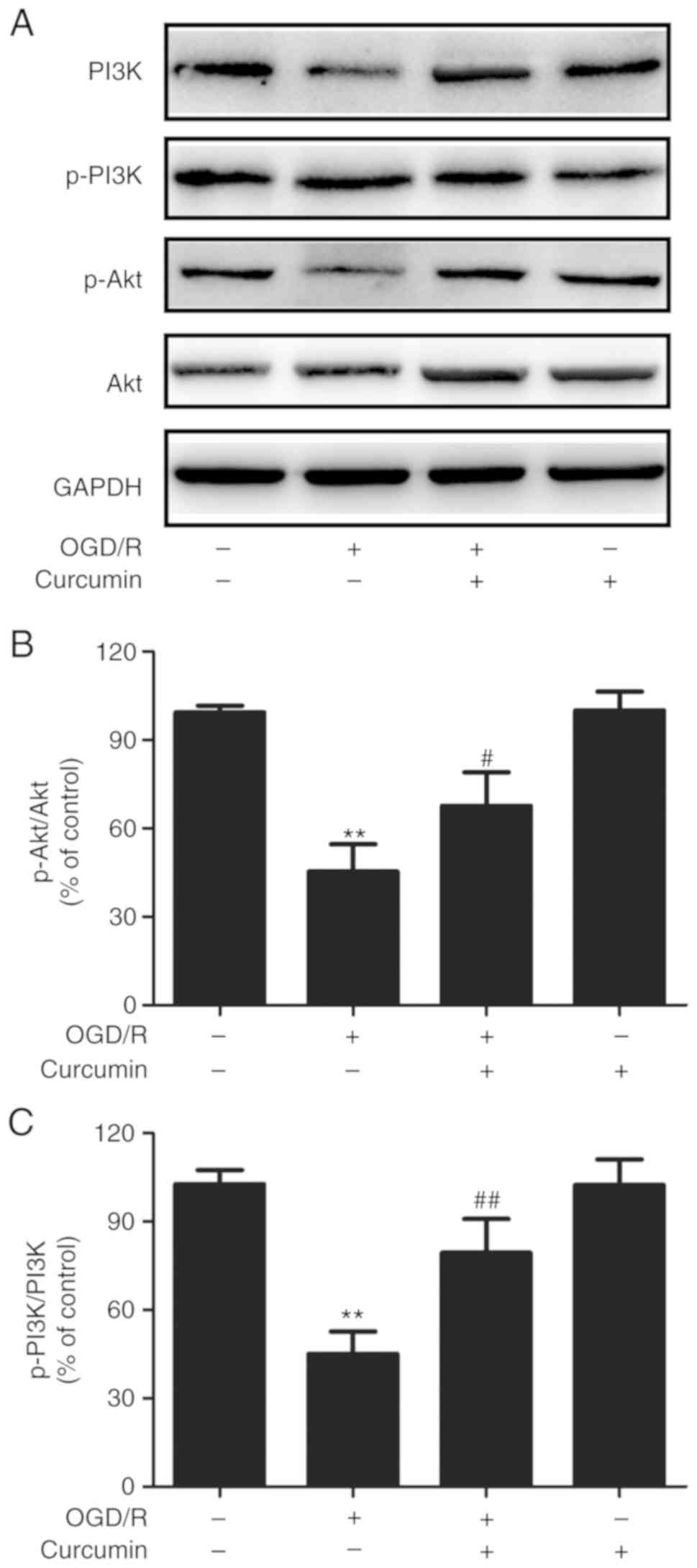
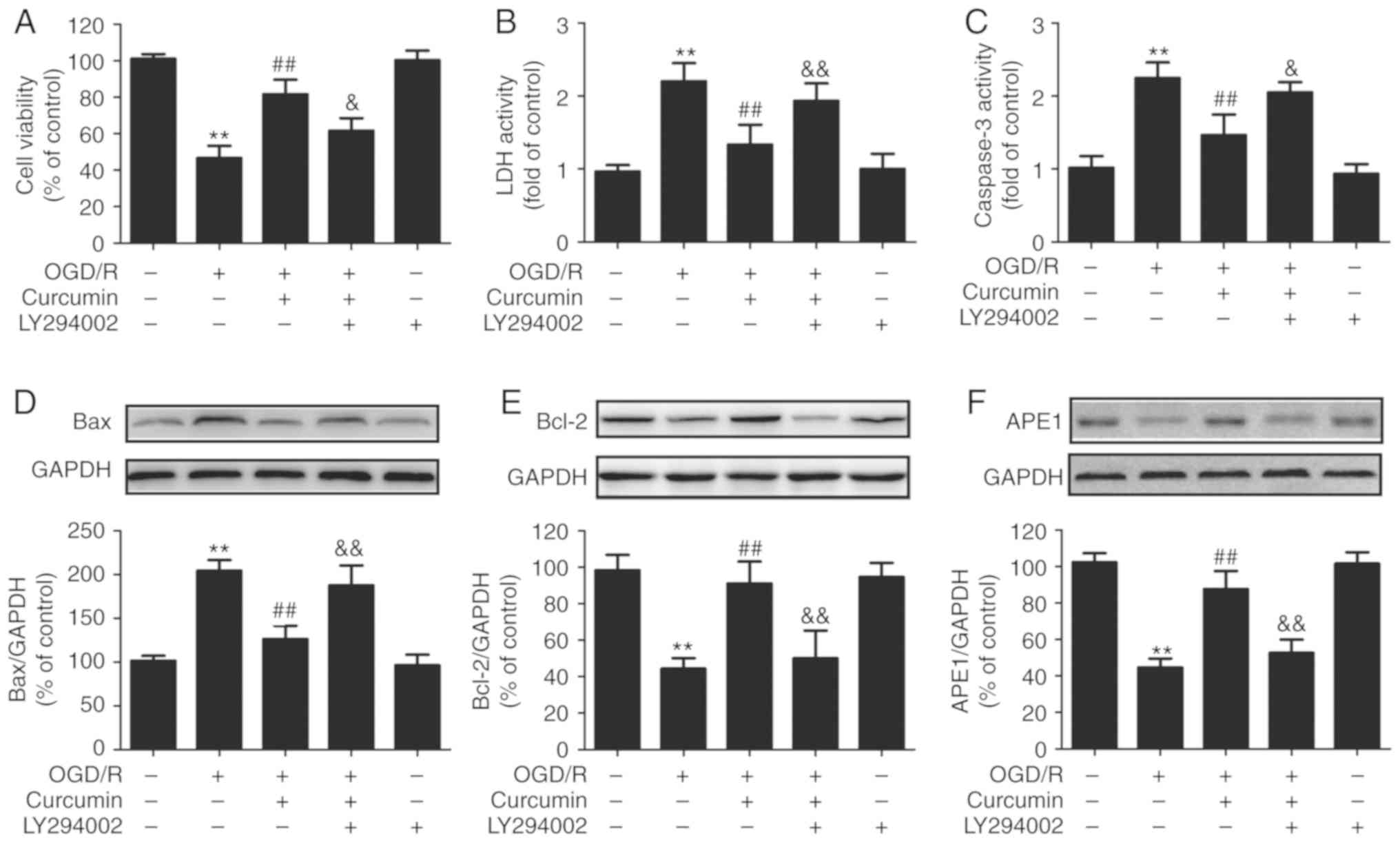
|
1
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: Ischaemic
conditioning and reperfusion injury. Nat Rev Cardiol. 13:193–209.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee RHC, Lee MHH, Wu CYC, Couto E, Silva
A, Possoit HE, Hsieh TH, Minagar A and Lin HW: Cerebral ischemia
and neuroregeneration. Neural Regen Res. 13:373–385. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Millar LJ, Shi L, Hoerder-Suabedissen A
and Molnar Z: Neonatal hypoxia ischaemia: Mechanisms, models, and
therapeutic challenges. Front Cell Neurosci. 11:782017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun MS, Jin H, Sun X, Huang S, Zhang FL,
Guo ZN and Yang Y: Free radical damage in ischemia-reperfusion
injury: An obstacle in acute ischemic stroke after
revascularization therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:38049792018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thornton C, Leaw B, Mallard C, Nair S,
Jinnai M and Hagberg H: Cell death in the developing brain after
hypoxia-ischemia. Front Cell Neurosci. 11:2482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Leiva-Salinas C, Patrie JT, Xin W, Michel
P, Jovin T and Wintermark M: Prediction of early arterial
recanalization and tissue fate in the selection of patients with
the greatest potential to benefit from intravenous tissue-type
plasminogen activator. Stroke. 47:397–403. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rother J, Ford GA and Thijs VN:
Thrombolytics in acute ischaemic stroke: Historical perspective and
future opportunities. Cerebrovasc Dis. 35:313–319. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cheng CY and Lee YC: Anti-inflammatory
effects of traditional chinese medicines against ischemic injury in
in vivo models of cerebral ischemia. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2016:57394342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Feigin VL: Herbal medicine in stroke: Does
it have a future? Stroke. 38:1734–1736. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ip FC, Zhao YM, Chan KW, Cheng EY, Tong
EP, Chandrashekar O, Fu GM, Zhao ZZ and Ip NY: Neuroprotective
effect of a novel Chinese herbal decoction on cultured neurons and
cerebral ischemic rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 16:4372016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lestari ML and Indrayanto G: Curcumin.
Profiles Drug Subst Excip Relat Methodol. 39:113–204. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maiti P and Dunbar GL: Use of curcumin, a
natural polyphenol for targeting molecular pathways in treating
age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci.
19:E16372018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rahmani AH, Alsahli MA, Aly SM, Khan MA
and Aldebasi YH: Role of curcumin in disease prevention and
treatment. Adv Biomed Res. 7:382018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee WH, Loo CY, Bebawy M, Luk F, Mason RS
and Rohanizadeh R: Curcumin and its derivatives: Their application
in neuropharmacology and neuroscience in the 21st century. Curr
Neuropharmacol. 11:338–378. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Wicha P, Tocharus J, Janyou A, Jittiwat J,
Changtam C, Suksamrarn A and Tocharus C: Hexahydrocurcumin protects
against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury, attenuates
inflammation, and improves antioxidant defenses in a rat stroke
model. PLoS One. 12:e01892112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu JX, Zhang LY, Chen YL, Yu SS, Zhao Y
and Zhao J: Curcumin pretreatment and post-treatment both improve
the antioxidative ability of neurons with oxygen-glucose
deprivation. Neural Regen Res. 10:481–489. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xanthoudakis S and Curran T:
Identification and characterization of Ref-1, a nuclear protein
that facilitates AP-1 DNA-binding activity. EMBO J. 11:653–665.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lan J, Li W, Zhang F, Sun FY, Nagayama T,
O'Horo C and Chen J: Inducible repair of oxidative DNA lesions in
the rat brain after transient focal ischemia and reperfusion. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 23:1324–1339. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Leak RK, Li P, Zhang F, Sulaiman HH, Weng
Z, Wang G, Stetler RA, Shi Y, Cao G, Gao Y and Chen J:
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 upregulation reduces oxidative
DNA damage and protects hippocampal neurons from ischemic injury.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 22:135–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Kim HW, Cho KJ, Lee BI, Kim HJ and Kim GW:
Post-ischemic administration of peptide with apurinic/apyrimidinic
endonu-clease activity inhibits induction of cell death after focal
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in mice. Neurosci Lett. 460:166–169.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim HW, Cho KJ, Park SC, Kim HJ and Kim
GW: The adenoviral vector-mediated increase in
apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease inhibits the induction of
neuronal cell death after transient ischemic stroke in mice. Brain
Res. 1274:1–10. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jia JY, Tan ZG, Liu M and Jiang YG:
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) contributes to
resveratrol-induced neuroprotection against oxygen-glucose
deprivation and re-oxygenation injury in HT22 cells: Involvement in
reducing oxidative DNA damage. Mol Med Rep. 16:9786–9794. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stetler RA, Gao Y, Zukin RS, Vosler PS,
Zhang L, Zhang F, Cao G, Bennett MV and Chen J:
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endo-nuclease APE1 is required for
PACAP-induced neuroprotection against global cerebral ischemia.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:3204–3209. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Liu Y, Eaton ED, Wills TE, McCann SK,
Antonic A and Howells DW: Human ischaemic cascade studies using
SH-SY5Y cells: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl Stroke
Res. 9:564–574. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Q, Jin Z, Xu Z, Yang H, Li L, Li G, Li
F, Gu S, Zong S, Zhou J, et al: Antioxidant effects of ginkgolides
and bilobalide against cerebral ischemia injury by activating the
Akt/Nrf2 pathway in vitro and in vivo. Cell Stress Chaperones.
24:441–452. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li M and Wilson DM III: Human
apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1. Antioxid Redox Signal.
20:678–707. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Thakur S, Sarkar B, Cholia RP, Gautam N,
Dhiman M and Mantha AK: APE1/Ref-1 as an emerging therapeutic
target for various human diseases: Phytochemical modulation of its
functions. Exp Mol Med. 46:e1062014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shioda N, Han F and Fukunaga K: Role of
Akt and ERK signaling in the neurogenesis following brain ischemia.
Int Rev Neurobiol. 85:375–387. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nagy Z and Nardai S: Cerebral
ischemia/repefusion injury: From bench space to bedside. Brain Res
Bull. 134:30–37. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhou G, Li MH, Tudor G, Lu HT, Kadirvel R
and Kallmes D: Remote ischemic conditioning in cerebral diseases
and neuro-interventional procedures: Recent researchprogress. Front
Neurol. 9:3392018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kalani A, Kamat PK, Kalani K and Tyagi N:
Epigenetic impact of curcumin on stroke prevention. Metab Brain
Dis. 30:427–435. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kaur C and Ling EA: Blood brain barrier in
hypoxic-ischemic conditions. Curr Neurovasc Res. 5:71–81. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Marchiani A, Rozzo C, Fadda A, Delogu G
and Ruzza P: Curcumin and curcumin-like molecules: From spice to
drugs. Curr Med Chem. 21:204–222. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Xie CJ, Gu AP, Cai J, Wu Y and Chen RC:
Curcumin protects neural cells against ischemic injury in N2a cells
and mouse brain with ischemic stroke. Brain Behav. 8:e009212018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang Y, Fang M, Sun Y, Zhang T, Shi N, Li
J, Jin L, Liu K and Fu J: Curcumin attenuates cerebral ischemia
injury in Sprague-Dawley rats and PC12 cells by suppressing
overactivated autophagy. J Photochem Photobiol B. 184:1–6. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li P, Stetler RA, Leak RK, Shi Y, Li Y, Yu
W, Bennett MVL and Chen J: Oxidative stress and DNA damage after
cerebral ischemia: Potential therapeutic targets to repair the
genome and improve stroke recovery. Neuropharmacology. 134:208–217.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhao M, Zhu P, Fujino M, Zhuang J, Guo H,
Sheikh I, Zhao L and Li XK: Oxidative stress in hypoxic-ischemic
encephalopathy: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.
Int J Mol Sci. 17:E20782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bavarsad K, Barreto GE, Hadjzadeh MA and
Sahebkar A: Protective effects of curcumin against
ischemia-reperfusion injury in the nervous system. Mol Neurobiol.
56:1391–1404. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chen H, Yoshioka H, Kim GS, Jung JE, Okami
N, Sakata H, Maier CM, Narasimhan P, Goeders CE and Chan PH:
Oxidative stress in ischemic brain damage: Mechanisms of cell death
and potential molecular targets for neuroprotection. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 14:1505–1517. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Li P, Hu X, Gan Y, Gao Y, Liang W and Chen
J: Mechanistic insight into DNA damage and repair in ischemic
stroke: Exploiting the base excision repair pathway as a model of
neuro-protection. Antioxid Redox Signal. 14:1905–1918. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Li H, Zhong C, Wang Q, Chen W and Yuan Y:
Curcumin is an APE1 redox inhibitor and exhibits an antiviral
activity against KSHV replication and pathogenesis. Antiviral Res.
167:98–103. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sarkar B, Dhiman M, Mittal S and Mantha
AK: Curcumin revitalizes Amyloid beta (25-35)-induced and
organophosphate pesticides pestered neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y and
IMR-32 cells via activation of APE1 and Nrf2. Metab Brain Dis.
32:2045–2061. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zaky A, Mahmoud M, Awad D, El Sabaa BM,
Kandeel KM and Bassiouny AR: Valproic acid potentiates
curcumin-mediated neuroprotection in lipopolysaccharide induced
rats. Front Cell Neurosci. 8:3372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen SD, Yang DI, Lin TK, Shaw FZ, Liou CW
and Chuang YC: Roles of oxidative stress, apoptosis, PGC-1α and
mitochondrial biogenesis in cerebral ischemia. Int J Mol Sci.
12:7199–7215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zhao J, Yu S, Zheng W, Feng G, Luo G, Wang
L and Zhao Y: Curcumin improves outcomes and attenuates focal
cerebral ischemic injury via antiapoptotic mechanisms in rats.
Neurochem Res. 35:374–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wang Q, Sun AY, Simonyi A, Jensen MD,
Shelat PB, Rottinghaus GE, MacDonald RS, Miller DK, Lubahn DE,
Weisman GA and Sun GY: Neuroprotective mechanisms of curcumin
against cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal apoptosis and behavioral
deficits. J Neurosci Res. 82:138–148. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lee YR, Kim KM, Jeon BH and Choi S:
Extracellularly secreted APE1/Ref-1 triggers apoptosis in
triple-negative breast cancer cells via RAGE binding, which is
mediated through acetylation. Oncotarget. 6:23383–23398.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Muller UR, Dudler T, Schneider T, Crameri
R, Fischer H, Skrbic D, Maibach R, Blaser K and Suter M: Type I
skin reactivity to native and recombinant phospholipase A2 from
honeybee venom is similar. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 96:395–402.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tell G, Quadrifoglio F, Tiribelli C and
Kelley MR: The many functions of APE1/Ref-1: Not only a DNA repair
enzyme. Antioxid Redox Signal. 11:601–620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Shan JL, He HT, Li MX, Zhu JW, Cheng Y, Hu
N, Wang G, Wang D, Yang XQ, He Y, et al: APE1 promotes antioxidant
capacity by regulating Nrf-2 function through a redox-dependent
mechanism. Free Radic Biol Med. 78:11–22. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Xie J, Zhang L, Li M, Du J, Zhou L, Yang
S, Zeng L, Li Z, Wang G and Wang D: Functional analysis of the
involvement of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 in the
resistance to melphalan in multiple myeloma. BMC Cancer. 14:112014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Fan YY, Hu WW, Nan F and Chen Z:
Postconditioning-induced neuroprotection, mechanisms and
applications in cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Int. 107:43–56. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Matsuda S, Nakagawa Y, Tsuji A, Kitagishi
Y, Nakanishi A and Murai T: Implications of PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling
on superoxide dismutases expression and in the pathogenesis of
Alzheimer's disease. Diseases. 6:E282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Davis SM and Pennypacker KR: Targeting
antioxidant enzyme expression as a therapeutic strategy for
ischemic stroke. Neurochem Int. 107:23–32. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sang Q, Sun D, Chen Z and Zhao W: NGF and
PI3K/Akt signaling participate in the ventral motor neuronal
protection of curcumin in sciatic nerve injury rat models. Biomed
Pharmacother. 103:1146–1153. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Srivastava P, Dhuriya YK, Kumar V,
Srivastava A, Gupta R, Shukla RK, Yadav RS, Dwivedi HN, Pant AB and
Khanna VK: PI3K/Akt/GSK3beta induced CREB activation ameliorates
arsenic mediated alterations in NMDA receptors and associated
signaling in rat hippocampus: Neuroprotective role of curcumin.
Neurotoxicology. 67:190–205. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhong W, Qian K, Xiong J, Ma K, Wang A and
Zou Y: Curcumin alleviates lipopolysaccharide induced sepsis and
liver failure by suppression of oxidative stress-related
inflammation via PI3K/AKT and NF-KB related signaling. Biomed
Pharmacother. 83:302–313. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|