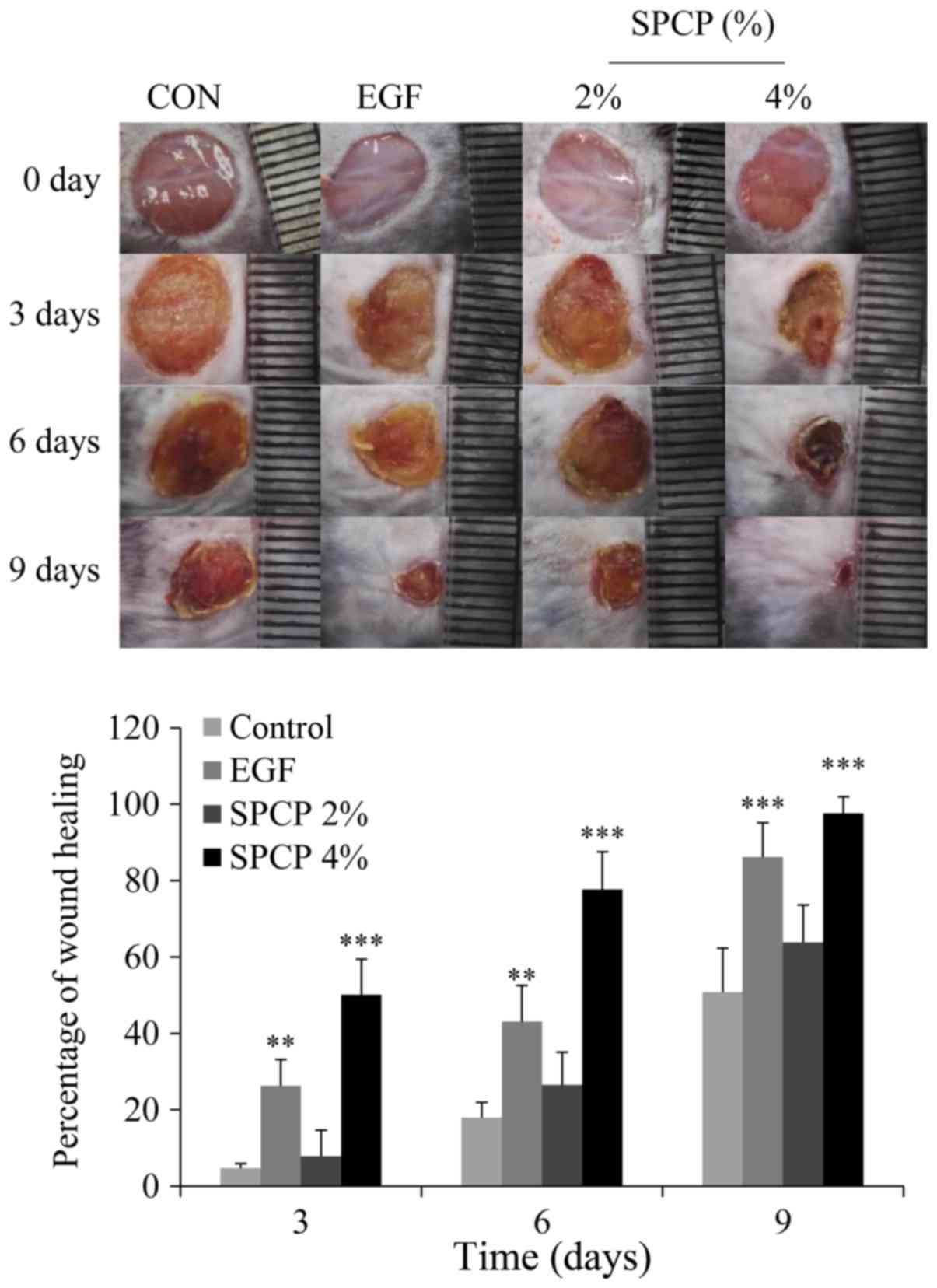
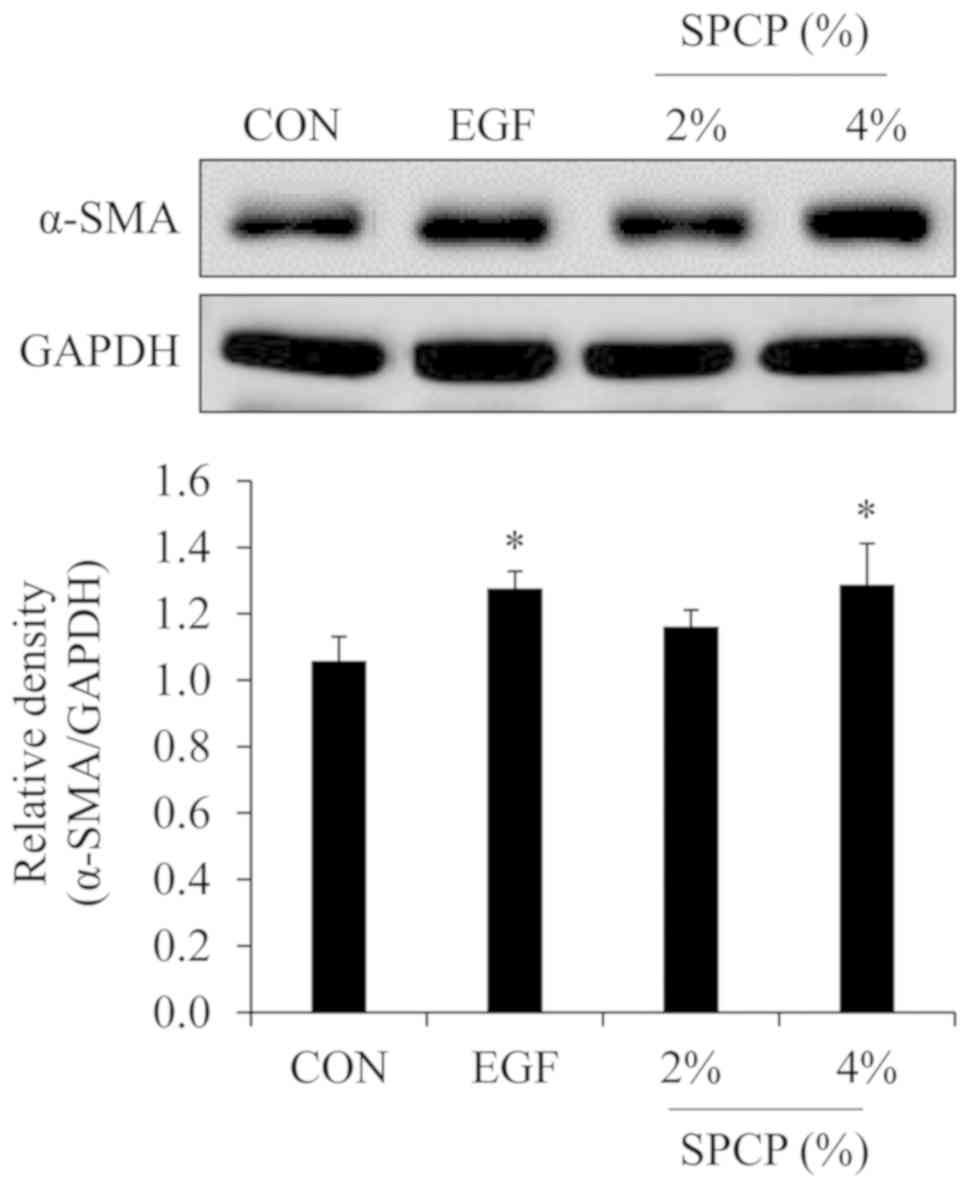
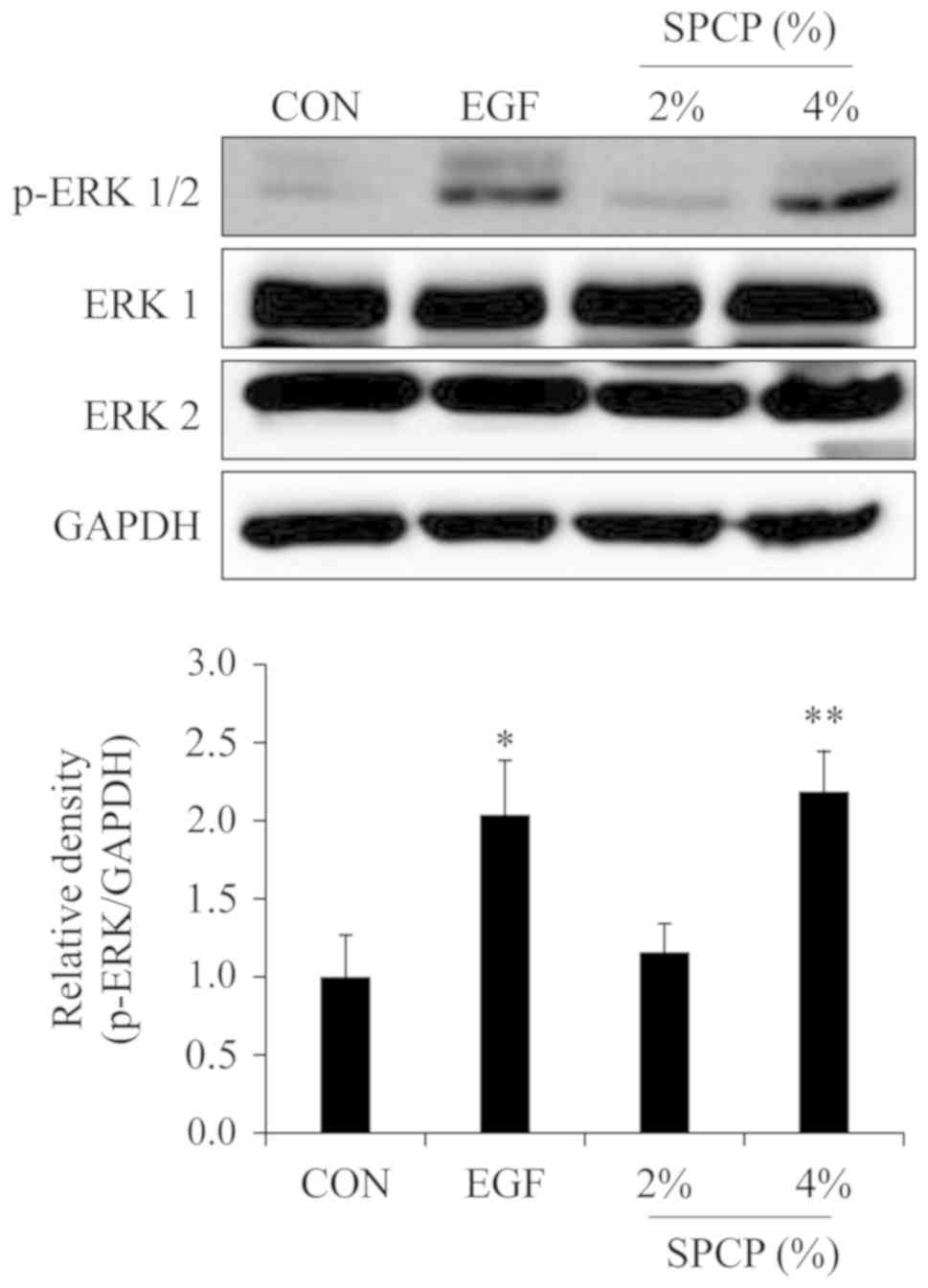
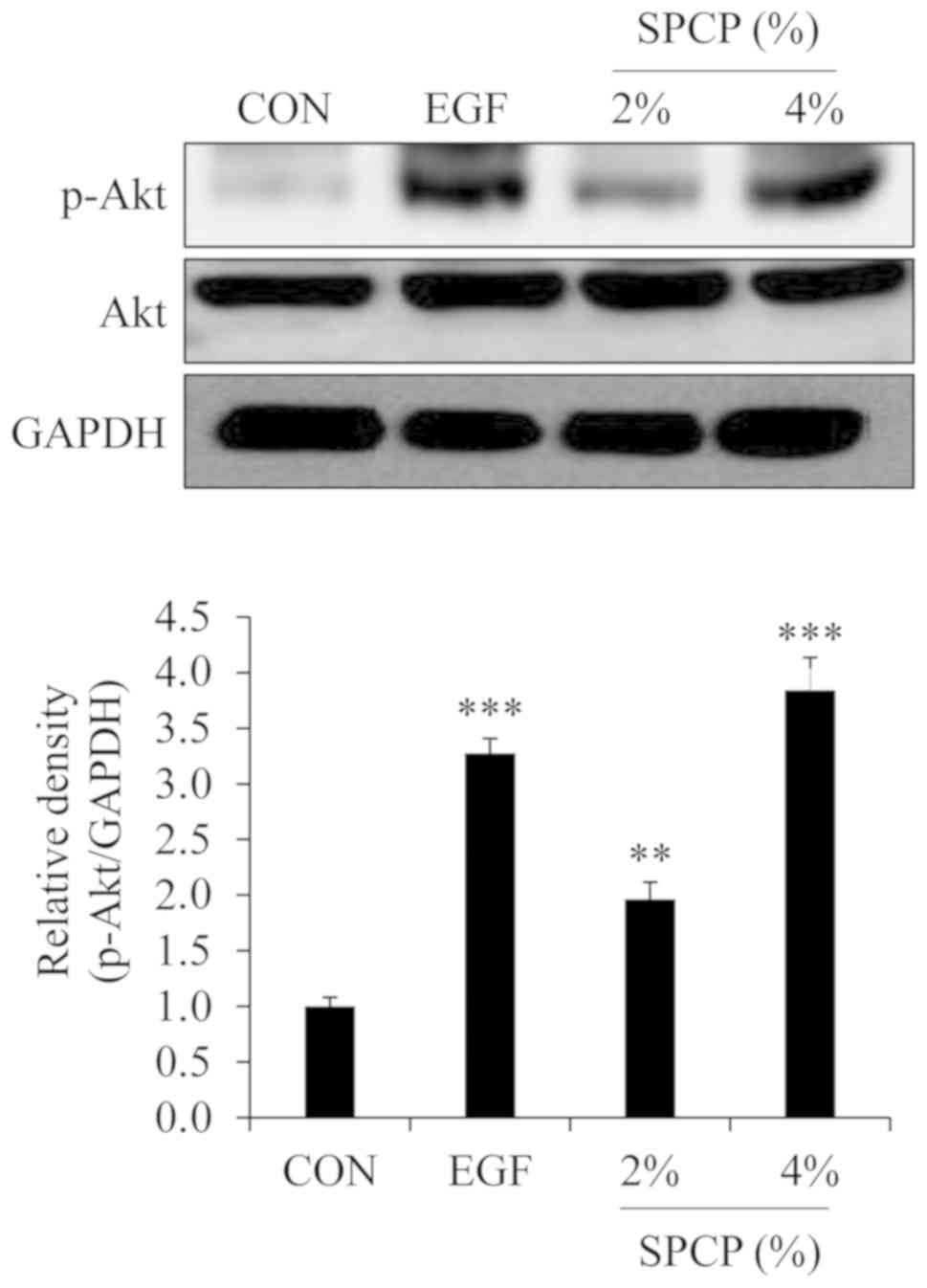
|
1
|
Kageyama H and Waditee-Sirisattha R:
Antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-aging properties of
mycosporine-like amino acids: Molecular and cellular mechanisms in
the protection of skin-aging. Mar Drugs. 17:pii: E222. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hyun YJ, Piao MJ, Kang KA, Zhen AX,
Madushan Fernando PDS, Kang HK, Ahn YS and Hyun JW: Effect of
fermented fish oil on fine particulate matter-induced skin aging.
Mar Drugs. 17:pii: E61. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Takeo M, Lee W and Ito M: Wound healing
and skin regeneration. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.
5:a0232672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Martin P: Wound healing-aiming for perfect
skin regeneration. Science. 276:75–81. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hu L, Wang J, Zhou X, Xiong Z, Zhao J, Yu
R, Huang F, Zhang H and Chen L: Exosomes derived from human adipose
mensen-chymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via
optimizing the characteristics of fibroblasts. Sci Rep.
6:329932016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chiquet M, Katsaros C and Kletsas D:
Multiple functions of gingival and mucoperiosteal fibroblasts in
oral wound healing and repair. Periodontol 2000. 68:21–40. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barrientos S, Stojadinovic O, Golinko MS,
Brem H and Tomic-Canic M: Growth factors and cytokines in wound
healing. Wound Repair Regen. 16:585–601. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Crowe MJ, Doetschman T and Greenhalgh DG:
Delayed wound healing in immunodeficient TGF-beta 1 knockout mice.
J Invest Dermatol. 115:3–11. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Philipp K, Riedel F, Sauerbier M, Hörmann
K and Germann G: Targeting TGF-beta in human keratinocytes and its
potential role in wound healing. Int J Mol Med. 14:589–593.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tracy LE, Minasian RA and Caterson EJ:
Extracellular matrix and dermal fibroblast function in the healing
wound. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 5:119–136. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhou ZQ, Chen Y, Chai M, Tao R, Lei YH,
Jia YQ, Shu J, Ren J, Li G, Wei WX, et al: Adipose extracellular
matrix promotes skin wound healing by inducing the differentiation
of adipose-derived stem cells into fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med.
43:890–900. 2019.
|
|
12
|
Xue M and Jackson CJ: Extracellular matrix
reorganization during wound healing and its impact on abnormal
scarring. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 4:119–136. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Guo S and Dipietro LA: Factors affecting
wound healing. J Dent Res. 89:219–229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang Y, Xia T, Zhi W, Wei L, Weng J, Zhang
C and Li X: Promotion of skin regeneration in diabetic rats by
electrospun core-sheath fibers loaded with basic fibroblast growth
factor. Biomaterials. 32:4243–4254. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moulin V: Growth factors in skin wound
healing. Eur J Cell Biol. 68:1–7. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Derynck R, Zhang Y and Feng XH: Smads:
Transcriptional activators of TGF-beta responses. Cell. 95:737–740.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rolfe KJ, Richardson J, Vigor C, Irvine
LM, Grobbelaar AO and Linge C: A role for TGF-beta 1-induced
cellular responses during wound healing of the non-scarring early
human fetus? J Invest Dermatol. 127:2656–2667. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wynn TA: Cellular and molecular mechanisms
of fibrosis. J Pathol. 214:199–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sauer H, Wartenberg M and Hescheler J:
Reactive oxygen species as intracellular messengers during cell
growth and differentiation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 11:173–186. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dunnill C, Patton T, Brennan J, Barrett J,
Dryden M, Cooke J, Leaper D and Georgopoulos NT: Reactive oxygen
species (ROS) and wound healing: The functional role of ROS and
emerging ROS-modulating technologies for augmentation of the
healing process. Int Wound J. 14:89–96. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sen CK, Khanna S, Babior BM, Hunt TK,
Ellison EC and Roy S: Oxidant-induced vascular endothelial growth
factor expression in human keratinocytes and cutaneous wound
healing. J Biol Chem. 277:33284–33290. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park HH, Park NY, Kim SG, Jeong KT, Lee EJ
and Lee E: Potential wound healing activities of galla rhois in
human fibroblasts and keratinocytes. Am J Chin Med. 43:1625–1636.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pozzolini M, Millo E, Oliveri C, Mirata S,
Salis A, Damonte G, Arkel M and Scarfì S: Elicited ROS scavenging
activity, photo-protective, and wound-healing properties of
collagen-derived peptides from the marine sponge chondrosia
reniformis. Mar Drugs. 16:pii: E465. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Son DH, Yang DJ, Sun JS, Kim SK, Kang N,
Kang JY, Choi YH, Lee JH, Moh SH, Shin DM and Kim KW: A novel
peptide, nicotinyl-isoleucine-valine-histidine (NA-IVH), promotes
antioxidant gene expression and wound healing in HaCaT cells. Mar
Drugs. 16:pii: E262. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kubatka P, Kapinová A, Kružliak P, Kello
M, Výbohová D, Kajo K, Novák M, Chripková M, Adamkov M, Péč M, et
al: Antineoplastic effects of Chlorella pyrenoidosa in the breast
cancer model. Nutrition. 31:560–569. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sheih IC, Fang TJ, Wu TK and Lin PH:
Anticancer and antioxidant activities of the peptide fraction from
algae protein waste. J Agric Food Chem. 58:1202–1207. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu P, Lee MK, Choi JW, Choi Y and Nam TJ:
Crude protein from spirulina increases the viability of CCD-986sk
cells via the EGFR/MAPK signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med.
43:771–778. 2019.
|
|
28
|
Liu P, Choi JW, Lee MK, Choi YH and Nam
TJ: Wound healing potential of spirulina protein on CCD-986sk
cells. Mar Drugs. 17:pii: E130. 2019.
|
|
29
|
Plikus MV, Guerrero-Juarez CF, Ito M, Li
YR, Dedhia PH, Zheng Y, Shao M, Gay DL, Ramos R, Hsi TC, et al:
Regeneration of fat cells from myofibroblasts during wound healing.
Science. 355:748–752. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Verrecchia F and Mauviel A: Transforming
growth factor-beta signaling through the Smad pathway: Role in
extracellular matrix gene expression and regulation. J Invest
Dermatol. 118:211–215. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu HY, Wu JL and Ni ZL: Overexpression of
microRNA-202-3p protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury through activation of TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway by
targeting TRPM6. Cell Cycle. 18:621–637. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Joshi A, Joshi VK, Pandey D and Hemalatha
S: Systematic investigation of ethanolic extract from Leea
macrophylla: Implications in wound healing. J Ethnopharmacol.
191:95–106. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao X, Wu H, Guo B, Dong R, Qiu Y and Ma
PX: Antibacterial anti-oxidant electroactive injectable hydrogel as
self-healing wound dressing with hemostasis and adhesiveness for
cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials. 122:34–47. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim HS, Park SY, Moon SH, Lee JD and Kim
S: Autophagy in human skin fibroblasts: Impact of age. Int J Mol
Sci. 19:pii: E2254. 2018.
|
|
35
|
Pereira RF and Bártolo PJ: Traditional
therapies for skin wound healing. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle).
5:208–229. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Schäfer M and Werner S: Oxidative stress
in normal and impaired wound repair. Pharmacol Res. 58:165–171.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Landén NX, Li D and Ståhle M: Transition
from inflammation to proliferation: A critical step during wound
healing. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:3861–3885. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nimse SB and Pal D: Free radicals, natural
antioxidants, and their reaction mechanisms. RSC Adv. 5:27986–8006.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sies H: Hydrogen peroxide as a central
redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress:
Oxidative eustress. Redox Biol. 11:613–619. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Meloche S and Pouysségur J: The ERK1/2
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway as a master regulator of
the G1-to S-phase transition. Oncogene. 26:3227–3239. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
He Z, Jiang J, Kokkinaki M, Golestaneh N,
Hofmann MC and Dym M: Gdnf upregulates c-Fos transcription via the
Ras/Erk1/2 pathway to promote mouse spermatogonial stem cell
proliferation. Stem Cells. 26:266–278. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Mebratu Y and Tesfaigzi Y: How ERK1/2
activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is
subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle. 8:1168–1175. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Coutant A, Rescan C, Gilot D, Loyer P,
Guguen-Guillouzo C and Baffet G: PI3K-FRAP/mTOR pathway is critical
for hepatocyte proliferation whereas MEK/ERK supports both
proliferation and survival. Hepatology. 36:1079–1088. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Engelman JA, Luo J and Cantley LC: The
evolution of phospha-tidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of
growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 7:606–619. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kornasio R, Riederer I, Butler-Browne G,
Mouly V, Uni Z and Halevy O: Beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB)
stimulates myogenic cell proliferation, differentiation and
survival via the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1793:755–763. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Schultz GS and Wysocki A: Interactions
between extracellular matrix and growth factors in wound healing.
Wound Repair Regen. 17:153–162. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hinz B: Formation and function of the
myofibroblast during tissue repair. J Invest Dermatol. 127:526–537.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kadler KE, Baldock C, Bella J and
Boot-Handford RP: Collagens at a glance. J Cell Sci. 120:1955–1958.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lenselink EA: Role of fibronectin in
normal wound healing. Int Wound J. 12:313–316. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|