|
1
|
Rahbari M, Pecqueux M, Aust D, Stephan H,
Tiebel O, Chatzigeorgiou A, Tonn T, Baenke F, Rao V, Ziegler N, et
al: Expression of glypican 3 is an independent prognostic biomarker
in primary gastro-esophageal adenocarcinoma and corresponding serum
exosomes. J Clin Med. 8:E6962019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang YL, Liu LC, Hung Y, Chen CJ, Lin YZ,
Wu WR and Wang SC: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in circulatory
exosomes is correlated with ErbB2/HER2 positivity in breast cancer.
Breast. 46:64–69. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhao A, Guo L, Xu J, Zheng L, Guo Z, Ling
Z, Wang L and Mao W: Identification and validation of circulating
exosomes-based liquid biopsy for esophageal cancer. Cancer Med.
8:3566–3574. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Han S, Huo Z, Nguyen K, Zhu F, Underwood
PW, Basso KBG, George TJ and Hughes SJ: The proteome of pancreatic
cancer-derived exosomes reveals signatures rich in key signaling
pathways. Proteomics. 19:e18003942019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Grange C, Brossa A and Bussolati B, Grange
C, Brossa A and Bussolati B: Extracellular vesicles and carried
miRNAs in the progression of renal cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci.
20:E18322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wong CH and Chen YC: Clinical significance
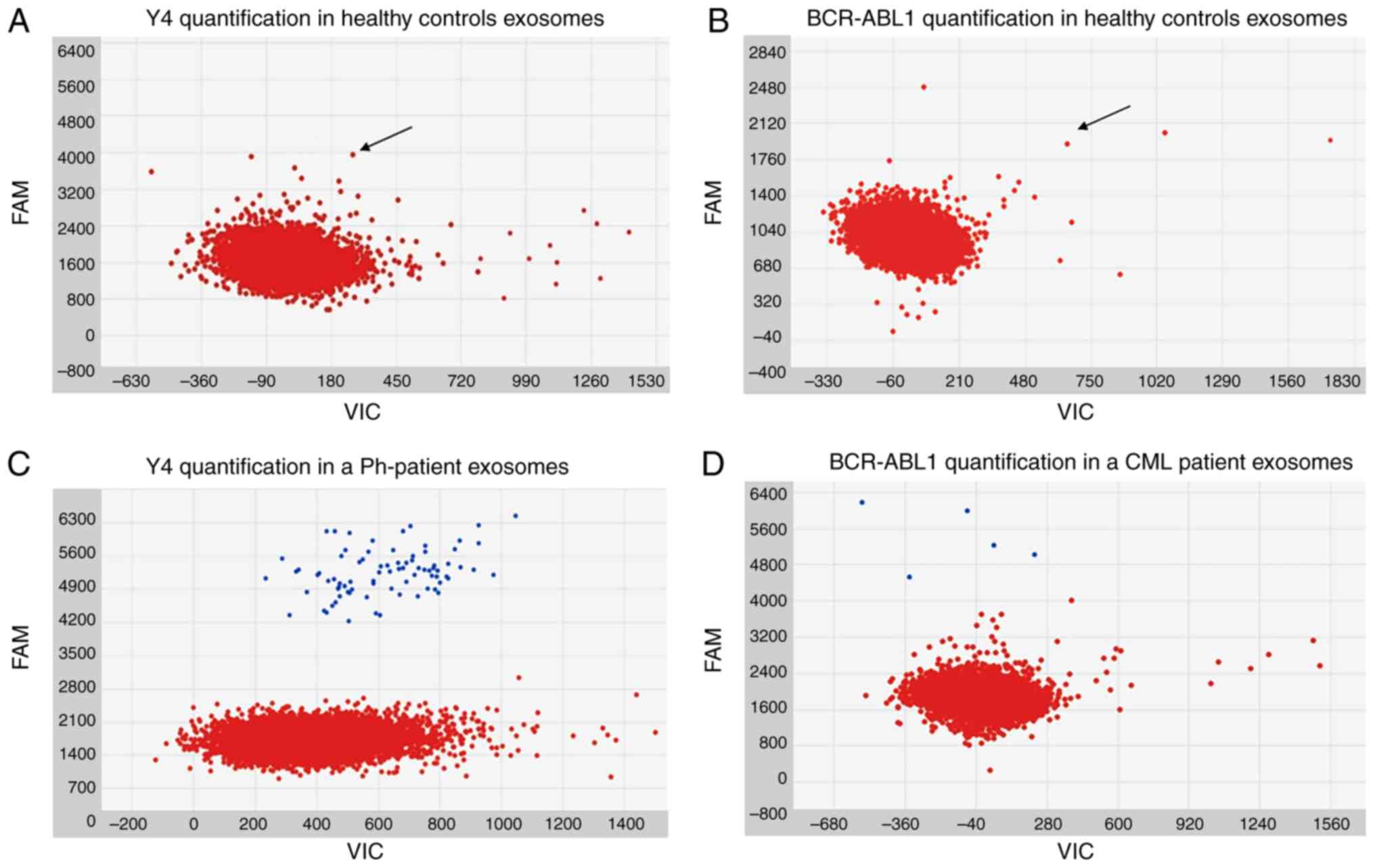
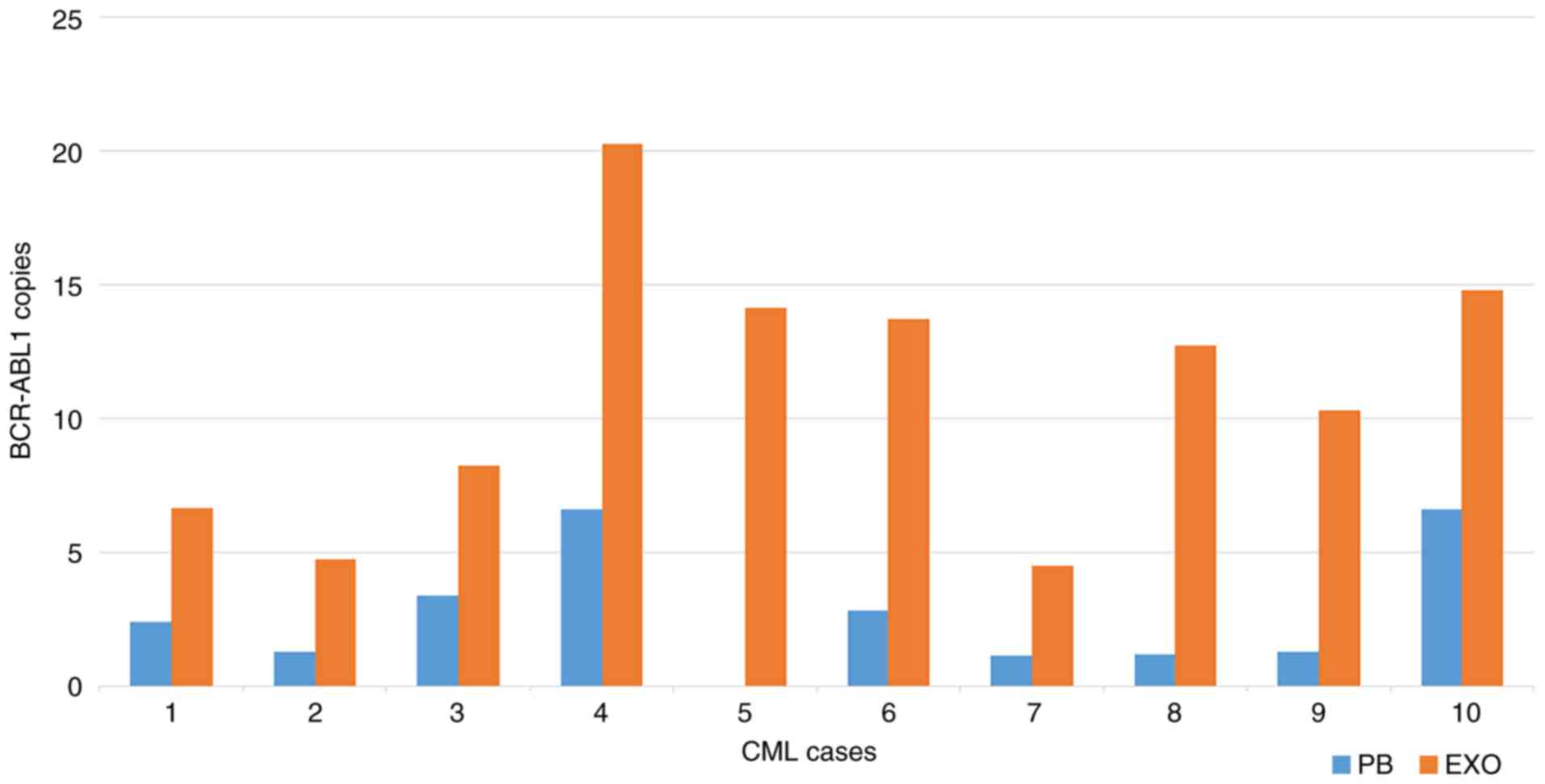
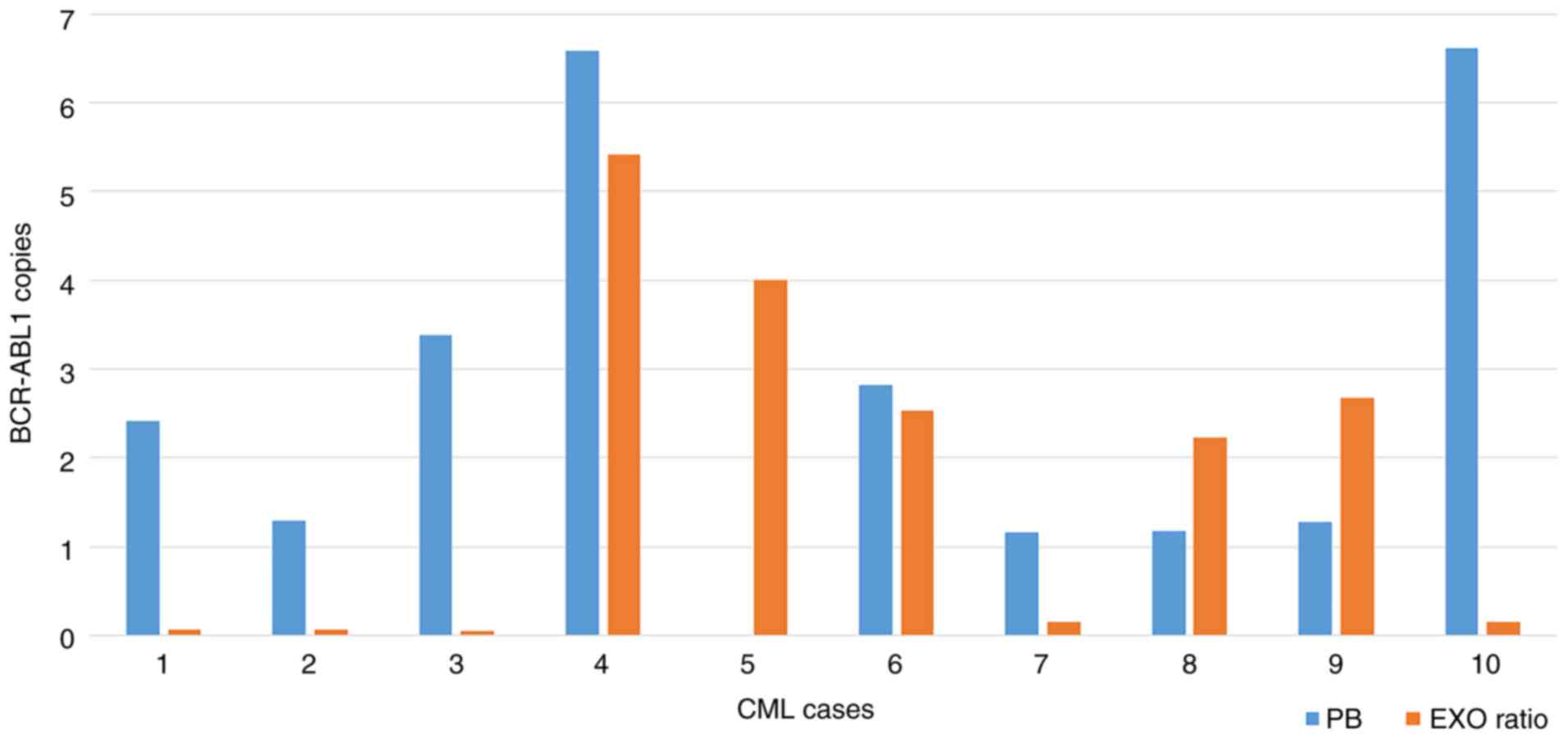
of exosomes as potential biomarkers in cancer. World J Clin Cases.
7:171–190. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kinjyo I, Bragin D, Grattan R, Winter SS
and Wilson BS: Leukemia-derived exosomes and cytokines pave the way
for entry into the brain. J Leukoc Biol. 105:741–753. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zarovni N, Corrado A, Guazzi P, Zocco D,
Lari E, Radano G, Muhhina J, Fondelli C, Gavrilova J and Chiesi A:
Integrated isolation and quantitative analysis of exosome shuttled
proteins and nucleic acids using immunocapture approaches. Methods.
87:46–58. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mathivanan S, Ji H and Simpson RJ:
Exosomes: Extracellular organelles important in intercellular
communication. J Proteomics. 73:1907–1920. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lakkaraju A and Rodriguez-Boulan E:
Itinerant exosomes: Emerging roles in cell and tissue polarity.
Trends Cell Biol. 18:199–209. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
van Niel G, Porto-Carreiro I, Simoes S and
Raposo G: Exosomes: A common pathway for a specialized function. J
Biochem. 140:13–21. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Février B and Raposo G: Exosomes:
Endosomal-derived vesicles shipping extracellular messages. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 16:415–421. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miller IV and Grunewald TG: Tumour-derived
exosomes: Tiny envelopes for big stories. Biol Cell. 107:287–305.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Simpson RJ, Jensen SS and Lim JW:
Proteomic profiling of exosomes: Current perspectives. Proteomics.
8:4083–4099. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zocco D, Ferruzzi P, Cappello F, Kuo WP
and Fais S: Extracellular vesicles as shuttles of tumor biomarkers
and anti-tumor drugs. Front Oncol. 4:2672014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
The fifth international meeting of ISEV,
ISEV2016, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, 4-7 May, 2016, OPW 3.8. J
Extracell Vesicles. 5:315522016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jiang S, Hu C, Liu P and Lu M:
Tumor-derived exosomes in cancer metastasis risk diagnosis and
metastasis therapy. Clin Transl Oncol. 21:152–159. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wen SW, Lima LG, Lobb RJ, Norris EL,
Hastie ML, Krumeich S and Möller A: Breast cancer-derived exosomes
reflect the cell-of-origin phenotype. Proteomics. 19:e18001802019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tatischeff I: Prostate cancer under the
light of tumor cells-derived extracellular vesicles. Cancer Res
Front. 3:83–111. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Théry C and Witwer K: ISEV2018 abstract
book. J Extracell Vesicles. 7(Suppl 1): 14614502018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Jafarzadeh N, Safari Z, Pornour M,
Amirizadeh N, Forouzandeh Moghadam M and Sadeghizadeh M: Alteration
of cellular and immune-related properties of bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells and macrophages by K562 chronic myeloid
leukemia cell derived exosomes. J Cell Physiol. 234:3697–3710.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wierz M, Pierson S, Gargiulo E, Guerin C,
Moussay E and Paggetti J: Purification of leukemia-derived exosomes
to study microenvironment modulation. Methods Mol Biol.
1884:231–245. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cheng H, Sun G and Cheng T: Hematopoiesis
and microenvironment in hematological malignancies. Cell Regen
(Lond). 7:22–26. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bouyssou JM, Liu CJ, Bustoros M,
Sklavenitis-Pistofidis R, Aljawai Y, Manier S, Yosef A, Sacco A,
Kokubun K, Tsukamoto S, et al: Profiling of circulating exosomal
miRNAs in patients with waldenström macroglobulinemia. PLoS One.
13:e02045892018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Tadokoro H, Umezu T, Ohyashiki K, Hirano T
and Ohyashiki JH: Exosomes derived from hypoxic leukemia cells
enhance tube formation in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem.
288:34343–34351. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sharifi H, Shafiee A, Molavi G, Razi E,
Mousavi N, Sarvizadeh M and Taghizadeh M: Leukemia-derived
exosomes: Bringing onco-genic signals to blood cells. J Cell
Biochem. 120:16307–16315. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yao Y, Wang C, Wei W, Shen C, Deng X, Chen
L, Ma L and Hao S: Dendritic cells pulsed with leukemia
cell-derived exosomes more efficiently induce antileukemic
immunities. PLoS One. 9:e914632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Szczepanski MJ, Szajnik M, Welsh A,
Whiteside TL and Boyiadzis M: Blast-derived microvesicles in sera
from patients with acute myeloid leukemia suppress natural killer
cell function via membrane-associated transforming growth
factor-beta1. Haematologica. 96:1302–1309. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wojtuszkiewicz A, Schuurhuis GJ, Kessler
FL, Piersma SR, Knol JC, Pham TV, Jansen G, Musters RJ, van Meerloo
J, Assaraf YG, et al: Exosomes secreted by apoptosis-resistant
acute myeloid leukemia (AML) blasts harbor regulatory network
proteins potentially involved in antagonism of apoptosis. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 15:1281–1298. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huan J, Hornick NI, Goloviznina NA,
Kamimae-Lanning AN, David LL, Wilmarth PA, Mori T, Chevillet JR,
Narla A, Roberts CT Jr, et al: Coordinate regulation of residual
bone marrow function by paracrine trafficking of AML exosomes.
Leukemia. 29:2285–2295. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang J, De Veirman K, Faict S, Frassanito
MA, Ribatti D, Vacca A and Menu E: Multiple myeloma exosomes
establish a favourable bone marrow microenvironment with enhanced
angiogenesis and immunosuppression. J Pathol. 239:162–173. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yeh YY, Ozer HG, Lehman AM, Maddocks K, Yu
L, Johnson AJ and Byrd JC: Characterization of CLL exosomes reveals
a distinct microRNA signature and enhanced secretion by activation
of BCR signaling. Blood. 125:3297–3305. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Corrado C, Saieva L, Raimondo S, Santoro
A, De Leo G and Alessandro R: Chronic myelogenous leukaemia
exosomes modulate bone marrow microenvironment through activation
of epidermal growth factor receptor. J Cell Mol Med. 20:1829–1839.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rowley JD: Letter: A new consistent
chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified
by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature.
243:290–293. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Druker BJ, Sawyers CL, Kantarjian H, Resta
DJ, Reese SF, Ford JM, Capdeville R and Talpaz M: Activity of a
specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in the blast
crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia
with the philadelphia chromosome. N Engl J Med. 344:1038–1042.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sonoyama J, Matsumura I, Ezoe S, Satoh Y,
Zhang X, Kataoka Y, Takai E, Mizuki M, Machii T, Wakao H and
Kanakura Y: Functional cooperation among Ras, STAT5, and
phosphati-dylinositol 3-kinase is required for full oncogenic
activities of BCR/ABL in K562 cells. J Biol Chem. 277:8076–8082.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cross NC, White HE, Colomer D, Ehrencrona
H, Foroni L, Gottardi E, Lange T, Lion T, Machova Polakova K,
Dulucq S, et al: Laboratory recommendations for scoring deep
molecular responses following treatment for chronic myeloid
leukemia. Leukemia. 29:999–1003. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Egan D and Radich J: Monitoring disease
burden in chronic myeloid leukemia: Past, present, and future. Am J
Hematol. 91:742–746. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mahon FX, Réa D, Guilhot J, Guilhot F,
Huguet F, Nicolini F, Legros L, Charbonnier A, Guerci A, Varet B,
et al: Discontinuation of imatinib in patients with chronic myeloid
leukaemia who have maintained complete molecular remission for at
least 2 years: The prospective, multicentre stop imatinib (STIM)
trial. Lancet Oncol. 11:1029–1035. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Russo D, Malagola M, Skert C, Cancelli V,
Turri D, Pregno P, Bergamaschi M, Fogli M, Testoni N, De Vivo A, et
al: Managing chronic myeloid leukaemia in the elderly with
intermittent imatinib treatment. Blood Cancer J. 5:e3472015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ross DM, Masszi T, Gómez Casares MT,
Hellmann A, Stentoft J, Conneally E, Garcia-Gutierrez V, Gattermann
N, le Coutre PD, Martino B, et al: Durable treatment-free remission
in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase
following frontline nilotinib: 96-week update of the ENESTfreedom
study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 144:945–954. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cortes J, Rea D and Lipton JH:
Treatment-free remission with first- and second-generation tyrosine
kinase inhibitors. Am J Hematol. 94:346–357. 2019.
|
|
43
|
Bocchia M, Sicuranza A, Abruzzese E, Iurlo
A, Sirianni S, Gozzini A, Galimberti S, Aprile L, Martino B, Pregno
P, et al: Residual peripheral blood CD26+ leukemic stem
cells in chronic myeloid leukemia patients during TKI therapy and
during treatment-free remission. Front Oncol. 8:1942018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kang KW, Jung JH, Hur W, Park J, Shin H,
Choi B, Jeong H, Kim DS, Yu ES, Lee SR, et al: The potential of
exosomes derived from chronic myelogenous leukaemia cells as a
biomarker. Anticancer Res. 38:3935–3942. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bernardi S, Ruggieri G, Malagola M,
Cancelli V, Cattina F, Polverelli N, Zanaglio C, Perucca S, Re F,
Montanelli A and Russo D: Digital PCR (Dpcr) a step forward to
detection and quantification of minimal residual disease (MRD) in
Ph+/BCR-ABL1 chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). J Mol Biomark Diagn.
8:3302017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Bernardi S, Malagola M, Zanaglio C,
Polverelli N, Dereli Eke E, D'Adda M, Farina M, Bucelli C, Scaffidi
L, Toffoletti E, et al: Digital PCR improves the quantitation of
DMR and the selection of CML candidates to TKIs discontinuation.
Cancer Med. 8:2041–2055. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tosar JP, Gámbaro F, Sanguinetti J,
Bonilla B, Witwer KW and Cayota A: Assessment of small RNA sorting
into different extracellular fractions revealed by high-throughput
sequencing of breast cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:5601–5616.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yeri A, Courtright A, Reiman R, Carlson E,
Beecroft T, Janss A, Siniard A, Richholt R, Balak C, Rozowsky J, et
al: Total extracellular small RNA profiles from plasma, saliva, and
urine of healthy subjects. Sci Rep. 7:440612017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li C, Qin F, Hu F, Xu H, Sun G, Han G,
Wang T and Guo M: Characterization and selective incorporation of
small non-coding RNAs in non-small cell lung cancer extracellular
vesicles. Cell Biosci. 8:22018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Skog J, Würdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer
DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, Curry WT Jr, Carter BS, Krichevsky
AM and Breakefield XO: Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and
proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic
biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 10:1470–1476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Slonchak A, Clarke B, Mackenzie J,
Amarilla AA, Setoh YX and Khromykh AA: West Nile virus infection
and interferon alpha treatment alter the spectrum and the levels of
coding and noncoding host RNAs secreted in extracellular vesicles.
BMC Genomics. 20:4742019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bardi GT, Al-Rayan N, Richie JL,
Yaddanapudi K and Hood JL: Detection of inflammation-related
melanoma small extracellular vesicle (sEV) mRNA content using
primary melanocyte sEVs as a reference. Int J Mol Sci.
20:E12352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chen T, Zhang G, Kong L, Xu S, Wang Y and
Dong M: Leukemia-derived exosomes induced IL-8 production in bone
marrow stromal cells to protect the leukemia cells against
chemotherapy. Life Sci. 221:187–195. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Anfossi S, Babayan A, Pantel K and Calin
GA: Clinical utility of circulating non-coding RNAs-an update. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 15:541–563. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Park SJ, Lee HW, Jeong SH, Park JS, Kim
HC, Seok JY, Kim HJ and Cho SR: Acquisition of a BCR-ABL1
transcript in a patient with disease progression from MDS with
fibrosis to AML with myelodysplasia-related changes. Ann Clin Lab
Sci. 41:379–384. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Miki K, Obara N, Makishima K, Sakamoto T,
Kusakabe M, Kato T, Kurita N, Nishikii H, Yokoyama Y,
Sakata-Yanagimoto M, et al: An unprecedented case of p190 BCR-ABL
chronic myeloid leukemia diagnosed during treatment for multiple
myeloma: A case report and review of the literature. Case Rep
Hematol. 2018:78639432018.
|
|
57
|
Boquett JA, Alves JR and de Oliveira CE:
Analysis of BCR/ABL transcripts in healthy individuals. Genet Mol
Res. 12:4967–4971. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Serrano-Pertierra E, Oliveira-Rodríguez M,
Rivas M, Oliva P, Villafani J, Navarro A, Blanco-López MC and
Cernuda-Morollón E: Characterization of plasma-derived
extracellular vesicles isolated by different methods: A comparison
study. Bioengineering (Basel). 6. pp. E82019, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Navarro-Tableros V, Gomez Y, Camussi G and
Brizzi MF: Extracellular vesicles: New players in ymphomas. Int J
Mol Sci. 20:E412018. View Article : Google Scholar
|