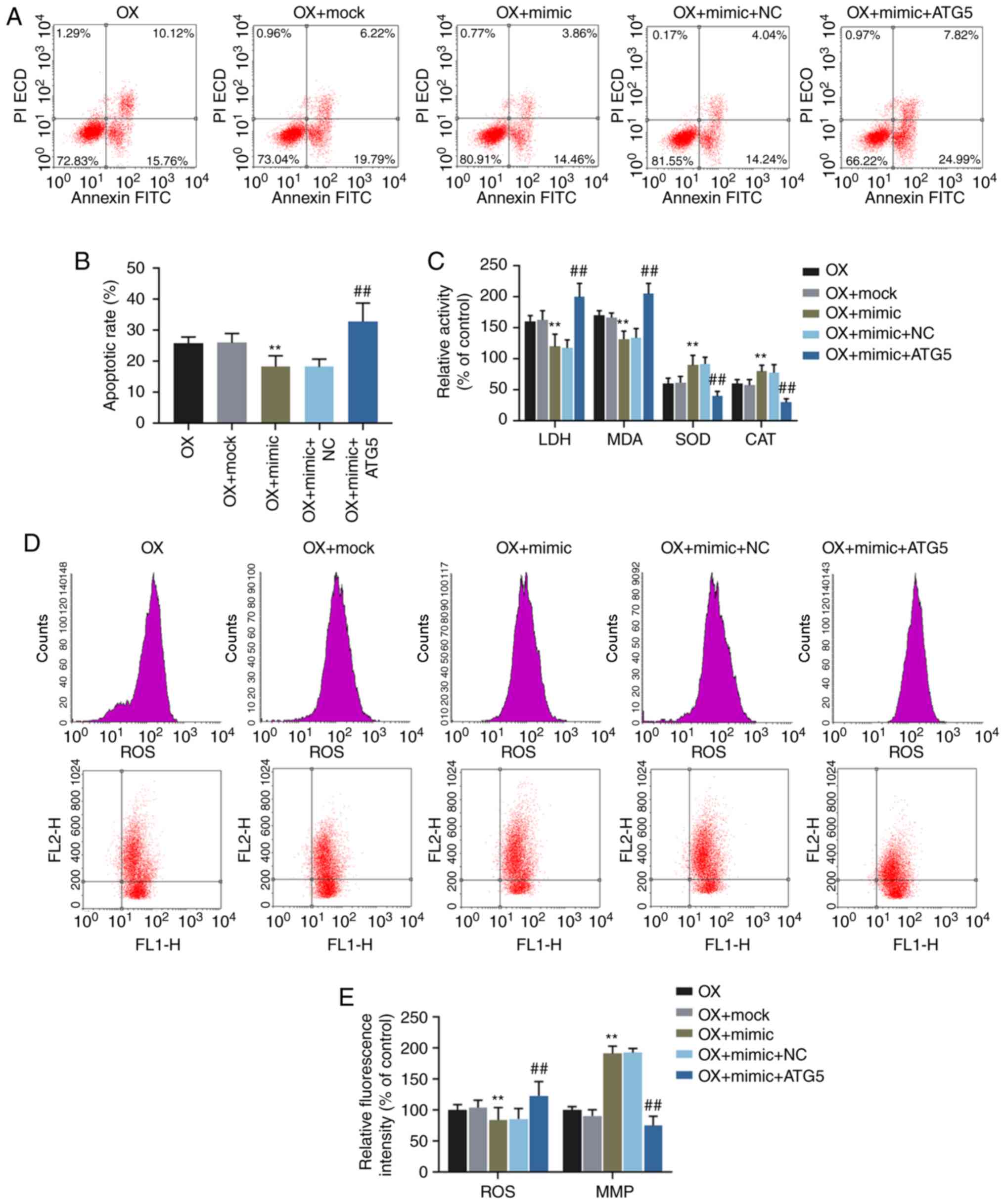
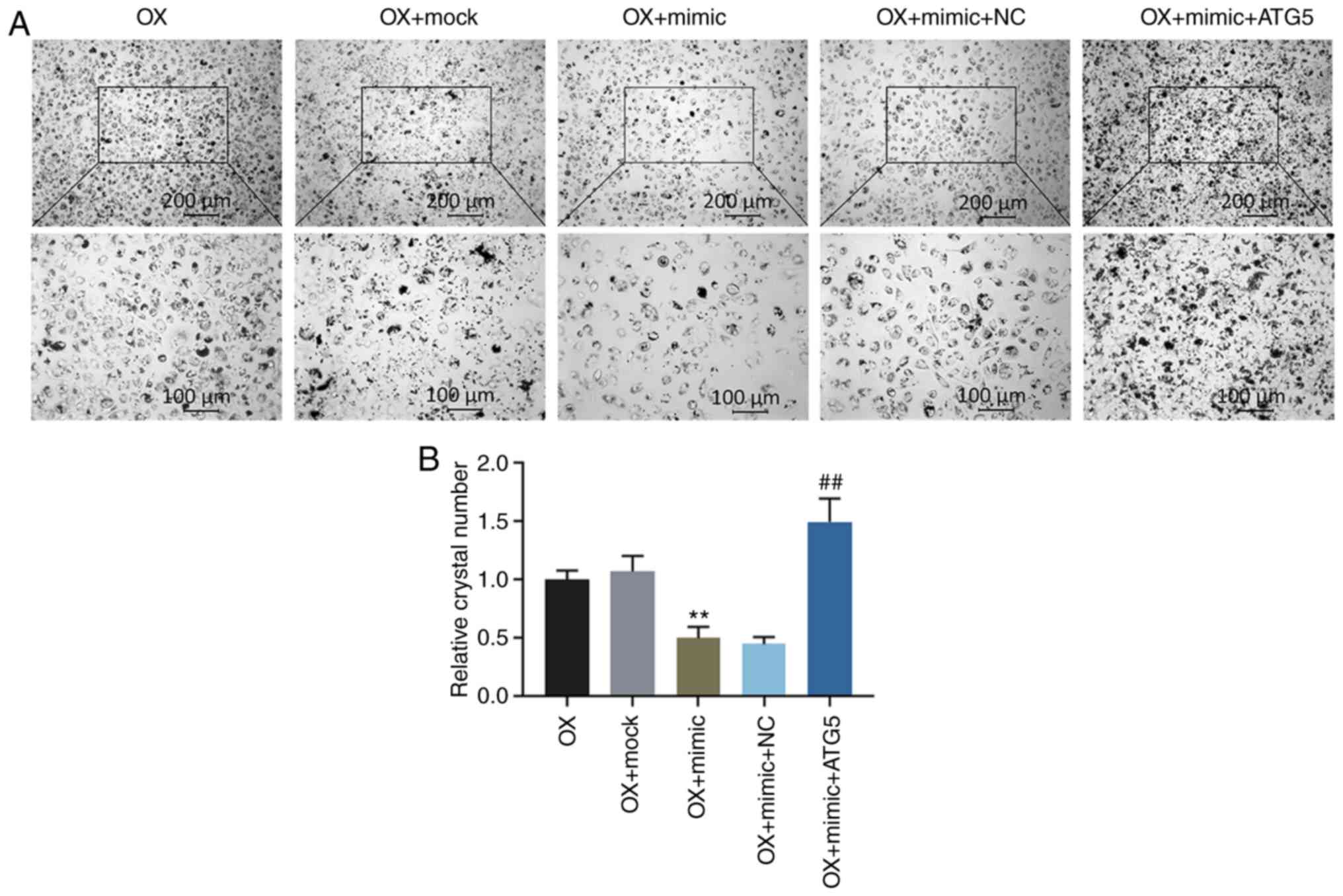
|
1
|
Stern JM, Moazami S, Qiu Y, Kurland I,
Chen Z, Agalliu I, Burk R and Davies KP: Evidence for a distinct
gut microbiome in kidney stone formers compared to non-stone
formers. Urolithiasis. 44:399–407. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Worcester EM and Coe FL: Clinical
practice. Calcium kidney stones. N Engl J Med. 363:954–963. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ye Z, Zeng G, Huan Y, Li J, Tang K, Wang
G, Wang S, Yu Y, Wang Y, Zhang T, et al: The status and
characteristics of urinary stone composition in China. BJU Int. Apr
8–2019.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Khan SR: Reactive oxygen species as the
molecular modulators of calcium oxalate kidney stone formation:
Evidence from clinical and experimental investigations. J Urol.
189:803–811. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ma MC, Chen YS and Huang HS: Erythrocyte
oxidative stress in patients with calcium oxalate stones correlates
with stone size and renal tubular damage. Urology. 83:510.e9–e17.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Asselman M, Verhulst A, De Broe ME and
Verkoelen CF: Calcium oxalate crystal adherence to hyaluronan-,
osteopontin-, and CD44-expressing injured/regenerating tubular
epithelial cells in rat kidneys. J Am Soc Nephrol. 14:3155–3166.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miyazawa K, Suzuki K, Ikeda R, Moriyama
MT, Ueda Y and Katsuda S: Apoptosis and its related genes in renal
epithelial cells of the stone-forming rat. Urol Res. 33:31–38.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Liu Y, Li D, He Z, Liu Q, Wu J, Guan X,
Tao Z and Deng Y: Inhibition of autophagy-attenuated calcium
oxalate crystal-induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury in
vivo and in vitro. Oncotarget. 9:4571–4582. 2017.
|
|
9
|
Taguchi K, Hamamoto S, Okada A, Unno R,
Kamisawa H, Naiki T, Ando R, Mizuno K, Kawai N, Tozawa K, et al:
Genome-wide gene expression profiling of randall's plaques in
calcium oxalate stone formers. J Am Soc Nephrol. 28:333–347. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yu L, Gan X, Liu X and An R: Calcium
oxalate crystals induces tight junction disruption in distal renal
tubular epithelial cells by activating ROS/Akt/p38 MAPK signaling
pathway. Ren Fail. 39:440–451. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Convento MB, Pessoa EA, Cruz E, da Glória
MA, Schor N and Borges FT: Calcium oxalate crystals and oxalate
induce an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in the proximal
tubular epithelial cells: Contribution to oxalate kidney injury.
Sci Rep. 7:457402017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang B, Wu B, Liu J, Yao W, Xia D, Li L,
Chen Z, Ye Z and Yu X: Analysis of altered microRNA expression
profiles in proximal renal tubular cells in response to calcium
oxalate monohydrate crystal adhesion: implications for kidney stone
disease. PLoS One. 9:e1013062014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hou J: Lecture: New light on the role of
claudins in the kidney. Organogenesis. 8:1–9. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gong Y, Renigunta V, Himmerkus N, Zhang J,
Renigunta A, Bleich M and Hou J: Claudin-14 regulates renal
Ca++ transport in response to CaSR signalling via a
novel microRNA pathway. EMBO J. 31:1999–2012. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lan C, Chen D, Liang X, Huang J, Zeng T,
Duan X, Chen K, Lai Y, Yang D, Li S, et al: Integrative analysis of
miRNA and mRNA expression profiles in calcium oxalate
nephrolithiasis rat model. Biomed Res Int. 2017:83067362017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hu YY, Dong WD, Xu YF, Yao XD, Peng B, Liu
M and Zheng JH: Elevated levels of miR-155 in blood and urine from
patients with nephrolithiasis. Biomed Res Int. 2014:2956512014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang C, Yu S, Zheng B, Liu D, Wan F, Ma
Y, Wang J, Gao Z and Shan Z: miR-30c-5p reduces renal
ischemia-reperfusion involving macrophage. Med Sci Monit.
25:4362–4369. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zou YF, Wen D, Zhao Q, Shen PY, Shi H,
Zhao Q, Chen YX and Zhang W: Urinary MicroRNA-30c-5p and
MicroRNA-192-5p as potential biomarkers of
ischemia-reperfusion-induced kidney injury. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
242:657–667. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Du B, Dai XM, Li S, Qi GL, Cao GX, Zhong
Y, Yin PD and Yang XS: MiR-30c regulates cisplatin-induced
apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells by targeting Bnip3L and
Hspa5. Cell Death Dis. 8:e29872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gutiérrez-Escolano A, Santacruz-Vázquez E
and Gómez-Pérez F: Dysregulated microRNAs involved in
contrast-induced acute kidney injury in rat and human. Ren Fail.
37:1498–1506. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zheng W, Xie W, Yin D, Luo R, Liu M and
Guo F: ATG5 and ATG7 induced autophagy interplays with UPR via PERK
signaling. Cell Commun Signal. 17:422019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Manissorn J, Fong-Ngern K, Peerapen P and
Thongboonkerd V: Systematic evaluation for effects of urine pH on
calcium oxalate crystallization, crystal-cell adhesion and
internalization into renal tubular cells. Sci Rep. 7:17982017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Abhishek A, Benita S, Kumari M, Ganesan D,
Paul E, Sasikumar P, Mahesh A, Yuvaraj S, Ramprasath T and Selvam
GS: Molecular analysis of oxalate-induced endoplasmic reticulum
stress mediated apoptosis in the pathogenesis of kidney stone
disease. J Physiol Biochem. 73:561–573. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fishman AI, Green D, Lynch A, Choudhury M,
Eshghi M and Konno S: Preventive effect of specific antioxidant on
oxidative renal cell injury associated with renal crystal
formation. Urology. 82:489.e1–e7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cheraft-Bahloul N, Husson C, Ourtioualous
M, Sinaeve S, Atmani D, Stévigny C, Nortier JL and Antoine MH:
Protective effects of pistacia lentiscus L. fruit extract against
calcium oxalate monohydrate induced proximal tubular injury. J
Ethnopharmacol. 209:248–254. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao Y, Yin Z, Li H, Fan J, Yang S, Chen C
and Wang DW: MiR-30c protects diabetic nephropathy by suppressing
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in db/db mice. Aging Cell.
16:387–400. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Davalos M, Konno S, Eshghi M and Choudhury
M: Oxidative renal cell injury induced by calcium oxalate crystal
and renoprotection with antioxidants: A possible role of oxidative
stress in nephrolithiasis. J Endourol. 24:339–345. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jeong BC, Kwak C, Cho KS, Kim BS, Hong SK,
Kim JI, Lee C and Kim HH: Apoptosis induced by oxalate in human
renal tubular epithelial HK-2 cells. Urol Res. 33:87–92. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu X, Li M, Peng Y, Hu X, Xu J, Zhu S, Yu
Z and Han S: miR-30c regulates proliferation, apoptosis and
differentiation via the Shh signaling pathway in P19 cells. Exp Mol
Med. 48:e2482016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Khan SR: Hyperoxaluria-induced oxidative
stress and antioxidants for renal protection. Urol Res. 33:349–357.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Khan SR: Reactive oxygen species,
inflammation and calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis. Transl Androl
Urol. 3:256–276. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liang Y, Dong B, Pang N and Hu J: ROS
generation and DNA damage contribute to abamectin-induced
cytotoxicity in mouse macrophage cells. Chemosphere. 234:328–337.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ren J, Yuan L, Wang W, Zhang M, Wang Q, Li
S, Zhang L and Hu K: Tricetin protects against 6-OHDA-induced
neurotoxicity in Parkinson's disease model by activating Nrf2/HO-1
signaling pathway and preventing mitochondria-dependent apoptosis
pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 378:1146172019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao J, Zhang M, Zhang W, Liu F, Huang K
and Lin K: Insight into the tolerance, biochemical and
antioxidative response in three moss species on exposure to BDE-47
and BDE-209. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 181:445–454. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang C, Zhang C, Wang H, Qi Y, Kan Y and
Ge Z: Effects of miR-103a-3p on the autophagy and apoptosis of
cardiomyocytes by regulating Atg5. Int J Mol Med. 43:1951–1960.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Young MM, Takahashi Y, Khan O, Park S,
Hori T, Yun J, Sharma AK, Amin S, Hu CD, Zhang J, et al:
Autophagosomal membrane serves as platform for intracellular
death-inducing signaling complex (iDISC)-mediated caspase-8
activation and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 287:12455–12468. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao P, Zhang BL, Liu K, Qin B and Li ZH:
Overexpression of miR-638 attenuated the effects of
hypoxia/reoxygenation treatment on cell viability, cell apoptosis
and autophagy by targeting ATG5 in the human cardiomyocytes. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:8462–8471. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zheng Y, Tan K and Huang H: Long noncoding
RNA HAGLROS regulates apoptosis and autophagy in colorectal cancer
cells via sponging miR-100 to target ATG5 expression. J Cell
Biochem. 120:3922–3933. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Shroff A and Reddy KVR: Autophagy gene
ATG5 knockdown upregulates apoptotic cell death during Candida
albicans infection in human vaginal epithelial cells. Am J Reprod
Immunol. 80:e130562018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liao Z, Dai Z, Cai C, Zhang X, Li A, Zhang
H, Yan Y, Lin W, Wu Y, Li H, et al: Knockout of Atg5 inhibits
proliferation and promotes apoptosis of DF-1 cells. In Vitro Cell
Dev Biol Anim. 55:341–348. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hollomon MG, Gordon N, Santiago-O'Farrill
JM and Kleinerman ES: Knockdown of autophagy-related protein 5,
ATG5, decreases oxidative stress and has an opposing effect on
camptothecin-induced cytotoxicity in osteosarcoma cells. BMC
Cancer. 13:5002013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Khan SR: Renal tubular damage/dysfunction:
Key to the formation of kidney stones. Urol Res. 34:86–91. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Duan X, Kong Z, Mai X, Lan Y, Liu Y, Yang
Z, Zhao Z, Deng T, Zeng T, Cai C, et al: Autophagy inhibition
attenuates hyperoxaluria-induced renal tubular oxidative injury and
calcium oxalate crystal depositions in the rat kidney. Redox Biol.
16:414–425. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|