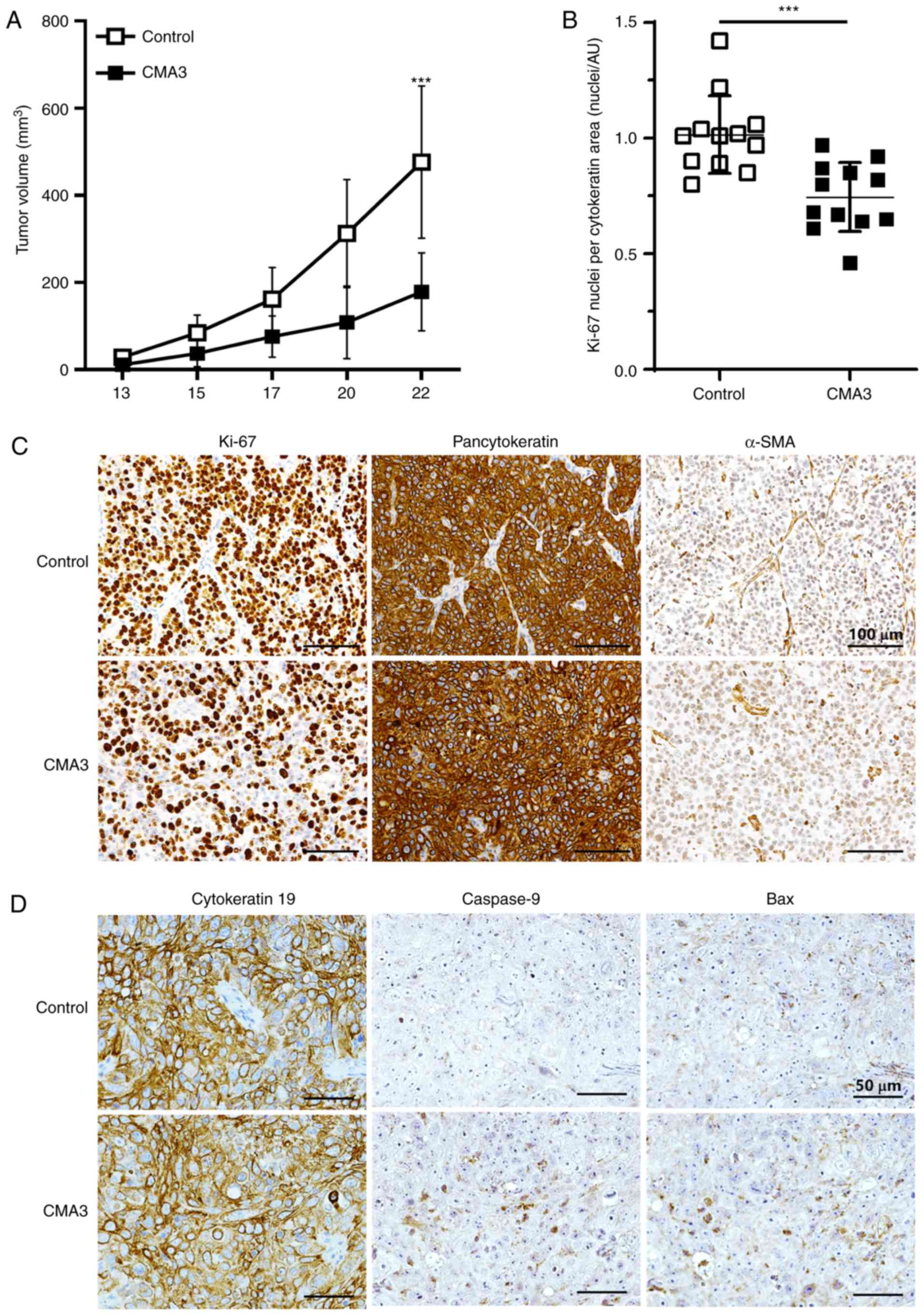
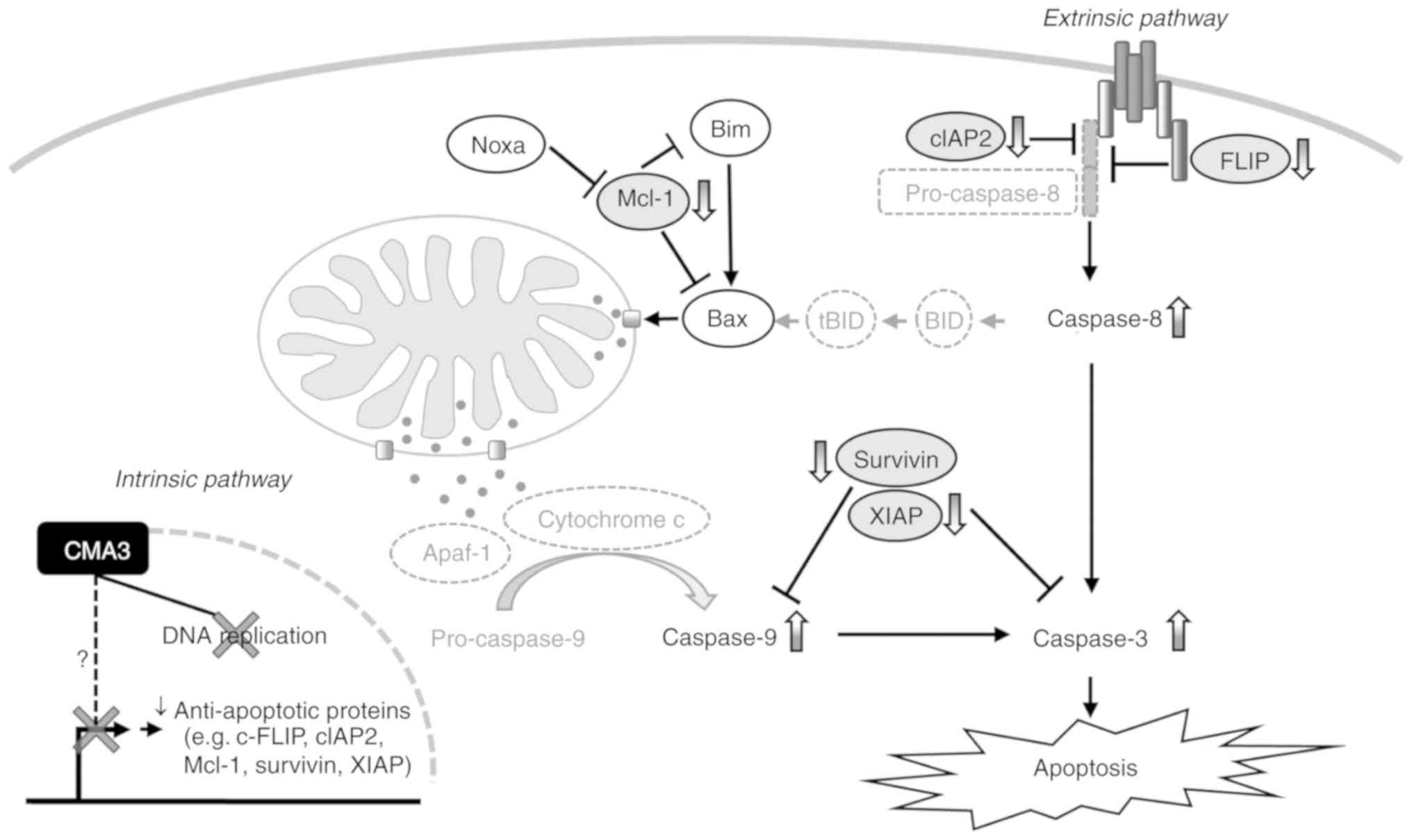
|
1
|
Banales JM, Cardinale V, Carpino G,
Marzioni M, Andersen JB, Invernizzi P, Lind GE, Folseraas T, Forbes
SJ, Fouassier L, et al: Expert consensus document:
Cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and future perspectives
consensus statement from the European network for the study of
cholangiocarcinoma (ENS-CCA). Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
13:261–280. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sripa B, Bethony JM, Sithithaworn P,
Kaewkes S, Mairiang E, Loukas A, Mulvenna J, Laha T, Hotez PJ,
Brindley PJ, et al: Opisthorchiasis and opisthorchis-associated
cholangiocarcinoma in Thailand and Laos. Acta Trop. 120(Suppl 1):
S158–S168. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Khan SA, Taylor-Robinson SD, Toledano MB,
Beck A, Elliott P and Thomas HC: Changing international trends in
mortality rates for liver, biliary and pancreatic tumours. J
Hepatol. 37:806–813. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bridgewater J, Galle PR, Khan SA, Llovet
JM, Park JW, Patel T, Pawlik TM and Gores GJ: Guidelines for the
diagnosis and management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J
Hepatol. 60:1268–1289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marin JJ, Romero MR and Briz O: Molecular
bases of liver cancer refractoriness to pharmacological treatment.
Curr Med Chem. 17:709–740. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dhanasekaran R, Hemming AW, Zendejas I,
George T, Nelson DR, Soldevila-Pico C, Firpi RJ, Morelli G, Clark V
and Cabrera R: Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of
intra-hepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 29:1259–1267. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Srimunta U, Sawanyawisuth K, Kraiklang R,
Pairojkul C, Puapairoj A, Titipungul T, Hahnvajanawong C,
Tassaneeyakul W, Wongkham C, Wongkham S and Vaeteewoottacharn K:
High expression of ABCC1 indicates poor prognosis in intrahepatic
chol-angiocarcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13(Suppl): S125–S130.
2012.
|
|
8
|
Prakobwong S, Gupta SC, Kim JH, Sung B,
Pinlaor P, Hiraku Y, Wongkham S, Sripa B, Pinlaor S and Aggarwal
BB: Curcumin suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in
human biliary cancer cells through modulation of multiple cell
signaling pathways. Carcinogenesis. 32:1372–1380. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pawar P, Ma L, Byon CH, Liu H, Ahn EY,
Jhala N, Arnoletti JP, McDonald JM and Chen Y: Molecular mechanisms
of tamoxifen therapy for cholangiocarcinoma: Role of calmodulin.
Clin Cancer Res. 15:1288–1296. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Taniai M, Grambihler A, Higuchi H,
Werneburg N, Bronk SF, Farrugia DJ, Kaufmann SH and Gores GJ: Mcl-1
mediates tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
resistance in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res.
64:3517–3524. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamagiwa Y, Marienfeld C, Meng F, Holcik M
and Patel T: Translational regulation of X-linked inhibitor of
apoptosis protein by interleukin-6: A novel mechanism of tumor cell
survival. Cancer Res. 64:1293–1298. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chang Q, Liu ZR, Wang DY, Kumar M, Chen YB
and Qin RY: Survivin expression induced by doxorubicin in
cholangiocar-cinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 10:415–418. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Beishline K and Azizkhan-Clifford J: Sp1
and the 'hallmarks of cancer'. FEBS J. 282:224–258. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang L, Wei D, Huang S, Peng Z, Le X, Wu
TT, Yao J, Ajani J and Xie K: Transcription factor Sp1 expression
is a significant predictor of survival in human gastric cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:6371–6380. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang NY, Woda BA, Banner BF, Whalen GF,
Dresser KA and Lu D: Sp1, a new biomarker that identifies a subset
of aggressive pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 17:1648–1652. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vizcaino C, Mansilla S and Portugal J: Sp1
transcription factor: A long-standing target in cancer
chemotherapy. Pharmacol Ther. 152:111–124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee TJ, Jung EM, Lee JT, Kim S, Park JW,
Choi KS and Kwon TK: Mithramycin A sensitizes cancer cells to
TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by down-regulation of XIAP gene promoter
through Sp1 sites. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:2737–2746. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Choi ES, Nam JS, Jung JY, Cho NP and Cho
SD: Modulation of specificity protein 1 by mithramycin A as a novel
therapeutic strategy for cervical cancer. Sci Rep. 4:71622014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Barcelo F, Ortiz-Lombardia M, Martorell M,
Oliver M, Méndez C, Salas JA and Portugal J: DNA binding
characteristics of mithramycin and chromomycin analogues obtained
by combinatorial biosynthesis. Biochemistry. 49:10543–10552. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chatterjee S, Zaman K, Ryu H, Conforto A
and Ratan RR: Sequence-selective DNA binding drugs mithramycin A
and chromomycin A3 are potent inhibitors of neuronal apoptosis
induced by oxidative stress and DNA damage in cortical neurons. Ann
Neurol. 49:345–354. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gause GF: Olivomycin, mithramycin,
chromomycin: Three related cancerostatic antibiotics. Adv
Chemother. 2:179–195. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schmitz H, Heinemann B, Lein J and Hooper
IR: NSC A-649, an antitumor antibiotic. Antibiot Chemother
(Northfield). 10:740–746. 1960.
|
|
23
|
Reynolds RD, Fisher JI, Jensen PA, Pajak
TF and Bateman JR: Phase I alternate-day dose study of chromomycin
A3. Cancer Treat Rep. 60:1251–1255. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Samal B, Jones S, Brownlee RW, Morrison F,
Hoogstraten B, Caoili E and Baker L: Chromomycin A3 for advanced
breast cancer: A Southwest oncology group study. Cancer Treat Rep.
62:19–22. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Iranpour FG, Nasr-Esfahani MH, Valojerdi
MR and al-Taraihi TM: Chromomycin A3 staining as a useful tool for
evaluation of male fertility. J Assist Reprod Genet. 17:60–66.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boer DR, Canals A and Coll M: DNA-binding
drugs caught in action: The latest 3D pictures of drug-DNA
complexes. Dalton Trans. 399–414. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Miller SC, Huang R, Sakamuru S, Shukla SJ,
Attene-Ramos MS, Shinn P, Van Leer D, Leister W, Austin CP and Xia
M: Identification of known drugs that act as inhibitors of
NF-kappaB signaling and their mechanism of action. Biochem
Pharmacol. 79:1272–1280. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sripa B, Leungwattanawanit S, Nitta T,
Wongkham C, Bhudhisawasdi V, Puapairoj A, Sripa C and Miwa M:
Establishment and characterization of an opisthorchiasis-associated
cholan-giocarcinoma cell line (KKU-100). World J Gastroenterol.
11:3392–3397. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Saisomboon S, Kariya R, Vaeteewoottacharn
K, Wongkham S, Sawanyawisuth K and Okada S: Antitumor effects of
flavopiridol, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, on human
cholangiocar-cinoma in vitro and in an in vivo xenograft model.
Heliyon. 5:e016752019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:671–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Phoomak C, Silsirivanit A, Park D,
Sawanyawisuth K, Vaeteewoottacharn K, Wongkham C, Lam EW, Pairojkul
C, Lebrilla CB and Wongkham S: O-GlcNAcylation mediates metastasis
of cholangiocarcinoma through FOXO3 and MAN1A1. Oncogene.
37:5648–5665. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cerella C, Muller F, Gaigneaux A, Radogna
F, Viry E, Chateauvieux S, Dicato M and Diederich M: Early
downregulation of Mcl-1 regulates apoptosis triggered by cardiac
glycoside UNBS1450. Cell Death Dis. 6:e17822015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cai J, Wang D, Bai ZG, Yin J, Zhang J and
Zhang ZT: The long noncoding RNA XIAP-AS1 promotes XIAP
transcription by XIAP-AS1 interacting with Sp1 in gastric cancer
cells. PLoS One. 12:e01824332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Obchoei S, Weakley SM, Wongkham S,
Wongkham C, Sawanyawisuth K, Yao Q and Chen C: Cyclophilin A
enhances cell proliferation and tumor growth of liver
fluke-associated cholangiocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 10:1022011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ono A, Hattori S, Kariya R, Iwanaga S,
Taura M, Harada H, Suzu S and Okada S: Comparative study of human
hematopoietic cell engraftment into BALB/c and C57BL/6 strain of
rag-2/jak3 double-deficient mice. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2011:5397482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Harlow E and Lane D: Preparing paraffin
tissue sections for immunostaining. CSH Protoc.
2006:pdb.prot43292006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vaeteewoottacharn K, Kariya R, Dana P,
Fujikawa S, Matsuda K, Ohkuma K, Kudo E, Kraiklang R, Wongkham C,
Wongkham S and Okada S: Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase
potentiates bevacizumab treatment in cholangiocarcinoma. Tumour
Biol. 37:9023–9035. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Parrish AB, Freel CD and Kornbluth S:
Cellular mechanisms controlling caspase activation and function.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5:a0086722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bedolla RG, Gong J, Prihoda TJ, Yeh IT,
Thompson IM, Ghosh R and Kumar AP: Predictive value of Sp1/Sp3/FLIP
signature for prostate cancer recurrence. PLoS One. 7:e449172012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lau R, Niu MY and Pratt MA: cIAP2
represses IKKα/β-mediated activation of MDM2 to prevent p53
degradation. Cell Cycle. 11:4009–4019. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Patel T: Cholangiocarcinoma-controversies
and challenges. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:189–200. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kobayashi S, Werneburg NW, Bronk SF,
Kaufmann SH and Gores GJ: Interleukin-6 contributes to Mcl-1
up-regulation and TRAIL resistance via an Akt-signaling pathway in
cholangiocarcinoma cells. Gastroenterology. 128:2054–2065. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sleire L, Forde HE, Netland IA, Leiss L,
Skeie BS and Enger PO: Drug repurposing in cancer. Pharmacol Res.
124:74–91. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Guimaraes LA, Jimenez PC, Sousa Tda S,
Freitas HP, Rocha DD, Wilke DV, Martín J, Reyes F, Deusdênia Loiola
Pessoa O and Costa-Lotufo LV: Chromomycin A2 induces autophagy in
melanoma cells. Mar Drugs. 12:5839–5855. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|