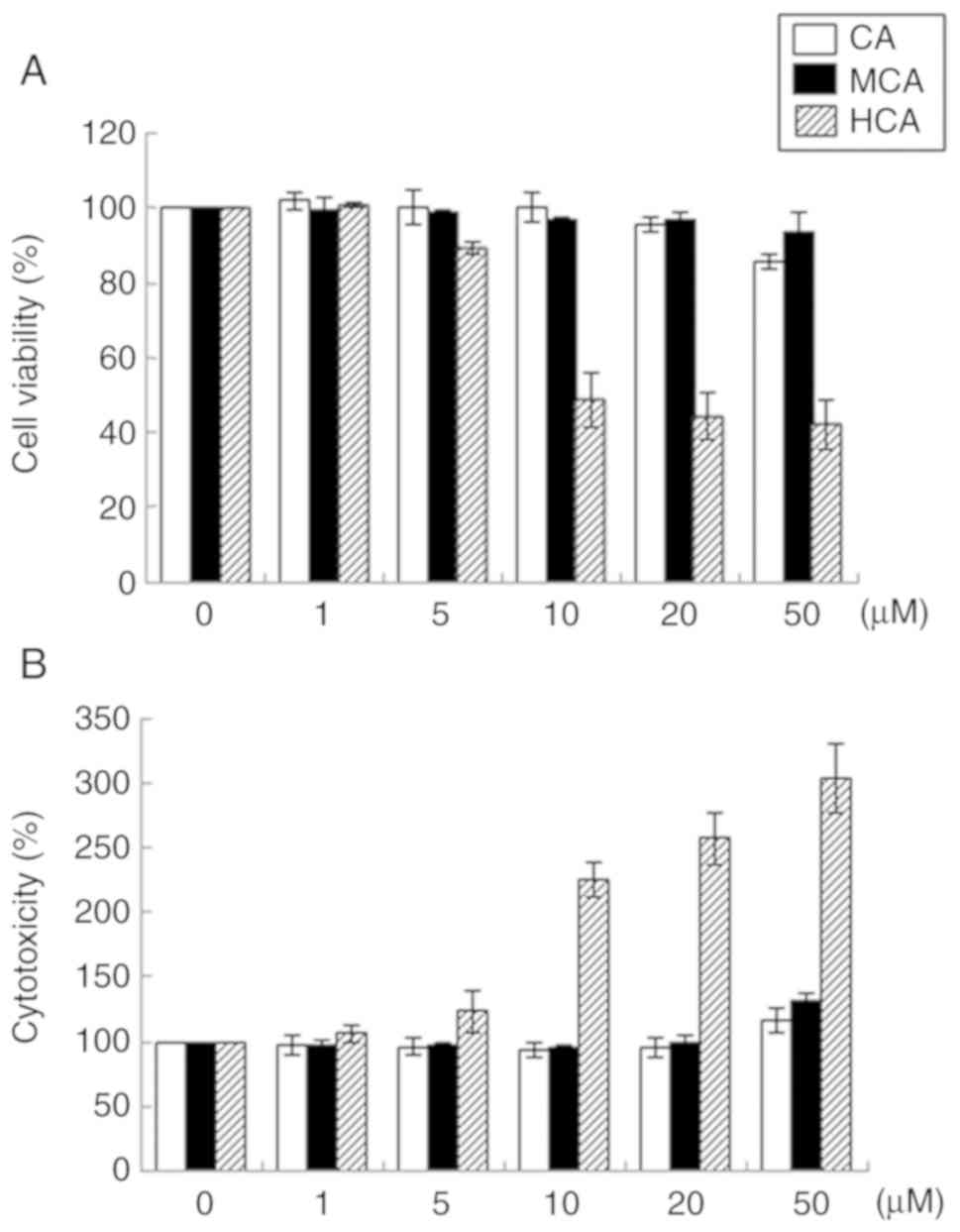
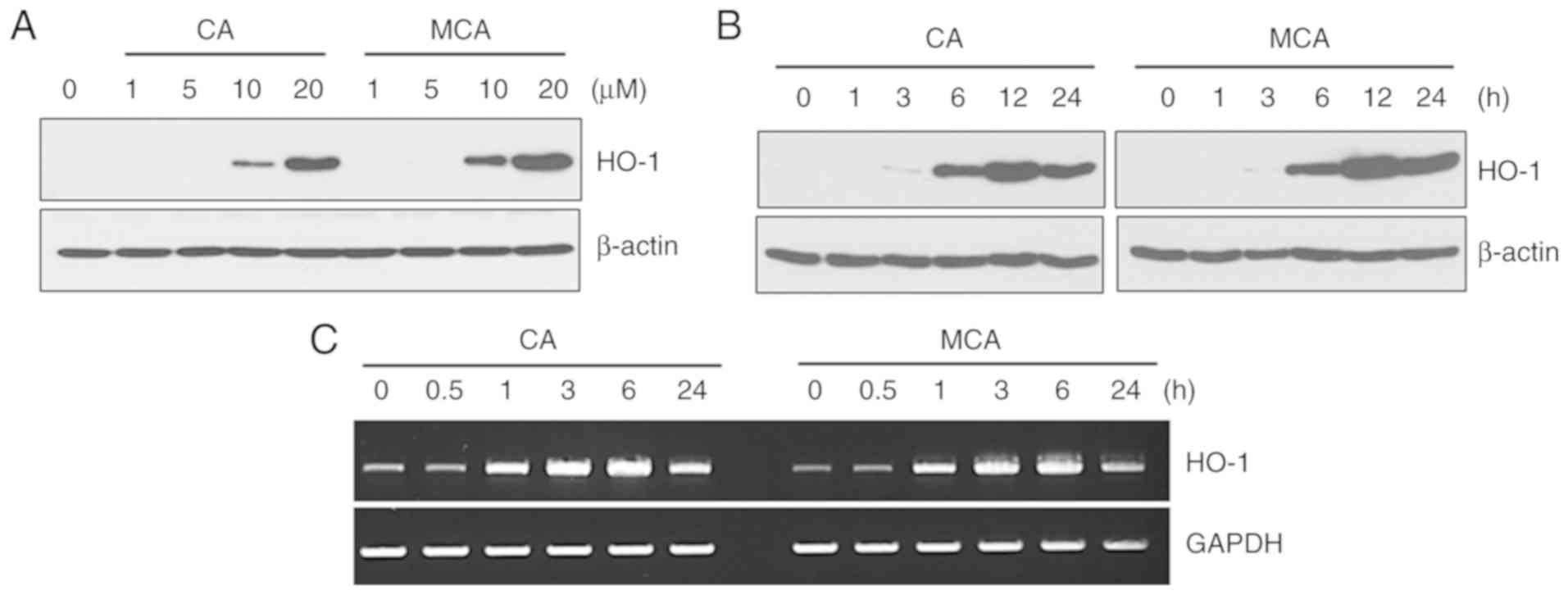
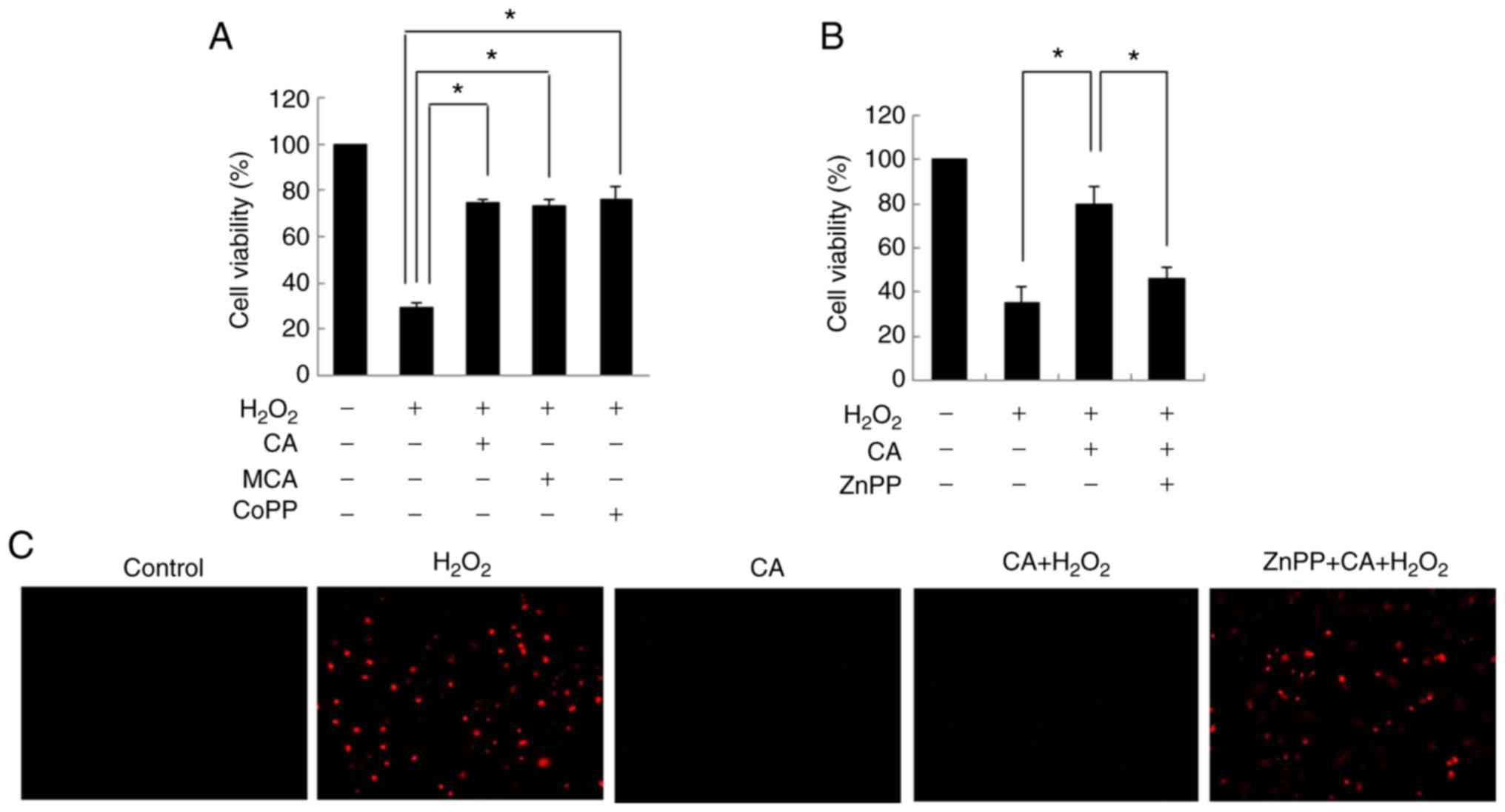
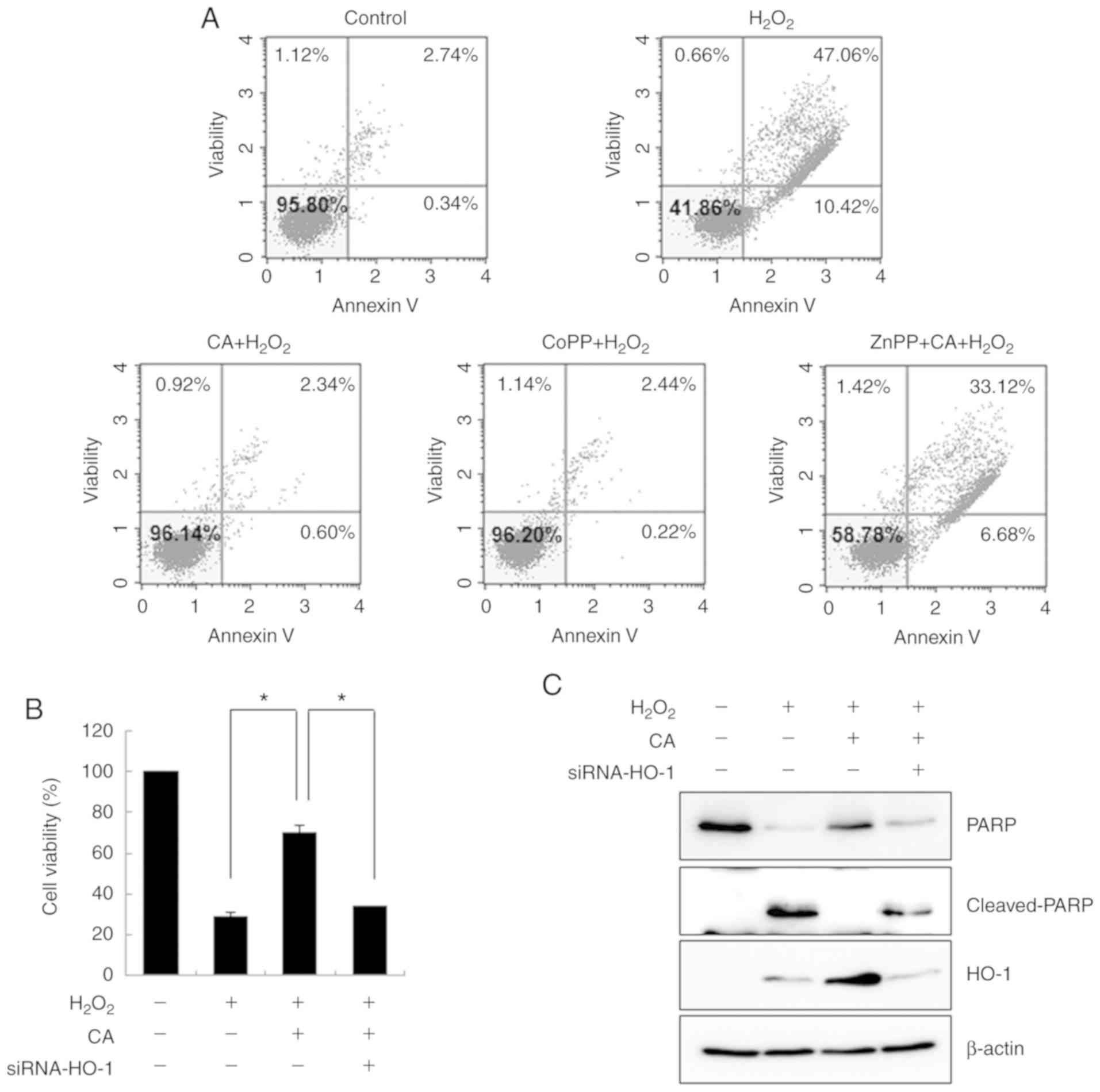
|
1
|
Apel K and Hirt H: Reactive oxygen
species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction.
Annu Rev Plant Biol. 55:373–399. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
D'Autreaux B and Toledano MB: ROS as
signaling molecules: Mechanisms that generate specificity in ROS
homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:813–824. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kim SM, Hwang KA and Choi KC: Potential
roles of reactive oxygen species derived from chemical substances
involved in cancer development in the female reproductive system.
BMB Rep. 51:557–562. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pisoschi AM and Pop A: The role of
antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur J
Med Chem. 97:55–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ochoa CD, Wu RF and Terada LS: ROS
signaling and ER stress in cardiovascular disease. Mol Aspects Med.
63:18–29. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pignatelli P, Menichelli D, Pastori D and
Violi F: Oxidative stress and cardiovascular disease: New insights.
Kardiol Pol. 76:713–722. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shen Y, Jia LN, Honma N, Hosono T, Ariga T
and Seki T: Beneficial effects of cinnamon on the metabolic
syndrome, inflammation, and pain, and mechanisms underlying these
effects-a review. J Tradit Complement Med. 2:27–32. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ahn SG, Jin YH, Yoon JH and Kim SA: The
anticancer mechanism of 2′-hydroxycinnamaldehyde in human head and
neck cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 47:1793–1800. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chao LK, Hua KF, Hsu HY, Cheng SS, Lin IF,
Chen CJ, Chen ST and Chang ST: Cinnamaldehyde inhibits
pro-inflammatory cytokines secretion from monocytes/macrophages
through suppression of intracellular signaling. Food Chem Toxicol.
46:220–231. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kwon JA, Yu CB and Park HD: Bacteriocidal
effects and inhibition of cell separation of cinnamic aldehyde on
Bacillus cereus. Lett Appl Microbiol. 37:61–65. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Song F, Li H, Sun J and Wang S: Protective
effects of cinnamic acid and cinnamic aldehyde on
isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial ischemia in rats. J
Ethnopharmacol. 150:125–130. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fan J and Watanabe T: Inflammatory
reactions in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler
Thromb. 10:63–71. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Incalza MA, D'Oria R, Natalicchio A,
Perrini S, Laviola L and Giorgino F: Oxidative stress and reactive
oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction associated with
cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Vascul Pharmacol. 100:1–19.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kim SM, Huh JW, Kim EY, Shin MK, Park JE,
Kim SW, Lee W, Choi B and Chang EJ: Endothelial dysfunction induces
atherosclerosis: Increased aggrecan expression promotes apoptosis
in vascular smooth muscle cells. BMB Rep. 52:145–150. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
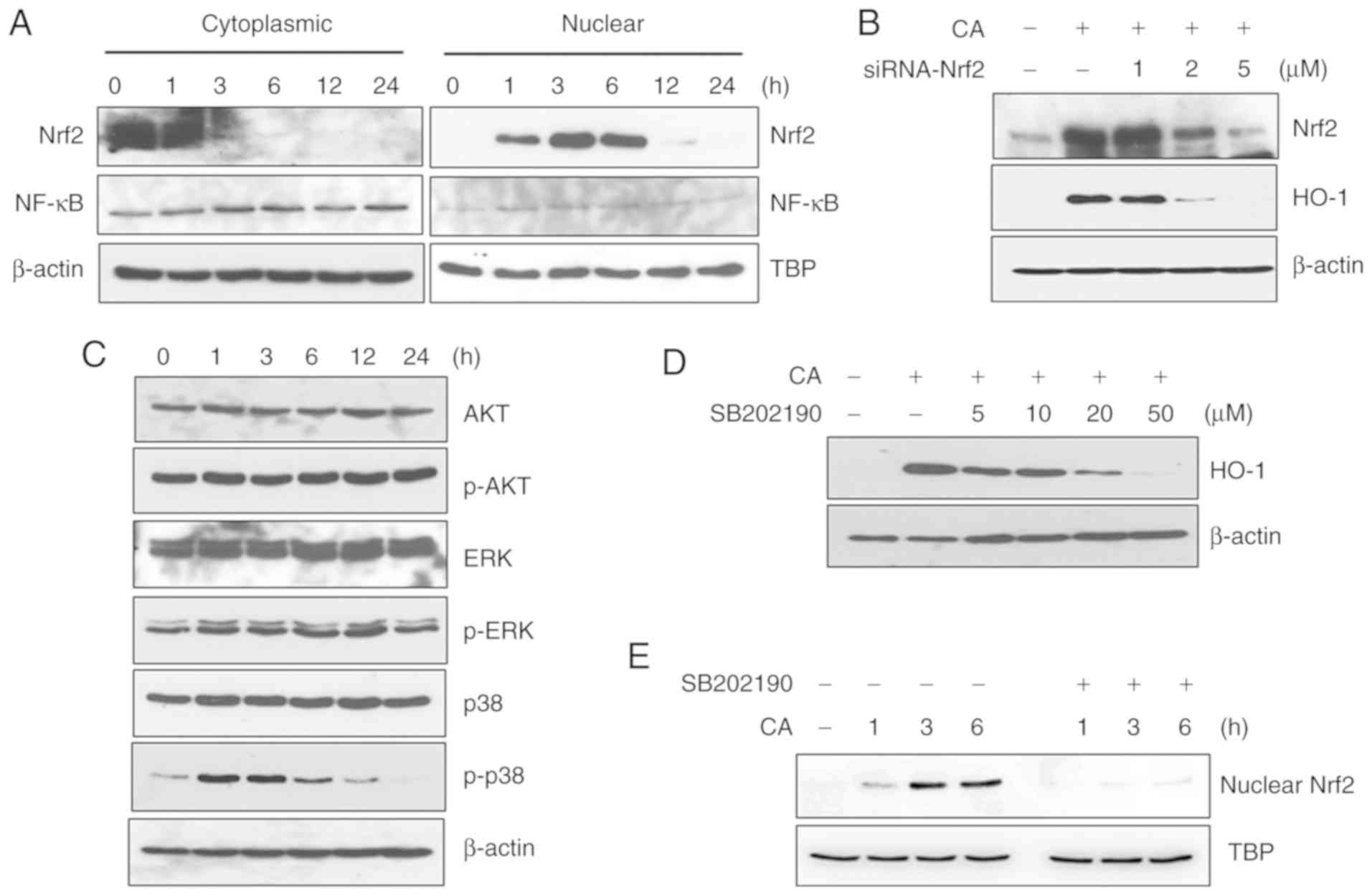
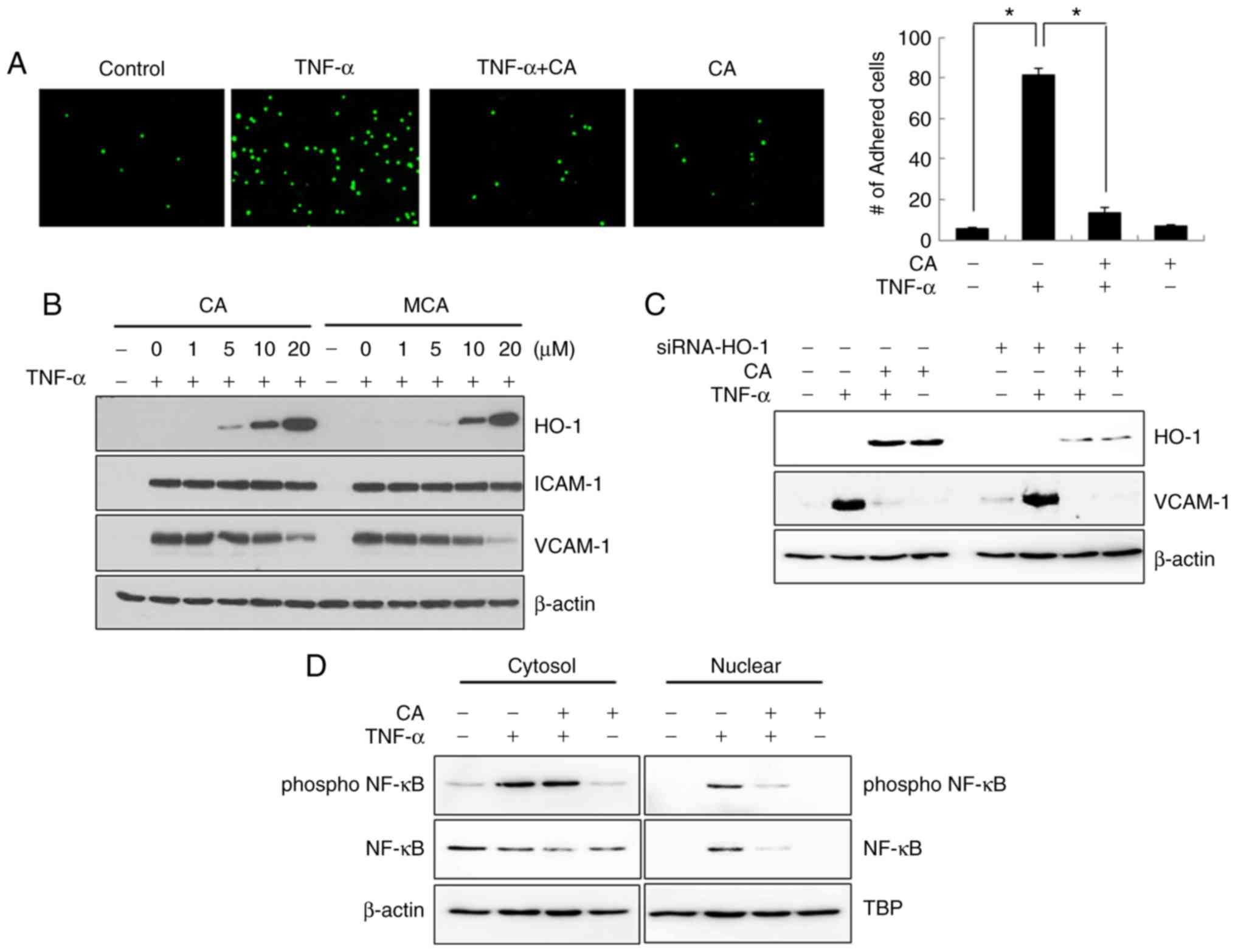
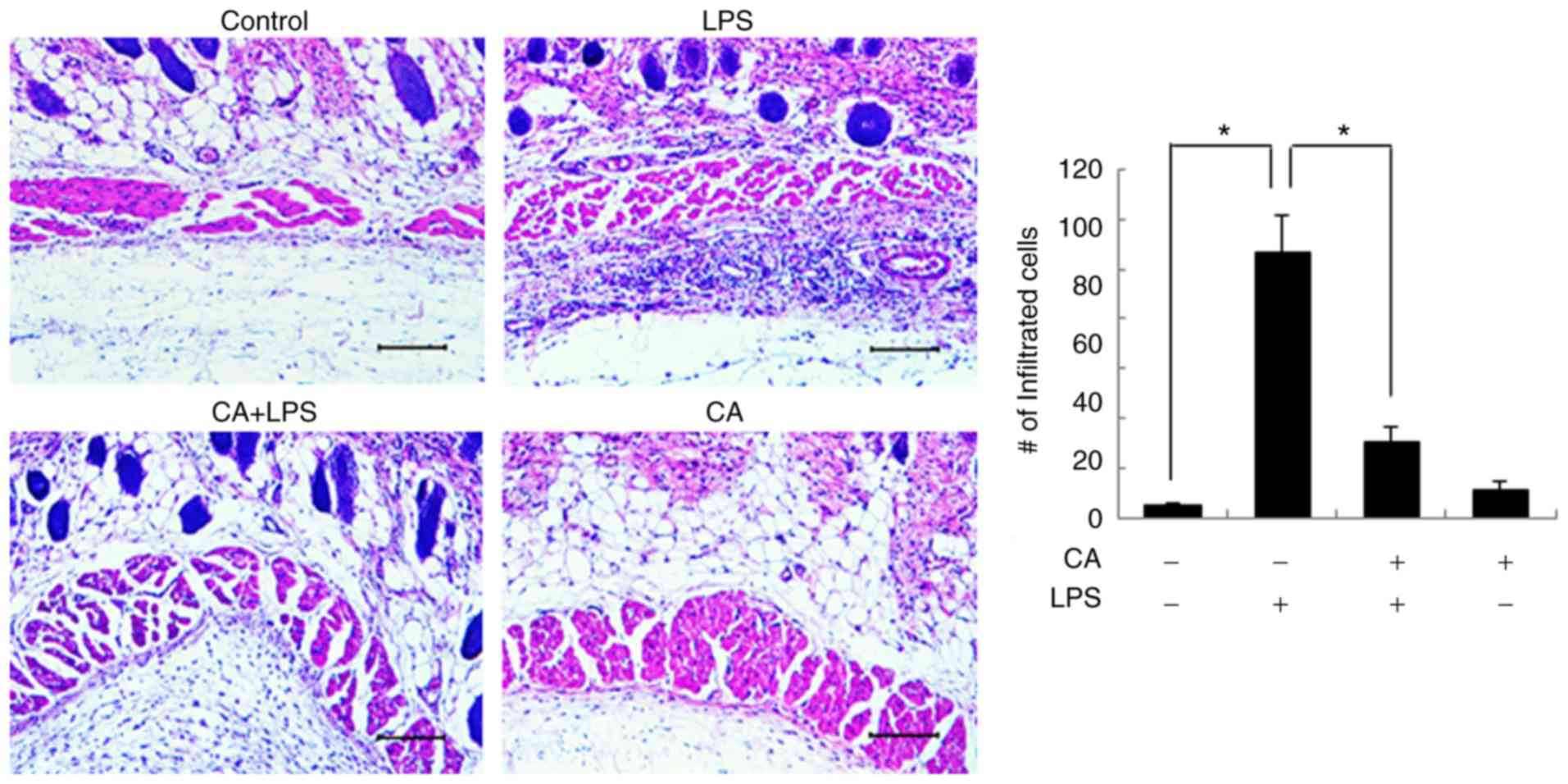
Kim NY, Ahn SG and Kim SA: Cinnamaldehyde
protects human dental pulp cells against oxidative stress through
the Nrf2/HO-1-dependent antioxidant response. Eur J Pharmacol.
815:73–79. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen XL and Kunsch C: Induction of
cytoprotective genes through Nrf2/antioxidant response element
pathway: A new therapeutic approach for the treatment of
inflammatory diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 10:879–891. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Niture SK, Khatri R and Jaiswal AK:
Regulation of Nrf2-an update. Free Radic Biol Med. 66:36–44. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li W, Zhi W, Zhao J, Yao Q, Liu F and Niu
X: Cinnamaldehyde protects VSMCs against ox-LDL-induced
proliferation and migration through S arrest and inhibition of p38,
JNK/MAPKs and NF-κB. Vascul Pharmacol. 108:57–66. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jin YH and Kim SA: 2-methoxycinnamaldehyde
inhibits the TNF-α-induced proliferation and migration of human
aortic smooth muscle cells. Int J Mol Med. 39:191–198. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kim SA, Kim YC, Kim SW, Lee SH, Min JJ,
Ahn SG and Yoon JH: Antitumor activity of novel indirubin
derivatives in rat tumor model. Clin Cancer Res. 13:253–259. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jin YH, Ahn SG and Kim SA: BAG3 affects
the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of HSF1 upon heat stress. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 464:561–567. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mo L, Yang C, Gu M, Zheng D, Lin L, Wang
X, Lan A, Hu F and Feng J: PI3K/Akt signaling pathway-induced heme
oxygenase-1 upregulation mediates the adaptive cytoprotection of
hydrogen peroxide preconditioning against oxidative injury in PC12
cells. Int J Mol Med. 30:314–320. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Takahashi T, Morita K, Akagi R and Sassa
S: Heme oxygenase-1: A novel therapeutic target in oxidative tissue
injuries. Curr Med Chem. 11:1545–1561. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chiang YF, Chen HY, Huang KC, Lin PH and
Hsia SM: Dietary antioxidant trans-cinnamaldehyde reduced
visfatin-induced breast cancer progression: In vivo and in vitro
study. Antioxidants (Basel). 8:E6252019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Patra K, Jana S, Sarkar A, Mandal DP and
Bhattacharjee S: The inhibition of hypoxia-induced angiogenesis and
metastasis by cinnamaldehyde is mediated by decreasing HIF-1α
protein synthesis via PI3K/Akt pathway. Biofactors. 45:401–415.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Holmstrom KM and Finkel T: Cellular
mechanisms and physiological consequences of redox-dependent
signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:411–421. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schieber M and Chandel NS: ROS function in
redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol. 24:R453–R462.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li B, Lee YJ, Kim YC, Yoon JJ, Lee SM, Lee
YP, Kang DG and Lee HS: Sauchinone from saururus chinensis protects
vascular inflammation by heme oxygenase-1 induction in human
umbilical vein endothelial cells. Phytomedicine. 21:101–108. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lee CW, Lee SH, Lee JW, Ban JO, Lee SY,
Yoo HS, Jung JK, Moon DC, Oh KW and Hong JT:
2-hydroxycinnamaldehyde inhibits SW620 colon cancer coll growth
through AP-1 inactivation. J Pharmacol Sci. 104:19–28. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim SA, Sung YK, Kwon BM, Yoon JH, Lee H,
Ahn SG and Hong SH: 2′-hydroxycinnamaldehyde shows antitumor
activity against oral cancer in vitro and in vivo in a rat tumor
model. Anticancer Res. 30:489–494. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nguyen HA and Kim SA:
2′-hydroxycinnamaldehyde induces apoptosis through HSF1-mediated
BAG3 expression. Int J Oncol. 50:283–289. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Luo Y, Lu S, Dong X, Xu L, Sun G and Sun
X: Dihydromyricetin protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells
from injury through ERK and Akt mediated Nrf2/HO-1 signaling
pathway. Apoptosis. 22:1013–1024. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang TC, Chung YL, Wu ML and Chuang SM:
Cinnamaldehyde enhances Nrf2 nuclear translocation to upregulate
phase II detoxifying enzyme expression in HepG2 cells. J Agric Food
Chem. 59:5164–5171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim EJ, Park WH, Ahn SG, Yoon JH, Kim SW
and Kim SA: 5′-nitro-indirubinoxime inhibits inflammatory response
in TNF-alpha stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
Atherosclerosis. 211:77–83. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Barath P, Fishbein MC, Cao J, Berenson J,
Helfant RH and Forrester JS: Detection and localization of tumor
necrosis factor in human atheroma. Am J Cardiol. 65:297–302. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|