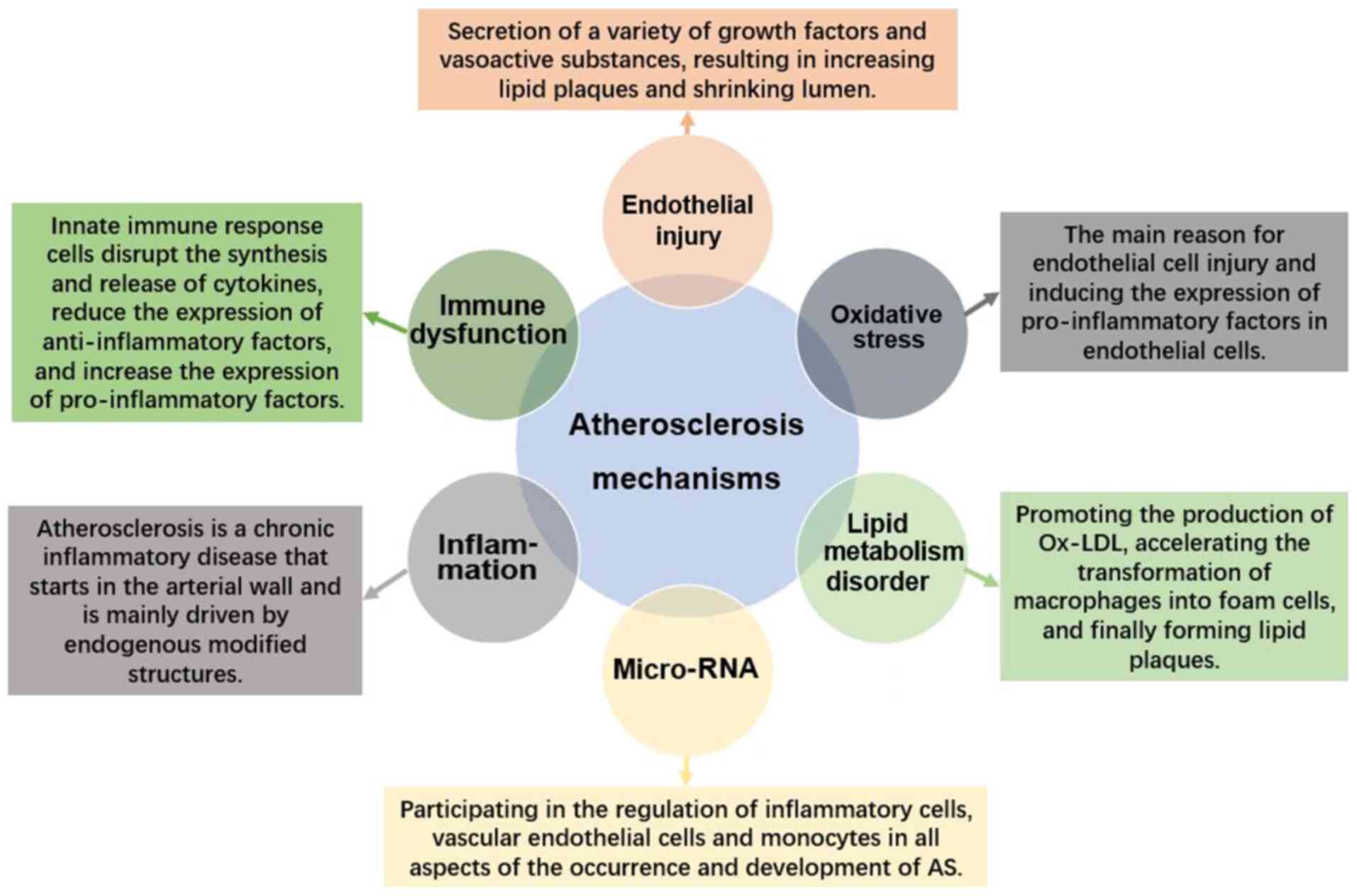
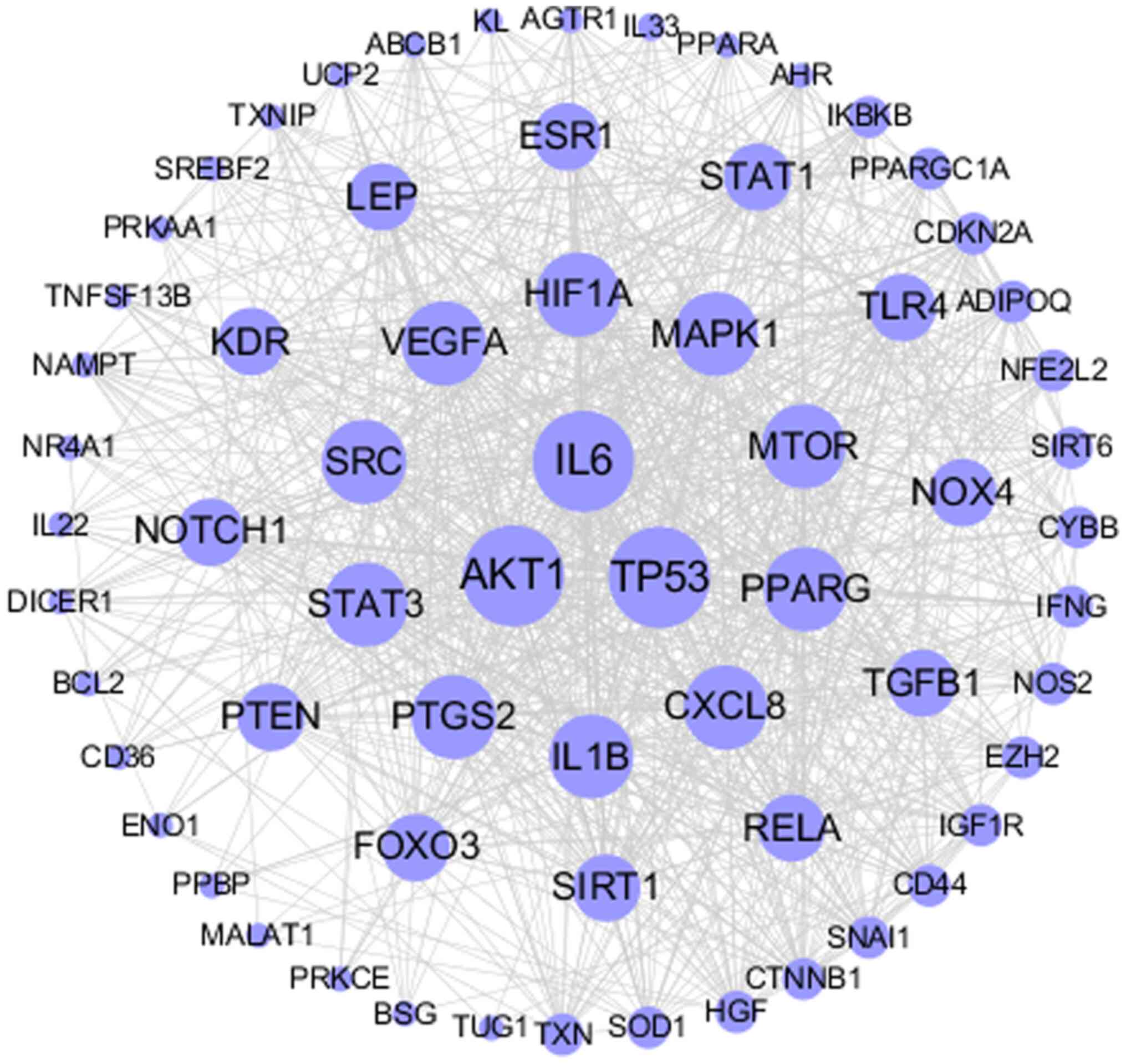
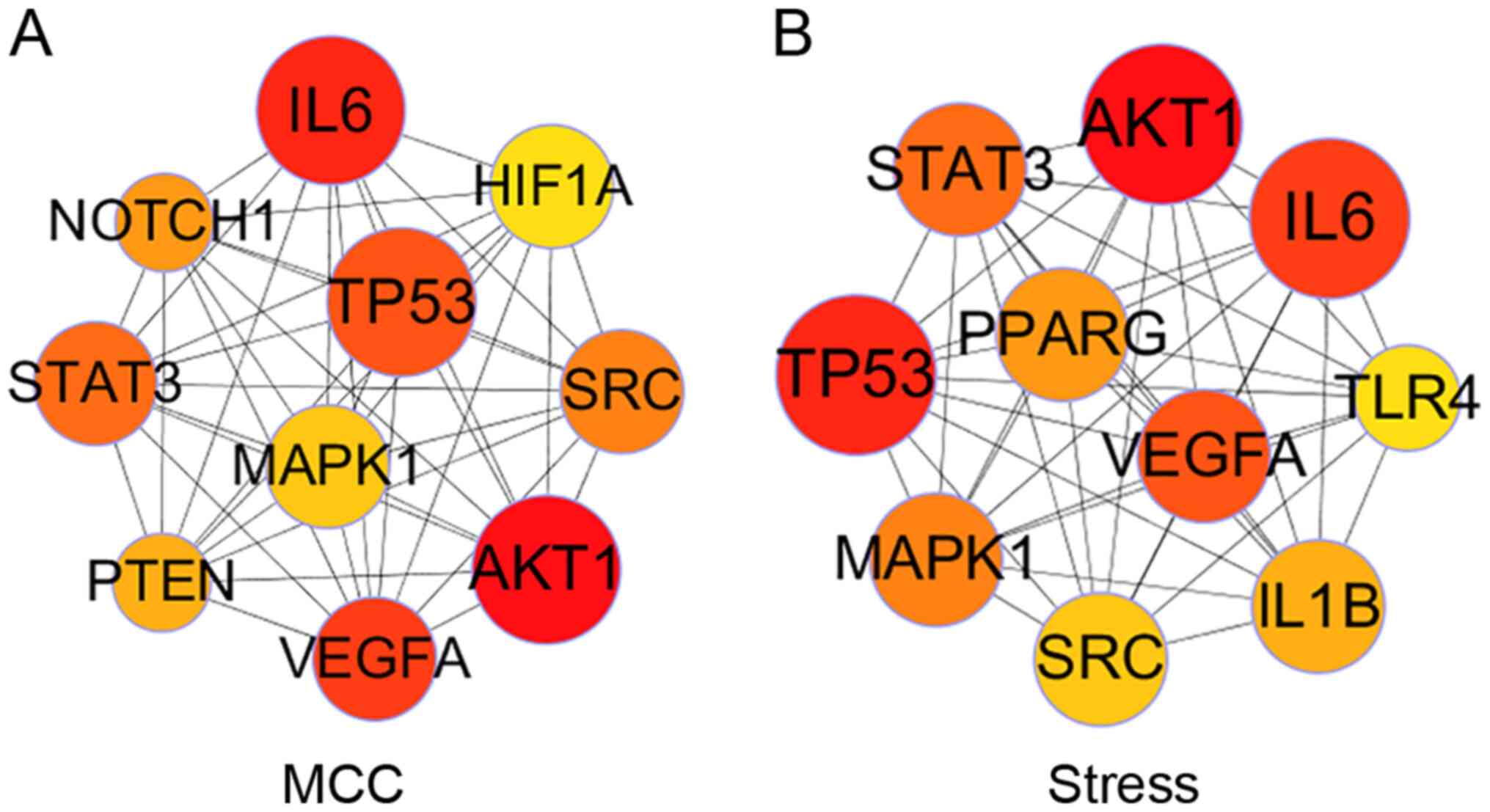
|
1
|
Kobiyama K and Ley K: Atherosclerosis.
Circ Res. 123:1118–1120. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Spinelli FR, Barone F, Cacciapaglia F,
Pecani A and Piga M: Atherosclerosis and autoimmunity. Mediators
Inflamm. 2018:67304212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu H and Daugherty A: Atherosclerosis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:485–491. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Libby P, Buring JE, Badimon L, Hansson GK,
Deanfield J, Bittencourt MS, Tokgözoğlu L and Lewis EF:
Atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 5:562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bories GFP and Leitinger N: Macrophage
metabolism in athero-sclerosis. FEBS Lett. 591:3042–3060. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao Y, Qu H, Wang Y, Xiao W, Zhang Y and
Shi D: Small rodent models of atherosclerosis. Biomed Pharmacother.
129:1104262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Goonewardena SN, Prevette LE and Desai AA:
Metabolomics and atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 12:267–272.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sitia S, Tomasoni L, Atzeni F, Ambrosio G,
Cordiano C, Catapano A, Tramontana S, Perticone F, Naccarato P,
Camici P, et al: From endothelial dysfunction to atherosclerosis.
Autoimmun Rev. 9:830–834. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen PY, Schwartz MA and Simons M:
Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition, vascular inflammation, and
atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 7:532020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gao F, Chen J and Zhu H: A potential
strategy for treating athero-sclerosis: Improving endothelial
function via AMP-activated protein kinase. Sci China Life Sci.
61:1024–1029. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pircher A, Treps L, Bodrug N and Carmeliet
P: Endothelial cell metabolism: A novel player in atherosclerosis?
Basic principles and therapeutic opportunities. Atherosclerosis.
253:247–257. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao X, Tan F, Cao X, Cao Z, Li B, Shen Z
and Tian Y: PKM2-dependent glycolysis promotes the proliferation
and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells during
atherosclerosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 52:9–17.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ilhan F and Kalkanli ST: Atherosclerosis
and the role of immune cells. World J Clin Cases. 3:345–352. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiao W, Jia Z, Zhang Q, Wei C, Wang H and
Wu Y: Inflammation and oxidative stress, rather than hypoxia, are
predominant factors promoting angiogenesis in the initial phases of
atherosclerosis. Mol Med Rep. 12:3315–3322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dinh QN, Chrissobolis S, Diep H, Chan CT,
Ferens D, Drummond GR and Sobey CG: Advanced atherosclerosis is
associated with inflammation, vascular dysfunction and oxida-tive
stress, but not hypertension. Pharmacol Res. 116:70–76. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yang K, Zhang H, Luo Y, Zhang J, Wang M,
Liao P, Cao L, Guo P, Sun G and Sun X: Gypenoside XVII prevents
atherosclerosis by attenuating endothelial apoptosis and oxidative
stress: Insight into the ERα-Mediated PI3K/Akt Pathway. Int J Mol
Sci. 18:772017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Feletou M, Cohen RA, Vanhoutte PM and
Verbeuren TJ: TP receptors and oxidative stress hand in hand from
endothelial dysfunction to atherosclerosis. Adv Pharmacol.
60:85–106. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Armstrong AW, Voyles SV, Armstrong EJ,
Fuller EN and Rutledge JC: Angiogenesis and oxidative stress:
Common mechanisms linking psoriasis with atherosclerosis. J
Dermatol Sci. 63:1–9. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gupta M, Blumenthal C, Chatterjee S,
Bandyopadhyay D, Jain V, Lavie CJ, Virani SS, Ray KK, Aronow WS and
Ghosh RK: Novel emerging therapies in atherosclerosis targeting
lipid metabolism. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 29:611–622. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee J, Jung S, Kim N, Shin MJ, Ryu DH and
Hwang GS: Myocardial metabolic alterations in mice with
diet-induced atherosclerosis: Linking sulfur amino acid and lipid
metabolism. Sci Rep. 7:135972017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Novák J, Olejníčková V, Tkáčová N and
Santulli G: Mechanistic role of MicroRNAs in coupling lipid
metabolism and atherosclerosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 887:79–100. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shao D, Lian Z, Di Y, Zhang L, Rajoka MSR,
Zhang Y, Kong J, Jiang C and Shi J: Dietary compounds have
potential in controlling atherosclerosis by modulating macrophage
cholesterol metabolism and inflammation via miRNA. NPJ Sci Food.
2:132018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Giral H, Kratzer A and Landmesser U:
MicroRNAs in lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis. Best Pract Res
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 30:665–676. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gimbrone MA Jr and García-Cardeña G:
Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 118:620–636. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mudau M, Genis A, Lochner A and Strijdom
H: Endothelial dysfunction: The early predictor of atherosclerosis.
Cardiovasc J Afr. 23:222–231. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Brix B, Mesters JR, Pellerin L and Johren
O: Endothelial cell-derived nitric oxide enhances aerobic
glycolysis in astrocytes via HIF-1α-mediated target gene
activation. J Neurosci. 32:9727–9735. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Legein B, Temmerman L, Biessen EA and
Lutgens E: Inflammation and immune system interactions in
atherosclerosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:3847–3869. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Libby P and Hansson GK: Taming immune and
inflammatory responses to treat atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol.
71:173–176. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wolf D and Ley K: Immunity and
Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 124:315–327. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hansson GK and Hermansson A: The immune
system in athero-sclerosis. Nat Immunol. 12:204–212. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Iwata H and Nagai R: Novel immune signals
and atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 14:484–490. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kuosmanen SM, Kansanen E, Kaikkonen MU,
Sihvola V, Pulkkinen K, Jyrkkänen HK, Tuoresmäki P, Hartikainen J,
Hippeläinen M, Kokki H, et al: NRF2 regulates endothelial
glycolysis and proliferation with miR-93 and mediates the effects
of oxidized phospholipids on endothelial activation. Nucleic Acids
Res. 46:1124–1138. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Ouimet M, Ediriweera HN, Gundra UM, Sheedy
FJ, Ramkhelawon B, Hutchison SB, Rinehold K, van Solingen C,
Fullerton MD, Cecchini K, et al: MicroRNA-33-dependent regulation
of macrophage metabolism directs immune cell polarization in
atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 125:4334–4348. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kumar S, Kim CW, Simmons RD and Jo H: Role
of flow-sensitive microRNAs in endothelial dysfunction and
atherosclerosis: Mechanosensitive athero-miRs. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 34:2206–2216. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Barton M: Mechanisms and therapy of
atherosclerosis and its clinical complications. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 13:149–153. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gonzalez L and Trigatti BL: Macrophage
apoptosis and necrotic core development in atherosclerosis: A
rapidly advancing field with clinical relevance to imaging and
therapy. Can J Cardiol. 33:303–312. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen C, Wang Y, Cao Y, Wang Q, Anwaier G,
Zhang Q and Qi R: Mechanisms underlying the inhibitory effects of
probucol on elastase-induced abdominal aortic aneurysm in mice. Br
J Pharmacol. 177:204–216. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Guo X, Wang L, Xia X, Wang P and Li X:
Effects of atorvastatin and/or probucol on recovery of
atherosclerosis in high-fat-diet-fed apolipoprotein E-deficient
mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 109:1445–1453. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Profumo E, Buttari B, D'Arcangelo D,
Tinaburri L, Dettori MA, Fabbri D, Delogu G and Riganò R: The
nutraceutical dehydroz-ingerone and its dimer counteract
inflammation- and oxidative stress-induced dysfunction of in vitro
cultured human endothelial cells: A novel perspective for the
prevention and therapy of atherosclerosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:12464852016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Jiang Y, Jin M, Chen J, Yan J, Liu P, Yao
M, Cai W and Pi R: Discovery of a novel niacin-lipoic acid dimer
N2L attenuating atherosclerosis and dyslipidemia with non-flushing
effects. Eur J Pharmacol. 868:1728712020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ren Y, Qiao W, Fu D, Han Z, Liu W, Ye W
and Liu Z: Traditional Chinese medicine protects against cytokine
production as the potential immunosuppressive agents in
atherosclerosis. J Immunol Res. 2017:74243072017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li TT, Wang ZB, Li Y, Cao F, Yang BY and
Kuang HX: The mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine underlying
the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis. Chin J Nat Med.
17:401–412. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tian F, Gu L, Si A, Yao Q, Zhang X, Zhao J
and Hu D: Metabolomic study on the faecal extracts of
atherosclerosis mice and its application in a traditional Chinese
Medicine. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
1007:140–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fan Q, Liu Y, Rao J, Zhang Z, Xiao W, Zhu
T, Chai X, Ye K, Ning N, Yin Z, et al: Anti-atherosclerosis effect
of angong niuhuang pill via regulating Th17/Treg immune balance and
inhibiting chronic inflammatory on ApoE−/− mice model of
early and mid-term atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol. 10:15842020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhu ZB, Song K, Huang WJ, Li H, Yang H,
Bai YQ, Guo KT, Yang RB, Lou WJ, Xia CH, et al: Si-Miao-Yong-An
(SMYA) decoction may protect the renal function through regulating
the autophagy-mediated degradation of ubiquitinated protein in an
atherosclerosis model. Front Pharmacol. 11:8372020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li L, Yu AL, Wang ZL, Chen K, Zheng W,
Zhou JJ, Xie Q, Yan HB, Ren P and Huang X: Chaihu-Shugan-San and
absorbed meranzin hydrate induce anti-atherosclerosis and
behavioral improvements in high-fat diet ApoE−/− mice
via anti-inflammatory and BDNF-TrkB pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
115:1088932019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Haskard DO, Boyle JJ, Evans PC, Mason JC
and Randi AM: Cytoprotective signaling and gene expression in
endothelial cells and macrophages-lessons for atherosclerosis.
Microcirculation. 20:203–216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Dong Y, Fernandes C, Liu Y, Wu Y, Wu H,
Brophy ML, Deng L, Song K, Wen A, Wong S, et al: Role of
endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling in diabetic endothelial
dysfunction and athero-sclerosis. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 14:14–23.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Chrysohoou C, Kollia N and Tousoulis D:
The link between depression and atherosclerosis through the
pathways of inflammation and endothelium dysfunction. Maturitas.
109:1–5. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Jensen HA and Mehta JL: Endothelial cell
dysfunction as a novel therapeutic target in atherosclerosis.
Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 14:1021–1033. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Theodorou K and Boon RA: Endothelial cell
metabolism in atherosclerosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 6:822018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Verma I, Syngle A, Krishan P and Garg N:
Endothelial progenitor cells as a marker of endothelial dysfunction
and atherosclerosis in Ankylosing Spondylitis: A cross-sectional
study. Int J Angiol. 26:36–42. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lee DY and Chiu JJ: Atherosclerosis and
flow: Roles of epigenetic modulation in vascular endothelium. J
Biomed Sci. 26:562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Georgescu A, Alexandru N, Andrei E, Dragan
E, Cochior D and Dias S: Effects of transplanted circulating
endothelial progenitor cells and platelet microparticles in
atherosclerosis development. Biol Cell. 108:219–243. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Xiang W, Hu ZL, He XJ and Dang XQ:
Intravenous transfusion of endothelial progenitor cells that
overexpress vitamin D receptor inhibits atherosclerosis in
apoE-deficient mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:1233–1242. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kong M, Zhao Y, Chen A and Lin A: The
importance of physiologic ischemia training in preventing the
development of atherosclerosis: The role of endothelial progenitor
cells in athero-sclerotic rabbits. Coron Artery Dis. 30:377–383.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Pákozdi A, Besenyei T, Paragh G, Koch AE
and Szekanecz Z: Endothelial progenitor cells in
arthritis-associated vasculogenesis and atherosclerosis. Joint Bone
Spine. 76:581–583. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hu X, Cai X, Ma R, Fu W, Zhang C and Du X:
Iron-load exacerbates the severity of atherosclerosis via inducing
inflammation and enhancing the glycolysis in macrophages. J Cell
Physiol. 234:18792–18800. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Flynn MC, Kraakman MJ, Tikellis C, Lee
MKS, Hanssen NMJ, Kammoun HL, Pickering RJ, Dragoljevic D,
Al-Sharea A, Barrett TJ, et al: Transient intermittent
hyperglycemia accelerates atherosclerosis by promoting
myelopoiesis. Circ Res. 127:877–892. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Matsuura Y, Yamashita A, Zhao Y, Iwakiri
T, Yamasaki K, Sugita C, Koshimoto C, Kitamura K, Kawai K, Tamaki
N, et al: Altered glucose metabolism and hypoxic response in
alloxan-induced diabetic atherosclerosis in rabbits. PLoS One.
12:e01759762017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Vojinovic D, van der Lee SJ, van Duijn CM,
Vernooij MW, Kavousi M, Amin N, Demirkan A, Ikram MA, van der Lugt
A and Bos D: Metabolic profiling of intra- and extracranial carotid
artery atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 272:60–65. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Akins NS, Nielson TC and Le HV: Inhibition
of glycolysis and glutaminolysis: An emerging drug discovery
approach to combat cancer. Curr Top Med Chem. 18:494–504. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Deng F, Zhou R, Lin C, Yang S, Wang H, Li
W, Zheng K, Lin W, Li X, Yao X, et al: Tumor-secreted dickkopf2
accelerates aerobic glycolysis and promotes angiogenesis in
colorectal cancer. Theranostics. 9:1001–1014. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Godfrey R and Quinlivan R: Skeletal muscle
disorders of glycogenolysis and glycolysis. Nat Rev Neurol.
12:393–402. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Schoors S, De Bock K, Cantelmo AR,
Georgiadou M, Ghesquière B, Cauwenberghs S, Kuchnio A, Wong BW,
Quaegebeur A, Goveia J, et al: Partial and transient reduction of
glycolysis by PFKFB3 blockade reduces pathological angiogenesis.
Cell Metab. 19:37–48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Fernie AR, Carrari F and Sweetlove LJ:
Respiratory metabolism: Glycolysis, the TCA cycle and mitochondrial
electron transport. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 7:254–261. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Tang BL: Glucose, glycolysis, and
neurodegenerative diseases. J Cell Physiol. 235:7653–7662. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Paik JY, Lee KH, Ko BH, Choe YS, Choi Y
and Kim BT: Nitric oxide stimulates 18F-FDG uptake in human
endothelial cells through increased hexokinase activity and GLUT1
expression. J Nucl Med. 46:365–370. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kim JW, Gao P, Liu YC, Semenza GL and Dang
CV: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and dysregulated c-Myc cooperatively
induce vascular endothelial growth factor and metabolic switches
hexokinase 2 and pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1. Mol Cell Biol.
27:7381–7393. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Song J, Li Y, Song J, Hou F, Liu B and Li
A: Mangiferin protects mitochondrial function by preserving
mitochondrial hexokinase-II in vessel endothelial cells. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:1829–1839. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wang Y, Han X, Fu M, Wang J, Song Y, Liu
Y, Zhang J, Zhou J and Ge J: Qiliqiangxin attenuates
hypoxia-induced injury in primary rat cardiac microvascular
endothelial cells via promoting HIF-1α-dependent glycolysis. J Cell
Mol Med. 22:2791–2803. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wik JA, Lundbäck P, la Cour Poulsen L,
Haraldsen G, Skålhegg BS and Hol J: 3PO inhibits inflammatory NFκB
and stress-activated kinase signaling in primary human endothelial
cells independently of its target PFKFB3. PLoS One.
15:e02293952020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Zhang R, Li R, Liu Y, Li L and Tang Y: The
glycolytic enzyme PFKFB3 controls TNF-α-induced endothelial
proinflammatory responses. Inflammation. 42:146–155. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Lu S, Deng J, Liu H, Liu B, Yang J, Miao
Y, Li J, Wang N, Jiang C, Xu Q, et al: PKM2-dependent metabolic
reprogramming in CD4+ T cells is crucial for
hyperhomocysteinemia-accelerated atherosclerosis. J Mol Med (Berl).
96:585–600. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Zhang X, Chen B, Wu J, Sha J, Yang B, Zhu
J, Sun J, Hartung J and Bao E: Aspirin enhances the protection of
Hsp90 from heat-stressed injury in cardiac microvascular
endothelial cells through PI3K-Akt and PKM2 pathways. Cells.
9:2432020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
76
|
Serganova I, Cohen IJ, Vemuri K, Shindo M,
Maeda M, Mane M, Moroz E, Khanin R, Satagopan J, Koutcher JA and
Blasberg R: LDH-A regulates the tumor microenvironment via
HIF-signaling and modulates the immune response. PLoS One.
13:e02039652018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Chen SF, Pan MX, Tang JC, Cheng J, Zhao D,
Zhang Y, Liao HB, Liu R, Zhuang Y, Zhang ZF, et al: Arginine is
neuroprotective through suppressing HIF-1α/LDHA-mediated
inflammatory response after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Mol Brain. 13:632020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Fernández-Hernando C, József L, Jenkins
D, Di Lorenzo A and Sessa WC: Absence of Akt1 reduces vascular
smooth muscle cell migration and survival and induces features of
plaque vulnerability and cardiac dysfunction during
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:2033–2040. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Pan C, Liu Q and Wu X:
HIF1α/miR-520a-3p/AKT1/mTOR feedback promotes the proliferation and
glycolysis of gastric cancer cells. Cancer Manag Res.
11:10145–10156. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
80
|
Zhong ZW, Zhou WC, Sun XF, Wu QC, Chen WK
and Miao CH: Dezocine regulates the malignant potential and aerobic
glycolysis of liver cancer targeting Akt1/GSK-3β pathway. Ann
Transl Med. 8:4802020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Zhao X, Wu X, Wang H, Yu H and Wang J:
USP53 promotes apoptosis and inhibits glycolysis in lung
adenocarcinoma through FKBP51-AKT1 signaling. Mol Carcinog.
59:1000–1011. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Song L and Schindler C: IL-6 and the acute
phase response in murine atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis.
177:43–51. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhang P, Chen X, Zhang Y, Su H, Zhang Y,
Zhou X, Sun M, Li L and Xu Z: Tet3 enhances IL-6 expression through
up-regulation of 5-hmC in IL-6 promoter in chronic hypoxia induced
athero-sclerosis in offspring rats. Life Sci. 232:1166012019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Bozic M, Alvarez A, de Pablo C,
Sanchez-Niño MD, Ortiz A, Dolcet X, Encinas M, Fernandez E and
Valdivielso JM: Impaired vitamin D signaling in endothelial cell
leads to an enhanced leukocyte-endothelium interplay: Implications
for atheroscle-rosis development. PLoS One. 10:e01368632015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Han J, Meng Q, Xi Q, Zhang Y, Zhuang Q,
Han Y, Jiang Y, Ding Q and Wu G: Interleukin-6 stimulates aerobic
glycolysis by regulating PFKFB3 at early stage of colorectal
cancer. Int J Oncol. 48:215–224. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Li H, Liang Q and Wang L: Icaritin
inhibits glioblastoma cell viability and glycolysis by blocking the
IL-6/Stat3 pathway. J Cell Biochem. Nov 2–2018.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Zhao N and Zhang J: Role of alternative
splicing of VEGF-A in the development of atherosclerosis. Aging
(Albany NY). 10:2695–2708. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Wang X, Hu Z, Wang Z, Cui Y and Cui X:
Angiopoietin-like protein 2 is an important facilitator of tumor
proliferation, metastasis, angiogenesis and glycolysis in
osteosarcoma. Am J Transl Res. 11:6341–6355. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Peek CB, Levine DC, Cedernaes J, Taguchi
A, Kobayashi Y, Tsai SJ, Bonar NA, McNulty MR, Ramsey KM and Bass
J: Circadian clock interaction with HIF1α mediates oxygenic
metabolism and anaerobic glycolysis in skeletal muscle. Cell Metab.
25:86–92. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Zhao M, Fan J, Liu Y, Yu Y, Xu J, Wen Q,
Zhang J, Fu S, Wang B, Xiang L, et al: Oncogenic role of the
TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma through NF-κB pathway modulation. Int J Oncol.
48:756–764. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Ko YH, Domingo-Vidal M, Roche M, Lin Z,
Whitaker-Menezes D, Seifert E, Capparelli C, Tuluc M, Birbe RC,
Tassone P, et al: TP53-inducible glycolysis and apoptosis regulator
(TIGAR) metabolically reprograms carcinoma and stromal cells in
breast cancer. J Biol Chem. 291:26291–26303. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Xiong Y, Yepuri G, Forbiteh M, Yu Y,
Montani JP, Yang Z and Ming XF: ARG2 impairs endothelial autophagy
through regulation of MTOR and PRKAA/AMPK signaling in advanced
atherosclerosis. Autophagy. 10:2223–2238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Li X, Wu L, Zopp M, Kopelov S and Du W:
p53-TP53-Induced glycolysis regulator mediated glycolytic
suppression attenuates DNA damage and genomic instability in
fanconi anemia hematopoietic stem cells. Stem Cells. 37:937–947.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Chen Q, Lv J, Yang W, Xu B, Wang Z, Yu Z,
Wu J, Yang Y and Han Y: Targeted inhibition of STAT3 as a potential
treatment strategy for atherosclerosis. Theranostics. 9:6424–6442.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Zhou X, Li D, Yan W and Li W: Pravastatin
prevents aortic atherosclerosis via modulation of signal
transduction and activation of transcription 3 (STAT3) to attenuate
interleukin-6 (IL-6) action in ApoE knockout mice. Int J Mol Sci.
9:2253–2264. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Li Y, Wang Y, Liu Z, Guo X, Miao Z and Ma
S: Atractylenolide I induces apoptosis and suppresses glycolysis by
blocking the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in colorectal cancer
cells. Front Pharmacol. 11:2732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Zheng M, Cao MX, Yu XH, Li L, Wang K, Wang
SS, Wang HF, Tang YJ, Tang YL and Liang XH: STAT3 promotes invasion
and aerobic glycolysis of human oral squamous cell carcinoma via
inhibiting FoxO1. Front Oncol. 9:11752019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Seki N, Hashimoto N, Taira M, Yagi S,
Yoshida Y, Ishikawa K, Suzuki Y, Sano H, Horiuchi S, Yoshida S, et
al: Regulation of Src homology 2-containing protein tyrosine
phosphatase by advanced glycation end products: The role on
atherosclerosis in diabetes. Metabolism. 56:1591–1598. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Park JS, Lee S, Jeong AL, Han S, Ka HI,
Lim JS, Lee MS, Yoon DY, Lee JH and Yang Y: Hypoxia-induced IL-32β
increases glycolysis in breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
356:800–808. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Nam K, Oh S and Shin I: Ablation of CD44
induces glycolysis-to-oxidative phosphorylation transition via
modulation of the c-Src-Akt-LKB1-AMPKα pathway. Biochem J.
473:3013–3030. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Byun S, Jung H, Chen J, Kim YC, Kim DH,
Kong B, Guo G, Kemper B and Kemper JK: Phosphorylation of hepatic
farnesoid X receptor by FGF19 signaling-activated Src maintains
cholesterol levels and protects from atherosclerosis. J Biol Chem.
294:8732–8744. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Lovren F, Pan Y, Shukla PC, Quan A, Teoh
H, Szmitko PE, Peterson MD, Gupta M, Al-Omran M and Verma S:
Visfatin activates eNOS via Akt and MAP kinases and improves
endothelial cell function and angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo:
Translational implications for atherosclerosis. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 296:1440–1449. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Gupta A, Mohanty P and Bhatnagar S:
Integrative analysis of ocular complications in atherosclerosis
unveils pathway convergence and crosstalk. J Recept Signal
Transduct Res. 35:149–164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Perrotta P, Emini Veseli B, Van der Veken
B, Roth L, Martinet W and De Meyer GRY: Pharmacological strategies
to inhibit intra-plaque angiogenesis in atherosclerosis. Vascul
Pharmacol. 112:72–78. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|