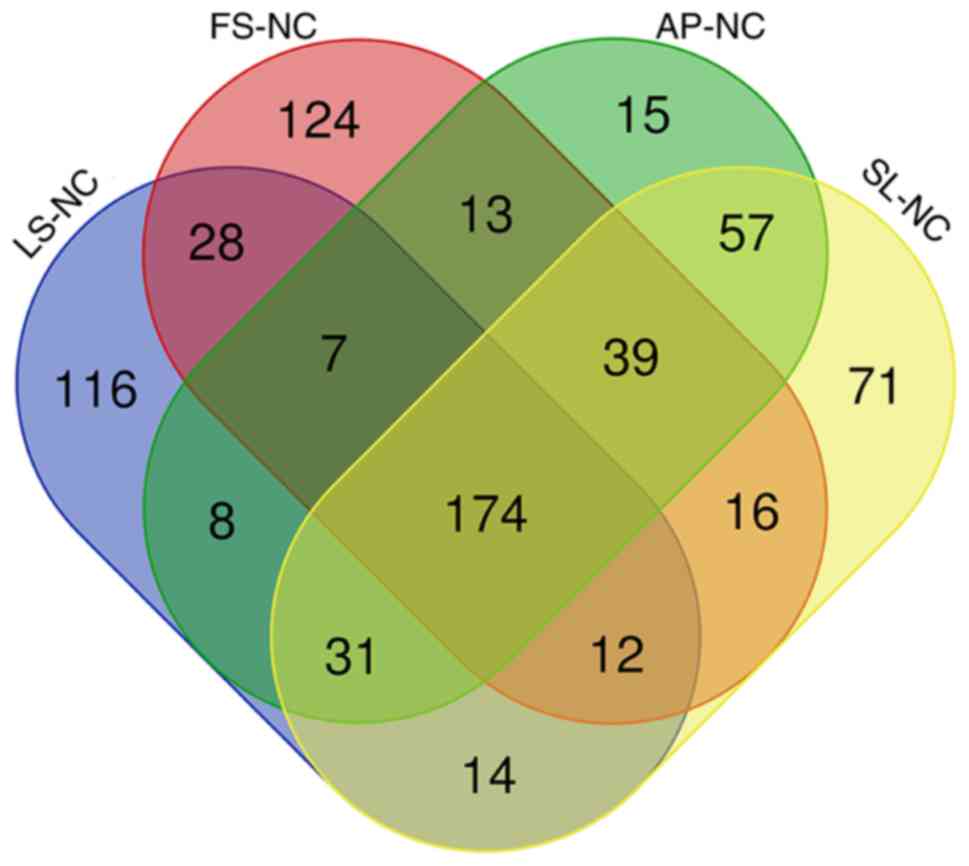
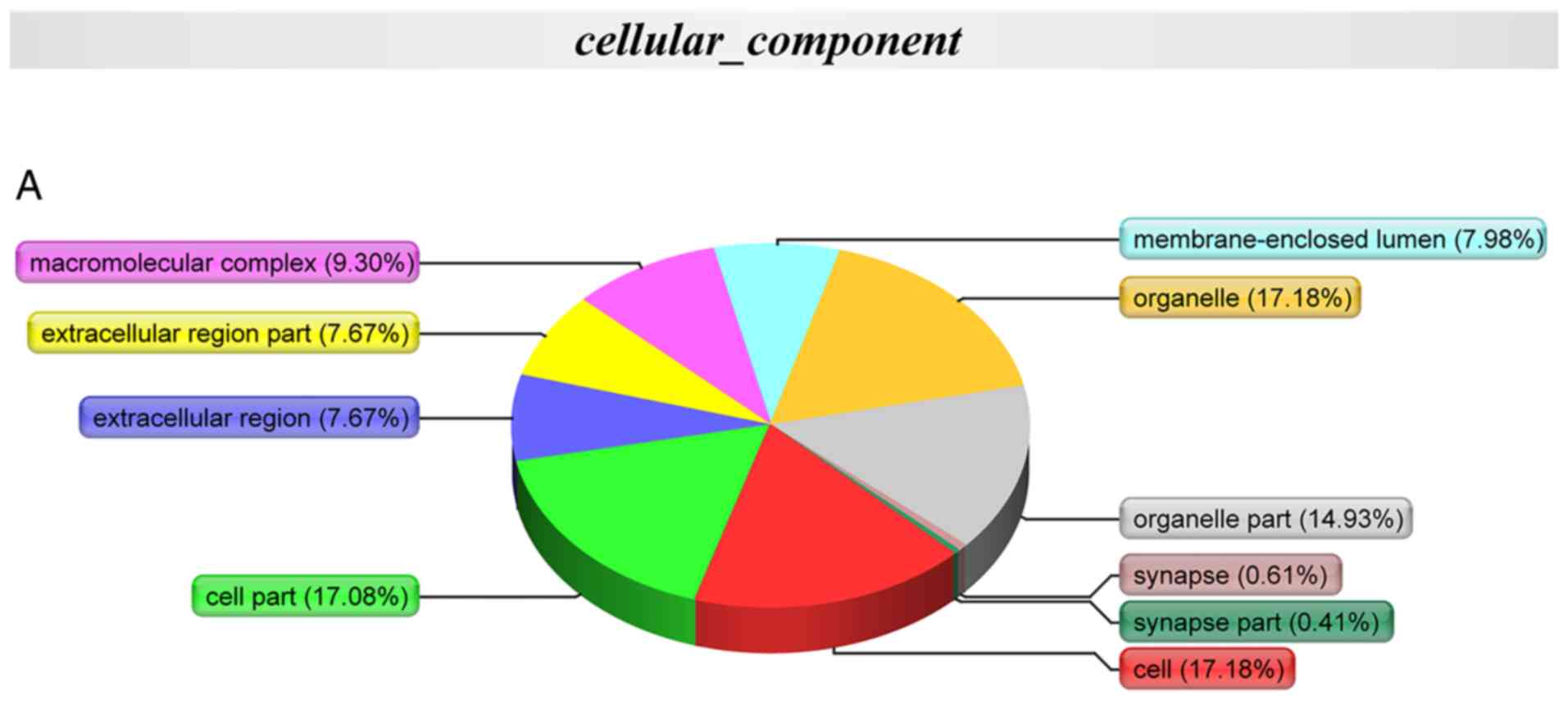
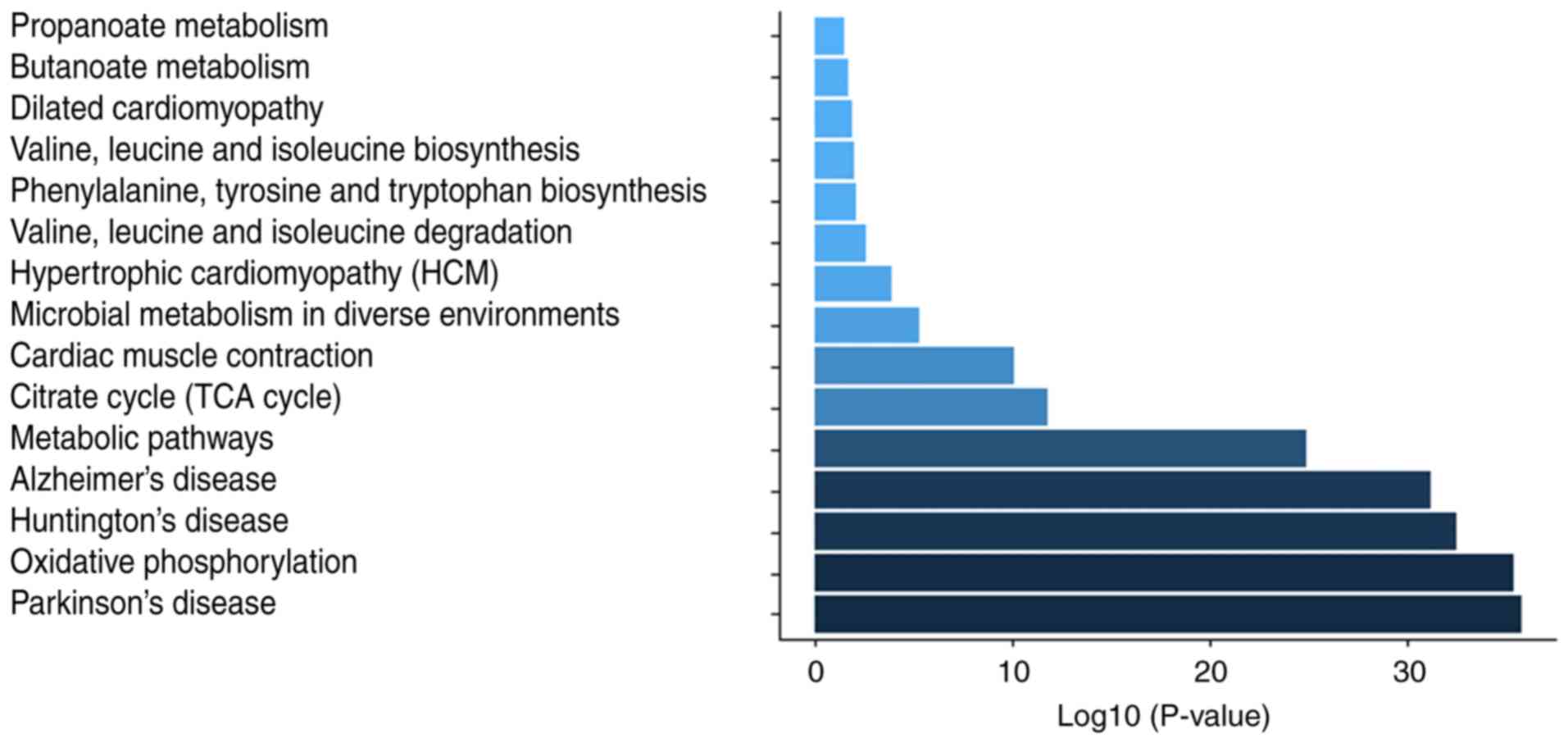
|
1
|
Lobingier BT, Hüttenhain R, Eichel K,
Miller KB, Ting AY, von Zastrow M and Krogan NJ: An Approach to
spatiotemporally resolve protein interaction networks in living
cells. Cell. 169:350–360.e12. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thul PJ, Åkesson L, Wiking M, Mahdessian
D, Geladaki A, Ait Blal H, Alm T, Asplund A, Björk L, Breckels LM,
et al: A subcellular map of the human proteome. Science.
356:eaal33212017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Van Rooden EJ, Florea BI, Deng H,
Baggelaar MP, van Esbroeck ACM, Zhou J, Overkleeft HS and van der
Stelt M: Mapping in vivo target interaction profiles of covalent
inhibitors using chemical proteomics with label-free
quantification. Nat Protoc. 13:752–767. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li KS, Shi L and Gross ML: Mass
spectrometry-based fast photochemical oxidation of proteins (FPOP)
for higher order structure characterization. Acc Chem Res.
51:736–744. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Distler U, Kuharev J, Navarro P and Tenzer
S: Label-free quantification in ion mobility-enhanced
data-independent acquisition proteomics. Nat Protoc. 11:795–812.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Herrington DM, Mao C, Parker SJ, Fu Z, Yu
G, Chen L, Venkatraman V, Fu Y, Wang Y, Howard TD, et al: Proteomic
architecture of human coronary and aortic atherosclerosis.
Circulation. 137:2741–2756. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bagnato C, Thumar J, Mayya V, Hwang SI,
Zebroski H, Claffey KP, Haudenschild C, Eng JK, Lundgren DH and Han
DK: Proteomics analysis of human coronary atherosclerotic plaque: A
feasibility study of direct tissue proteomics by liquid
chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics.
6:1088–1102. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stary HC: Natural history and histological
classification of atherosclerotic lesions: An update. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 20:1177–1178. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fernández-Coto DL, Gil J, Hernández A,
Herrera-Goepfert R, Castro-Romero I, Hernández-Márquez E,
Arenas-Linares AS, Calderon- Sosa VT, Sanchez-Aleman MÁ Mendez-,
Tenorio A, et al: Quantitative proteomics reveals proteins involved
in the progression from non-cancerous lesions to gastric cancer. J
Proteomics. 186:15–27. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tyanova S, Temu T and Cox J: The MaxQuant
computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun
proteomics. Nat Protoc. 11:2301–2319. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Aebersold R and Mann M: Mass
spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature. 422:198–207. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Florens L, Washburn MP, Raine JD, Anthony
RM, Grainger M, Haynes JD, Moch JK, Muster N, Sacci JB, Tabb DL, et
al: A proteomic view of the Plasmodium falciparum life cycle.
Nature. 419:520–526. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Koller A, Washburn MP, Lange BM, Andon NL,
Deciu C, Haynes PA, Hays L, Schieltz D, Ulaszek R, Wei J, et al:
Proteomic survey of metabolic pathways in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:11969–11974. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Washburn MP, Wolters D and Yates JR III:
Large-scale analysis of the yeast proteome by multidimensional
protein identification technology. Nat Biotechnol. 19:242–247.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun H, Wang D, Liu D, Guo Z, Shao C, Sun W
and Zeng Y: Differential urinary proteins to diagnose coronary
heart disease based on iTRAQ quantitative proteomics. Anal Bioanal
Chem. 411:2273–2282. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li SM, Liu WT, Yang F, Yi QJ, Zhang S and
Jia HL: Phosphorylated proteomics analysis of human coronary artery
endothelial cells stimulated by Kawasaki disease patients serum.
BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 19:212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Anwar MA, Dai DL, Wilson-McManus J, Smith
D, Francis GA, Borchers CH, McManus BM, Hill JS and Cohen Freue GV:
Multiplexed LC-ESI-MRM-MS-based assay for identification of
coronary artery disease biomarkers in human plasma. Proteomics Clin
Appl. 11:e17001112019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Taanman JW: The mitochondrial genome:
Structure, transcription, translation and replication. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1410:103–123. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ait-Aissa K, Blaszak SC, Beutner G, Tsaih
SW, Morgan G, Santos JH, Flister MJ, Joyce DL, Camara AKS,
Gutterman DD, et al: Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation defect
in the heart of subjects with coronary artery disease. Sci Rep.
9:76232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mercer JR, Cheng KK, Figg N, Gorenne I,
Mahmoudi M, Griffin J, Vidal-Puig A, Logan A, Murphy MP and Bennett
M: DNA damage links mitochondrial dysfunction to atherosclerosis
and the metabolic syndrome. Circ Res. 107:1021–1031. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sergin I, Evans TD, Zhang X, Bhattacharya
S, Stokes CJ, Song E, Ali S, Dehestani B, Holloway KB, Micevych PS,
et al: Exploiting macrophage autophagy-lysosomal biogenesis as a
therapy for atherosclerosis. Nat Commun. 8:157502017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|