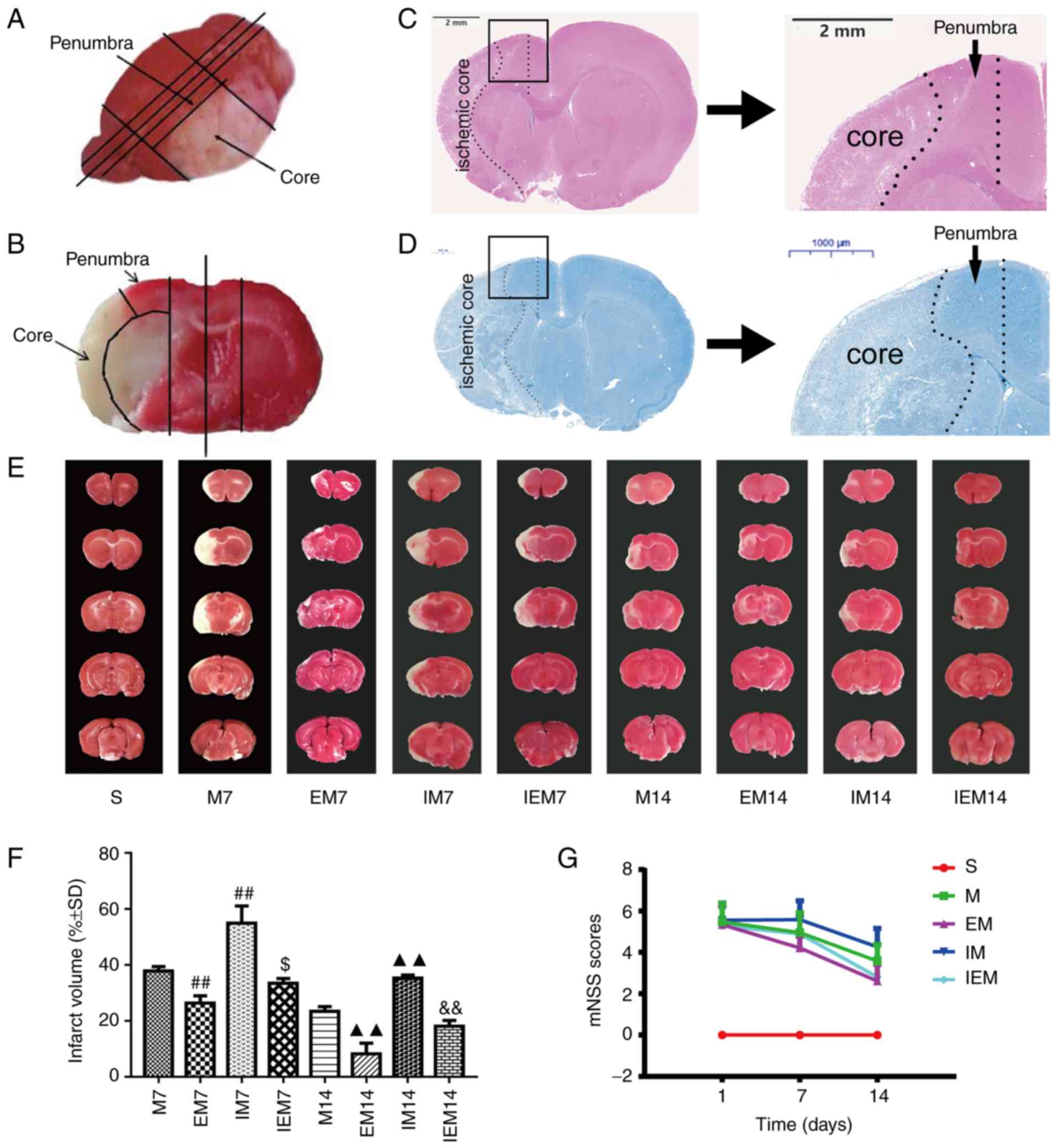
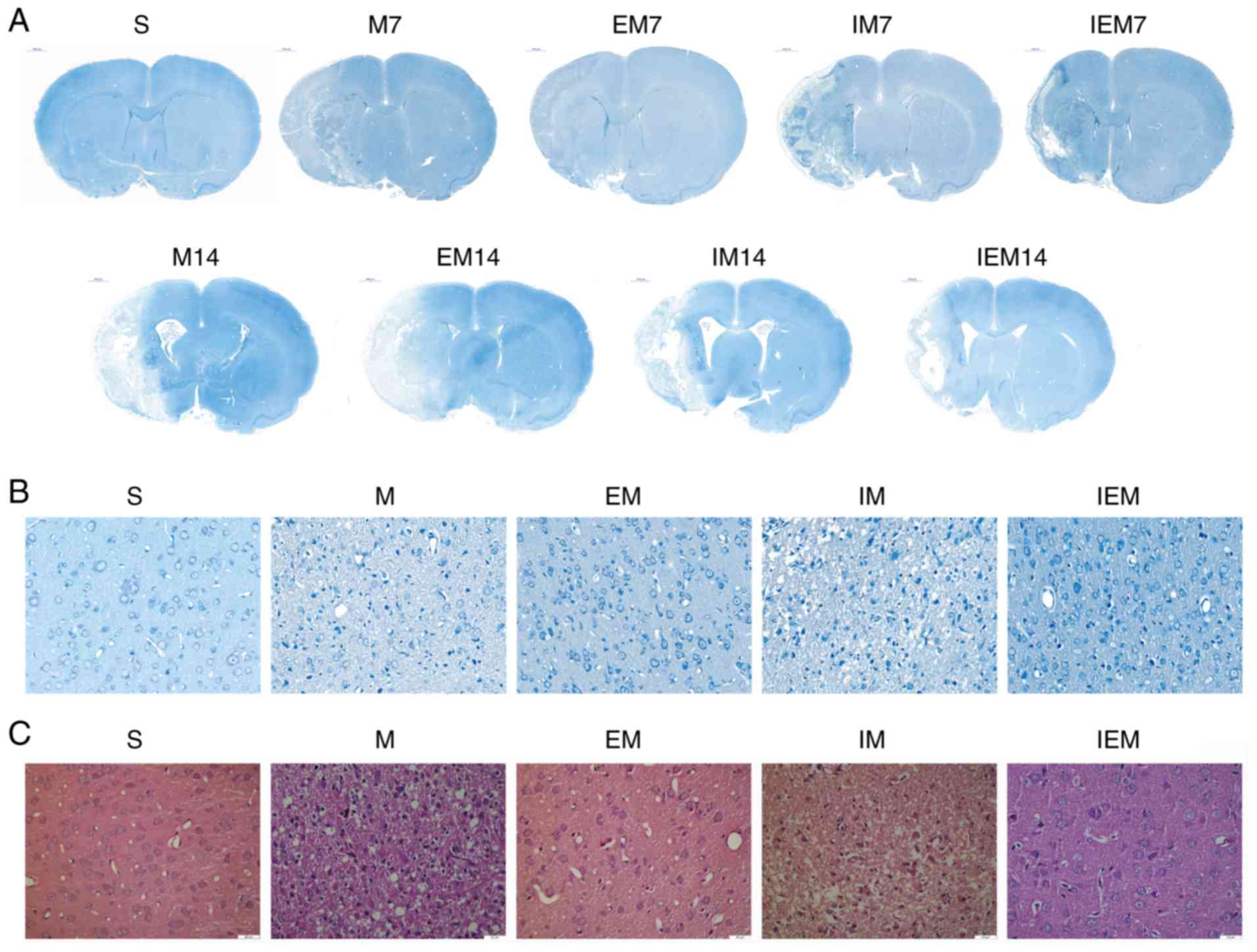
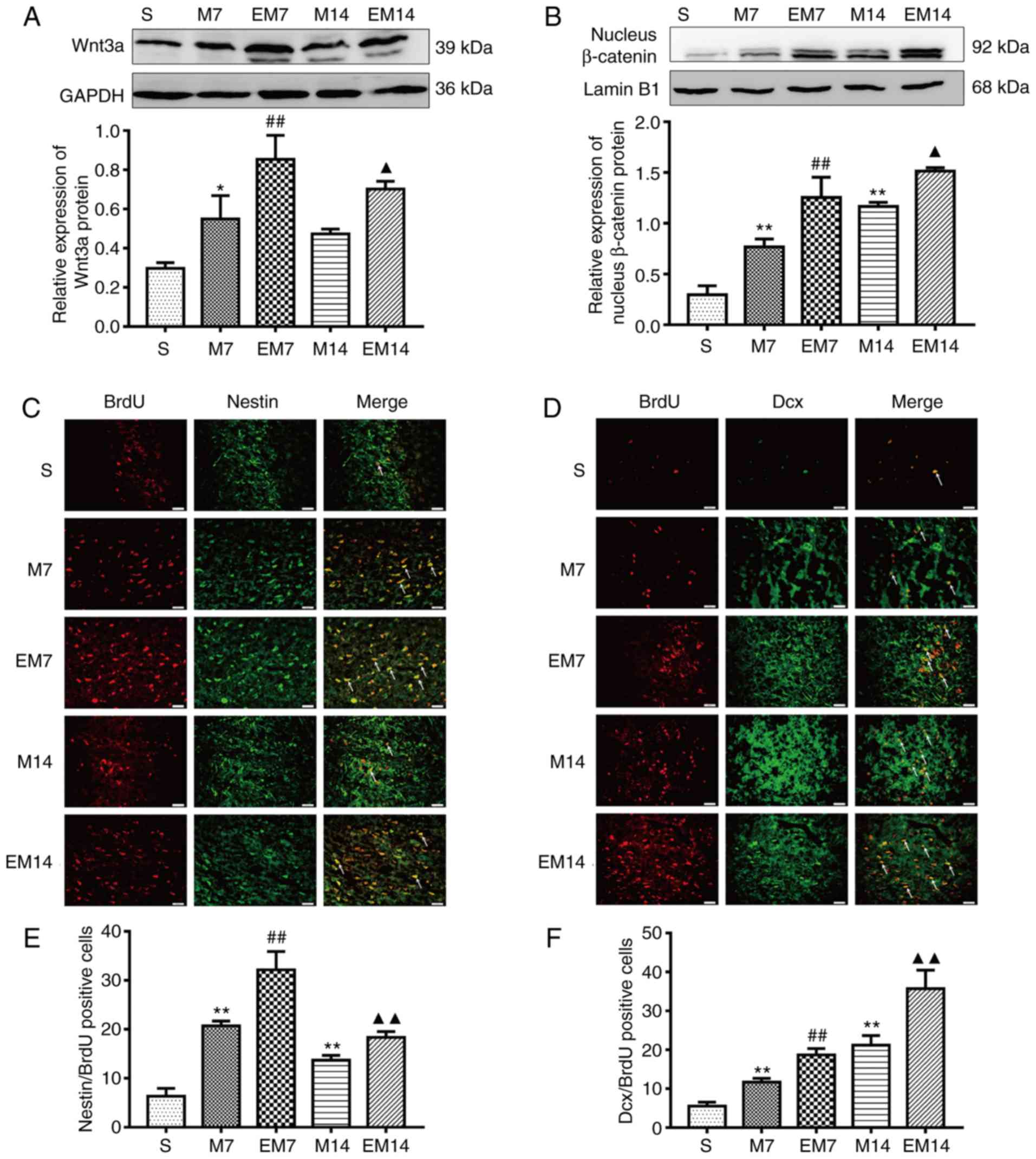
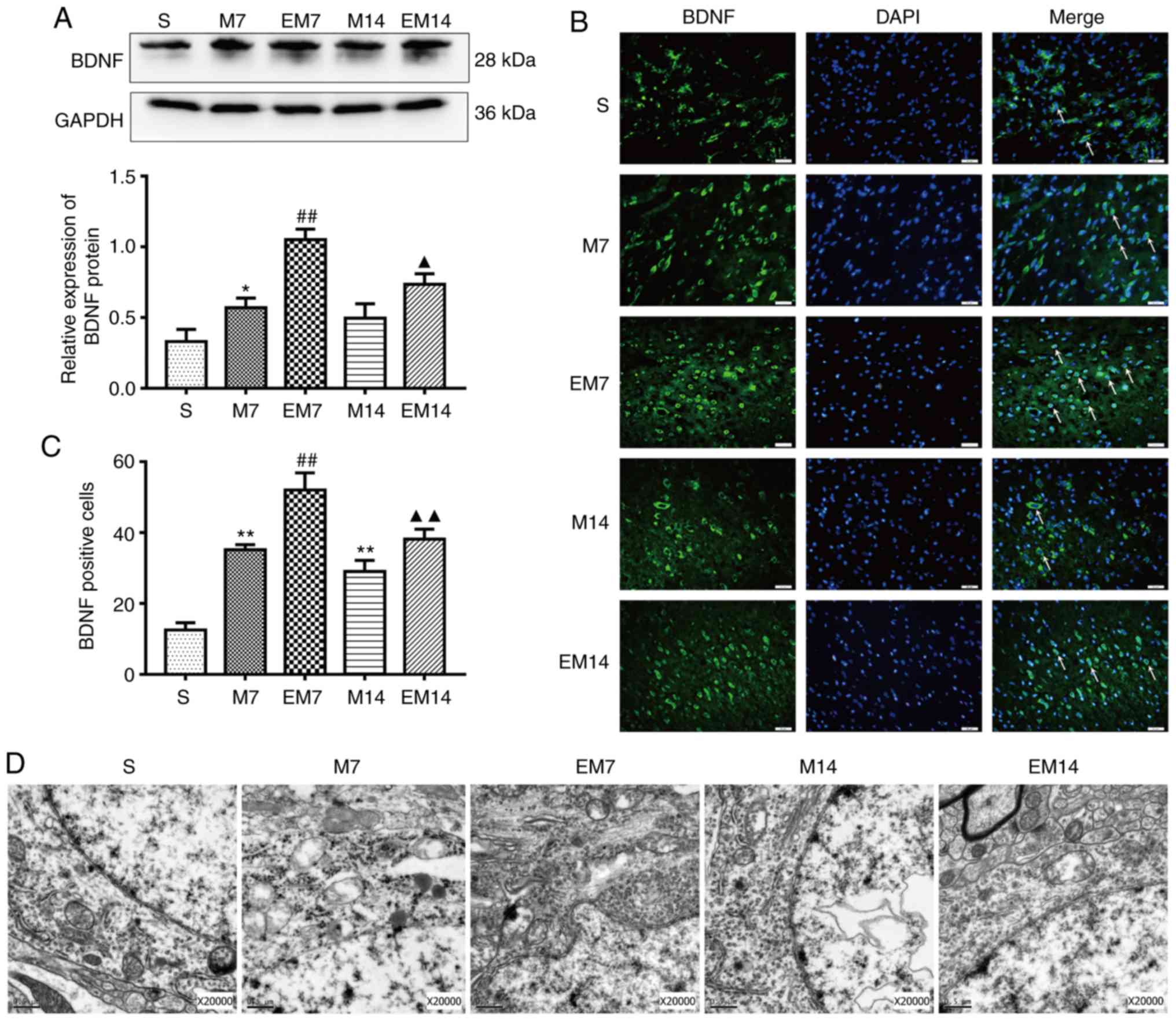
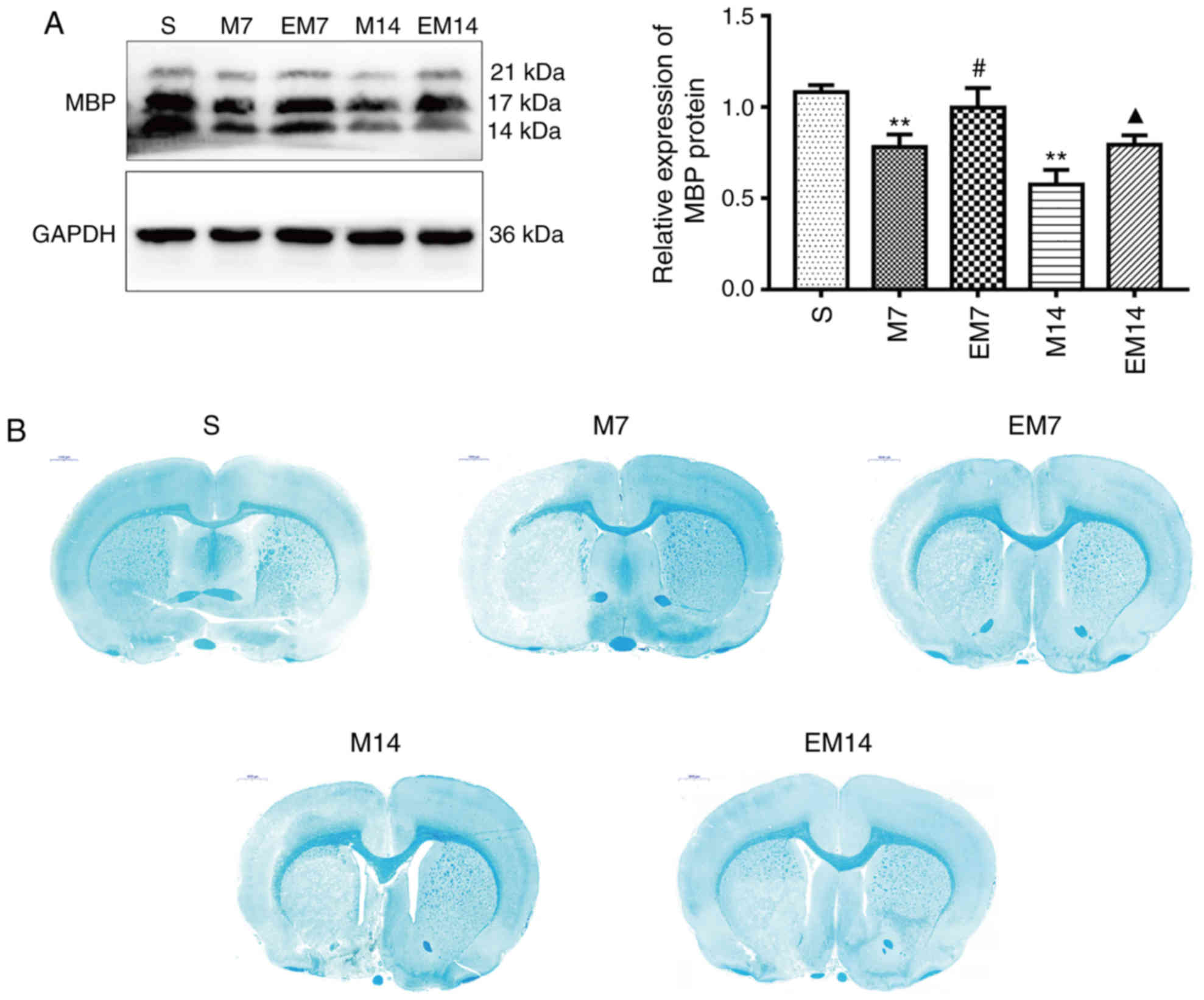
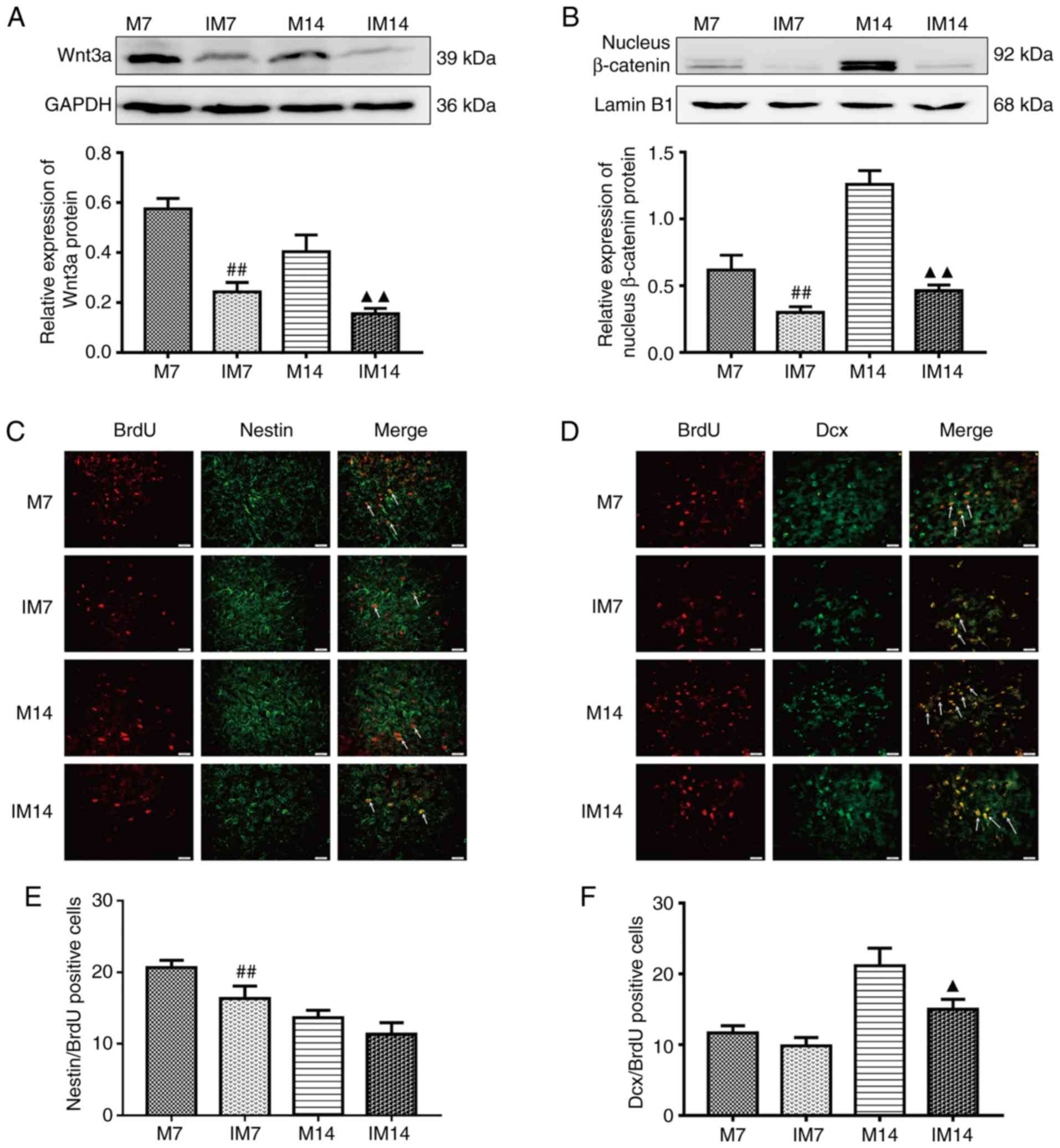
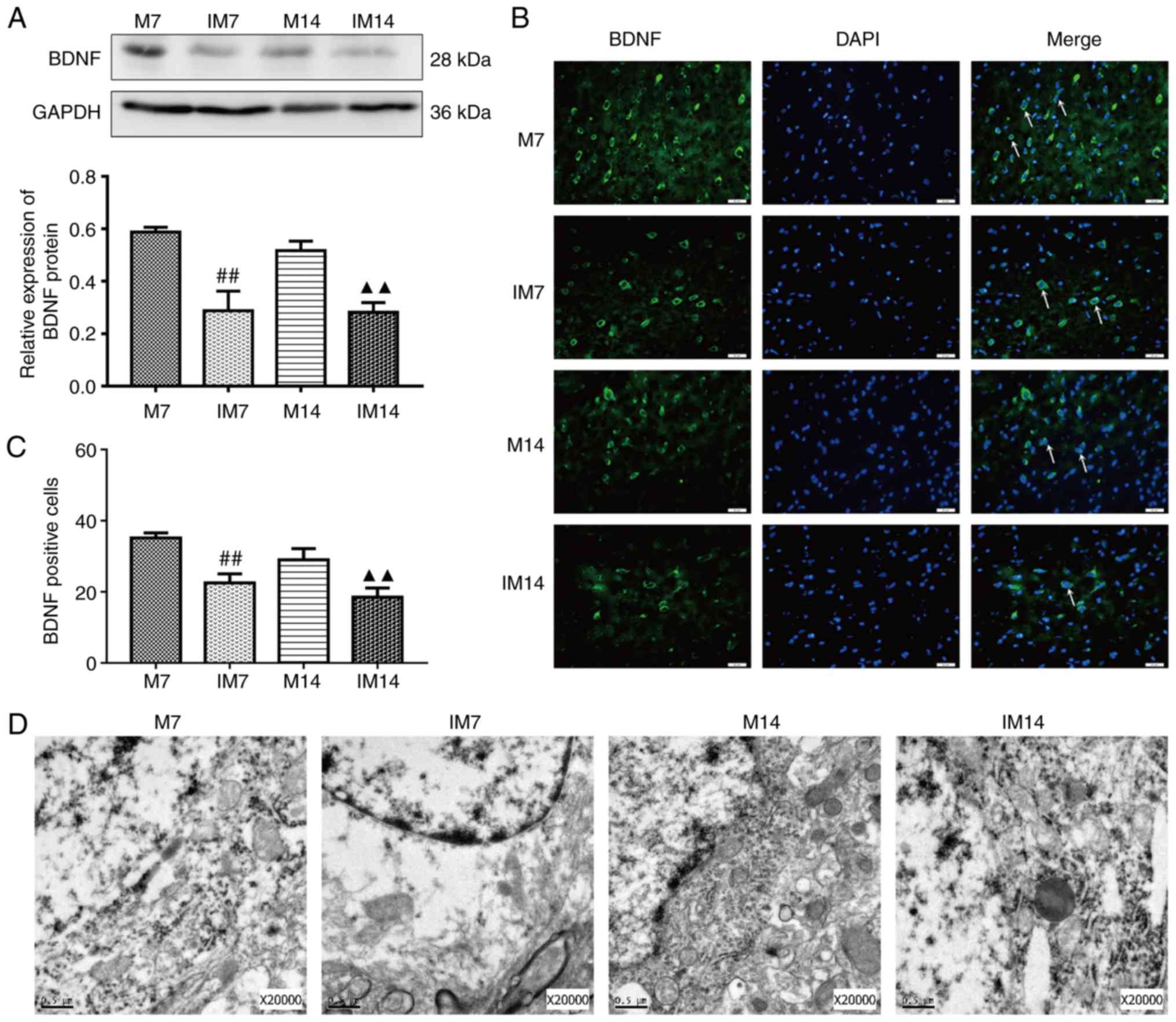
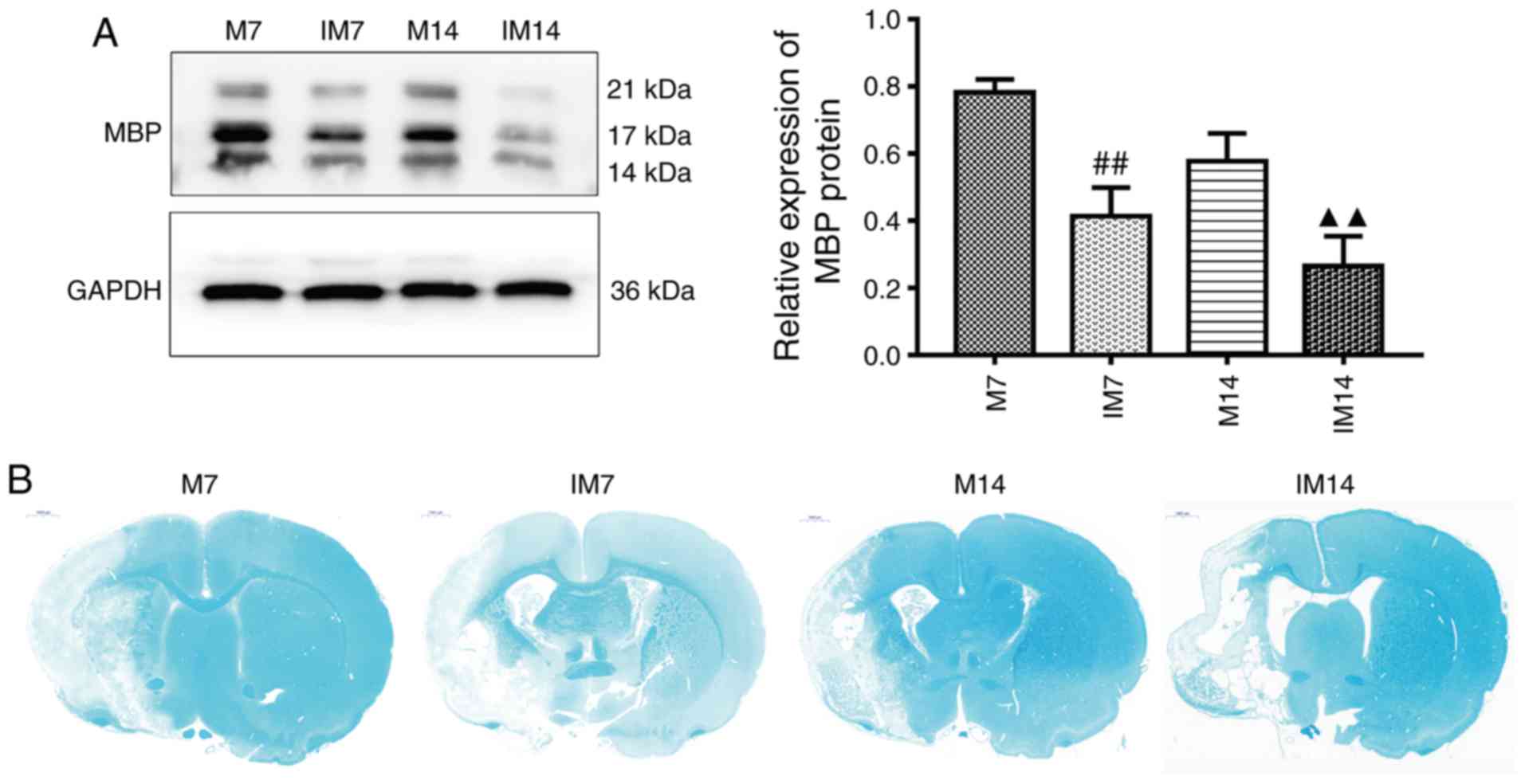
|
1
|
Feigin VL, Norrving B, George MG, Foltz
JL, Roth GA and Mensah GA: Prevention of stroke: A strategic global
imperative. Nat Rev Neurol. 12:501–512. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH and Iadecola C: The
science of stroke: Mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron.
67:181–198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ginsberg MD: Neuroprotection for ischemic
stroke: Past, present and future. Neuropharmacology. 55:363–389.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Minnerup J, Sutherland BA, Buchan AM and
Kleinschnitz C: Neuroprotection for stroke: Current status and
future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 13:11753–11772. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Magnusson JP, Goritz C, Tatarishvili J,
Dias DO, Smith EM, Lindvall O, Kokaia Z and Frisén J: A latent
neurogenic program in astrocytes regulated by Notch signaling in
the mouse. Science. 346:237–241. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ji Y, Teng L, Zhang R, Sun J and Guo Y:
NRG-1β exerts neuroprotective effects against ischemia
reperfusion-induced injury in rats through the JNK signaling
pathway. Neuroscience. 362:13–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Astrup J, Siesjo BK and Symon L:
Thresholds in cerebral ischemia-the ischemic penumbra. Stroke.
12:723–725. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lo EH: A new penumbra: Transitioning from
injury into repair after stroke. Nat Med. 14:497–500. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jackman K and Iadecola C: Neurovascular
regulation in the ischemic brain. Antioxid Redox Signal.
22:149–160. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Rodgers KM, Ahrendsen JT, Patsos OP,
Strnad FA, Yonchek JC, Traystman RJ, Macklin WB and Herson PS:
Endogenous neuronal replacement in the juvenile brain following
cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience. 380:1–13. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Zhao Z, Rege SV, Wang M, Si G,
Zhou Y, Wang S, Griffin JH, Goldman SA and Zlokovic BV:
3K3A-activated protein C stimulates postischemic neuronal repair by
human neural stem cells in mice. Nat Med. 22:1050–1055. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun FL, Wang W, Zuo W, Xue JL, Xu JD, Ai
HX, Zhang L, Wang XM and Ji XM: Promoting neurogenesis via
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway accounts for the neurorestorative
effects of morroniside against cerebral ischemia injury. Eur J
Pharmacol. 738:214–221. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pak ME, Jung DH, Lee HJ, Shin MJ, Kim SY,
Shin YB, Yun YJ, Shin HK and Choi BT: Combined therapy involving
electroacupuncture and treadmill exercise attenuates demyelination
in the corpus callosum by stimulating oligodendrogenesis in a rat
model of neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Exp Neurol. 300:222–231. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hao XZ, Yin LK, Tian JQ, Li CC, Feng XY,
Yao ZW, Jiang M and Yang YM: Inhibition of Notch1 signaling at the
subacute stage of stroke promotes endogenous neurogenesis and motor
recovery after stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 12:2452018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Danzer SC: Postnatal and adult
neurogenesis in the development of human disease. Neuroscientist.
14:446–458. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Piccin D and Morshead CM: Wnt signaling
regulates symmetry of division of neural stem cells in the adult
brain and in response to injury. Stem Cells. 29:528–538. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yoshinaga Y, Kagawa T, Shimizu T, Inoue T,
Takada S, Kuratsu J and Taga T: Wnt3a promotes hippocampal
neurogenesis by shortening cell cycle duration of neural progenitor
cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 30:1049–1058. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Munji RN, Choe Y, Li G, Siegenthaler JA
and Pleasure SJ: Wnt signaling regulates neuronal differentiation
of cortical intermediate progenitors. J Neurosci. 31:1676–1687.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wei ZZ, Zhang JY, Taylor TM, Gu X, Zhao Y
and Wei L: Neuroprotective and regenerative roles of intranasal
Wnt-3a administration after focal ischemic stroke in mice. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 38:404–421. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Lie DC, Colamarino SA, Song HJ, Désiré L,
Mira H, Consiglio A, Lein ES, Jessberger S, Lansford H, Dearie AR
and Gage FH: Wnt signalling regulates adult hippocampal
neurogenesis. Nature. 437:1370–1375. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qu Q, Sun G, Murai K, Ye P, Li W, Asuelime
G, Cheung YT and Shi Y: Wnt7a regulates multiple steps of
neurogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 33:2551–2559. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang J, Chen T and Shan G: MiR-148b
regulates proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells
via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in rat ischemic stroke model. Front
Cell Neurosci. 11:3292017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xu D, Hou K, Li F, Chen S, Fang W and Li
Y: XQ-1H alleviates cerebral ischemia in mice through inhibition of
apoptosis and promotion of neurogenesis in a Wnt/β-catenin
signaling dependent way. Life Sci. 235:1168442019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Adachi K, Mirzadeh Z, Sakaguchi M,
Yamashita T, Nikolcheva T, Gotoh Y, Peltz G, Gong L, Kawase T,
Alvarez-Buylla A, et al: Beta-catenin signaling promotes
proliferation of progenitor cells in the adult mouse subventricular
zone. Stem Cells. 25:2827–2836. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie Q, Cheng J, Pan G, Wu S, Hu Q, Jiang
H, Wang Y, Xiong J, Pang Q and Chen X: Treadmill exercise
ameliorates focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced
neurological deficit by promoting dendritic modification and
synaptic plasticity via upregulating caveolin-1/VEGF signaling
pathways. Exp Neurol. 313:60–78. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chen Z, Hu Q, Xie Q, Wu S, Pang Q, Liu M,
Zhao Y, Tu F, Liu C and Chen X: Effects of treadmill exercise on
motor and cognitive function recovery of MCAO mice through the
caveolin-1/VEGF signaling pathway in ischemic penumbra. Neurochem
Res. 44:930–946. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schabitz WR, Berger C, Kollmar R, Seitz M,
Tanay E, Kiessling M, Schwab S and Sommer C: Effect of
brain-derived neurotrophic factor treatment and forced arm use on
functional motor recovery after small cortical ischemia. Stroke.
35:992–997. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ahn JH, Choi JH, Park JH, Kim IH, Cho JH,
Lee JC, Koo HM, Hwangbo G, Yoo KY, Lee CH, et al: Long-term
exercise improves memory deficits via restoration of myelin and
microvessel damage, and enhancement of neurogenesis in the aged
gerbil hippocampus after ischemic stroke. Neurorehabil Neural
Repair. 30:894–905. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pang Q, Zhang H, Chen Z, Wu Y, Bai M, Liu
Y, Zhao Y, Tu F, Liu C and Chen X: Role of caveolin-1/vascular
endothelial growth factor pathway in basic fibroblast growth
factor-induced angiogenesis and neurogenesis after treadmill
training following focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res.
1663:9–19. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao Y, Pang Q, Liu M, Pan J, Xiang B,
Huang T, Tu F, Liu C and Chen X: Treadmill exercise promotes
neurogenesis in ischemic rat brains via caveolin-1/VEGF signaling
pathways. Neurochem Res. 42:389–397. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Saver JL, Albers GW, Dunn B, Johnston KC
and Fisher M; STAIR VI Consortium. Stroke Therapy Academic Industry
Roundtable (STAIR) recommendations for extended window acute stroke
therapy trials. Stroke. 40:2594–2600. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jean LeBlanc N, Menet R, Picard K, Parent
G, Tremblay ME and ElAli A: Canonical Wnt pathway maintains
blood-brain barrier integrity upon ischemic stroke and its
activation ameliorates tissue plasminogen activator therapy. Mol
Neurobiol. 56:6521–6538. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang YZ, Yamagami T, Gan Q, Wang Y, Zhao
T, Hamad S, Lott P, Schnittke N, Schwob JE and Zhou CJ: Canonical
Wnt signaling promotes the proliferation and neurogenesis of
peripheral olfactory stem cells during postnatal development and
adult regeneration. J Cell Sci. 124:1553–1563. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, Zhang Z, Lu D, Lu M
and Chopp M: Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of
bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke.
32:1005–1011. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ding YH, Ding Y, Li J, Bessert DA and
Rafols JA: Exercise pre-conditioning strengthens brain
microvascular integrity in a rat stroke model. Neurol Res.
28:184–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gao Y, Zhao Y, Pan J, Yang L, Huang T,
Feng X, Li C, Liang S, Zhou D, Liu C, et al: Treadmill exercise
promotes angiogenesis in the ischemic penumbra of rat brains
through caveolin-1/VEGF signaling pathways. Brain Res. 1585:83–90.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ashwal S, Tone B, Tian HR, Cole DJ,
Liwnicz BH and Pearce WJ: Core and penumbral nitric oxide synthase
activity during cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in the rat pup.
Pediatr Res. 46:390–400. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao C, Deng W and Gage FH: Mechanisms and
functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell. 132:645–660.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang X, Zhang M, Yang SD, Li WB, Ren SQ,
Zhang J and Zhang F: Pre-ischemic treadmill training alleviates
brain damage via GLT-1-mediated signal pathway after ischemic
stroke in rats. Neuroscience. 274:393–402. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim HN, Pak ME, Shin MJ, Kim SY, Shin YB,
Yun YJ, Shin HK and Choi BT: Comparative analysis of the beneficial
effects of treadmill training and electroacupuncture in a rat model
of neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Int J Mol Med. 39:1393–1402. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gallo V and Armstrong RC: Myelin repair
strategies: A cellular view. Curr Opin Neurol. 21:278–283. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dewar D, Underhill SM and Goldberg MP:
Oligodendrocytes and ischemic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 23:263–274. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Micu I, Jiang Q, Coderre E, Ridsdale A,
Zhang L, Woulfe J, Yin X, Trapp BD, McRory JE, Rehak R, et al: NMDA
receptors mediate calcium accumulation in myelin during chemical
ischaemia. Nature. 439:988–992. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
McTigue DM and Tripathi RB: The life,
death, and replacement of oligodendrocytes in the adult CNS. J
Neurochem. 107:1–19. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yi H, Hu J, Qian J and Hackam AS:
Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor is regulated by the
Wnt signaling pathway. Neuroreport. 23:189–194. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Lu B, Nagappan G, Guan X, Nathan PJ and
Wren P: BDNF-based synaptic repair as a disease-modifying strategy
for neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci. 14:401–416. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bekinschtein P, Oomen CA, Saksida LM and
Bussey TJ: Effects of environmental enrichment and voluntary
exercise on neurogenesis, learning and memory, and pattern
separation: BDNF as a critical variable? Semin Cell Dev Biol.
22:536–542. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Greenberg ME, Xu B, Lu B and Hempstead BL:
New insights in the biology of BDNF synthesis and release:
Implications in CNS function. J Neurosci. 29:12764–12767. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Brigadski T, Hartmann M and Lessmann V:
Differential vesicular targeting and time course of synaptic
secretion of the mammalian neurotrophins. J Neurosci. 25:7601–7614.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Matsuda N, Lu H, Fukata Y, Noritake J, Gao
H, Mukherjee S, Nemoto T, Fukata M and Poo MM: Differential
activity-dependent secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor
from axon and dendrite. J Neurosci. 29:14185–14198. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Scharfman H, Goodman J, Macleod A, Phani
S, Antonelli C and Croll S: Increased neurogenesis and the ectopic
granule cells after intrahippocampal BDNF infusion in adult rats.
Exp Neurol. 192:348–356. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Benraiss A, Chmielnicki E, Lerner K, Roh D
and Goldman SA: Adenoviral brain-derived neurotrophic factor
induces both neostriatal and olfactory neuronal recruitment from
endogenous progenitor cells in the adult forebrain. J Neurosci.
21:6718–6731. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jones KR, Farinas I, Backus C and
Reichardt LF: Targeted disruption of the BDNF gene perturbs brain
and sensory neuron development but not motor neuron development.
Cell. 76:989–999. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Obernier K, Tong CK and Alvarez-Buylla A:
Restricted nature of adult neural stem cells: Re-evaluation of
their potential for brain repair. Front Neurosci. 8:1622014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Carmichael ST, Ohab J and Nguyen J:
Post-stroke neurogenesis and the neurovascular niche: Newly born
neuroblasts localize to peri-infarct cortex in close association
with the vascular endothelium. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 25:S214.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Parmalee NL and Kitajewski J: Wnt
signaling in angiogenesis. Curr Drug Targets. 9:558–564. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Xu Y, Zhang G, Kang Z, Xu Y, Jiang W and
Zhang S: Cornin increases angiogenesis and improves functional
recovery after stroke via the Ang1/Tie2 axis and the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway. Arch Pharm Res. 39:133–142. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Ciani L and Salinas PC: WNTs in the
vertebrate nervous system: From patterning to neuronal
connectivity. Nat Rev Neurosci. 6:351–362. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Salinas PC: Wnt signaling in the
vertebrate central nervous system: From axon guidance to synaptic
function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4:pii: a008003. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Patel AK, Park KK and Hackam AS: Wnt
signaling promotes axonal regeneration following optic nerve injury
in the mouse. Neuroscience. 343:372–383. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
62
|
Yin ZS, Zu B, Chang J and Zhang H: Repair
effect of Wnt3a protein on the contused adult rat spinal cord.
Neurol Res. 30:480–486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kalani MY, Cheshier SH, Cord BJ, Bababeygy
SR, Vogel H, Weissman IL, Palmer TD and Nusse R: Wnt-mediated
self-renewal of neural stem/progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:16970–16975. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ikeya M and Takada S: Wnt-3a is required
for somite specification along the anteroposterior axis of the
mouse embryo and for regulation of cdx-1 expression. Mech Dev.
103:27–33. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Mastroiacovo F, Busceti CL, Biagioni F,
Moyanova SG, Meisler MH, Battaglia G, Caricasole A, Bruno V and
Nicoletti F: Induction of the Wnt antagonist, Dickkopf-1,
contributes to the development of neuronal death in models of brain
focal ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29:264–276. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Mussmann C, Hubner R, Trilck M, Rolfs A
and Frech MJ: HES5 is a key mediator of Wnt-3a-induced neuronal
differentiation. Stem Cells Dev. 23:1328–1339. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Giuliani D, Zaffe D, Ottani A, Spaccapelo
L, Galantucci M, Minutoli L, Bitto A, Irrera N, Contri M, Altavilla
D, et al: Treatment of cerebral ischemia with melanocortins acting
at MC4 receptors induces marked neurogenesis and long-lasting
functional recovery. Acta Neuropathol. 122:443–453. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Spaccapelo L, Galantucci M, Neri L, Contri
M, Pizzala R, D’Amico R, Ottani A, Sandrini M, Zaffe D, Giuliani D
and Guarini S: Up-regulation of the canonical Wnt-3A and Sonic
hedgehog signaling underlies melanocortin-induced neurogenesis
after cerebral ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol. 707:78–86. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Inestrosa NC, Urra S and Colombres M:
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)-amyloid-beta-peptide complexes in
Alzheimer’s disease. The Wnt signaling pathway. Curr Alzheimer Res.
1:249–254. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Toledo EM, Colombres M and Inestrosa NC:
Wnt signaling in neuroprotection and stem cell differentiation.
Prog Neurobiol. 86:281–296. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Tourette C, Farina F, Vazquez-Manrique RP,
Orfila AM, Voisin J, Hernandez S, Offner N, Parker JA, Menet S, Kim
J, et al: The Wnt receptor Ryk reduces neuronal and cell survival
capacity by repressing FOXO activity during the early phases of
mutant huntingtin pathogenicity. PLoS Biol. 12:e10018952014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|