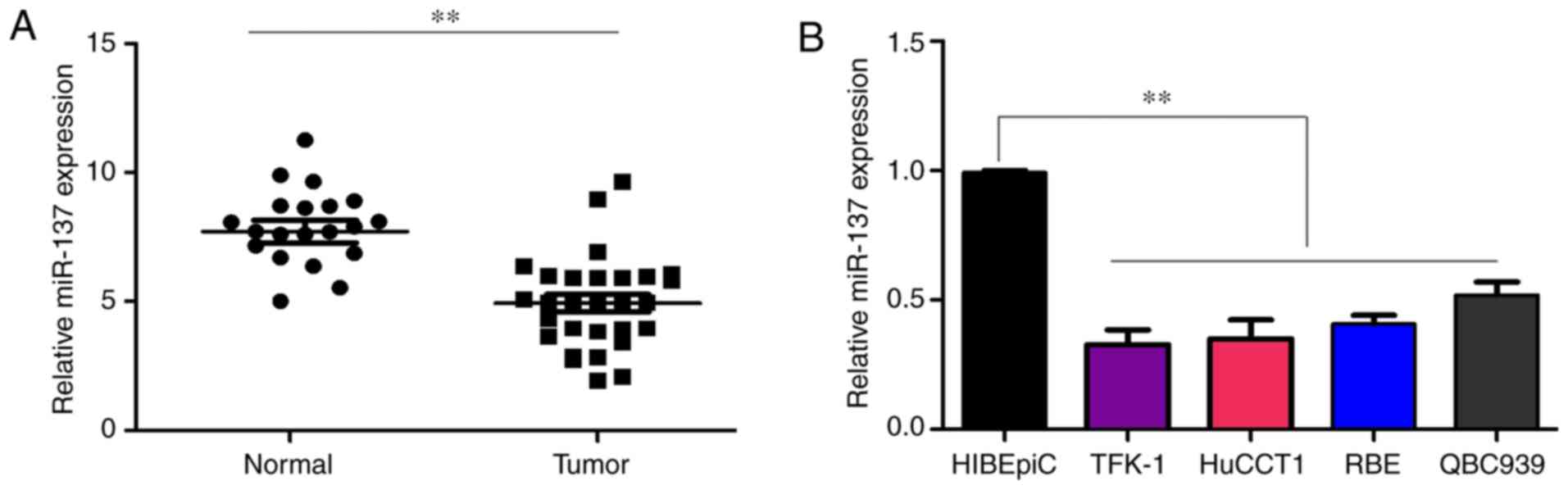
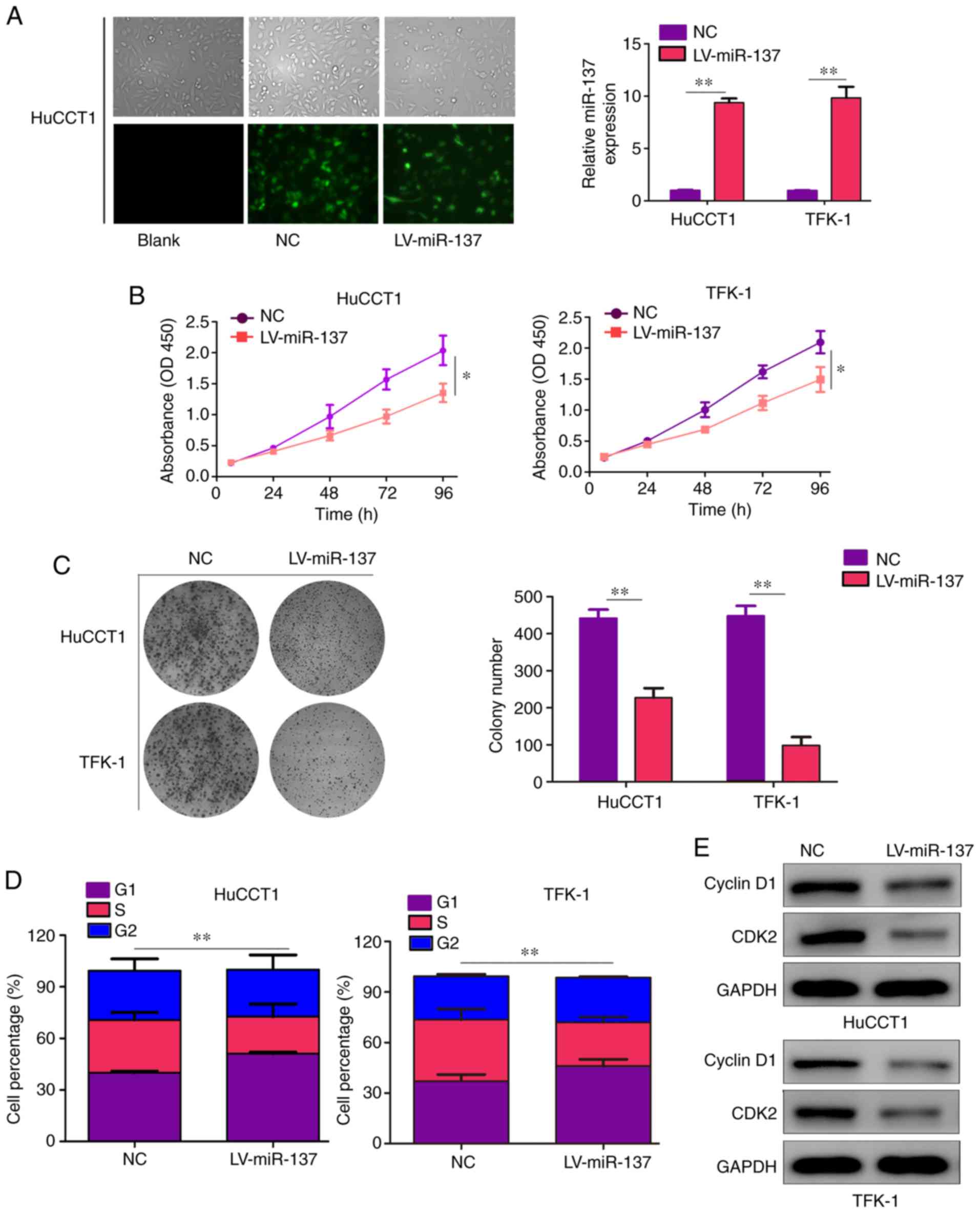
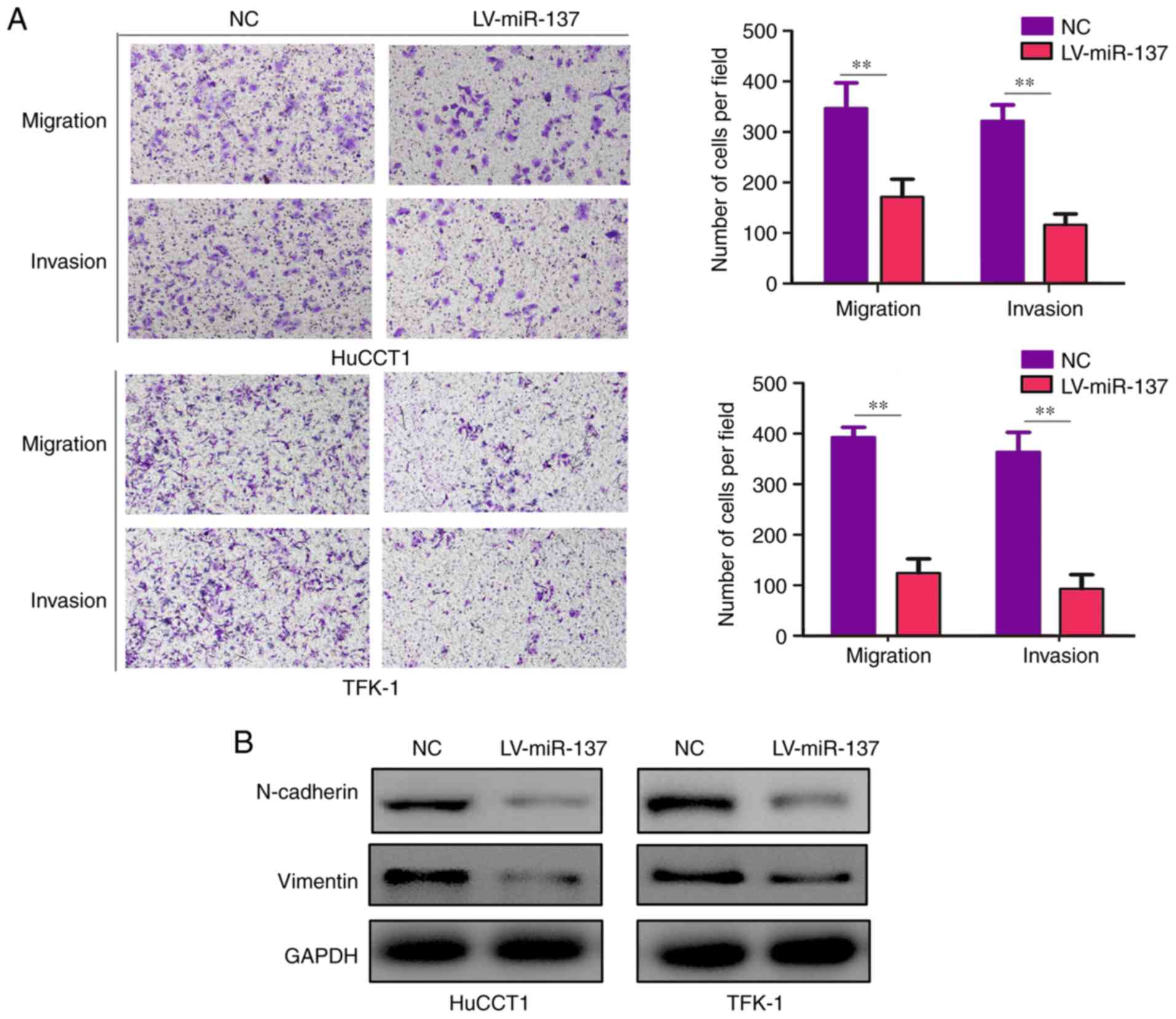
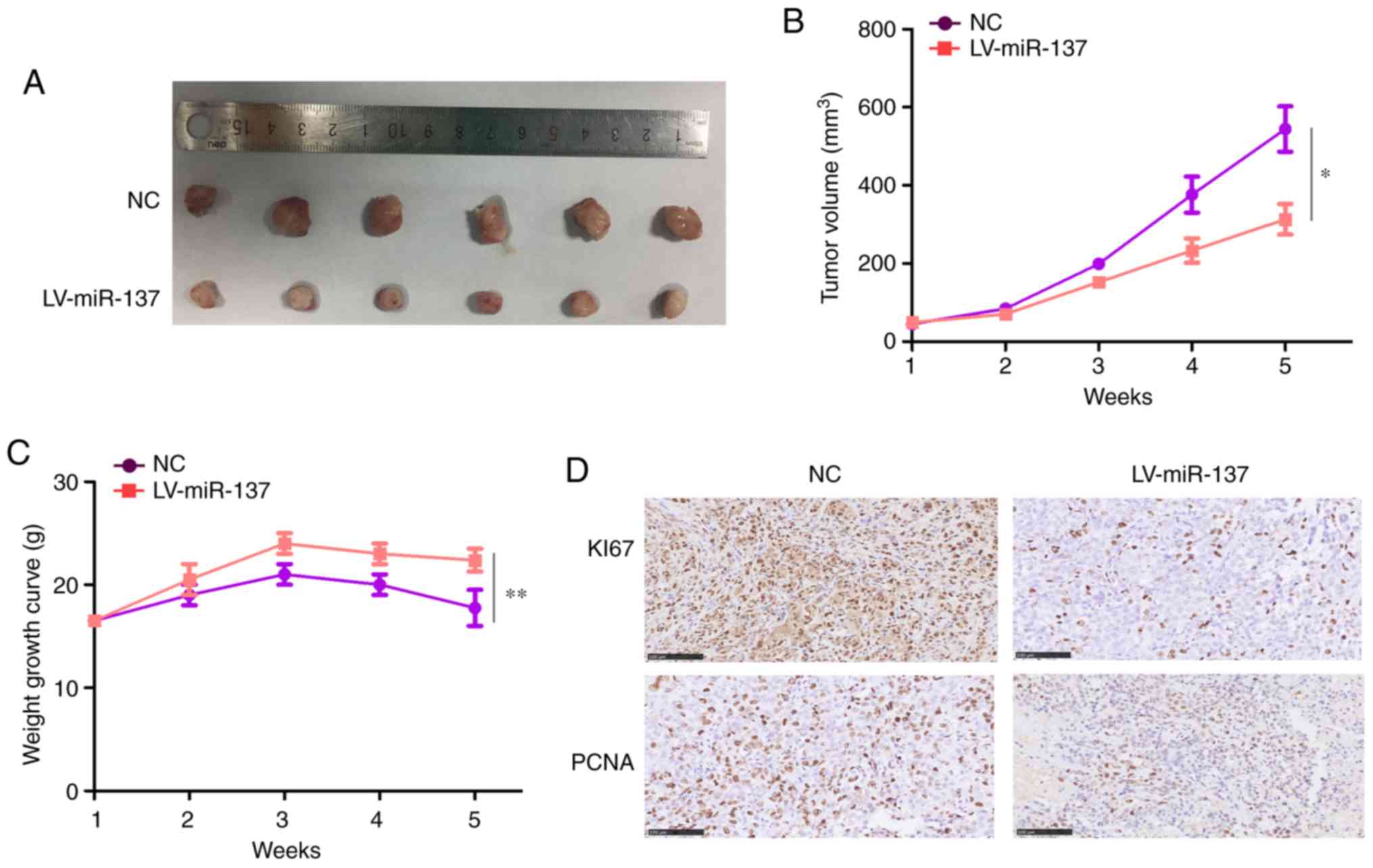
|
1
|
Ma WJ, Wu ZR, Shrestha A, Yang Q, Hu HJ,
Wang JK, Liu F, Zhou RX, Li QS and Li FY: Effectiveness of
additional resection of the invasive cancer-positive proximal bile
duct margin in cases of hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatobiliary
Surg Nutr. 7:251–269. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liang W, Xu L, Yang P, Zhang L, Wan D,
Huang Q, Niu T and Chen F: Novel nomogram for preoperative
prediction of early recurrence in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Front Oncol. 8:3602018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Beal EW, Tumin D, Moris D, Zhang XF,
Chakedis J, Dilhoff M, Schmidt CM and Pawlik TM: Cohort
contributions to trends in the incidence and mortality of
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr.
7:270–276. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rizvi S, Khan SA, Hallemeier CL, Kelley RK
and Gores GJ: Cholangiocarcinoma-evolving concepts and therapeutic
strategies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 15:95–111. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Burroughs AM and Ando Y: Identifying and
characterizing functional 3' nucleotide addition in the miRNA
pathway. Methods. 152:23–30. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lee D and Shin C: MicroRNA-target
interactions: New insights from genome-wide approaches. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1271:118–128. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Puik JR, Meijer LL, Le Large TY, Prado MM,
Frampton AE, Kazemier G and Giovannetti E: miRNA profiling for
diagnosis, prognosis and stratification of cancer treatment in
cholangiocarcinoma. Pharmacogenomics. 18:1343–1358. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wan P, Chi X, Du Q, Luo J, Cui X, Dong K,
Bing Y, Heres C and Geller DA: miR-383 promotes cholangiocarcinoma
cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through targeting IRF1.
J Cell Biochem. 119:9720–9729. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu Z, Liu G, Zhang M, Zhang Z, Jia Y, Peng
L, Zhu Y, Hu J, Huang R and Sun X: miR-122-5p inhibits the
proliferation, invasion and growth of bile duct carcinoma cells by
targeting ALDOA. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:2596–2606. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma J, Weng L, Wang Z, Jia Y, Liu B, Wu S,
Cao Y, Sun X, Yin X, Shang M and Mao A: MiR-124 induces
autophagy-related cell death in cholangiocarcinoma cells through
direct targeting of the EZH2-STAT3 signaling axis. Exp Cell Res.
366:103–113. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He Z, Guo X, Tian S, Zhu C, Chen S, Yu C,
Jiang J and Sun C: MicroRNA-137 reduces stemness features of
pancreatic cancer cells by targeting KLF12. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
38:1262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xiao J, Peng F, Yu C, Wang M, Li X, Li Z,
Jiang J and Sun C: microRNA-137 modulates pancreatic cancer cells
tumor growth, invasion and sensitivity to chemotherapy. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:7442–7450. 2014.
|
|
13
|
Min L, Wang F, Hu S, Chen Y, Yang J, Liang
S and Xu X: Aberrant microRNA-137 promoter methylation is
associated with lymph node metastasis and poor clinical outcomes in
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:7744–7750.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu QQ, Zheng B, Weng GB, Yang HM, Ren Y,
Weng XJ, Zhang SW and Zhu WZ: Downregulated NOX4 underlies a novel
inhibitory role of microRNA-137 in prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem.
120:10215–10227. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao X, Lu C, Chu W, Zhang B, Zhen Q, Wang
R, Zhang Y, Li Z, Lv B, Li H and Liu J: MicroRNA-124 suppresses
proliferation and glycolysis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by
targeting AKT-GLUT1/HKII. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177062152017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sakaguchi M, Hisamori S, Oshima N, Sato F,
Shimono Y and Sakai Y: miR-137 regulates the tumorigenicity of
colon cancer stem cells through the inhibition of DCLK1. Mol Cancer
Res. 14:354–362. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bi WP, Xia M and Wang XJ: miR-137
suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer
cell lines by targeting TCF4. Oncol Lett. 15:8744–8748.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang XY, Gao PT, Yang X, Cai JB, Ding GY,
Zhu XD, Ji Y, Shi GM, Shen YH, Zhou J, et al: Reduced
selenium-binding protein 1 correlates with a poor prognosis in
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and promotes the cell
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Am J Transl Res. 10:3567–3578.
2018.
|
|
20
|
Zou Z, Zheng B, Li J, Lv X, Zhang H, Yu F,
Kong L, Li Y, Yu M, Fang L and Liang B: TPX2 level correlates with
cholangiocarcinoma cell proliferation, apoptosis, and EMT. Biomed
Pharmacother. 107:1286–1293. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Peng R, Zhang PF, Zhang C, Huang XY, Ding
YB, Deng B, Bai DS and Xu YP: Elevated TRIM44 promotes intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma progression by inducing cell EMT via MAPK
signaling. Cancer Med. 7:796–808. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang B, Sun L, Li J and Jiang R: miR-577
suppresses cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
by regulating the WNT2B mediated Wnt/β-catenin pathway in non-small
cell lung cancer. Mol Med Rep. 18:2753–2761. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang Z, Jiang C and Fang J: Up-regulated
lnc-SNHG1 contributes to osteosarcoma progression through
sequestration of miR-577 and activation of WNT2B/Wnt/β-catenin
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 495:238–245. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Plieskatt JL, Rinaldi G, Feng Y, Peng J,
Yonglitthipagon P, Easley S, Laha T, Pairojkul C, Bhudhisawasdi V,
Sripa B, et al: Distinct miRNA signatures associate with subtypes
of cholangiocarcinoma from infection with the tumourigenic liver
fluk Opisthorchis viverrini. J Hepatol. 61:850–858. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen Y, Liu D, Liu P, Chen Y, Yu H and
Zhang Q: Identification of biomarkers of intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma via integrated analysis of mRNA and miRNA
microarray data. Mol Med Rep. 15:1051–1056. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wei G, Yuan Y, He X, Jin L and Jin D:
Enhanced plasma miR-142-5p promotes the progression of intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma via targeting PTEN. Exp Ther Med. 17:4190–4196.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liang HQ, Wang RJ, Diao CF, Li JW, Su JL
and Zhang S: The PTTG1-targeting miRNAs miR-329, miR-300, miR-381,
and miR-655 inhibit pituitary tumor cell tumorigenesis and are
involved in a p53/PTTG1 regulation feedback loop. Oncotarget.
6:29413–29427. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu X, Yuan C, Tian C, Li C, Nie F, Song
X, Zeng R, Wu D, Hao X and Li L: The plant sesquiterpene lactone
parthenolide inhibits Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by blocking
synthesis of the transcriptional regulators TCF4/LEF1. J Biol Chem.
293:5335–5344. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Y, Lin P, Wang Q, Zheng M and Pang L:
Wnt3a-regulated TCF4/β-catenin complex directly activates the key
Hedgehog signalling genes Smo and Gli1. Exp Ther Med. 16:2101–2107.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li SJ, Yang XN and Qian HY: Antitumor
effects of WNT2B silencing in GLUT1 overexpressing cisplatin
resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res.
5:300–308. 2014.
|
|
31
|
Jiang H, Li F, He C, Wang X, Li Q and Gao
H: Expression of Gli1 and Wnt2B correlates with progression and
clinical outcome of pancreatic cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:4531–4538. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|