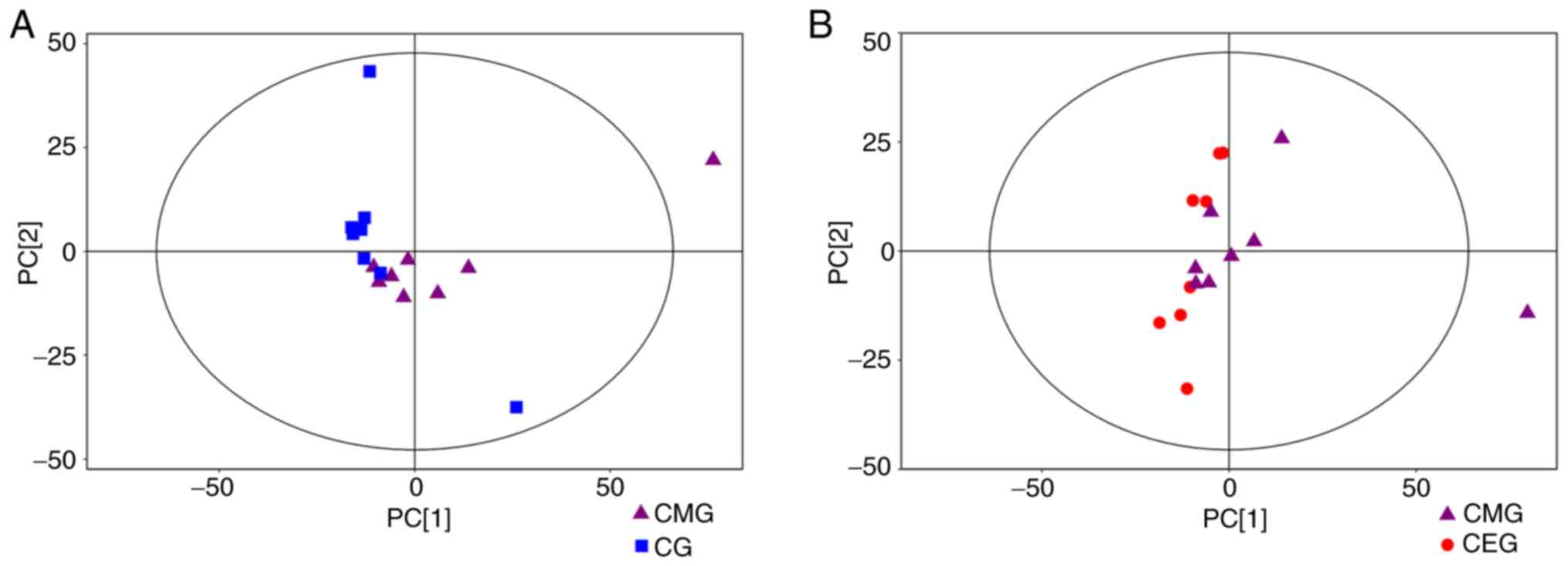
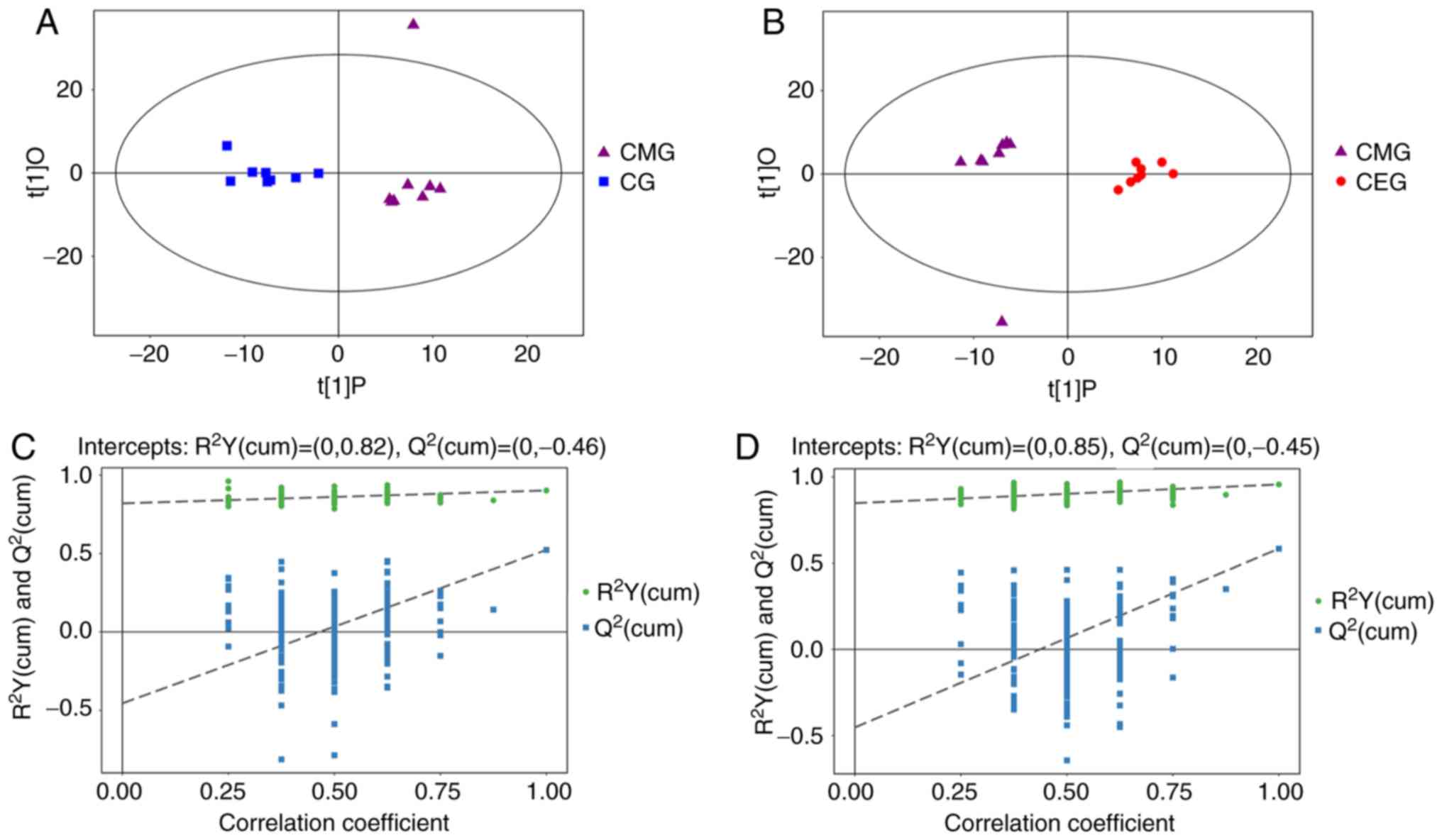
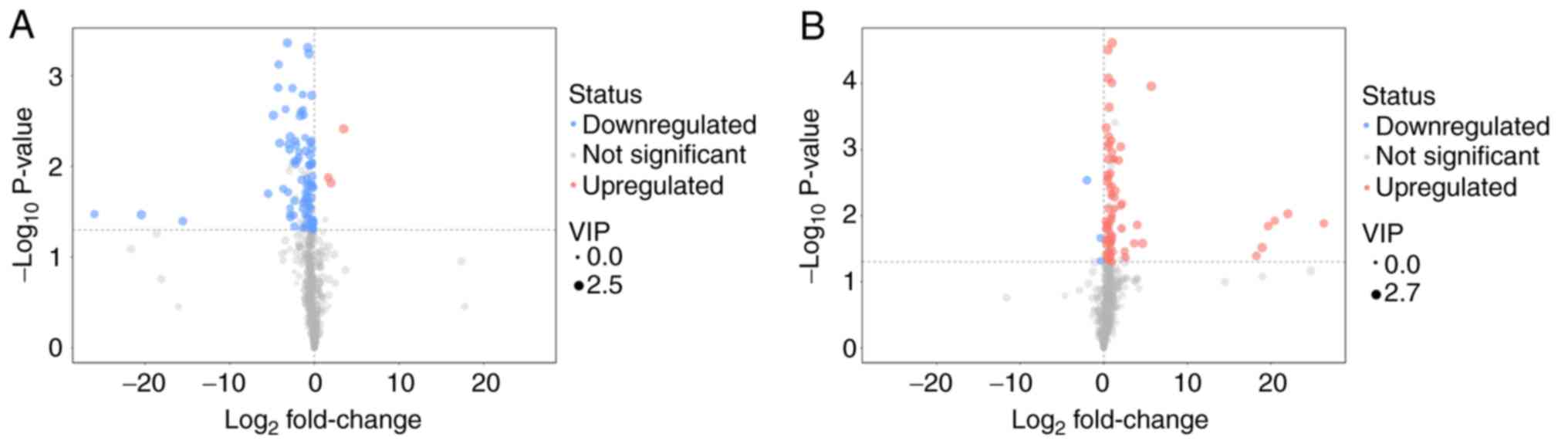
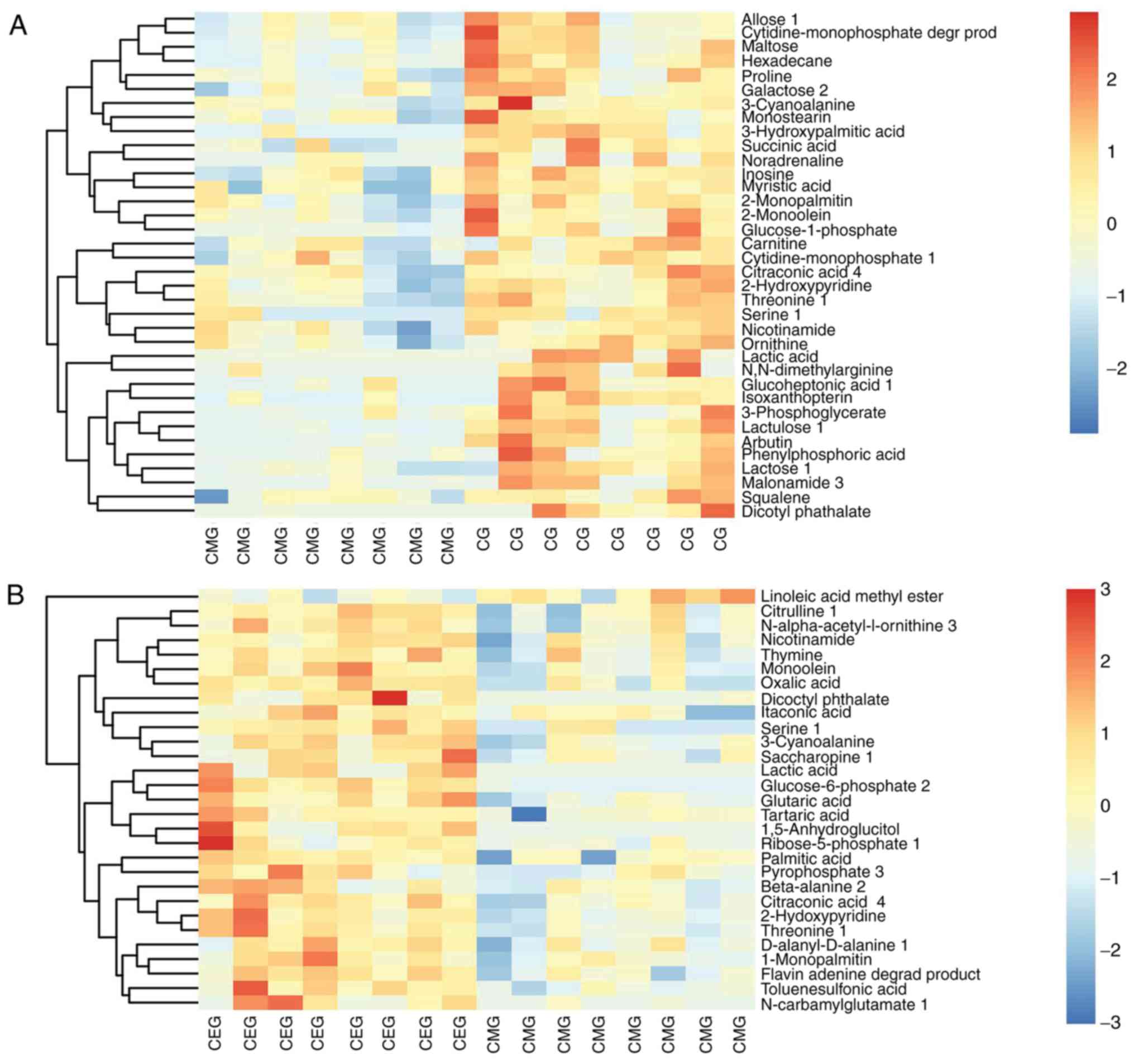
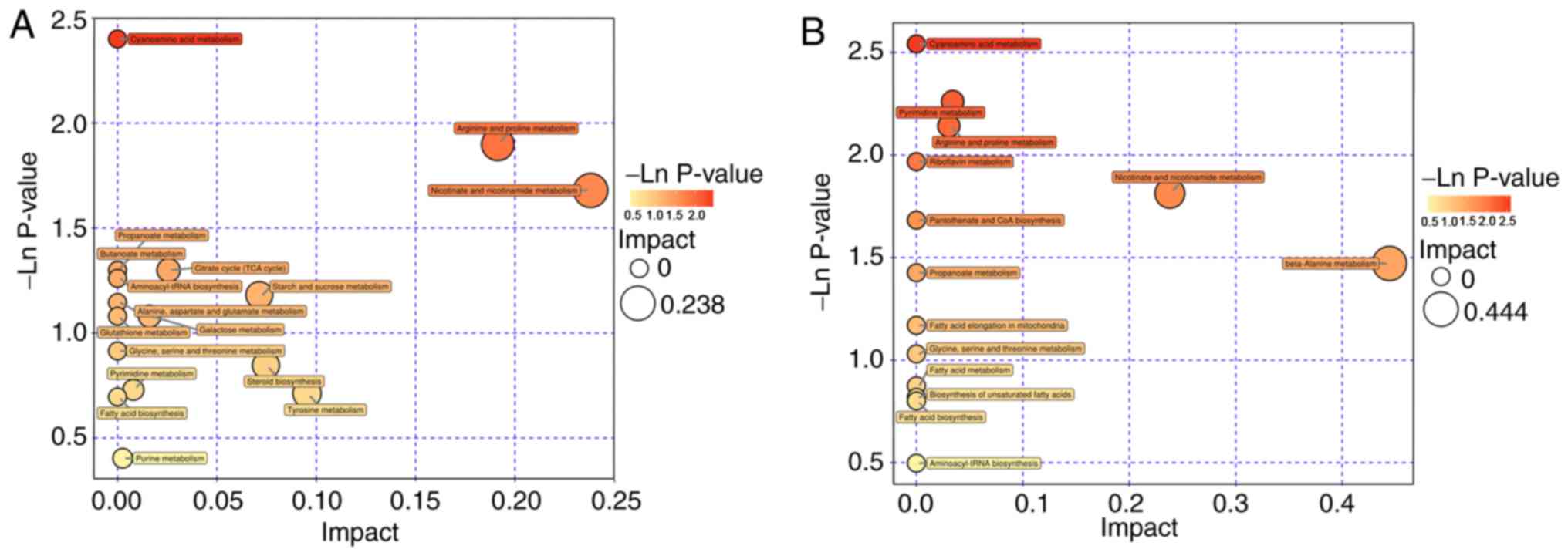
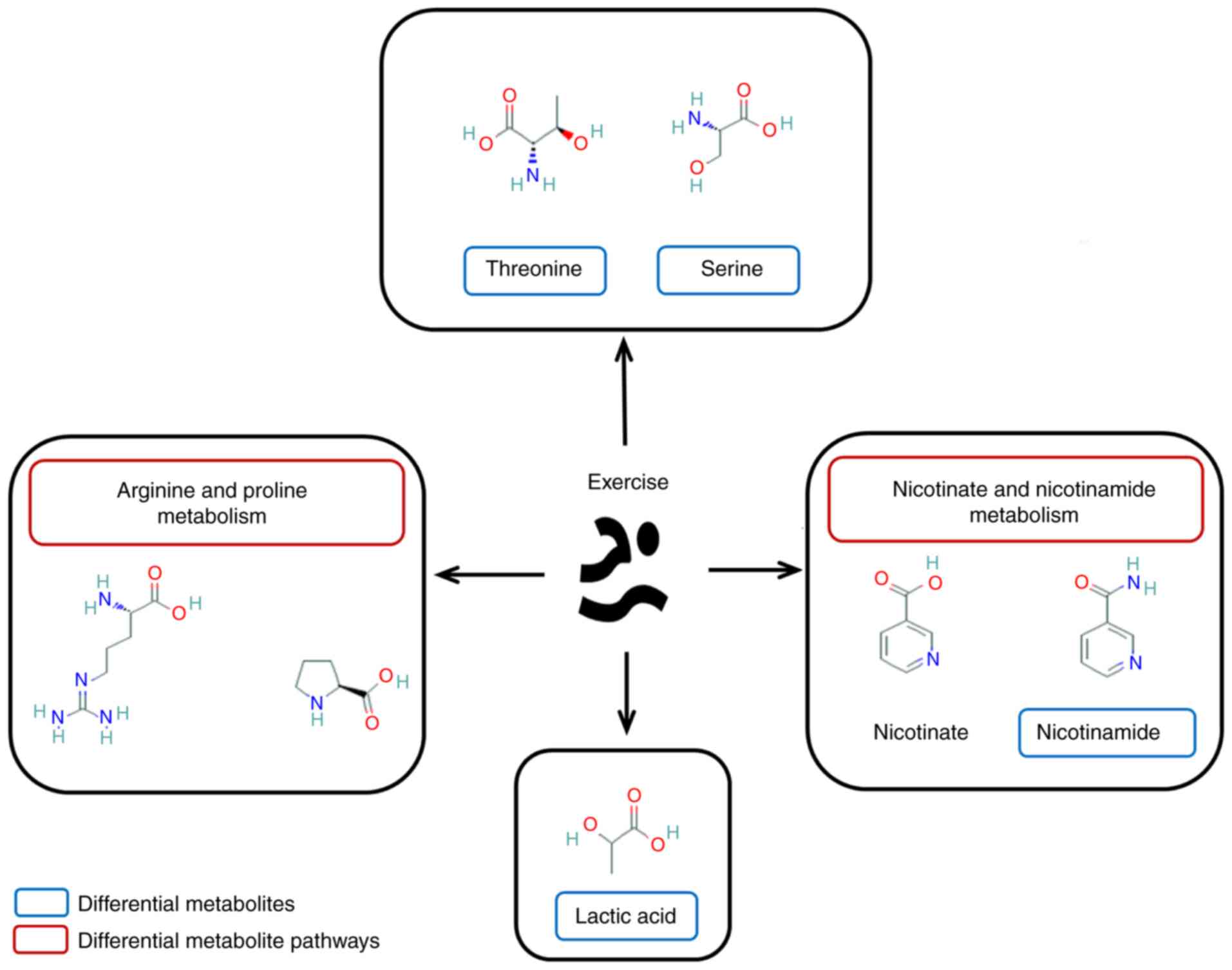
|
1
|
Horner A, Soriano JB, Puhan MA, Studnicka
M, Kaiser B, Vanfleteren LEGW, Gnatiuc L, Burney P, Miravitlles M,
García-Rio F, et al: Altitude and COPD prevalence: Analysis of the
PREPOCOL-PLATINO-BOLD-EPI-SCAN study. Respir Res. 18:1622017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mesquita R, Donária L, Genz IC, Pitta F
and Probst VS: Respiratory muscle strength during and after
hospitalization for COPD exacerbation. Respir Care. 58:2142–2149.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hodgev VA and Kostianev SS: Maximal
inspiratory pressure predicts mortality in patients with chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease in a five-year follow-up. Folia Med.
48:36–41. 2006.
|
|
4
|
Newell SZ, McKenzie DK and Gandevia SC:
Inspiratory and skeletal muscle strength and endurance and
diaphragmatic activation in patients with chronic airflow
limitation. Thorax. 44:903–912. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fabbri LM and Rabe KF: From COPD to
chronic systemic inflammatory syndrome? Lancet. 370:797–799. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kirkham PA and Barnes PJ: Oxidative stress
in COPD. Chest. 144:266–273. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rochester DF: The diaphragm in COPD.
Better than expected, but not good enough. New Engl J Med.
325:961–962. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Scott A, Wang X, Road JD and Reid WD:
Increased injury and intramuscular collagen of the diaphragm in
COPD: Autopsy observations. Eur Respir J. 27:51–59. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Doucet M, Debigare R, Joanisse DR, Côté C,
Leblanc P, Grégoire J, Deslauriers J, Vaillancourt R and Maltais F:
Adaptation of the diaphragm and the vastus lateralis in
mild-to-moderate COPD. Eur Respir J. 24:971–979. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Haegens A, Schols AM, Gorissen SH, van
Essen AL, Snepvangers F, Gray DA, Shoelson SE and Langen RC: NF-κB
activation and polyubiquitin conjugation are required for pulmonary
inflammation-induced diaphragm atrophy. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 302:L103–L110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wijnhoven HJ, Heunks LM, Geraedts MC,
Hafmans T, Viña JR and Dekhuijzen PN: Oxidative and nitrosative
stress in the diaphragm of patients with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct
Pulmon Dis. 1:173–179. 2006.
|
|
12
|
Barreiro E and Gea J: Respiratory and limb
muscle dysfunction in COPD. COPD. 12:413–426. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nici L, Donner C, Wouters E, Zuwallack R,
Ambrosino N, Bourbeau J, Carone M, Celli B, Engelen M, Fahy B, et
al: American thoracic society/European respiratory society
statement on pulmonary rehabilitation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
173:1390–1413. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ricci C, Terzoni S, Gaeta M, Sorgente A,
Destrebecq A and Gigliotti F: Physical training and noninvasive
ventilation in COPD patients: A meta-analysis. Respir Care.
59:709–717. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Polkey MI, Kyroussis D, Hamnegard CH,
Mills GH, Green M and Moxham J: Diaphragm strength in chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
154:1310–1317. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Koulmann N and Bigard AX: Interaction
between signalling pathways involved in skeletal muscle responses
to endurance exercise. Pflugers Arch. 452:125–139. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rowell LB, Sheriff DD, Wyss CR and Scher
AM: The nature of the exercise stimulus. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl.
556:7–14. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Casado-Vela J, Cebrián A, Gómez del Pulgar
MT and Lacal JC: Approaches for the study of cancer: Towards the
integration of genomics, proteomics and metabolomics. Clin Transl
Oncol. 13:617–628. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cox J and Mann M: Is proteomics the new
genomics? Cell. 130:395–398. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lindon JC, Holmes E and Nicholson JK:
Metabonomics techniques and applications to pharmaceutical research
& development. Pharm Res. 23:1075–1088. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lindon JC, Holmes E, Bollard ME, Stanley
EG and Nicholson JK: Metabonomics technologies and their
applications in physiological monitoring, drug safety assessment
and disease diagnosis. Biomarkers. 9:1–31. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wadell K: Water-based exercise is more
effective than land-based exercise for people with COPD and
physical comorbidities. J Physiother. 60:572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu W, Liu X, Liu J, Li P and Wang Z:
Effectiveness of water-based Liuzijue exercise on respiratory
muscle strength and peripheral skeletal muscle function in patients
with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 13:1713–1726. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Carlos SP, Dias AS, Forgiarini Júnior LA,
Patricio PD, Graciano T, Nesi RT, Valença S, Chiappa AM, Cipriano G
Jr, Souza CT and Chiappa GR: Oxidative damage induced by cigarette
smoke exposure in mice: Impact on lung tissue and diaphragm muscle.
J Bras Pneumol. 40:411–420. 2014.In English, Portuguese. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vieira Ramos G, Choqueta de Toledo-Arruda
A, Maria Pinheiro-Dardis C, Liyoko Suehiro C, Luiz de Russo T,
Vieira RP, Arruda Martins M, Salvini TF and Durigan JLQ: Exercise
prevents diaphragm wasting induced by cigarette smoke through
modulation of antioxidant genes and metalloproteinases. Biomed Res
Int. 2018:59090532018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bowen TS, Aakerøy L, Eisenkolb S, Kunth P,
Bakkerud F, Wohlwend M, Ormbostad AM, Fischer T, Wisloff U, Schuler
G, et al: Exercise training reverses extrapulmonary impairments in
smoke-exposed mice. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 49:879–887. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Barreiro E, del Puerto-Nevado L,
Puig-Vilanova E, Pérez-Rial S, Sánchez F, Martínez-Galán L, Rivera
S, Gea J, González-Mangado N and Peces-Barba G: Cigarette
smoke-induced oxidative stress in skeletal muscles of mice. Respir
Physiol Neurobiol. 182:9–17. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Krüger K, Dischereit G, Seimetz M, Wilhelm
J, Weissmann N and Mooren FC: Time course of cigarette
smoke-induced changes of systemic inflammation and muscle
structure. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 309:L119–L128. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wüst RCI and Degens H: Factors
contributing to muscle wasting and dysfunction in COPD patients.
Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2:289–300. 2007.
|
|
30
|
Nie YC, Wu H, Li PB, Luo YL, Zhang CC,
Shen JG and Su WW: Characteristic comparison of three rat models
induced by cigarette smoke or combined with LPS: To establish a
suitable model for study of airway mucus hypersecretion in chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 25:349–356.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Caron MA, Morissette MC, Thériault ME,
Nikota JK, Stämpfli MR and Debigaré R: Alterations in skeletal
muscle cell homeostasis in a mouse model of cigarette smoke
exposure. PLoS One. 8:e664332013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Totou NL, Moura SS, Coelho DB, Oliveira
EC, Becker LK and Lima WG: Swimming exercise demonstrates
advantages over running exercise in reducing proteinuria and
glomerulosclerosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Physiol Int.
105:76–85. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Barbosa Neto O, Abate DT, Marocolo Júnior
M, Mota GR, Orsatti FL, Rossi e Silva RC, Reis MA and da Silva VJ:
Exercise training improves cardiovascular autonomic activity and
attenuates renal damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J
Sports Sci Med. 12:52–59. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Egawa T, Tsuda S, Goto A, Ohno Y, Yokoyama
S, Goto K and Hayashi T: Potential involvement of dietary advanced
glycation end products in impairment of skeletal muscle growth and
muscle contractile function in mice. Br J Nutr. 117:21–29. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yao S, Zhang J, Chen H, Sheng Y, Zhang X,
Liu Z and Zhang C: Diagnostic value of immunohistochemical staining
of GP73, GPC3, DCP, CD34, CD31, and reticulin staining in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Histochem Cytochem. 61:639–648. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kind T, Wohlgemuth G, Lee DY, Lu Y,
Palazoglu M, Shahbaz S and Fiehn O: FiehnLib: Mass spectral and
retention index libraries for metabolomics based on quadrupole and
time-of-flight gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Chem.
81:10038–10048. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dunn WB, Broadhurst D, Begley P, Zelena E,
Francis-McIntyre S, Anderson N, Brown M, Knowles JD, Halsall A,
Haselden JN, et al: Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling
of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid
chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat Protoc.
6:1060–1083. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Alfakih A, Khandani A and Wolkowicz H:
Solving Euclidean distance matrix completion problems via
semidefinite programming. Comput Optim Appl. 12:13–30. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Furumichi
M and Tanabe M: KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein
annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44(D1): D457–D462. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Toledo AC, Magalhaes RM, Hizume DC, Vieira
RP, Biselli PJ, Moriya HT, Mauad T, Lopes FD and Martins MA:
Aerobic exercise attenuates pulmonary injury induced by exposure to
cigarette smoke. Eur Respir J. 39:254–264. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ma WL, Cai PC, Xiong XZ and Ye H: Exercise
training attenuated chronic cigarette smoking-induced up-regulation
of FIZZ1/RELMα in lung of rats. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med
Sci. 33:22–26. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nishii Y, Kawata S, Fujita N, Tomoda K and
Imagita H: Moderate exercise attenuated airway resistance and
inflammation induced by cigarette smoke solution and endotoxin in
rats. Sport Sci Health. 12:91–97. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Eklund BM, Nilsson S, Hedman L and
Lindberg I: Why do smokers diagnosed with COPD not quit smoking?-a
qualitative study. Tob Induc Dis. 10:172012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Taghizadeh N, Vonk JM and Boezen HM:
Lifetime smoking history and cause-specific mortality in a cohort
study with 43 years of follow-up. PLoS One. 11:e01533102016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Klaude M, Gedik CM and Collins AR: DNA
damage and repair after low doses of UV-C radiation; comparable
rates of repair in rodent and human cells. Int J Radiat Biol.
67:501–508. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rees DC, Wood RW and Laties VG: Stimulus
control and the development of behavioral tolerance to daily
injections of d-amphetamine in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
240:65–73. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Siegel S and Sdao-Jarvie K: Attenuation of
ethanol tolerance by a novel stimulus. Psychopharmacology.
88:258–261. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Swanny A, Morton RF and Lee LY: Acute
effect of cigarette smoke on breathing is attenuated by chronic
smoking in rats. J Appl Physiol (1985). 74:333–338. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Thames HD Jr, Withers HR and Peters LJ:
Tissue repair capacity and repair kinetics deduced from
multifractionated or continuous irradiation regimens with
incomplete repair. Br J Cancer Suppl. 6:263–269. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rinaldi M, Maes K, De Vleeschauwer S,
Thomas D, Verbeken EK, Decramer M, Janssens W and Gayan-Ramirez GN:
Long-term nose-only cigarette smoke exposure induces emphysema and
mild skeletal muscle dysfunction in mice. Dis Model Mech.
5:333–341. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Berry CE and Wise RA: Interpretation of
pulmonary function test: Issues and controversies. Clin Rev Allergy
Immunol. 37:173–180. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cukic V, Lovre V and Ustamujic A: The
changes of pulmonary function in COPD during four-year period.
Mater Sociomed. 25:88–92. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang J, Zhou XM, Yang X, Zhao ST, Ma QL
and Wang CZ: A three years longitudinal follow-up study of
pulmonary function changes in patients with chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease. Chin J Intern Med. 55:302–306. 2016.In
Chinese.
|
|
55
|
Talaminos Barroso A, Márquez Martin E, Roa
Romero LM and Ortega Ruiz F: Factors affecting lung function: A
review of the literature. Arch Bronconeumol. 54:327–332. 2018.In
English, Spanish. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Davidson WJ, Verity WS, Traves SL, Leigh
R, Ford GT and Eves ND: Effect of incremental exercise on airway
and systemic inflammation in patients with COPD. J Appl Physiol
(1985). 112:2049–2056. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Silva RA, Almeida FM, Olivo CR,
Saraiva-Romanholo BM, Martins MA and Carvalho CR: Airway remodeling
is reversed by aerobic training in a murine model of chronic
asthma. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 25:e258–e266. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Vieira RP, Claudino RC, Duarte AC, Santos
AB, Perini A, Faria Neto HC, Mauad T, Martins MA, Dolhnikoff M and
Carvalho CR: Aerobic exercise decreases chronic allergic lung
inflammation and airway remodeling in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 176:871–877. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lan CC, Chu WH, Yang MC, Lee CH, Wu YK and
Wu CP: Benefits of pulmonary rehabilitation in patients with COPD
and normal exercise capacity. Respir Care. 58:1482–1488. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ambrosino N, Foglio K, Balzano G, Paggiaro
PL, Lessi P and Kesten S; Tiotropium Multicentric Italian Study
Group: Tiotropium and exercise training in COPD patients: Effects
on dyspnea and exercise tolerance. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis.
3:771–780. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Leelarungrayub J, Pinkaew D, Puntumetakul
R and Klaphajone J: Effects of a simple prototype respiratory
muscle trainer on respiratory muscle strength, quality of life and
dyspnea, and oxidative stress in COPD patients: A preliminary
study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 12:1415–1425. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Armbruster C, Dassow C, Gamerdinger K,
Guttmann J, Schneider M and Schumann S: In vitro muscle contraction
force measurements on isolated and entire rat diaphragms. Critical
Care. 14:P2042010. View
Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
63
|
Gea J, Agusti A and Roca J:
Pathophysiology of muscle dysfunction in COPD. J Appl Physiol
(1985). 114:1222–1234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Levine S, Bashir MH, Clanton TL, Powers SK
and Singhal S: COPD elicits remodeling of the diaphragm and vastus
lateralis muscles in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985). 114:1235–1245.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Gayan-Ramirez G and Decramer M: Mechanisms
of striated muscle dysfunction during acute exacerbations of COPD.
J Appl Physiol (1985). 114:1291–1299. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Levine S, Kaiser L, Leferovich J and
Tikunov B: Cellular adaptations in the diaphragm in chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 337:1799–1806. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Marin-Corral J, Minguella J,
Ramirez-Sarmiento AL, Hussain SN, Gea J and Barreiro E: Oxidised
proteins and superoxide anion production in the diaphragm of severe
COPD patients. Eur Respir J. 33:1309–1319. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Spruit MA, Gosselink R, Troosters T, De
Paepe K and Decramer M: Resistance versus endurance training in
patients with COPD and peripheral muscle weakness. Eur Respir J.
19:1072–1078. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Franssen FM, Broekhuizen R, Janssen PP,
Wouters EF and Schols AM: Effects of whole-body exercise training
on body composition and functional capacity in normal-weight
patients with COPD. Chest. 125:2021–2028. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Cortopassi F, Castro AA, Porto EF, Colucci
M, Fonseca G, Torre-Bouscoulet L, Iamonti V and Jardim JR:
Comprehensive exercise training improves ventilatory muscle
function and reduces dyspnea perception in patients with COPD.
Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 71:106–112. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wada JT, Borges-Santos E, Porras DC,
Paisani DM, Cukier A, Lunardi AC and Carvalho CR: Effects of
aerobic training combined with respiratory muscle stretching on the
functional exercise capacity and thoracoabdominal kinematics in
patients with COPD: A randomized and controlled trial. Int J Chron
Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 11:2691–2700. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ries AL, Bauldoff GS, Carlin BW, Casaburi
R, Emery CF, Mahler DA, Make B, Rochester CL, Zuwallack R and
Herrerias C: Pulmonary rehabilitation: Joint ACCP/AACVPR
evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 131(5 Suppl):
4S–42S. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wanke T, Formanek D, Lahrmann H, Brath H,
Wild M, Wagner C and Zwick H: Effects of combined inspiratory
muscle and cycle ergometer training on exercise performance in
patients with COPD. Eur Respir J. 7:2205–2211. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
de Souto Araujo ZT, de Miranda Silva
Nogueira PA, Cabral EE, de Paula Dos Santos L, da Silva IS and
Ferreira GM: Effectiveness of low-intensity aquatic exercise on
COPD: A randomized clinical trial. Respir Med. 106:1535–1543. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wackerhage H and Ratkevicius A: Signal
transduction pathways that regulate muscle growth. Essays Biochem.
44:99–108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Chaouloff F, Kennett GA, Serrurrier B,
Merino D and Curzon G: Amino acid analysis demonstrates that
increased plasma free tryptophan causes the increase of brain
tryptophan during exercise in the rat. J Neurochem. 46:1647–1650.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Inuzuka M, Hayakawa M and Ingi T: Serinc,
an activity-regulated protein family, incorporates serine into
membrane lipid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 280:35776–35783. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Pantaleo A, Ferru E, Carta F, Mannu F,
Giribaldi G, Vono R, Lepedda AJ, Pippia P and Turrini F: Analysis
of changes in tyro-sine and serine phosphorylation of red cell
membrane proteins induced by P. falciparum growth. Proteomics.
10:3469–3479. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hu SI, Katz M, Chin S, Qi X, Cruz J,
Ibebunjo C, Zhao S, Chen A and Glass DJ: MNK2 inhibits eIF4G
activation through a pathway involving serine-arginine-rich protein
kinase in skeletal muscle. Sci Signal. 5:ra142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Talanian JL, Tunstall RJ, Watt MJ, Duong
M, Perry CG, Steinberg GR, Kemp BE, Heigenhauser GJ and Spriet LL:
Adrenergic regulation of HSL serine phosphorylation and activity in
human skeletal muscle during the onset of exercise. Am J Physiol
Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 291:R1094–R1099. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Li F, Chong ZZ and Maiese K: Cell life
versus cell longevity: The mysteries surrounding the NAD+ precursor
nicotinamide. Curr Med Chem. 13:883–895. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Ungerstedt JS, Blömback M and Söderström
T: Nicotinamide is a potent inhibitor of proinflammatory cytokines.
Clin Exp Immunol. 131:48–52. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Traister A, Breitman I, Bar-Lev E, Zvibel
I, Harel A, Halpern Z and Oren R: Nicotinamide induces apoptosis
and reduces collagen I and pro-inflammatory cytokines expression in
rat hepatic stellate cells. Scand J Gastroenterol. 40:1226–1234.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Chlopicki S, Swies J, Mogielnicki A,
Buczko W, Bartus M, Lomnicka M, Adamus J and Gebicki J:
1-Methylnicotinamide (MNA), a primary metabolite of nicotinamide,
exerts anti-thrombotic activity mediated by a
cyclooxygenase-2/prostacyclin pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 152:230–239.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Surenkok O, Kin-Isler A, Aytar A and
Gültekin Z: Effect of trunk-muscle fatigue and lactic acid
accumulation on balance in healthy subjects. J Sport Rehabil.
17:380–386. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Robergs RA, Ghiasvand F and Parker D:
Biochemistry of exercise-induced metabolic acidosis. Am J Physiol
Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 287:R502–R516. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Gladden LB: Lactate metabolism: A new
paradigm for the third millennium. J Physiol. 558:5–30. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Lewis SF and Haller RG: The
pathophysiology of McArdle's disease: Clues to regulation in
exercise and fatigue. J Appl Physiol (1985). 61:391–401. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Hunt TK, Aslam R, Hussain Z and Beckert S:
Lactate, with oxygen, incites angiogenesis. Adv Exp Med Biol.
614:73–80. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Groussard C, Morel I, Chevanne M, Monnier
M, Cillard J and Delamarche A: Free radical scavenging and
antioxidant effects of lactate ion: An in vitro study. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 89:169–175. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Thiele I, Swainston N, Fleming RM, Hoppe
A, Sahoo S, Aurich MK, Haraldsdottir H, Mo ML, Rolfsson O, Stobbe
MD, et al: A community-driven global reconstruction of human
metabolism. Nat Biotechnol. 31:419–425. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Stoltz JF and Nicolas A: Study of amino
groups of the human platelet membrane. Acta Haematol. 60:304–309.
1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Menon R, Tolbert D and Cefali E: The
comparative bioavailability of an extended-release niacin and
lovastatin fixed dose combination tablet versus extended-release
niacin tablet, lovastatin tablet and a combination of
extended-release niacin tablet and lovastatin tablet. Biopharm Drug
Dispos. 28:297–306. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Shibata K, Matsumoto K, Fushiki T and
Sugimoto E: Effects of exercise on the metabolism of NAD in rats.
Biosci Biotech Bioch. 58:1763–1766. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
White AT and Schenk S: NAD(+)/NADH and
skeletal muscle mitochondrial adaptations to exercise. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 303:E308–E321. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Wu G and Morris SM Jr: Arginine
metabolism: Nitric oxide and beyond. Biochem J. 336:1–17. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Barton ER, Morris L, Kawana M, Bish LT and
Toursel T: Systemic administration of L-arginine benefits mdx
skeletal muscle function. Muscle nerve. 32:751–760. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Wu G, Bazer FW, Datta S, Johnson GA, Li P,
Satterfield MC and Spencer TE: Proline metabolism in the conceptus:
Implications for fetal growth and development. Amino Acids.
35:691–702. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Ruzsics I, Nagy L, Keki S, Sarosi V, Illes
B, Illes Z, Horvath I, Bogar L and Molnar T: L-arginine pathway in
COPD patients with acute exacerbation: A new potential biomarker.
COPD. 13:139–145. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Dohm GL, Beecher GR, Warren RQ and
Williams RT: Influence of exercise on free amino acid
concentrations in rat tissues. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc
Physiol. 50:41–44. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Parmaksız ET, Inal A, Salepci B, Comert S,
Fidan A, Kiral N, Doǧan C and Caglayan B: Relationship of
asymmetric dimethylarginine levels with disease severity and
pulmonary hypertension in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Lung India. 35:199–203. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
van den Berg MP, Meurs H and Gosens R:
Targeting arginase and nitric oxide metabolism in chronic airway
diseases and their comorbidities. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 40:126–133.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Hörster I, Weigt-Usinger K, Carmann C,
Chobanyan-Jürgens K, Köhler C, Schara U, Kayacelebi AA, Beckmann B,
Tsikas D and Lücke T: The L-arginine/NO pathway and homoarginine
are altered in Duchenne muscular dystrophy and improved by
glucocorticoids. Amino Acids. 47:1853–1863. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Wang W, Wu Z, Dai Z, Yang Y, Wang J and Wu
G: Glycine metabolism in animals and humans: Implications for
nutrition and health. Amino Acids. 45:463–477. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Bruno A, Chanez P, Chiappara G, Siena L,
Giammanco S, Gjomarkaj M, Bonsignore G, Bousquet J and Vignola AM:
Does leptin play a cytokine-like role within the airways of COPD
patients? Eur Respir J. 26:398–405. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Bianco A, Mazzarella G, Turchiarelli V,
Nigro E, Corbi G, Scudiero O, Sofia M and Daniele A: Adiponectin:
An attractive marker for metabolic disorders in chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease (COPD). Nutrients. 5:4115–4125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Al Mutairi SS, Mojiminiyi OA,
Shihab-Eldeen A, Al Rammah T and Abdella N: Putative roles of
circulating resistin in patients with asthma, COPD and cigarette
smokers. Dis Markers. 31:1–7. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Tomaki M, Sugiura H, Koarai A, Komaki Y,
Akita T, Matsumoto T, Nakanishi A, Ogawa H, Hattori T and Ichinose
M: Decreased expression of antioxidant enzymes and increased
expression of chemokines in COPD lung. Pulm Pharmacol Ther.
20:596–605. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Tilg H and Moschen AR: Adipocytokines:
Mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat
Rev Immunol. 6:772–783. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Horowitz JF and Klein S: Lipid metabolism
during endurance exercise. Am J Clin Nutr. 72(2 Suppl): 558S–563S.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Gill JM, Frayn KN, Wootton SA, Miller GJ
and Hardman AE: Effects of prior moderate exercise on exogenous and
endogenous lipid metabolism and plasma factor VII activity. Clin
Sci (Lond). 100:517–527. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
de Batlle J, Sauleda J, Balcells E, Gómez
FP, Méndez M, Rodriguez E, Barreiro E, Ferrer JJ, Romieu I, Gea J,
et al: Association between Ω3 and Ω6 fatty acid intakes and serum
inflammatory markers in COPD. J Nutr Biochem. 23:817–821. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Warnakulasuriya SN, Ziaullah and
Rupasinghe HP: Novel long chain fatty acid derivatives of
quercetin-3-O-glucoside reduce cytotoxicity induced by cigarette
smoke toxicants in human fetal lung fibroblasts. Eur J Pharmacol.
781:128–138. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Garrod R, Ansley P, Canavan J and Jewell
A: Exercise and the inflammatory response in chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease (COPD)-Does training confer anti-inflammatory
prop-erties in COPD? Med Hypotheses. 68:291–298. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Spurzem JR and Rennard SI: Pathogenesis of
COPD. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 26:142–153. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|