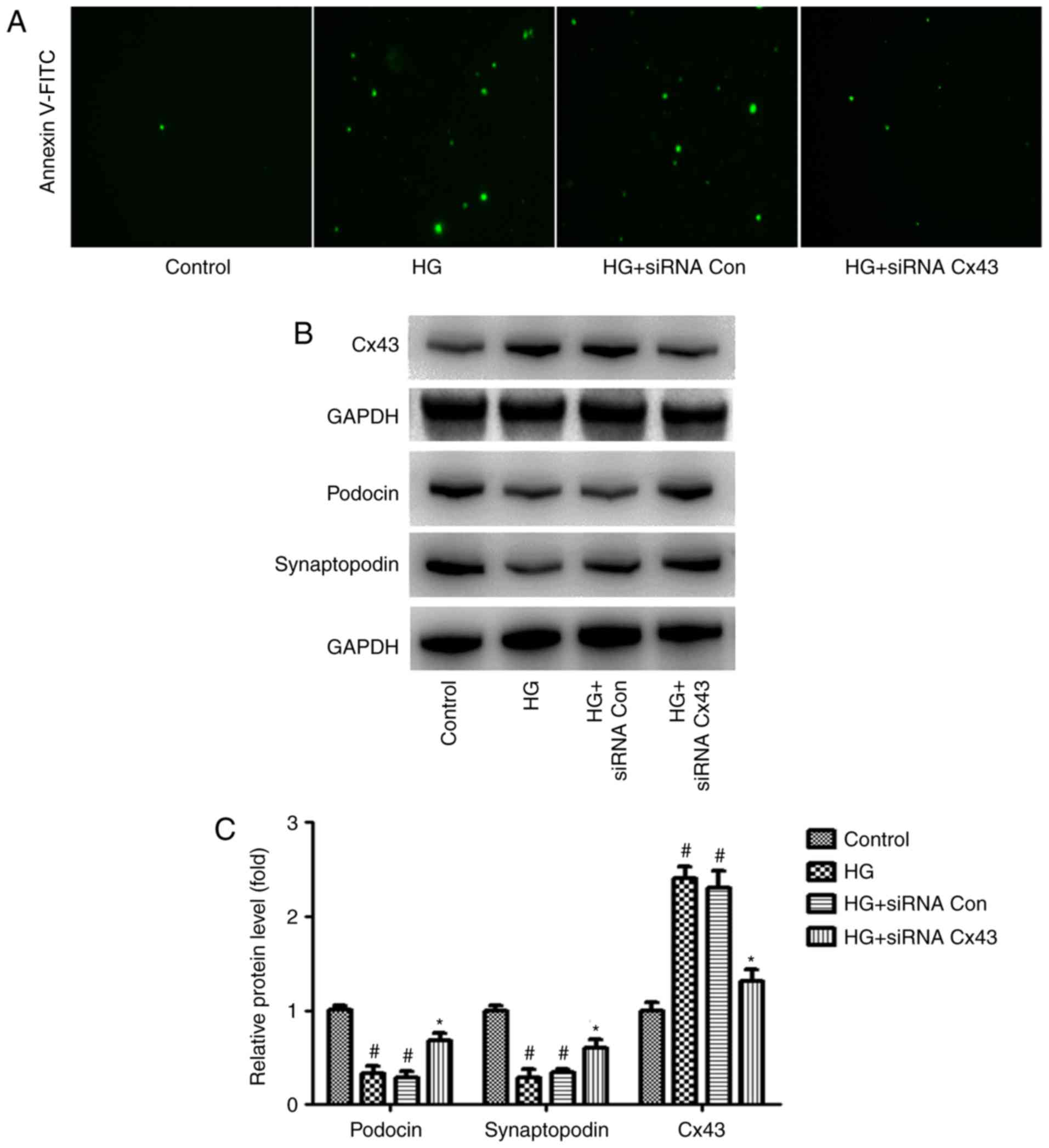
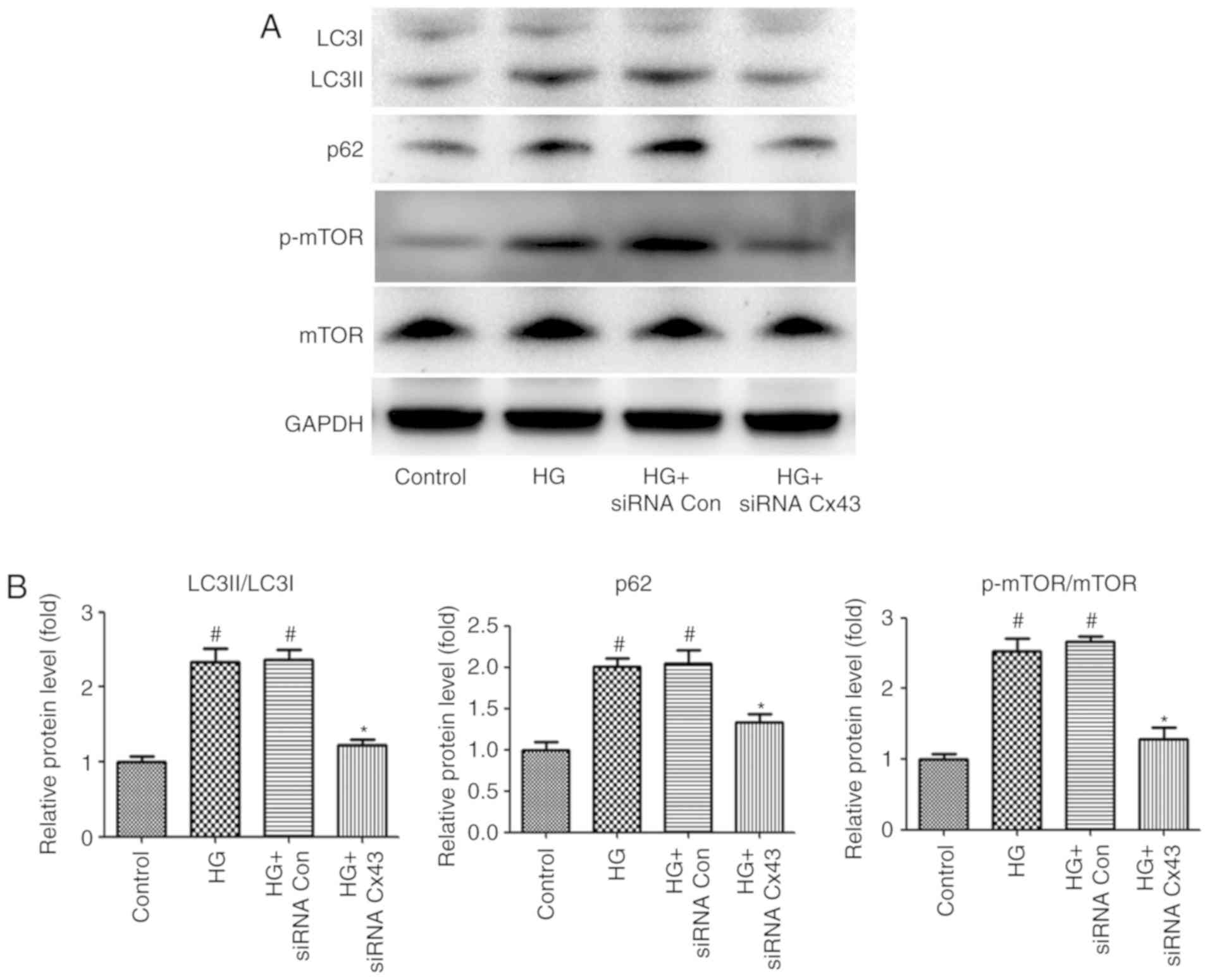
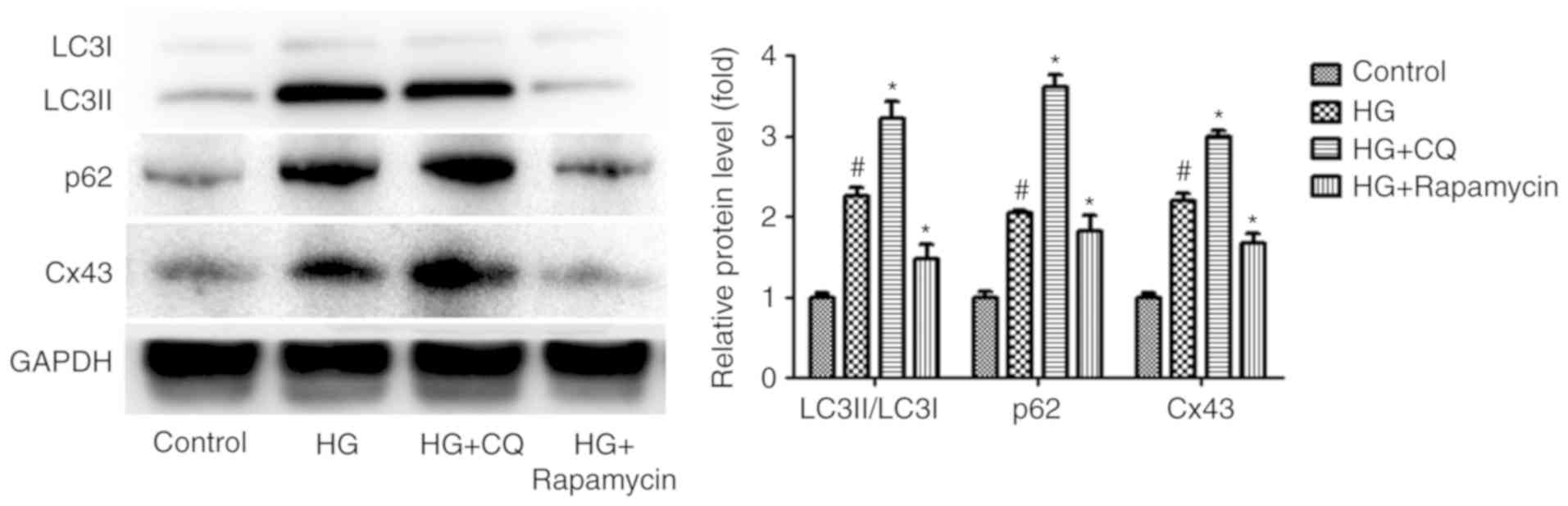
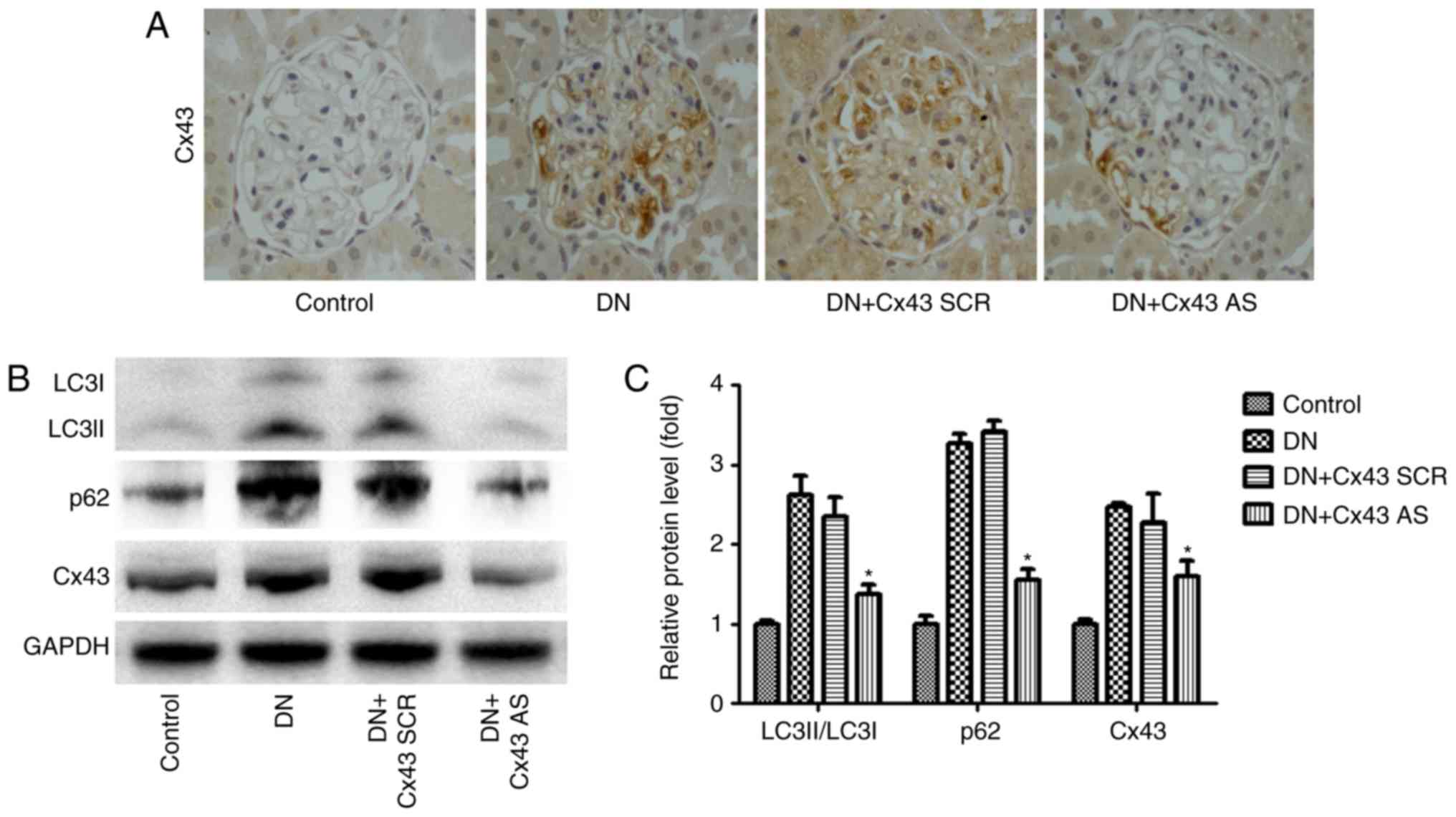
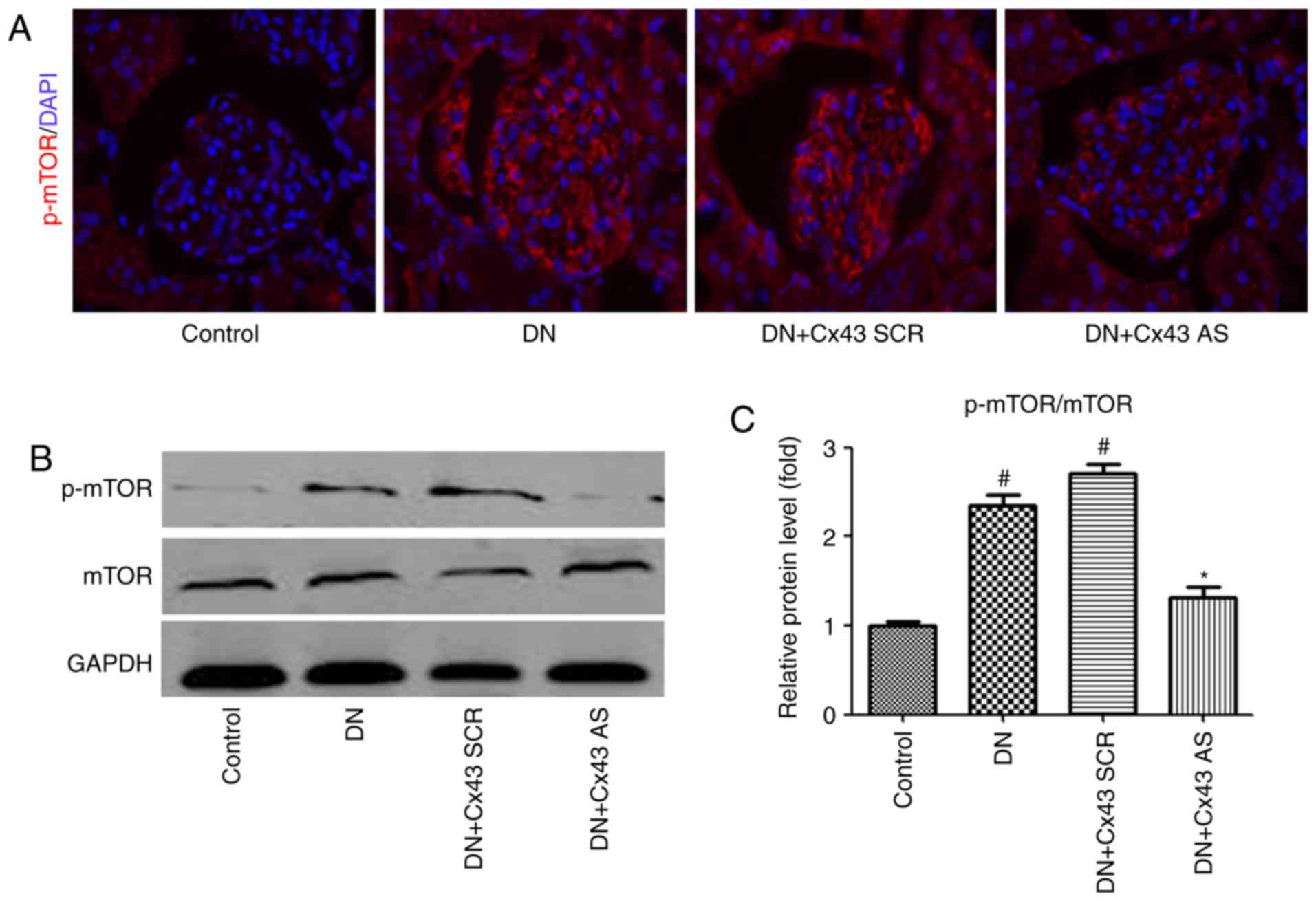
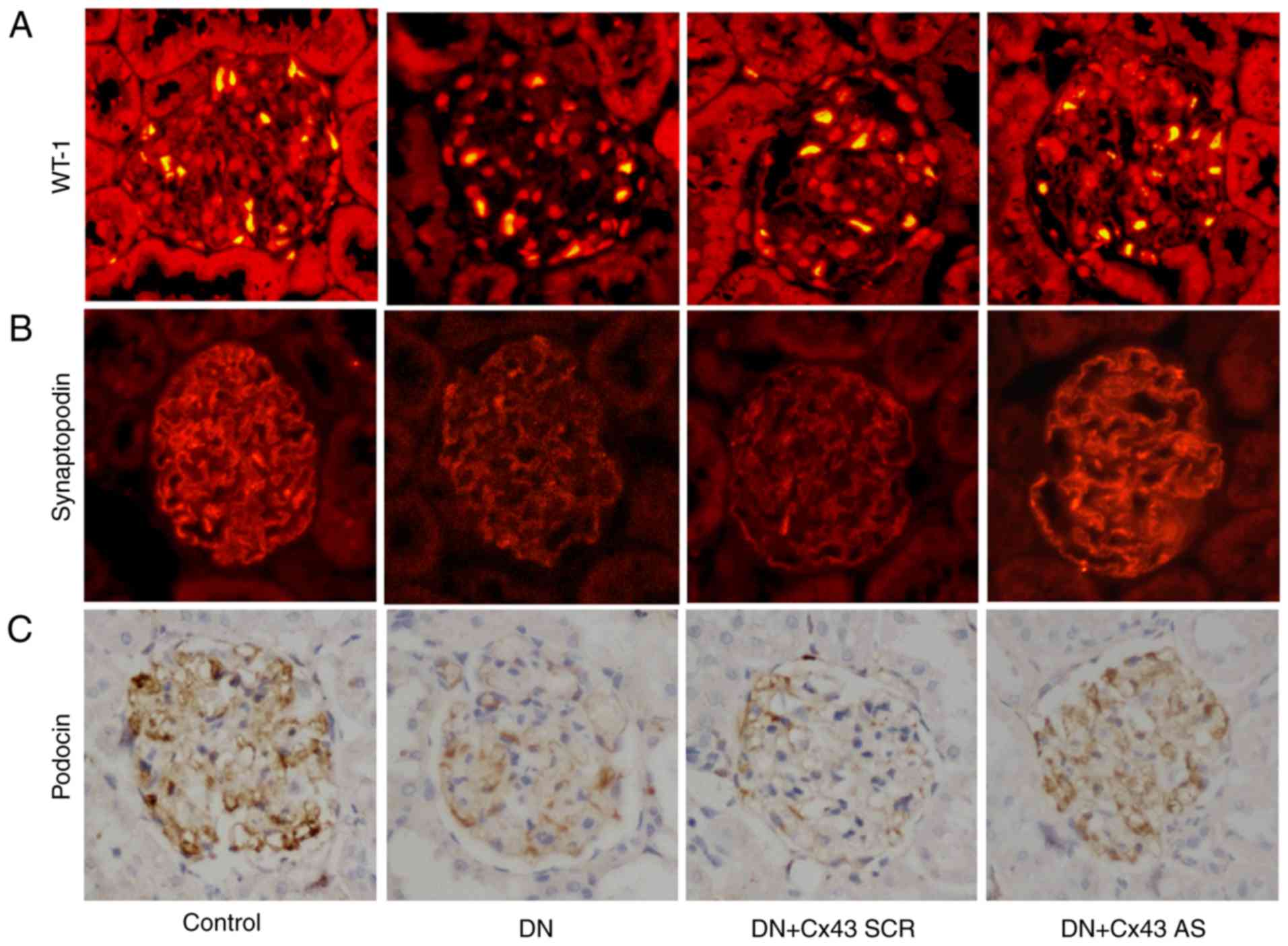
|
1
|
Gnudi L, Coward RJ and Long DA: Diabetic
nephropathy: Perspective on novel molecular mechanisms. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 27:820–830. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Susztak K, Raff AC, Schiffer M and
Böttinger EP: Glucose- induced reactive oxygen species cause
apoptosis of podocytes and podocyte depletion at the onset of
diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 55:225–233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Madhusudhan T, Wang H, Dong W, Ghosh S,
Bock F, Thangapandi VR, Ranjan S, Wolter J, Kohli S, Shahzad K, et
al: Defective podocyte insulin signalling through p85-XBP-1
promotes ATF6-dependent maladaptive ER-stress response in diabetic
nephropathy. Nat Commun. 6:64962015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Long J, Badal SS, Ye Z, Wang Y, Ayanga BA,
Galvan DL, Green NH, Chang BH, Overbeek PA and Danesh FR: Long
noncoding RNA Tug1 regulates mitochondrial bioenergetics in
diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Invest. 126:4205–4218. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mizushima N and Komatsu M: Autophagy:
Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 147:728–741. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tagawa A, Yasuda M, Kume S, Yamahara K,
Nakazawa J, Chin-Kanasaki M, Araki H, Araki S, Koya D, Asanuma K,
et al: Impaired podocyte autophagy exacerbates proteinuria in
diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 65:755–767. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu Y, Zhang J, Wang Y and Zeng X: Apelin
involved in progression of diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting
autophagy in podocytes. Cell Death Dis. 8:e30062017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kume S, Yamahara K, Yasuda M, Maegawa H
and Koya D: Autophagy: Emerging therapeutic target for diabetic
nephrop-athy. Semin Nephrol. 34:9–16. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ribeiro-Rodrigues TM, Martins-Marques T,
Morel S, Kwak BR and Girão H: Role of connexin 43 in different
forms of intercel-lular communication-gap junctions, extracellular
vesicles and tunneling nanotubes. J Cell Sci. 130:3619–3630. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sawai K, Mukoyama M, Mori K, Yokoi H,
Koshikawa M, Yoshioka T, Takeda R, Sugawara A, Kuwahara T, Saleem
MA, et al: Redistribution of connexin43 expression in glomerular
podocytes predicts poor renal prognosis in patients with type 2
diabetes and overt nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
21:2472–2477. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang M, Wang B, Li M and Jiang B: Connexin
43 is involved in aldosterone-induced podocyte injury. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 34:1652–1662. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Prakoura N, Kavvadas P and Chadjichristos
CE: Connexin 43: A new therapeutic target against chronic kidney
disease. Cell Physiol Biochem. 49:9852018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Murphy SF, Varghese RT, Lamouille S, Guo
S, Pridham KJ, Kanabur P, Osimani AM, Sharma S, Jourdan J, Rodgers
CM, et al: Connexin 43 inhibition sensitizes chemoresistant
glioblastoma cells to temozolomide. Cancer Res. 76:139–149. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Zhang A, Han Y, Wang B, Li S and Gan W:
Beyond gap junction channel function: The expression of Cx43
contributes to aldosterone-induced mesangial cell proliferation via
the ERK1/2 and PKC pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:1210–1222.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang B, Xu X, He X, Wang Z and Yang M:
Berberine improved aldo-induced podocyte injury via inhibiting
oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways both in
vivo and in vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem. 39:217–228. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bejarano E, Yuste A, Patel B, Stout RF Jr,
Spray DC and Cuervo AM: Connexins modulate autophagosome
biogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 16:401–414. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim YC and Guan KL: mTOR: A pharmacologic
target for autophagy regulation. J Clin Invest. 125:25–32. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lichtenstein A, Minogue PJ, Beyer EC and
Berthoud VM: Autophagy: A pathway that contributes to connexin
degradation. J Cell Sci. 124:910–920. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Martins-Marques T, Catarino S, Zuzarte M,
Marques C, Matafome P, Pereira P and Girão H: Ischaemia-induced
autophagy leads to degradation of gap junction protein connexin43
in cardiomyocytes. Biochem J. 467:231–245. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li C, Ye L, Yang L, Yu X, He Y, Chen Z, Li
L and Zhang D: Rapamycin promotes the survival and adipogenesis of
ischemia-challenged adipose derived stem cells by improving
autophagy. Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:1762–1774. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kimura T, Takabatake Y, Takahashi A and
Isaka Y: Chloroquine in cancer therapy: A double-edged sword of
autophagy. Cancer Res. 73:3–7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yasuda-Yamahara M, Kume S, Tagawa A,
Maegawa H and Uzu T: Emerging role of podocyte autophagy in the
progression of diabetic nephropathy. Autophagy. 11:2385–2386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu M, Liang K, Zhen J, Zhou M, Wang X,
Wang Z, Wei X, Zhang Y, Sun Y, Zhou Z, et al: Sirt6 deficiency
exacerbates podo-cyte injury and proteinuria through targeting
Notch signaling. Nat Commun. 8:4132017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kim SN, Kwon HJ, Im SW, Son YH, Akindehin
S, Jung YS, Lee SJ, Rhyu IJ, Kim IY, Seong JK, et al: Connexin 43
is required for the maintenance of mitochondrial integrity in brown
adipose tissue. Sci Rep. 7:71592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kroemer G: Autophagy: A druggable process
that is deregulated in aging and human disease. J Clin Invest.
125:1–4. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Choi AM, Ryter SW and Levine B: Autophagy
in human health and disease. N Engl J Med. 368:651–662. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang B, Ding W, Zhang M, Li H, Guo H, Lin
L, Chen J and Gu Y: Role of FOXO1 in aldosterone-induced autophagy:
A compensatory protective mechanism related to podocyte injury.
Oncotarget. 7:45331–45351. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Haefliger JA, Demotz S, Braissant O, Suter
E, Waeber B, Nicod P and Meda P: Connexins 40 and 43 are
differentially regulated within the kidneys of rats with
renovascular hypertension. Kidney Int. 60:190–201. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
in growth control and disease. Cell. 149:274–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shimobayashi M and Hall MN: Making new
contacts: The mTOR network in metabolism and signalling crosstalk.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:155–162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gödel M, Hartleben B, Herbach N, Liu S,
Zschiedrich S, Lu S, Debreczeni-Mór A, Lindenmeyer MT, Rastaldi MP,
Hartleben G, et al: Role of mTOR in podocyte function and diabetic
nephrop-athy in humans and mice. J Clin Invest. 121:2197–2209.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cinà DP, Onay T, Paltoo A, Li C, Maezawa
Y, De Arteaga J, Jurisicova A and Quaggin SE: Inhibition of MTOR
disrupts autophagic flux in podocytes. J Am Soc Nephrol.
23:412–420. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin
MJ, Abeliovich H, Acevedo Arozena A, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD,
Adeli K, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays
for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 12:1–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|