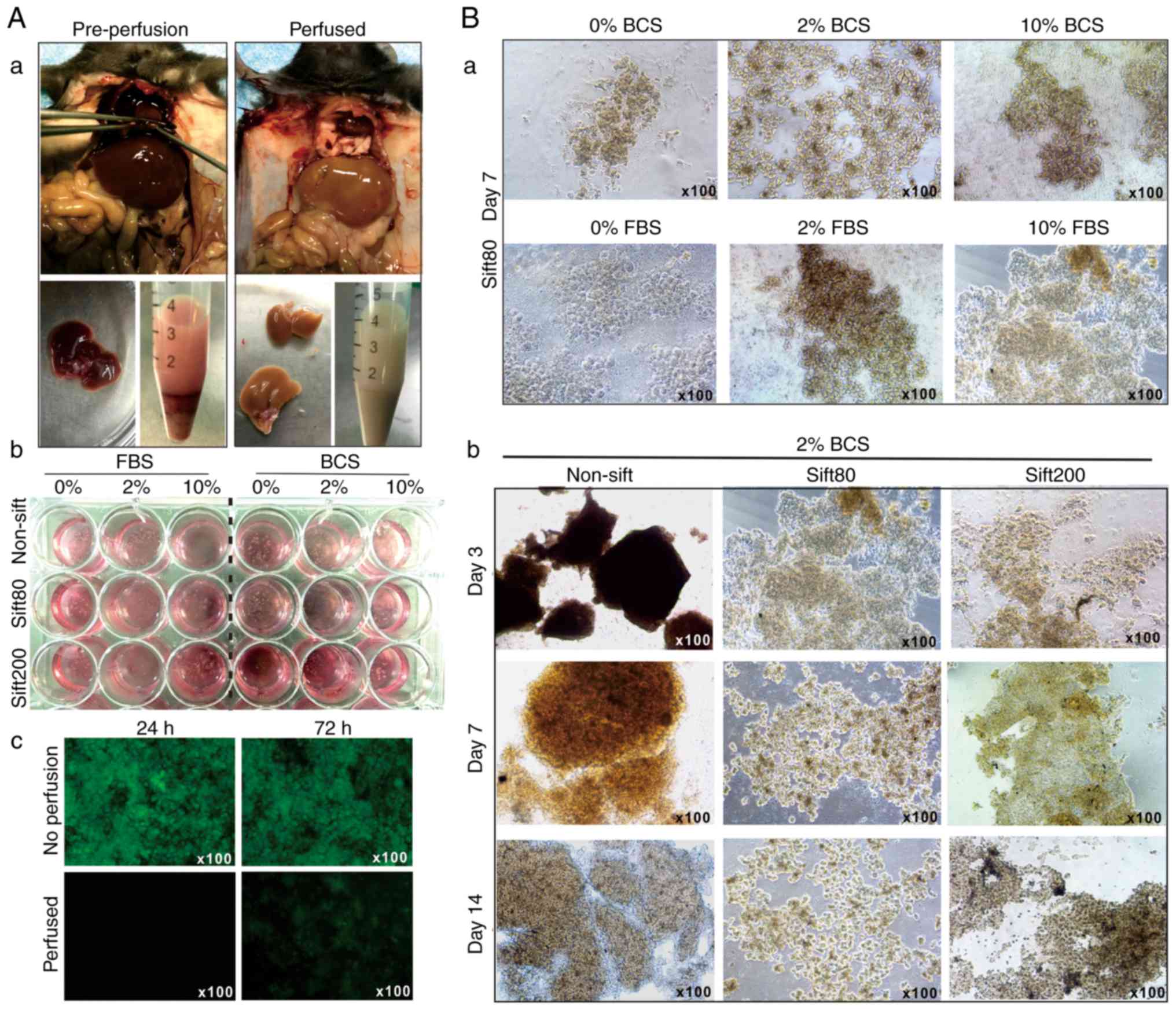
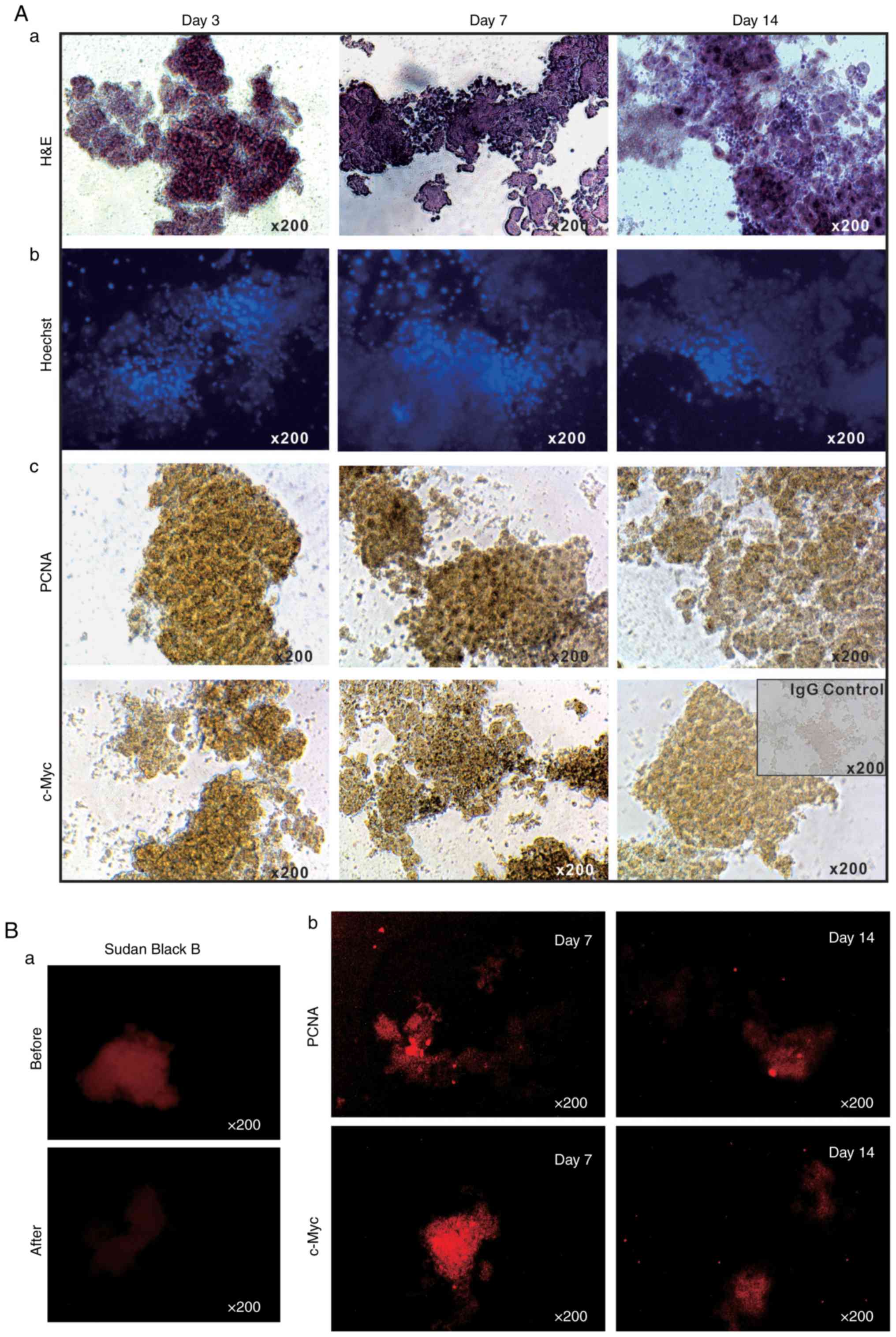
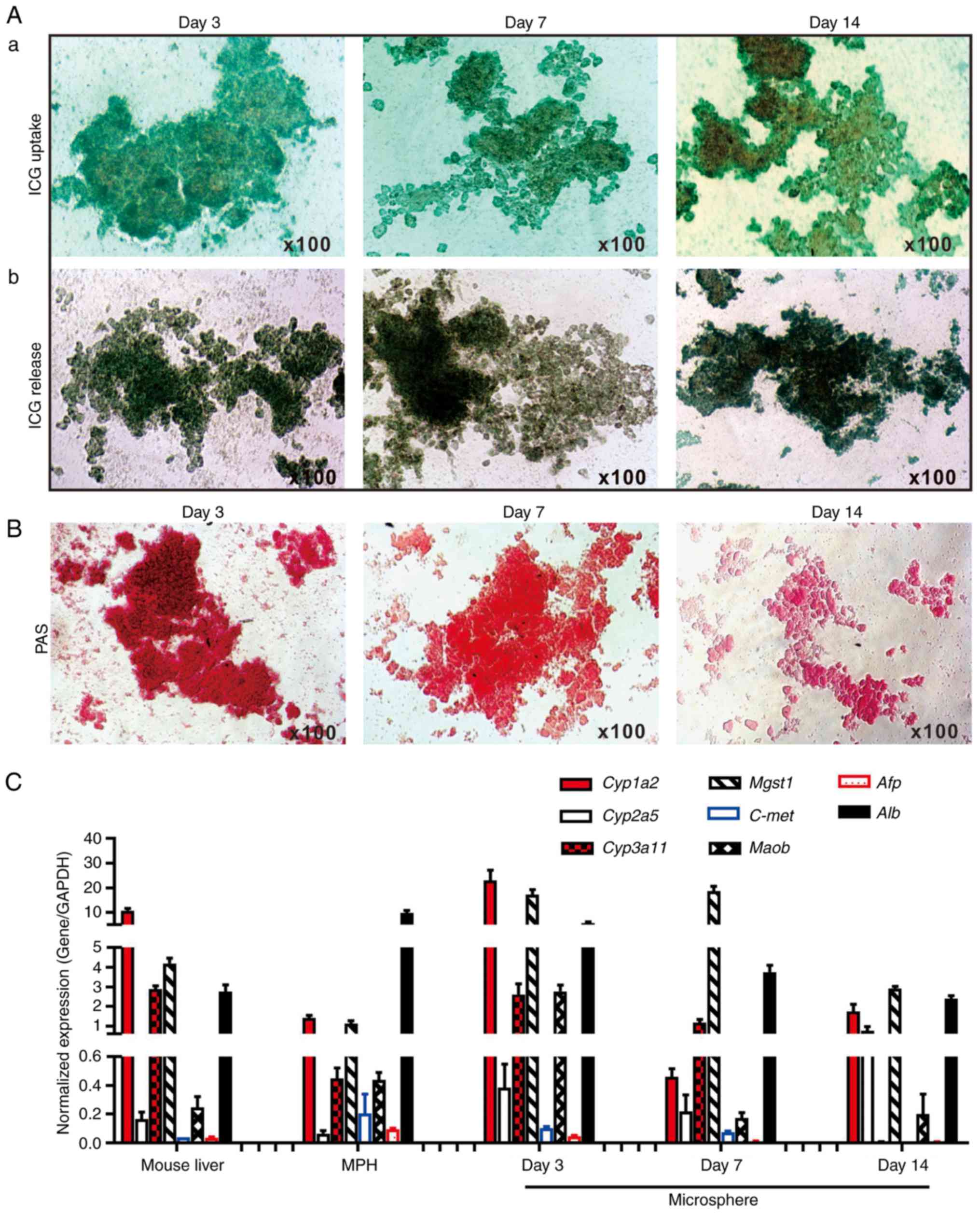
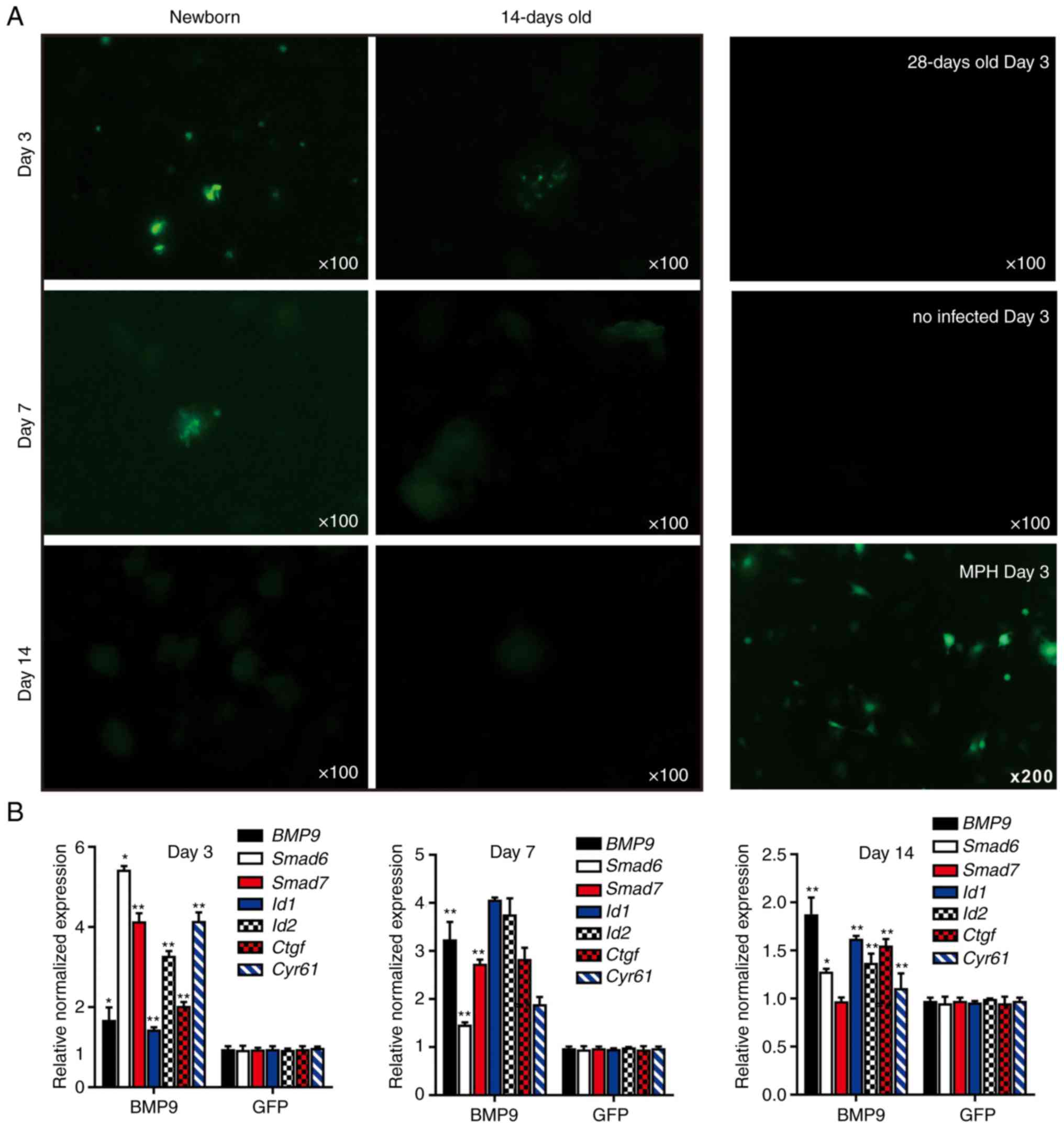
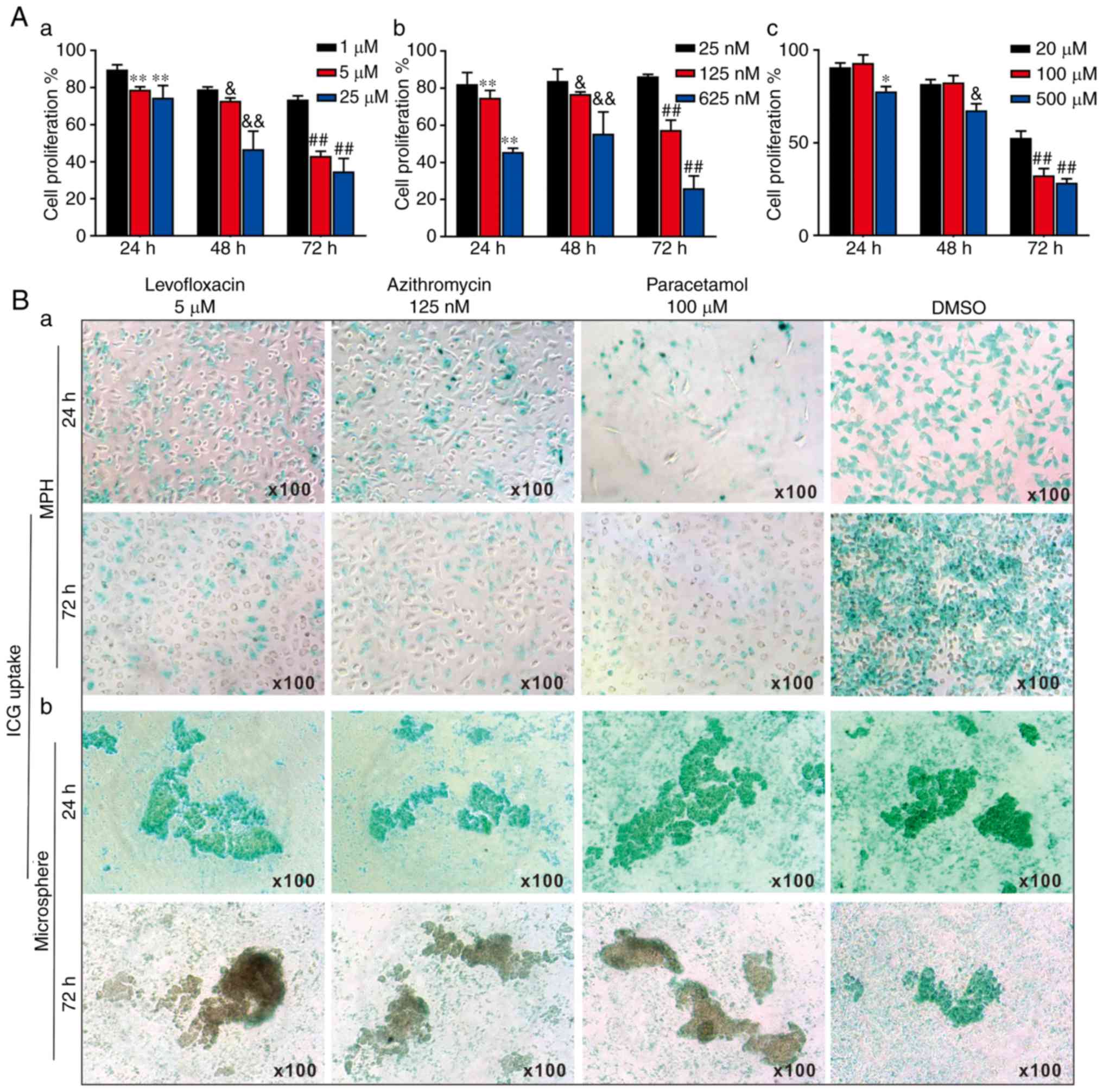
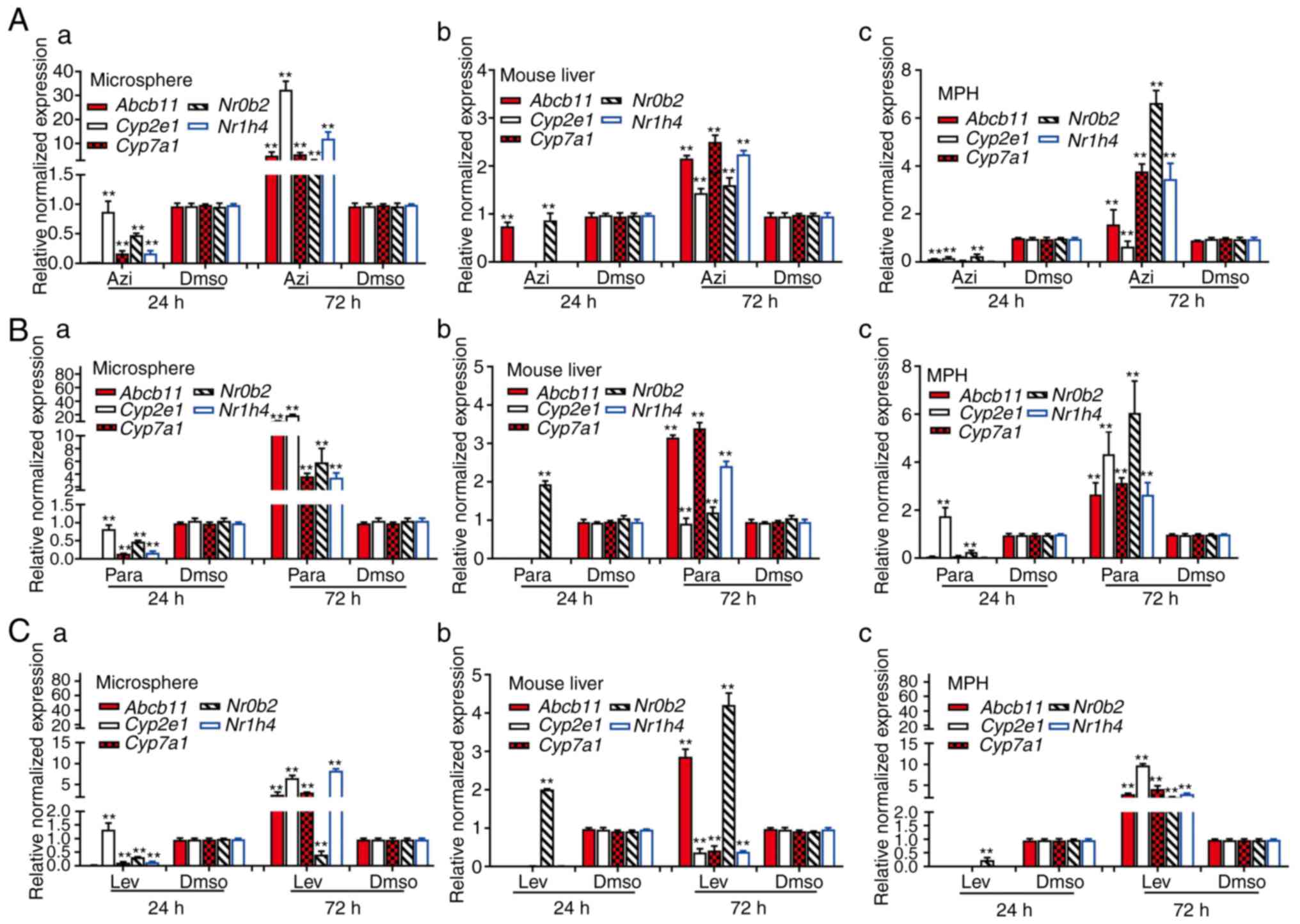
|
1
|
Beckwitt CH, Clark AM, Wheeler S, Taylor
DL, Stolz DB, Griffith L and Wells A: Liver 'organ on a chip'. Exp
Cell Res. 363:15–25. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Si-Tayeb K, Lemaigre FP and Duncan SA:
Organogenesis and development of the liver. Dev Cell. 82:175–189.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ware BR and Khetani SR: Engineered liver
platforms for different phases of drug development. Trends
Biotechnol. 35:172–183. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Thapa BR and Walia A: Liver function tests
and their interpretation. Indian J Pediatr. 74:663–671. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kaplowitz N: Idiosyncratic drug
hepatotoxicity. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 4:489–499. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jaeschke H, Gores GJ, Cederbaum AI, Hinson
JA, Pessayre D and Lemasters JJ: Mechanisms of hepatotoxicity.
Toxicol Sci. 65:166–176. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Godoy P, Hewitt NJ, Albrecht U, Andersen
ME, Ansari N, Bhattacharya S, Bode JG, Bolleyn J, Borner C, Böttger
J, et al: Recent advances in 2D and 3D in vitro systems using
primary hepatocytes, alternative hepatocyte sources and
non-parenchymal liver cells and their use in investigating
mechanisms of hepatotoxicity, cell signaling and ADME. Arch
Toxicol. 87:1315–1530. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gebhardt R, Hengstler JG, Müller D,
Glöckner R, Buenning P, Laube B, Schmelzer E, Ullrich M, Utesch D,
Hewitt N, et al: New hepatocyte in vitro systems for drug
metabolism: metabolic capacity and recommendations for application
in basic research and drug development, standard operation
procedures. Drug Metab Rev. 35:145–213. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bhushan A, Senutovitch N, Bale SS, McCarty
WJ, Hegde M, Jindal R, Golberg I, Berk Usta O, Yarmush ML, Vernetti
L, et al: Towards a three-dimensional microfluidic liver platform
for predicting drug efficacy and toxicity in humans. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 4(Suppl 1): pp. S162013, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Soldatow VY, Lecluyse EL, Griffith LG and
Rusyn I: In vitro models for liver toxicity testing. Toxicol Res
(Camb). 2:23–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pandit A, Sachdeva T and Bafna P:
Drug-induced hepatotoxicity: A review. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2:233–243.
2012.
|
|
12
|
Groneberg DA, Grosse-Siestrup C and
Fischer A: In vitro models to study hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Pathol.
30:394–399. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Olson H, Betton G, Robinson D, Thomas K,
Monro A, Kolaja G, Lilly P, Sanders J, Sipes G, Bracken W, et al:
Concordance of the toxicity of pharmaceuticals in humans and in
animals. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 32:56–67. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Maes M, Vinken M and Jaeschke H:
Experimental models of hepatotoxicity related to acute liver
failure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 290:86–97. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Clark M and Steger-Hartmann T: A big data
approach to the concordance of the toxicity of pharmaceuticals in
animals and humans. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 96:94–105. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Granhall C, Floby E, Nordmark A,
Orzechowski A, Thorne A, Tybring G and Sohlenius-Sternbeck AK:
Characterization of testosterone metabolism and 7-hydroxycoumarin
conjugation by rat and human liver slices after storage in liquid
nitrogen for 1 h up to 6 months. Xenobiotica. 32:985–996. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Omura T and Sato R: The carbon
monoxide-binding pigment of liver microsomes. I. Evidence for its
hemoprotein nature. J Biol Chem. 239:2370–2378. 1964.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Houston JB and Carlile DJ: Prediction of
hepatic clearance from microsomes, hepatocytes, and liver slices.
Drug Metab Rev. 29:891–922. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bi Y, He Y, Huang J, Su Y, Zhu GH, Wang Y,
Qiao M, Zhang BQ, Zhang H, Wang Z, et al: Functional
characteristics of reversibly immortalized hepatic progenitor cells
derived from mouse embryonic liver. Cell Physiol Biochem.
34:1318–1338. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cogger VC, O'Reilly JN, Warren A and Le
Couteur DG: A standardized method for the analysis of liver
sinusoidal endothelial cells and their fenestrations by scanning
electron microscopy. J Vis Exp. 98:pp. e526982015
|
|
21
|
Bale SS, Moore L, Yarmush M and Jindal R:
Emerging in vitro liver technologies for drug metabolism and
inter-organ interactions. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 22:383–394. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bale SS, Vernetti L, Senutovitch N, Jindal
R, Hegde M, Gough A, McCarty WJ, Bakan A, Bhushan A, Shun TY, et
al: In vitro platforms for evaluating liver toxicity. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 239:1180–1191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bhakuni GS, Bedi O, Bariwal J, Deshmukh R
and Kumar P: Animal models of hepatotoxicity. Inflamm Res.
65:13–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
May JE, Xu J, Morse HR, Avent ND and
Donaldson C: Toxicity testing: The search for an in vitro
alternative to animal testing. Br J Biomed Sci. 66:160–165. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Seglen PO: Preparation of isolated rat
liver cells. Methods Cell Biol. 13:29–83. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bi Y, Gong M, Zhang X, Zhang X, Jiang W,
Zhang Y, Chen J, Liu Y, He TC and Li T: Pre-activation of retinoid
signaling facilitates neuronal differentiation of mesenchymal stem
cells. Dev Growth Differ. 52:419–431. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bi Y, Huang J, He Y, Zhu GH, Su Y, He BC,
Luo J, Wang Y, Kang Q, Luo Q, et al: Wnt antagonist SFRP3 inhibits
the differentiation of mouse hepatic progenitor cells. J Cell
Biochem. 108:295–303. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang J, Bi Y, Zhu GH, He Y, Su Y, He BC,
Wang Y, Kang Q, Chen L, Zuo GW, et al: Retinoic acid signalling
induces the differentiation of mouse fetal liver-derived hepatic
progenitor cells. Liver Int. 29:1569–1581. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang X, Cui J, Zhang BQ, Zhang H, Bi Y,
Kang Q, Wang N, Bie P, Yang Z, Wang H, et al: Decellularized liver
scaffolds effectively support the proliferation and differentiation
of mouse fetal hepatic progenitors. J Biomed Mater Res A. 102:pp.
1017–1025. 2014, View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Fan J, Wei Q, Liao J, Zou Y, Song D, Xiong
D, Ma C, Hu X, Qu X, Chen L, et al: Noncanonical Wnt signaling
plays an important role in modulating canonical Wnt-regulated
stemness, proliferation and terminal differentiation of hepatic
progenitors. Oncotarget. 8:pp. 27105–27119. 2017, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu N, Zhang H, Deng F, Li R, Zhang W, Chen
X, Wen S, Wang N, Zhang J, Yin L, et al: Overexpression of Ad5
precursor terminal protein accelerates recombinant adenovirus
packaging and amplification in HEK-293 packaging cells. Gene Ther.
21:629–637. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
National Research Council(US): Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National
Academies Press; (US), Washington, DC: pp. 963–965. 2011
|
|
33
|
Cabral F, Miller CM, Kudrna KM, Hass BE,
Daubendiek JG, Kellar BM and Harris EN: Purification of hepatocytes
and sinusoidal endothelial cells from mouse liver perfusion. J Vis
Exp. Feb 12–2018, Epub ahead of print. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu J, Huang X, Werner M, Broering R, Yang
D and Lu M: Advanced method for isolation of mouse hepatocytes,
liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, and kupffer cells. Methods Mol
Biol. 1540:249–258. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Choi WM, Eun HS, Lee YS, Kim SJ, Kim MH,
Lee JH, Shim YR, Kim HH, Kim YE, Yi HS and Jeong WI: Experimental
applications of in situ liver perfusion machinery for the study of
liver disease. Mol Cells. 42:45–55. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zelepukin IV, Yaremenko AV, Petersen EV,
Deyev SM, Cherkasov VR, Nikitin PI and Nikitin MP: Magnetometry
based method for investigation of nanoparticle clearance from
circulation in a liver perfusion model. Nanotechnology.
30:1051012019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mederacke I, Dapito DH, Affo S, Uchinami H
and Schwabe RF: High-yield and high-purity isolation of hepatic
stellate cells from normal and fibrotic mouse livers. Nat Protoc.
102:305–315. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
He TC, Zhou S, da Costa LT, Yu J, Kinzler
KW and Vogelstein B: A simplified system for generating recombinant
adenoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 955:2509–2514. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Luo J, Deng ZL, Luo X, Tang N, Song WX,
Chen J, Sharff KA, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Kinzler KW, et al: A protocol
for rapid generation of recombinant adenoviruses using the AdEasy
system. Nat Protoc. 2:1236–1247. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee CS, Bishop ES, Zhang R, Yu X, Farina
EM, Yan S, Zhao C, Zheng Z, Shu Y, Wu X, et al: Adenovirus-mediated
gene delivery: Potential applications for gene and cell-based
therapies in the new era of personalized medicine. Genes Dis.
4:43–63. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cheng H, Jiang W, Phillips FM, Haydon RC,
Peng Y, Zhou L, Luu HH, An N, Breyer B, Vanichakarn P, et al:
Osteogenic activity of the fourteen types of human bone
morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 85:1544–1552.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kang Q, Song WX, Luo Q, Tang N, Luo J, Luo
X, Chen J, Bi Y, He BC, Park JK, et al: A comprehensive analysis of
the dual roles of BMPs in regulating adipogenic and osteogenic
differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev.
18:545–559. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kang Q, Sun MH, Cheng H, Peng Y, Montag
AG, Deyrup AT, Jiang W, Luu HH, Luo J, Szatkowski JP, et al:
Characterization of the distinct orthotopic bone-forming activity
of 14 BMPs using recombinant adenovirus-mediated gene delivery.
Gene Ther. 11:1312–1320. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li R, Zhang W, Cui J, Shui W, Yin L, Wang
Y, Zhang H, Wang N, Wu N, Nan G, et al: Targeting BMP9-promoted
human osteosarcoma growth by inactivation of notch signaling. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 14:274–285. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li R, Yan Z, Ye J, Huang H, Wang Z, Wei Q,
Wang J, Zhao L, Lu S, Wang X, et al: The prodomain-containing BMP9
produced from a stable line effectively regulates the
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Med Sci. 13:8–18.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhao C, Wu N, Deng F, Zhang H, Wang N,
Zhang W, Chen X, Wen S, Zhang J, Yin L, et al: Adenovirus-mediated
gene transfer in mesenchymal stem cells can be significantly
enhanced by the cationic polymer polybrene. PLoS One. 9:pp.
e929082014, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kong Y, Zhang H, Chen X, Zhang W, Zhao C,
Wang N, Wu N, He Y, Nan G, Zhang H, et al: Destabilization of
heterologous proteins mediated by the GSK3beta phosphorylation
domain of the β-catenin protein. Cell Physiol Biochem.
32:1187–1199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zhao C, Zeng Z, Qazvini NT, Xu X, Zhang R,
Yan S, Shu Y, Zhu Y, Duan C, Bishop E, et al: Thermoresponsive
citrate-based graphene oxide scaffold enhances bone regeneration
from BMP9-stimulated adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. ACS
Biomater Sci Eng. 4:2943–2955. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Gao Y, Huang E, Zhang H, Wang J, Wu N,
Chen X, Wang N, Wen S, Nan G, Deng F, et al: Crosstalk between
Wnt/beta-catenin and estrogen receptor signaling synergistically
promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor
cells. PLoS One. 8:pp. e824362013, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Yan Z, Yin L, Wang Z, Ye J, Zhang Z, Li R,
Denduluri SK, Wang J, Wei Q, Zhao L, et al: A novel organ culture
model of mouse intervertebral disc tissues. Cells Tissues Organs.
201:38–50. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
51
|
Liao J, Wei Q, Zou Y, Fan J, Song D, Cui
J, Zhang W, Zhu Y, Ma C, Hu X, et al: Notch signaling augments
BMP9-induced bone formation by promoting the
osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling process in mesenchymal stem
cells (MSCs). Cell Physiol Biochem. 41:1905–1923. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cui J, Zhang W, Huang E, Wang J, Liao J,
Li R, Yu X, Zhao C, Zeng Z, Shu Y, et al: BMP9-induced osteoblastic
differentiation requires functional Notch signaling in mesenchymal
stem cells. Lab Invest. 99:58–71. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Yu X, Xia Y, Zeng L, Zhang X, Chen L, Yan
S, Zhang R, Zhao C, Zeng Z, Shu Y, et al: A blockade of PI3Kgamma
signaling effectively mitigates angiotensin II-induced renal injury
and fibrosis in a mouse model. Sci Rep. 8:109882018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Zhang Q, Wang J, Deng F, Yan Z, Xia Y,
Wang Z, Ye J, Deng Y, Zhang Z, Qiao M, et al: TqPCR: A touchdown
qPCR assay with significantly improved detection sensitivity and
amplification efficiency of SYBR Green qPCR. PLoS One. 10:pp.
e01326662016, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Yu X, Liu F, Zeng L, He F, Zhang R, Yan S,
Zeng Z, Shu Y, Zhao C, Wu X, et al: Niclosamide exhibits potent
anticancer activity and synergizes with sorafenib in human renal
cell cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 47:957–971. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shu Y, Yang C, Ji X, Zhang L, Bi Y, Yang
K, Gong M, Liu X, Guo Q, Su Y, et al: Reversibly immortalized human
umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) are
responsive to BMP9-induced osteogenic and adipogenic
differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 119:8872–8886. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wang N, Zhang W, Cui J, Zhang H, Chen X,
Li R, Wu N, Chen X, Wen S, Zhang J, et al: The piggyBac
transposon-mediated expression of SV40 T antigen efficiently
immortalizes mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). PLoS One. 9:pp.
e973162014, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liao Z, Nan G, Yan Z, Zeng L, Deng Y, Ye
J, Zhang Z, Qiao M, Li R, Denduluri S, et al: The anthelmintic drug
niclosamide inhibits the proliferative activity of human
osteosarcoma cells by targeting multiple signal pathways. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 15:726–738. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Desmettre T, Devoisselle JM, Soulie-Begu S
and Mordon S: Fluorescence properties and metabolic features of
indocyanine green (ICG). J Fr Ophtalmol. 22:1003–1016. 1999.In
French. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Bi Y, He Y, Huang JY, Xu L, Tang N, He TC
and Feng T: Induced maturation of hepatic progenitor cells in
vitro. Braz J Med Biol Res. 46:559–566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kim DS, Ryu JW, Son MY, Oh JH, Chung KS,
Lee S, Lee JJ, Ahn JH, Min JS, Ahn J, et al: A liver-specific gene
expression panel predicts the differentiation status of in vitro
hepatocyte models. Hepatology. 66:1662–1674. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nikoozad Z, Ghorbanian MT and Rezaei A:
Comparison of the liver function and hepatic specific genes
expression in cultured mesenchymal stem cells and hepatocytes. Iran
J Basic Med Sci. 17:27–33. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Luu HH, Song WX, Luo X, Manning D, Luo J,
Deng ZL, Sharff KA, Montag AG, Haydon RC and He TC: Distinct roles
of bone morphogenetic proteins in osteogenic differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 25:665–677. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lamplot JD, Qin J, Nan G, Wang J, Liu X,
Yin L, Tomal J, Li R, Shui W, Zhang H, et al: BMP9 signaling in
stem cell differentiation and osteogenesis. Am J Stem Cells.
2:1–21. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Luther G, Wagner ER, Zhu G, Kang Q, Luo Q,
Lamplot J, Bi Y, Luo X, Luo J, Teven C, et al: BMP-9 induced
osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells: Molecular
mechanism and therapeutic potential. Curr Gene Ther. 11:229–240.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wagner ER, Luther G, Zhu G, Luo Q, Shi Q,
Kim SH, Gao JL, Huang E, Gao Y, Yang K, et al: Defective osteogenic
differentiation in the development of osteosarcoma. Sarcoma.
2011:3252382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wang RN, Green J, Wang Z, Deng Y, Qiao M,
Peabody M, Zhang Q, Ye J, Yan Z, Denduluri S, et al: Bone
Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signaling in development and human
diseases. Genes Dis. 1:87–105. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhou L, An N, Jiang W, Haydon R, Cheng H,
Zhou Q, Breyer B, Feng T and He TC: Fluorescence-based functional
assay for Wnt/beta-catenin signaling activity. Biotechniques.
33:1126–1128. 1130–1132, passim. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Luo Q, Kang Q, Si W, Jiang W, Park JK,
Peng Y, Li X, Luu HH, Luo J, Montag AG, et al: Connective tissue
growth factor (CTGF) is regulated by Wnt and bone morphogenetic
proteins signaling in osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal
stem cells. J Biol Chem. 279:55958–55968. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Peng Y, Kang Q, Cheng H, Li X, Sun MH,
Jiang W, Luu HH, Park JY, Haydon RC and He TC: Transcriptional
characterization of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs)-mediated
osteogenic signaling. J Cell Biochem. 90:1149–1165. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Peng Y, Kang Q, Luo Q, Jiang W, Si W, Liu
BA, Luu HH, Park JK, Li X, Luo J, et al: Inhibitor of DNA
binding/differentiation helix-loop-helix proteins mediate bone
morphogenetic protein-induced osteoblast differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells. J Biol Chem. 279:32941–32949. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Si W, Kang Q, Luu HH, Park JK, Luo Q, Song
WX, Jiang W, Luo X, Li X, Yin H, et al: CCN1/Cyr61 is regulated by
the canonical Wnt signal and plays an important role in
Wnt3A-induced osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.
Mol Cell Biol. 26:2955–2964. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ramappa V and Aithal GP: Hepatotoxicity
related to anti-tuberculosis drugs: Mechanisms and management. J
Clin Exp Hepatol. 3:37–49. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Njoku DB: Drug-induced hepatotoxicity:
Metabolic, genetic and immunological basis. Int J Mol Sci.
15:6990–7003. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Perwitasari DA, Atthobari J and Wilffert
B: Pharmacogenetics of isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab
Rev. 47:222–228. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Bale SS, Golberg I, Jindal R, McCarty WJ,
Luitje M, Hegde M, Bhushan A, Usta OB and Yarmush ML: Long-term
coculture strategies for primary hepatocytes and liver sinusoidal
endothelial cells. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 21:413–422. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
78
|
Hughes DJ, Kostrzewski T and Sceats EL:
Opportunities and challenges in the wider adoption of liver and
interconnected microphysiological systems. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
242:1593–1604. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Kegel V, Deharde D, Pfeiffer E, Zeilinger
K, Seehofer D and Damm G: Protocol for isolation of primary human
hepatocytes and corresponding major populations of non-parenchymal
liver cells. J Vis Exp. pp. e530692016, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Riccalton-Banks L, Liew C, Bhandari R, Fry
J and Shakesheff K: Long-term culture of functional liver tissue:
Three-dimensional coculture of primary hepatocytes and stellate
cells. Tissue Eng. 9:401–410. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Rebelo SP, Costa R, Silva MM, Marcelino P,
Brito C and Alves PM: Three-dimensional co-culture of human
hepatocytes and mesenchymal stem cells: Improved functionality in
long-term bioreactor cultures. J Tissue Eng Regen Med.
11:2034–2045. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Chen L, Jiang W, Huang J, He BC, Zuo GW,
Zhang W, Luo Q, Shi Q, Zhang BQ, Wagner ER, et al: Insulin-like
growth factor 2 (IGF-2) potentiates BMP-9-induced osteogenic
differentiation and bone formation. J Bone Miner Res. 25:2447–2459.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Huang E, Zhu G, Jiang W, Yang K, Gao Y,
Luo Q, Gao JL, Kim SH, Liu X, Li M, et al: Growth hormone
synergizes with BMP9 in osteogenic differentiation by activating
the JAK/STAT/IGF1 pathway in murine multilineage cells. J Bone
Miner Res. 27:1566–1575. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Khetani SR and Bhatia SN: Microscale
culture of human liver cells for drug development. Nat Biotechnol.
26:120–126. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Vorrink SU, Zhou Y, Ingelman-Sundberg M
and Lauschke VM: Prediction of drug-induced hepatotoxicity using
long-term stable primary hepatic 3D spheroid cultures in chemically
defined conditions. Toxicol Sci. 163:655–665. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|