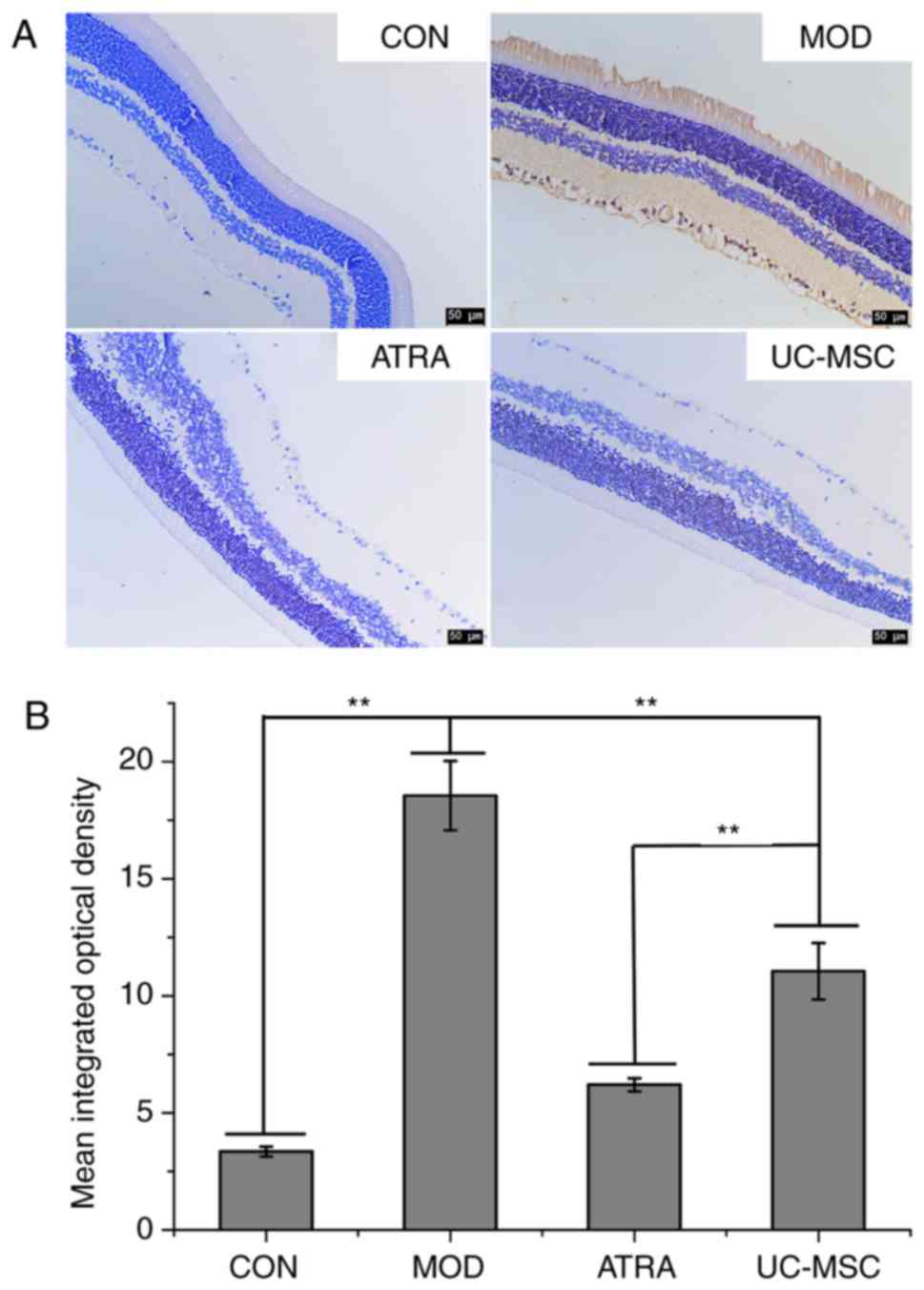
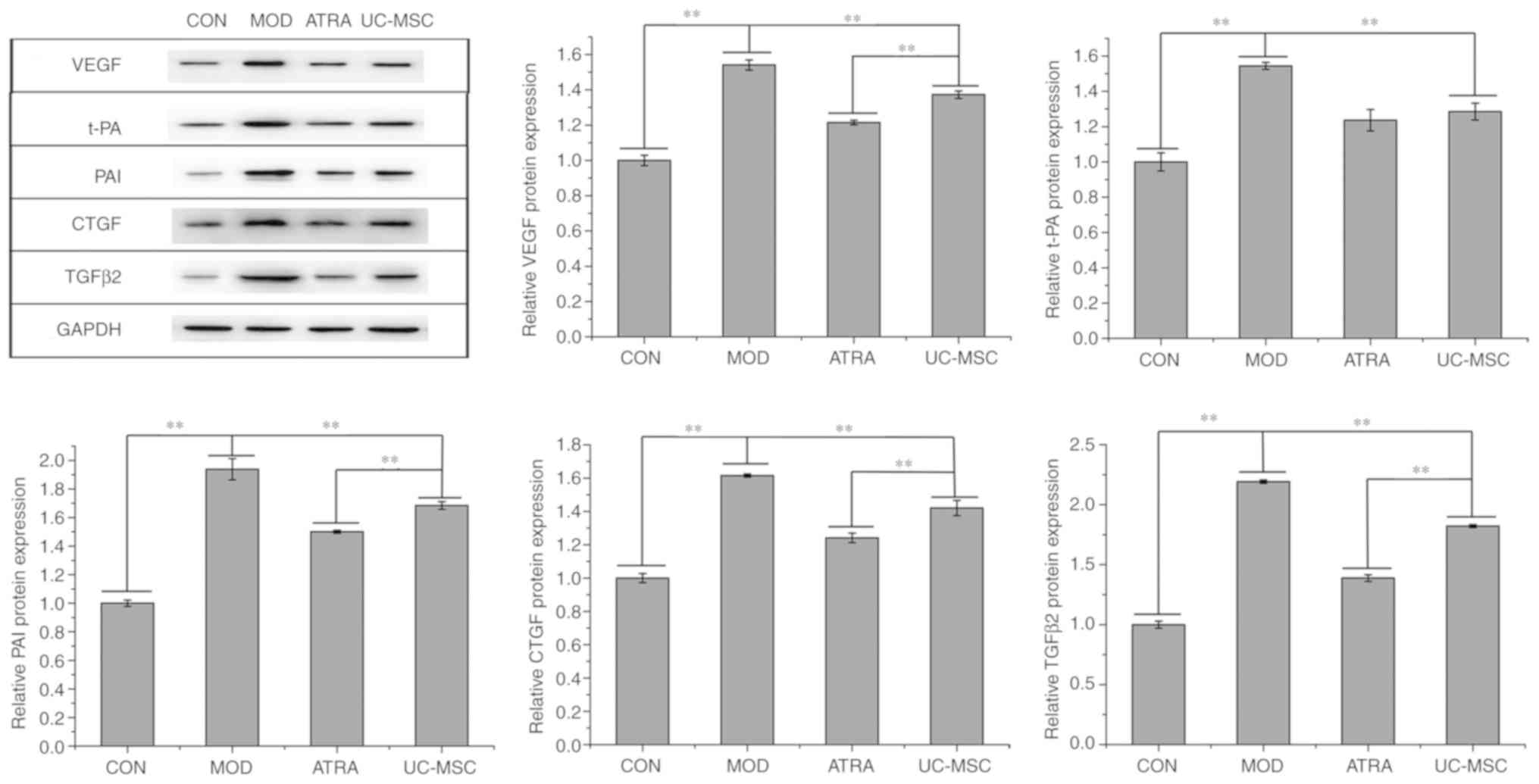
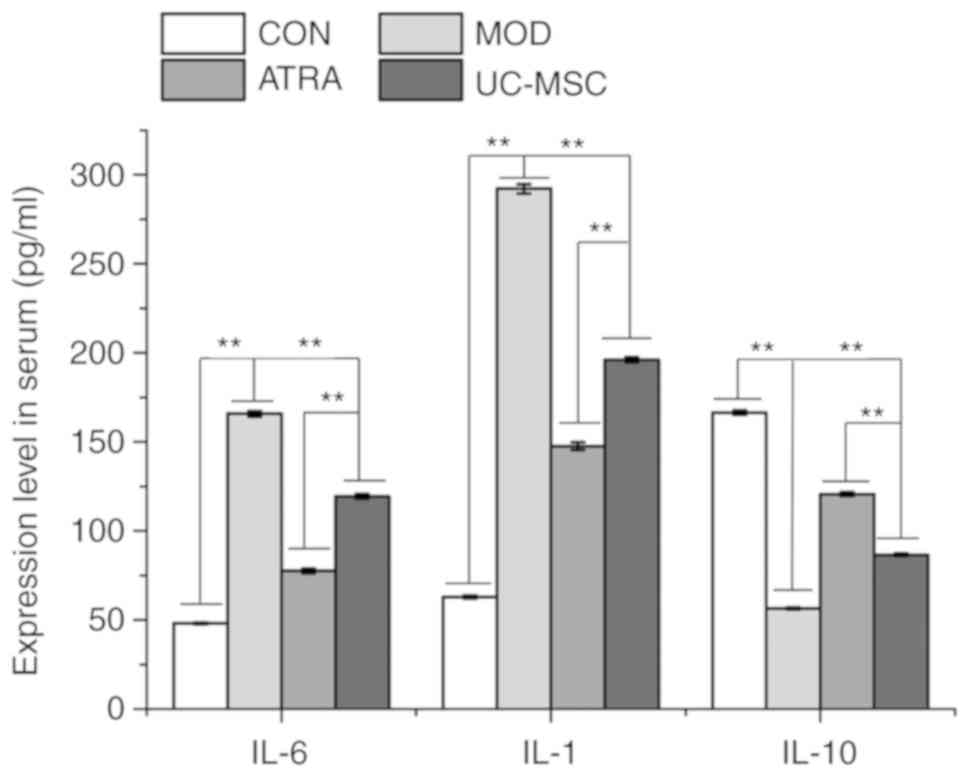
|
1
|
Fiori A, Terlizzi V, Kremer H, Gebauer J,
Hammes HP, Harmsen MC and Bieback K: Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells
as potential therapy in diabetic retinopathy. Immunobiology.
223:729–743. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C and Shaw
J: IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates of the prevalence of
diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 94:311–321.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yau JW, Rogers SL, Kawasaki R, Lamoureux
EL, Kowalski JW, Bek T, Chen SJ, Dekker JM, Fletcher A, Grauslund
J, et al: Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic
retinopathy. Diabetes Care. 35:556–564. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Selvaraj K, Gowthamarajan K, Karri VV,
Barauah UK, Ravisankar V and Jojo GM: Current treatment strategies
and nanocarrier based approaches for the treatment and management
of diabetic retinopathy. J Drug Target. 25:386–405. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang C, Xu Y, Tan HY, Li S, Wang N, Zhang
Y and Feng Y: Neuroprotective effect of He-Ying-Qing-Re formula on
retinal ganglion cell in diabetic retinopathy. J Ethnopharmacol.
214:179–189. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ding DC, Shyu WC and Lin SZ: Mesenchymal
stem cells. Cell Transplant. 20:5–14. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nagamura-Inoue T and He H: Umbilical
cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Their advantages and potential
clinical utility. World J Stem Cells. 6:195–202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gu X, Yu X, Zhao C, Duan P, Zhao T, Liu Y,
Li S, Yang Z, Li Y, Qian C, et al: Efficacy and safety of
autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in
patients with diabetic retinopathy. Cell Physiol Biochem. 49:40–52.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang J, Zhang W, He GH, Wu B and Chen S:
Transfection with CXCR4 potentiates homing of mesenchymal stem
cells in vitro and therapy of diabetic retinopathy in vivo. Int J
Ophthalmol. 11:766–772. 2018.
|
|
10
|
Scalinci SZ, Scorolli L, Corradetti G,
Domanico D, Vingolo EM, Meduri A, Bifani M and Siravo D: Potential
role of intravitreal human placental stem cell implants in
inhibiting progression of diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes:
Neuroprotective growth factors in the vitreous. Clin Ophthalmol.
5:691–696. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang Z, Li K, Yan X, Dong F and Zhao C:
Amelioration of diabetic retinopathy by engrafted human
adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in streptozotocin diabetic
rats. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 248:1415–1422. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hsieh JY, Wang HW, Chang SJ, Liao KH, Lee
IH, Lin WS, Wu CH, Lin WY and Cheng SM: Mesenchymal stem cells from
human umbilical cord express preferentially secreted factors
related to neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis. PLoS
One. 8:e726042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang W, Wang Y, Kong J, Dong M, Duan H
and Chen S: Therapeutic efficacy of neural stem cells originating
from umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in diabetic
retinopathy. Sci Rep. 7:4082017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mottaghi S, Larijani B and Sharifi AM:
Atorvastatin: An efficient step forward in mesenchymal stem cell
therapy of diabetic retinopathy. Cytotherapy. 15:263–266. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Siddikuzzaman, Guruvayoorappan C and
Berlin Grace VM: All trans retinoic acid and cancer.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 33:241–249. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gong M, Bi Y, Jiang W, Zhang Y, Chen L,
Hou N, Chen J and Li T: Retinoic acid receptor beta mediates
all-trans retinoic acid facilitation of mesenchymal stem cells
neuronal differentiation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:866–875.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tanaka K, Tamiya-Koizumi K, Hagiwara K,
Ito H, Takagi A, Kojima T, Suzuki M, Iwaki S, Fujii S, Nakamura M,
et al: Role of down-regulated neutral ceramidase during all-trans
retinoic acid-induced neuronal differentiation in SH-SY5Y
neuroblastoma cells. J Biochem. 151:611–620. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Murashov AK, Pak ES, Hendricks WA, Owensby
JP, Sierpinski PL, Tatko LM and Fletcher PL: Directed
differentiation of embryonic stem cells into dorsal interneurons.
FASEB J. 19:252–254. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xi J and Yang Z: Expression of RALDHs
(ALDH1As) and CYP26s in human tissues and during the neural
differentiation of P19 embryonal carcinoma stem cell. Gene Expr
Patterns. 8:438–442. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pourjafar M, Saidijam M, Etemadi K and
Najafi R: All-trans retinoic acid enhances in vitro mesenchymal
stem cells migration by targeting matrix metalloproteinases 2 and
9. Biotechnol Lett. 39:1263–1268. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jin W, Xu YP, Yang AH and Xing YQ: In
vitro induction and differentiation of umbilical cord mesenchymal
stem cells into neuron-like cells by all-trans retinoic acid. Int J
Ophthalmol. 8:250–256. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yin Y, Chen F, Wang W, Wang H and Zhang X:
Resolvin D1 inhibits inflammatory response in STZ-induced diabetic
retinopathy rats: Possible involvement of NLRP3 inflammasome and
NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol Vis. 23:242–250. 2017.
|
|
23
|
Jenkins AJ, Joglekar MV, Hardikar AA,
Keech AC, O'Neal DN and Januszewski AS: Biomarkers in diabetic
retinopathy. Rev Diabet Stud. 12:159–195. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xie X, Peng J, Huang K, Huang J, Shen X,
Liu P and Huang H: Polydatin ameliorates experimental
diabetes-induced fibronectin through inhibiting the activation of
NF-κB signaling pathway in rat glomerular mesangial cells. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 362:183–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fu X, Li S, Zhou S, Wu Q, Jin F and Shi J:
Stimulatory effect of icariin on the proliferation of neural stem
cells from rat hippo-campus. BMC Complement Altern Med. 18:342018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ding SSL, Subbiah SK, Khan MSA, Farhana A
and Mok PL: Empowering mesenchymal stem cells for ocular
degenerative disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 20:pii: E1784. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yue X, Zhifeng G, Biyu S, Guofeng X,
Tianqiu Z, Jinxia J, Jing X, Suzhe L, Man L, Wei T, et al: Roles of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in retinal neuron-like differentiation of
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from nonobese diabetic mice. J
Mol Neurosci. 49:250–261. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wu W, Lei H, Shen J and Tang L: The role
of netrin-1 in angiogenesis and diabetic retinopathy: A promising
therapeutic strategy. Discov Med. 23:315–323. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gardlik R and Fusekova I: Pharmacologic
therapy for diabetic retinopathy. Semin Ophthalmol. 30:252–263.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Khan AA, Rahmani AH and Aldebasi YH:
Diabetic retinopathy: Recent updates on different biomarkers and
some therapeutic agents. Curr Diabetes Rev. 14:523–533. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang SX and Ma JX: Ocular
neovascularization: Implication of endogenous angiogenic inhibitors
and potential therapy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 26:1–37. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Boyer DS, Hopkins JJ, Sorof J and Ehrlich
JS: Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy for diabetic
macular edema. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 4:151–169. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Stewart MW: Anti-vascular endothelial
growth factor drug treatment of diabetic macular edema: The
evolution continues. Curr Diabetes Rev. 8:237–246. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bahrami B, Hong T, Gilles MC and Chang A:
Anti-VEGF therapy for diabetic eye diseases. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol
(Phila). 6:535–545. 2017.
|
|
36
|
Wu SL, Zhan DM, Xi SH and He XL: Roles of
tissue plasminogen activator and its inhibitor in proliferative
diabetic retinopathy. Int J Ophthalmol. 7:764–767. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu S and He X: The correlation study of
the expression of VEGF with t-PA and PAI expression in plasma and
intraocular tissue in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Zhonghua
Yan Ke Za Zh. 50:448–453. 2014.In Chinese.
|
|
38
|
Zhang M, Chu S, Zeng F and Xu H:
Bevacizumab modulates the process of fibrosis in vitro. Clin Exp
Ophthalmol. 43:173–179. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Van Geest RJ, Lesnik-Oberstein SY, Tan HS,
Mura M, Goldschmeding R, Van Noorden CJ, Klaassen I and
Schlingemann RO: A shift in the balance of vascular endothelial
growth factor and connective tissue growth factor by bevacizumab
causes the angiofibrotic switch in proliferative diabetic
retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. 96:587–590. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kuiper EJ, Van Nieuwenhoven FA, de Smet
MD, van Meurs JC, Tanck MW, Oliver N, Klaassen I, Van Noorden CJ,
Goldschmeding R and Schlingemann RO: The angio-fibrotic switch of
VEGF and CTGF in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. PLoS One.
3:e26752008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang Q, Qi Y, Chen L, Shi X, Bai Y, Huang
L, Yu W, Jiang Y, Zhao M and Li X: The relationship between
anti-vascular endothelial growth factor and fibrosis in
proliferative retinopathy: Clinical and laboratory evidence. Br J
Ophthalmol. 100:1443–1450. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hu B, Zhang Y, Zeng Q, Han Q, Zhang L, Liu
M and Li X: Intravitreal injection of ranibizumab and CTGF shRNA
improves retinal gene expression and microvessel ultrastructure in
a rodent model of diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 15:1606–1624. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cheung N, Mitchell P and Wong TY: Diabetic
retinopathy. Lancet. 376:124–136. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Regmi S, Pathak S, Kim JO, Yong CS and
Jeong JH: Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for the treatment of
inflammatory diseases: Challenges, opportunities, and future
perspectives. Eur J Cell Biol. 98:1510412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Navarro-Gonzalez JF and Mora-Fernandez C:
The role of inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 19:433–442. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Petersen AM and Pedersen BK: The
anti-inflammatory effect of exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985).
98:1154–1162. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|