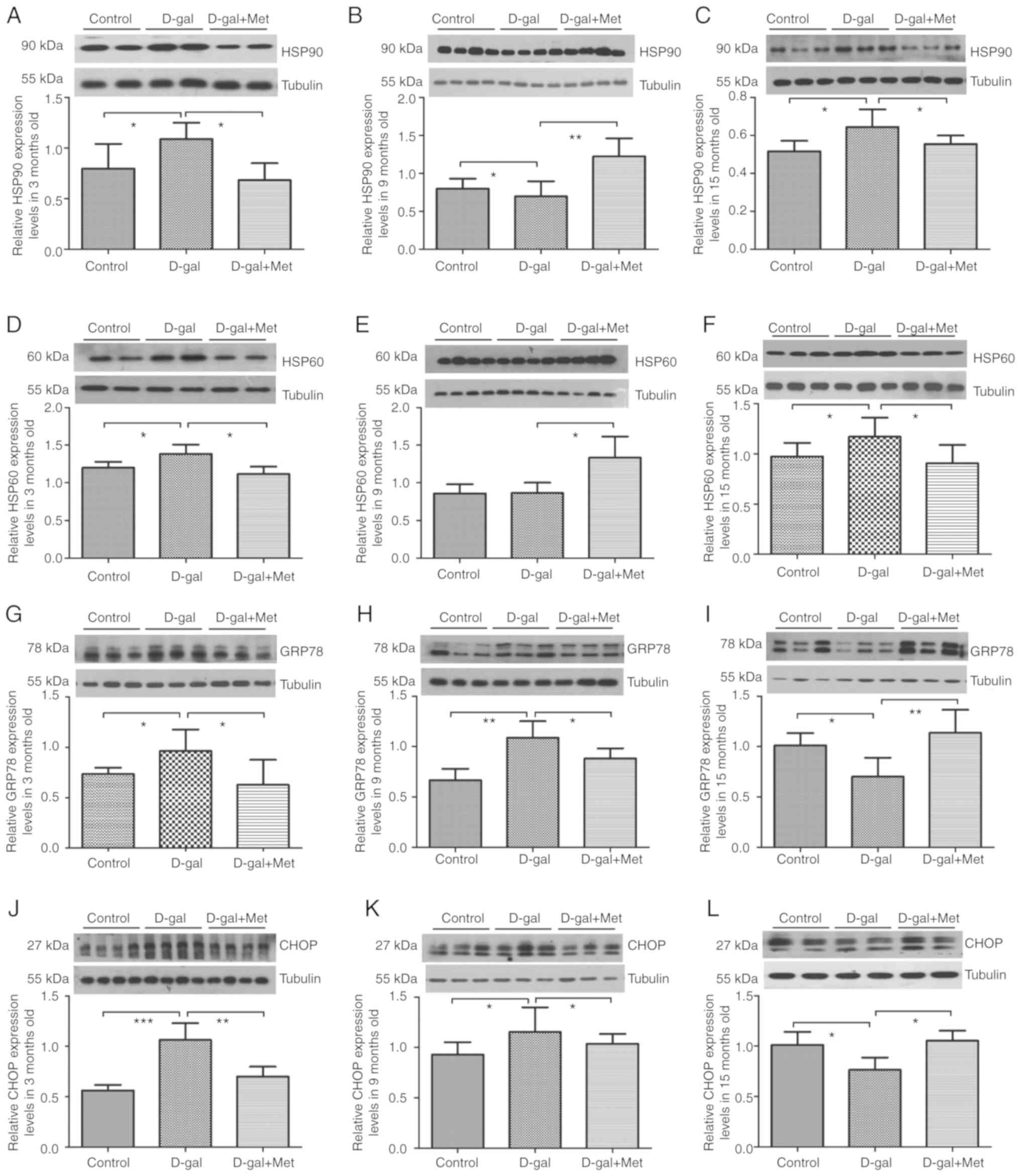
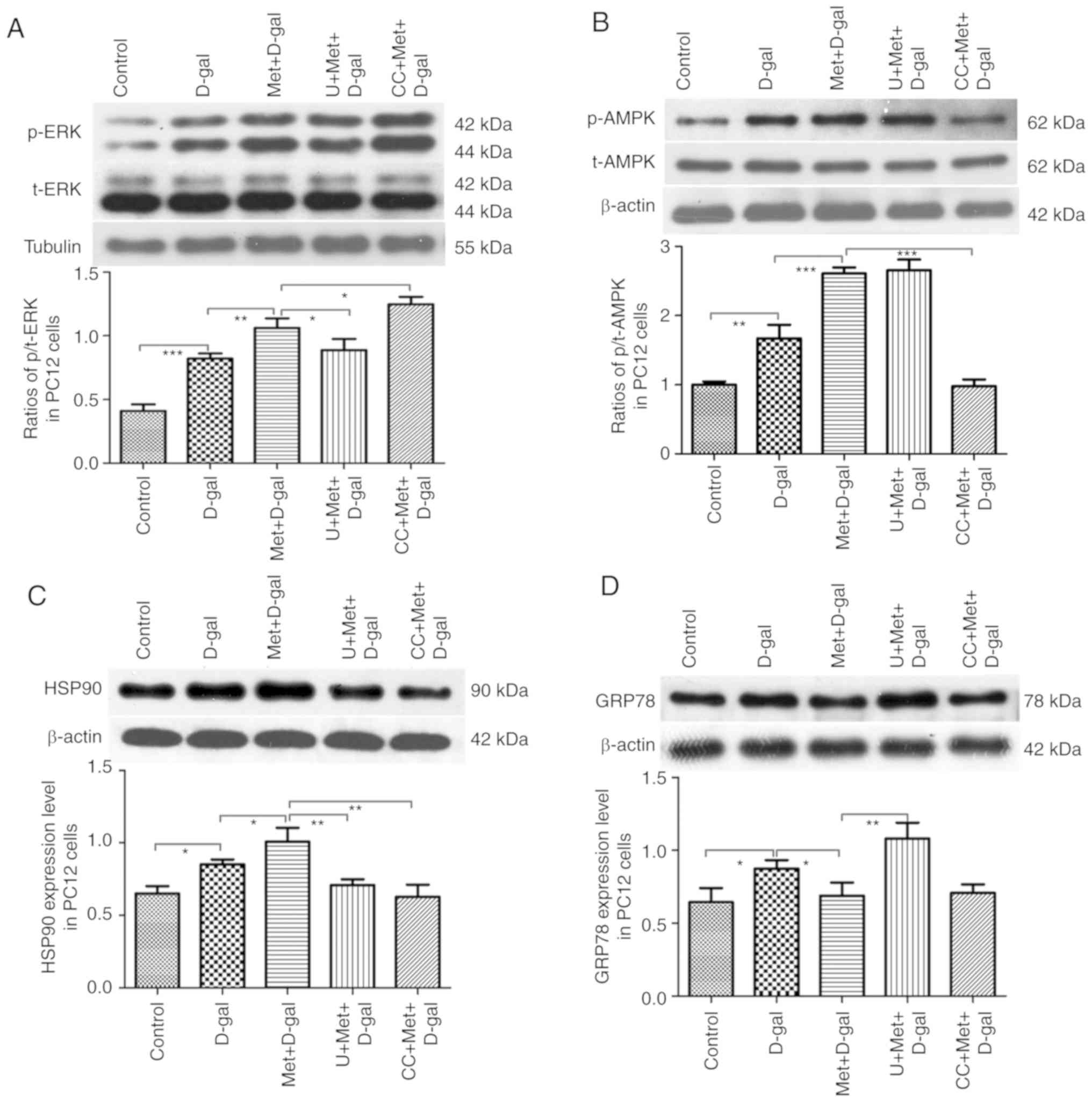
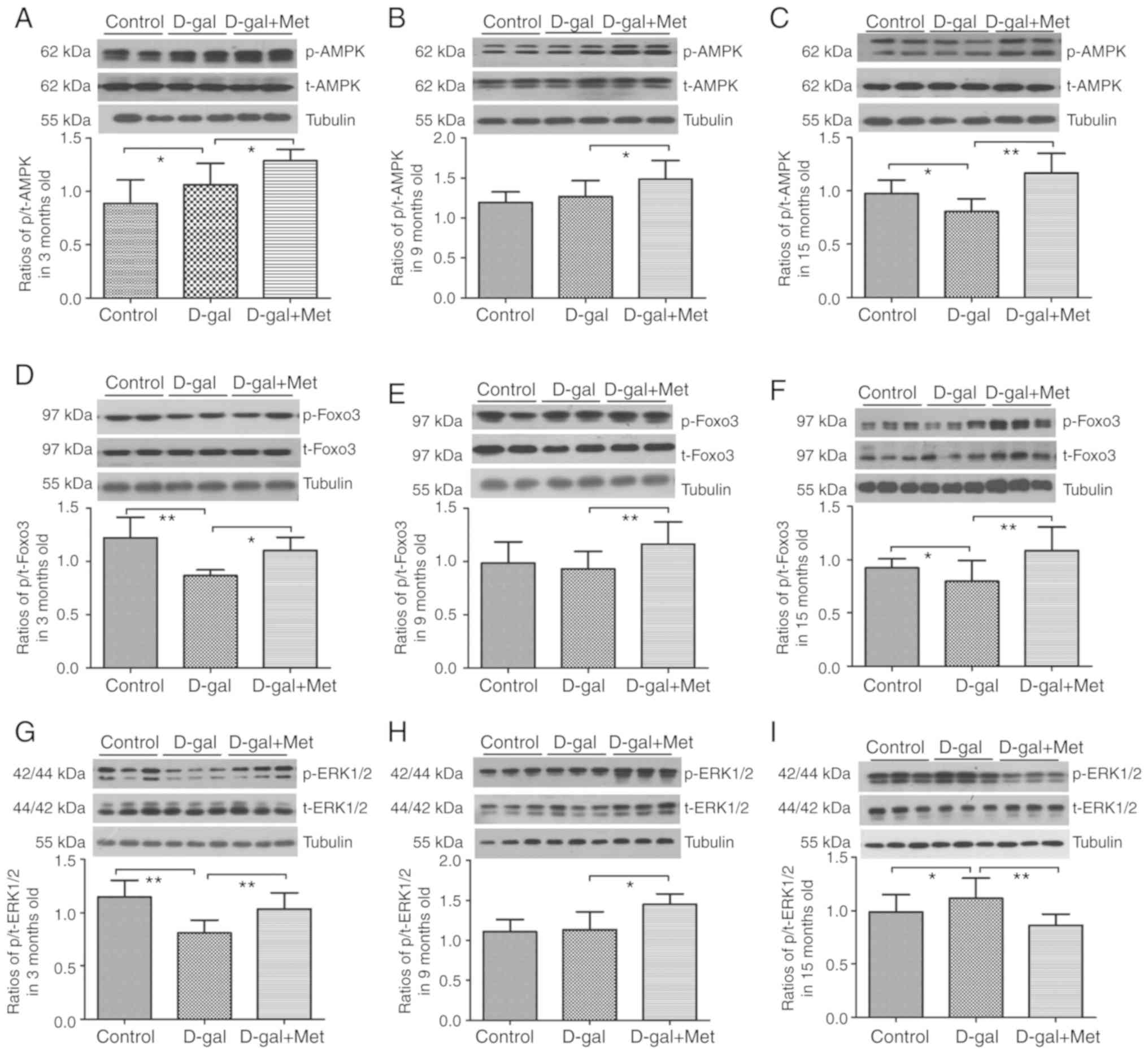
|
1
|
Du Z, Yang Y, Hu Y, Sun Y, Zhang S, Peng
W, Zhong Y, Huang X and Kong W: A long-term high-fat diet increases
oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in the inner
ear of D-galactose-induced aging rats. Hear Res. 287:15–24. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gates GA and Mills JH: Presbycusis.
Lancet. 366:1111–1120. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Humes LE, Dubno JR, Gordon-Salant S,
Lister JJ, Cacace AT, Cruickshanks KJ, Gates GA, Wilson RH and
Wingfield A: Central presbycusis: A review and evaluation of the
evidence. J Am Acad Audiol. 23:635–666. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Taylor RC and Dillin A: Aging as an event
of proteostasis collapse. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
3:a0044402011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jensen MB and Jasper H: Mitochondrial
proteostasis in the control of aging and longevity. Cell Metab.
20:214–225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li J, Akil O, Rouse SL, McLaughlin CW,
Matthews IR, Lustig LR, Chan DK and Sherr EH: Deletion of Tmtc4
activates the unfolded protein response and causes postnatal
hearing loss. J Clin Invest. 128:5150–5162. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chaube R: Can UPR integrate fasting and
stem cell regeneration? FRONT CHEM. 3:52015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Duran-Aniotz C, Martínez G and Hetz C:
Memory loss in Alzheimer's disease: Are the alterations in the UPR
network involved in the cognitive impairment? Front Aging Neurosci.
6:82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Woehlbier U and Hetz C: Modulating stress
responses by the UPRosome: A matter of life and death. Trends
Biochem Sci. 36:329–337. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao RR, Xu XC, Xu F, Zhang WL, Zhang WL,
Liu LM and Wang WP: Metformin protects against seizures, learning
and memory impairments and oxidative damage induced by
pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling in mice. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 448:414–417. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Patil SP, Jain PD, Ghumatkar PJ, Tambe R
and Sathaye S: Neuroprotective effect of metformin in MPTP-induced
Parkinson's disease in mice. Neuroscience. 277:747–754. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liang D, Song Z, Liang W, Li Y and Liu S:
Metformin inhibits TGF-beta 1-induced MCP-1 expression through
BAMBI-mediated suppression of MEK/ERK1/2 signalling. Nephrology
(Carlton). 24:481–488. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tao L, Li D, Liu H, Jiang F, Xu Y, Cao Y,
Gao R and Chen G: Neuroprotective effects of metformin on traumatic
brain injury in rats associated with NF-κB and MAPK signaling
pathway. Brain Res Bull. 140:154–161. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National
Academies Press; Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
15
|
Khallaghi B, Safarian F, Nasoohi S,
Ahmadiani A and Dargahi L: Metformin-induced protection against
oxidative stress is associated with AKT/mTOR restoration in PC12
cells. Life Sci. 148:286–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang HY, Yang Y, Zhang YY, Xie Z, Zhao
XY, Sun Y and Kong WJ: The dual role of poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase-1 in modulating parthanatos and autophagy under
oxidative stress in rat cochlear marginal cells of the stria
vascularis. Redox Biol. 14:361–370. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Itahana K, Campisi J and Dimri GP: Methods
to detect biomarkers of cellular senescence: The
senescence-associated beta-galactosidase assay. Methods Mol Biol.
371:21–31. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu X, Wang Y, Sun Y, Chen S, Zhang S, Shen
L, Huang X, Lin X and Kong W: Reduced expression of Connexin26 and
its DNA promoter hypermethylation in the inner ear of mimetic aging
rats induced by d-galactose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
452:340–346. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kong WJ, Hu YJ, Wang Q, Wang Y, Han YC,
Cheng HM, Kong W and Guan MX: The effect of the mtDNA4834 deletion
on hearing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 344:425–430. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nicklas JA, Brooks EM, Hunter TC, Single R
and Branda RF: Development of a quantitative PCR (TaqMan) assay for
relative mitochondrial DNA copy number and the common mitochondrial
DNA deletion in the rat. Environ Mol Mutagen. 44:313–320. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sun HY, Hu YJ, Zhao XY, Zhong Y, Zeng LL,
Chen XB, Yuan J, Wu J, Sun Y, Kong W and Kong WJ: Age-related
changes in mitochondrial antioxidant enzyme Trx2 and
TXNIP-Trx2-ASK1 signal pathways in the auditory cortex of a mimetic
aging rat model: Changes to Trx2 in the auditory cortex. FEBS J.
282:2758–2774. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xia MY, Zhao XY, Huang QL, Sun HY, Sun C,
Yuan J, He C, Sun Y, Huang X, Kong W and Kong WJ: Activation of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling by lithium chloride attenuates
d-galactose-induced neurodegeneration in the auditory cortex of a
rat model of aging. FEBS Open Bio. 7:759–776. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tian YY, Jiang B, An LJ and Bao YM:
Neuroprotective effect of catalpol against MPP(+)-induced oxidative
stress in mesencephalic neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 568:142–148.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kong WJ, Wang Y, Wang Q, Hu YJ, Han YC and
Liu J: The relation between D-galactose injection and mitochondrial
DNA 4834 bp deletion mutation. Exp Gerontol. 41:628–634. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zeng L, Yang Y, Hu Y, Sun Y, Du Z, Xie Z,
Zhou T and Kong W: Age-related decrease in the mitochondrial
sirtuin deacetylase Sirt3 expression associated with ROS
accumulation in the auditory cortex of the mimetic aging rat model.
PLoS One. 9:e880192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bernales S, Soto MM and McCullagh E:
Unfolded protein stress in the endoplasmic reticulum and
mitochondria: A role in neuro-degeneration. Front Aging Neurosci.
4:52012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang W, Sun Y, Chen S, Zhou X, Wu X and
Kong W and Kong W: Impaired unfolded protein response in the
degeneration of cochlea cells in a mouse model of age-related
hearing loss. Exp Gerontol. 70:61–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen J, Huang Z, Wu X, Kang J, Ren Y, Gao
W, Lu X, Wang J, Ding W, Nakabeppu Y, et al: Oxidative stress
induces different tissue dependent effects on Mutyh-deficient mice.
Free Radic Biol Med. 143:482–493. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mendoza MC, Er EE and Blenis J: The
Ras-ERK and PI3K-mTOR pathways: Cross-talk and compensation. Trends
Biochem Sci. 36:320–328. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ho SC, Liu JH and Wu RY: Establishment of
the mimetic aging effect in mice caused by D-galactose.
Biogerontology. 4:15–18. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kong W, Hu Y, Wang Q, Xu L, Wang Y, Han Y,
Li J, Liu B and Kong W: Establishment of model with inner ear
mimetic aging and mtDNA 4834 bp deletion in rats. Lin Chuang Er Bi
Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 20:888–890. 8932006.In Chinese.
|
|
33
|
Zhong Y, Hu Y, Peng W, Sun Y, Yang Y, Zhao
X, Huang X, Zhang H and Kong W: Age-related decline of the
cytochrome c oxidase subunit expression in the auditory cortex of
the mimetic aging rat model associated with the common deletion.
Hear Res. 294:40–48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Balaban RS, Nemoto S and Finkel T:
Mitochondria, oxidants, and aging. Cell. 120:483–495. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin MT and Beal MF: Mitochondrial
dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases.
Nature. 443:787–795. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sands WA, Page MM and Selman C:
Proteostasis and ageing: Insights from long-lived mutant mice. J
Physiol. 595:6383–6390. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
McBride HM, Neuspiel M and Wasiak S:
Mitochondria: More than just a powerhouse. Curr Biol. 16:R551–R560.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Klinge CM: Estrogenic control of
mitochondrial function and biogenesis. J Cell Biochem.
105:1342–1351. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Weinberg F and Chandel NS: Mitochondrial
metabolism and cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1177:66–73. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Houtkooper RH, Mouchiroud L, Ryu D,
Moullan N, Katsyuba E, Knott G, Williams RW and Auwerx J:
Mitonuclear protein imbalance as a conserved longevity mechanism.
Nature. 497:451–457. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yoneda T, Benedetti C, Urano F, Clark SG,
Harding HP and Ron D: Compartment-specific perturbation of protein
handling activates genes encoding mitochondrial chaperones. J Cell
Sci. 117:4055–4066. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shpilka T and Haynes CM: The mitochondrial
UPR: Mechanisms, physiological functions and implications in
ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 19:109–120. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Beck JS, Mufson EJ and Counts SE: Evidence
for mitochondrial UPR gene activation in familial and sporadic
Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 13:610–614. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zarse K, Schmeisser S, Groth M, Priebe S,
Beuster G, Kuhlow D, Guthke R, Platzer M, Kahn CR and Ristow M:
Impaired insulin/IGF1 signaling extends life span by promoting
mitochondrial L-proline catabolism to induce a transient ROS
signal. Cell Metab. 15:451–465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mohamed SA, Hanke T, Erasmi AW, Bechtel
MJ, Scharfschwerdt M, Meissner C, Sievers HH and Gosslau A:
Mitochondrial DNA deletions and the aging heart. Exp Gerontol.
41:508–517. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen B, Zhong Y, Peng W, Sun Y, Hu YJ,
Yang Y and Kong WJ: Increased mitochondrial DNA damage and
decreased base excision repair in the auditory cortex of
D-galactose-induced aging rats. Mol Biol Rep. 38:3635–3642. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Zeng Z, Zhang Z, Yu H, Corbley MJ, Tang Z
and Tong T: Mitochondrial DNA deletions are associated with
ischemia and aging in Balb/c mouse brain. J Cell Biochem.
73:545–553. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Chen B, Zhong Y, Peng W, Sun Y and Kong
WJ: Age-related changes in the central auditory system: Comparison
of D-galactose-induced aging rats and naturally aging rats. Brain
Res. 1344:43–53. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Eletto D, Chevet E, Argon Y and
Appenzeller-Herzog C: Redox controls UPR to control redox. J Cell
Sci. 127:3649–3658. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hill S and Van Remmen H: Mitochondrial
stress signaling in longevity: A new role for mitochondrial
function in aging. Redox Biol. 2:936–944. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cohen E, Bieschke J, Perciavalle RM, Kelly
JW and Dillin A: Opposing activities protect against age-onset
proteotoxicity. Science. 313:1604–1610. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Labunskyy VM, Gerashchenko MV, Delaney JR,
Kaya A, Kennedy BK, Kaeberlein M and Gladyshev VN: Lifespan
extension conferred by endoplasmic reticulum secretory pathway
deficiency requires induction of the unfolded protein response.
PLoS Genet. 10:e10040192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Correia S, Carvalho C, Santos MS, Proença
T, Nunes E, Duarte AI, Monteiro P, Seiça R, Oliveira CR and Moreira
PI: Metformin protects the brain against the oxidative imbalance
promoted by type 2 diabetes. Med Chem. 4:358–364. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kurioka T, Matsunobu T, Satoh Y, Niwa K,
Endo S, Fujioka M and Shiotani A: ERK2 mediates inner hair cell
survival and decreases susceptibility to noise-induced hearing
loss. Sci Rep. 5:168392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Arthur DB, Georgi S, Akassoglou K and
Insel PA: Inhibition of apoptosis by P2Y2 receptor activation:
Novel pathways for neuronal survival. J Neurosci. 26:3798–3804.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ
and Greenberg ME: Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases
on apoptosis. Science. 270:1326–1331. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Stanciu M, Wang Y, Kentor R, Burke N,
Watkins S, Kress G, Reynolds I, Klann E, Angiolieri MR, Johnson JW
and DeFranco DB: Persistent activation of ERK contributes to
glutamate-induced oxidative toxicity in a neuronal cell line and
primary cortical neuron cultures. J Biol Chem. 275:12200–12206.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, Zhang X, McNabola A,
Wilkie D, Wilhelm S, Lynch M and Carter C: Sorafenib blocks the
RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor
cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer
Res. 66:11851–11858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Tavares R and Pathak SK: Helicobacter
pylori Secreted protein HP1286 triggers apoptosis in macrophages
via TNF-independent and ERK MAPK-dependent pathways. Front Cell
Infect Microbiol. 7:582017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
60
|
Feng X, Sun T, Bei Y, Ding S, Zheng W, Lu
Y and Shen P: S-nitrosylation of ERK inhibits ERK phosphorylation
and induces apoptosis. Sci Rep. 3:18142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Allen EN, Potdar S, Tapias V, Parmar M,
Mizuno CS, Rimando A and Cavanaugh JE: Resveratrol and pinostilbene
confer neuroprotection against aging-related deficits through an
ERK1/2-dependent mechanism. J Nutr Biochem. 54:77–86. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Zhen X, Uryu K, Cai G, Johnson GP and
Friedman E: Age-associated impairment in brain MAPK signal pathways
and the effect of caloric restriction in Fischer 344 rats. J
Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 54:B539–B548. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Zhuang S and Schnellmann RG: A
death-promoting role for extracellular signal-regulated kinase. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 319:991–997. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sinha D, Bannergee S, Schwartz JH,
Lieberthal W and Levine JS: Inhibition of ligand-independent ERK1/2
activity in kidney proximal tubular cells deprived of soluble
survival factors up-regulates Akt and prevents apoptosis. J Biol
Chem. 279:10962–10972. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Moelling K, Schad K, Bosse M, Zimmermann S
and Schweneker M: Regulation of Raf-Akt cross-talk. J Biol Chem.
277:31099–31106. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|