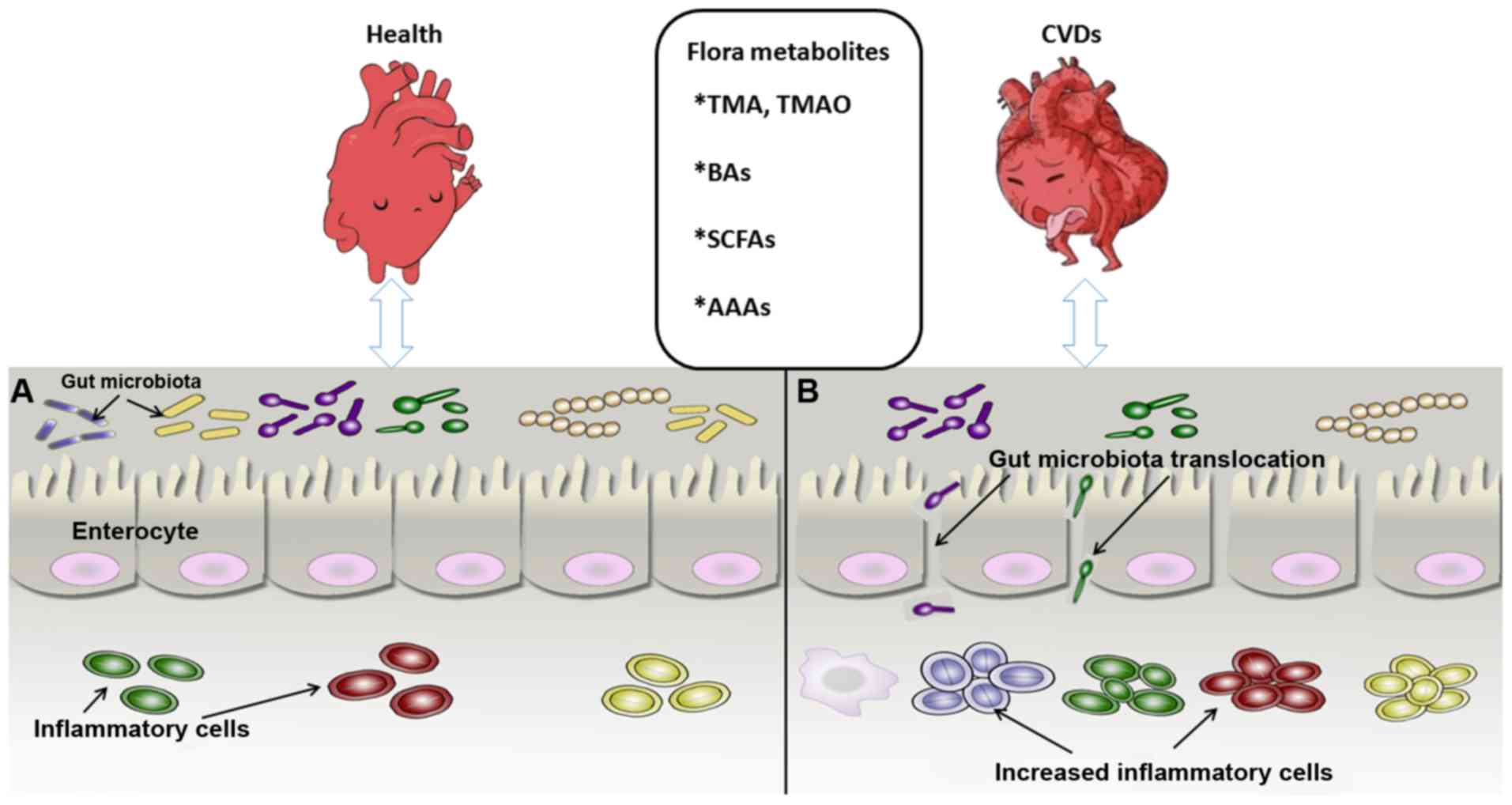
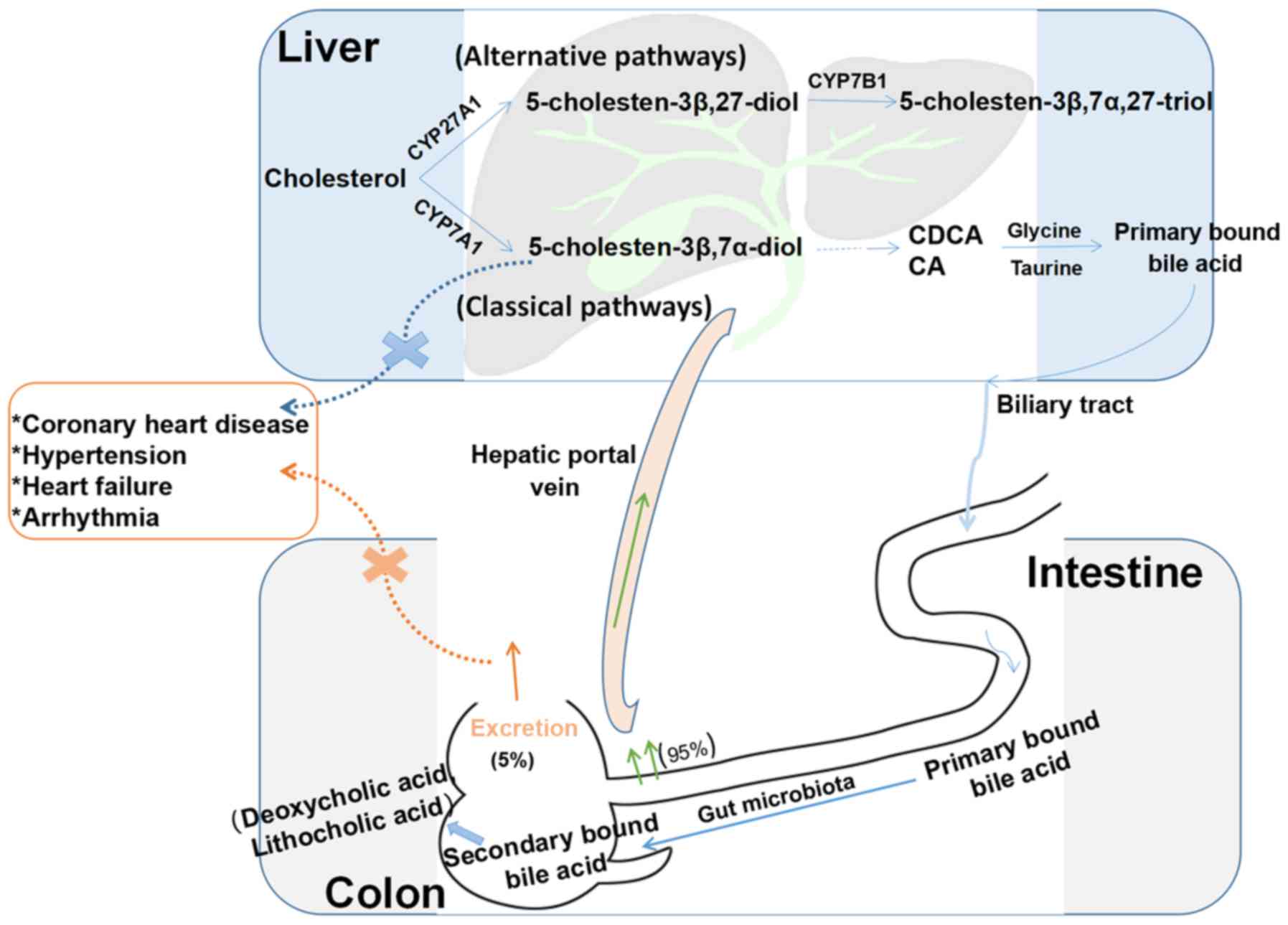
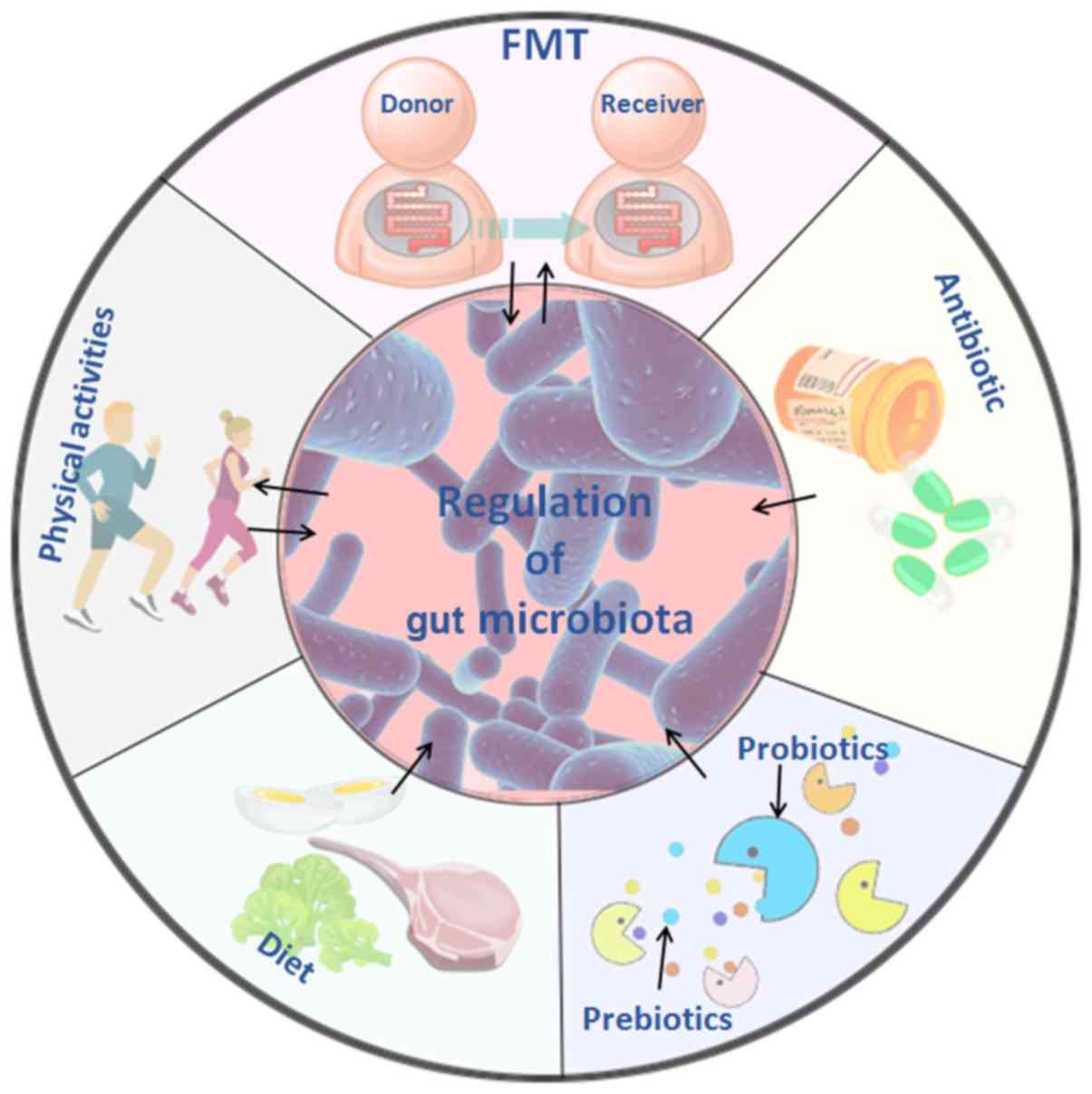
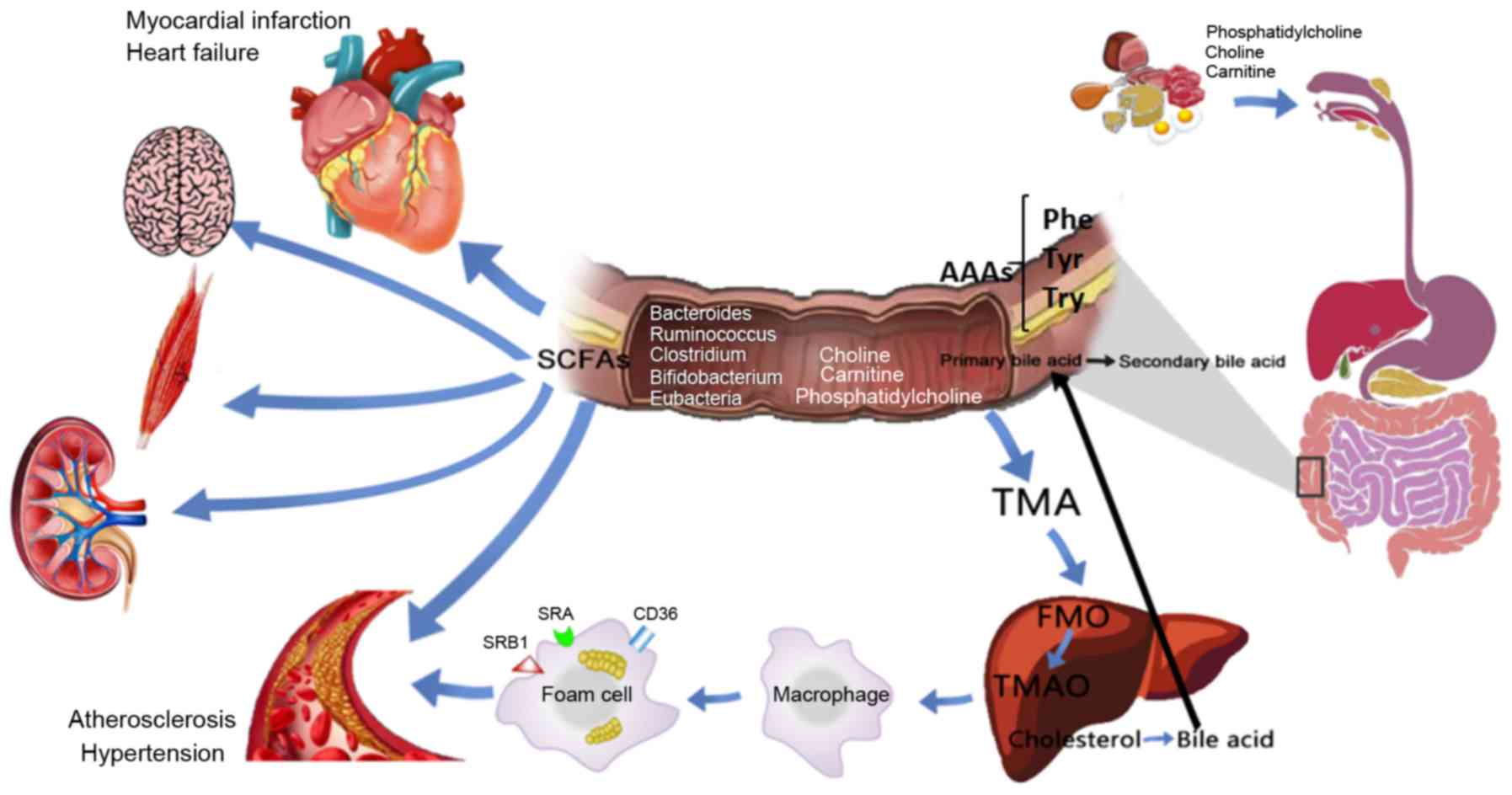
|
1
|
GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death
Collaborators: Global, regional, and national life expectancy,
all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of
death, 1980-2015: A systematic analysis for the global burden of
disease study 2015. Lancet. 388:1459–1544. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Drouin N, Kloots T, Schappler J, Rudaz S,
Kohler I, Harms A, Lindenburg PW and Hankemeier T: Electromembrane
extraction of highly polar compounds: Analysis of cardiovascular
biomarkers in plasma. Metabolites. 10:42019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Andersson C and Vasan RS: Epidemiology of
cardiovascular disease in young individuals. Nat Rev Cardiol.
15:230–240. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Maqbool M, Cooper ME and Jandeleit-Dahm
KAM: Cardiovascular disease and diabetic kidney disease. Semin
Nephrol. 38:217–232. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Defesche JC, Gidding SS, Harada-Shiba M,
Hegele RA, Santos RD and Wierzbicki AS: Familial
hypercholesterolaemia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 3:170932017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jabbar A, Pingitore A, Pearce SH, Zaman A,
Iervasi G and Razvi S: Thyroid hormones and cardiovascular disease.
Nat Rev Cardiol. 14:39–55. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Backhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh
GY, Nagy A, Semenkovich CF and Gordon JI: The gut microbiota as an
environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 101:15718–15723. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhu W, Gregory JC, Org E, Buffa JA, Gupta
N, Wang Z, Li L, Fu X, Wu Y, Mehrabian M, et al: Gut microbial
metabolite TMAO enhances platelet hyperreactivity and thrombosis
risk. Cell. 165:111–124. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Perez NB, Dorsen C and Squires A:
Dysbiosis of the gut micro-biome: A concept analysis. J Holist
Nurs. 8980101198795272019.Epub ahead of print.
|
|
10
|
Skye SM, Zhu W, Romano KA, Guo CJ, Wang Z,
Jia X, Kirsop J, Haag B, Lang JM, DiDonato JA, et al: Microbial
transplantation with human gut commensals containing CutCis
sufficient to transmit enhanced platelet reactivity and thrombosis
potential. Circ Res. 123:1164–1176. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fu J and Kuipers F: Systems genetics
approach reveals cross-talk between bile acids and intestinal
microbes. PLoS Genet. 15:e10083072019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ohira H, Tsutsui W and Fujioka Y: Are
short chain fatty acids in gut microbiota defensive players for
inflammation and atherosclerosis? J Atheroscler Thromb. 24:660–672.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Devlin AS, Marcobal A, Dodd D, Nayfach S,
Plummer N, Meyer T, Pollard KS, Sonnenburg JL and Fischbach MA:
Modulation of a circulating uremic solute via rational genetic
manipulation of the gut microbiota. Cell Host Microbe. 20:709–715.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yao C, Chen BH, Joehanes R, Otlu B, Zhang
X, Liu C, Huan T, Tastan O, Cupples LA, Meigs JB, et al: Integromic
analysis of genetic variation and gene expression identifies
networks for cardiovascular disease phenotypes. Circulation.
131:536–549. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Zhang WQ, Zhao TT, Gui DK, Gao CL, Gu JL,
Gan WJ, Huang W, Xu Y, Zhou H, Chen WN, et al: Sodium butyrate
improves liver glycogen metabolism in Type 2 diabetes mellitus. J
Agric Food Chem. 67:7694–7705. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Odegaard AO, Koh WP, Gross MD, Yuan JM and
Pereira MA: Combined lifestyle factors and cardiovascular disease
mortality in Chinese men and women: The Singapore Chinese health
study. Circulation. 124:2847–2854. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Macfarlane GT and Macfarlane S: Bacteria,
colonic fermentation, and gastrointestinal health. J AOAC Int.
95:50–60. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang WH, Kitai T and Hazen SL: Gut
microbiota in cardiovascular health and disease. Circ Res.
120:1183–1196. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lam V, Su J, Hsu A, Gross GJ, Salzman NH
and Baker JE: Intestinal microbial metabolites are linked to
severity of myocardial infarction in rats. PLoS One.
11:e01608402016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Caro-Gomez E, Sierra JA, Escobar JS,
Alvarez-Quintero R, Naranjo M, Medina S, Velasquez-Mejia EP,
Tabares-Guevara JH, Jaramillo JC, Leon-Varela YM, et al: Green
coffee extract improves cardiometabolic parameters and modulates
gut micro-biota in High-Fat-Diet-Fed ApoE−/− Mice.
Nutrients. 11:4972019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tran HQ, Ley RE, Gewirtz AT and Chassaing
B: Flagellin-elicited adaptive immunity suppresses flagellated
microbiota and vaccinates against chronic inflammatory diseases.
Nat Commun. 10:56502019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Z, Roberts AB, Buffa JA, Levison BS,
Zhu W, Org E, Gu X, Huang Y, Zamanian-Daryoush M, Culley MK, et al:
Non-lethal inhibition of gut microbial trimethylamine production
for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Cell. 163:1585–1595. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grabherr F, Grander C, Effenberger M,
Adolph TE and Tilg H: Gut dysfunction and non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 10:6112019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ramirez-Perez O, Cruz-Ramon V,
Chinchilla-Lopez P and Mendez-Sanchez N: The role of the gut
microbiota in bile acid metabolism. Ann Hepato. 16(Suppl. 1:
S3-105): S21–S20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chen H, Peng L, Perez de Nanclares M,
Trudeau MP, Yao D, Cheng Z, Urriola PE, Mydland LT, Shurson GC,
Overland M and Chen C: Identification of sinapine-derived choline
from a rapeseed diet as a source of serum Trimethylamine N-Oxide in
pigs. J Agric Food Chem. 67:7748–7754. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Z, Klipfell E, Bennett BJ, Koeth R,
Levison BS, Dugar B, Feldstein AE, Britt EB, Fu X, Chung YM, et al:
Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular
disease. Nature. 472:57–63. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ufnal M, Zadlo A and Ostaszewski R: TMAO:
A small molecule of great expectations. Nutrition. 31:1317–1323.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Koeth RA, Wang Z, Levison BS, Buffa JA,
Org E, Sheehy BT, Britt EB, Fu X, Wu Y, Li L, et al: Intestinal
microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat,
promotes atherosclerosis. Nat Med. 19:576–585. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Suzuki H, Kurihara Y, Takeya M, Kamada N,
Kataoka M, Jishage K, Ueda O, Sakaguchi H, Higashi T, Suzuki T, et
al: A role for macrophage scavenger receptors in atherosclerosis
and susceptibility to infection. Nature. 386:292–296. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Brown JM and Hazen SL: The gut microbial
endocrine organ: Bacterially derived signals driving
cardiometabolic diseases. Annu Rev Med. 66:343–359. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li XS, Obeid S, Klingenberg R, Gencer B,
Mach F, Raber L, Windecker S, Rodondi N, Nanchen D, Muller O, et
al: Gut microbiota-dependent trimethylamine N-oxide in acute
coronary syndromes: A prognostic marker for incident cardiovascular
events beyond traditional risk factors. Eur Heart J. 38:814–824.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu TX, Niu HT and Zhang SY: Intestinal
microbiota metabolism and atherosclerosis. Chin Med J (Engl).
128:2805–2811. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ott SJ, El Mokhtari NE, Musfeldt M,
Hellmig S, Freitag S, Rehman A, Kuhbacher T, Nikolaus S, Namsolleck
P, Blaut M, et al: Detection of diverse bacterial signatures in
atherosclerotic lesions of patients with coronary heart disease.
Circulation. 113:929–937. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Winther SA, Ollgaard JC, Tofte N, Tarnow
L, Wang Z, Ahluwalia TS, Jorsal A, Theilade S, Parving HH, Hansen
TW, et al: Utility of plasma concentration of Trimethylamine
N-Oxide in predicting cardiovascular and renal complications in
individuals with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 42:1512–1520.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li X, Geng J, Zhao J, Ni Q, Zhao C, Zheng
Y, Chen X and Wang L: Trimethylamine N-Oxide exacerbates cardiac
fibrosis via activating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Front Physiol.
10:8662019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shepshelovich J, Goldstein-Magal L,
Globerson A, Yen PM, Rotman-Pikielny P and Hirschberg K: Protein
synthesis inhibitors and the chemical chaperone TMAO reverse
endoplasmic reticulum perturbation induced by overexpression of the
iodide transporter pendrin. J Cell Sci. 118(Pt 8): 1577–1586. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen S, Henderson A, Petriello MC, Romano
KA, Gearing M, Miao J, Schell M, Sandoval-Espinola WJ, Tao J, Sha
B, et al: Trimethylamine N-Oxide binds and activates PERK to
promote metabolic dysfunction. Cell Metab. 30:1141–1151.e5. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ma G, Pan B, Chen Y, Guo C, Zhao M, Zheng
L and Chen B: Trimethylamine N-oxide in atherogenesis: Impairing
endothelial self-repair capacity and enhancing monocyte adhesion.
Biosci Rep. 37:BSR201602442017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shiffka SJ, Kane MA and Swaan PW: Planar
bile acids in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr.
1859:2269–2276. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chiang JY: Bile acid regulation of gene
expression: Roles of nuclear hormone receptors. Endocr Rev.
23:443–463. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lefebvre P, Cariou B, Lien F, Kuipers F
and Staels B: Role of bile acids and bile acid receptors in
metabolic regulation. Physiol Rev. 89:147–191. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hoving LR, Katiraei S, Heijink M, Pronk A,
van der Wee-Pals L, Streefland T, Giera M, Willems van Dijk K and
van Harmelen V: Dietary mannan oligosaccharides modulate gut
microbiota, increase fecal bile acid excretion, and decrease plasma
cholesterol and atherosclerosis development. Mol Nutr Food Res.
62:e17009422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sun L, Pang Y, Wang X, Wu Q, Liu H, Liu B,
Liu G, Ye M, Kong W and Jiang C: Ablation of gut microbiota
alleviates obesity-induced hepatic steatosis and glucose
intolerance by modulating bile acid metabolism in hamsters. Acta
Pharm Sin B. 9:702–710. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tsuei J, Chau T, Mills D and Wan YJ: Bile
acid dysregulation, gut dysbiosis, and gastrointestinal cancer. Exp
Biol Med (Maywood). 239:1489–1504. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Dodd D, Spitzer MH, Van Treuren W, Merrill
BD, Hryckowian AJ, Higginbottom SK, Le A, Cowan TM, Nolan GP,
Fischbach MA and Sonnenburg JL: A gut bacterial pathway metabolizes
aromatic amino acids into nine circulating metabolites. Nature.
551:648–652. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jia ET, Liu ZY, Pan M, Lu JF and Ge QY:
Regulation of bile acid metabolism-related signaling pathways by
gut microbiota in diseases. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 20:781–792.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Merritt ME and Donaldson JR: Effect of
bile salts on the DNA and membrane integrity of enteric bacteria. J
Med Microbiol. 58(Pt 12): 1533–1541. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lin S, Yang X, Yuan P, Yang J, Wang P,
Zhong H, Zhang X, Che L, Feng B, Li J, et al: Undernutrition shapes
the gut microbiota and bile acid profile in association with
altered gut-liver FXR signaling in weaning pigs. J Agric Food Chem.
67:3691–3701. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wu P, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Wang X, Guo Z, Zhang
Y, Liang X and Lai W: Effects of cholic acid on blood pressure and
production of vascular aldosterone and corticosterone. Steroids.
64:291–295. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Valdivia C, Carvajal CA, Campino C,
Allende F, Martinez-Aguayo A, Baudrand R, Vecchiola A, Lagos CF,
Tapia-Castillo A, Fuentes CA, et al: Citosine-adenine-repeat
microsatellite of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 gene in
hypertensive children. Am J Hypertens. 29:25–32. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wan Y, Wang F, Yuan J, Li J, Jiang D,
Zhang J, Li H, Wang R, Tang J, Huang T, et al: Effects of dietary
fat on gut microbiota and faecal metabolites, and their
relationship with cardiometabolic risk factors: A 6-month
randomised controlled-feeding trial. Gut. 68:1417–1429. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Charach G, Karniel E, Novikov I, Galin L,
Vons S, Grosskopf I and Charach L: Reduced bile acid excretion is
an independent risk factor for stroke and mortality: A prospective
follow-up study. Atherosclerosis. 293:79–85. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Fedorova OV, Zernetkina VI, Shilova VY,
Grigorova YN, Juhasz O, Wei W, Marshall CA, Lakatta EG and Bagrov
AY: Synthesis of an Endogenous steroidal Na Pump inhibitor
mari-nobufagenin, implicated in human cardiovascular diseases, is
initiated by CYP27A1 via Bile Acid pathway. Circ Cardiovasc Genet.
8:736–745. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Rainer PP, Primessnig U, Harenkamp S,
Doleschal B, Wallner M, Fauler G, Stojakovic T, Wachter R, Yates A,
Groschner K, et al: Bile acids induce arrhythmias in human atrial
myocardium-implications for altered serum bile acid composition in
patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart. 99:1685–1692. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Pu J, Yuan A, Shan P, Gao E, Wang X, Wang
Y, Lau WB, Koch W, Ma XL and He B: Cardiomyocyte-expressed
farnesoid-X-receptor is a novel apoptosis mediator and contributes
to myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Eur Heart J.
34:1834–1845. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
56
|
Chen ML, Yi L, Zhang Y, Zhou X, Ran L,
Yang JN, Zhu JD, Zhang QY and Mi MT: Resveratrol attenuates
Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO)-Induced atherosclerosis by regulating
TMAO Synthesis and bile acid metabolism via remodeling of the Gut
microbiota. mBio. 7:e02210–15. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Nguyen MT, Favelyukis S, Nguyen AK,
Reichart D, Scott PA, Jenn A, Liu-Bryan R, Glass CK, Neels JG and
Olefsky JM: A subpopulation of macrophages infiltrates hypertrophic
adipose tissue and is activated by free fatty acids via Toll-like
receptors 2 and 4 and JNK-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem.
282:35279–35292. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Calderon-Perez L, Gosalbes MJ, Yuste S,
Valls RM, Pedret A, Llaurado E, Jimenez-Hernandez N, Artacho A,
Pla-Paga L, Companys J, et al: Gut metagenomic and short chain
fatty acids signature in hypertension: A cross-sectional study. Sci
Rep. 10:64362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Morrison DJ and Preston T: Formation of
short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on
human metabolism. Gut Microbes. 7:189–200. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Manrique Vergara D and González Sánchez
ME: Short chain fatty acids (butyric acid) and intestinal diseases.
Nutr Hosp. 34(Suppl 4): S58–S61. 2017.In Spanish.
|
|
61
|
Sun M, Wu W, Liu Z and Cong Y: Microbiota
metabolite short chain fatty acids, GPCR, and inflammatory bowel
diseases. J Gastroenterol. 52:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Smith PM, Howitt MR, Panikov N, Michaud M,
Gallini CA, Bohlooly-Y M, Glickman JN and Garrett WS: The microbial
metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell
homeostasis. Science. 341:569–573. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li J, Zhao F, Wang Y, Chen J, Tao J, Tian
G, Wu S, Liu W, Cui Q, Geng B, et al: Gut microbiota dysbiosis
contributes to the development of hypertension. Microbiome.
5:142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Le B, Bůžková P, Robbins JA, Fink HA,
Raiford M, Isales CM, Shikany JM, Coughlin SS and Carbone LD: The
association of aromatic amino acids with incident hip fracture,
aBMD, and body composition from the cardiovascular health study.
Calcif Tissue Int. 105:161–172. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Tessari P, Lante A and Mosca G: Essential
amino acids: Master regulators of nutrition and environmental
footprint? Sci Rep. 6:260742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Fernstrom JD and Fernstrom MH: Tyrosine,
phenylalanine, and catecholamine synthesis and function in the
brain. J Nutr. 137(6 Suppl 1): 1539S–1547S; discussion 1548S. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Shishehbor MH, Aviles RJ, Brennan ML, Fu
X, Goormastic M, Pearce GL, Gokce N, Keaney JF Jr, Penn MS,
Sprecher DL, et al: Association of nitrotyrosine levels with
cardiovascular disease and modulation by statin therapy. JAMA.
289:1675–1680. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Thomson L: 3-nitrotyrosine modified
proteins in atherosclerosis. Dis Markers. 2015:7082822015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Haase S, Haghikia A, Wilck N, Müller DN
and Linker RA: Impacts of microbiome metabolites on immune
regulation and autoimmunity. Immunology. 154:230–238. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Brawner KM, Yeramilli VA, Duck LW, Van Der
Pol W, Smythies LE, Morrow CD, Elson CO and Martin CA: Depletion of
dietary aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands alters microbiota
composition and function. Sci Rep. 9:147242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zelante T, Iannitti RG, Cunha C, De Luca
A, Giovannini G, Pieraccini G, Zecchi R, D'Angelo C,
Massi-Benedetti C, Fallarino F, et al: Tryptophan catabolites from
microbiota engage aryl hydrocarbon receptor and balance mucosal
reactivity via interleukin-22. Immunity. 39:372–385. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Metghalchi S, Ponnuswamy P, Simon T,
Haddad Y, Laurans L, Clément M, Dalloz M, Romain M, Esposito B,
Koropoulis V, et al: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase fine-tunes immune
homeostasis in atherosclerosis and colitis through repression of
interleukin-10 production. Cell Metab. 22:460–471. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Laurans L, Venteclef N, Haddad Y,
Chajadine M, Alzaid F, Metghalchi S, Sovran B, Denis RGP, Dairou J,
Cardellini M, et al: Genetic deficiency of indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase promotes gut microbiota-mediated metabolic health.
Nat Med. 24:1113–1120. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Lamas B, Richard ML, Leducq V, Pham HP,
Michel ML, Da Costa G, Bridonneau C, Jegou S, Hoffmann TW,
Natividad JM, et al: CARD9 impacts colitis by altering gut
microbiota metabolism of tryptophan into aryl hydrocarbon receptor
ligands. Nat Med. 22:598–605. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hoyles L, Fernández-Real JM, Federici M,
Serino M, Abbott J, Charpentier J, Heymes C, Luque JL, Anthony E,
Barton RH, et al: Molecular phenomics and metagenomics of hepatic
steatosis in non-diabetic obese women. Nat Med. 24:1070–1080. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kakihana K, Fujioka Y, Suda W, Najima Y,
Kuwata G, Sasajima S, Mimura I, Morita H, Sugiyama D, Nishikawa H,
et al: Fecal microbiota transplantation for patients with
steroid-resistant acute graft-versus-host disease of the gut.
Blood. 128:2083–2088. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Moludi J, Maleki V, Jafari-Vayghyan H,
Vaghef-Mehrabany E and Alizadeh M: Metabolic endotoxemia and
cardiovascular disease: A systematic review about potential roles
of prebiotics and probiotics. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
47:927–939. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Gregory JC, Buffa JA, Org E, Wang Z,
Levison BS, Zhu W, Wagner MA, Bennett BJ, Li L, DiDonato JA, et al:
Transmission of atherosclerosis susceptibility with gut microbial
transplantation. J Biol Chem. 290:5647–5660. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Lu F, Liu F, Zhou Q, Hu X and Zhang Y:
Effects of grape pomace and seed polyphenol extracts on the
recovery of gut microbiota after antibiotic treatment in high-fat
diet-fed mice. Food Sci Nutr. 7:2897–2906. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Liao X, Song L, Zeng B, Liu B, Qiu Y, Qu
H, Zheng Y, Long M, Zhou H, Wang Y, et al: Alteration of gut
microbiota induced by DPP-4i treatment improves glucose
homeostasis. EBioMedicine. 44:665–674. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wan JJ, Lin CH, Ren ED, Su Y and Zhu WY:
Effects of early intervention with maternal fecal bacteria and
antibiotics on liver metabolome and transcription in neonatal pigs.
Front Physiol. 10:1712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Janeiro MH, Ramirez MJ, Milagro FI,
Martinez JA and Solas M: Implication of trimethylamine N-Oxide
(TMAO) in disease: Potential biomarker or new therapeutic target.
Nutrients. 10:13982018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
83
|
Queipo-Ortuño MI, Seoane LM, Murri M,
Pardo M, Gomez-Zumaquero JM, Cardona F, Casanueva F and Tinahones
FJ: Gut microbiota composition in male rat models under different
nutritional status and physical activity and its association with
serum leptin and ghrelin levels. PLoS One. 8:e654652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Roy Le T, Lécuyer E, Chassaing B, Rhimi M,
Lhomme M, Boudebbouze S, Ichou F, Haro Barceló J, Huby T, Guerin M,
et al: The intestinal microbiota regulates host cholesterol
homeostasis. BMC Biol. 17:942019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Heymsfield SB and Wadden TA: Mechanisms,
pathophysiology, and management of obesity. N Engl J Med.
376:254–266. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Guirro M, Costa A, Gual-Grau A, Herrero P,
Torrell H, Canela N and Arola L: Effects from diet-induced gut
microbiota dysbiosis and obesity can be ameliorated by fecal
microbiota transplantation: A multiomics approach. PLoS One.
14:e02181432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Enright EF, Joyce SA, Gahan CG and Griffin
BT: Impact of gut microbiota-mediated bile acid metabolism on the
solubilization capacity of bile salt micelles and drug solubility.
Mol Pharm. 14:1251–1263. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Langlands SJ, Hopkins MJ, Coleman N and
Cummings JH: Prebiotic carbohydrates modify the mucosa associated
micro-flora of the human large bowel. Gut. 53:1610–1616. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Hill C, Guarner F, Reid G, Gibson GR,
Merenstein DJ, Pot B, Morelli L, Canani RB, Flint HJ, Salminen S,
et al: Expert consensus document. The International Scientific
Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on
the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 11:506–514. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Gallo A, Passaro G, Gasbarrini A, Landolfi
R and Montalto M: Modulation of microbiota as treatment for
intestinal inflammatory disorders: An uptodate. World J
Gastroenterol. 22:7186–7202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Quigley EM: Prebiotics and probiotics:
Their role in the management of gastrointestinal disorders in
adults. Nutr Clin Pract. 27:195–200. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Mozaffarian D: Dairy foods, obesity, and
metabolic health: The role of the food matrix compared with single
nutrients. Adv Nutr. 10:917S–923S. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Chen Q, Liu M, Zhang P, Fan S, Huang J, Yu
S, Zhang C and Li H: Fucoidan and galactooligosaccharides
ameliorate high-fat diet-induced dyslipidemia in rats by modulating
the gut micro-biota and bile acid metabolism. Nutrition. 65:50–59.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Francavilla G, Abrignani MG, Braschi A,
Sciacca R, Francavilla VC, Caracciolo MM, Renda N, Riccio C,
Scaglione A and Braschi G: Physical exercise and sport activities
in patients with and without coronary heart disease. Monaldi Arch
Chest Dis. 68:87–95. 2007.In Italian. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Cheng YJ, Zhao XJ, Zeng W, Xu MC, Ma YC
and Wang M: Effect of intradialytic exercise on physical
performance and cardiovascular risk factors in patients receiving
maintenance hemodialysis: A pilot and feasibility study. Blood
Purif. 1–10. 2019.Epub ahead of print.
|
|
96
|
Codella R, Luzi L and Terruzzi I: Exercise
has the guts: How physical activity may positively modulate gut
microbiota in chronic and immune-based diseases. Dig Liver Dis.
50:331–341. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Chen J, Guo Y, Gui Y and Xu D: Physical
exercise, gut, gut microbiota, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular
diseases. Lipids Health Dis. 17:172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Ito S: High-intensity interval training
for health benefits and care of cardiac diseases-The key to an
efficient exercise protocol. World J Cardiol. 11:171–188. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Kang Y and Cai Y: Gut microbiota and
hypertension: From pathogenesis to new therapeutic strategies. Clin
Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 42:110–117. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Petriz BA, Castro AP, Almeida JA, Gomes
CP, Fernandes GR, Kruger RH, Pereira RW and Franco OL: Exercise
induction of gut microbiota modifications in obese, non-obese and
hypertensive rats. BMC Genomics. 15:5112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Verdam FJ, Fuentes S, de Jonge C,
Zoetendal EG, Erbil R, Greve JW, Buurman WA, de Vos WM and Rensen
SS: Human intestinal microbiota composition is associated with
local and systemic inflammation in obesity. Obesity (Silver
Spring). 21:E607–E615. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Denou E, Marcinko K, Surette MG, Steinberg
GR and Schertzer JD: High-intensity exercise training increases the
diversity and metabolic capacity of the mouse distal gut
micro-biota during diet-induced obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 310:E982–E993. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Hsu YJ, Chiu CC, Li YP, Huang WC, Huang
YT, Huang CC and Chuang HL: Effect of intestinal microbiota on
exercise performance in mice. J Strength Cond Res. 29:552–558.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Starkie R, Ostrowski SR, Jauffred S,
Febbraio M and Pedersen BK: Exercise and IL-6 infusion inhibit
endotoxin-induced TNF-alpha production in humans. FASEB J.
17:884–886. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Pedersen BK and Saltin B: Exercise as
medicine-evidence for prescribing exercise as therapy in 26
different chronic diseases. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 25(Suppl 3):
S1–S72. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Fung TT, Rexrode KM, Mantzoros CS, Manson
JE, Willett WC and Hu FB: Mediterranean diet and incidence of and
mortality from coronary heart disease and stroke in women.
Circulation. 119:1093–1100. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Holscher HD, Guetterman HM, Swanson KS, An
R, Matthan NR, Lichtenstein AH, Novotny JA and Baer DJ: Walnut
consumption alters the gastrointestinal microbiota, microbially
derived secondary bile acids, and health markers in healthy adults:
A randomized controlled trial. J Nutr. 148:861–867. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Psaltopoulou T, Hatzis G, Papageorgiou N,
Androulakis E, Briasoulis A and Tousoulis D: Socioeconomic status
and risk factors for cardiovascular disease: Impact of dietary
mediators. Hellenic J Cardiol. 58:32–42. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Tindall AM, Mclimans CJ, Petersen KS,
Kris-Etherton PM and Lamendella R: Walnuts and vegetable oils
containing oleic acid differentially affect the gut microbiota and
associations with cardiovascular risk factors: Follow-up of a
randomized, controlled, feeding trial in adults at risk for
cardiovascular disease. J Nutr. 150:806–817. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|