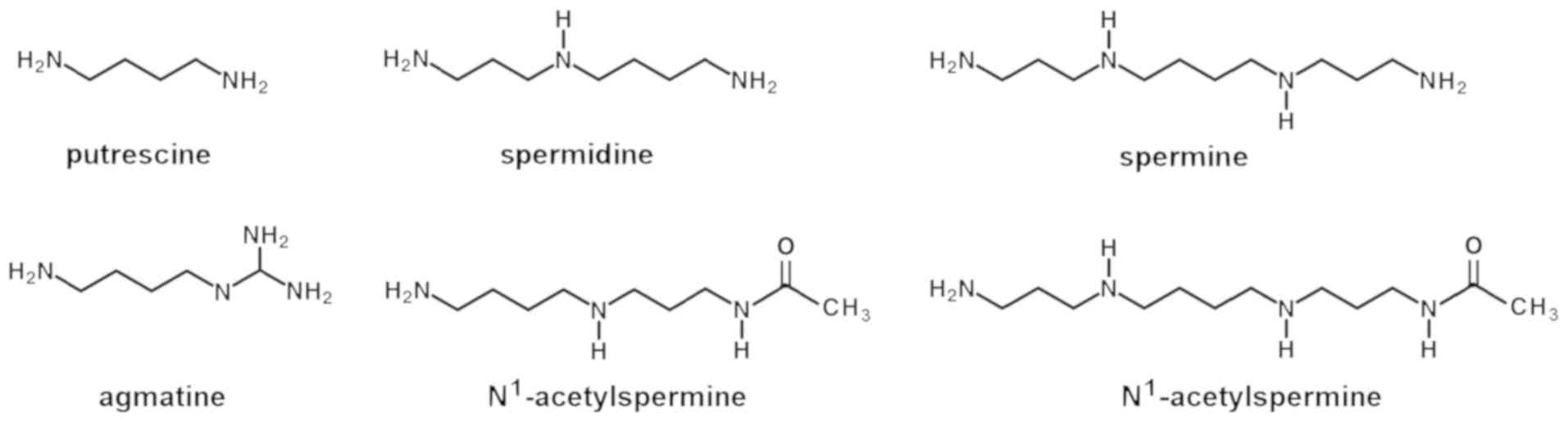
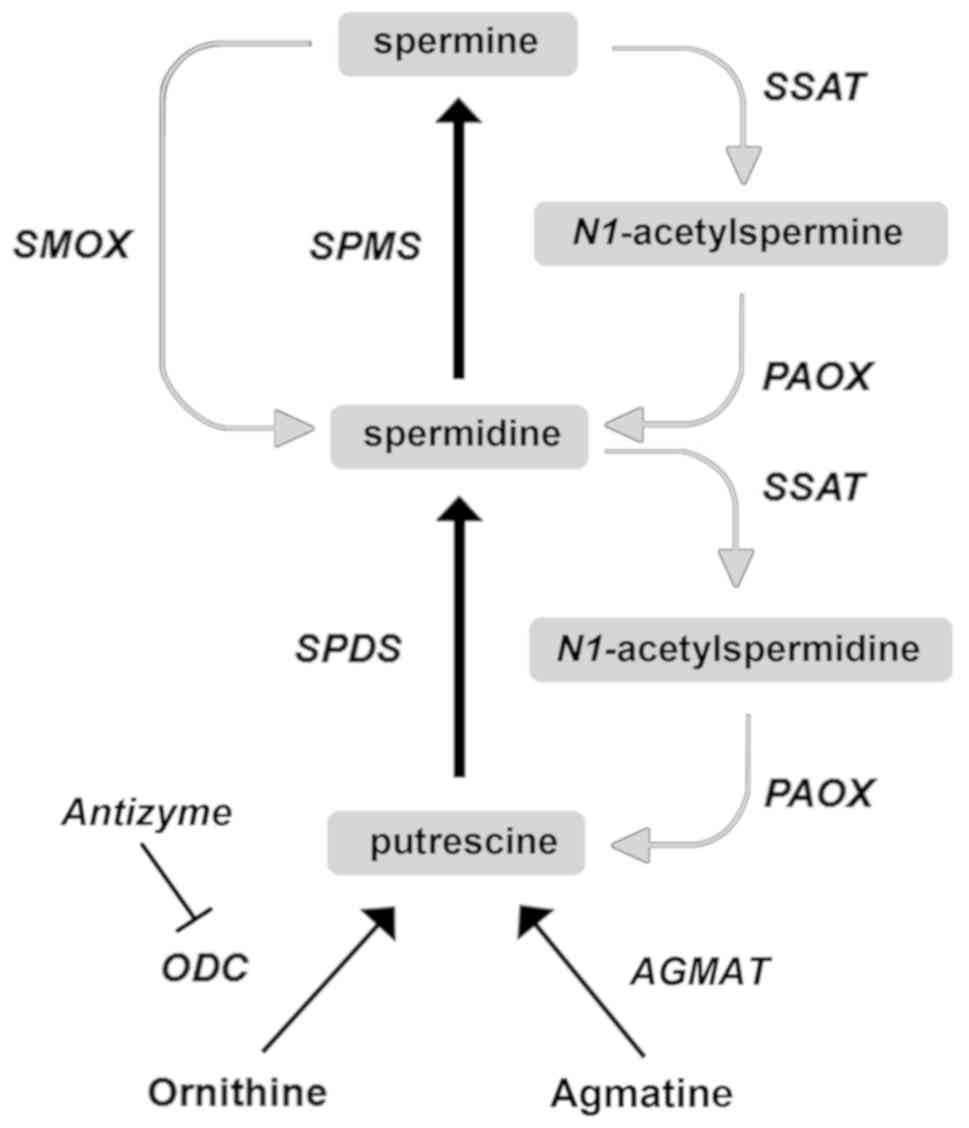
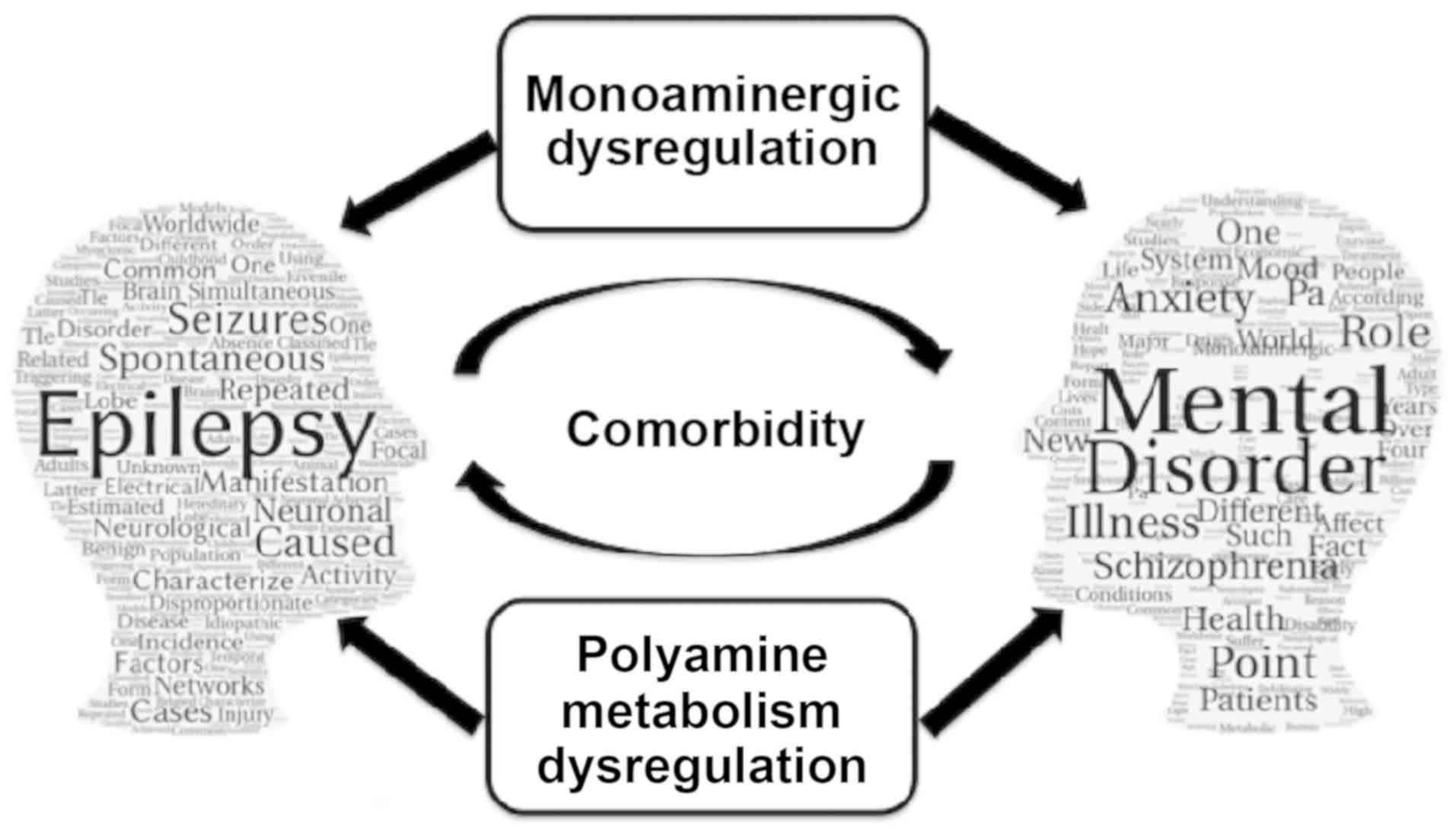
|
1
|
Thomas T and Thomas TJ: Polyamines in cell
growth and cell death: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic
applications. Cell Mol Life Sci. 58:244–258. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rea G, Bocedi A and Cervelli M: Question:
What is the biological function of the polyamines? IUBMB Life.
56:167–169. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wallace HM, Fraser AV and Hughes A: A
perspective of poly-amine metabolism. Biochem J. 376:1–14. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li G, Regunathan S and Reis DJ: Agmatine
is synthesized by a mitochondrial arginine decarboxylase in rat
brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 763:325–329. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sastre M, Regunathan S, Galea E and Reis
DJ: Agmatinase activity in rat brain: A metabolic pathway for the
degradation of agmatine. J Neurochem. 67:1761–1765. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moretti M, Matheus FC, de Oliveira PA,
Neis VB, Ben J, Walz R, Rodrigues AL and Prediger RD: Role of
agmatine in neurode-generative diseases and epilepsy. Front Biosci
(Elite Ed). 6:341–359. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Cervelli M, Angelucci E, Stano P, Leboffe
L, Federico R, Antonini G, Mariottini P and Polticelli F: The
Glu216/Ser218 pocket is a major determinant
of spermine oxidase substrate specificity. Biochem J. 461:453–459.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cervelli M, Bellavia G, Fratini E,
Amendola R, Polticelli F, Barba M, Federico R, Signore F, Gucciardo
G, Grillo R, et al: Spermine oxidase (SMO) activity in breast tumor
tissues and biochemical analysis of the anticancer spermine
analogues BENSpm and CPENSpm. BMC Cancer. 10:5552010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cervelli M, Angelucci E, Germani F,
Amendola R and Mariottini P: Inflammation, carcinogenesis and
neurodegeneration studies in transgenic animal models for polyamine
research. Amino Acids. 46:521–530. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Casero RA Jr, Murray Stewart T and Pegg
AE: Polyamine metabolism and cancer: Treatments, challenges and
opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:681–695. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Amendola R, Cervelli M, Fratini E,
Polticelli F, Sallustio DE and Mariottini P: Spermine metabolism
and anticancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 9:118–130. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Polticelli F, Salvi D, Mariottini P,
Amendola R and Cervelli M: Molecular evolution of the polyamine
oxidase gene family in Metazoa. BMC Evol Biol. 12:902012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cervelli M, Salvi D, Polticelli F,
Amendola R and Mariottini P: Structure-function relationships in
the evolutionary framework of spermine oxidase. J Mol Evol.
76:365–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tavladoraki P, Cervelli M, Antonangeli F,
Minervini G, Stano P, Federico R, Mariottini P and Polticelli F:
Probing mammalian spermine oxidase enzyme-substrate complex through
molecular modeling, site-directed mutagenesis and biochemical
characterization. Amino Acids. 40:1115–1126. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cervelli M, Polticelli F, Federico R and
Mariottini P: Heterologous expression and characterization of mouse
spermine oxidase. J Biol Chem. 278:5271–5276. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cervelli M, Amendola R, Polticelli F and
Mariottini P: Spermine oxidase: Ten years after. Amino Acids.
42:441–450. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Poulin R, Casero RA and Soulet D: Recent
advances in the molecular biology of metazoan polyamine transport.
Amino Acids. 42:711–723. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Abdulhussein AA and Wallace HM: Polyamines
and membrane transporters. Amino Acids. 46:655–660. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Seiler N and Atanassov CL: The natural
polyamines and the immune system. Prog Drug Res. 43:87–141.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mastrantonio R, Cervelli M, Pietropaoli S,
Mariottini P, Colasanti M and Persichini T: HIV-Tat induces the
Nrf2/ARE pathway through NMDA receptor-elicited spermine oxidase
activation in human neuroblastoma cells. PLoS One. 11:e01498022016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Igarashi K, Uemura T and Kashiwagi K:
Acrolein: An effective biomarker for tissue damage produced from
polyamines. Methods Mol Biol. 1694:459–468. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Pietropaoli S, Leonetti A, Cervetto C,
Venturini A, Mastrantonio R, Baroli G, Persichini T, Colasanti M,
Maura G, Marcoli M, et al: Glutamate excitotoxicity linked to
spermine oxidase overexpression. Mol Neurobiol. 55:7259–7270. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Leonetti A, Baroli G, Fratini E,
Pietropaoli S, Marcoli M, Mariottini P and Cervelli M: Epileptic
seizures and oxidative stress in a mouse model overexpressing
spermine oxidase. Amino Acids. Jun 13–2019.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Skatchkova SN, Antonovb SM and Eatona MJ:
Glia and glial polyamines. Role in brain function in health and
disease. Biochemistry (Moscow) Suppl Ser A Membr Cell Biol.
10:73–98. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Oliver D, Baukrowitz T and Fakler B:
Polyamines as gating molecules of inward-rectifier K+
channels. Eur J Biochem. 267:5824–5829. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li J, Doyle KM and Tatlisumak T:
Polyamines in the brain: Distribution, biological interactions, and
their potential therapeutic role in brain ischaemia. Curr Med Chem.
14:1807–1813. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Williams K: Interactions of polyamines
with ion channels. Biochem J. 325:289–297. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pegg AE: Functions of polyamines in
mammals. J Biol Chem. 291:14904–14912. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Williams K, Dawson VL, Romano C, Dichter
MA and Molinoff PB: Characterization of polyamines having agonist,
antagonist, and inverse agonist effects at the polyamine
recognition site of the NMDA receptor. Neuron. 5:199–208. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Elsayed M and Magistretti PJ: A new
outlook on mental illnesses: Glial involvement beyond the glue.
Front Cell Neurosci. 9:4682015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sayers J: The world health report
2001-Mental health: New understanding, new hope. Bull World Health
Organ. 79:10852001.
|
|
32
|
Merikangas KR, Nakamura EF and Kessler RC:
Epidemiology of mental disorders in children and adolescents.
Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 11:7–20. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kamal R, Cox C and Rousseau D: Kaiser
Family Foundation: Costs and outcomes of mental health and
substance use disorders in the US. JAMA. 318:4152017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Mkrtchian A, Aylward J, Dayan P, Roiser JP
and Robinson OJ: Modeling avoidance in mood and anxiety disorders
using reinforcement learning. Biol Psychiatry. 82:532–539. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Benarous X, Consoli A, Cohen D, Renaud J,
Lahaye H and Guilé JM: Suicidal behaviors and irritability in
children and adolescents: A systematic review of the nature and
mechanisms of the association. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry.
28:667–683. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ferrúa CP, Giorgi R, da Rosa LC, do Amaral
CC, Ghisleni GC, Pinheiro RT and Nedel F: MicroRNAs expressed in
depression and their associated pathways: A systematic review and a
bioin-formatics analysis. J Chem Neuroanat. 100:1016502019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Furuyashiki T and Kitaoka S: Neural
mechanisms underlying adaptive and maladaptive consequences of
stress: Roles of dopaminergic and inflammatory responses.
Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. Jun 19–2019.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jin Y, Sun LH, Yang W, Cui RJ and Xu SB:
The role of BDNF in the neuroimmune axis regulation of mood
disorders. Front Neurol. 10:5152019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Peirce JM and Alviña K: The role of
inflammation and the gut microbiome in depression and anxiety. J
Neurosci Res. May 29–2019.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Schildkraut JS: The catecholamine
hypothesis of affective disorders: A review of supporting evidence.
Am J Psychiatry. 122:509–522. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Whitaker-Azmitia PM: Serotonin and brain
development: Role in human developmental diseases. Brain Res Bull.
56:479–485. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu Y, Zhao J, Fan X and Guo W:
Dysfunction in serotonergic and noradrenergic systems and somatic
symptoms in psychiatric disorders. Front Psychiatry. 10:2862019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fiori LM, Wanner B, Jomphe V, Croteau J,
Vitaro F, Tremblay RE, Bureau A and Turecki G: Association of
polyaminergic loci with anxiety, mood disorders, and attempted
suicide. PLoS One. 5:e151462010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Andrews RC: The side effects of
antimalarial drugs indicates a polyamine involvement in both
schizophrenia and depression. Med Hypotheses. 18:11–18. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fiori LM and Turecki G: Implication of the
polyamine system in mental disorders. J Psychiatry Neurosci.
33:102–110. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Das I, de Belleroche J, Essali MA,
Richardson-Andrews RC and Hirsch SR: Blood polyamine in
schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2:1461989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Meltzer HY, Arora RC, Jackman H, Pscheidt
G and Smith MD: Platelet monoamine oxidase and plasma amine oxidase
in psychiatric patients. Schizophr Bull. 6:213–219. 1980.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Baron M, Asnis L, Gruen R and Levitt M:
Plasma amine oxidase and genetic vulnerability to schizophrenia.
Arch Gen Psychiatry. 40:275–279. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dahel KA, Al-Saffar NM and Flayeh KA:
Polyamine oxidase activity in sera of depressed and schizophrenic
patients after ECT treatment. Neurochem Res. 26:415–418. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bernstein HG, Grecksch G, Becker A, Höllt
V and Bogerts B: Cellular changes in rat brain areas associated
with neonatal hippocampal damage. Neuroreport. 10:2307–2311. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Middleton FA, Mirnics K, Pierri JN, Lewis
DA and Levitt P: Gene expression profiling reveals alterations of
specific metabolic pathways in schizophrenia. J Neurosci.
22:2718–2729. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
He Y, Yu Z, Giegling I, Xie L, Hartmann
AM, Prehn C, Adamski J, Kahn R, Li Y, Illig T, et al: Schizophrenia
shows a unique metabolomics signature in plasma. Trans Psychiatry.
2:e1492012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Liu P, Jing Y, Collie ND, Dean B, Bilkey
DK and Zhang H: Altered brain arginine metabolism in schizophrenia.
Trans Psychiatry. 6:e8712016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Genedani S, Saltini S, Benelli A,
Filaferro M and Bertolini A: Influence of SAMe on the modifications
of brain polyamine levels in an animal model of depression.
Neuroreport. 12:3939–3942. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Reis DJ and Regunathan S: Is agmatine a
novel neurotransmitter in brain? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 21:187–193.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Askalany AR, Yamakura T, Petrenko AB,
Kohno T, Sakimura K and Baba H: Effect of agmatine on heteromeric
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels. Neurosci Res. 52:387–392.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gross JA and Turecki G: Suicide and the
polyamine system. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 12:980–988. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Turecki G: Polyamines and suicide risk.
Mol Psychiatry. 18:1242–1243. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Naseer MI, Ullah I, Al-Qahtani MH, Karim
S, Ullah N, Ansari SA, Kim MO and Bibi F: Decreased GABABR
expression and increased neuronal cell death in developing rat
brain after PTZ-induced seizure. Neurol Sci. 34:497–503. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Hauser WA and Kurland RT: The epidemiology
of epilepsy in Rochester, Minnesota, 1935 through 1967. Epilepsia.
16:1–66. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Genton P and Bureau M: Epilepsy with
myoclonic absences. CNS Drugs. 20:911–916. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Téllez-Zenteno JF and Hernández-Ronquillo
L: A review of the epidemiology of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy
Res Treat. 2012:6308532012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Halmekytö M, Alhonen L, Wahlfors J,
Sinervirta R, Eloranta T and Jänne J: Characterization of a
transgenic mouse line over-expressing the human ornithine
decarboxylase gene. Biochem J. 278:895–898. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Halonen T, Sivenius J, Miettinen R,
Halmekytö M, Kauppinen R, Sinervirta R, Alakuijala L, Alhonen L,
MacDonald E and Jänne J: Elevated seizure threshold and impaired
spatial learning in transgenic mice with putrescine overproduction
in the brain. Eur J Neurosci. 5:1233–1239. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lukkarinen JA, Kauppinen RA, Gröhn OH, Oja
JM, Sinervirta R, Järvinen A, Alhonen LI and Jänne J:
Neuroprotective role of ornithine decarboxylase activation in
transient focal cerebral ischaemia: A study using ornithine
decarboxylase-overexpressing transgenic rats. Eur J Neurosci.
10:2046–2055. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Pietilä M, Alhonen L, Halmekytö M, Kanter
P, Jänne J and Porter CW: Activation of polyamine catabolism
profoundly alters tissue polyamine pools and affects hair growth
and female fertility in transgenic mice overexpressing
spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase. J Biol Chem.
272:18746–18751. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kaasinen K, Koistinaho J, Alhonen L and
Jänne J: Overexpression of spermidine/spermine N-acetyltransferase
in transgenic mice protects the animals from kainate-induced
toxicity. Eur J Neurosci. 12:540–548. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kaasinen SK, Gröhn OH, Keinänen TA,
Alhonen L and Jänne J: Overexpression of spermidine/spermine
N1-acetyltransferase elevates the threshold to
pentylenetetrazol-induced seizure activity in transgenic mice. Exp
Neurol. 183:645–652. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kaasinen SK, Oksman M, Alhonen L, Tanila H
and Jänne J: Spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase
overexpression in mice induces hypoactivity and spatial learning
impairment. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 78:35–45. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Cervelli M, Bellavia G, D'Amelio M,
Cavallucci V, Moreno S, Berger J, Nardacci R, Marcoli M, Maura G,
Piacentini M, et al: A new transgenic mouse model for studying the
neurotoxicity of spermine oxidase dosage in the response to
excitotoxic injury. PLoS One. 8:e648102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Cervetto C, Vergani L, Passalacqua M,
Ragazzoni M, Venturini A, Cecconi F, Berretta N, Mercuri N,
D'Amelio M, Maura G, et al: Astrocyte-dependent vulnerability to
excitotoxicity in spermine oxidase-overexpressing mouse.
Neuromolecular Med. 18:50–68. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Alhonen L, Uimari A, Pietilä M, Hyvönen
MT, Pirinen E and Keinänen TA: Transgenic animals modelling
polyamine metabolism-related diseases. Essays Biochem. 46:125–144.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Fleidervish IA, Libman L, Katz E and
Gutnick MJ: Endogenous polyamines regulate cortical neuronal
excitability by blocking voltage-gated Na+ channels.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:18994–18999. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Traynelis SF, Wollmuth LP, McBain CJ,
Menniti FS, Vance KM, Ogden KK, Hansen KB, Yuan H, Myers SJ and
Dingledine R: Glutamate receptor ion channels: Structure,
regulation, and function. Pharmacol Rev. 62:405–496. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Jänne J, Alhonen L, Pietilä M and Keinänen
TA: Genetic approaches to the cellular functions of polyamines in
mammals. Eur J Biochem. 271:877–894. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Chapouthier G and Venault P: A
pharmacological link between epilepsy and anxiety? Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 22:491–493. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Harden CL and Goldstein MA: Mood disorders
in patients with epilepsy: Epidemiology and management. CNS Drugs.
16:291–302. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kanner AM: Epilepsy and mood disorders.
Epilepsia. 48:20–22. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Stahl SM: Brainstorms: Symptoms and
circuits, part 2: Anxiety disorders. J Clin Psychiatry.
64:1408–1409. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Jackson MJ and Turkington D: Depression
and anxiety in epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 76(Suppl
1): i45–i47. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Aroniadou-Anderjaska V, Qashu F and Braga
MF: Mechanisms regulating GABAergic inhibitory transmission in the
basolateral amygdala: Implications for epilepsy and anxiety
disorders. Amino Acids. 32:305–315. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Hamid H, Ettinger AB and Mula M: Anxiety
symptoms in epilepsy: Salient issues for future research. Epilepsy
Behav. 22:63–68. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Gaitatzis A, Carroll K, Majeed A and W
Sander J: The epidemiology of the comorbidity of epilepsy in the
general population. Epilepsia. 45:1613–1622. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Rogawski MA and Löscher W: The
neurobiology of antiepileptic drugs for the treatment of
nonepileptic conditions. Nat Med. 10:685–692. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Pitkänen A and Sutula TP: Is epilepsy a
progressive disorder? Prospects for new therapeutic approaches in
temporal-lobe epilepsy. Lancet Neurol. 1:173–181. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Mula M, Pini S and Cassano GB: The role of
anticonvulsant drugs in anxiety disorders: A critical review of the
evidence. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 27:263–272. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Hitiris N, Mohanraj R, Norrie J, Sills GJ
and Brodie MJ: Predictors of pharmacoresistant epilepsy. Epilepsy
Res. 75:192–196. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Kanner AM: Psychiatric issues in epilepsy:
The complex relation of mood, anxiety disorders, and epilepsy.
Epilepsy Behav. 15:83–87. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Theodore WH: Does serotonin play a role in
epilepsy? Epilepsy Curr. 3:173–177. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Richerson GB: Serotonin: The anti-sudden
death amine? Epilepsy Curr. 13:241–244. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Maia GH, Soares JI, Almeida SG, Leite JM,
Baptista HX, Lukoyanova AN, Brazete CS and Lukoyanov NV: Altered
serotonin innervation in the rat epileptic brain. Brain Res Bull.
152:95–106. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Jobe PC and Browning RA: The serotonergic
and noradrenergic effects of antidepressant drugs are
anticonvulsant, not proconvulsant. Epilepsy Behav. 7:602–619. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|