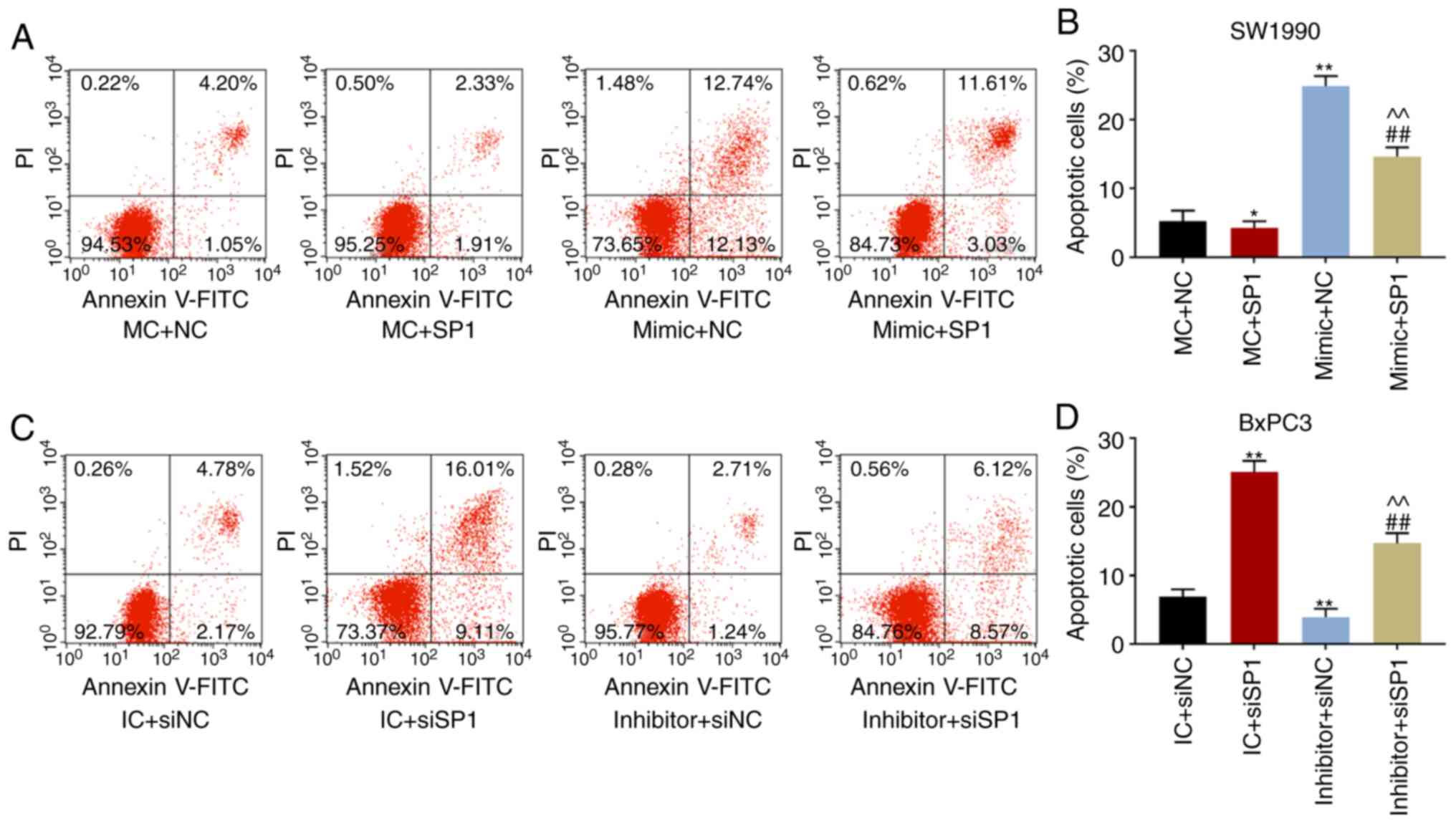
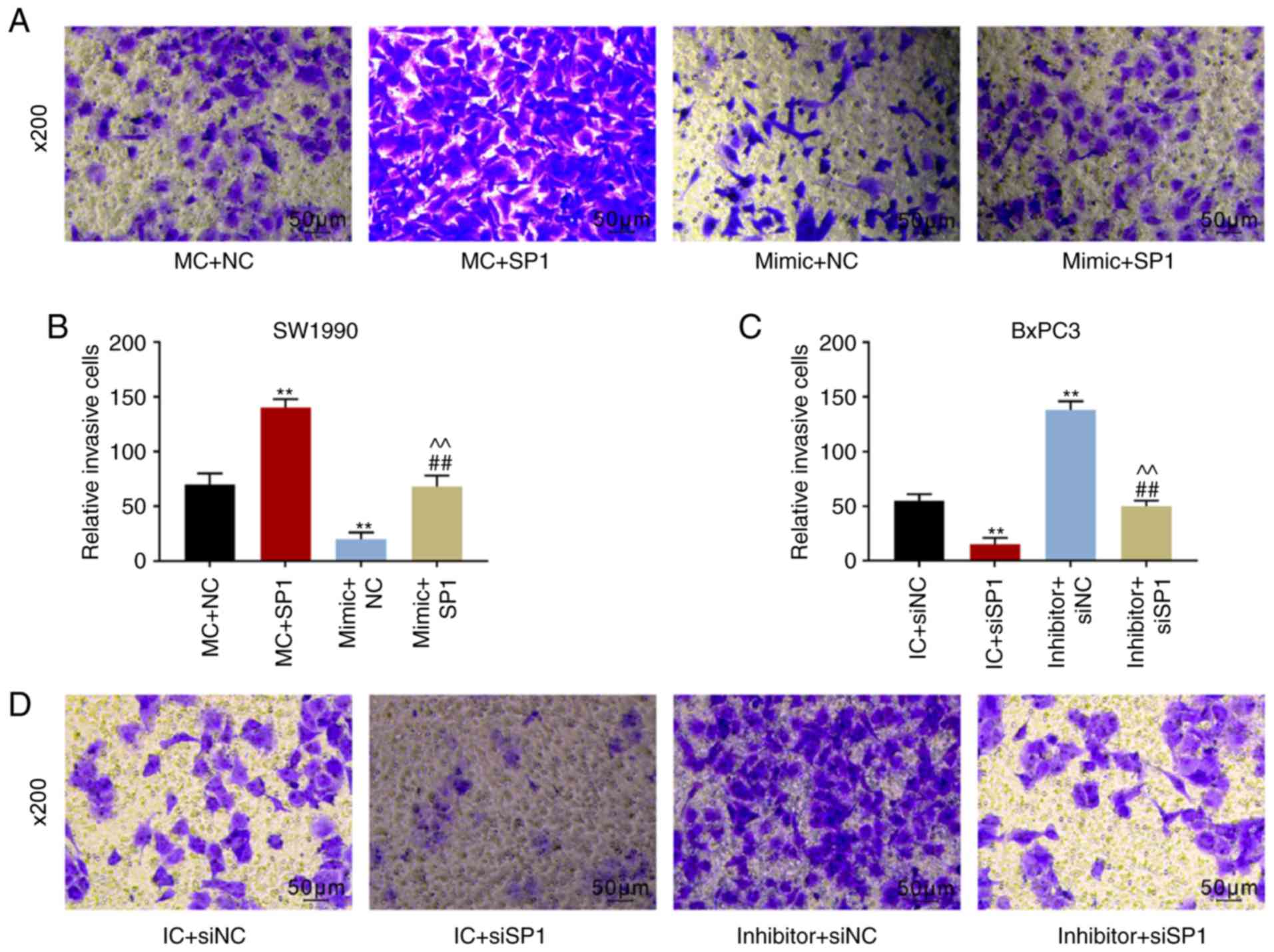
|
1
|
Lin QJ, Yang F, Jin C and Fu DL: Current
status and progress of pancreatic cancer in China. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:7988–8003. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee ES and Lee JM: Imaging diagnosis of
pancreatic cancer: A state-of-the-art review. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:7864–7877. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ilic M and Ilic I: Epidemiology of
pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 22:9694–9705. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Puleo F, Maréchal R, Demetter P, Bali MA,
Calomme A, Closset J, Bachet JB, Deviere J and Van Laethem JL: New
challenges in perioperative management of pancreatic cancer. World
J Gastroenterol. 21:2281–2293. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu Q, Yang Z, Nie Y, Shi Y and Fan D:
Multi-drug resistance in cancer chemotherapeutics: Mechanisms and
lab approaches. Cancer Lett. 347:159–166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Davudian S,
Shirjang S and Baradaran B: The different mechanisms of cancer drug
resistance: A brief review. Adv Pharm Bull. 7:339–348. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang Y, Tang Y and Cheng YS: miR-34a
inhibits pancreatic cancer progression through Snail1-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the Notch signaling pathway.
Sci Rep. 7:382322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wei W, Liu Y, Lu Y, Yang B and Tang L:
LncRNA XIST promotes pancreatic cancer proliferation through
miR-133a/EGFR. J Cell Biochem. 118:3349–3358. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang B, Liu C, Wu Q, Zhang J, Min Q,
Sheng T, Wang X and Zou Y: Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 facilitates
pancreatic cancer progression through negative modulation of
miR-506-3p. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 482:828–834. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Feng YH and Tsao CJ: Emerging role of
microRNA-21 in cancer. Biomed Rep. 5:395–402. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao G, Wang B, Liu Y, Zhang JG, Deng SC,
Qin Q, Tian K, Li X, Zhu S, Niu Y, et al: miRNA-141, downregulated
in pancreatic cancer, inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by
directly targeting MAP4K4. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:2569–2580. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gambari R, Brognara E, Spandidos DA and
Fabbri E: Targeting oncomiRNAs and mimicking tumor suppressor
miRNAs: New trends in the development of miRNA therapeutic
strategies in oncology (Review). Int J Oncol. 49:5–32. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tutar L, Özgür A and Tutar Y: Involvement
of miRNAs and pseudogenes in cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 1699:45–66.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sun Y, Zhang T, Wang C, Jin X, Jia C, Yu S
and Chen J: Correction: miRNA-615-5p functions as a tumor
suppressor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by targeting AKT2.
PLoS One. 10:e01282572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bai Z, Sun J, Wang X, Wang H, Pei H and
Zhang Z: MicroRNA-153 is a prognostic marker and inhibits cell
migration and invasion by targeting SNAI1 in human pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 34:595–602. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Keklikoglou I, Hosaka K, Bender C, Bott A,
Koerner C, Mitra D, Will R, Woerner A, Muenstermann E, Wilhelm H,
et al: MicroRNA-206 functions as a pleiotropic modulator of cell
proliferation, invasion and lymphangiogenesis in pancreatic
adenocarcinoma by targeting ANXA2 and KRAS genes. Oncogene.
34:4867–4878. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Ouyang H, Gore J, Deitz S and Korc M:
microRNA-10b enhances pancreatic cancer cell invasion by
suppressing TIP30 expression and promoting EGF and TGF-beta
actions. Oncogene. 36:49522017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ma C, Nong K, Wu B, Dong B, Bai Y, Zhu H,
Wang W, Huang X, Yuan Z and Ai K: miR-212 promotes pancreatic
cancer cell growth and invasion by targeting the hedgehog signaling
pathway receptor patched-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:542014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu Z, Xu Y, Zhao J, Liu Q, Feng W, Fan J
and Wang P: miR-367 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
and invasion of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells by targeting
the Smad7-TGF-β signalling pathway. Br J Cancer. 112:1367–1375.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ding S and Zhang Y: MicroRNA539 inhibits
the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by
targeting SRYbox 5 gene. Mol Med Rep. 20:2533–2540. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun B, Fan Y, Yang A, Liang L and Cao J:
MicroRNA-539 functions as a tumour suppressor in prostate cancer
via the TGF-β/Smad4 signalling pathway by down-regulating DLX1. J
Cell Mol Med. 23:5934–5948. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun H and Sun Y: Lidocaine inhibits
proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer cell via regulation of
miR-539/EGFR axis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:2866–2874.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gong YB and Fan XH: miR-539-3p promotes
the progression of epithelial ovarian cancer by targeting SPARCL1.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:2366–2373. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jin W, Han H and Liu D: Downregulation
miR-539 is associated with poor prognosis of gastric cancer
patients and aggressive progression of gastric cancer cells. Cancer
Biomark. 26:183–191. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kadonaga JT, Carner KR, Masiarz FR and
Tjian R: Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and
functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 51:1079–1090.
1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Roder K, Kim KH and Sul HS: Induction of
murine H-rev107 gene expression by growth arrest and histone
acetylation: Involvement of an Sp1/Sp3-binding GC-box. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 294:63–70. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen F, Zhang F, Rao J and Studzinski GP:
Ectopic expression of truncated Sp1 transcription factor prolongs
the S phase and reduces the growth rate. Anticancer Res.
20:661–667. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wei D, Wang L, He Y, Xiong HQ, Abbruzzese
JL and Xie K: Celecoxib inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor
expression in and reduces angiogenesis and metastasis of human
pancreatic cancer via suppression of Sp1 transcription factor
activity. Cancer Res. 64:2030–2038. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wright C, Angus B, Napier J, Wetherall M,
Udagawa Y, Sainsbury JR, Johnston S, Carpenter F and Horne CH:
Prognostic factors in breast cancer: Immunohistochemical staining
for SP1 and NCRC 11 related to survival, tumour epidermal growth
factor receptor and oestrogen receptor status. J Pathol.
153:325–331. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rao X, Huang X, Zhou Z and Lin X: An
improvement of the 2ˆ(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative
real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat
Bioinforma Biomath. 3:71–85. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vincent A, Herman J, Schulick R, Hruban RH
and Goggins M: Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 378:607–620. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Witkowski ER, Smith JK and Tseng JF:
Outcomes following resection of pancreatic cancer. J Surg Oncol.
107:97–103. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Mohammed S, Van Buren G II and Fisher WE:
Pancreatic cancer: Advances in treatment. World J Gastroenterol.
20:9354–9360. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ansari D, Gustafsson A and Andersson R:
Update on the management of pancreatic cancer: Surgery is not
enough. World J Gastroenterol. 21:3157–3165. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Abreu FB, Liu X and Tsongalis GJ: miRNA
analysis in pancreatic cancer: The Dartmouth experience. Clin Chem
Lab Med. 55:755–762. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vorvis C, Koutsioumpa M and Iliopoulos D:
Developments in miRNA gene signaling pathways in pancreatic cancer.
Future Oncol. 12:1135–1150. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang H, Li S, Yang X, Qiao B, Zhang Z and
Xu Y: miR-539 inhibits prostate cancer progression by directly
targeting SPAG5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jin H and Wang W: MicroRNA-539 suppresses
osteosarcoma cell invasion and migration in vitro and targeting
Matrix metal-lopeptidase-8. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:8075–8082.
2015.
|
|
40
|
Yu H, Gao G, Cai J, Song H, Ma Z, Jin X,
Ji W and Pan B: miR-539 functions as a tumor suppressor in
pancreatic cancer by targeting TWIST1. Exp Mol Pathol. 108:143–149.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Deng H, Qianqian G, Ting J and Aimin Y:
miR-539 enhances chemosensitivity to cisplatin in non-small cell
lung cancer by targeting DCLK1. Biomed Pharmacother. 106:1072–1081.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lv LY, Wang YZ, Zhang Q, Zang HR and Wang
XJ: miR-539 induces cell cycle arrest in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
by targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 4. Cell Biochem Funct.
33:534–540. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kahlert UD, Joseph JV and Kruyt FAE: EMT-
and MET-related processes in nonepithelial tumors: Importance for
disease progression, prognosis, and therapeutic opportunities. Mol
Oncol. 11:860–877. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu JB, Feng CY, Deng M, Ge DF, Liu DC, Mi
JQ and Feng XS: E-cadherin expression phenotypes associated with
molecular subtypes in invasive non-lobular breast cancer: Evidence
from a retrospective study and meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol.
15:1392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Song PP, Qian XY, Zhou H, Shen XH, Liu DD,
Feng AN and Gao X: Expression of E-cadherin, N-cadherin,
beta-catenin and their clinical significance in laryngeal
carcinoma. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi.
51:440–445. 2016.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang L, Sun J, Wang B, Ren JC, Su W and
Zhang T: MicroRNA-10b triggers the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) of laryngeal carcinoma Hep-2 cells by directly
targeting the E-cadherin. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 176:33–44. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Vizcaíno C, Mansilla S and Portugal J: Sp1
transcription factor: A long-standing target in cancer
chemotherapy. Pharmacol Ther. 152:111–124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Beishline K and Azizkhan-Clifford J: Sp1
and the 'hallmarks of cancer'. FEBS J. 282:224–258. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Xia B, Hou Y, Chen H, Yang S, Liu T, Lin M
and Lou G: Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 interacts with miR-150-5p to
regulate Sp1 expression and ovarian cancer cell malignancy.
Oncotarget. 8:19534–19546. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mei LL, Wang WJ, Qiu YT, Xie XF, Bai J and
Shi ZZ: miR-145-5p suppresses tumor cell migration, invasion and
epithelial to mesenchymal transition by Regulating the Sp1/NF-κB
signaling pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol
Sci. 18:E18332017. View Article : Google Scholar
|