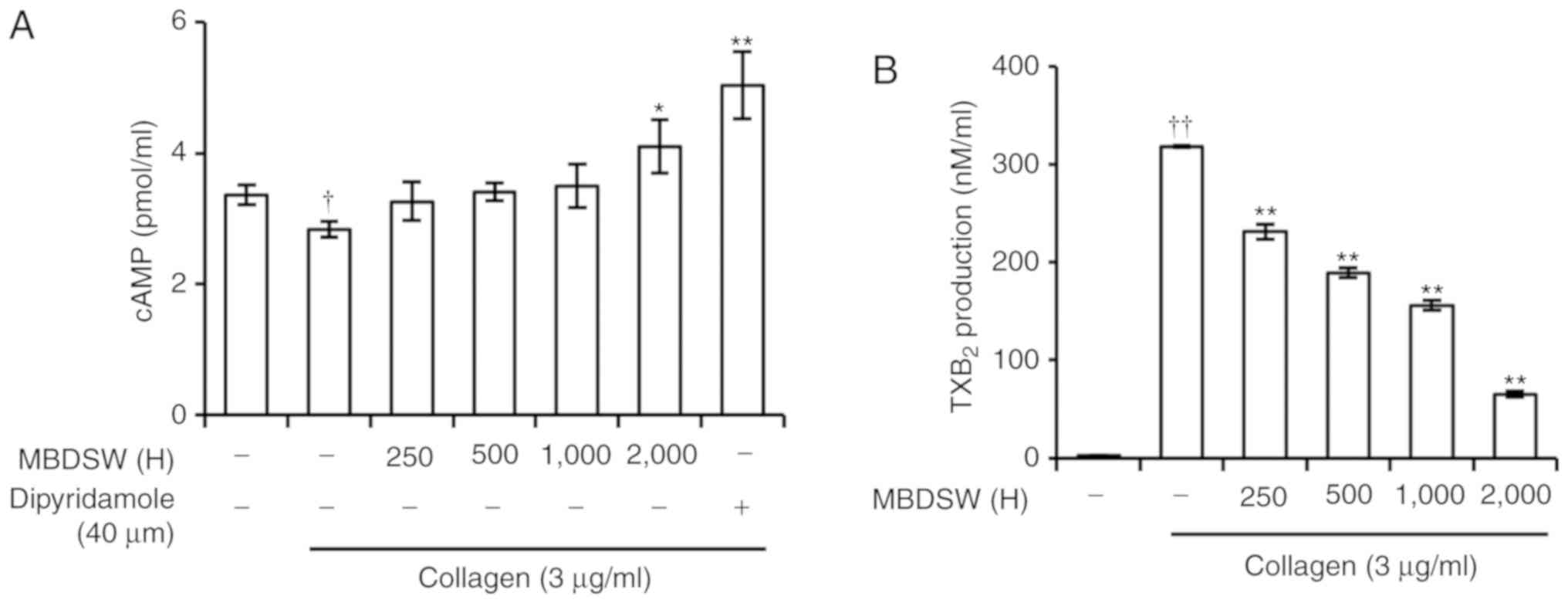
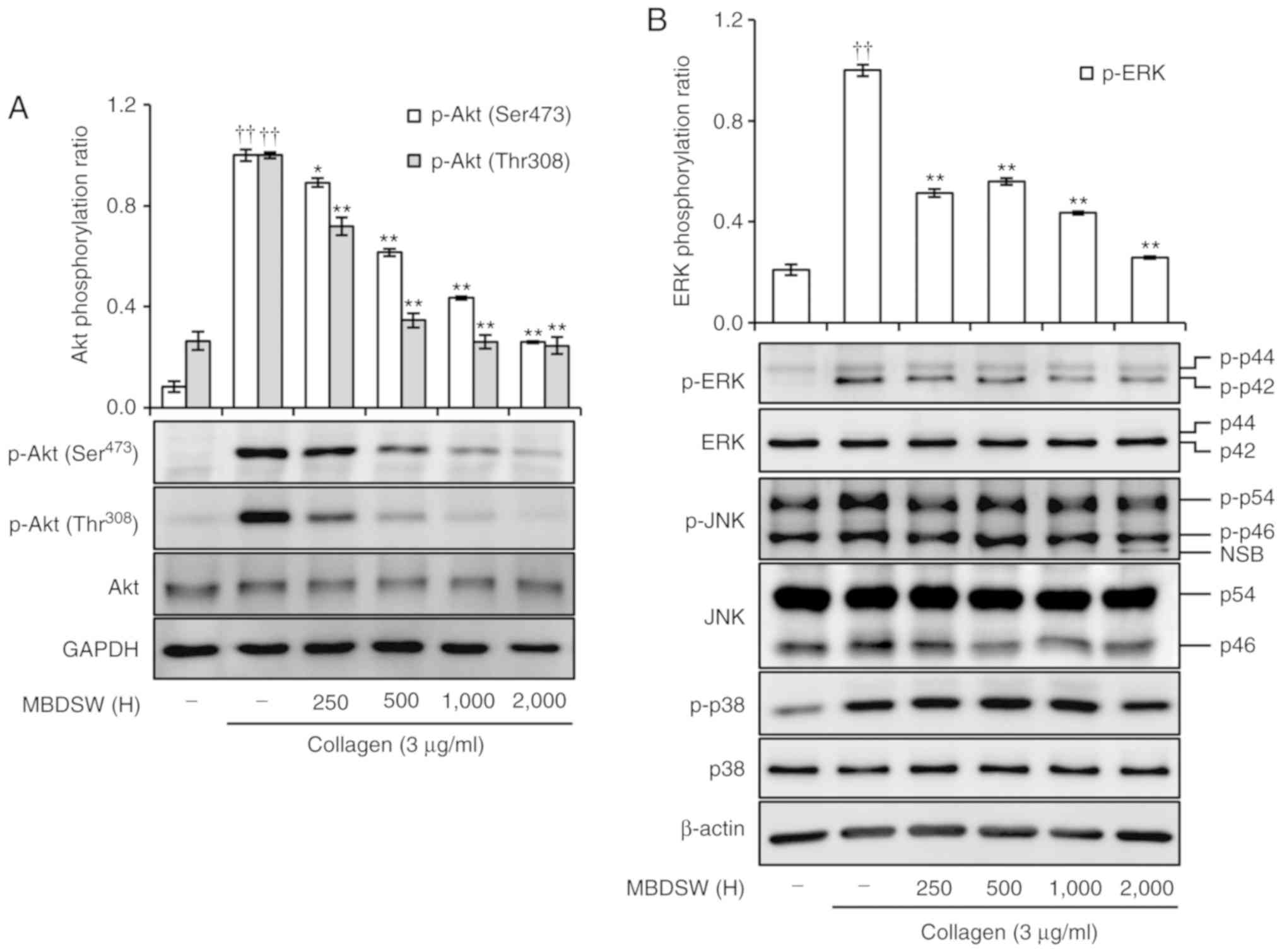
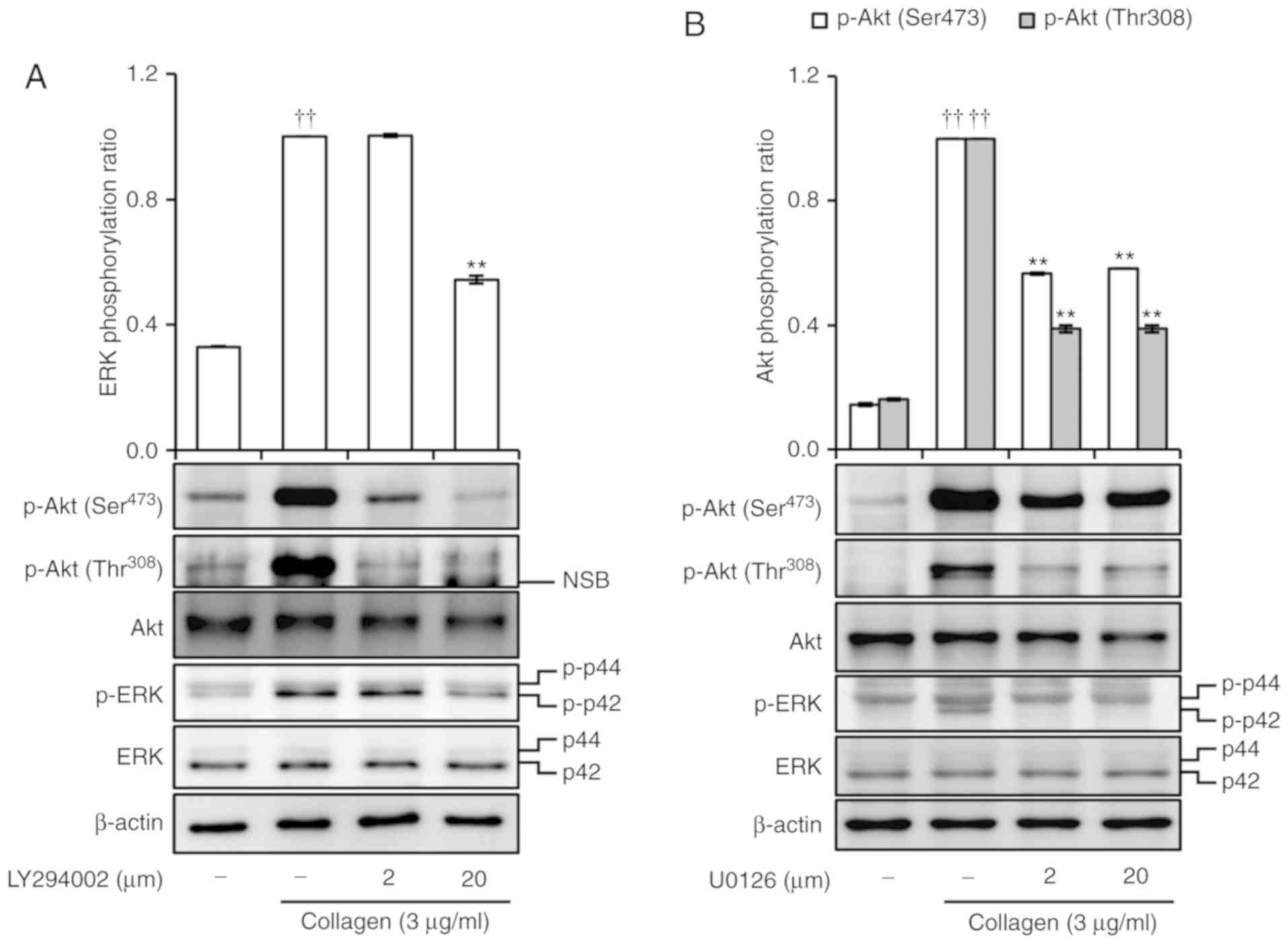
|
1
|
Kuter DJ: The physiology of platelet
production. Stem Cells. 14(Suppl 1): S88–S101. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Huo Y and Ley KF: Role of platelets in the
development of atherosclerosis. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 14:18–22.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Farndale RW, Sixma JJ, Barnes MJ and de
Groot PG: The role of collagen in thrombosis and hemostasis. J
Thromb Haemost. 2:561–573. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barnes MJ and Farndale RW: Collagens and
atherosclerosis. Exp Gerontol. 34:513–525. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jin J, Quinton TM, Zhang J, Rittenhouse SE
and Kunapuli SP: Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-induced thromboxane
A(2) generation in human platelets requires coordinated signaling
through integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3) and ADP receptors. Blood.
99:193–198. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Flaumenhaft R: Molecular basis of platelet
granule secretion. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:1152–1160.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hwang HS, Kim HA, Lee SH and Yun JW:
Anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects of deep sea water on ob/ob
mice. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 11:531–539. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hataguchi Y, Tai H, Nakajima H and Kimata
H: Drinking deep-sea water restores mineral imbalance in atopic
eczema/dermatitis syndrome. Eur J Clin Nutr. 59:1093–1096. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee KS, Kwon YS, Kim S, Moon DS, Kim HJ
and Nam KS: Regulatory mechanism of mineral-balanced deep sea water
on hypocholesterolemic effects in HepG2 hepatic cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 86:405–413. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lee KS, Chun SY, Lee MG, Kim S, Jang TJ
and Nam KS: The prevention of TNF-α/IFN-γ mixture-induced
inflammation in human keratinocyte and atopic dermatitis-like skin
lesions in Nc/Nga mice by mineral-balanced deep sea water. Biomed
Pharmacother. 97:1331–1340. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sheu MJ, Chou PY, Lin WH, Pan CH, Chien
YC, Chung YL, Liu FC and Wu CH: Deep sea water modulates blood
pressure and exhibits hypolipidemic effects via the AMPK-ACC
pathway: An in vivo study. Mar Drugs. 11:2183–2202. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee KS, Shin JS, Kwon YS, Moon DS and Nam
KS: Suppression of cancer progression and metastasis in HT-29 human
colorectal adenocarcinomas by deep sea water. Biotechnol Bioprocess
Eng. 18:194–200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Miyamura M, Yoshioka S, Hamada A, Takuma
D, Yokota J, Kusunose M, Kyotani S, Kawakita H, Odani K, Tsutsui Y
and Nishioka Y: Difference between deep seawater and surface
seawater in the preventive effect of atherosclerosis. Biol Pharm
Bull. 27:1784–1787. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee KS, Chun SY, Kwon YS, Kim S and Nam
KS: Deep sea water improves hypercholesterolemia and hepatic lipid
accumulation through the regulation of hepatic lipid metabolic gene
expression. Mol Med Rep. 15:2814–2822. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chun SY, Kim S and Nam KS: The inhibitory
effects of deep-sea water on doxorubicin-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Rep. 38:1163–1171. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen J, De S, Damron DS, Chen WS, Hay N
and Byzova TV: Impaired platelet responses to thrombin and collagen
in AKT-1-deficient mice. Blood. 104:1703–1710. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stojanovic A, Marjanovic JA, Brovkovych
VM, Peng X, Hay N, Skidgel RA and Du X: A phosphoinositide
3-kinase-AKT-nitric oxide-cGMP signaling pathway in stimulating
platelet secretion and aggregation. J Biol Chem. 281:16333–16339.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Flevaris P, Li Z, Zhang G, Zheng Y, Liu J
and Du X: Two distinct roles of mitogen-activated protein kinases
in platelets and a novel Rac1-MAPK-dependent integrin outside-in
retractile signaling pathway. Blood. 113:893–901. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Heemskerk JW, Bevers EM and Lindhout T:
Platelet activation and blood coagulation. Thromb Haemost.
88:186–193. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rittenhouse-Simmons S and Deykin D:
Isolation of membranes from normal and thrombin treated
gel-filtered platelets using a lectin marker. Biochim Biophys Acta.
426:688–696. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schaeffer J and Blaustein MP: Platelet
free calcium concentrations measured with fura-2 are influenced by
the transmembrane sodium gradient. Cell Calcium. 10:101–113. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nesbitt WS, Giuliano S, Kulkarni S,
Dopheide SM, Harper IS and Jackson SP: Intercellular calcium
communication regulates platelet aggregation and thrombus growth. J
Cell Biol. 160:1151–1161. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shattil SJ and Newman PJ: Integrins:
Dynamic scaffolds for adhesion and signaling in platelets. Blood.
104:1606–1615. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Reinhard M, Jarchau T and Walter U:
Actin-based motility: Stop and go with Ena/VASP proteins. Trends
Biochem Sci. 26:243–249. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gambaryan S, Kobsar A, Rukoyatkina N,
Herterich S, Geiger J, Smolenski A, Lohmann SM and Walter U:
Thrombin and collagen induce a feedback inhibitory signaling
pathway in platelets involving dissociation of the catalytic
subunit of protein kinase A from an NFkappaB-IkappaB complex. J
Biol Chem. 285:18352–18363. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Paul BZ, Jin J and Kunapuli SP: Molecular
mechanism of throm-boxane A(2)-induced platelet aggregation
Essential role for p2t(ac) and alpha(2a) receptors. J Biol Chem.
274:29108–29114. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mathur RK: Role of diabetes, hypertension,
and cigarette smoking on atherosclerosis. J Cardiovasc Dis Res.
1:64–68. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
O'Donnell CJ and Elosua R: Cardiovascular
risk factors. Insights from Framingham Heart Study. Rev Esp
Cardiol. 61:299–310. 2008.In Spanish. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Willoughby S, Holmes A and Loscalzo J:
Platelets and cardiovascular disease. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs.
1:273–288. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ha BG, Shin EJ, Park JE and Shon YH:
Anti-diabetic effect of balanced deep-sea water and its mode of
action in high-fat diet induced diabetic mice. Mar Drugs.
11:4193–4212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Katsuda S, Yasukawa T, Nakagawa K, Miyake
M, Yamasaki M, Katahira K, Mohri M, Shimizu T and Hazama A:
Deep-sea water improves cardiovascular hemodynamics in kurosawa and
kusanagi-hypercholesterolemic (KHC) rabbits. Biol Pharm Bull.
31:38–44. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yoshioka S, Hamada A, Cui T, Yokota J,
Yamamoto S, Kusunose M, Miyamura M, Kyotani S, Kaneda R, Tsutsui Y,
et al: Pharmacological activity of deep-sea water: Examination of
hyperlipemia prevention and medical treatment effect. Biol Pharm
Bull. 26:1552–1559. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Borissoff JI, Spronk HM, Heeneman S and
ten Cate H: Is thrombin a key player in the
'coagulation-atherogenesis' maze? Cardiovasc Res. 82:392–403. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gawaz M, Ott I, Reininger AJ and Neumann
FJ: Effects of magnesium on platelet aggregation and adhesion
Magnesium modulates surface expression of glycoproteins on
platelets in vitro and ex vivo. Thromb Haemost. 72:912–918. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gow IF, Padfield PL, Reid M, Stewart SE,
Edwards CR and Williams BC: High sodium intake increases platelet
aggregation in normal females. J Hypertens. (Suppl 5)–S246.
1987.
|
|
36
|
Togna G, Gallozzi S and Caprino L:
Influence of strontium chloride on blood platelet function. Arch
Toxicol. 63:366–369. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Komalavilas P and Lincoln TM:
Phosphorylation of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor by
cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 269:8701–8707.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Supattapone S, Danoff SK, Theibert A,
Joseph SK, Steiner J and Snyder SH: Cyclic AMP-dependent
phosphorylation of a brain inositol trisphosphate receptor
decreases its release of calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
85:8747–8750. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nishikawa M, Tanaka T and Hidaka H:
Ca2+-calmodulin- dependent phosphorylation and platelet secretion.
Nature. 287:863–865. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Reed GL, Fitzgerald ML and Polgár J:
Molecular mechanisms of platelet exocytosis: Insights into the
'secrete' life of thrombocytes. Blood. 96:3334–3342.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Payrastre B, Missy K, Trumel C, Bodin S,
Plantavid M and Chap H: The integrin alpha IIb/ beta 3 in human
platelet signal transduction. Biochem Pharmacol. 60:1069–1074.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Smolenski A: Novel roles of
cAMP/cGMP-dependent signaling in platelets. J Thromb Haemost.
10:167–176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kim S, Jee K, Kim D, Koh H and Chung J:
Cyclic AMP inhibits Akt activity by blocking the membrane
localization of PDK1. J Biol Chem. 276:12864–12870. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lin LL, Wartmann M, Lin AY, Knopf JL, Seth
A and Davis RJ: cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP
kinase. Cell. 72:269–278. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Birk AV, Broekman MJ, Gladek EM, Robertson
HD, Drosopoulos JH, Marcus AJ and Szeto HH: Role of extracellular
ATP metabolism in regulation of platelet reactivity. J Lab Clin
Med. 140:166–175. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cerrito F, Lazzaro MP, Gaudio E, Arminio P
and Aloisi G: 5HT2-receptors and serotonin release: Their role in
human platelet aggregation. Life Sci. 53:209–215. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bröijersén A, Hamsten A, Eriksson M,
Angelin B and Hjemdahl P: Platelet activity in vivo in
hyperlipoproteinemia-importance of combined hyperlipidemia. Thromb
Haemost. 79:268–275. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Nityanand S, Pande I, Bajpai VK, Singh L,
Chandra M and Singh BN: Platelets in essential hypertension. Thromb
Res. 72:447–454. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nowak J, Murray JJ, Oates JA and
FitzGerald GA: Biochemical evidence of a chronic abnormality in
platelet and vascular function in healthy individuals who smoke
cigarettes. Circulation. 76:6–14. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Manduteanu I, Calb M, Lupu C, Simionescu N
and Simionescu M: Increased adhesion of human diabetic platelets to
cultured valvular endothelial cells. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol.
24:539–547. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Eikelboom JW, Hirsh J, Spencer FA, Baglin
TP and Weitz JI: Antiplatelet drugs: Antithrombotic therapy and
prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American college of chest
physicians evidence-based clinical practice Guidelines. Chest.
141(2 Suppl): e89S–e119S. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|