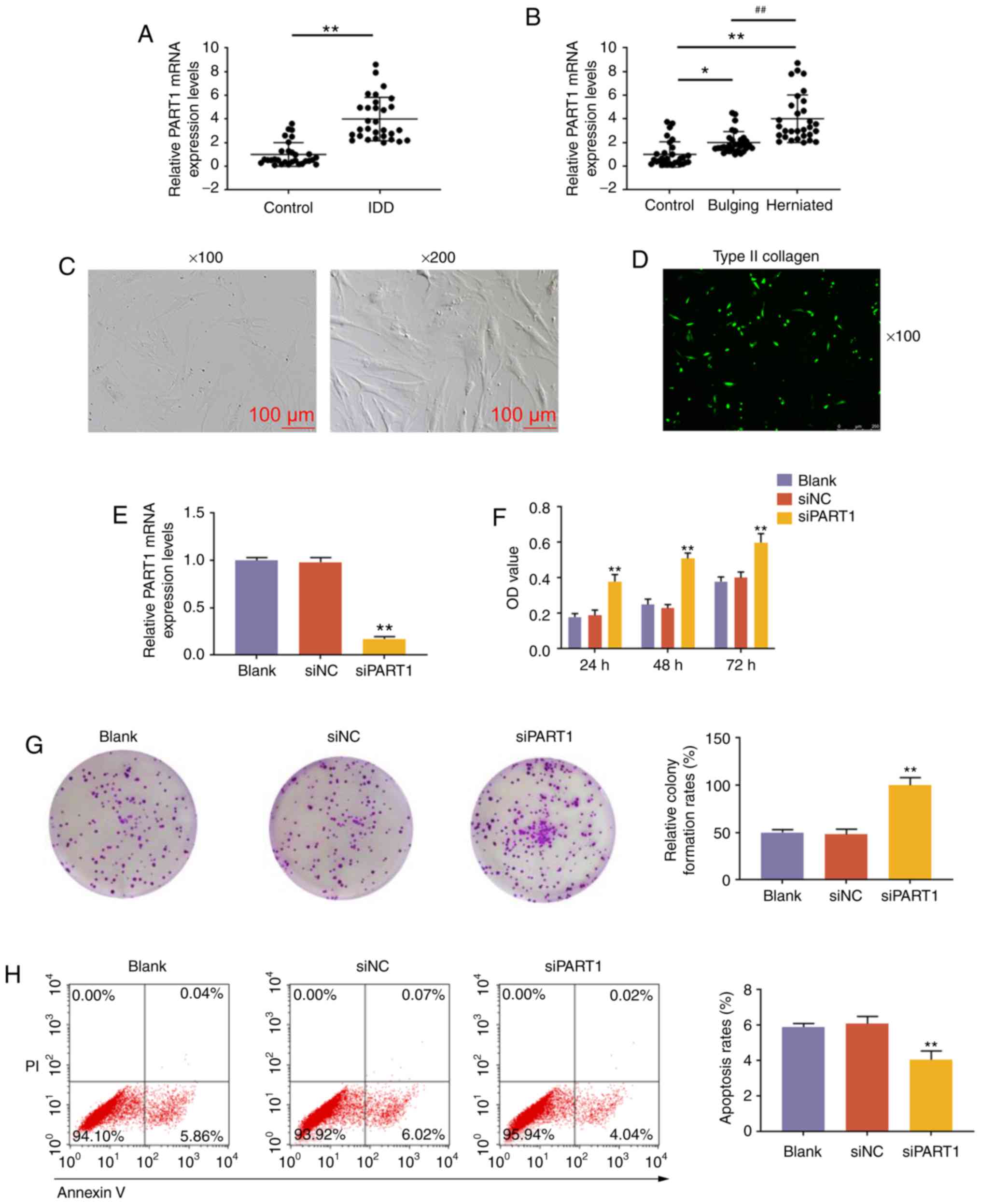
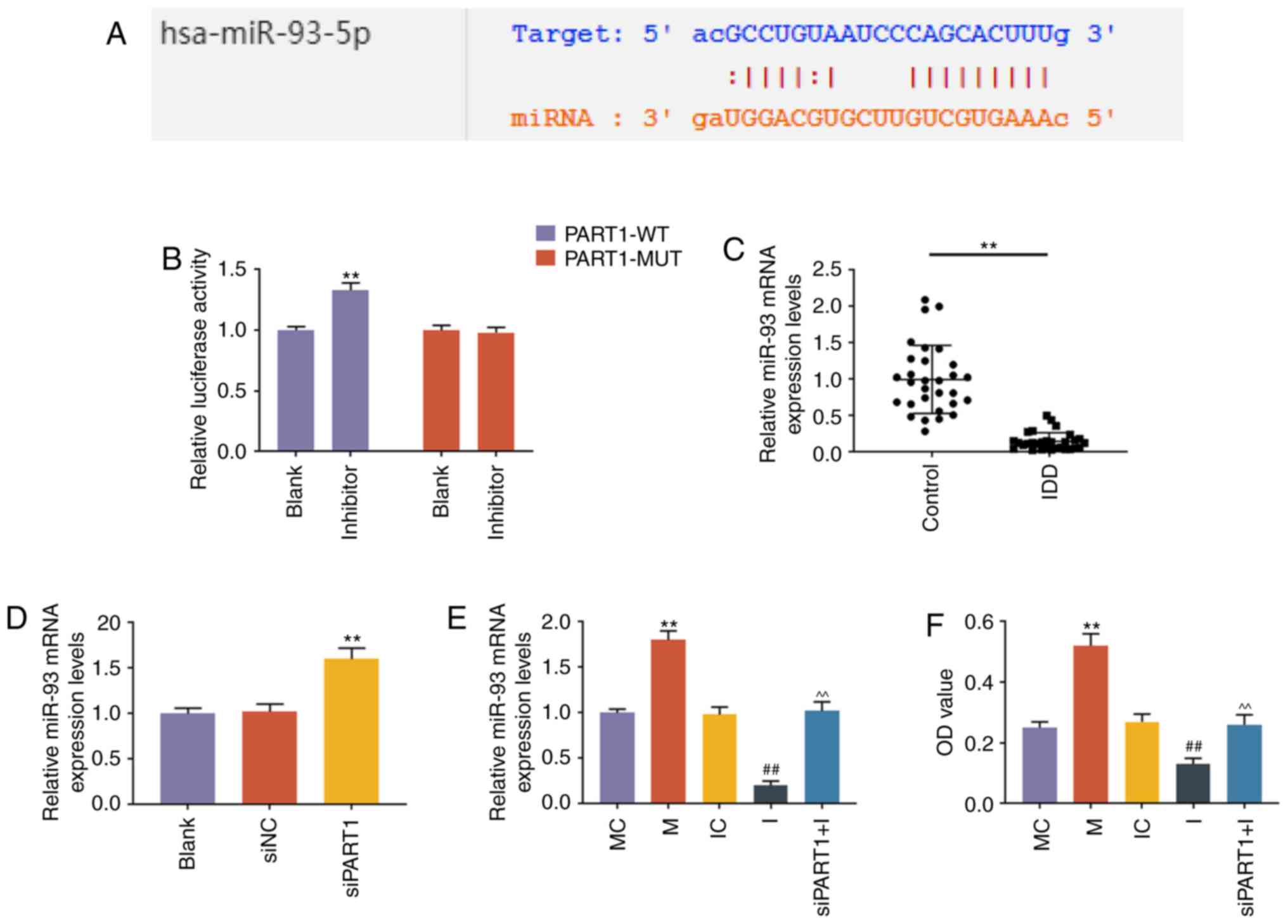
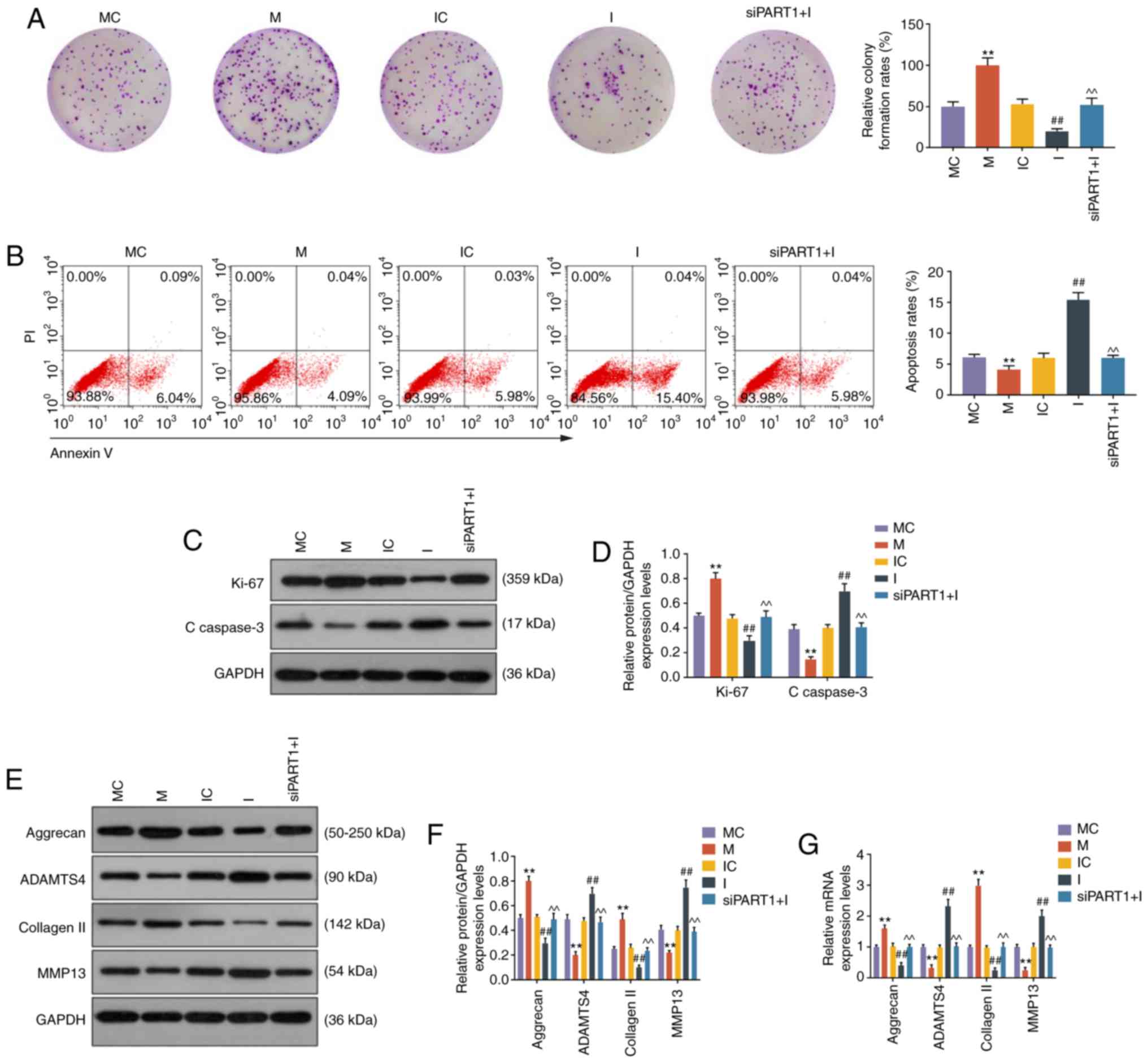
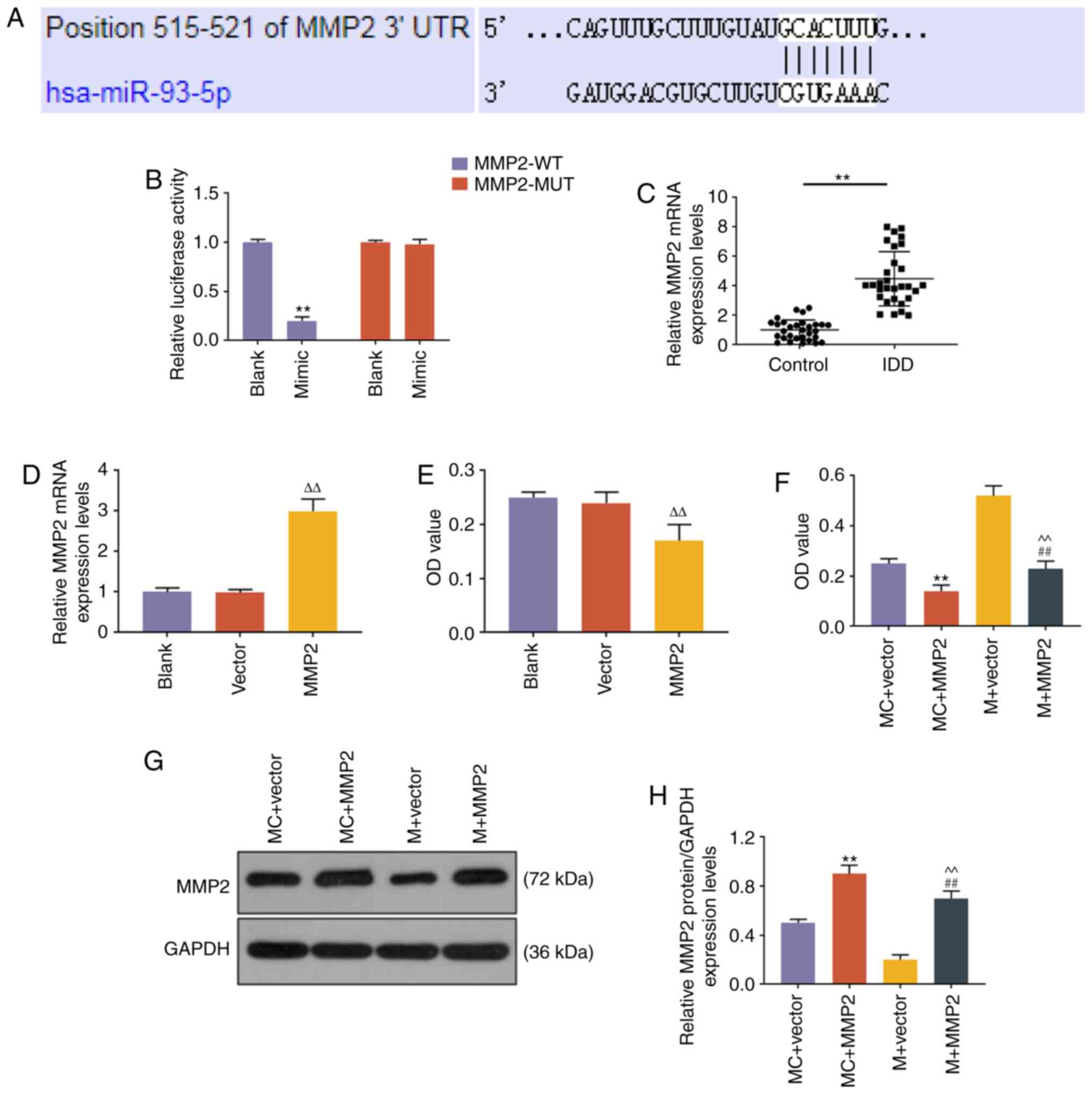
|
1
|
van Uden S, Silva-Correia J, Oliveira JM
and Reis RL: Current strategies for treatment of intervertebral
disc degeneration: Substitution and regeneration possibilities.
Biomater Res. 21:222017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Priyadarshani P, Li Y and Yao L: Advances
in biological therapy for nucleus pulposus regeneration.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 24:206–212. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
He F and Pei M: Rejuvenation of nucleus
pulposus cells using extracellular matrix deposited by
synovium-derived stem cells. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 37:459–469.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li P, Liang Z, Hou G, Song L, Zhang R, Gan
Y, Zhang C, Xu Y and Zhou Q: N-Cadherin-mediated activation of
PI3K/Akt-GSK-3β signaling attenuates nucleus pulposus cell
apoptosis under high-magnitude compression. Cell Physiol Biochem.
44:229–239. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Clarke LE, McConnell JC and Sherratt MJ:
Derby B, Richardson SM and Hoyland JA: Growth differentiation
factor 6 and transforming growth factor-beta differentially mediate
mesenchymal stem cell differentiation, composition, and
micromechanical properties of nucleus pulposus constructs.
Arthritis Res Ther. 16:R672014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chen J, Xie JJ, Jin MY, Gu YT, Wu CC, Guo
WJ, Yan YZ, Zhang ZJ, Wang JL, Zhang XL, et al: Sirt6
overexpression suppresses senescence and apoptosis of nucleus
pulposus cells by inducing autophagy in a model of intervertebral
disc degeneration. Cell Death Dis. 9:562018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang W, Li P, Xu J, Wu X, Guo Z, Fan L,
Song R, Wang J, Wei L and Teng H: Resveratrol attenuates high
glucose-induced nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and senescence
through activating the ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway. Biosci Rep.
38:BSR201714542018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Séguin CA, Pilliar RM, Roughley PJ and
Kandel RA: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha modulates matrix production
and catabolism in nucleus pulposus tissue. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
30:1940–1948. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li P, Gan Y, Xu Y, Song L, Wang L, Ouyang
B, Zhang C and Zhou Q: The inflammatory cytokine TNF-α promotes the
premature senescence of rat nucleus pulposus cells via the PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 7:429382017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li P, Gan Y, Xu Y, Wang L, Ouyang B, Zhang
C, Luo L, Zhao C and Zhou Q: 17beta-estradiol attenuates
TNF-α-induced premature senescence of nucleus pulposus cells
through regulating the ROS/NF-κB pathway. Int J Biol Sci.
13:145–156. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Wan ZY, Song F, Sun Z, Chen YF, Zhang WL,
Samartzis D, Ma CJ, Che L, Liu X, Ali MA, et al: Aberrantly
expressed long noncoding RNAs in human intervertebral disc
degeneration: A microarray related study. Arthritis Res Ther.
16:4652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen WK, Yu XH, Yang W, Wang C, He WS, Yan
YG, Zhang J and Wang WJ: lncRNAs: Novel players in intervertebral
disc degeneration and osteoarthritis. Cell Prolif. 50:2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhang S, Cao R, Li Q, Yao M, Chen Y and
Zhou H: Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA-associated competing
endogenous RNA network in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. PeerJ.
7:e63972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lv Y, Wei W, Huang Z, Chen Z, Fang Y, Pan
L, Han X and Xu Z: Long non-coding RNA expression profile can
predict early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma after curative
resection. Hepatol Res. 48:1140–1148. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li M, Zhang W, Zhang S, Wang C and Lin Y:
PART1 expression is associated with poor prognosis and tumor
recurrence in stage I-III non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer.
8:1795–1800. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun M, Geng D, Li S, Chen Z and Zhao W:
LncRNA PART1 modulates toll-like receptor pathways to influence
cell proliferation and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Biol
Chem. 399:387–395. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kang M, Ren M, Li Y, Fu Y, Deng M and Li
C: Exosome-mediated transfer of lncRNA PART1 induces gefitinib
resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via functioning as
a competing endogenous RNA. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:1712018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wei R, Chen Y, Zhao Z, Gu Q and Wu J:
LncRNA FAM83H-AS1 induces nucleus pulposus cell growth via
targeting the Notch signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol.
234:22163–22171. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu L, Hao Y, Xu C, Zhu G and Cai Y:
LINC00969 promotes the degeneration of intervertebral disk by
sponging miR-335-3p and regulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
IUBMB Life. 71:611–618. 2019. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cheng X, Zhang L, Zhang K, Zhang G, Hu Y,
Sun X, Zhao C, Li H, Li YM and Zhao J: Circular RNA VMA21 protects
against intervertebral disc degeneration through targeting miR-200c
and X linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein. Ann Rheum Dis.
77:770–779. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mern DS, Fontana J, Beierfuß A, Thomé C
and Hegewald AA: A combinatorial relative mass value evaluation of
endogenous bioactive proteins in three-dimensional cultured nucleus
pulposus cells of herniated intervertebral discs: Identification of
potential target proteins for gene therapeutic approaches. PLoS
One. 8:e814672013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Patil P, Dong Q, Wang D, Chang J, Wiley C,
Demaria M, Lee J, Kang J, Niedernhofer LJ, Robbins PD, et al:
Systemic clearance of p16INK4a -positive senescent cells
mitigates age-associated intervertebral disc degeneration. Aging
Cell. 18:e129272019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ji ML, Jiang H, Zhang XJ, Shi PL, Li C, Wu
H, Wu XT, Wang YT, Wang C and Lu J: Preclinical development of a
microRNA-based therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat
Commun. 9:50512018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hu Y, Ma Z, He Y, Liu W, Su Y and Tang Z:
PART-1 functions as a competitive endogenous RNA for promoting
tumor progression by sponging miR-143 in colorectal cancer. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 490:317–323. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guo G, Kang Q, Zhu X, Chen Q, Wang X, Chen
Y, Ouyang J, Zhang L, Tan H, Chen R, et al: A long noncoding RNA
critically regulates Bcr-Abl-mediated cellular transformation by
acting as a competitive endogenous RNA. Oncogene. 34:1768–1779.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang L, Liang X and Li Y: Long non-coding
RNA MEG3 inhibits cell growth of gliomas by targeting miR-93 and
inactivating PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncol Rep. 38:2408–2416. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Y, Wang J, Sun L and Zhu S: LncRNA
myocardial infarction-associated transcript (MIAT) contributed to
cardiac hypertrophy by regulating TLR4 via miR-93. Eur J Pharmacol.
818:508–517. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yu X, Mi L, Dong J and Zou J: Long
intergenic non-protein-coding RNA 1567 (LINC01567) acts as a
'sponge' against microRNA-93 in regulating the proliferation and
tumorigenesis of human colon cancer stem cells. BMC Cancer.
17:7162017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Peng W, Zhu SX, Wang J, Chen LL, Weng JQ
and Chen SL: Lnc-NTF3-5 promotes osteogenic differentiation of
maxillary sinus membrane stem cells via sponging miR-93-3p. Clin
Implant Dent Relat Res. 20:110–121. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Petrocca F, Visone R, Onelli MR, Shah MH,
Nicoloso MS, de Martino I, Iliopoulos D, Pilozzi E, Liu CG, Negrini
M, et al: E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent
cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer cell.
13:272–286. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Badal SS, Wang Y, Long J, Corcoran DL,
Chang BH, Truong LD, Kanwar YS, Overbeek PA and Danesh FR: miR-93
regulates Msk2-mediated chromatin remodelling in diabetic
nephropathy. Nat Commun. 7:120762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu MZ, Cheng WC, Chen SF, Nieh S, O'Connor
C, Liu CL, Tsai WW, Wu CJ, Martin L, Lin YS, et al: miR-25/93
mediates hypoxia-induced immunosuppression by repressing cGAS. Nat
Cell Biol. 19:1286–1296. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang C, Zhang Y, Zhu H, Hu J and Xie Z:
MiR-34a/miR-93 target c-Ski to modulate the proliferaton of rat
cardiac fibroblasts and extracellular matrix deposition in vivo and
in vitro. Cell Signal. 46:145–153. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Islam MS, Ciavattini A, Petraglia F,
Castellucci M and Ciarmela P: Extracellular matrix in uterine
leiomyoma pathogenesis: A potential target for future therapeutics.
Hum Reprod Update. 24:59–85. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Xunlu Y, Minshan F, Liguo Z, Jiawen Z, Xu
W, Jie Y, Shangquan W, He Y, Long L, Tao H and Xuepeng L:
Integrative bioinformatics analysis reveals potential gene
biomarkers and analysis of function in human degenerative disc
annulus fibrosus cells. Biomed Res Int. 2019:98902792019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ji ML, Lu J, Shi PL, Zhang XJ, Wang SZ,
Chang Q, Chen H and Wang C: Dysregulated miR-98 contributes to
extracellular matrix degradation by targeting IL-6/STAT3 signaling
pathway in human intervertebral disc degeneration. J Bone Miner
Res. 31:900–909. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Han Y, Ma L, Zhao L, Feng W and Zheng X:
Rosmarinic inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and migration via
up-regulating miR-506 and suppressing MMP2/16 expression in
pancreatic cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 115:1088782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Y, Su X and Pan H: Inhibition of lncRNA
PANDAR reduces cell proliferation, cell invasion and suppresses EMT
pathway in breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. 25:185–192. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wang T, Hou J, Jian S, Luo Q, Wei J, Li Z,
Wang X, Bai P, Duan B, Xing J and Cai J: miR-29b negatively
regulates MMP2 to impact gastric cancer development by suppress
gastric cancer cell migration and tumor growth. J Cancer.
9:3776–3786. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang L, Song X, Zhu J, Li M, Ji Y, Wu F,
Chen Y, Cui X, Hu J, Wang L, et al: Tumor suppressor microRNA-34a
inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting
MMP-2/MMP-9/FNDC3B in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J
Oncol. 51:378–388. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|