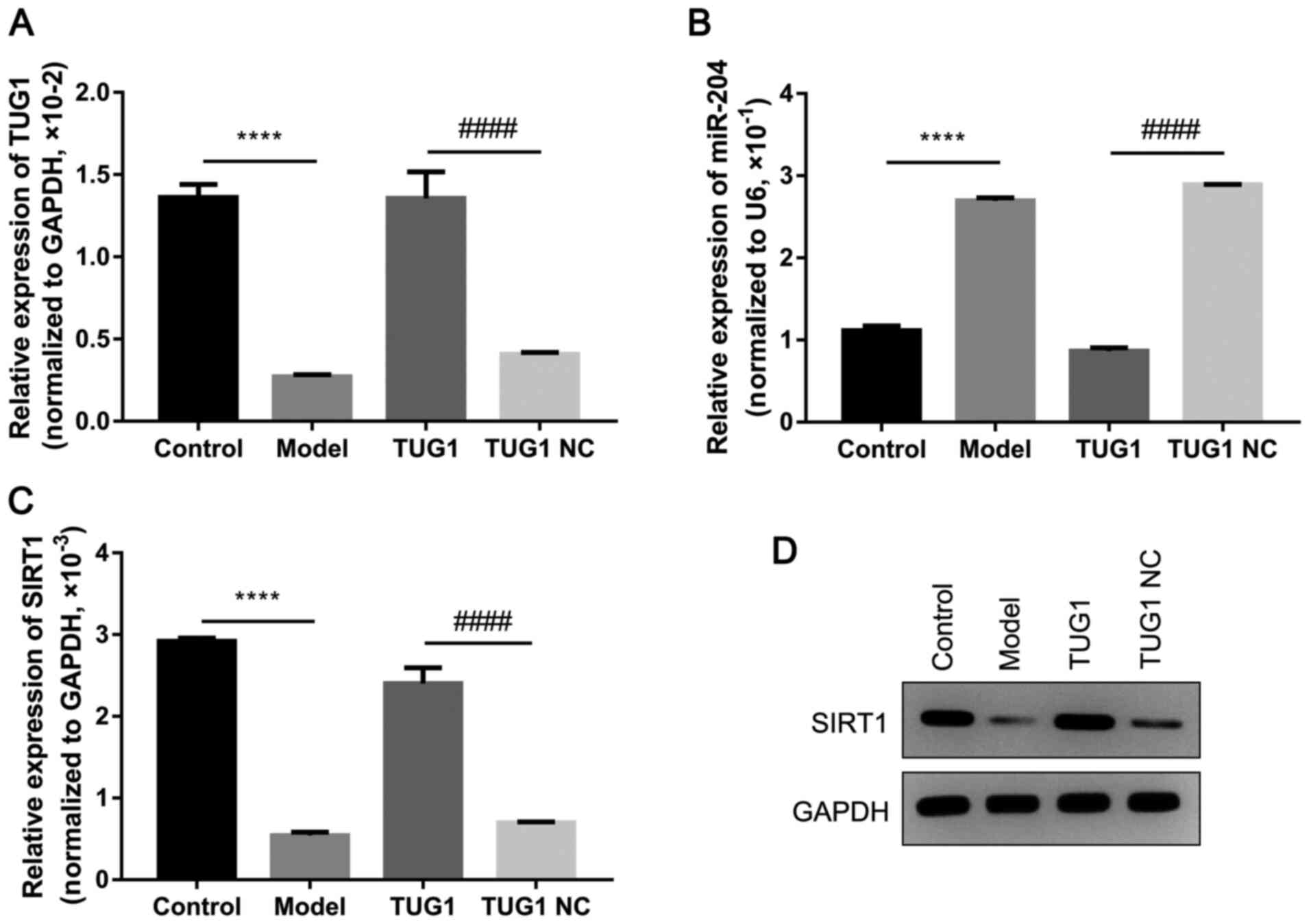
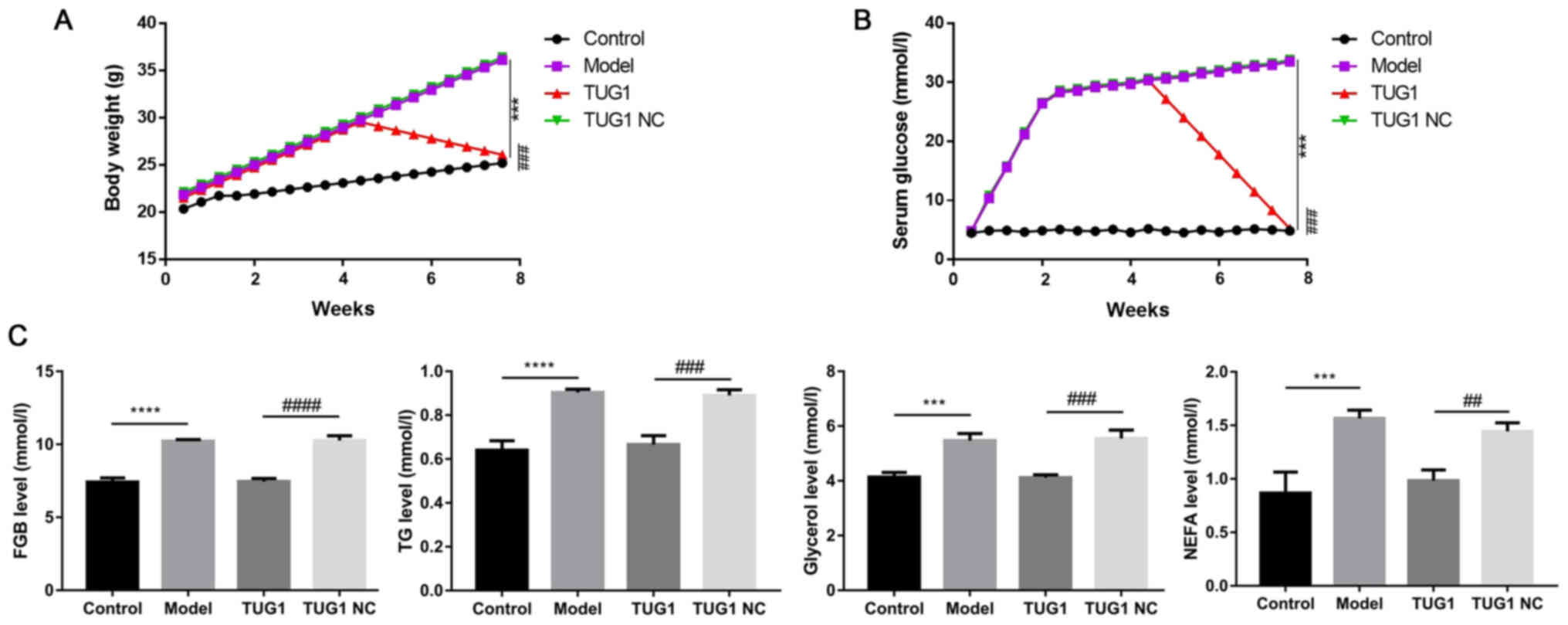
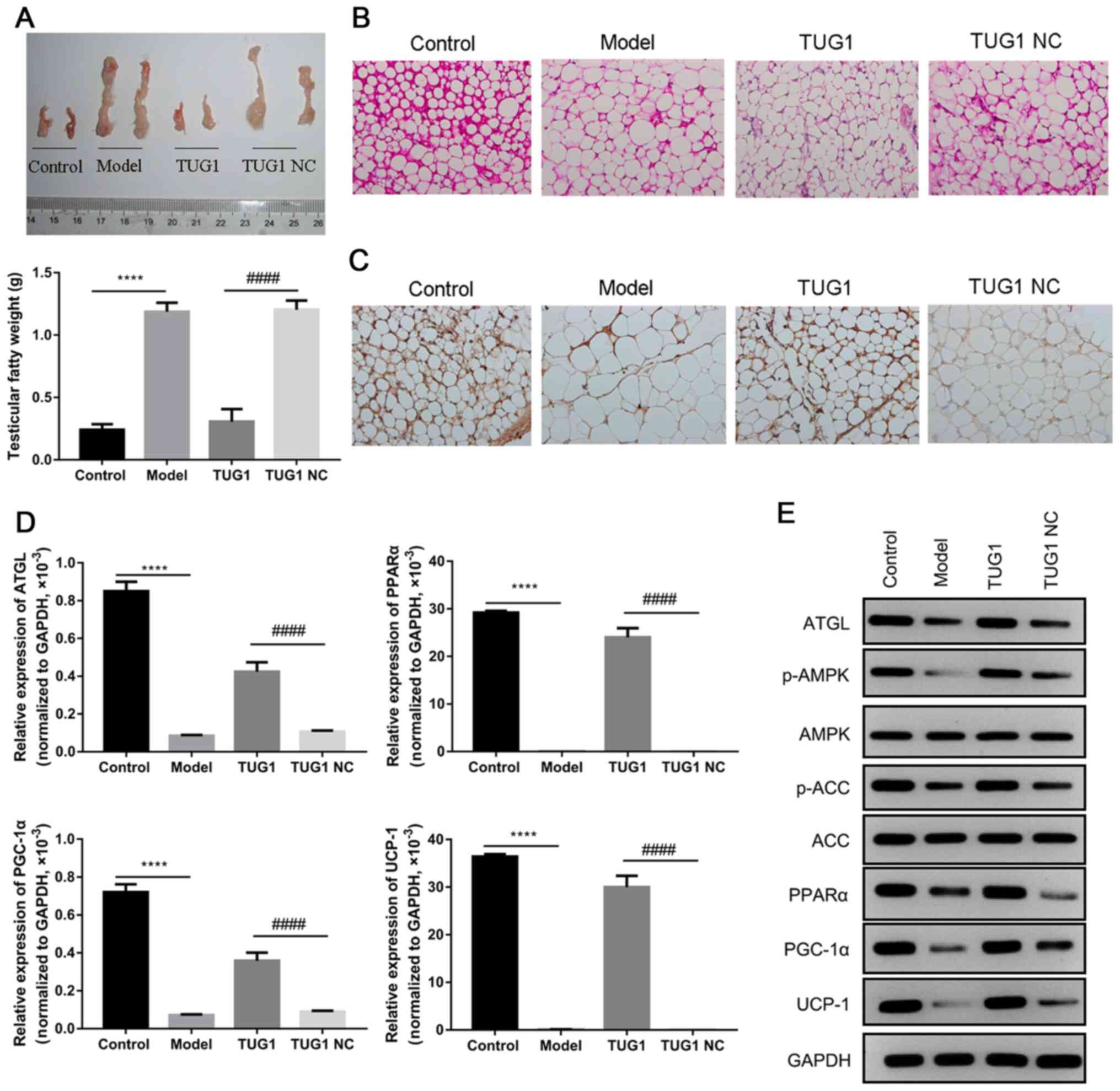
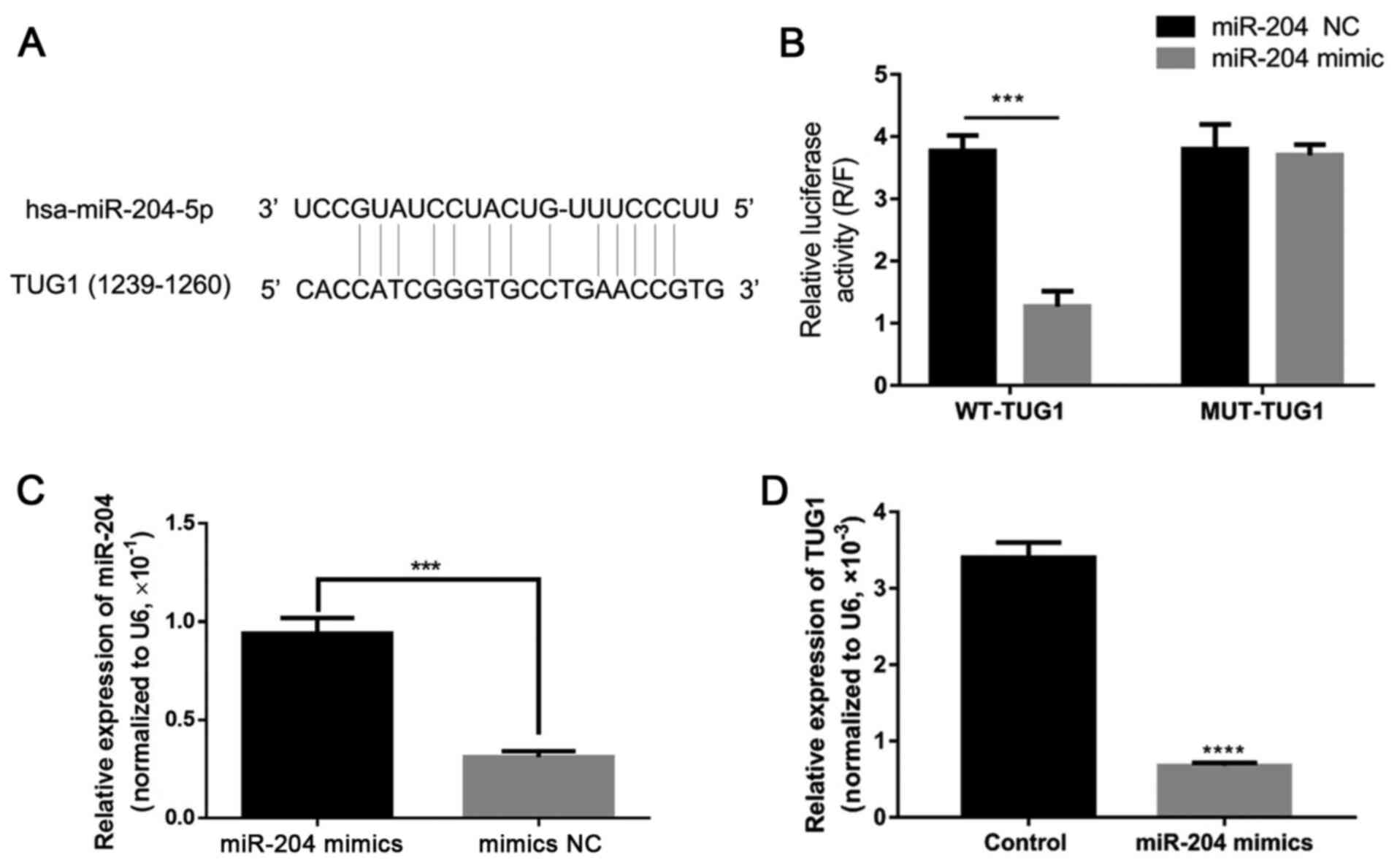
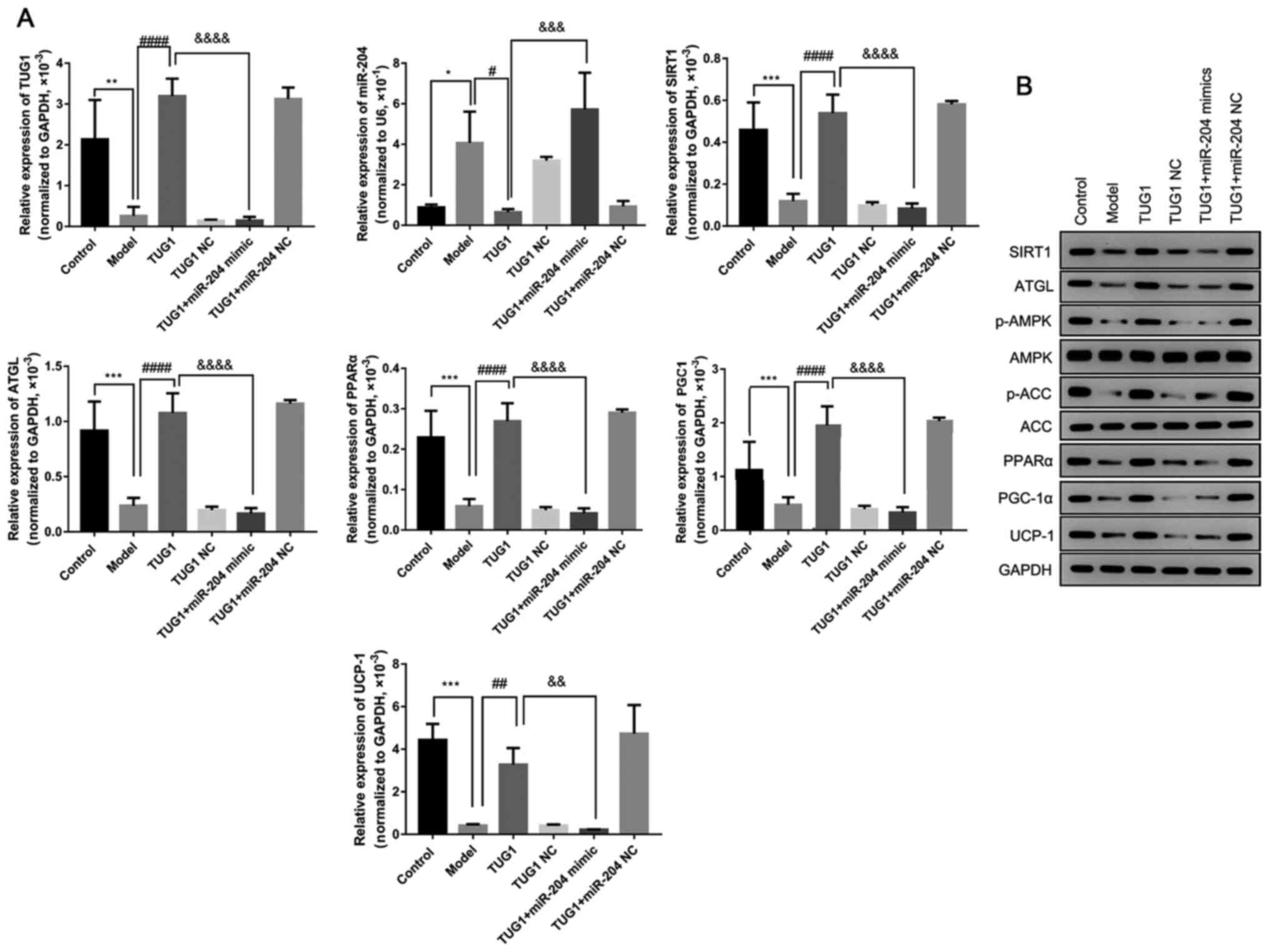
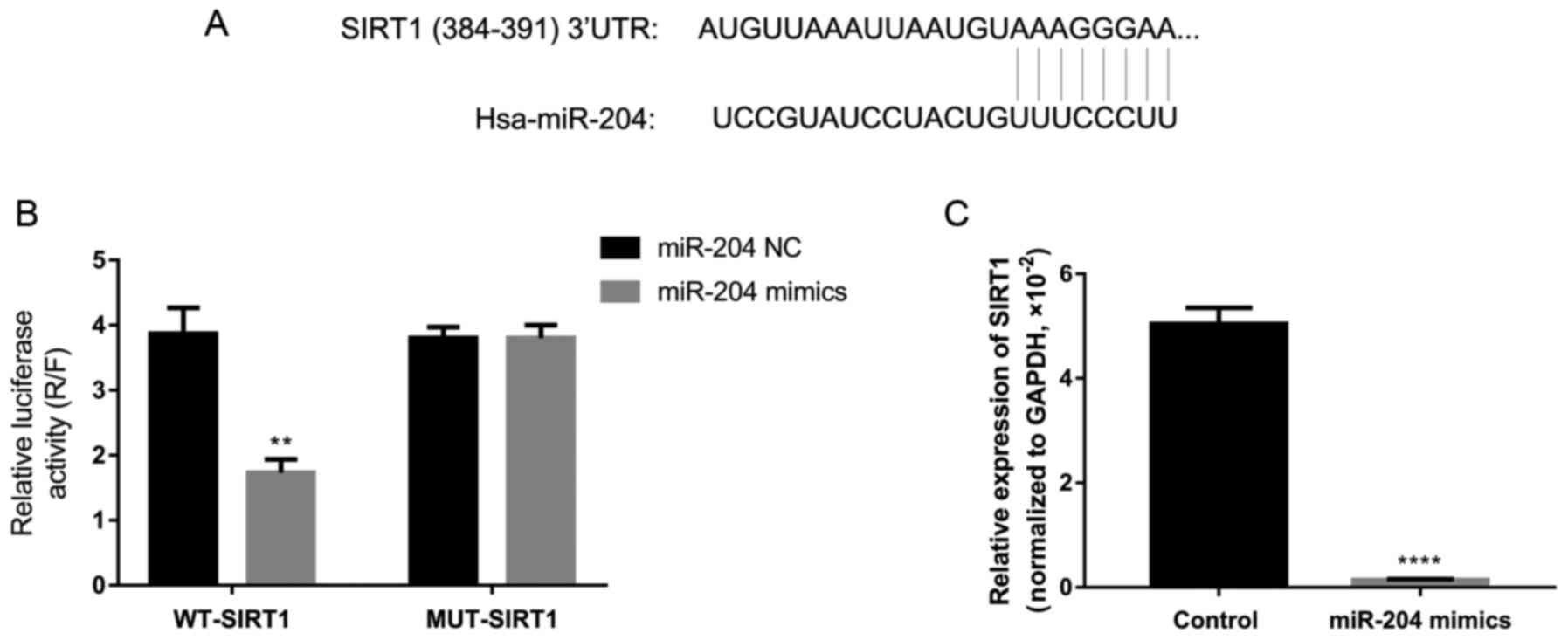
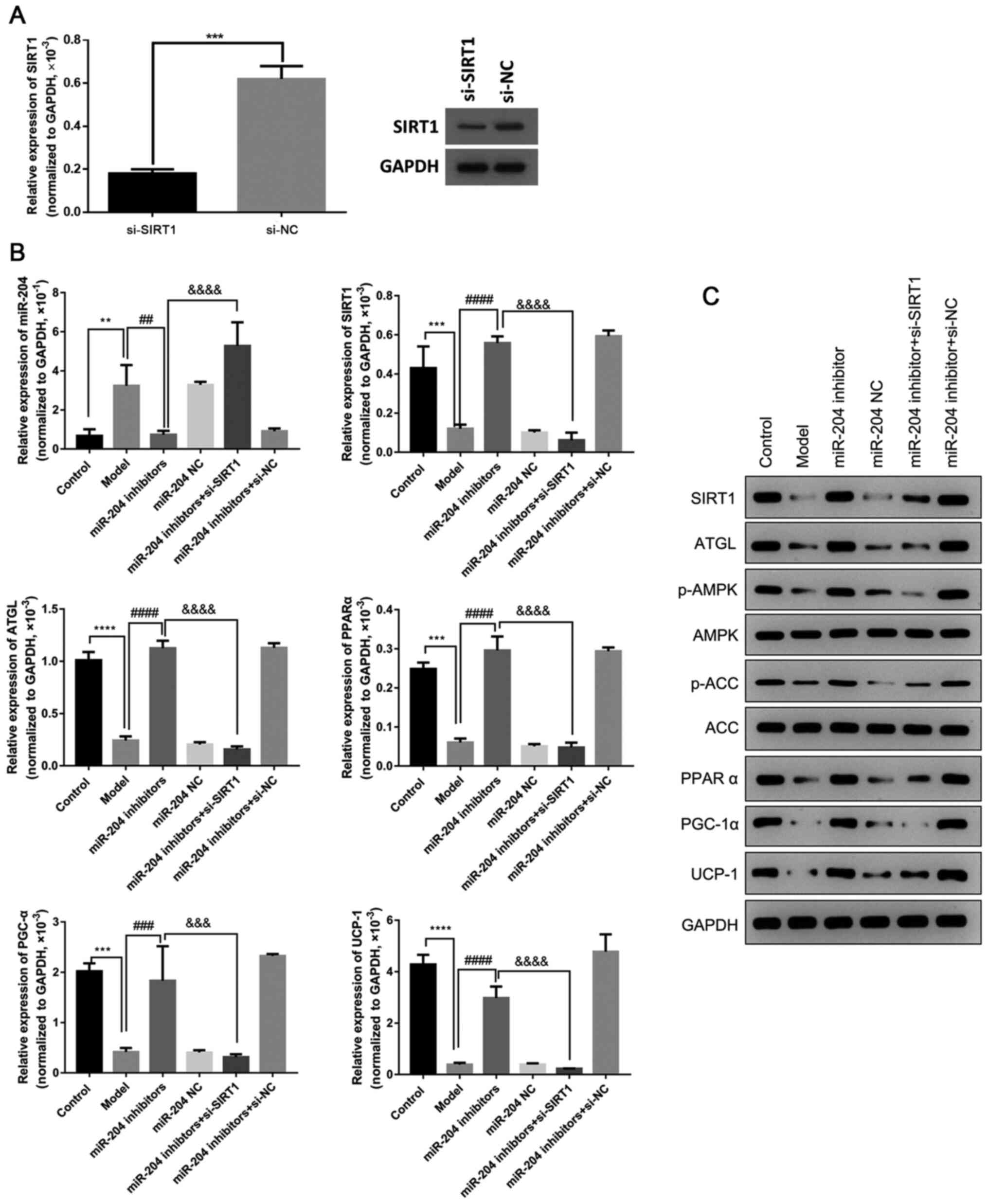
|
1
|
Hoch E, Rusu V, Schreiber SL, Florez JC,
Jacobs SB and Lander ES: Type 2 diabetes-associated variants
disrupt function of SLC16A11, a proton-coupled monocarboxylate
transporter, through two distinct mechanisms. FASEB J.
31:S950.22017.
|
|
2
|
Samuel VT and Shulman GI: Mechanisms for
insulin resistance: Common threads and missing links. Cell.
148:852–871. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nunes MK, Silva AS, de Queiroga
Evangelista IW, Filho JM, Gomes CN, Nascimento RA, Luna RC, de
Carvalho Costa MJ, de Oliveira NF and Persuhn DC: Hypermethylation
in the promoter of the MTHFR gene is associated with diabetic
complications and biochemical indicators. Diabetol Metab Syndr.
9:842017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
American Diabetes Association: 2.
Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care
in diabetes-2018. Diabetes Care. 41(Suppl 1): S13–S27. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rathwa N, Patel R, Palit SP, Ramachandran
AV and Begum R: Genetic variants of resistin and its plasma levels:
Association with obesity and dyslipidemia related to type 2
diabetes susceptibility. Genomics. 111:980–985. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pramanik S, Rathwa N, Patel R,
Ramachandran AV and Begum R: Treatment avenues for type 2 diabetes
and current perspectives on adipokines. Curr Diabetes Rev.
14:201–221. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peirce V and Vidal-Puig A: Regulation of
glucose homoeostasis by brown adipose tissue. Lancet Diabetes
Endocrinol. 1:353–360. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhao S, Mugabo Y, Ballentine G, Attane C,
Iglesias J, Poursharifi P, Zhang D, Nguyen TA, Erb H, Prentki R, et
al: α/β-Hydrolase domain 6 deletion induces adipose browning and
prevents obesity and type 2 diabetes. Cell Rep. 14:2872–2888. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Perry RJ, Camporez JP, Kursawe R,
Titchenell PM, Zhang D, Perry CJ, Jurczak MJ, Abudukadier A, Han
MS, Zhang XM, et al: Hepatic acetyl CoA links adipose tissue
inflammation to hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Cell. 160:745–758. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Timothy JP and Guy RA: Could lncRNAs
contribute to β-cell identity and its loss in type 2 diabetes?
Biochem Soc Trans. 41:797–801. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Carter G, Miladinovic B, Patel AA, Deland
L, Mastorides S and Patel NA: Circulating long noncoding RNA GAS5
levels are correlated to prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
BBA Clin. 4:102–107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peng H, Zou L, Xie J, Wu H, Wu B, Zhu G,
Lv Q, Zhang X, Liu S, Li G, et al: lncRNA NONRATT021972 siRNA
decreases diabetic neuropathic pain mediated by the P2X 3 receptor
in dorsal root ganglia. Mol Neurobiol. 54:511–523. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Leti F and DiStefano JK: Long noncoding
RNAs as diagnostic and therapeutic targets in type 2 diabetes and
related complications. Genes. 8:2072017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Duan LJ, Ding M, Hou LJ, Cui YT, Li CJ and
Yu DM: Long noncoding RNA TUG1 alleviates extracellular matrix
accumulation via mediating microRNA-377 targeting of PPARγ in
diabetic nephropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 484:598–604.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lei X, Zhang L, Li Z and Ren J:
Astragaloside IV/lncrna-TUg1/TraF5 signaling pathway participates
in podocyte apoptosis of diabetic nephropathy rats. Drug Des Dev
Ther. 12:2785–2793. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Price NL, Gomes AP, Ling AJ, Duarte FV,
Martin-Montalvo A, North BJ, Agarwal B, Ye L, Ramadori G, Teodoro
JS, et al: SIRT1 Is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial
effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function. Cell Metab.
15:675–690. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Milne JC, Lambert PD, Schenk S, Carney DP,
Smith JJ, Gagne DJ, Jin L, Boss O, Perni RB, Vu CB, et al: Small
molecule activators of SIRT1 as therapeutics for the treatment of
type 2 diabetes. Nature. 450:712–716. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Banks AS, Kon N, Knight C, Matsumoto M,
Gutiérrez-Juárez R, Rossetti L, Gu W and Accili D: SirT1 gain of
function increases energy efficiency and prevents diabetes in mice.
Cell Metab. 8:333–341. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu SY, Dong B, Fang ZF, Hu XQ, Tang L and
Zhou SH: Knockdown of lnc RNA AK 139328 alleviates myocardial
ischaemia/reperfusion injury in diabetic mice via modulating
miR-204-3p and inhibiting autophagy. J Cell Mol Med. 22:4886–4898.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gnavi R, Migliardi A, Maggini M and Costa
G: Prevalence of and secular trends in diagnosed diabetes in Italy:
1980-2013. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 28:219–225. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yin DD, Zhang EB, You LH, Wang N, Wang LT,
Jin FY, Zhu YN, Cao LH, Yuan QX, De W and Tang W: Downregulation of
lncRNA TUG1 affects apoptosis and insulin secretion in mouse
pancreatic β cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:1892–1904. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cao LH, Yin DD, Xia CC, Wang N and De W:
Function of lncRNA TUG1 in insulin secretion from pancreatic beta
cells. Xian Dai Sheng Wu Yi Xue Jin Zhan. 25:4847–4851. 2017.In
Chinese.
|
|
23
|
Long J, Badal SS, Ye Z, Wang Y, Ayanga BA,
Galvan DL, Green NH, Chang BH, Overbeek PA and Danesh FR: Long
noncoding RNA Tug1 regulates mitochondrial bioenergetics in
diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Invest. 126:4205–4218. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Paiva MA, Rutter-Locher Z, Gonçalves LM,
Providência LA, Davidson SM, Yellon DM and Mocanu MM: Enhancing
AMPK activation during ischemia protects the diabetic heart against
reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
300:H2123–H2134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yi X, Cao S, Chang B, Zhao D, Gao H, Wan
Y, Shi J, Wei W and Guan Y: Effects of acute exercise and chronic
exercise on the liver leptin-AMPK-ACC signaling pathway in rats
with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Res. 2013:9464322013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
He H, Chen K, Wang F, Zhao L, Wan X, Wang
L and Mo Z: MiR-204-5p promotes the adipogenic differentiation of
human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells by modulating DVL3
expression and suppressing wnt/β-catenin signaling. Int J Mol Med.
35:1587–1595. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu C, Li L, Xie F, Guo S, Liu F, Dong N
and Wang Y: LncRNA TUG1 sponges miR-204-5p to promote osteoblast
differen-tiation through upregulating Runx2 in aortic valve
calcification. Cardiovas Res. 114:168–179. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhanguo G, Zhang J, Kheterpal I, Kennedy
N, Davis RJ and Ye J: Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) protein degradation in
response to persistent c-jun n-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) activation
contributes to hepatic steatosis in obesity. J Biol Chem.
286:22227–22234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chen WL, Kang CH, Wang SG and Lee HM:
α-Lipoic acid regulates lipid metabolism through induction of
sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) and activation of AMP-activated protein kinase.
Diabetologia. 55:1824–1835. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang Y, Li W, Liu Y, Sun Y, Li Y, Yao Q,
Li J, Zhang Q, Gao Y, Gao L and Zhao J: Alpha-Lipoic acid improves
high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis by modulating the
transcription factors SREBP-1, FoxO1 and Nrf2 via the
SIRT1/LKB1/AMPK pathway. J Nutr Biochem. 25:1207–1217. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|