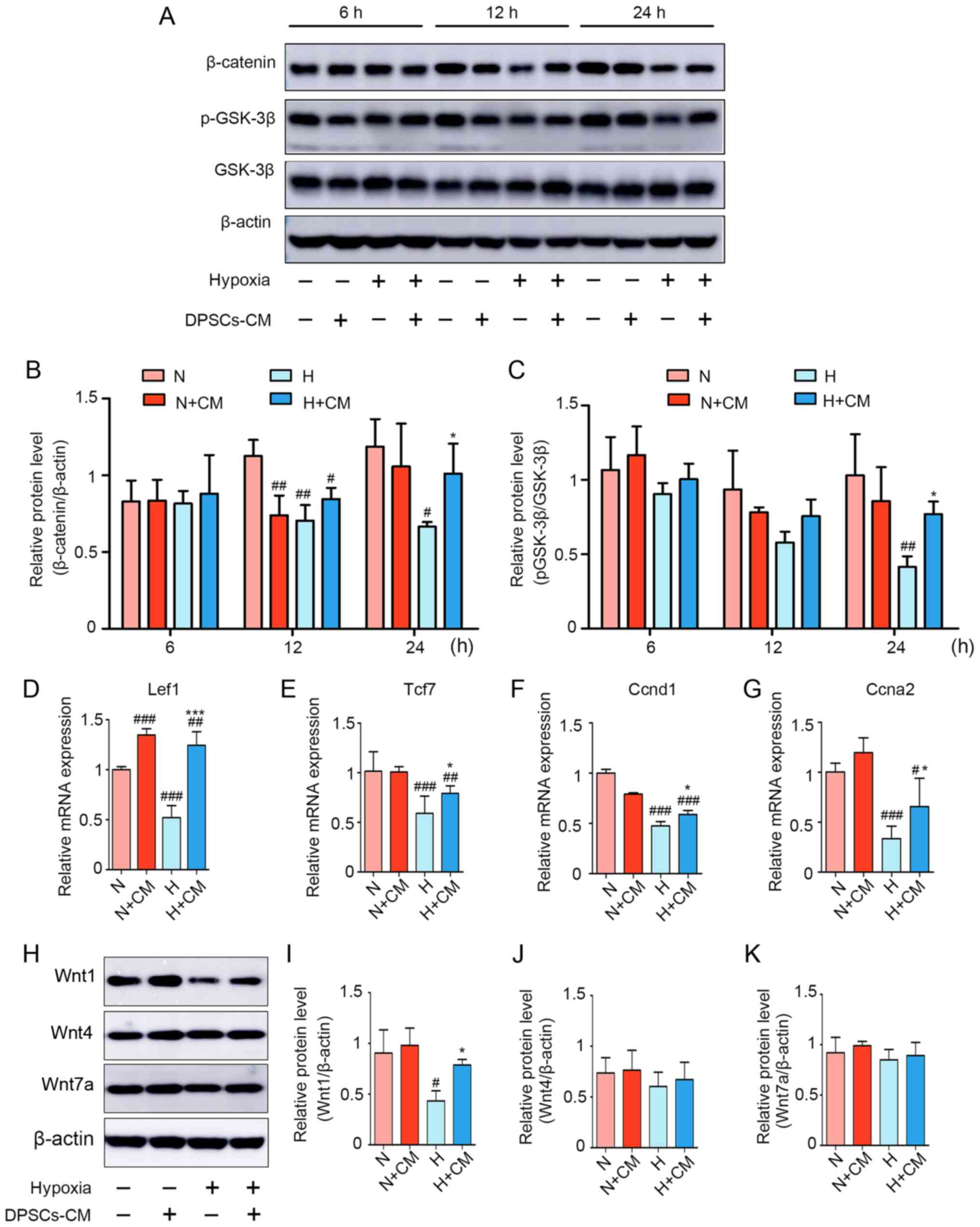
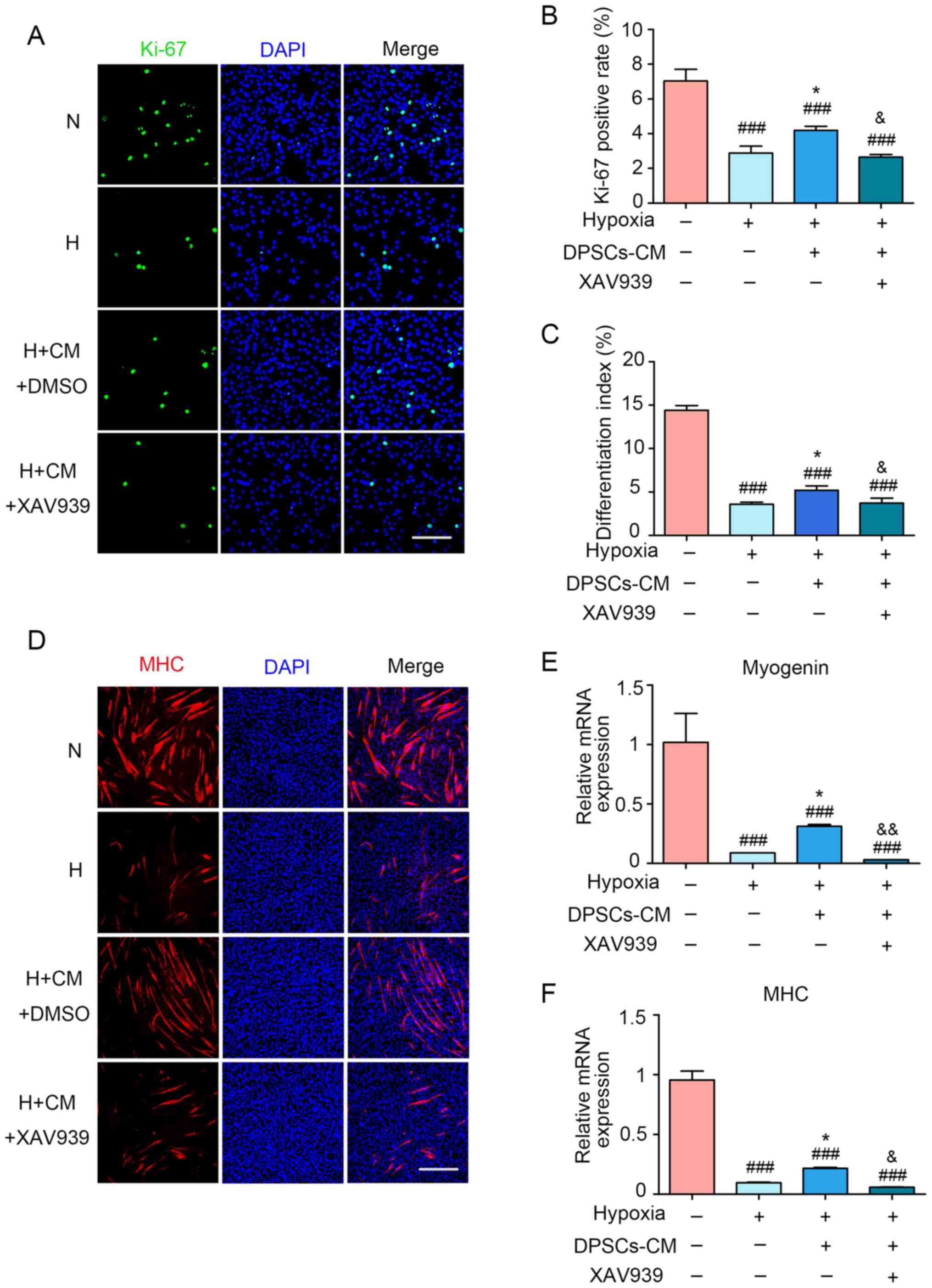
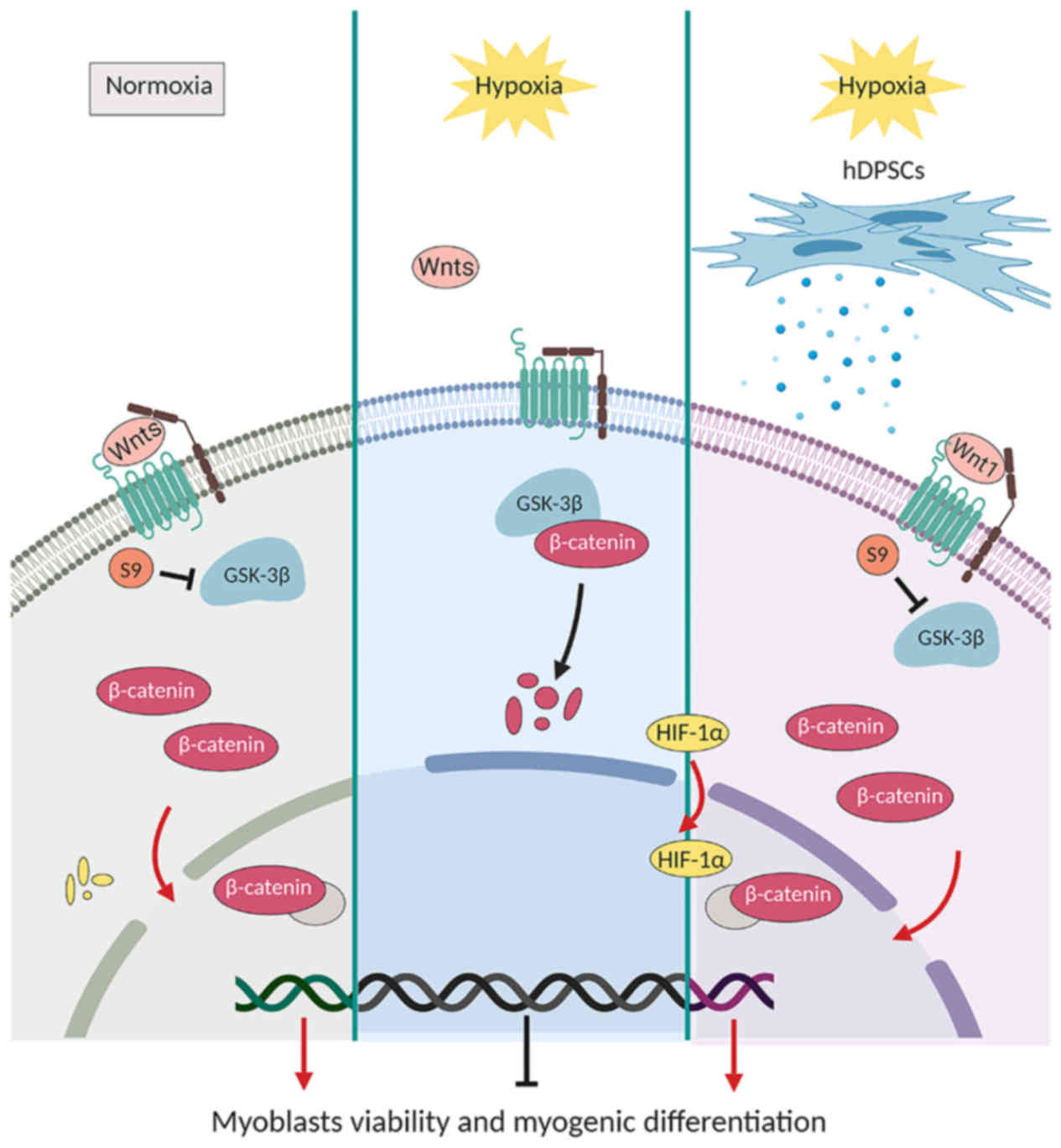
|
1
|
Koh MY and Powis G: Passing the baton: The
HIF switch. Trends Biochem Sci. 37:364–372. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chaillou T: Skeletal muscle fiber type in
hypoxia: Adaptation to high-altitude exposure and under conditions
of pathological hypoxia. Front Physiol. 9:14502018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Adams V, Linke A and Winzer E: Skeletal
muscle alterations in HFrEF vs. HFpEF Current Heart Failure
Reports. 14:489–497. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gea J, Agusti A and Roca J:
Pathophysiology of muscle dysfunction in COPD. J Appl Physiol.
1985. 114:1222–1234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Putti R, Migliaccio V, Sica R and Lionetti
L: Skeletal muscle mitochondrial bioenergetics and morphology in
high fat diet induced obesity and insulin resistance: Focus on
dietary fat source. Front Physiol. 6:4262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lu Y, Liu Y and Li Y: Comparison of
natural estrogens and synthetic derivative on genioglossus function
and estrogen receptors expression in rats with chronic intermittent
hypoxia. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 140:71–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Williams R, Lemaire P, Lewis P, McDonald
FB, Lucking E, Hogan S, Sheehan D, Healy V and O’Halloran KD:
Chronic intermittent hypoxia increases rat sternohyoid muscle NADPH
oxidase expression with attendant modest oxidative stress. Front
Physiol. 6:152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Beaudry M, Hidalgo M, Launay T, Bello V
and Darribère T: Regulation of myogenesis by environmental hypoxia.
J Cell Sci. 129:2887–2896. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chaillou T, Koulmann N, Meunier A, Chapot
R, Serrurier B, Beaudry M and Bigard X: Effect of hypoxia exposure
on the recovery of skeletal muscle phenotype during regeneration.
Mol Cell Biochem. 390:31–40. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Favier FB, Britto FA, Freyssenet DG,
Bigard XA and Benoit H: HIF-1-driven skeletal muscle adaptations to
chronic hypoxia: Molecular insights into muscle physiology. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 72:4681–4696. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Quadrilatero J, Alway SE and
Dupont-Versteegden EE: Skeletal muscle apoptotic response to
physical activity: Potential mechanisms for protection. Appl
Physiol Nutr Metab. 36:608–617. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
L’honoré A, Commère PH, Ouimette JF,
Montarras D, Drouin J and Buckingham M: Redox regulation by Pitx2
and Pitx3 is critical for fetal myogenesis. Dev Cell. 39:7562016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Muñoz-Sánchez J and Chánez-Cárdenas ME:
The use of cobalt chloride as a chemical hypoxia model. J Appl
Toxicol. 39:556–570. 2019. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hayot M, Rodriguez J, Vernus B, Carnac G,
Jean E, Allen D, Goret L, Obert P, Candau R and Bonnieu A:
Myostatin up-regulation is associated with the skeletal muscle
response to hypoxic stimuli. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 332:38–47. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen R, Xu J, She Y, Jiang T, Zhou S, Shi
H and Li C: Necrostatin-1 protects C2C12 myotubes from
CoCl2-induced hypoxia. Int J Mol Med. 41:2565–2572. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baskaran R, Kalaiselvi P, Huang CY and
Padma VV: Neferine, a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid, offers
protection against cobalt chloride-mediated hypoxia-induced
oxidative stress in muscle cells. Integr Med Res. 4:231–241. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen R, Jiang T, She Y, Xu J, Li C, Zhou
S, Shen H, Shi H and Liu S: Effects of cobalt chloride, a
hypoxia-mimetic agent, on autophagy and atrophy in skeletal C2C12
myotubes. Biomed Res Int. 2017:7097580. 2017.
|
|
18
|
Rovetta F, Stacchiotti A, Faggi F,
Catalani S, Apostoli P, Fanzani A and Aleo MF: Cobalt triggers
necrotic cell death and atrophy in skeletal C2C12 myotubes. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 271:196–205. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jaitovich A and Barreiro E: Skeletal
muscle dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. What
we know and can do for our patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
198:175–186. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hirai DM, Musch TI and Poole DC: Exercise
training in chronic heart failure: Improving skeletal muscle O2
transport and utilization. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
309:H1419–H1439. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guimarães KC, Drager LF, Genta PR,
Marcondes BF and Lorenzi-Filho G: Effects of oropharyngeal
exercises on patients with moderate obstructive sleep apnea
syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 179:962–966. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chaudhary P, Sharma YK, Sharma S, Singh SN
and Suryakumar G: High altitude mediated skeletal muscle atrophy:
Protective role of curcumin. Biochimie. 156:138–147. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kerkis I, Ambrosio CE, Kerkis A, Martins
DS, Zucconi E, Fonseca SA, Cabral RM, Maranduba CM, Gaiad TP,
Morini AC, et al: Early transplantation of human immature dental
pulp stem cells from baby teeth to golden retriever muscular
dystrophy (GRMD) dogs: Local or systemic. J Transl Med. 6:352008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Nakatsuka R, Nozaki T, Uemura Y, Matsuoka
Y, Sasaki Y, Shinohara M, Ohura K and Sonoda Y:
5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine treatment induces skeletal myogenic
differentiation of mouse dental pulp stem cells. Arch Oral Biol.
55:350–357. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Spath L, Rotilio V, Alessandrini M,
Gambara G, De Angelis L, Mancini M, Mitsiadis TA, Vivarelli E, Naro
F, Filippini A and Papaccio G: Explant-derived human dental pulp
stem cells enhance differentiation and proliferation potentials. J
Cell Mol Med. 14:1635–1644. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kichenbrand C, Velot E, Menu P and Moby V:
Dental pulp stem cell-derived conditioned medium: An attractive
alternative for regenerative therapy. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.
25:78–88. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Madrigal M, Rao KS and Riordan NH: A
review of therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell secretions
and induction of secretory modification by different culture
methods. J Transl Med. 12:2602014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Assoni A, Coatti G, Valadares MC, Beccari
M, Gomes J, Pelatti M, Mitne-Neto M, Carvalho VM and Zatz M:
Different donors mesenchymal stromal cells secretomes reveal
heterogeneous profile of relevance for therapeutic use. Stem Cells
Dev. 26:206–214. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liang X, Ding Y, Zhang Y, Tse HF and Lian
Q: Paracrine mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy:
Current status and perspectives. Cell Transplant. 23:1045–1059.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Park CM, Kim MJ, Kim SM, Park JH, Kim ZH
and Choi YS: Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned media
prevent muscle atrophy by suppressing muscle atrophy-related
proteins and ROS generation. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 52:68–76.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kim MJ, Kim ZH, Kim SM and Choi YS:
Conditioned medium derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem
cells regenerates atrophied muscles. Tissue Cell. 48:533–543. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cho KA, Park M, Kim YH, Woo SY and Ryu KH:
Conditioned media from human palatine tonsil mesenchymal stem cells
regulates the interaction between myotubes and fibroblasts by
IL-1Ra activity. J Cell Mol Med. 21:130–141. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mouse Genome Sequencing Consortium.
Waterston RH, Lindblad-Toh K, Birney E, Rogers J, Abril JF, Agarwal
P, Agarwala R, Ainscough R, Alexandersson M, et al: Initial
sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature.
420:520–562. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Naskar S, Kumaran V, Markandeya YS, Mehta
B and Basu B: Neurogenesis-on-Chip: Electric field modulated
transdifferentiation of human mesenchymal stem cell and mouse
muscle precursor cell coculture. Biomaterials. 226:1195222020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhao Y, Li N, Li Z, Zhang D, Chen L, Yao Z
and Niu W: Conditioned medium from contracting skeletal muscle
cells reverses insulin resistance and dysfunction of endothelial
cells. Metabolism. 82:36–46. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kwon S, Ki SM, Park SE, Kim MJ, Hyung B,
Lee NK, Shim S, Choi BO, Na DL, Lee JE and Chang JW: Anti-apoptotic
effects of human Wharton’s Jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells on
skeletal muscle cells mediated via secretion of XCL1. Mol Ther.
24:1550–1560. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Girardi F and Le Grand F: Wnt signaling in
skeletal muscle development and regeneration. Prog Mol Biol Transl
Sci. 153:157–179. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Comai G and Tajbakhsh S: Molecular and
cellular regulation of skeletal myogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol.
110:1–73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cho OH, Mallappa C, Hernández-Hernández
JM, Rivera-Pérez JA and Imbalzano AN: Contrasting roles for MyoD in
organizing myogenic promoter structures during embryonic skeletal
muscle development. Dev Dyn. 244:43–55. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhu X and Lu X: MiR-423-5p inhibition
alleviates cardiomyocyte apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction
caused by hypoxia/reoxygenation through activation of the
wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via targeting MYBL2. J Cell
Physiol. 234:22034–22043. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Majmundar AJ, Lee DS, Skuli N, Mesquita
RC, Kim MN, Yodh AG, Nguyen-McCarty M, Li B and Simon MC: HIF
modulation of Wnt signaling regulates skeletal myogenesis in vivo.
Development. 142:2405–2412. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Drouin G, Couture V, Lauzon MA, Balg F,
Faucheux N and Grenier G: Muscle injury-induced hypoxia alters the
proliferation and differentiation potentials of muscle resident
stromal cells. Skelet Muscle. 9:182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rahar B, Chawla S, Pandey S, Bhatt AN and
Saxena S: Sphingosine-1-phosphate pretreatment amends
hypoxia-induced metabolic dysfunction and impairment of myogenic
potential in differentiating C2C12 myoblasts by stimulating
viability, calcium homeostasis and energy generation. J Physiol
Sci. 68:137–151. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Pagé M, Maheux C, Langlois A, Brassard J,
Bernatchez É, Martineau S, Henry C, Beaulieu MJ, Bossé Y,
Morissette MC, et al: CD34 regulates the skeletal muscle response
to hypoxia. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 40:309–318. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Di Carlo A, De Mori R, Martelli F,
Pompilio G, Capogrossi MC and Germani A: Hypoxia inhibits myogenic
differentiation through accelerated MyoD degradation. J Biol Chem.
279:16332–16338. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Aziz A, Sebastian S and Dilworth FJ: The
origin and fate of muscle satellite cells. Stem Cell Rev.
8:609–622. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Leroux L, Descamps B, Tojais NF, Séguy B,
Oses P, Moreau C, Daret D, Ivanovic Z, Boiron JM, Lamazière JM, et
al: Hypoxia preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells improve vascular
and skeletal muscle fiber regeneration after ischemia through a
Wnt4-dependent pathway. Mol Ther. 18:1545–1552. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gao T, Yu Y, Cong Q, Wang Y, Sun M, Yao L,
Xu C and Jiang W: Human mesenchymal stem cells in the tumour
microenvironment promote ovarian cancer progression: The role of
platelet-activating factor. BMC Cancer. 18:9992018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chen B, Ni Y, Liu J, Zhang Y and Yan F:
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells exert diverse effects on
different macrophage subsets. Stem Cells Int. 2018:8348121. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Azhdari Tafti Z, Mahmoodi M, Hajizadeh MR,
Ezzatizadeh V, Baharvand H, Vosough M and Piryaei A: Conditioned
media derived from human adipose tissue mesenchymal stromal cells
improves primary hepatocyte maintenance. Cell J. 20:377–387.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Periasamy R, Surbek DV and Schoeberlein A:
In vitro-microenvironment directs preconditioning of human chorion
derived MSC promoting differentiation of OPC-like cells. Tissue
Cell. 52:65–70. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nagata M, Iwasaki K, Akazawa K, Komaki M,
Yokoyama N, Izumi Y and Morita I: Conditioned medium from
periodontal ligament stem cells enhances periodontal regeneration.
Tissue Eng Part A. 23:367–377. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
54
|
von Maltzahn J, Chang NC, Bentzinger CF
and Rudnicki MA: Wnt signaling in myogenesis. Trends Cell Biol.
22:602–609. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang L, Qing L, Liu H, Liu N, Qiao J, Cui
C, He T, Zhao R, Liu F, Yan F, et al: Mesenchymal stromal cells
ameliorate oxidative stress-induced islet endothelium apoptosis and
functional impairment via Wnt4-β-catenin signaling. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 8:1882017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Guo X, Gu X, Hareshwaree S, Rong X, Li L
and Chu M: Induced pluripotent stem cell-conditional medium
inhibits H9C2 cardiomyocytes apoptosis via autophagy flux and
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 23:4358–4374. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Guo X, Chen Y, Hong T, Chen X, Duan Y, Li
C and Ge R: Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived conditional
medium promotes Leydig cell anti-apoptosis and proliferation via
autophagy and Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 22:3614–3626.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lim JH, Chun YS and Park JW:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha obstructs a Wnt signaling pathway
by inhibiting the hARD1-mediated activation of beta-catenin. Cancer
Res. 68:5177–5184. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Rochat A, Fernandez A, Vandromme M, Molès
JP, Bouschet T, Carnac G and Lamb NJ: Insulin and wnt1 pathways
cooperate to induce reserve cell activation in differentiation and
myotube hypertrophy. Mol Biol Cell. 15:4544–4555. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|