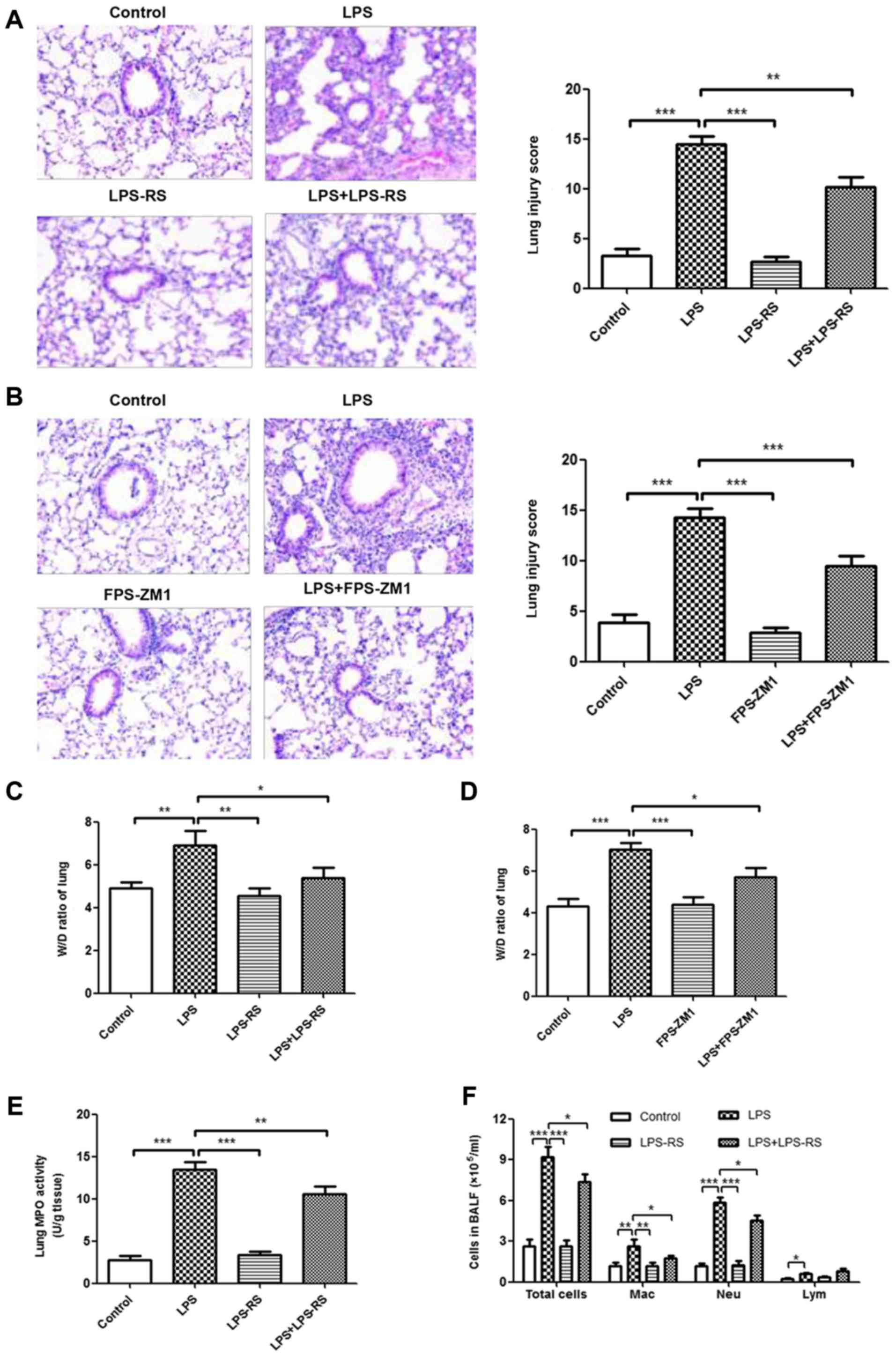
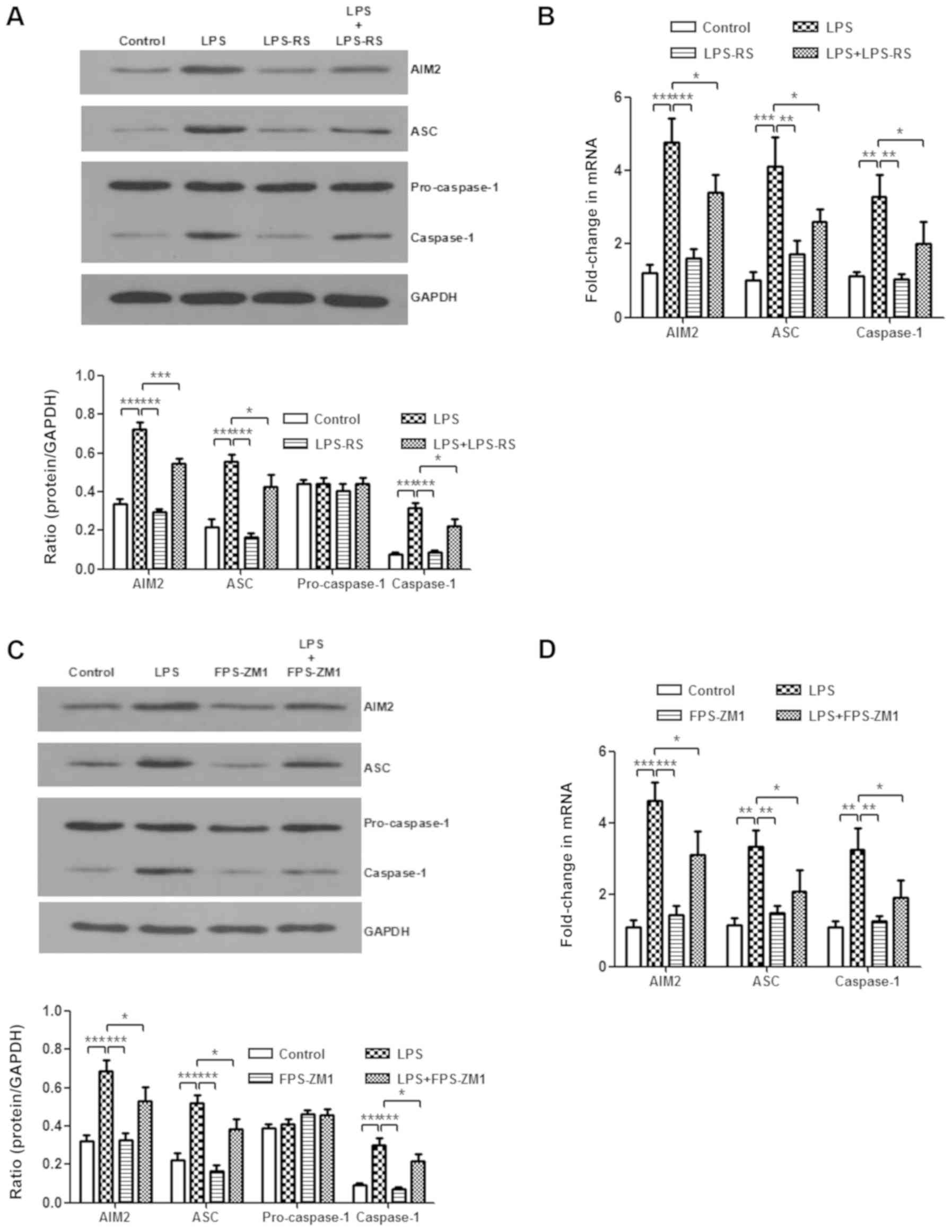
|
1
|
Matthay MA, Ware LB and Zimmerman GA: The
acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest. 122:2731–2740.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, Fan E,
Brochard L, Esteban A, Gattinoni L, van Haren F, Larsson A, McAuley
DF, et al LUNG SAFE Investigators; ESICM Trials Group:
Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients With
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50
Countries. JAMA. 315:788–800. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Levy BD and Serhan CN: Resolution of acute
inflammation in the lung. Annu Rev Physiol. 76:467–492. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Standiford TJ and Ward PA: Therapeutic
targeting of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress
syndrome. Transl Res. 167:183–191. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kang R, Chen R, Zhang Q, Hou W, Wu S, Cao
L, Huang J, Yu Y, Fan XG, Yan Z, et al: HMGB1 in health and
disease. Mol Aspects Med. 40:1–116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bae JS: Role of high mobility group box 1
in inflammatory disease: Focus on sepsis. Arch Pharm Res.
35:1511–1523. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lotze MT and Tracey KJ: High-mobility
group box 1 protein (HMGB1): Nuclear weapon in the immune arsenal.
Nat Rev Immunol. 5:331–342. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Klune JR, Dhupar R, Cardinal J, Billiar TR
and Tsung A: HMGB1: Endogenous danger signaling. Mol Med.
14:476–484. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ueno H, Matsuda T, Hashimoto S, Amaya F,
Kitamura Y, Tanaka M, Kobayashi A, Maruyama I, Yamada S, Hasegawa
N, et al: Contributions of high mobility group box protein in
experimental and clinical acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 170:1310–1316. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sundén-Cullberg J, Norrby-Teglund A,
Rouhiainen A, Rauvala H, Herman G, Tracey KJ, Lee ML, Andersson J,
Tokics L and Treutiger CJ: Persistent elevation of high mobility
group box-1 protein (HMGB1) in patients with severe sepsis and
septic shock. Crit Care Med. 33:564–573. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee JW, Park JW, Shin NR, Park SY, Kwon
OK, Park HA, Lim Y, Ryu HW, Yuk HJ, Kim JH, et al: Picrasma
quassiodes (D. Don) Benn. attenuates lipopolysaccharide
(LPS)-induced acute lung injury. Int J Mol Med. 38:834–844. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Duan JX, Zhou Y, Zhou AY, Guan XX, Liu T,
Yang HH, Xie H and Chen P: Calcitonin gene-related peptide exerts
anti-inflammatory property through regulating murine macrophages
polarization in vitro. Mol Immunol. 91:105–113. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu YC, Zou XB, Chai YF and Yao YM:
Macrophage polarization in inflammatory diseases. Int J Biol Sci.
10:520–529. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
de Zoete MR, Palm NW, Zhu S and Flavell
RA: Inflammasomes. Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 6:a0162872014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang H, Luo J, Alcorn JF, Chen K, Fan S,
Pilewski J, Liu A, Chen W, Kolls JK and Wang J: AIM2 Inflammasome
Is Critical for Influenza-Induced Lung Injury and Mortality. J
Immunol. 198:4383–4393. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang R, Chen R, Xie M, Cao L, Lotze MT,
Tang D and Zeh HJ III: The Receptor for Advanced Glycation End
Products Activates the AIM2 Inflammasome in Acute Pancreatitis. J
Immunol. 196:4331–4337. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ngoungoure FP and Owona BA: Withaferin A
modulates AIM2 inflammasome and caspase-1 expression in THP-1
polarized macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 383:1115642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vande Walle L, Kanneganti TD and Lamkanfi
M: HMGB1 release by inflammasomes. Virulence. 2:162–165. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu L, Yang M, Kang R, Dai Y, Yu Y, Gao F,
Wang H, Sun X, Li X, Li J, et al: HMGB1-DNA complex-induced
autophagy limits AIM2 inflammasome activation through RAGE. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 450:851–856. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun Q, Loughran P, Shapiro R, Shrivastava
IH, Antoine DJ, Li T, Yan Z, Fan J, Billiar TR and Scott MJ:
Redox-dependent regulation of hepatocyte absent in melanoma 2
inflammasome activation in sterile liver injury in mice.
Hepatology. 65:253–268. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhou H, Wang Y, Wang W, Jia J, Li Y, Wang
Q, Wu Y and Tang J: Generation of monoclonal antibodies against
highly conserved antigens. PLoS One. 4:e60872009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Han L, Zhang M, Wang M, Jia J, Zhao M, Fan
Y and Li X: High Mobility Group Box-1 Promotes Inflammation-Induced
Lymphangiogenesis via Toll-Like Receptor 4-Dependent Signalling
Pathway. PLoS One. 11:e01541872016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang C, Liu XX, Huang KB, Yin SB, Wei JJ,
Hu YF, Gu Y and Zheng GQ: Preconditioning with recombinant
high-mobility group box 1 induces ischemic tolerance in a rat model
of focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. J Neurochem. 137:576–588.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen Y, Huang XJ, Yu N, Xie Y, Zhang K,
Wen F, Liu H and Di Q: HMGB1 Contributes to the Expression of
P-Glycoprotein in Mouse Epileptic Brain through Toll-Like Receptor
4 and Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products. PLoS One.
10:e01409182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Abdelmageed ME, El-Awady MS, Abdelrahim M
and Suddek GM: LPS-RS attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced
acute lung injury involves NF-κB inhibition. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 94:140–146. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Krikun G, Trezza J, Shaw J, Rahman M,
Guller S, Abrahams VM and Lockwood CJ: Lipopolysaccharide appears
to activate human endometrial endothelial cells through
TLR-4-dependent and TLR-4-independent mechanisms. Am J Reprod
Immunol. 68:233–237. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Deane R, Singh I, Sagare AP, Bell RD, Ross
NT, LaRue B, Love R, Perry S, Paquette N, Deane RJ, et al: A
multimodal RAGE-specific inhibitor reduces amyloid β-mediated brain
disorder in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Clin Invest.
122:1377–1392. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhong WT, Wu YC, Xie XX, Zhou X, Wei MM,
Soromou LW, Ci XX and Wang DC: Phillyrin attenuates LPS-induced
pulmonary inflammation via suppression of MAPK and NF-κB activation
in acute lung injury mice. Fitoterapia. 90:132–139. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiao X, Yang M, Sun D and Sun S: Curcumin
protects against sepsis-induced acute lung injury in rats. J Surg
Res. 176:e31–e39. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang F, Huang G, Hu B, Fang LP, Cao EH,
Xin XF, Song Y and Shi Y: Anti-HMGB1 neutralizing antibody
ameliorates neutrophilic airway inflammation by suppressing
dendritic cell-mediated Th17 polarization. Mediators Inflamm.
2014:2579302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang F, Huang G, Hu B, Qian GS and Song
Y: Recombinant HMGB1 A box protein inhibits Th17 responses in mice
with neutrophilic asthma by suppressing dendritic cell-mediated
Th17 polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. 24:110–118. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Aggarwal NR, King LS and D'Alessio FR:
Diverse macrophage populations mediate acute lung inflammation and
resolution. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 306:L709–L725.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nie H, Wang A, He Q, Yang Q, Liu L, Zhang
G, Huang Y, Ding X, Yu H and Hu S: Phenotypic switch in lung
interstitial macrophage polarization in an ovalbumin-induced mouse
model of asthma. Exp Ther Med. 14:1284–1292. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mathie SA, Dixon KL, Walker SA, Tyrrell V,
Mondhe M, O'Donnell VB, Gregory LG and Lloyd CM: Alveolar
macrophages are sentinels of murine pulmonary homeostasis following
inhaled antigen challenge. Allergy. 70:80–89. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Pilzweger C and Holdenrieder S:
Circulating HMGB1 and RAGE as Clinical Biomarkers in Malignant and
Autoimmune Diseases. Diagnostics (Basel). 5:219–253. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Fang F and Jiang D: IL-1β/HMGB1 signalling
promotes the inflammatory cytokines release via TLR signalling in
human intervertebral disc cells. Biosci Rep. 36:pii: e00379. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Watanabe K, Karuppagounder V, Arumugam S,
Thandavarayan RA, Pitchaimani V, Sreedhar R, Afrin R, Harima M,
Suzuki H, Suzuki K, et al: Pruni cortex ameliorates skin
inflammation possibly through HMGB1-NFκB pathway in house dust mite
induced atopic dermatitis NC/Nga transgenic mice. J Clin Biochem
Nutr. 56:186–194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kang N, Hai Y, Yang J, Liang F and Gao CJ:
Hyperbaric oxygen intervention reduces secondary spinal cord injury
in rats via regulation of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:1141–1153. 2015.
|
|
41
|
Tian S, Zhang L, Tang J, Guo X, Dong K and
Chen SY: HMGB1 exacerbates renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis
through facilitating M1 macrophage phenotype at the early stage of
obstructive injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 308:F69–F75. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Son M, Porat A, He M, Suurmond J,
Santiago-Schwarz F, Andersson U, Coleman TR, Volpe BT, Tracey KJ,
Al-Abed Y, et al: C1q and HMGB1 reciprocally regulate human
macrophage polarization. Blood. 128:2218–2228. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Schaper F, de Leeuw K, Horst G, Bootsma H,
Limburg PC, Heeringa P, Bijl M and Westra J: High mobility group
box 1 skews macrophage polarization and negatively influences
phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Rheumatology (Oxford).
55:2260–2270. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Cavone L, Cuppari C, Manti S, Grasso L,
Arrigo T, Calamai L, Salpietro C and Chiarugi A: Increase in the
Level of Proinflammatory Cytokine HMGB1 in Nasal Fluids of Patients
With Rhinitis and its Sequestration by Glycyrrhizin Induces
Eosinophil Cell Death. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 8:123–128. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cuppari C, Manti S, Chirico V, Caruso R,
Salpietro V, Giacchi V, Laganà F, Arrigo T, Salpietro C and
Leonardi S: Sputum high mobility group box-1 in asthmatic children:
A noninvasive sensitive biomarker reflecting disease status. Ann
Allergy Asthma Immunol. 115:103–107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gangemi S, Casciaro M, Trapani G,
Quartuccio S, Navarra M, Pioggia G and Imbalzano E: Association
between HMGB1 and COPD: A Systematic Review. Mediators Inflamm.
2015:1649132015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kim JY, Park JS, Strassheim D, Douglas I,
Diaz del Valle F, Asehnoune K, Mitra S, Kwak SH, Yamada S, Maruyama
I, et al: HMGB1 contributes to the development of acute lung injury
after hemorrhage. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
288:L958–L965. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nogueira-Machado JA and de Oliveira Volpe
CM: HMGB-1 as a target for inflammation controlling. Recent Pat
Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 6:201–209. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lamkanfi M, Sarkar A, Vande Walle L,
Vitari AC, Amer AO, Wewers MD, Tracey KJ, Kanneganti TD and Dixit
VM: Inflammasome-dependent release of the alarmin HMGB1 in
endotoxemia. J Immunol. 185:4385–4392. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Deng Y, Yang Z, Gao Y, Xu H, Zheng B,
Jiang M, Xu J, He Z and Wang X: Toll-like receptor 4 mediates acute
lung injury induced by high mobility group box-1. PLoS One.
8:e643752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hidaka S, Iwasaka H, Hagiwara S and
Noguchi T: Gabexate mesilate inhibits the expression of HMGB1 in
lipopolysac-charide-induced acute lung injury. J Surg Res.
165:142–150. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Entezari M, Javdan M, Antoine DJ, Morrow
DM, Sitapara RA, Patel V, Wang M, Sharma L, Gorasiya S, Zur M, et
al: Inhibition of extracellular HMGB1 attenuates hyperoxia-induced
inflammatory acute lung injury. Redox Biol. 2:314–322. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ludlow LE, Johnstone RW and Clarke CJ: The
HIN-200 family: More than interferon-inducible genes? Exp Cell Res.
308:1–17. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Rathinam VA, Jiang Z, Waggoner SN, Sharma
S, Cole LE, Waggoner L, Vanaja SK, Monks BG, Ganesan S, Latz E, et
al: The AIM2 inflammasome is essential for host defense against
cytosolic bacteria and DNA viruses. Nat Immunol. 11:395–402. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hu S, Peng L, Kwak YT, Tekippe EM, Pasare
C, Malter JS, Hooper LV and Zaki MH: The DNA Sensor AIM2 Maintains
Intestinal Homeostasis via Regulation of Epithelial Antimicrobial
Host Defense. Cell Rep. 13:1922–1936. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Fernandes-Alnemri T, Yu JW, Juliana C,
Solorzano L, Kang S, Wu J, Datta P, McCormick M, Huang L, McDermott
E, et al: The AIM2 inflammasome is critical for innate immunity to
Francisella tularensis. Nat Immunol. 11:385–393. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Man SM, Karki R and Kanneganti TD: AIM2
inflammasome in infection, cancer, and autoimmunity: Role in DNA
sensing, inflammation, and innate immunity. Eur J Immunol.
46:269–280. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Karki R, Man SM, Malireddi RKS, Gurung P,
Vogel P, Lamkanfi M and Kanneganti TD: Concerted activation of the
AIM2 and NLRP3 inflammasomes orchestrates host protection against
Aspergillus infection. Cell Host Microbe. 17:357–368. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Herold S, Mayer K and Lohmeyer J: Acute
lung injury: How macrophages orchestrate resolution of inflammation
and tissue repair. Front Immunol. 2:652011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lawrence T and Natoli G: Transcriptional
regulation of macrophage polarization: Enabling diversity with
identity. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:750–761. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Gordon S and Martinez FO: Alternative
activation of macrophages: Mechanism and functions. Immunity.
32:593–604. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Davis MJ, Tsang TM, Qiu Y, Dayrit JK,
Freij JB, Huffnagle GB and Olszewski MA: Macrophage M1/M2
polarization dynamically adapts to changes in cytokine
microenvironments in Cryptococcus neoformans infection. MBio.
4:e00264–e13. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lu G, Zhang R, Geng S, Peng L, Jayaraman
P, Chen C, Xu F, Yang J, Li Q, Zheng H, et al: Myeloid cell-derived
inducible nitric oxide synthase suppresses M1 macrophage
polarization. Nat Commun. 6:66762015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wolf L, Herr C, Niederstraßer J,
Beisswenger C and Bals R: Receptor for advanced glycation
endproducts (RAGE) maintains pulmonary structure and regulates the
response to cigarette smoke. PLoS One. 12:e01800922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Fallah MP, Chelvarajan RL, Garvy BA and
Bondada S: Role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt signaling pathway
in the age-related cytokine dysregulation in splenic macrophages
stimulated via TLR-2 or TLR-4 receptors. Mech Ageing Dev.
132:274–286. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|