|
1
|
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel
RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin.
64:252–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
He J, Shen J, Yang C, Jiang L, Liang W,
Shi X, Xu X and He J: Adjuvant chemotherapy for the completely
resected stage IB nonsmall cell lung cancer: A Systematic review
and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e9032015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lai WY, Wang WY, Chang YC, Chang CJ, Yang
PC and Peck K: Synergistic inhibition of lung cancer cell invasion,
tumor growth and angiogenesis using aptamer-siRNA chimeras.
Biomaterials. 35:2905–2914. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hong S, Tan M, Wang S, Luo S, Chen Y and
Zhang L: Efficacy and safety of angiogenesis inhibitors in advanced
non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 141:909–921. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Qin Y, Zhang Q, Lee S, Zhong WL, Liu YR,
Liu HJ, Zhao D, Chen S, Xiao T, Meng J, et al: Doxycycline reverses
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and suppresses the
proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer cells. Oncotarget.
6:40667–40679. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fischer KR, Durrans A, Lee S, Sheng J, Li
F, Wong ST, Choi H, El Rayes T, Ryu S, Troeger J, et al:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung
metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature. 527:472–476.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Chao Y, Fang Y, Wang J, Wang M,
Zhang H, Ying M, Zhu X and Wang H: MTA1 promotes the invasion and
migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells by downregulating
miR-125b. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 32:332013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen L, Gibbons DL, Goswami S, Cortez MA,
Ahn YH, Byers LA, Zhang X, Yi X, Dwyer D, Lin W, et al: Metastasis
is regulated via microRNA-200/ZEB1 axis control of tumour cell
PD-L1 expression and intratumoral immunosuppression. Nat Commun.
5:52412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li H, Chen Y, Xu N, Yu M, Tu X, Chen Z,
Lin M, Xie B, Fu J and Han L: AMD3100 inhibits brain-specific
metastasis in lung cancer via suppressing the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis and
protecting blood-brain barrier. Am J Transl Res. 9:5259–5274.
2017.
|
|
10
|
Xie S, Zeng W, Fan G, Huang J, Kang G,
Geng Q, Cheng B, Wang W and Dong P: Effect of CXCL12/CXCR4 on
increasing the metastatic potential of non-small cell lung cancer
in vitro is inhibited through the downregulation of CXCR4 chemokine
receptor expression. Oncol Lett. 7:941–947. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kamaraj S, Ramakrishnan G, Anandakumar P,
Jagan S and Devaki T: Antioxidant and anticancer efficacy of
hesperidin in benzo(a)pyrene induced lung carcinogenesis in mice.
Invest New Drugs. 27:214–22. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Khamis AAA, Ali EMM, El-Moneim MAA,
Abd-Alhaseeb MM, El-Magd MA and Salim EI: Hesperidin, piperine and
bee venom synergistically potentiate the anticancer effect of
tamoxifen against breast cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother.
105:1335–1343. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Roohbakhsh A, Parhiz H, Soltani F, Rezaee
R and Iranshahi M: Molecular mechanisms behind the biological
effects of hesperidin and hesperetin for the prevention of cancer
and cardiovascular diseases. Life Sci. 124:64–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
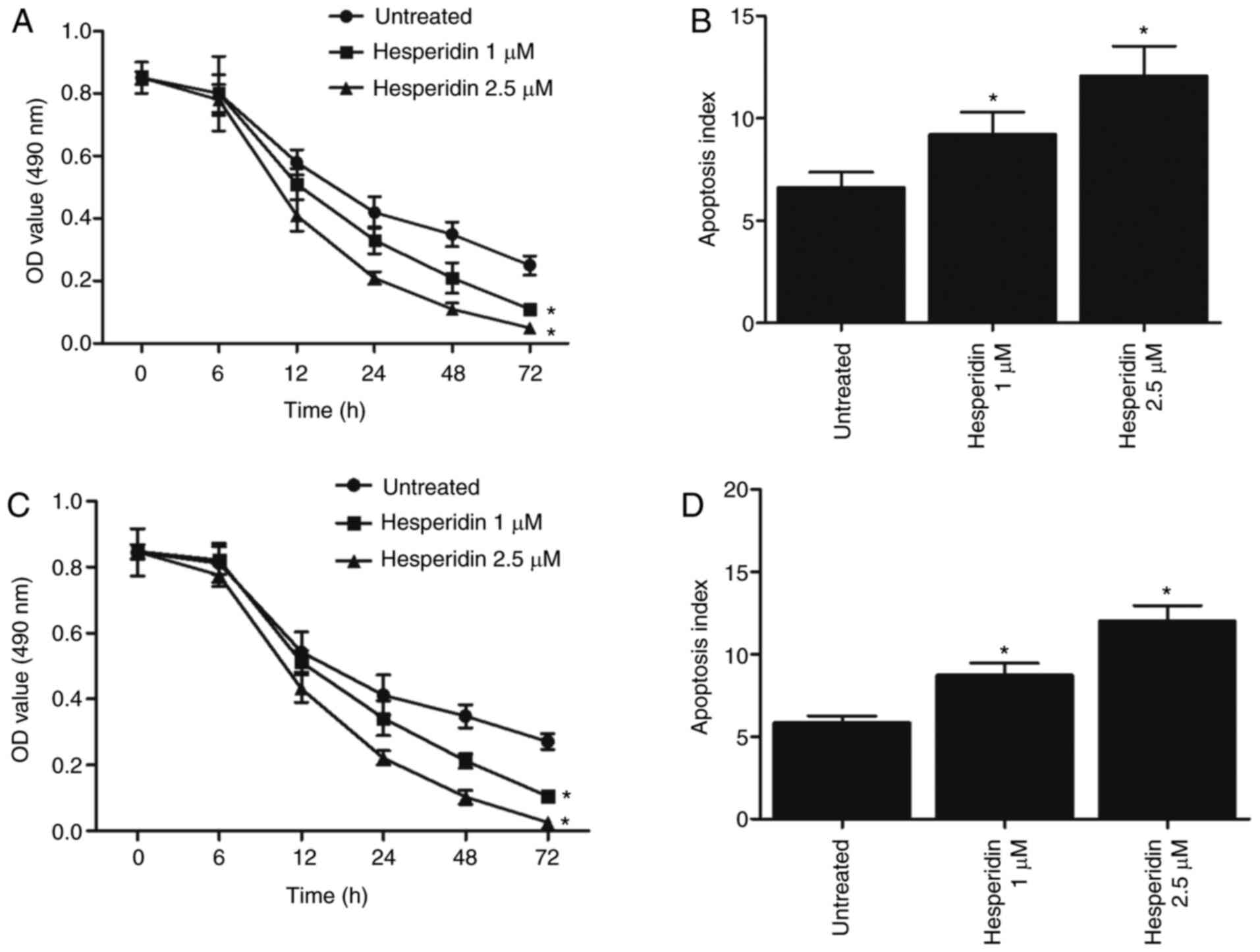
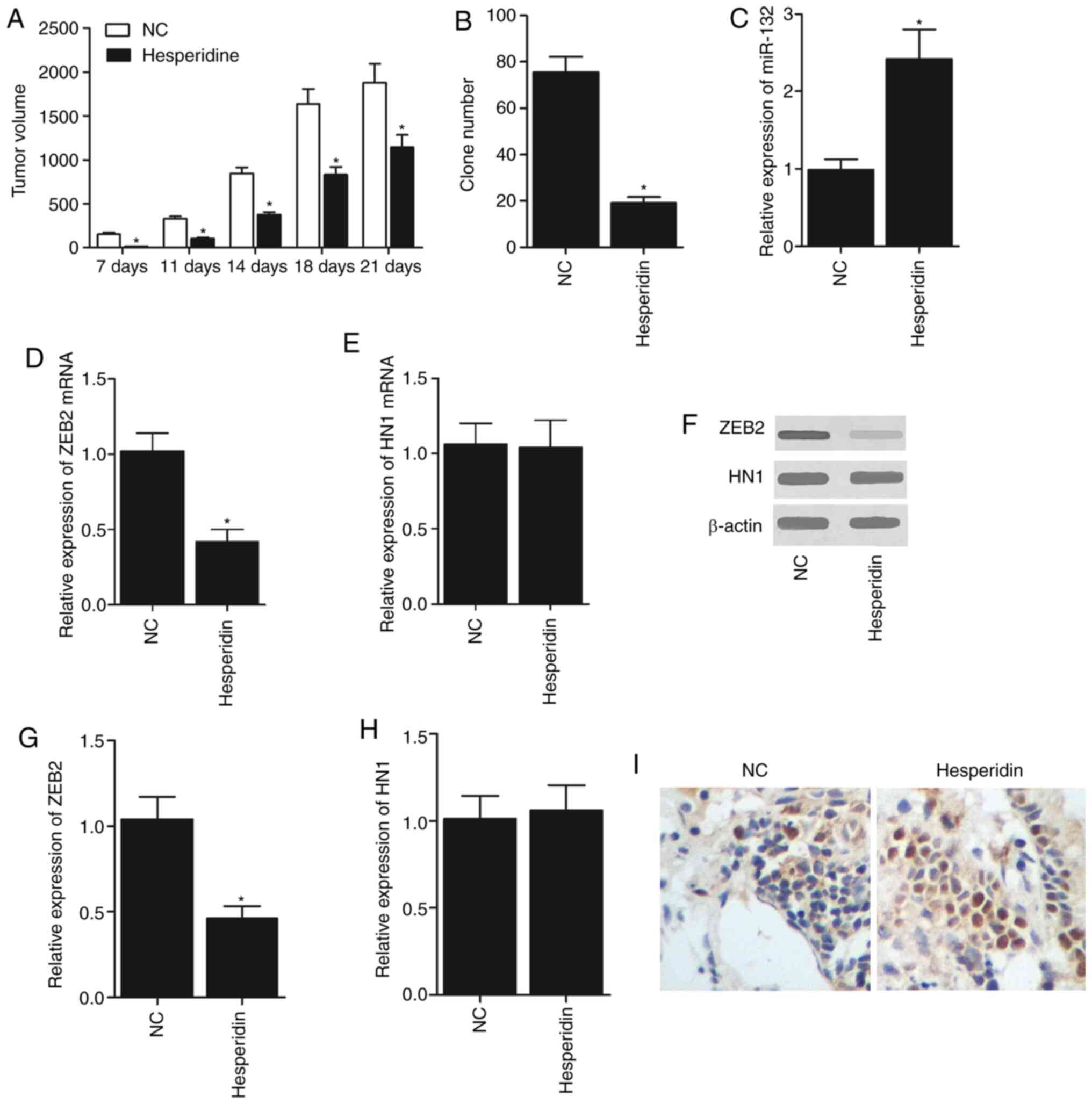
Xia R, Xu G, Huang Y, Sheng X, Xu X and Lu
H: Hesperidin suppresses the migration and invasion of non-small
cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting the SDF-1/CXCR-4 pathway. Life
Sci. 201:111–120. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xia R, Sheng X, Xu X, Yu C and Lu H:
Hesperidin induces apoptosis and G0/G1 arrest in human non-small
cell lung cancer A549 cells. Int J Mol Med. 1:464–472. 2017.
|
|
16
|
Kataoka M and Wang DZ: Non-coding RNAs
including miRNAs and lncRNAs in cardiovascular biology and disease.
Cells. 3:883–898. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moreno-Moya JM, Vilella F and Simon C:
MicroRNA: Key gene expression regulators. Fertil Steril.
101:1516–1523. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ell B and Kang Y: MicroRNAs as regulators
of bone homeostasis and bone metastasis. Bonekey Rep. 3:5492014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Janaki Ramaiah M, Lavanya A, Honarpisheh
M, Zarea M, Bhadra U and Bhadra MP: MiR-15/16 complex targets p70S6
kinase 1 and controls cell proliferation in MDA-MB-231 breast
cancer cells. Gene. 552:255–264. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li W, Zang W, Liu P, Wang Y, Du Y, Chen X,
Deng M, Sun W, Wang L, Zhao G and Zhai B: MicroRNA-124 inhibits
cellular proliferation and invasion by targeting Ets-1 in breast
cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:10897–10904. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
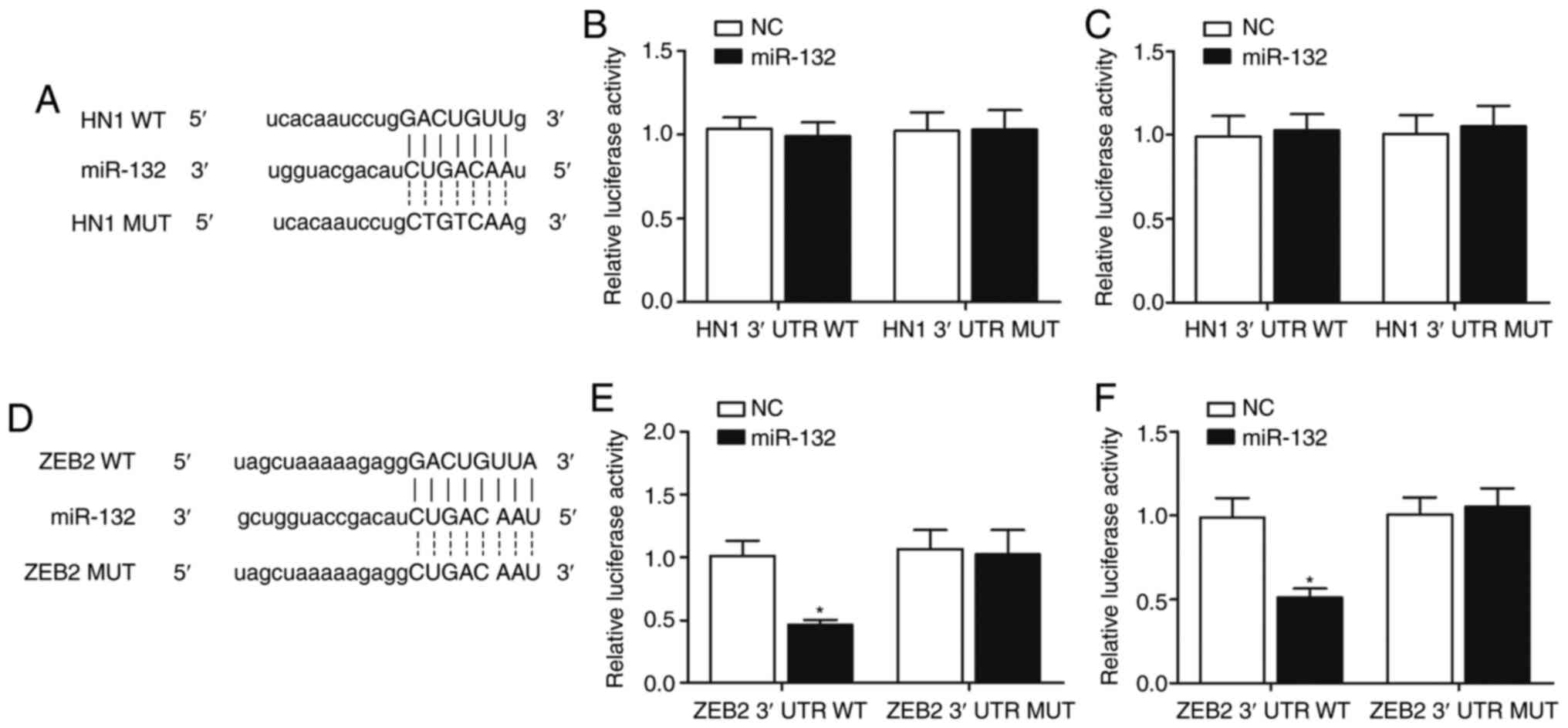
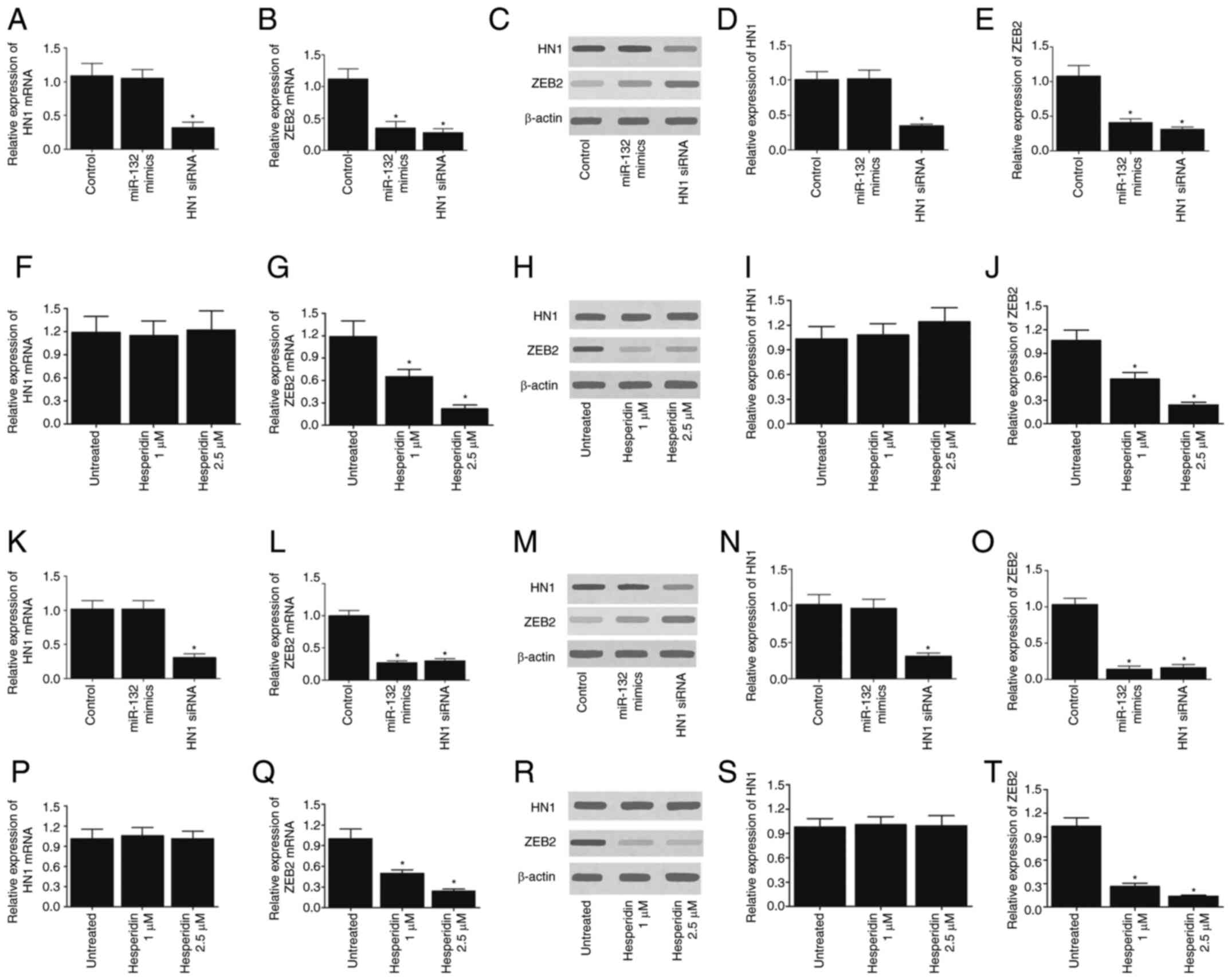
You J, Li Y, Fang N, Liu B, Zu L, Chang R,
Li X and Zhou Q: MiR-132 suppresses the migration and invasion of
lung cancer cells via targeting the EMT regulator ZEB2. PLoS One.
9:e918272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hansen KF, Karelina K, Sakamoto K, Wayman
GA, Impey S and Obrietan K: miRNA-132: A dynamic regulator of
cognitive capacity. Brain Struct Funct. 218:817–831. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Marler KJ, Suetterlin P, Dopplapudi A,
Rubikaite A, Adnan J, Maiorano NA, Lowe AS, Thompson ID, Pathania
M, Bordey A, et al: BDNF promotes axon branching of retinal
ganglion cells via miRNA-132 and p250GAP. J Neurosci. 34:969–979.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marques-Rocha JL, Samblas M, Milagro FI,
Bressan J, Martínez JA and Marti A: Noncoding RNAs, cytokines, and
inflammation-related diseases. FASEB J. 29:3595–3611. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li M, Shao H, Zhang X and Qin B:
Hesperidin alleviates lipopoly-saccharide-induced neuroinflammation
in mice by promoting the miRNA-132 pathway. Inflammation.
39:1681–1689. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yi LT, Li J, Liu BB, Luo L, Liu Q and Geng
D: BDNF-ERK-CREB signalling mediates the role of miR-132 in the
regulation of the effects of oleanolic acid in male mice. J
Psychiatry Neurosci. 39:348–359. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pan B and Liu Y: Effects of duloxetine on
microRNA expression profile in frontal lobe and hippocampus in a
mouse model of depression. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:15454–15461.
2015.
|
|
28
|
You J, Li Y, Fang N, Liu B, Zu L, Chang R,
Li X and Zhou Q: MiR-132 suppresses the migration and invasion of
lung cancer cells via targeting the EMT regulator ZEB2. PLoS One.
9:e918272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang B, Lu L and Zhang X, Ye W, Wu J, Xi
Q and Zhang X: Hsa-miR-132 regulates apoptosis in non-small cell
lung cancer independent of acetylcholinesterase. J Mol Neurosci.
53:335–344. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang JX, Zhai JF, Yang XT and Wang J:
MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in
human non-small cell lung cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
20:3793–3801. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen YK, Wang HC, Ho CT, Chen HY, Li S,
Chan HL, Chung TW, Tan KT, Li YR and Lin CC: 5-demethylnobiletin
promotes the formation of polymerized tubulin, leads to G2/M phase
arrest and induces autophagy via JNK activation in human lung
cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem. 26:484–504. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jayaprakasha GK, Mandadi KK, Poulose SM,
Jadegoud Y, Nagana Gowda GA and Patil BS: Novel triterpenoid from
Citrus aurantium L. possesses chemopreventive properties against
human colon cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 16:5939–5951. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee DH, Park KI, Park HS, Kang SR,
Nagappan A, Kim JA, Kim EH, Lee WS, Hah YS, Chung HJ, et al:
Flavonoids isolated from Korea Citrus aurantium L. induce G2/M
phase arrest and apoptosis in human gastric cancer AGS cells. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:5159012012.
|
|
34
|
Leclere L, Fransolet M, Cote F, Cambier P,
Arnould T, Van Cutsem P and Michiels C: Heat-modified citrus pectin
induces apoptosis-like cell death and autophagy in HepG2 and A549
cancer cells. PLoS One. 10:e01158312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yang T, Wan Z, Liu Z, Li H, Wang H, Lu N,
Chen Z, Mei X and Ren X: In situ mineralization of anticancer drug
into calcium carbonate monodisperse nanospheres and their
pH-responsive release property. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.
63:384–392. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Galati EM, Monforte MT, Kirjavainen S,
Forestieri AM, Trovato A and Tripodo MM: Biological effects of
hesperidin, a citrus flavonoid. (Note I): Antiinflammatory and
analgesic activity. Farmaco. 40:709–712. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang MT, Wood AW, Newmark HL, Sayer JM,
Yagi H, Jerina DM and Conney AH: Inhibition of the mutagenicity of
bay-region diolepoxides of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by
phenolic plant flavonoids. Carcinogenesis. 4:1631–1637. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tanaka T, Makita H, Ohnishi M, Mori H,
Satoh K, Hara A, Sumida T, Fukutani K, Tanaka T and Ogawa H:
Chemoprevention of 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide-induced oral
carcinogenesis in rats by flavonoids diosmin and hesperidin, each
alone and in combi-nation. Cancer Res. 57:246–252. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Balakrishnan A and Menon VP: Effect of
hesperidin on matrix metalloproteinases and antioxidant status
during nico-tine-induced toxicity. Toxicology. 238:90–98. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kamaraj S, Anandakumar P, Jagan S,
Ramakrishnan G and Devaki T: Modulatory effect of hesperidin on
benzo(a)pyrene induced experimental lung carcinogenesis with
reference to COX-2, MMP-2 and MMP-9. Eur J Pharmacol. 649:320–327.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yumnam S, Park HS, Kim MK, Nagappan A,
Hong GE, Lee HJ, Lee WS, Kim EH, Cho JH, Shin SC and Kim GS:
Hesperidin induces paraptosis like cell death in hepatoblastoma,
HepG2 Cells: Involvement of ERK1/2 MAPK [corrected]. PLoS One.
9:e1013212014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Birsu Cincin Z, Unlu M, Kiran B, Sinem
Bireller E, Baran Y and Cakmakoglu B: Anti-proliferative, apoptotic
and signal transduction effects of hesperidin in non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 38:195–204. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Cincin ZB, Kiran B, Baran Y and Cakmakoglu
B: Hesperidin promotes programmed cell death by downregulation of
nonge-nomic estrogen receptor signalling pathway in endometrial
cancer cells. Biomed Pharmaco. 103:336–345. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Shaked I, Meerson A, Wolf Y, Avni R,
Greenberg D, Gilboa-Geffen A and Soreq H: MicroRNA-132 potentiates
cholinergic anti-inflammatory signaling by targeting
acetylcho-linesterase. Immunity. 31:965–973. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu F, Li Y, Jiang R, Nie C, Zeng Z, Zhao
N, Huang C, Shao Q, Ding C, Qing C, et al: miR-132 inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in alveolar macrophages by
the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Exp Lung Res.
41:261–269. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kong H, Yin F, He F, Omran A, Li L, Wu T,
Wang Y and Peng J: The effect of miR-132, miR-146a, and miR-155 on
MRP8/TLR4-induced astrocyte-related inflammation. J Mol Neurosci.
57:28–37. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|