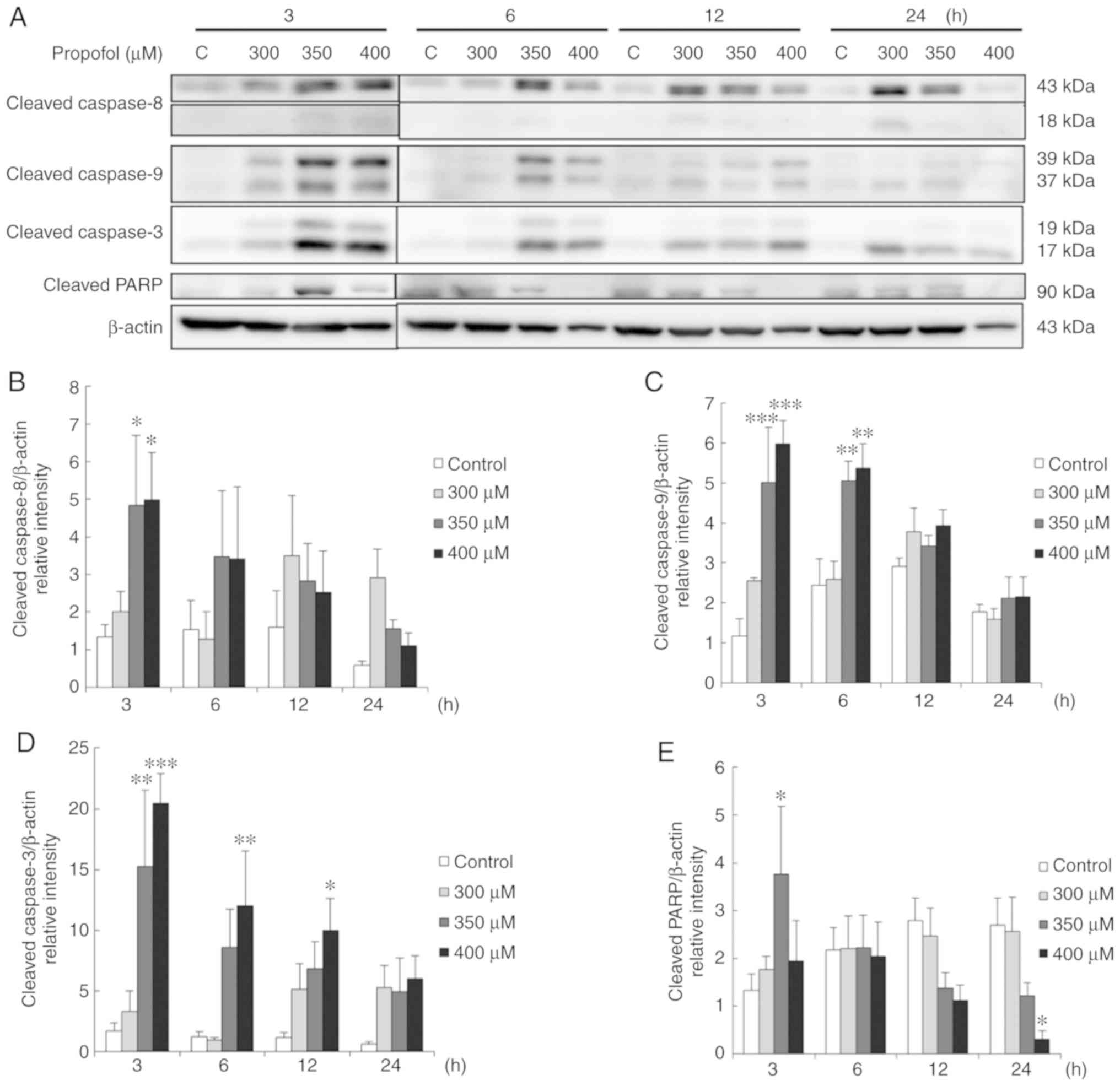
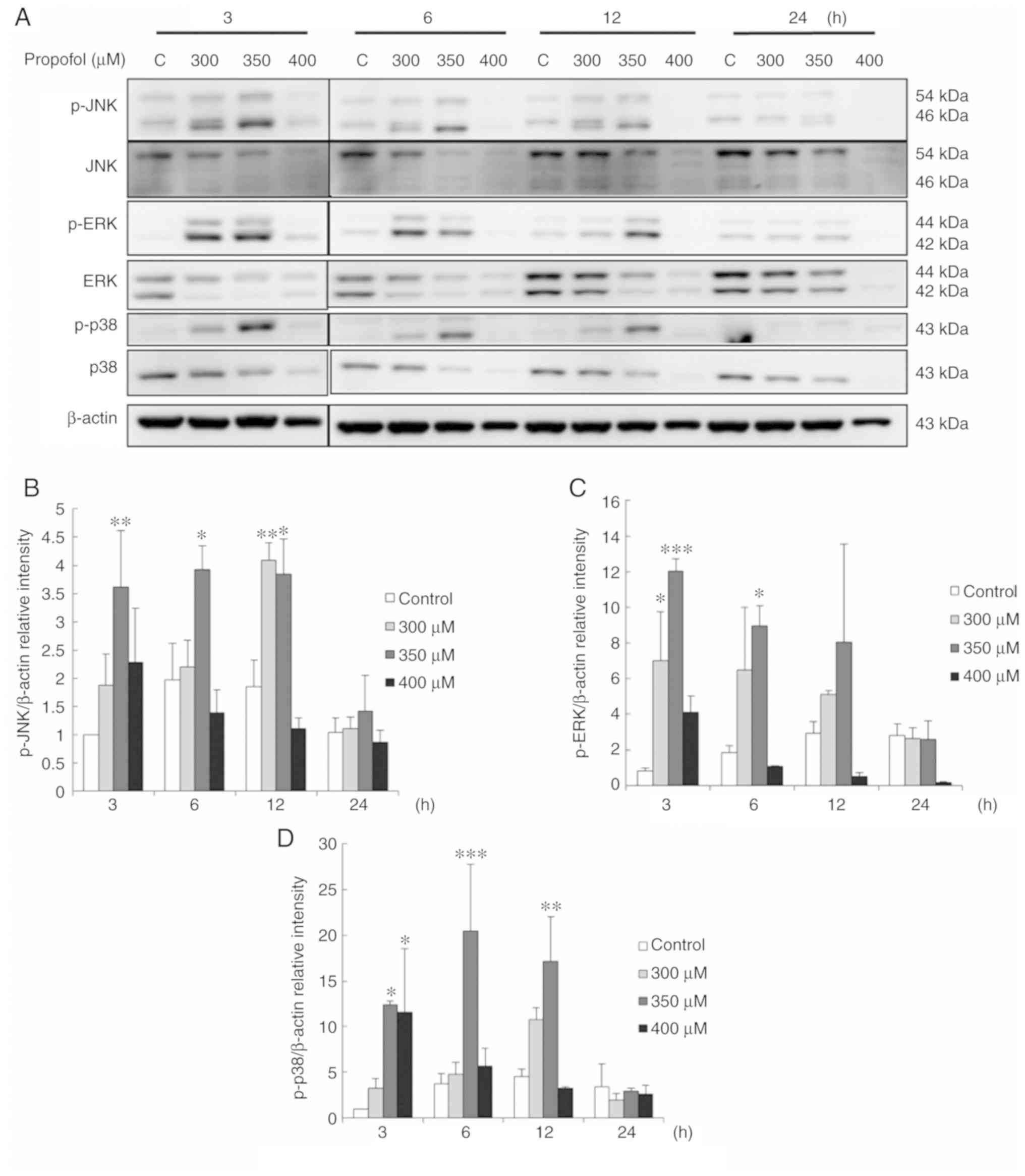
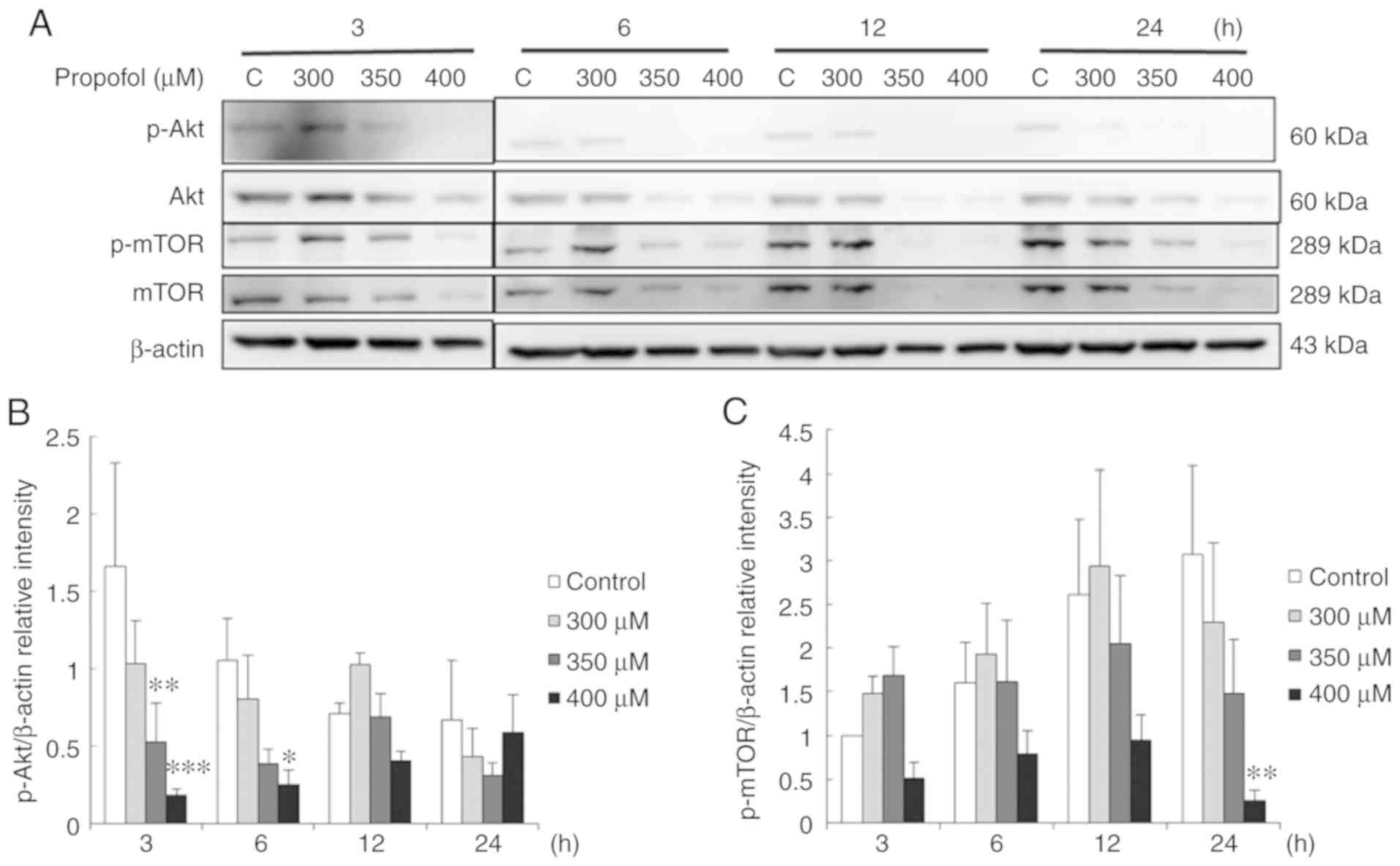
|
1
|
Busettini C and Frolich MA: Effects of
mild to moderate sedation on saccadic eye movements. Behav Brain
Res. 272:286–302. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jiang C, Logan S, Yan Y, Inagaki Y, Arzua
T, Ma P, Lu S, Bosnjak ZJ and Bai X: Signaling network between the
dysregulated expression of microRNAs and mRNAs in propofol-induced
developmental neurotoxicity in mice. Sci Rep. 8:141722018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Logan S, Jiang C, Yan Y, Inagaki Y, Arzua
T and Bai X: Propofol alters long non-coding RNA profiles in the
neonatal mouse hippocampus: Implication of novel mechanisms in
anesthetic-induced developmental neurotoxicity. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 49:2496–2510. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yan Y, Qiao S, Kikuchi C, Zaja I, Logan S,
Jiang C, Arzua T and Bai X: Propofol induces apoptosis of neurons
but not astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, or neural stem cells in the
neonatal mouse hippocampus. Brain Sci. 7:E1302017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Davidoff MS, Schulze W, Middendorff R and
Holstein AF: The leydig cell of the human testis-a new member of
the diffuse neuroendocrine system. Cell Tissue Res. 271:429–439.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Habert R, Lejeune H and Saez JM: Origin,
differentiation and regulation of fetal and adult leydig cells. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 179:47–74. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen H, Ge RS and Zirkin BR: Leydig cells:
From stem cells to aging. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 306:9–16. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu FX and Guan K: The Hippo pathway:
Regulators and regulations. Genes Dev. 27:355–371. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P,
Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, El-Deiry WS,
Golstein P and Green DR: et al Classification of cell death:
Recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2009.
Cell Death Differ. 16:3–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Oliveira JB and Gupta S: Disorders of
apoptosis: Mechanisms for autoimmunity in primary immunodeficiency
diseases. J Clin Immunol. 1(Suppl 28): S20–S28. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lewis-Wambi JS and Jordan VC: Estrogen
regulation of apoptosis: How can one hormone stimulate and inhibit?
Breast Cancer Res. 11:2062009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cossarizza A, Baccarani-Contri M,
Kalashnikova G and Franceschi C: A new method for the
cytofluorimetric analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential using
the J-aggregate forming lipophilic cation
5,5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethyl-benzimidazolcarbocyanine
iodide (JC-1). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 197:40–45. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Son Y, Cheong YK, Kim NH, Chung HT, Kang
DG and Pae HO: Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive
oxygen species: How can ROS activate MAPK pathways? J Signal
Transduct. 2011:7926392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Markman B, Dienstmann R and Tabernero J:
Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway-beyond rapalogs. Oncotarget.
1:530–543. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hein AL, Ouellette MM and Yan Y:
Radiation-induced signaling pathways that promote cancer cell
survival (review). Int J Oncol. 45:1813–1819. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou C, Zhao XM, Li XF, Wang C, Zhang XT,
Liu XZ, Ding XF, Xiang SL and Zhang J: Curcumin inhibits
AP-2γ-induced apoptosis in the human malignant testicular germ
cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 34:1192–1200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Geigerseder C, Doepner RF, Thalhammer A,
Krieger A and Mayerhofer A: Stimulation of TM3 Leydig cell
proliferation via GABA(A) receptors: A new role for testicular
GABA. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2:132004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Goldenberg RC, Fortes FS, Cristancho JM,
Morales MM, Franci CR, Varanda WA and Campos de Carvalho AC:
Modulation of gap junction mediated intercellular communication in
TM3 leydig cells. J Endocrinol. 177:327–335. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mather JP: Establishment and
characterization of two distinct mouse testicular epithelial cell
lines. Biol Reprod. 23:243–252. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Green LM, Reade JL and Ware CF: Rapid
colorimetric assay for cell viability: Application to the
quantitation of cytotoxic and growth inhibitory lymphokines. J
Immunol Methods. 70:257–268. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chang MM, Lai MS, Hong SY, Pan BS, Huang
H, Yang SH, Wu CC, Sun HS, Chuang JI, Wang CY and Huang BM:
FGF9/FGFR2 increase cell proliferation by activating ERK1/2,
Rb/E2F1 and cell cycle pathways in mouse leydig tumor cells. Cancer
Sci. 109:3503–3518. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kang FC, Wang SC, Chang MM, Pan BS, Wong
KL, Cheng KS, So EC and Huang BM: Midazolam activates caspase,
MAPKs and endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways, and inhibits cell
cycle and Akt pathway, to induce apoptosis in TM3 mouse leydig
progenitor cells. Onco Targets Ther. 11:1475–1490. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kang FC, Wang SC, So EC, Chang MM, Wong
KL, Cheng KS, Chen YC and Huang BM: Propofol could increase
caspases and MAPKs pathways and suppress Akt pathway to induce
apoptosis in MA-10 mouse leydig tumor cells. Oncol Rep.
41:3565–3574. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mu YF, Chen YH, Chang MM, Chen YC and
Huang BM: Arsenic compounds induce apoptosis through the caspase
pathway in MA-10 leydig tumor cells. Oncol Lett. 18:944–954.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
van Engeland M, Ramaekers FC, Schutte B
and Reutelingsperger CP: A novel assay to measure loss of plasma
membrane asymmetry during apoptosis of adherent cells in culture.
Cytometry. 24:131–139. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Creagh EM and Martin SJ: Caspases:
Cellular demolition experts. Biochem Soc Trans. 29:696–702. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu D, Jiang Y, Gao J, Liu B and Chen P:
Repeated exposure to propofol potentiates neuroapoptosis and
long-term behavioral deficits in neonatal rats. Neurosci Lett.
534:41–46. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Taylor RC, Cullen SP and Martin SJ:
Apoptosis: Controlled demolition at the cellular level. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:231–241. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Paul-Samojedny M, Suchanek R, Borkowska P,
Pudelko A, Owczarek A, Kowalczyk M, Machnik G, Fila-Danilow A and
Kowalski J: Knockdown of AKT3 (PKBγ) and PI3KCA suppresses cell
viability and proliferation and induces the apoptosis of
glioblastoma multiforme T98G cells. Biomed Res Int.
2014:7681812014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhang C, Chen Z, Zhou X, Xu W, Wang G,
Tang X, Luo L, Tu J, Zhu Y and Hu W: et al Cantharidin induces G2/M
phase arrest and apoptosis in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 and
BGC-823 cells. Oncol Lett. 8:2721–2726. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin MC, Chen CL, Yang TT, Choi PC, Hsing
CH and Lin CF: Anesthetic propofol overdose causes endothelial
cytotoxicity in vitro and endothelial barrier dysfunction in vivo.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 265:253–262. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lee JM, Lee JM, Kim KR, Im H and Kim YH:
Zinc preconditioning protects against neuronal apoptosis through
the mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated induction of heat
shock protein 70. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 459:220–226. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shen Y, Yang J, Zhao J, Xiao C, Xu C and
Xiang Y: The switch from ER stress-induced apoptosis to autophagy
via ROS-mediated JNK/p62 signals: A survival mechanism in
methotrexate-resistant choriocarcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res.
334:207–218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tang D, Wu D, Hirao A, Lahti JM, Liu L,
Mazza B, Kidd VJ, Mak TW and Ingram AJ: ERK activation mediates
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis after DNA damage independently of
p53. J Biol Chem. 277:12710–12717. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lin X, Fang Q, Chen S, Zhe N, Chai Q, Yu
M, Zhang Y, Wang Z and Wang J: Heme oxygenase-1 suppresses the
apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells via the JNK/c-JUN
signaling pathway. Leuk Res. 39:544–552. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang B, Wu T, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Wang J,
Yang B, Zhao Y, Rao Z and Gao J: p38MAPK activation mediates tumor
necrosis factor-α-induced apoptosis in glioma cells. Mol Med Rep.
11:3101–3107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wu KC, Yang ST, Hsia TC, Yang JS, Chiou
SM, Lu CC, Wu RS and Chung JG: Suppression of cell invasion and
migration by propofol are involved in down-regulating matrix
metal-loproteinase-2 and p38 MAPK signaling in A549 human lung
adenocarcinoma epithelial cells. Anticancer Res. 32:4833–4842.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li D, Wang C, Li N and Zhang L: Propofol
selectively inhibits nuclear factor-κB activity by suppressing p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in human EA.hy926
endothelial cells during intermittent hypoxia/reoxygenation. Mol
Med Rep. 9:1460–1466. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hsing CH, Chen YH, Chen CL, Huang WC, Lin
MC, Tseng PC, Wang CY, Tsai CC, Choi PC and Lin CF: Anesthetic
propofol causes glycogen synthase kinase-3β-regulated
lysosomal/mitochondrial apoptosis in macrophages. Anesthesiology.
116:868–881. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sun X, Gu J, Chi M, Li M, Lei S and Wang
G: Activation of PI3K-Akt through taurine is critical for propofol
to protect rat cardiomyocytes from doxorubicin-induced toxicity.
Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 92:155–161. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|