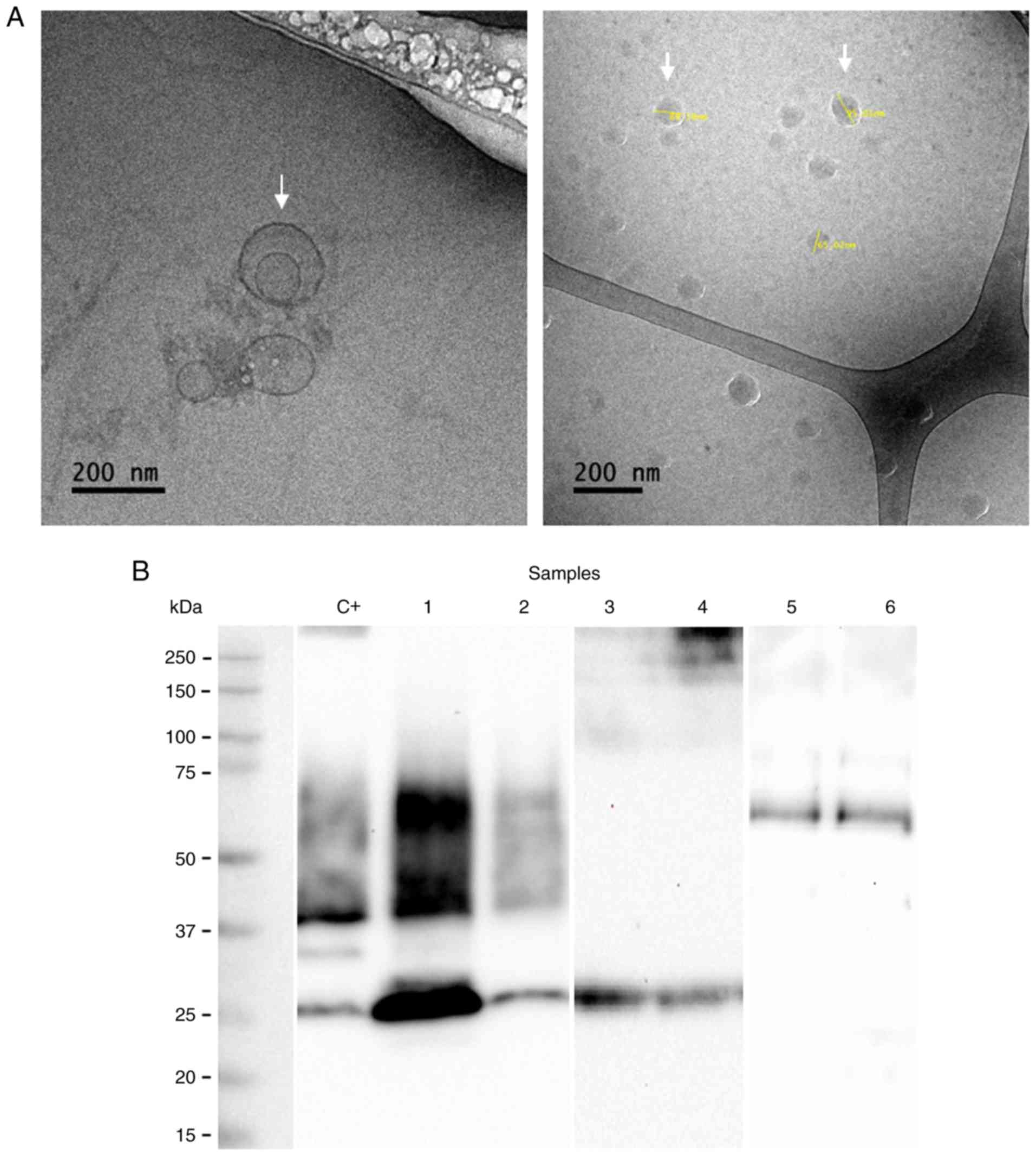
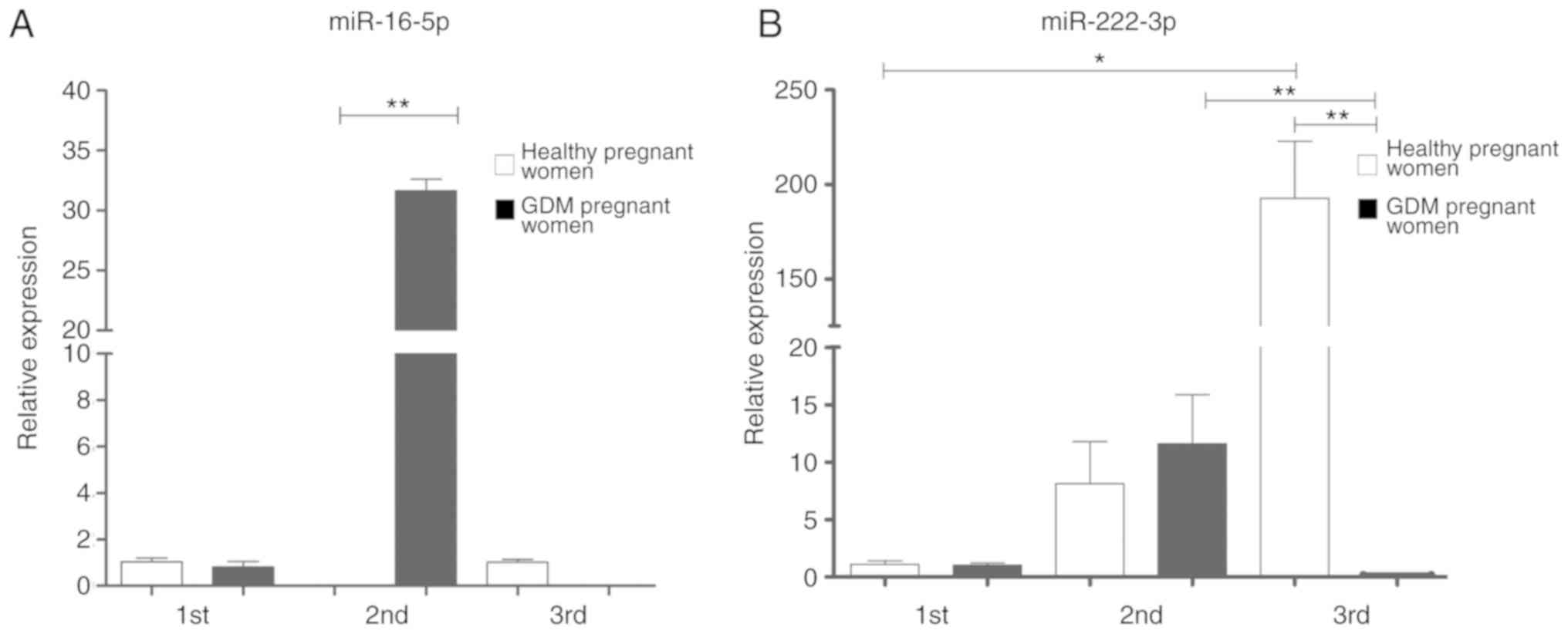
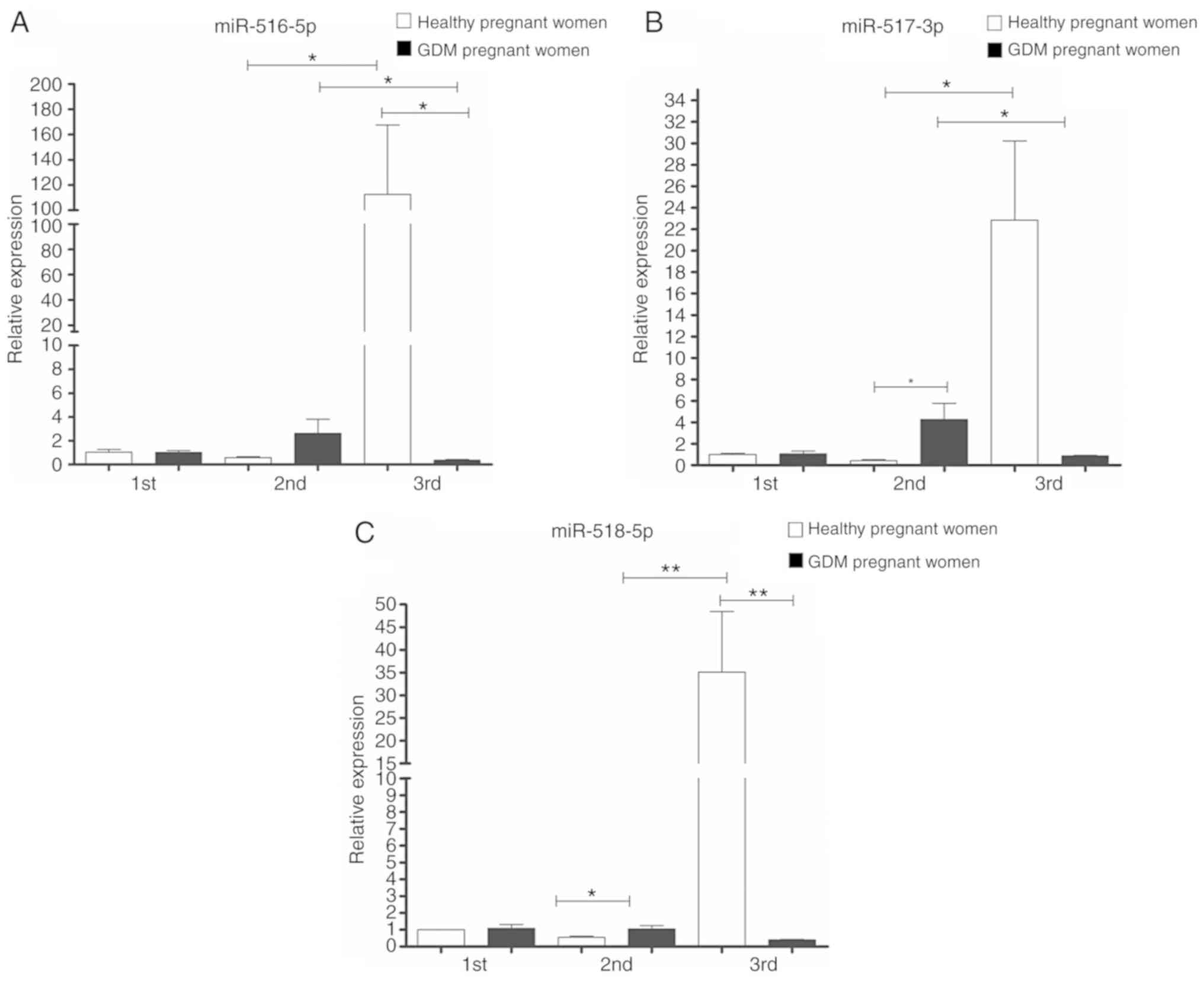
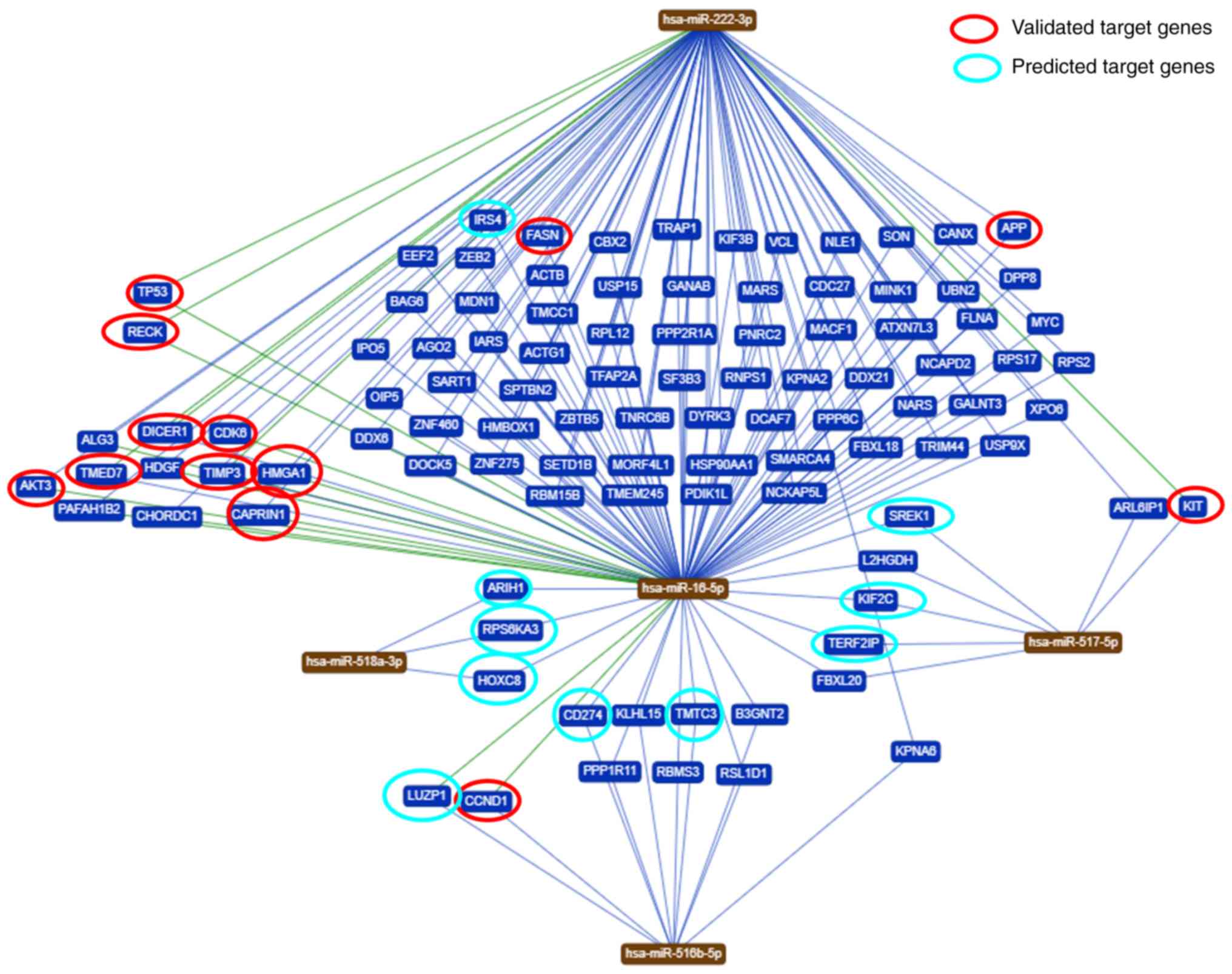
|
1
|
Basina M: Gestational diabetogenesis. J
Women's Health Care. 01:e1062012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sáez T, de Vos P, Sobrevia L and Faas MM:
Is there a role for exosomes in foetoplacental endothelial
dysfunction in gestational diabetes mellitus? Placenta. 61:48–54.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Powe CE: Early pregnancy biochemical
predictors of gestational diabetes mellitus. Curr Diab Rep.
17:122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rodrigo N and Glastras SJ: The emerging
role of biomarkers in the diagnosis of gestational diabetes
mellitus. J Clin Med. 7:1202018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Akgöl E, Abuşoğlu S, Gün FD and Ünlü A:
Prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus according to the
different criterias. Turk J Obstet Gynecol. 14:18–22. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Karcaaltincaba D, Calis P, Ocal N, Ozek A,
Altug Inan M and Bayram M: Prevalence of gestational diabetes
mellitus evaluated by universal screening with a 75-g,2-h oral
glucose tolerance test and IADPSG criteria. Int J Gynecol Obstet.
138:148–151. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ilekis JV, Tsilou E, Fisher S, Abrahams
VM, Soares MJ, Cross JC, Zamudio S, Illsley NP, Myatt L, Colvis C,
et al: Placental origins of adverse pregnancy outcomes: Potential
molecular targets: An executive workshop summary of the eunice
kennedy shriver national institute of child health and human
development. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 215(1 Suppl): S1–S46. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guarino E, Poggi CD, Grieco GE, Cenci V,
Ceccarelli E, Crisci I, Sebastiani G and Dotta F: Circulating
MicroRNAs as biomarkers of gestational diabetes mellitus: Updates
and perspectives. Int J Endocrinol. 2018:63804632018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kowal J, Tkach M and Théry C: Biogenesis
and secretion of exosomes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 29:116–125. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cuffe JSM, Holland O, Salomon C, Rice GE
and Perkins AV: Review: Placental derived biomarkers of pregnancy
disorders. Placenta. 54:104–110. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fu G, Brkić J, Hayder H and Peng C:
MicroRNAs in human placental development and pregnancy
complications. Int J Mol Sci. 14:5519–5544. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ouyang Y, Mouillet JF, Coyne CB and
Sadovsky Y: Review: Placenta-specific microRNAs in exosomes-good
things come in nano-packages. Placenta. 35(Suppl): S69–S73. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hromadnikova I, Kotlabova K, Ondrackova M,
Pirkova P, Kestlerova A, Novotna V, Hympanova L and Krofta L:
Expression profile of C19MC microRNAs in placental tissue in
pregnancy-related complications. DNA Cell Biol. 34:437–457. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu Y, Tian F, Li H, Zhou Y, Lu J and Ge
Q: Profiling maternal plasma microRNA expression in early pregnancy
to predict gestational diabetes mellitus. Int J Gynecol Obstet.
130:49–53. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Salomon C, Torres MJ, Kobayashi M,
Scholz-Romero K, Sobrevia L, Dobierzewska A, Illanes SE, Mitchell
MD and Rice GE: A gestational profile of placental exosomes in
maternal plasma and their effects on endothelial cell migration.
PLoS One. 9:e986672014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Salomon C, Scholz-Romero K, Sarker S,
Sweeney E, Kobayashi M, Correa P, Longo S, Duncombe G, Mitchell MD,
Rice GE and Illanes SE: Gestational diabetes mellitus is associated
with changes in the concentration and bioactivity of
placenta-derived exosomes in maternal circulation across gestation.
Diabetes. 65:598–609. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Diagnostic Criteria and Classification of
Hyperglycaemia First Detected in Pregnancy: A world health
organization guideline. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 103:341–363. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gonzales PA, Zhou H, Pisitkun T, Wang NS,
Star RA, Knepper MA and Yuen PS: Isolation and purification of
exosomes in urine. Methods Mol Biol. 641:89–99. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abdalla M: Comprehensive coverage of
exosomes purification and exosomal RNA isolation from different
types of liquid biopsies. https://www.exosome-rna.com/upcoming-webinar-comprehensive-coverage-of-exosome-purification-and-exosomal-rna-isolation-from-different-types-of-liquid-biopsies/.
Accessed April 15, 2019.
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kwon DN, Chang BS and Kim JH: MicroRNA
dysregulation in liver and pancreas of CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase null
mice disrupts insulin/PI3K-AKT signaling. Biomed Res Int.
2014:2363852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Spinetti G, Fortunato O, Caporali A,
Shantikumar S, Marchetti M, Meloni M, Descamps B, Floris I,
Sangalli E, Vono R, et al: MicroRNA-15a and MicroRNA-16 Impair
human circulating proangiogenic cell functions and are increased in
the proangiogenic cells and serum of patients with critical limb
ischemia. Circ Res. 112:335–346. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Kaddar T, Rouault JP, Chien WW, Chebel A,
Gadoux M, Salles G, Ffrench M and Magaud JP: Two new miR-16
targets: Caprin-1 and HMGA1, proteins implicated in cell
proliferation. Biol Cell. 101:511–524. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Palmieri D, D'Angelo D, Valentino T, De
Martino I, Ferraro A, Wierinckx A, Fedele M, Trouillas J and Fusco
A: Downregulation of HMGA-targeting microRNAs has a critical role
in human pituitary tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 31:3857–3865. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu Q, Fu H, Sun F, Zhang H, Tie Y, Zhu J,
Xing R, Sun Z and Zheng X: MiR-16 family induces cell cycle arrest
by regulating multiple cell cycle genes. Nucleic Acids Res.
36:5391–5404. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yin Y, Stephen CW, Luciani MG and Fåhraeus
R: p53 stability and activity is regulated by Mdm2-mediated
induction of alter-native p53 translation products. Nat Cell Biol.
4:462–467. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Marcel V, Perrier S, Aoubala M, Ageorges
S, Groves MJ, Diot A, Fernandes K, Tauro S and Bourdon JC: Δ160p53
is a novel N-terminal p53 isoform encoded by Δ133p53 transcript.
FEBS Lett. 584:4463–4468. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu Y, Xia Y, Niu H and Chen Y: MiR-16
induced the suppression of cell apoptosis while promote
proliferation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 33:1340–1348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Parsi S, Smith PY, Goupil C, Dorval V and
Hébert SS: Preclinical evaluation of miR-15/107 family members as
multifactorial drug targets for Alzheimer's disease. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 4:e2562015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bandi N, Zbinden S, Gugger M, Arnold M,
Kocher V, Hasan L, Kappeler A, Brunner T and Vassella E: MiR-15a
and miR-16 are implicated in cell cycle regulation in a
Rb-Dependent manner and are frequently deleted or down-regulated in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 69:5553–5559. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bonci D, Coppola V, Musumeci M, Addario A,
Giuffrida R, Memeo L, D'Urso L, Pagliuca A, Biffoni M, Labbaye C,
et al: The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by
targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat Med. 14:1271–1277.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lerner M, Harada M, Lovén J, Castro J,
Davis Z, Oscier D, Henriksson M, Sangfelt O, Grandér D and Corcoran
MM: DLEU2, frequently deleted in malignancy, functions as a
critical host gene of the cell cycle inhibitory microRNAs miR-15a
and miR-16-1. Exp Cell Res. 315:2941–2952. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sebastiani G, Guarino E, Grieco GE,
Formichi C, Poggi CD, Ceccarelli E and Dotta F: Circulating
microRNA (miRNA) expression profiling in plasma of patients with
gestational diabetes mellitus reveals upregulation of miRNA
miR-330-3p. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 8:3452017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Koralewska N, Ciechanowska K, Pokornowska
M, Figlerowicz M and Kurzyńska-Kokorniak A: Human ribonuclease
Dicer-structure and functions. Postepy Biochem. 65:173–182. 2019.In
Polish. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Doyle SL, Husebye H, Connolly DJ, Espevik
T, O'Neill LA and McGettrick AF: The GOLD domain-containing protein
TMED7 inhibits TLR4 signalling from the endosome upon LPS
stimu-lation. Nat Commun. 3:7072012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Füllekrug J, Suganuma T, Tang BL, Hong W,
Storrie B and Nilsson T: Localization and recycling of gp27
(hp24gamma3): Complex formation with other p24 family members. Mol
Biol Cell. 10:1939–1955. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wisniewska M, Goettig P, Maskos K,
Belouski E, Winters D, Hecht R, Black R and Bode W: Structural
determinants of the ADAM inhibition by TIMP-3: Crystal structure of
the TACE-N-TIMP-3 complex. J Mol Biol. 381:1307–1319. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kotronis K, Zafrakas M, Papasozomenou P,
Timologou A, Miliaras D, Tarlatzis BC and Grimbizis G: Protein
expression pattern of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3
(TIMP3) in endometriosis and normal endometrium. Gynecol
Endocrinol. 35:1103–1106. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Felicetti F, Errico MC, Bottero L,
Segnalini P, Stoppacciaro A, Biffoni M, Felli N, Mattia G, Petrini
M, Colombo MP, et al: The Promyelocytic leukemia zinc
Finger-MicroRNA-221/-222 pathway controls melanoma progression
through multiple oncogenic mechanisms. Cancer Res. 68:2745–2754.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Felicetti F, Errico MC, Segnalini P,
Mattia G and Carè A: MicroRNA-221 and -222 pathway controls
melanoma progression. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 8:1759–1765.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Garofalo M, Quintavalle C, Di Leva G,
Zanca C, Romano G, Taccioli C, Liu CG, Croce CM and Condorelli G:
MicroRNA signatures of TRAIL resistance in human non-small cell
lung cancer. Oncogene. 27:3845–3855. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
He H, Jazdzewski K, Li W, Liyanarachchi S,
Nagy R, Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu C G, Franssila K, Suster S, et al:
The role of microRNA genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:19075–19080. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Felli N, Fontana L, Pelosi E, Botta R,
Bonci D, Facchiano F, Liuzzi F, Lulli V, Morsilli O, Santoro S, et
al: MicroRNAs 221 and 222 inhibit normal erythropoiesis and
erythroleukemic cell growth via kit receptor down-modulation. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:18081–18086. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gits CM, van Kuijk PF, Jonkers MB, Boersma
AW, van Ijcken WF, Wozniak A, Sciot R, Rutkowski P, Schöffski P,
Taguchi T, et al: MiR-17-92 and miR-221/222 cluster members target
KIT and ETV1 in human gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Br J
Cancer. 109:1625–1635. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hafner M, Landthaler M, Burger L, Khorshid
M, Hausser J, Berninger P, Rothballer A, Ascano M Jr, Jungkamp AC,
Munschauer M, et al: Transcriptome-wide identification of
RNA-Binding protein and MicroRNA target sites by PAR-CLIP. Cell.
141:129–141. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Elmehdawi F, Wheway G, Szymanska K, Adams
M, High AS, Johnson CA and Robinson PA: Human homolog of drosophila
ariadne (HHARI) is a marker of cellular proliferation associated
with nuclear bodies. Exp Cell Res. 319:161–172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
von Stechow L, Typas D, Carreras Puigvert
J, Oort L, Siddappa R, Pines A, Vrieling H, van de Water B,
Mullenders LH and Danen EH: The E3 Ubiquitin ligase ARIH1 protects
against genotoxic stress by initiating a 4EHP-Mediated mRNA
translation arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 35:1254–1268. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kishore S, Jaskiewicz L, Burger L, Hausser
J, Khorshid M and Zavolan M: A quantitative analysis of CLIP
methods for identifying binding sites of RNA-binding proteins. Nat
Methods. 8:559–564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kennedy SA, Jarboui MA, Srihari S, Raso C,
Bryan K, Dernayka L, Charitou T, Bernal-Llinares M,
Herrera-Montavez C, Krstic A, et al: Extensive rewiring of the EGFR
network in colorectal cancer cells expressing transforming levels
of KRASG13D. Nat Commun. 11:4992020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Shen N, Liu Y, Zhang K, Lyu Y, Gao M, Ma
J, Xu L and Gai Z: Analysis of RPS6KA3 gene mutation in a Chinese
pedigree affected with coffinlowry syndrome. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi
Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 36:798–800. 2019.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang J, Yang M, Li D, Zhu S, Zou J, Xu S,
Wang Y, Shi J and Li Y: Homeobox C8 is a transcriptional repressor
of E-cadherin gene expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 114:1055572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gong C, Zou J, Zhang M, Zhang J, Xu S, Zhu
S, Yang M, Li D, Wang Y, Shi J and Li Y: Upregulation of MGP by
HOXC8 promotes the proliferation, migration, and EMT processes of
triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Carcinog. 58:1863–1875. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Fang X and Yan R: MiR-152 inhibits the
proliferation and invasion of chordoma cells by targeting HOXC8. J
Int Med Res. 47:5185–5193. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gottwein E, Corcoran DL, Mukherjee N,
Skalsky RL, Hafner M, Nusbaum JD, Shamulailatpam P, Love CL, Dave
SS, Tuschl T, et al: Viral MicroRNA targetome of KSHV-Infected
primary effusion lymphoma cell lines. Cell Host Microbe.
10:515–526. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat
Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
The Gene Ontology Consortium: The gene
ontology resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids
Res. 47:D330–D338. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
57
|
Cheng X, Veverka V, Radhakrishnan A,
Waters LC, Muskett FW, Morgan SH, Huo J, Yu C, Evans EJ, Leslie AJ,
et al: Structure and interactions of the human programmed cell
death 1 receptor. J Biol Chem. 288:11771–11785. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
He PX, Ma ZL, Han H, Zhang XY, Niu SH, Du
LN, Zheng YC and Liu HM: Expression of programmed death ligand 1
(PD-L1) is associated with metastasis and differentiation in
gastric cancer. Life Sci. 242:1172472020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Whisnant AW, Bogerd HP, Flores O, Ho P,
Powers JG, Sharova N, Stevenson M, Chen CH and Cullen BR: In-Depth
analysis of the interaction of HIV-1 with cellular microRNA
biogenesis and effector mechanisms. MBio. 4:e0001932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Racapé M, Duong Van Huyen JP, Danger R,
Giral M, Bleicher F, Foucher Y, Pallier A, Pilet P, Tafelmeyer P,
Ashton-Chess J, et al: The involvement of SMILE/TMTC3 in
endoplasmic reticulum stress response. PLoS One. 6:e193212011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Gan H, Lin L, Hu N, Yang Y, Gao Y, Pei Y,
Chen K and Sun B: KIF2C exerts an oncogenic role in nonsmall cell
lung cancer and is negatively regulated by miR-325-3p. Cell Biochem
Funct. 37:424–431. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
McHugh T, Zou J, Volkov VA, Aurélie Bertin
A, Talapatra SK, Rappsilber J, Dogterom M and Welburn JPI: The
depolymerase activity of MCAK shows a graded response to Aurora B
kinase phosphorylation through allosteric regulation. J Cell Sci.
132:jcs2283532019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
63
|
Nečasová I, Janoušková E, Klumpler T and
Hofr C: Basic domain of telomere guardian TRF2 reduces D-loop
unwinding whereas Rap1 restores it. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:12170–12180. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Karginov FV and Hannon GJ: Remodeling of
Ago2-mRNA interactions upon cellular stress reflects miRNA
complementarity and correlates with altered translation rates.
Genes Dev. 27:1624–1632. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Moldovan L, Batte KE, Trgovcich J, Wisler
J, Marsh CB and Piper M: Methodological challenges in utilizing
miRNAs as circulating biomarkers. Version 2 J Cell Mol Med.
18:371–390. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Munaut C, Tebache L, Blacher S, Noël A,
Nisolle M and Chantraine F: Dysregulated circulating miRNAs in
preeclampsia. Biomed Rep. 5:686–692. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Li D and Li J: Association of
miR-34a3p/5p, miR-1413p/5p, and miR-24 in decidual natural killer
cells with unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion. Med Sci
Monit. 22:922–929. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Song GY, Song WW, Han Y, Wang D and Na Q:
Characterization of the role of microRNA-517a expression in low
birth weight infants. J Dev Orig Health Dis. 4:522–526. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Li J, Chen L, Tang Q, Wu W, Gu H, Liu L,
Wu J, Jiang H, Ding H, Xia Y, et al: The role, mechanism and
potentially novel biomarker of microRNA-17-92 cluster in
macrosomia. Sci Rep. 5:172122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Cai M, Kolluru GK and Ahmed A: Small
molecule, big prospects: MicroRNA in pregnancy and its
complications. J Pregnancy. 2017:69727322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Cao YL, Jia YJ, Xing BH, Shi DD and Dong
XJ: Plasma microRNA-16-5p-17-5p and -20a-5p: Novel diagnostic
biomarkers for gestational diabetes mellitus. J Obstet Gynaecol
Res. 43:974–981. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Geng Y, Ju Y, Ren F, Qiu Y, Tomita Y,
Tomoeda M, Kishida M, Wang Y, Jin L, Su F, et al: Insulin receptor
substrate 1/2 (IRS1/2) regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling through
blocking autophagic degradation of dishevelled2. J Biol Chem.
289:11230–11241. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ortega FJ, Mercader JM, Moreno-Navarrete
JM, Rovira O, Guerra E, Esteve E, Xifra G, Martínez C, Ricart W,
Rieusset J, et al: Profiling of circulating MicroRNAs reveals
common micrornas linked to type 2 diabetes that change with insulin
sensitization. Diabetes Care. 37:1375–1383. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Demirsoy İH, Ertural DY, Balci Ş, Çınkır
Ü, Sezer K, Tamer L and Aras N: Profiles of circulating MiRNAs
following metformin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes. J
Med Biochem. 37:499–506. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Collares CV, Evangelista AF, Xavier DJ,
Rassi DM, Arns T, Foss-Freitas MC, Foss MC, Puthier D,
Sakamoto-Hojo ET, Passos GA, et al: Identifying common and specific
microRNAs expressed in peripheral blood mononuclear cell of type 1,
type 2, and gestational diabetes mellitus patients. BMC Res Notes.
6:4912013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhao C, Dong J, Jiang T, Shi Z, Yu B, Zhu
Y, Chen D, Xu J, Huo R, Dai J, et al: Early second-trimester serum
MiRNA profiling predicts gestational diabetes mellitus. PLoS One.
6:e239252011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Pheiffer C, Dias S, Rheeder P and Adam S:
Decreased expression of circulating miR-20a-5p in South African
women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Mol Diagn Ther.
22:345–352. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Shi Z, Zhao C, Guo X, Ding H, Cui Y, Shen
R and Liu J: Differential expression of microRNAs in omental
adipose tissue from gestational diabetes mellitus subjects reveals
miR-222 as a regulator of Erα expression in estrogen-induced
insulin resistance. Endocrinology. 155:1982–1990. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
López-Hernández Y, Herrera-Van Oostdam A,
Toro-Ortiz JC, López JA, Salgado-Bustamante M, Murgu M and
Torres-Torres LM: Urinary metabolites altered during the third
trimester in pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes
mellitus: Relationship with potential upcoming metabolic disorders.
Int J Mol Sci. 20:11862019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
80
|
Ibarra A, Vega-Guedes B, Brito-Casillas Y
and Wägner AM: Diabetes in pregnancy and MicroRNAs: Promises and
limitations in their clinical application. Noncoding RNA.
4:322018.
|
|
81
|
Sadovsky Y, Mouillet JF, Ouyang Y, Bayer A
and Coyne CB: The function of trophomirs and other micrornas in the
human placenta. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 5:a0230362015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Hromadnikova I, Kotlabova K, Ivankova K
and Krofta L: First trimester screening of circulating C19MC
microRNAs and the evaluation of their potential to predict the
onset of preeclampsia and IUGR. PLoS One. 12:e01717562017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Hromadnikova I, Dvorakova L, Kotlabova K
and Krofta L: The prediction of gestational hypertension,
preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction via the first trimester
screening of plasma exosomal C19MC microRNAs. Int J Mol Sci.
20:29722019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
84
|
Esteves JV, Enguita FJ and Machado UF:
MicroRNAs-Mediated regulation of skeletal muscle GLUT4 expression
and translocation in insulin resistance. J Diabetes Res.
2017:72679102017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|