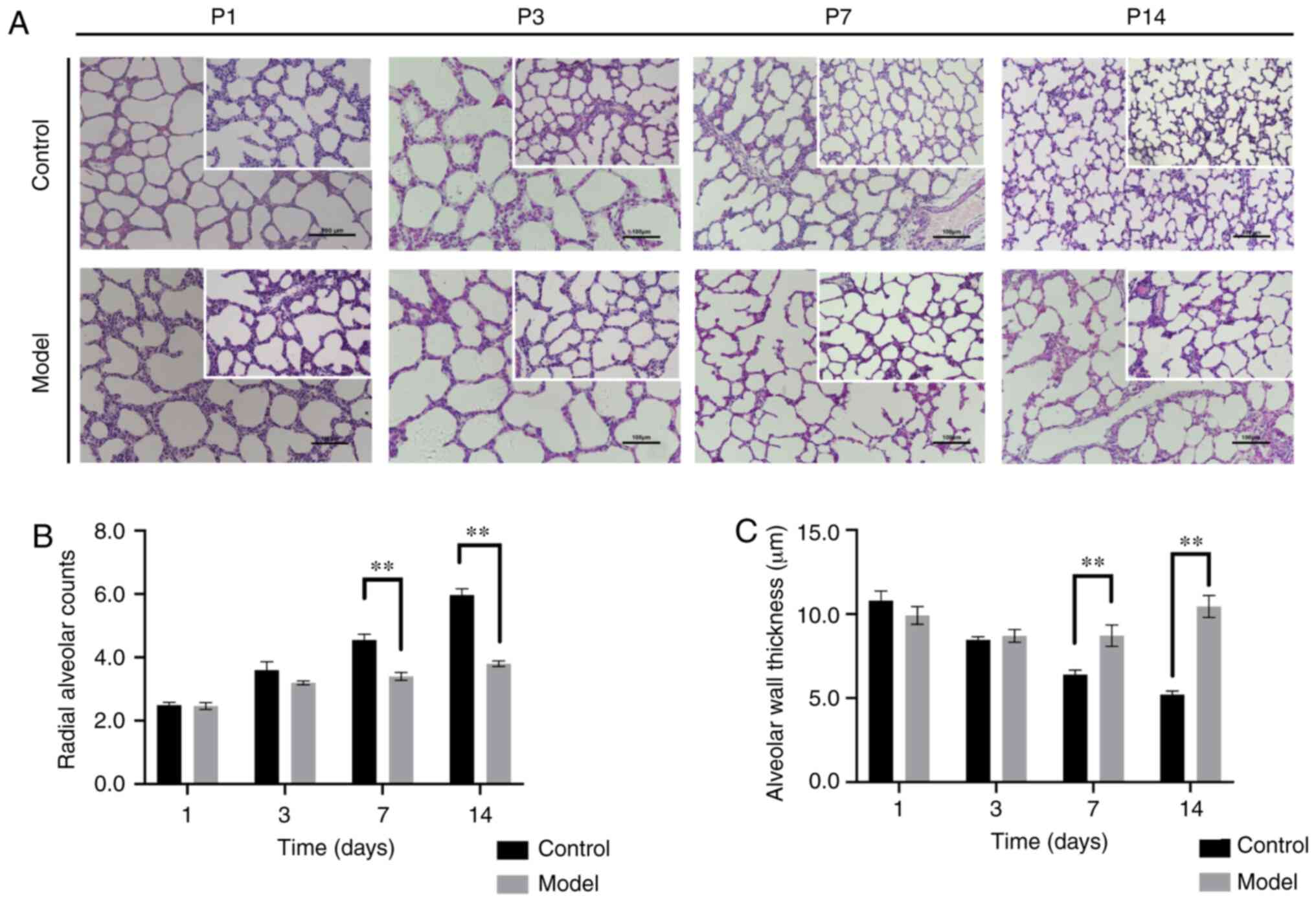
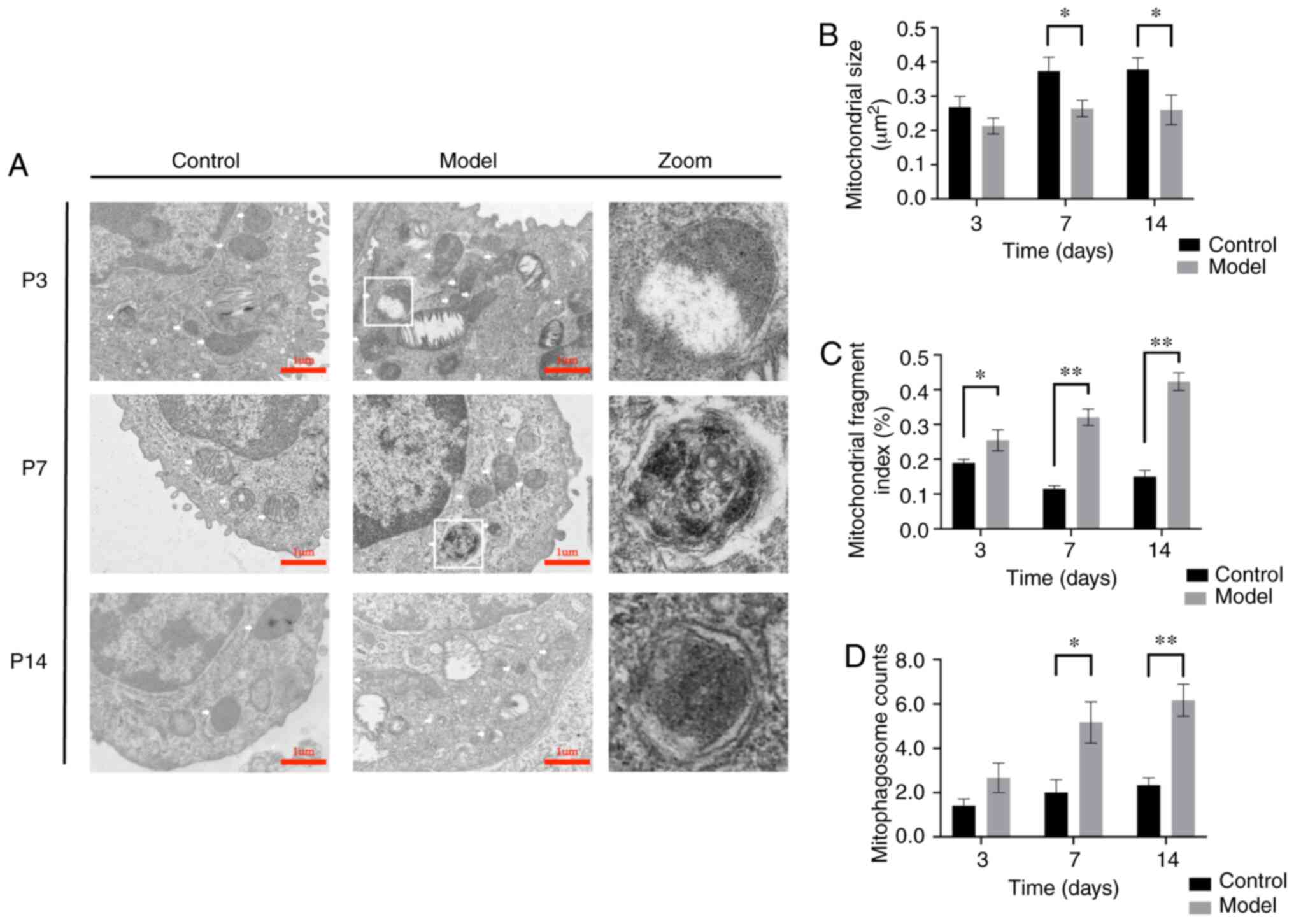
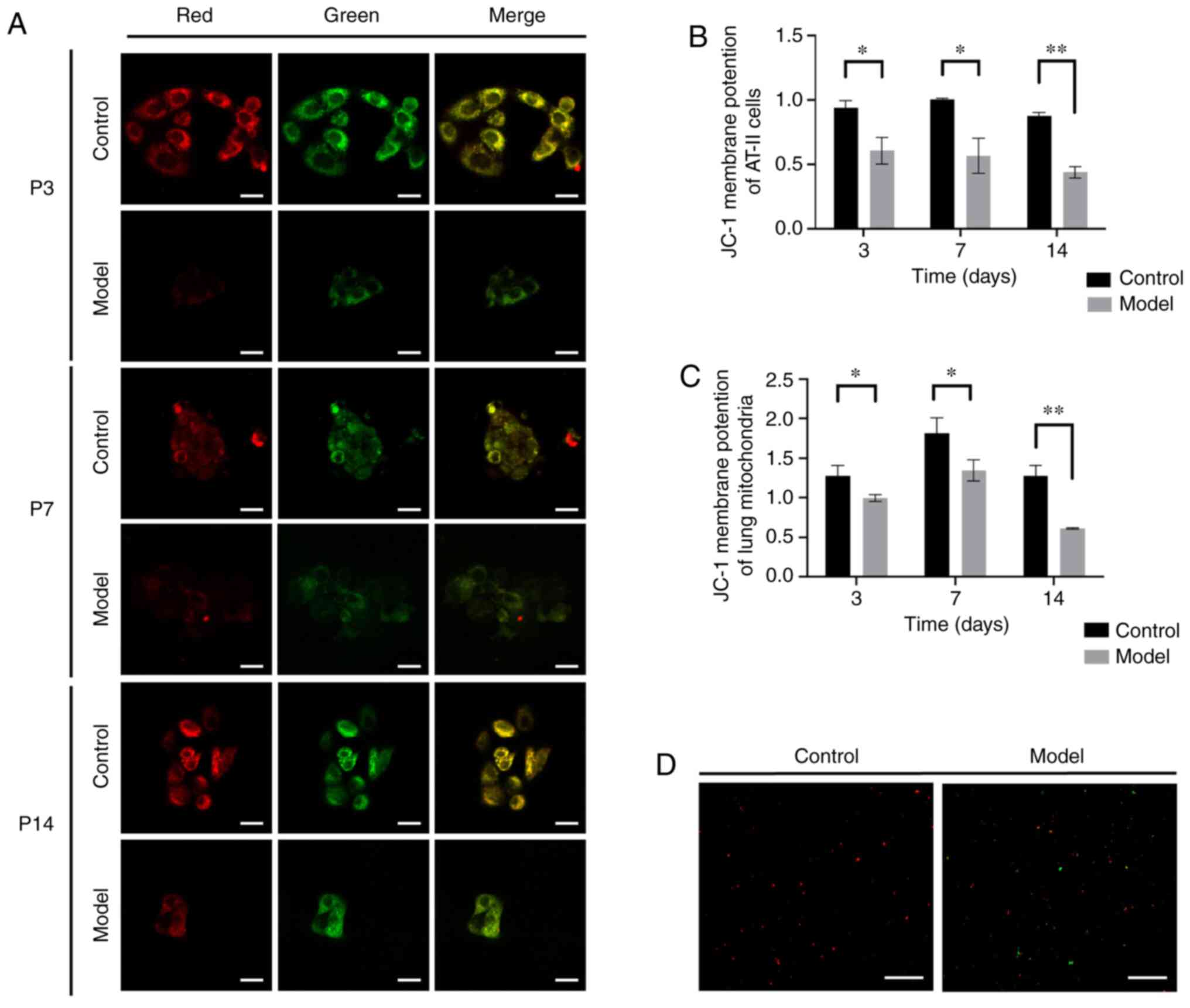
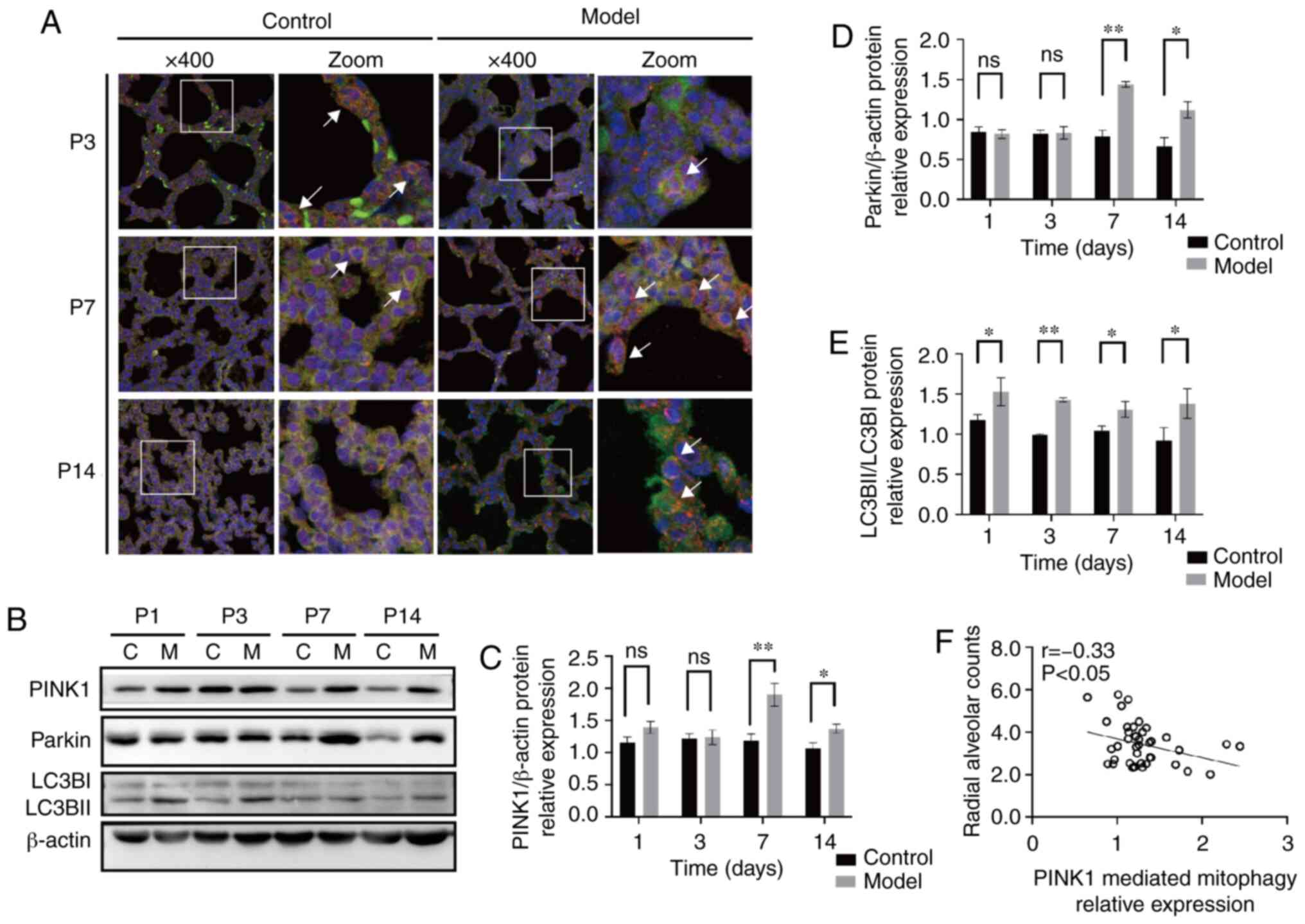
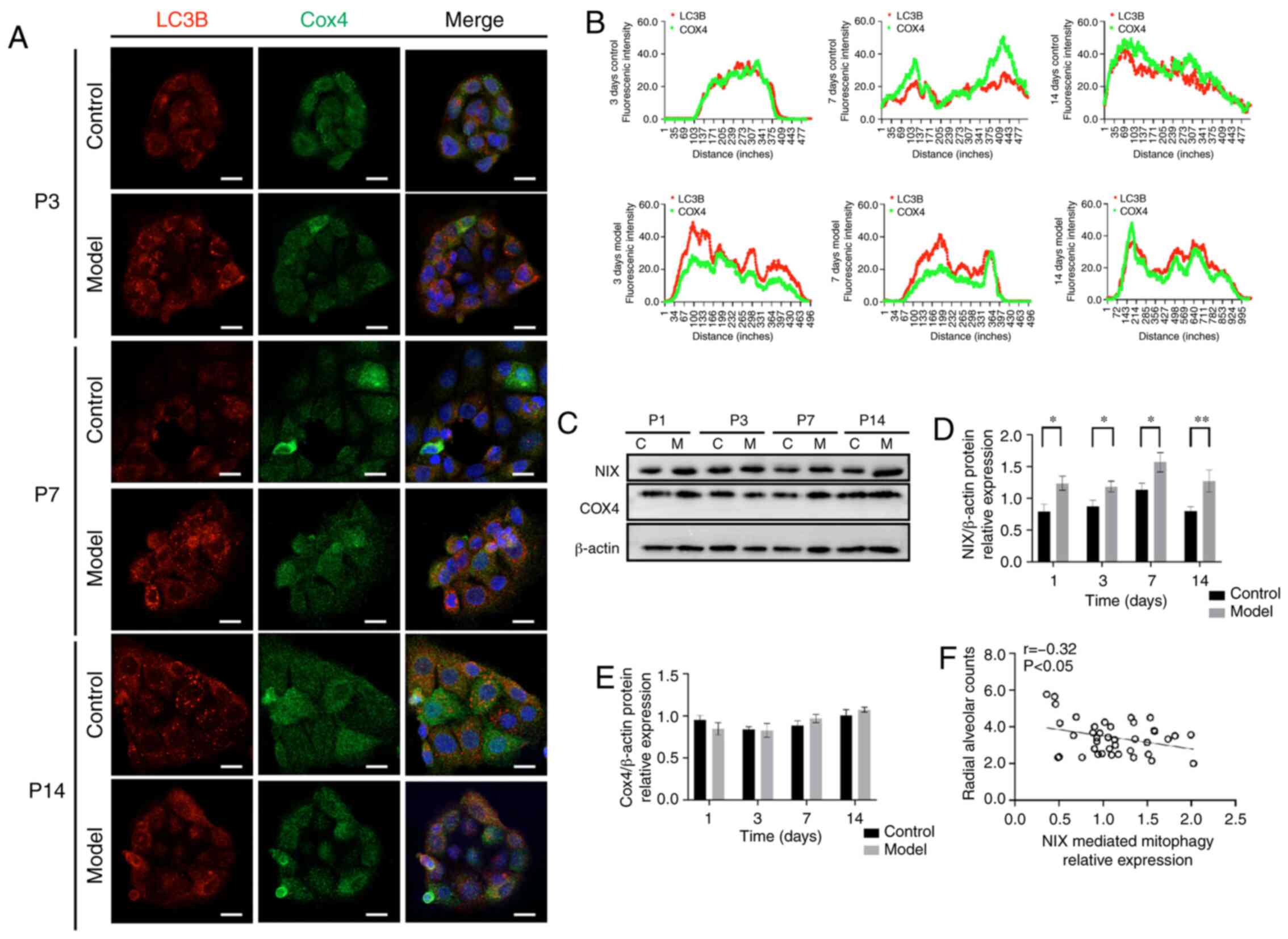
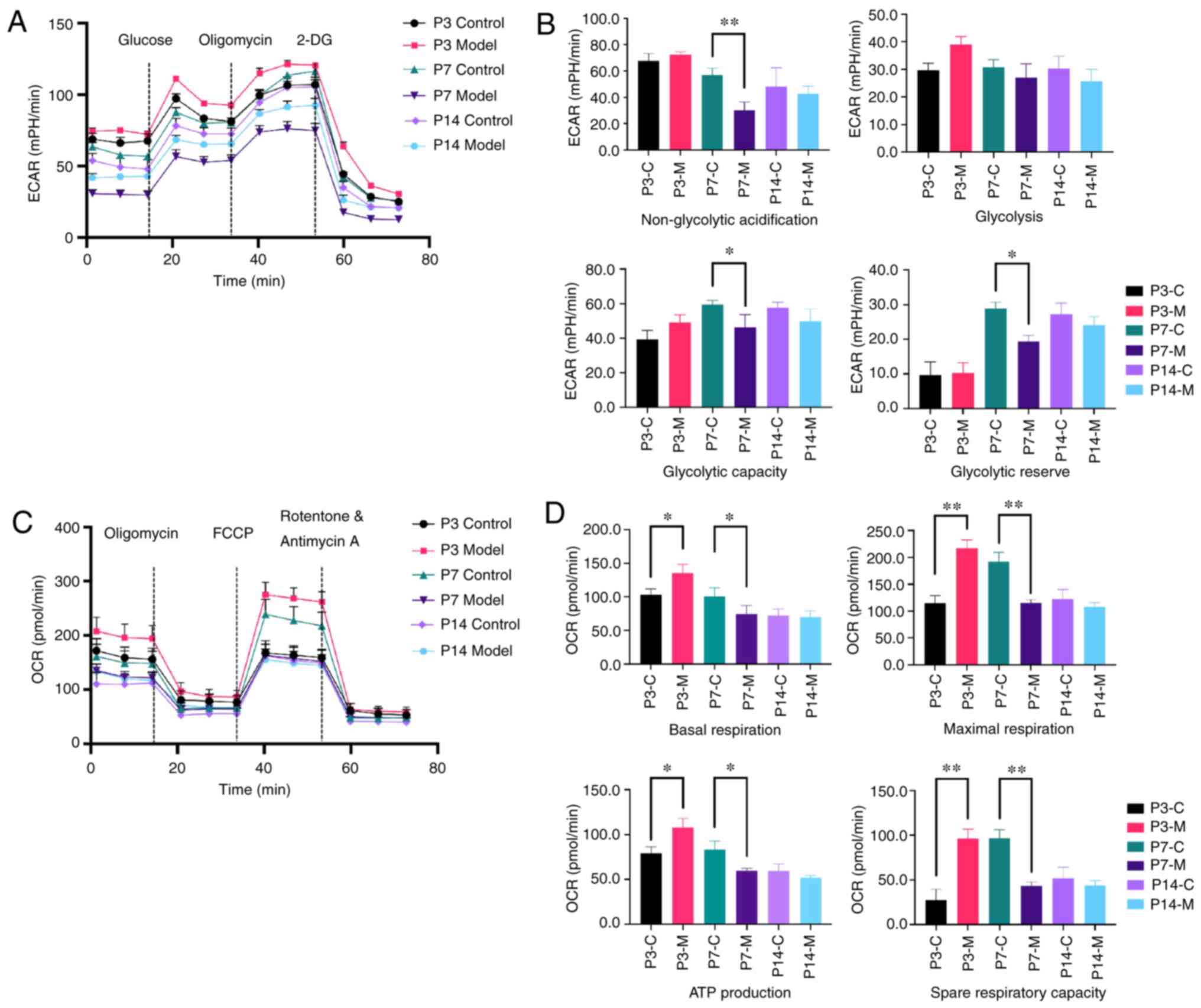
|
1
|
Abman SH, Bancalari E and Jobe A: The
evolution of bronchopulmonary dysplasia after 50 years. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 195:421–424. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Surate Solaligue DE, Rodriguez-Castillo
JA, Ahlbrecht K and Morty RE: Recent advances in our understanding
of the mechanisms of late lung development and bronchopulmonary
dysplasia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 313:L1101–L1153.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Bell EF, Shankaran S,
Laptook AR, Walsh MC, Hale EC, Newman NS, Schibler K, Carlo WA, et
al: Neonatal outcomes of extremely preterm infants from the NICHD
neonatal research network. Pediatrics. 126:443–456. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
García-Muñoz Rodrigo F, Losada Martínez A,
Elorza Fernández MD, Moreno Hernando J, Figueras Aloy J and Vento
Torres M: The burden of respiratory disease in
very-low-birth-weight infants: Changes in perinatal care and
outcomes in a decade in Spain. Neonatology. 112:30–39. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dumpa V and Bhandari V: Surfactant,
steroids and non-invasive ventilation in the prevention of BPD.
Semin Perinatol. 42:444–452. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kalikkot Thekkeveedu R, Guaman MC and
Shivanna B: Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: A review of pathogenesis
and pathophysiology. Respir Med. 132:170–177. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jobe AH and Abman SH: Bronchopulmonary
dysplasia: A continuum of lung disease from the fetus to the adult.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 200:659–660. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen Y, Chang L, Li W, Rong Z, Liu W, Shan
R and Pan R: Thioredoxin protects fetal type II epithelial cells
from hyperoxia-induced injury. Pediatr Pulmonol. 45:1192–1200.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
McGrath-Morrow SA and Stahl J: Apoptosis
in neonatal murine lung exposed to hyperoxia. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 25:150–155. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O'Reilly MA, Staversky RJ, Finkelstein JN
and Keng PC: Activation of the G2 cell cycle checkpoint enhances
survival of epithelial cells exposed to hyperoxia. Am J Physiol
Lung cell Mol Physiol. 284:L368–L375. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bayne AN and Trempe JF: Mechanisms of
PINK1, ubiquitin and Parkin interactions in mitochondrial quality
control and beyond. Cell Mol Life Sci. 76:4589–4611. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang Y, Liu N and Lu B: Mechanisms and
roles of mitophagy in neurodegenerative diseases. cNS Neurosci
Ther. 25:859–875. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sureshbabu A and Bhandari V: Targeting
mitochondrial dysfunction in lung diseases: Emphasis on mitophagy.
Front Physiol. 4:3842013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Meissner C, Lorenz H, Weihofen A, Selkoe
DJ and Lemberg MK: The mitochondrial intramembrane protease PARL
cleaves human Pink1 to regulate Pink1 trafficking. J Neurochem.
117:856–867. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nardin A, Schrepfer E and Ziviani E:
Counteracting PINK/Parkin deficiency in the activation of
mitophagy: A potential therapeutic intervention for Parkinson's
disease. Curr Neuropharmacol. 14:250–259. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Liu H, Dai C, Fan Y, Guo B, Ren K, Sun T
and Wang W: From autophagy to mitophagy: The roles of P62 in
neurodegenerative diseases. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 49:413–422. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wei H, Liu L and Chen Q: Selective removal
of mitochondria via mitophagy: Distinct pathways for different
mitochondrial stresses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1853:2784–2790. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Deczkowska A and Schwartz M: NIX-ing
mitochondria: From development to pathology. EMBO J. 36:1650–1652.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Um JH and Yun J: Emerging role of
mitophagy in human diseases and physiology. BMB Rep. 50:299–307.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yee M, Vitiello PF, Roper JM, Staversky
RJ, Wright TW, McGrath-Morrow SA, Maniscalco WM, Finkelstein JN and
O'Reilly MA: Type II epithelial cells are critical target for
hyperoxia-mediated impairment of postnatal lung development. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 291:L1101–L1111. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cliff TS and Dalton S: Metabolic switching
and cell fate decisions: Implications for pluripotency,
reprogramming and development. Curr Opin Genet dev. 46:44–49. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aravamudan B, Thompson MA, Pabelick CM and
Prakash YS: Mitochondria in lung diseases. Expert Rev Respir Med.
7:631–646. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hou A, Fu J, Yang H, Zhu Y, Pan Y, Xu S
and Xue X: Hyperoxia stimulates the transdifferentiation of type II
alveolar epithelial cells in newborn rats. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 308:L861–L872. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hara H, Araya J, Ito S, Kobayashi K,
Takasaka N, Yoshii Y, Wakui H, Kojima J, Shimizu K, Numata T, et
al: Mitochondrial fragmentation in cigarette smoke-induced
bronchial epithelial cell senescence. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 305:L737–L746. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Resseguie EA, Brookes PS and O'Reilly MA:
SMG-1 kinase attenuates mitochondrial ROS production but not cell
respiration deficits during hyperoxia. Exp Lung Res. 43:229–239.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Song SB, Jang SY, Kang HT, Wei B, Jeoun
UW, Yoon GS and Hwang ES: Modulation of mitochondrial membrane
potential and ROS generation by nicotinamide in a manner
independent of SIRT1 and mitophagy. Mol cells. 40:503–514.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Peixoto P, Grandvallet C, Feugeas JP,
Guittaut M and Hervouet E: Epigenetic control of autophagy in
cancer cells: A key process for cancer-related phenotypes. Cells.
8:16562019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zachari M and Ktistakis NT: Mammalian
mitophagosome formation: A focus on the early signals and steps.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:1712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Walsh BK, Brooks TM and Grenier BM: Oxygen
therapy in the neonatal care environment. Respir Care.
54:1193–1202. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jobe AH and Kallapur SG: Long term
consequences of oxygen therapy in the neonatal period. Semin Fetal
Neonatal Med. 15:230–235. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang J and Dong W: Oxidative stress and
bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Gene. 678:177–183. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bancalari E, Claure N and Sosenko IR:
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: Changes in pathogenesis, epidemiology
and definition. Semin Neonatol. 8:63–71. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Scherz-Shouval R and Elazar Z: Regulation
of autophagy by ROS: Physiology and pathology. Trends Biochem Sci.
36:30–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
El-Merhie N, Baumgart-Vogt E, Pilatz A,
Pfreimer S, Pfeiffer B, Pak O, Kosanovic D, Seimetz M, Schermuly
RT, Weissmann N and Karnati S: differential alterations of the
mitochondrial morphology and respiratory chain complexes during
postnatal development of the mouse lung. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017:91691462017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Anzell AR, Maizy R, Przyklenk K and
Sanderson TH: Mitochondrial quality control and disease: Insights
into ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Neurobiol. 55:2547–2564.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Eiyama A and Okamoto K:
PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in mammalian cells. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 33:95–101. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ahmad T, Sundar IK, Lerner CA, Gerloff J,
Tormos AM, Yao H and Rahman I: Impaired mitophagy leads to
cigarette smoke stress-induced cellular senescence: Implications
for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. FASEB J. 29:2912–2929.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Patel AS, Song JW, Chu SG, Mizumura K,
Osorio JC, Shi Y, El-chemaly S, Lee CG, Rosas IO, Elias JA, et al:
Epithelial cell mitochondrial dysfunction and PINK1 are induced by
transforming growth factor-beta1 in pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS One.
10:e01212462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Araya J, Tsubouchi K, Sato N, Ito S,
Minagawa S, Hara H, Hosaka Y, Ichikawa A, Saito N, Kadota T, et al:
PRKN-regulated mitophagy and cellular senescence during COPD
pathogenesis. Autophagy. 15:510–526. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Zhang D, Wu L, Du Y, Zhu Y, Pan B, Xue X
and Fu J: Autophagy inducers restore impaired autophagy, reduce
apoptosis, and attenuate blunted alveolarization in
hyperoxia-exposed newborn rats. Pediatr Pulmonol. 53:1053–1066.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Durcan TM and Fon EA: The three 'P's of
mitophagy: PARKIN, PINK1, and post-translational modifications.
Genes dev. 29:989–999. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Esteban-Martinez L, Sierra-Filardi E,
McGreal RS, Salazar-Roa M, Mariño G, Seco E, Durand S, Enot D,
Graña O, Malumbres M, et al: Programmed mitophagy is essential for
the glycolytic switch during cell differentiation. EMBO J.
36:1688–1706. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Esteban-Martinez L and Boya P:
BNIP3L/NIX-dependent mitophagy regulates cell differentiation via
metabolic reprogramming. Autophagy. 14:915–917. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Gao F, Chen D, Si J, Hu Q, Qin Z, Fang M
and Wang G: The mitochondrial protein BNIP3L is the substrate of
PARK2 and mediates mitophagy in PINK1/PARK2 pathway. Hum Mol Genet.
24:2528–2538. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhao H, Dennery PA and Yao H: Metabolic
reprogramming in the pathogenesis of chronic lung diseases,
including BPD, COPD, and pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 314:L544–L554. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lottes RG, Newton DA, Spyropoulos DD and
Baatz JE: Lactate as substrate for mitochondrial respiration in
alveolar epithelial type II cells. Am J Physiol Lung cell Mol
Physiol. 308:L953–L961. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ratner V, Starkov A, Matsiukevich D, Polin
RA and Ten VS: Mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to alveolar
developmental arrest in hyperoxia-exposed mice. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 40:511–518. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Das KC: Hyperoxia decreases glycolytic
capacity, glycolytic reserve and oxidative phosphorylation in
MLE-12 cells and inhibits complex I and II function, but not
complex IV in isolated mouse lung mitochondria. PLoS One.
8:e733582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Simon LM, Raffin TA, Douglas WH, Theodore
J and Robin ED: Effects of high oxygen exposure on bioenergetics in
isolated type II pneumocytes. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc
Physiol. 47:98–103. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Naik PP, Birbrair A and Bhutia SK:
Mitophagy-driven metabolic switch reprograms stem cell fate. cell
Mol Life Sci. 76:27–43. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
McCoy MK, Kaganovich A, Rudenko IN, Ding J
and Cookson MR: Hexokinase activity is required for recruitment of
parkin to depolarized mitochondria. Hum Mol Genet. 23:145–156.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Liu K, Li F, Han H, Chen Y, Mao Z, Luo J,
Zhao Y, Zheng B, Gu W and Zhao W: Parkin regulates the activity of
pyruvate kinase M2. J Biol chem. 291:10307–10317. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|