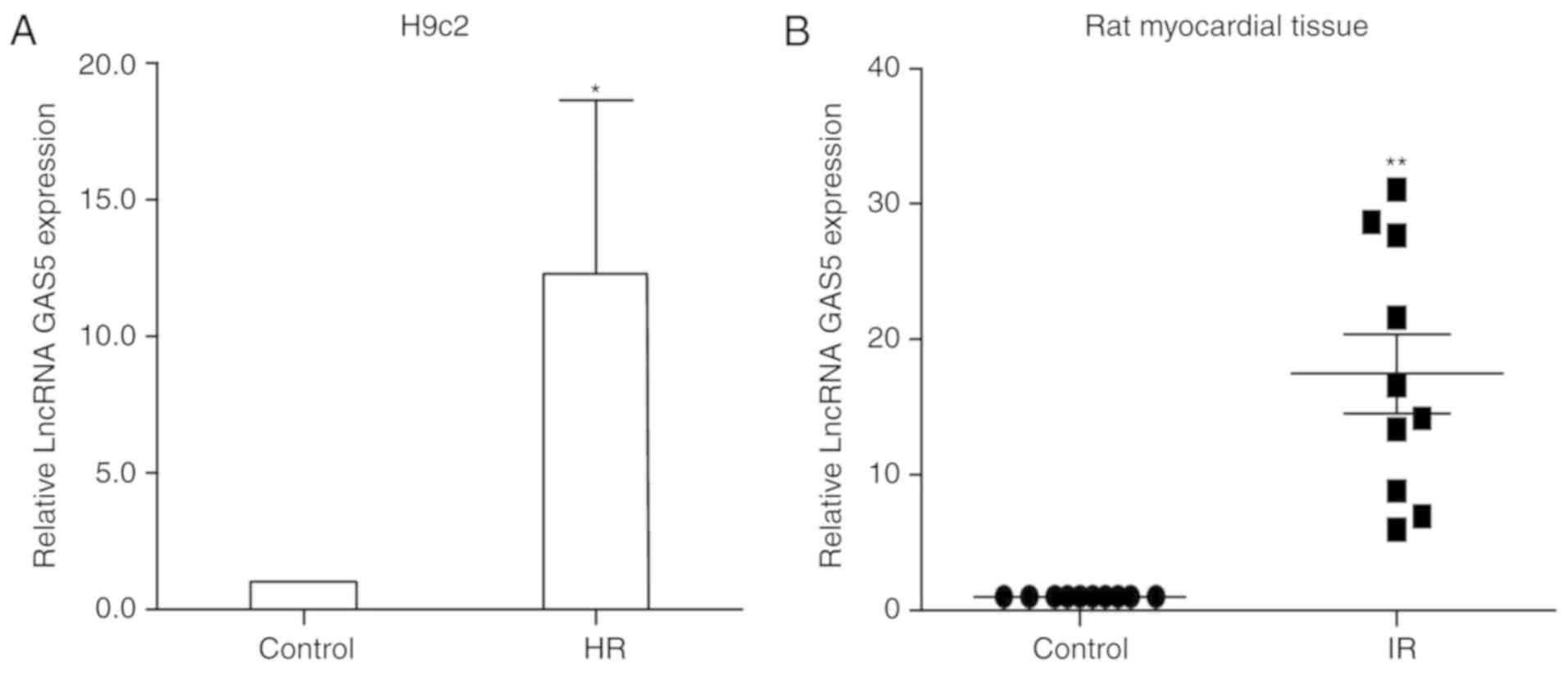
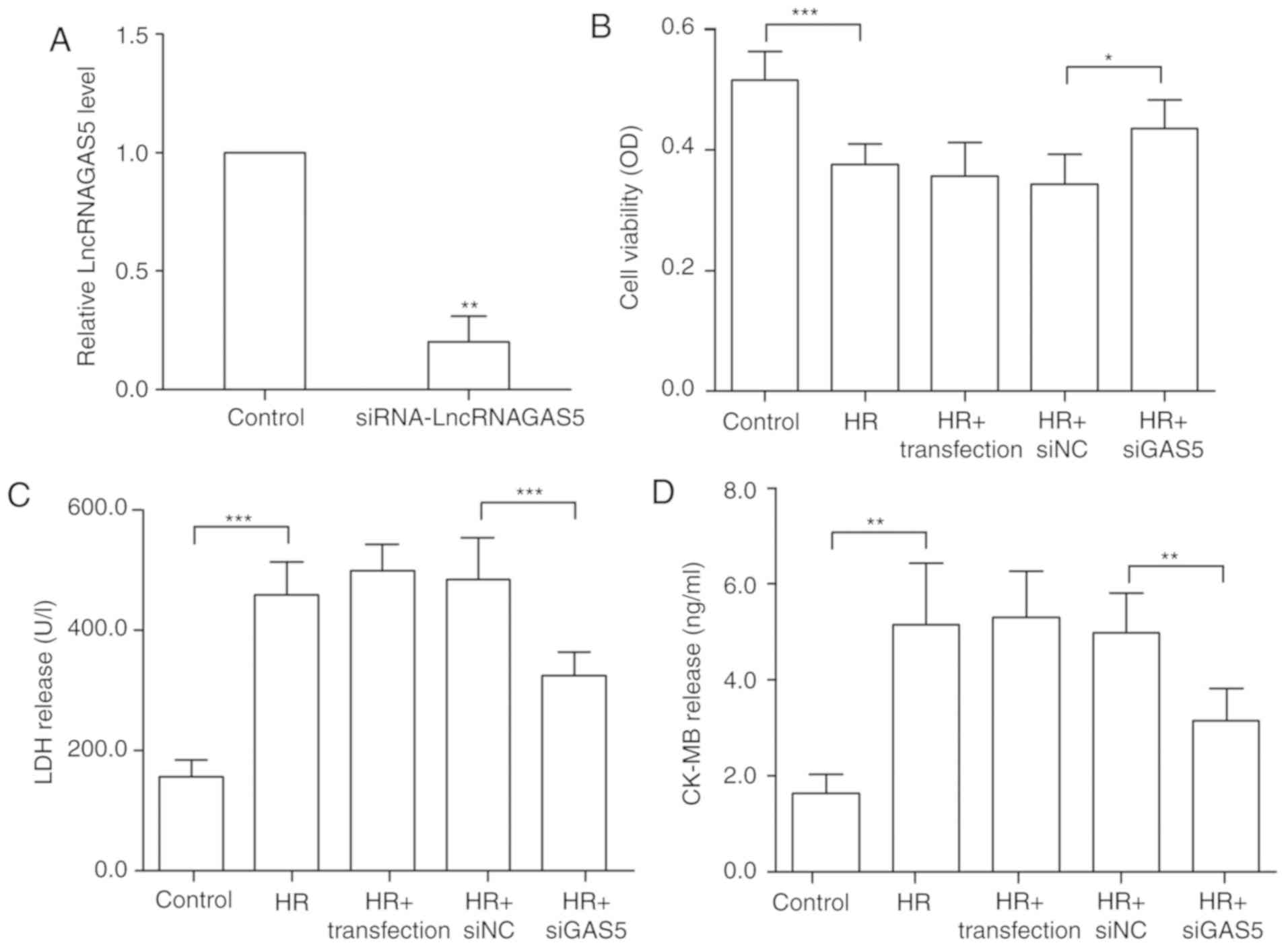
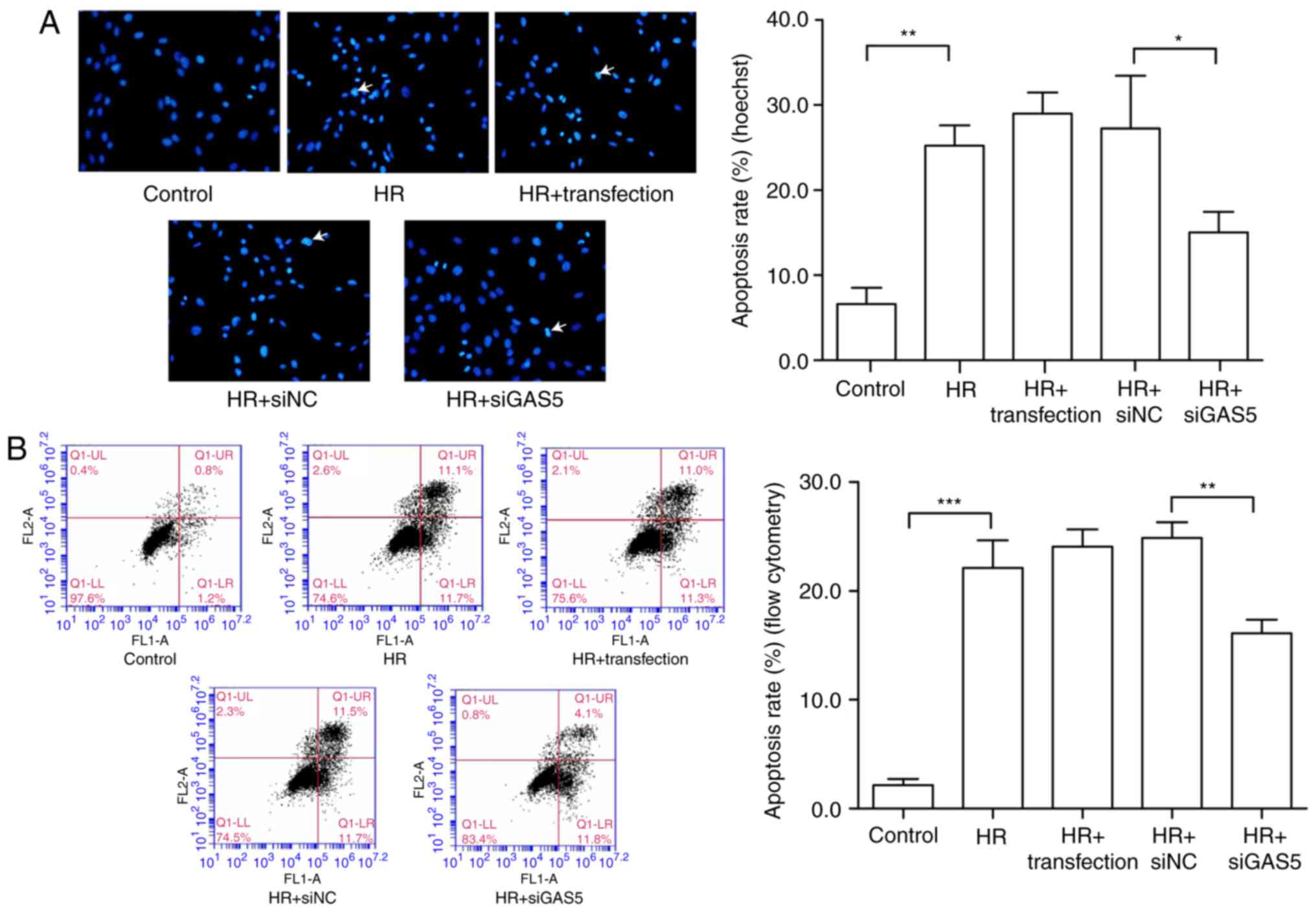
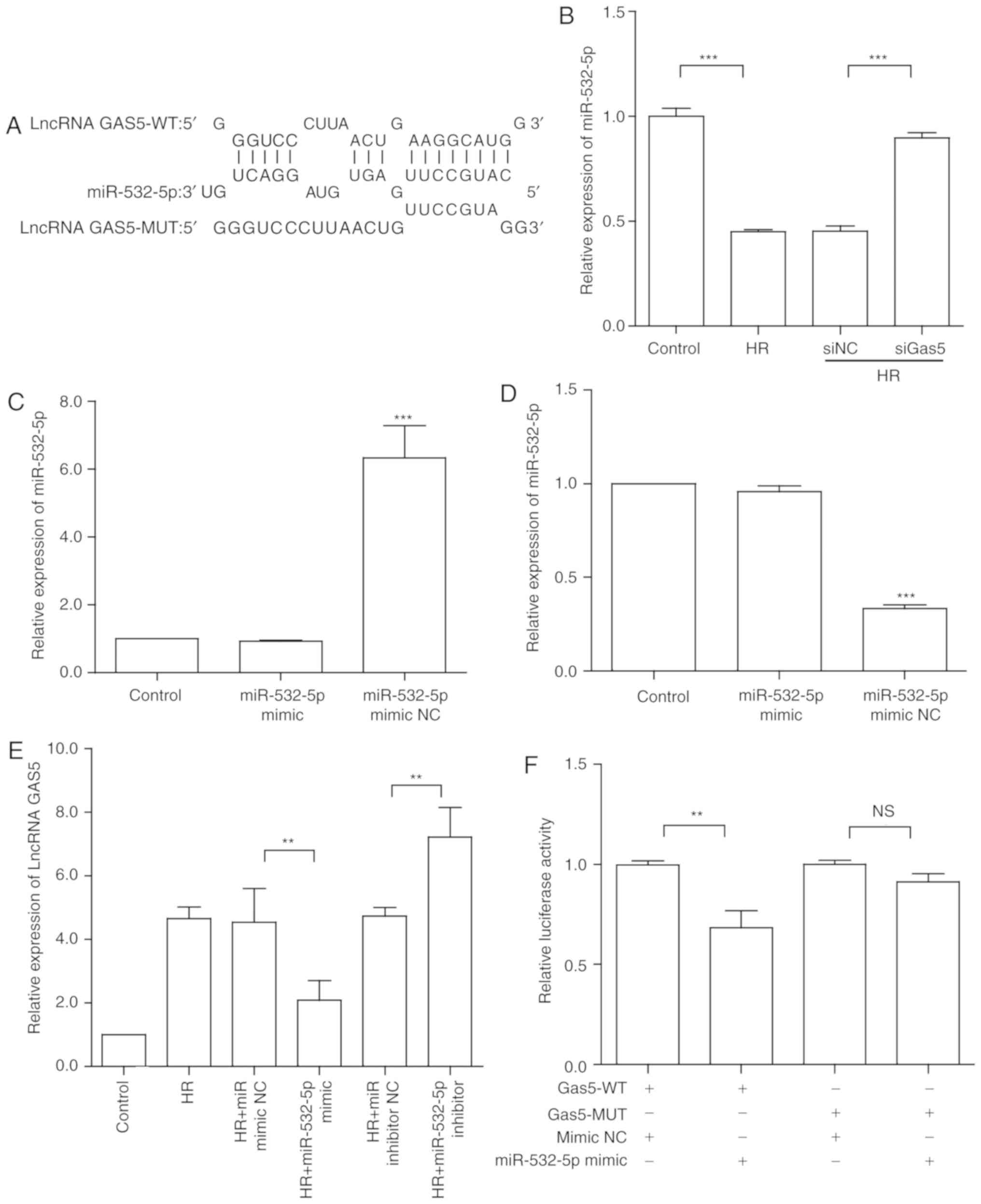
|
1
|
Gerczuk PZ and Kloner RA: An update on
cardioprotection: A review of the latest adjunctive therapies to
limit myocardial infarction size in clinical trials. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 59:969–978. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pollack A, Mohanty BD, Handa R, Looser PM,
Fuster V, King S III and Sharma SK: Preventive stenting in acute
myocardial infarction. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 8:131–138. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Majidi M, Kosinski AS, Al-Khatib SM,
Lemmert ME, Smolders L, van Weert A, Reiber JH, Tzivoni D, Bär FW,
Wellens HJ, et al: Reperfusion ventricular arrhythmia 'bursts'
predict larger infarct size despite TIMI 3 flow restoration with
primary angioplasty for anterior ST-elevation myocardial
infarction. Eur Heart J. 30:757–764. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Taggart DP and Neubauer S: Incidence,
predictors, and significance of abnormal cardiac enzyme rise in
patients treated with bypass surgery in the arterial
revascularization therapies study (ARTS). Circulation. 106:e55–e56.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Garcia-Dorado D, Ruiz-Meana M, Inserte J,
Rodriguez-Sinovas A and Piper HM: Calcium-mediated cell death
during myocardial reperfusion. Cardiovasc Res. 94:168–180. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Koshinuma S, Miyamae M, Kaneda K, Kotani J
and Figueredo VM: Combination of necroptosis and apoptosis
inhibition enhances cardioprotection against myocardial
isch-emia-reperfusion injury. J Anesth. 28:235–241. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Vilahur G and Badimon L:
Ischemia/reperfusion activates myocardial innate immune response:
The key role of the toll-like receptor. Front Physiol. 5:4962014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tang L, Mo Y, Li Y, Zhong Y, He S, Zhang
Y, Tang Y, Fu S, Wang X and Chen A: Urolithin A alleviates
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via PI3K/Akt pathway.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 486:774–780. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ren GD, Cui Y, Li WL, Li FF and Han XY:
Research on cardioprotective effect of irbesartan in rats with
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through MAPK-ERK signaling
pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:5487–5494. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bainey KR and Armstrong PW: Clinical
perspectives on reperfusion injury in acute myocardial infarction.
Am Heart J. 167:637–645. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ong SB, Katwadi K, Kwek XY, Ismail NI,
Chinda K, Ong SG and Hausenloy DJ: Non-coding RNAs as therapeutic
targets for preventing myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 22:247–261. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hombach S and Kretz M: Non-coding RNAs:
Classification, biology and functioning. Adv Exp Med Biol.
937:3–17. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qiu MT, Hu JW, Yin R and Xu L: Long
noncoding RNA: An emerging paradigm of cancer research. Tumour
Biol. 34:613–620. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vitiello M, Tuccoli A and Poliseno L: Long
non-coding RNAs in cancer: Implications for personalized therapy.
Cell Oncol (Dordr). 38:17–28. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zangrando J, Zhang L, Vausort M, Maskali
F, Marie PY, Wagner DR and Devaux Y: Identification of candidate
long non-coding RNAs in response to myocardial infarction. BMC
Genomics. 15:4602014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Saddic LA, Sigurdsson MI, Chang TW,
Mazaika E, Heydarpour M, Shernan SK, Seidman CE, Seidman JG, Aranki
SF, Body SC and Muehlschlegel JD: The long noncoding RNA landscape
of the ischemic human left ventricle. Circ Cardiovasc Genet.
10:pii: e001534. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gong LC, Xu HM, Guo GL, Zhang T, Shi JW
and Chang C: Long non-coding RNA H19 protects H9c2 cells against
hypoxia-induced injury by targeting MicroRNA-139. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 44:857–869. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu CY, Zhang YH, Li RB, Zhou LY, An T,
Zhang RC, Zhai M, Huang Y, Yan KW, Dong YH, et al: LncRNA CAIF
inhibits autophagy and attenuates myocardial infarction by blocking
p53-mediated myocardin transcription. Nat Commun. 9:292018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Y, Li G, Lu H, Li W, Li X, Liu H, Li
X, Li T and Yu B: Expression profiling and ontology analysis of
long noncoding RNAs in post-ischemic heart and their implied roles
in isch-emia/reperfusion injury. Gene. 543:15–21. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schneider C, King RM and Philipson L:
Genes specifically expressed at growth arrest of mammalian cells.
Cell. 54:787–793. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Smith CM and Steitz JA: Classification of
gas5 as a multi-small-nucleolar-RNA (snoRNA) host gene and a member
of the 5′-terminal oligopyrimidine gene family reveals common
features of snoRNA host genes. Mol Cell Biol. 18:6897–6909. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kino T, Hurt DE, Ichijo T, Nader N and
Chrousos GP: Noncoding RNA gas5 is a growth arrest- and
starvation-associated repressor of the glucocorticoid receptor. Sci
Signal. 3:ra82010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pickard MR, Mourtada-Maarabouni M and
Williams GT: Long non-coding RNA GAS5 regulates apoptosis in
prostate cancer cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832:1613–1623.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li J, Wang Y, Zhang CG, Xiao HJ, Hu JM and
He JD: Effect of long non-coding RNA Gas5 on proliferation,
migration, invasion and apoptosis of colorectal cancer HT-29 cell
line (vol 18, 4, 2018). Cancer Cell Int. 18:42018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cao Q, Wang N, Qi J, Gu Z and Shen H: Long
noncoding RNAGAS5 acts as a tumor suppressor in bladder
transitional cell carcinoma via regulation of chemokine (CC motif)
ligand 1 expression. Mol Med Rep. 13:27–34. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pickard MR and Williams GT: Molecular and
cellular mechanisms of action of tumour suppressor GAS5 LncRNA.
Genes (Basel). 6:484–499. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kastenmayer RJ, Moore RM, Bright AL,
Torres-Cruz R and Elkins WR: Select agent and toxin regulations:
Beyond the Eighth edition of the guide for the care and use of
laboratory animals. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 51:333–338.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu N, Li WN, Shu WQ and Jia DL: Protective
effect of picroside II on myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in
rats. Drug Des Dev Ther. 8:545–554. 2014.
|
|
30
|
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson
M and Altman DG: Improving bioscience research reporting: The
ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. Vet Clin Path.
41:27–31. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Murphy E and Steenbergen C: Mechanisms
underlying acute protection from cardiac ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Physiol Rev. 88:581–609. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Sun R and Zhang L: Long non-coding RNA
MALAT1 regulates cardiomyocytes apoptosis after hypoxia/reperfusion
injury via modulating miR-200a-3p/PDCD4 axis. Biomed Pharmacother.
111:1036–1045. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang W, Li Y and Wang P: Long non-coding
RNA-ROR aggravates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Braz J
Med Biol Res. 51:e65552018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zeng B, Li Y, Jiang F, Wei C, Chen G,
Zhang W, Zhao W and Yu D: LncRNA GAS5 suppresses proliferation,
migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral
squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the miR-21/PTEN axis. Exp
Cell Res. 374:365–373. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tao H, Zhang JG, Qin RH, Dai C, Shi P,
Yang JJ, Deng ZY and Shi KH: LncRNA GAS5 controls cardiac
fibroblast activation and fibrosis by targeting miR-21 via
PTEN/MMP-2 signaling pathway. Toxicology. 386:11–18. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rehmsmeier M, Steffen P, Hochsmann M and
Giegerich R: Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target
duplexes. RNA. 10:1507–1517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ma J, Zhang J, Wang Y, Long K, Wang X, Jin
L, Tang Q, Zhu L, Tang G, Li X and Li M: MiR-532-5p alleviates
hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targeting PDCD4. Gene.
675:36–43. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Han X, Shi H, Liu K, Zhong L, Wang F and
You Q: Protective effect of gastrodin on myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury and the expression of Bax and Bcl-2.
Exp Ther Med. 17:4389–4394. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu S, Wu N, Miao J, Huang Z, Li X, Jia P,
Guo Y and Jia D: Protective effect of morin on myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Int J Mol Med. 42:1379–1390.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang BF, Jiang H, Chen J, Guo X, Li Y, Hu
Q and Yang S: Nobiletin ameliorates myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum
stress-associated apoptosis through regulation of the PI3K/AKT
signal pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 73:98–107. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Siddall HK, Warrell CE, Yellon DM and
Mocanu MM: Ischemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection:
Investigating PTEN, the phosphatase that negatively regulates PI3K,
using a congenital model of PTEN haploinsufficiency. Basic Res
Cardiol. 103:560–568. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ruan H, Li J, Ren S, Gao J, Li G, Kim R,
Wu H and Wang Y: Inducible and cardiac specific PTEN inactivation
protects ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
46:193–200. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ke ZP, Xu P, Shi Y and Gao AM: MicroRNA-93
inhibits ischemia-reperfusion induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by
targeting PTEN. Oncotarget. 7:28796–28805. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wei H, Yang Z and Lin B: Overexpression of
long non coding RNA CA3-AS1 suppresses proliferation, invasion and
promotes apoptosis via miRNA-93/PTEN axis in colorectal cancer.
Gene. 687:9–15. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Cipolla GA, de Oliveira JC, Salviano-Silva
A, Lobo-Alves SC, Lemos DS, Oliveira LC, Jucoski TS, Mathias C,
Pedroso GA, Zambalde EP and Gradia DF: Long non-coding RNAs in
multifactorial diseases: Another layer of complexity. Noncoding
RNA. 4:pii: E13. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang KC and Chang HY: Molecular mechanisms
of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 43:904–914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sanchez Calle A, Kawamura Y, Yamamoto Y,
Takeshita F and Ochiya T: Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA in
cancer. Cancer Sci. 109:2093–2100. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Smolle MA and Pichler M: The role of long
non-coding RNAs in osteosarcoma. Noncoding RNA. 4:pii: E7.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Weirick T, Militello G and Uchida S: Long
non-coding RNAs in endothelial biology. Front Physiol. 9:5222018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang S, Yu W, Chen J, Yao T and Deng F:
LncRNA MALAT1 sponges miR-203 to promote inflammation in myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Cardiol. 268:2452018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Williams GT, Hughes JP, Stoneman V,
Anderson CL, McCarthy NJ, Mourtada-Maarabouni M, Pickard M, Hedge
VL, Trayner I and Farzaneh F: Isolation of genes controlling
apoptosis through their effects on cell survival. Gene Ther Mol
Biol. 10:255–261. 2006.
|
|
54
|
Esmatabadi MJD, Motamedrad M and
Sadeghizadeh M: Down-regulation of lncRNA, GAS5 decreases
chemotherapeutic effect of dendrosomal curcumin (DNC) in breast
cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 42:56–65. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Scorrano L and Korsmeyer SJ: Mechanisms of
cytochrome c release by proapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 304:437–444. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu SD, Meng WX, Xu L, Chi C, Sun X and
Liu HY: GAS5 promotes myocardial apoptosis in myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury via upregulating LAS1 expression. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:8447–8453. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Xue D, Zhou C, Lu H, Xu R, Xu X and He X:
LncRNA GAS5 inhibits proliferation and progression of prostate
cancer by targeting miR-103 through AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
Tumor Biol. 37:16187–16197. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Yang W, Hong L, Xu X, Wang Q, Huang J and
Jiang L: LncRNA GAS5 suppresses the tumorigenesis of cervical
cancer by downregulating miR-196a and miR-205. Tumor Biol.
39:10104283177113152017. View Article : Google Scholar
|