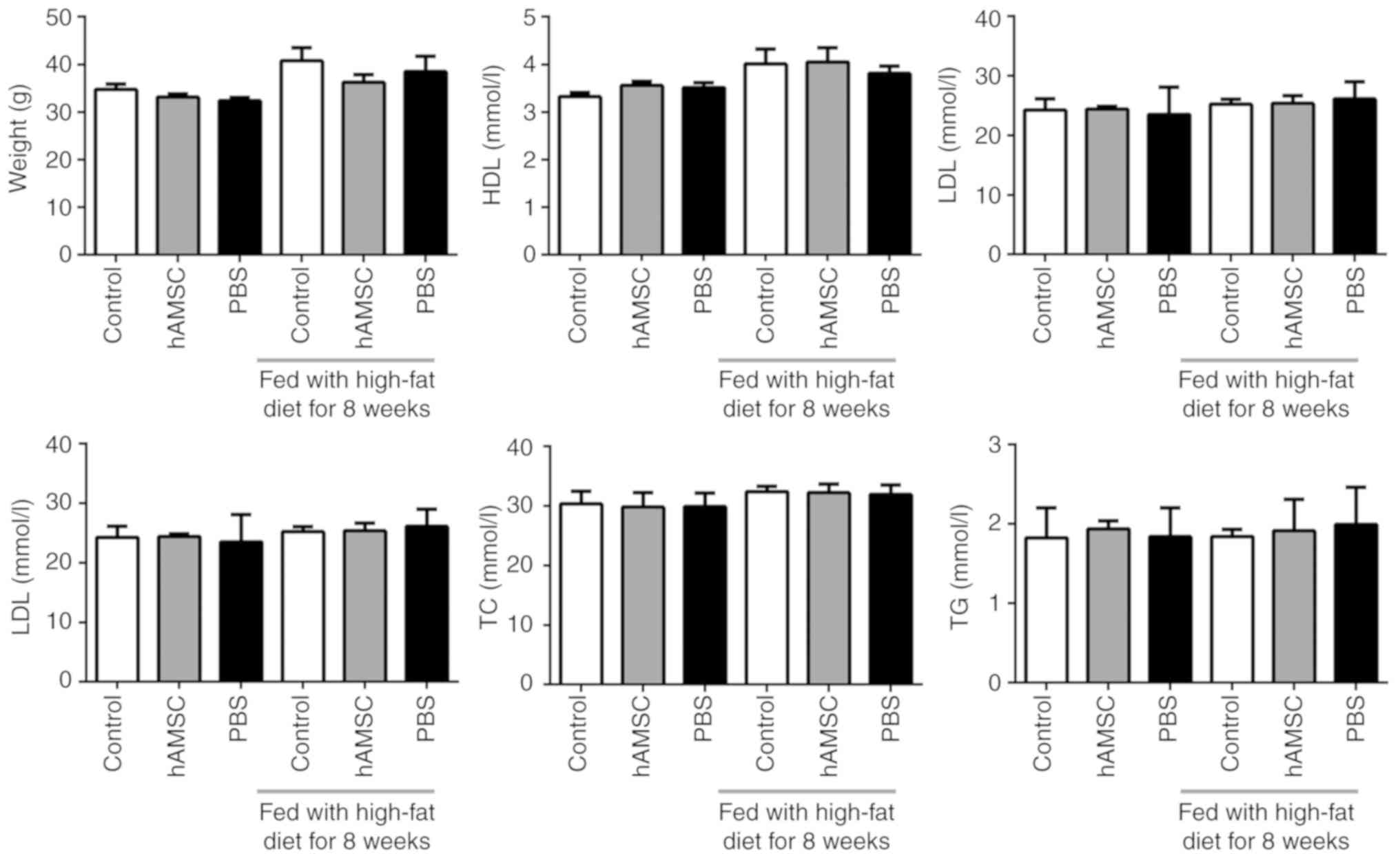
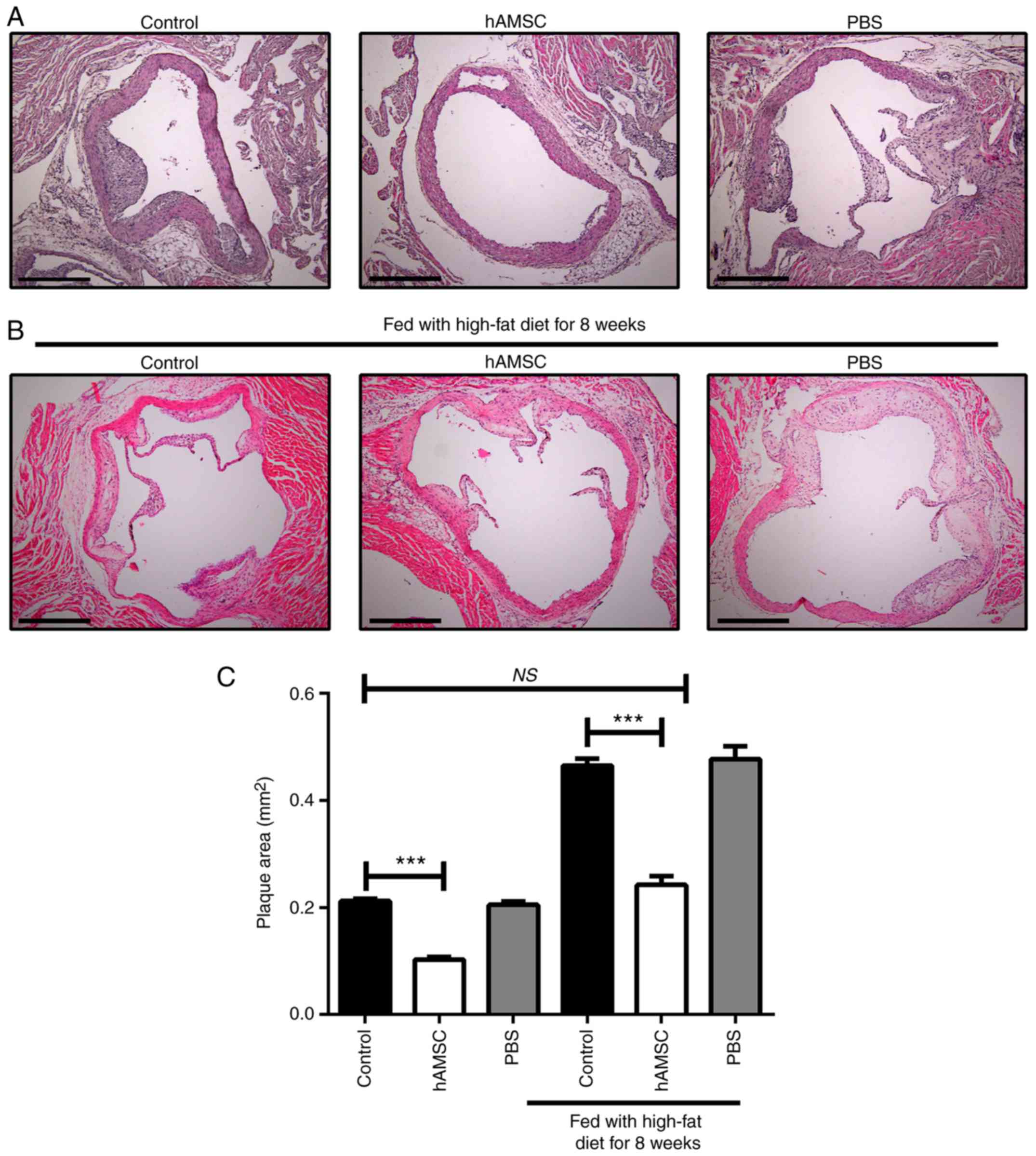
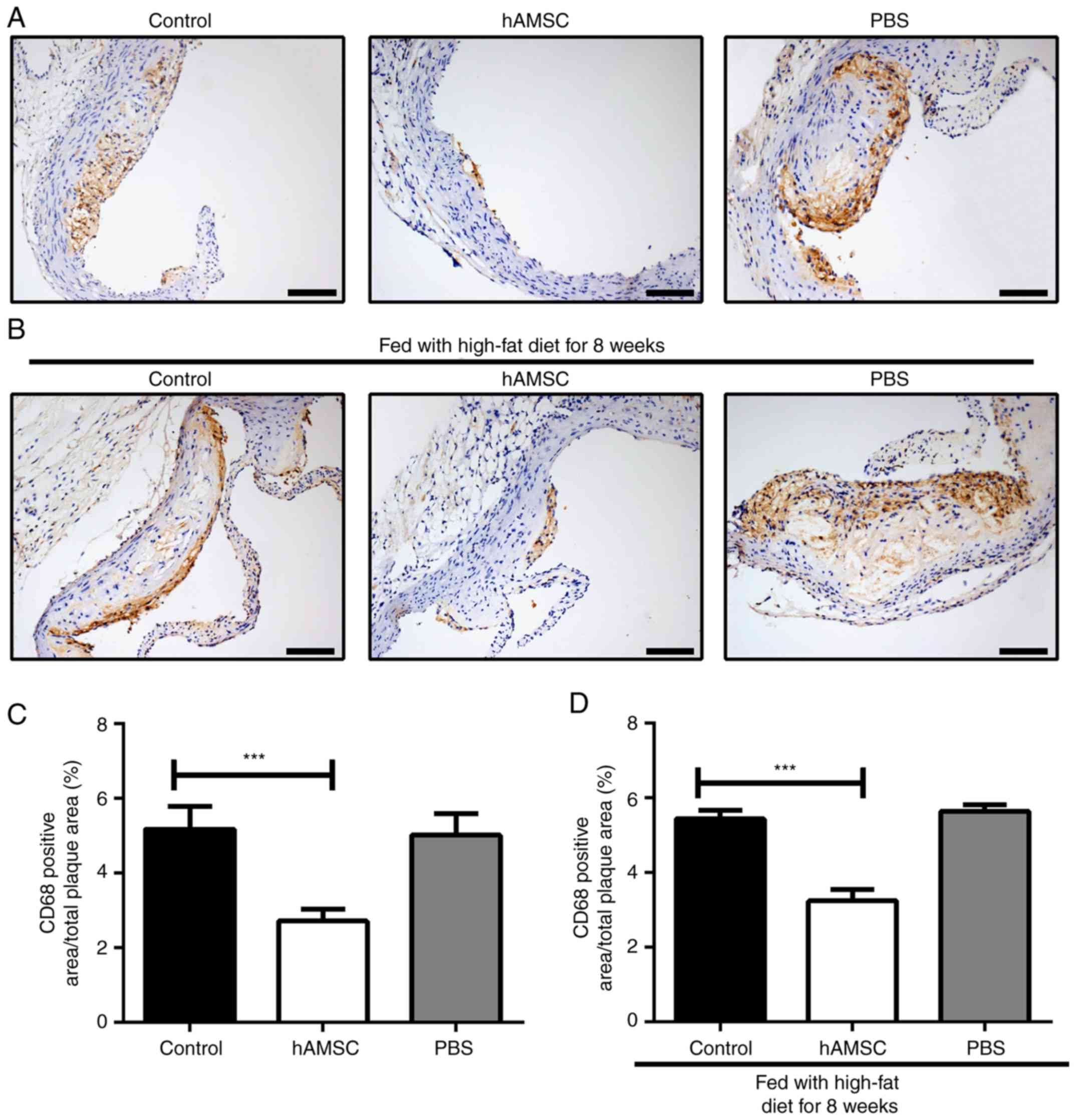
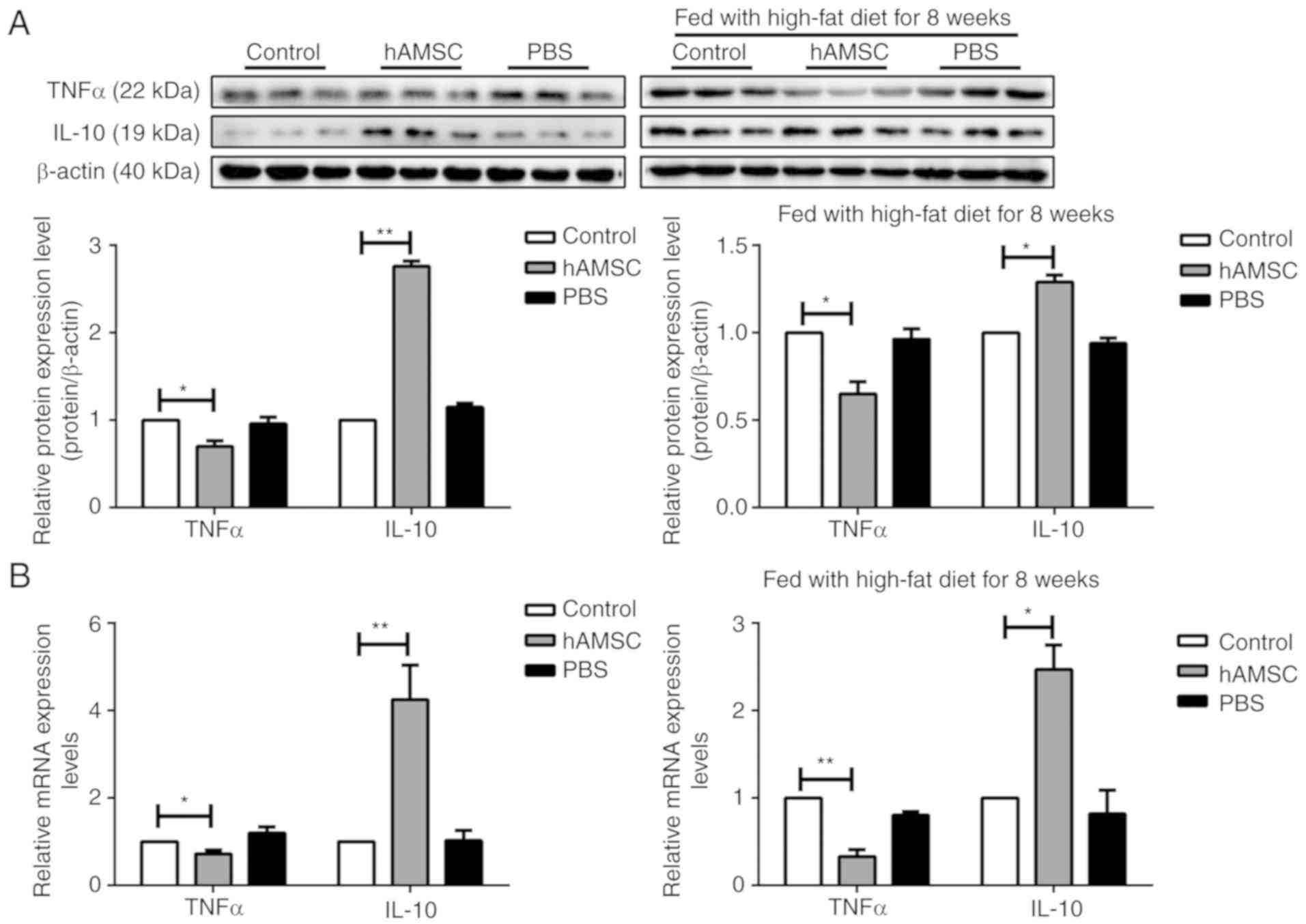
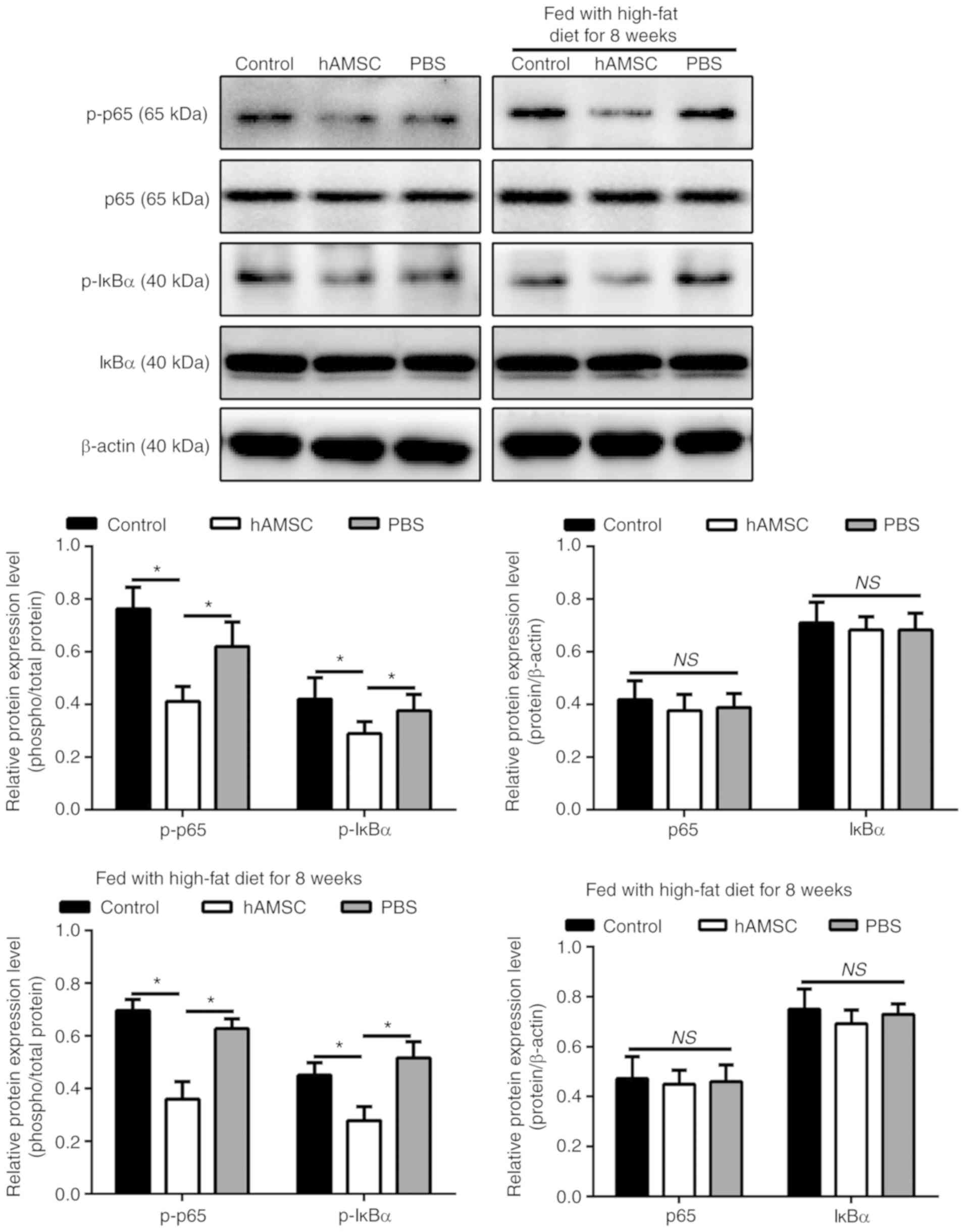
|
1
|
Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett
DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, de Ferranti S, Després JP, Fullerton HJ,
Howard VJ, et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2015 update:
A report from the american heart association. Circulation. 131. pp.
e29–e322. 2015
|
|
2
|
Frostegård J: Immunity, atherosclerosis
and cardiovascular disease. BMC Med. 11:1172013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang X, Huang F, Chen Y, Qian X and Zheng
SG: Progress and prospect of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy in
atherosclerosis. Am J Transl Res. 8:4017–4024. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu DJ, Xu JZ, Wu YJ, Jean-Charles L, Xiao
B, Gao PJ and Zhu DL: Effects of fasudil on early atherosclerotic
plaque formation and established lesion progression in
apolipoprotein E-knockout mice. Atherosclerosis. 207:68–73. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li Q, Sun W, Wang X, Zhang K, Xi W and Gao
P: Skin-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate atherosclerosis
via modulating macrophage function. Stem Cells Transl Med.
4:1294–1301. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
De Jager SC and Pasterkamp G: Crosstalk of
lipids and inflammation in atherosclerosis: The PRO of PGRN?
Cardiovasc Res. 100:4–6. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Johansson ME, Zhang XY, Edfeldt K,
Lundberg AM, Levin MC, Borén J, Li W, Yua XM, Folkersen L, Eriksson
P, et al: Innate immune receptor NOD2 promotes vascular
inflammation and formation of lipid-rich necrotic cores in
hypercholesterolemic mice. Eur J Immunol. 44:3081–3092. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Khan R, Spagnoli V, Tardif JC and L'Allier
PL: Novel anti-inflammatory therapies for the treatment of
atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 240:497–509. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mendel I, Yacov N, Harats D and Breitbart
E: Therapies targeting innate immunity for fighting inflammation in
atherosclerosis. Curr Pharm Des. 21:1185–1195. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Asciutto G, Dias NV, Edsfeldt A, Alm R,
Fredrikson GN, Gonçalves I and Nilsson J: Low levels of IgG
autoantibodies against the apolipoprotein B antigen p210 increases
the risk of cardiovascular death after carotid endarterectomy.
Atherosclerosis. 239:289–294. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tedgui A and Mallat Z: Cytokines in
atherosclerosis: Pathogenic and regulatory pathways. Physiol Rev.
86:515–581. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Little PJ, Chait A and Bobik A: Cellular
and cytokine-based inflammatory processes as novel therapeutic
targets for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis.
Pharmacol Ther. 131:255–268. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Han X and Boisvert WA: Interleukin-10
protects against atherosclerosis by modulating multiple atherogenic
macrophage function. Thromb Haemost. 113:505–512. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shapiro MD and Fazio S: From lipids to
inflammation: New approaches to reducing atherosclerotic risk. Circ
Res. 118:732–749. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hague W, Forder P, Simes J, Hunt D, Tonkin
A and Investigators L: Effect of pravastatin on cardiovascular
events and mortality in 1516 women with coronary heart disease:
Results from the long-term intervention with pravastatin in
ischemic disease (LIPID) study. Am Heart J. 145:643–651. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Libby P: The forgotten majority:
Unfinished business in cardiovascular risk reduction. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 46:1225–1228. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Serban MC, Banach M and Mikhailidis DP:
Clinical implications of the IMPROVE-IT trial in the light of
current and future lipid-lowering treatment options. Expert Opin
Pharmacother. 17:369–380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang QZ, Su WR, Shi SH, Wilder-Smith P,
Xiang AP, Wong A, Nguyen AL, Kwon CW and Le AD: Human
gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells elicit polarization of m2
macrophages and enhance cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cells.
28:1856–1868. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chai NL, Zhang XB, Chen SW, Fan KX and
Linghu EQ: Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate
liver fibrosis in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 22:6036–6048. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tan L, Dai T, Liu D, Chen Z, Wu L, Gao L,
Wang Y and Shi C: Contribution of dermal-derived mesenchymal cells
during liver repair in two different experimental models. Sci Rep.
6:253142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xie Z, Hao H, Tong C, Cheng Y, Liu J, Pang
Y, Si Y, Guo Y, Zang L, Mu Y and Han W: Human umbilical
cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells elicit macrophages into an
anti-inflammatory phenotype to alleviate insulin resistance in type
2 diabetic rats. Stem Cells. 34:627–639. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Seebach E, Freischmidt H, Holschbach J,
Fellenberg J and Richter W: Mesenchymal stroma cells trigger early
attraction of M1 macrophages and endothelial cells into fibrin
hydrogels, stimulating long bone healing without long-term
engraftment. Acta Biomater. 10:4730–4741. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Braza F, Dirou S, Forest V, Sauzeau V,
Hassoun D, Chesné J, Cheminant-Muller MA, Sagan C, Magnan A and
Lemarchand P: Mesenchymal stem cells induce suppressive
macrophages-through phagocytosis in a mouse model of asthma. Stem
Cells. 34:1836–1845. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maria ATJ, Toupet K, Maumus M, Fonteneau
G, Le Quellec A, Jorgensen C, Guilpain P and Noël D: Human adipose
mesenchymal stem cells as potent anti-fibrosis therapy for systemic
sclerosis. J Autoimmun. 70:31–39. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Frodermann V, van Duijn J, van Pel M, van
Santbrink PJ, Bot I, Kuiper J and de Jager SC: Mesenchymal stem
cells reduce murine atherosclerosis development. Sci Rep.
5:155592015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bobryshev YV, Ivanova EA, Chistiakov DA,
Nikiforov NG and Orekhov AN: Macrophages and their role in
atherosclerosis: Pathophysiology and transcriptome analysis. Biomed
Res Int. 2016:95824302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang ZX, Wang CQ, Li XY, Feng GK, Zhu HL,
Ding Y and Jiang XJ: Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate
atherosclerosis by elevating number and function of CD4(+)CD25
(+)FOXP3 (+) regulatory T-cells and inhibiting macrophage foam cell
formation. Mol Cell Biochem. 400:163–172. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, Fisher EA,
Gilroy DW, Goerdt S, Gordon S, Hamilton JA, Ivashkiv LB, Lawrence
T, et al: Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and
experimental guidelines. Immunity. 41:14–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Michaeli S, Dakwar V, Weidenfeld K,
Granski O, Gilon O, Schif-Zuck S, Mamchur A, Shams I and Barkan D:
Soluble mediators produced by pro-resolving macrophages inhibit
angiogenesis. Front Immunol. 9:7682018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Triantafyllou E, Woollard KJ, McPhail MJW,
Antoniades CG and Possamai LA: The role of monocytes and
macrophages in acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure. Front
Immunol. 9:29482018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hu Y, Liao L, Wang Q, Ma L, Ma G, Jiang X
and Zhao RC: Isolation and identification of mesenchymal stem cells
from human fetal pancreas. J Lab Clin Med. 141:342–349. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tsai MS, Lee JL, Chang YJ and Hwang SM:
Isolation of human multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from
second-trimester amniotic fluid using a novel two-stage culture
protocol. Hum Reprod. 19:1450–1456. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee OK, Kuo TK, Chen WM, Lee KD, Hsieh SL
and Chen TH: Isolation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from
umbilical cord blood. Blood. 103:1669–1675. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kmiecik G, Niklinska W, Kuc P,
Pancewicz-Wojtkiewicz J, Fil D, Karwowska A, Karczewski J and
Mackiewicz Z: Fetal membranes as a source of stem cells. Adv Med
Sci. 58:185–195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim EY, Lee KB and Kim MK: The potential
of mesenchymal stem cells derived from amniotic membrane and
amniotic fluid for neuronal regenerative therapy. BMB Rep.
47:135–140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xiao J: Human amniotic stem cells: Ideal
seed cells source for regenerative medicine. J Zunyi Med Univ.
38:439–449. 2015.
|
|
37
|
Kronsteiner B, Peterbauer-Scherb A,
Grillari-Voglauer R, Redl H, Gabriel C, van Griensven M and Wolbank
S: Human mesenchymal stem cells and renal tubular epithelial cells
differentially influence monocyte-derived dendritic cell
differentiation and maturation. Cell Immunol. 267:30–38. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Shu J, He X, Zhang L, Li H, Wang P and
Huang X: Human amnion mesenchymal cells inhibit
lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α and IL-1β production in THP-1
cells. Biol Res. 48:692015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Shoji M, Oskowitz A, Malone CD, Prockop DJ
and Pochampally R: Human mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) reduce
neointimal hyperplasia in a mouse model of flow-restriction by
transient suppression of anti-inflammatory cytokines. J Atheroscler
Thromb. 18:464–474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wu Q, Fang T, Lang H, Chen M, Shi P, Pang
X and Qi G: Comparison of the proliferation, migration and
angiogenic properties of human amniotic epithelial and mesenchymal
stem cells and their effects on endothelial cells. Int J Mol Med.
39:918–926. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Friedewald WT, Levy RI and Fredrickson DS:
Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein
cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative
ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 18:499–502. 1972.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Frost PH and Havel RJ: Rationale for use
of non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol rather than low-density
lipoprotein cholesterol as a tool for lipoprotein cholesterol
screening and assessment of risk and therapy. Am J Cardiol.
81:26B–31B. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Trusler O, Huang Z, Goodwin J and Laslett
AL: Cell surface markers for the identification and study of human
naive pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 26:36–43. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Fernandez Vallone VB, Romaniuk MA, Choi H,
Labovsky V, Otaegui J and Chasseing NA: Mesenchymal stem cells and
their use in therapy: What has been achieved? Differentiation.
85:1–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Murray RZ and Stow JL: Cytokine secretion
in macrophages: SNAREs, Rabs, and membrane trafficking. Front
Immunol. 5:5382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu Z, Han Y, Li L, Lu H, Meng G, Li X,
Shirhan M, Peh MT, Xie L, Zhou S, et al: The hydrogen sulfide
donor, GYY4137, exhibits anti-atherosclerotic activity in high fat
fed apolipo-protein E(−/−) mice. Br J Pharmacol. 169:1795–1809.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fisher EA: Regression of atherosclerosis:
The journey from the liver to the plaque and back. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 36:226–235. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Lu X: Impact of macrophages in
atherosclerosis. Curr Med Chem. 23:1926–1937. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Feig JE, Parathath S, Rong JX, Mick SL,
Vengrenyuk Y, Grauer L, Young SG and Fisher EA: Reversal of
hyperlipidemia with a genetic switch favorably affects the content
and inflammatory state of macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques.
Circulation. 123:989–998. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Potteaux S, Gautier EL, Hutchison SB, van
Rooijen N, Rader DJ, Thomas MJ, Sorci-Thomas MG and Randolph GJ:
Suppressed monocyte recruitment drives macrophage removal from
athero-sclerotic plaques of Apoe−/− mice during disease
regression. J Clin Invest. 121:2025–2036. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fang SM, Du DY, Li YT, van Rooijen N,
Rader DJ, Thomas MJ, Sorci-Thomas MG and Randolph GJ: Allogeneic
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation for stabilizing
and repairing of atherosclerotic ruptured plaque. Thromb Res.
131:e253–e257. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yao Y, Huang J, Geng Y, Qian H, Wang F,
Liu X, Shang M, Nie S, Liu N, Du X, et al: Paracrine action of
mesenchymal stem cells revealed by single cell gene profiling in
infarcted murine hearts. PLoS One. 10:e01291642015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Togel F, Weiss K, Yang Y, Hu Z, Zhang P
and Westenfelder C: Vasculotropic, paracrine actions of infused
mesenchymal stem cells are important to the recovery from acute
kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 292:F1626–F1635. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Perek B, Kowalska K, Kempisty B, Nowicki
A, Jankowski M, Nawrocki MJ and Malińska A: Role of macrophages in
the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and aortocoronary graft
disease. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 32:1055–1059. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ding Y, Huang L, Xian X, Yuhanna IS,
Wasser CR, Frotscher M, Mineo C, Shaul PW and Herz J: Loss of
Reelin protects against atherosclerosis by reducing
leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion and lesion macrophage
accumulation. Sci Signal. 9:ra292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Stewart CR, Stuart LM, Wilkinson K, van
Gils JM, Deng J, Halle A, Rayner KJ, Boyer L, Zhong R, Frazier WA,
et al: CD36 ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly
of a toll-like receptor 4 and 6 heterodimer. Nat Immunol.
11:155–161. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
58
|
Okabe Y and Medzhitov R: Tissue-specific
signals control reversible program of localization and functional
polarization of macrophages. Cell. 157:832–844. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yamamoto Y and Gaynor RB: IkappaB kinases:
Key regulators of the NF-kappaB pathway. Trends Biochem Sci.
29:72–79. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Putra A, Ridwan FB, Putridewi AI, Kustiyah
AR, Wirastuti K, Sadyah NAC, Rosdiana I and Munir D: The role of
TNF-α induced MSCs on suppressive inflammation by increasing TGF-β
and IL-10. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 6:1779–1783. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Maiti P, Peruzzaro S, Kolli N, Andrews M,
Al-Gharaibeh A, Rossignol J and Dunbar GL: Transplantation of
mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing interleukin-10 induces
autophagy response and promotes neuroprotection in a rat model of
TBI. J Cell Mol Med. Jun 4;2019(Epub ahead of print). http://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14396urisimpledoi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14396.
|
|
62
|
Nemeth K, Leelahavanichkul A, Yuen PS,
Mayer B, Parmelee A, Doi K, Robey PG, Leelahavanichkul K, Koller
BH, Brown JM, et al: Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via
prostaglandin E(2)-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to
increase their interleukin-10 production. Nat Med. 15:42–49. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Anderson LC: Institutional and IACUC
responsibilities for animal care and use education and training
programs. ILAR J. 48:90–95. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|