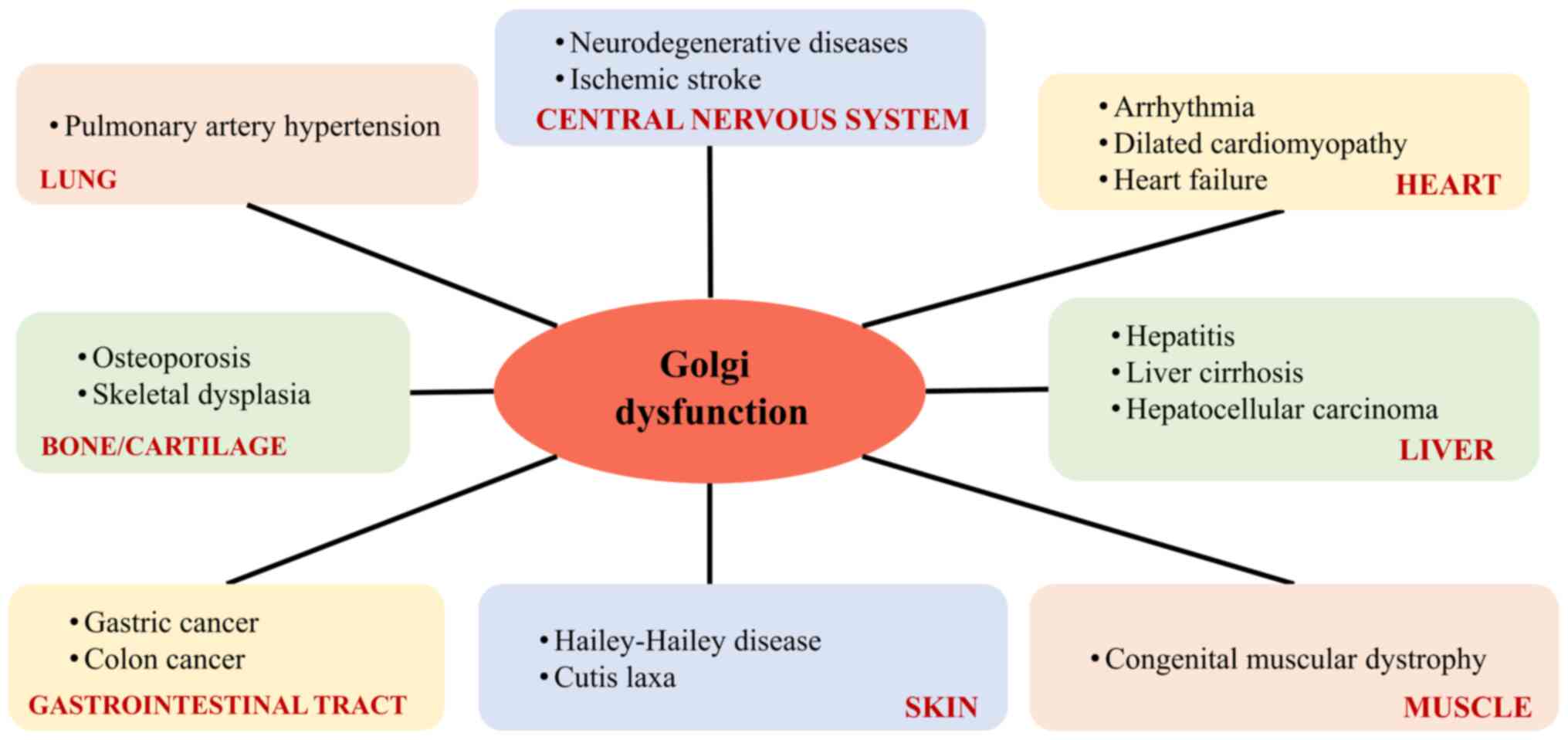
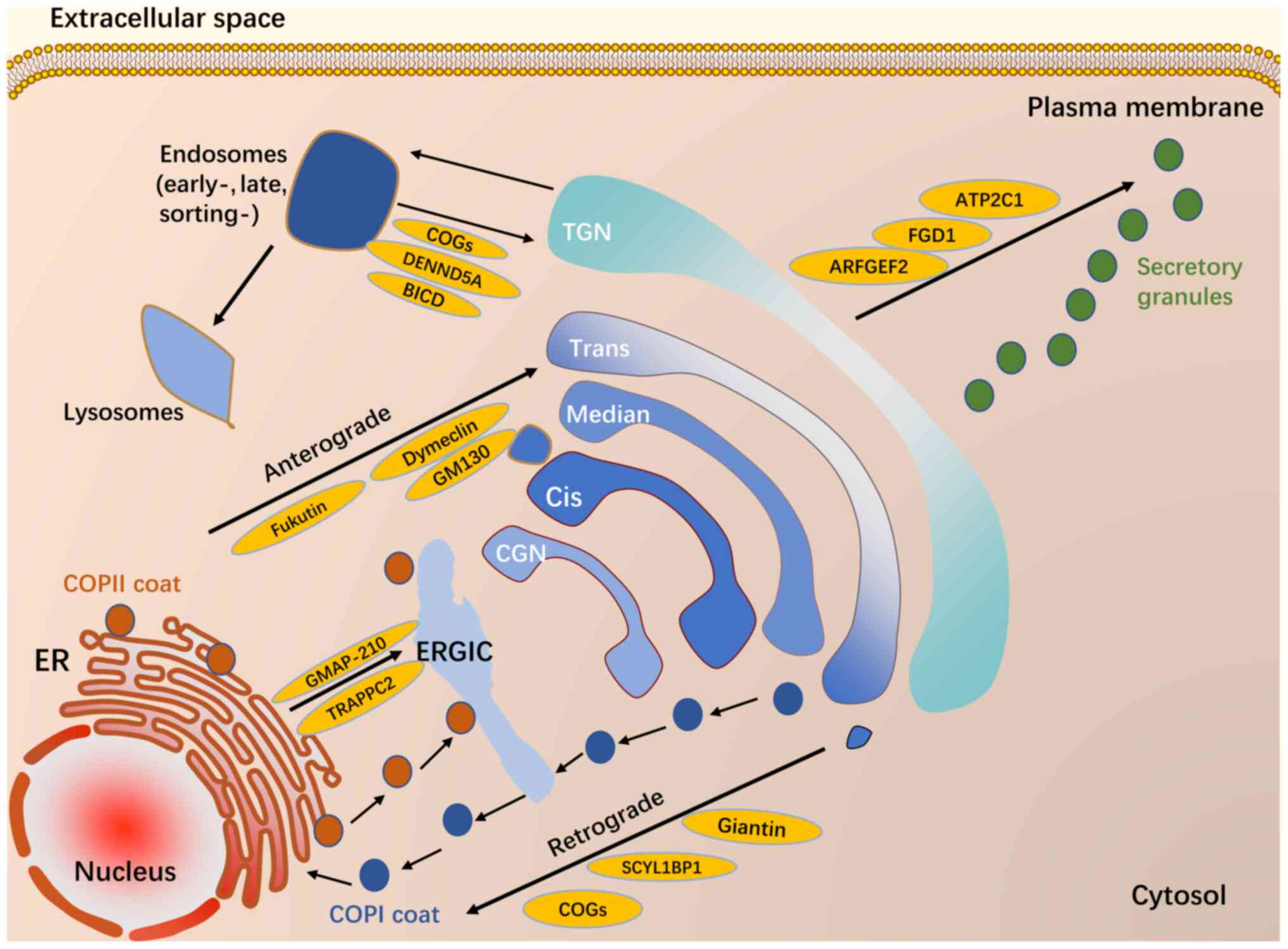
|
1
|
Rios RM and Bornens M: The Golgi apparatus
at the cell centre. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 15:60–66. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gautam M, Jara JH, Sekerkova G, Yasvoina
MV, Martina M and Özdinler PH: Absence of alsin function leads to
corticospinal motor neuron vulnerability via novel disease
mechanisms. Hum Mol Genet. 25:1074–1087. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rendón WO, Martínez-Alonso E, Tomás M,
Martínez-Martínez N and Martínez-Menárguez JA: Golgi fragmentation
is Rab and SNARE dependent in cellular models of Parkinson's
disease. Histochem Cell Biol. 139:671–684. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Brandstaetter H, Kruppa AJ and Buss F:
Huntingtin is required for ER-to-Golgi transport and for secretory
vesicle fusion at the plasma membrane. Dis Model Mech. 7:1335–1340.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yuan D, Liu C and Hu B: Dysfunction of
membrane trafficking leads to ischemia-reperfusion injury after
transient cerebral ischemia. Transl Stroke Res. 9:215–222. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Li T, You H, Mo X, He W, Tang X, Jiang Z,
Chen S, Chen Y, Zhang J and Hu Z: GOLPH3 mediated Golgi stress
response in modulating N2A cell death upon oxygen-glucose
deprivation and reoxygenation injury. Mol Neurobiol. 53:1377–1385.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tarazón E, Roselló-Lletí E, Ortega A,
Gil-Cayuela C, González-Juanatey JR, Lago F, Martínez-Dolz L,
Portolés M and Rivera M: Changes in human Golgi apparatus reflect
new left ventricular dimensions and function in dilated
cardiomyopathy patients. Eur J Heart Fail. 19:280–282. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Stancu CS, Toma L and Sima AV: Dual role
of lipoproteins in endothelial cell dysfunction in atherosclerosis.
Cell Tissue Res. 349:433–446. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee J, Reich R, Xu F and Sehgal PB: Golgi,
trafficking, and mitosis dysfunctions in pulmonary arterial
endothelial cells exposed to monocrotaline pyrrole and NO
scavenging. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 297:L715–L728.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sehgal PB, Mukhopadhyay S, Xu F, Patel K
and Shah M: Dysfunction of Golgi tethers, SNAREs, and SNAPs in
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 292:L1526–L1542. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu H, Li H, Wang P, Chen M, Huang Z, Li
K, Li Y, He J, Han J and Zhang Q: Persistent and acute chlamydial
infections induce different structural changes in the Golgi
apparatus. Int J Med Microbiol. 304:577–585. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rohde J, Emschermann F, Knittler MR and
Rziha HJ: Orf virus interferes with MHC class I surface expression
by targeting vesicular transport and Golgi. BMC Vet Res. 8:1142012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mousnier A, Swieboda D, Pinto A, Guedán A,
Rogers AV, Walton R, Johnston SL and Solari R: Human rhinovirus 16
causes Golgi apparatus fragmentation without blocking protein
secretion. J Virol. 88:11671–11685. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan X, Banerjee P, Guo HF, Ireland S,
Pankova D, Ahn YH, Nikolaidis IM, Liu X, Zhao Y, Xue Y, et al:
Epithelial-to- mesenchymal transition drives a pro-metastatic Golgi
compaction process through scaffolding protein PAQR11. J Clin
Invest. 127:117–131. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Golgi C: On the structure of nerve cells.
1898. J Microsc. 155:3–7. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mollenhauer HH and Morré DJ: Perspectives
on Golgi apparatus form and function. J Electron Microsc Tech.
17:2–14. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Storrie B, White J, Röttger S, Stelzer EH,
Suganuma T and Nilsson T: Recycling of golgi-resident
glycosyltransferases through the ER reveals a novel pathway and
provides an explanation for nocodazole-induced Golgi scattering. J
Cell Biol. 143:1505–1521. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Slusarewicz P, Nilsson T, Hui N, Watson R
and Warren G: Isolation of a matrix that binds medial Golgi
enzymes. J Cell Biol. 124:405–413. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Papanikou E and Glick BS: Golgi
compartmentation and identity. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 29:74–81. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Glick BS and Luini A: Models for Golgi
traffic: A critical assessment. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
3:a0052152011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sundaramoorthy V, Sultana JM and Atkin JD:
Golgi fragmentation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, an overview
of possible triggers and consequences. Front Neurosci. 9:4002015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gonatas NK, Stieber A and Gonatas JO:
Fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus in neurodegenerative diseases
and cell death. J Neurol Sci. 246:21–30. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang Z, Hu Z, Zeng L, Lu W, Zhang H, Li T
and Xiao H: The role of the Golgi apparatus in oxidative stress: Is
this organelle less significant than mitochondria? Free Radic Biol
Med. 50:907–917. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu JY, He JL, Huang Y, Xiao H, Jiang Z
and Hu ZP: The Golgi apparatus in neurorestoration. J
Neuroresstoratology. 7:116–128. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Fan J, Hu Z, Zeng L, Lu W, Tang X, Zhang J
and Li T: Golgi apparatus and neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Dev
Neurosci. 26:523–534. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu L, Zhou Q, Chen Z and Chen L: The
significant role of the Golgi apparatus in cardiovascular diseases.
J Cell Physiol. 233:2911–2919. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Millarte V and Farhan H: The Golgi in cell
migration: Regulation by signal transduction and its implications
for cancer cell metastasis. ScientificWorldJournal.
2012:4982782012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mourelatos Z, Gonatas NK, Stieber A,
Gurney ME and Dal Canto MC: The Golgi apparatus of spinal cord
motor neurons in transgenic mice expressing mutant Cu, Zn
superoxide dismutase becomes fragmented in early, preclinical
stages of the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:5472–5477. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Joshi G, Bekier ME II and Wang Y: Golgi
fragmentation in Alzheimer's disease. Front Neurosci. 9:3402015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Strehlow AN, Li JZ and Myers RM: Wild-type
huntingtin participates in protein trafficking between the Golgi
and the extracellular space. Hum Mol Genet. 16:391–409. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sakurai A, Okamoto K, Fujita Y, Nakazato
Y, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H and Gonatas NK: Fragmentation of the
Golgi apparatus of the ballooned neurons in patients with
corticobasal degeneration and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Acta
Neuropathol. 100:270–274. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sakurai A, Okamoto K, Yaguchi M, Fujita Y,
Mizuno Y, Nakazato Y and Gonatas NK: Pathology of the inferior
olivary nucleus in patients with multiple system atrophy. Acta
Neuropathol. 103:550–554. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
van Dis V, Kuijpers M, Haasdijk ED,
Teuling E, Oakes SA, Hoogenraad CC and Jaarsma D: Golgi
fragmentation precedes neuromuscular denervation and is associated
with endosome abnormalities in SOD1-ALS mouse motor neurons. Acta
Neuropathol Commun. 2:382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pottorf T, Mann A, Fross S, Mansel C and
Vohra BPS: Nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase 2
maintains neuronal structural integrity through the maintenance of
golgi structure. Neurochem Int. 121:86–97. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Joshi G and Wang Y: Golgi defects enhance
APP amyloidogenic processing in Alzheimer's disease. Bioessays.
37:240–247. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Covarrubias-Pinto A, Parra AV,
Mayorga-Weber G, Papic E, Vicencio I, Ehrenfeld P, Rivera FJ and
Castro MA: Impaired intracellular trafficking of sodium-dependent
vitamin C transporter 2 contributes to the redox imbalance in
Huntington's disease. J Neurosci Res. 99:223–235. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mani M, Thao DT, Kim BC, Lee UH, Kim DJ,
Jang SH, Back SH, Lee BJ, Cho WJ, Han IS and Park JW: DRG2 knock-
down induces Golgi fragmentation via GSK3β phosphorylation and
microtubule stabilization. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res.
1866:1463–1474. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rodríguez-Cruz F, Torres-Cruz FM,
Monroy-Ramírez HC, Escobar-Herrera J, Basurto-Islas G, Avila J and
García-Sierra F: Fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus in
neuroblastoma cells is associated with tau-induced ring-shaped
microtubule bundles. J Alzheimers Dis. 65:1185–1207. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sou YS, Kakuta S, Kamikubo Y, Niisato K,
Sakurai T, Parajuli LK, Tanida I, Saito H, Suzuki N, Sakimura K, et
al: Cerebellar neurodegeneration and neuronal circuit remodeling in
Golgi pH regulator-deficient mice. eNeuro. 6:ENEURO.0427-18.2019.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Heuer D, Rejman Lipinski A, Machuy N,
Karlas A, Wehrens A, Siedler F, Brinkmann V and Meyer TF: Chlamydia
causes fragmentation of the Golgi compartment to ensure
reproduction. Nature. 457:731–735. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Pruneda JN, Bastidas RJ, Bertsoulaki E,
Swatek KN, Santhanam B, Clague MJ, Valdivia RH, Urbé S and Komander
D: A chlamydia effector combining deubiquitination and acetylation
activities induces Golgi fragmentation. Nat Microbiol. 3:1377–1384.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hansen MD, Johnsen IB, Stiberg KA,
Sherstova T, Wakita T, Richard GM, Kandasamy RK, Meurs EF and
Anthonsen MW: Hepatitis C virus triggers Golgi fragmentation and
autophagy through the immunity-related GTPase M. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 114:E3462–E3471. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Aistleitner K, Clark T, Dooley C and
Hackstadt T: Selective frag- mentation of the trans-Golgi apparatus
by Rickettsia rickettsii. PLoS Pathog. 16:e10085822020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Ganesan M, Mathews S, Makarov E, Petrosyan
A, Kharbanda KK, Kidambi S, Poluektova LY, Casey CA and Osna NA:
Acetaldehyde suppresses HBV-MHC class I complex presentation on
hepatocytes via induction of ER stress and Golgi fragmentation. Am
J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 319:G432–G442. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Quiner CA and Jackson WT: Fragmentation of
the Golgi apparatus provides replication membranes for human
rhinovirus 1A. Virology. 407:185–195. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Barbosa NS, Mendonça LR, Dias MVS,
Pontelli MC, da Silva EZM, Criado MF, da Silva-Januário ME,
Schindler M, Jamur MC, Oliver C, et al: ESCRT machinery components
are required for orthobunyavirus particle production in Golgi
compartments. PLoS Pathog. 14:e10070472018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Petrosyan A, Holzapfel MS, Muirhead DE and
Cheng PW: Restoration of compact Golgi morphology in advanced
prostate cancer enhances susceptibility to galectin-1-induced
apoptosis by modifying mucin O-glycan synthesis. Mol Cancer Res.
12:1704–1716. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tokuda E, Itoh T, Hasegawa J, Ijuin T,
Takeuchi Y, Irino Y, Fukumoto M and Takenawa T:
Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate in the Golgi apparatus regulates
cell-cell adhesion and invasive cell migration in human breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 74:3054–3066. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhao J, Yang C, Guo S and Wu Y: GM130
regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and invasion of
gastric cancer cells via snail. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:10784–10791. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pinho SS and Reis CA: Glycosylation in
cancer: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat Rev Cancer.
15:540–555. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pinho SS, Seruca R, Gärtner F, Yamaguchi
Y, Gu J, Taniguchi N and Reis CA: Modulation of E-cadherin function
and dysfunction by N-glycosylation. Cell Mol Life Sci.
68:1011–1020. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Baschieri F, Confalonieri S, Bertalot G,
Di Fiore PP, Dietmaier W, Leist M, Crespo P, Macara IG and Farhan
H: Spatial control of Cdc42 signalling by a GM130-RasGRF complex
regulates polarity and tumorigenesis. Nat Commun. 5:48392014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Taniguchi N and Kizuka Y: Glycans and
cancer: Role of N-glycans in cancer biomarker, progression and
metastasis, and therapeutics. Adv Cancer Res. 126:11–51. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Rizzo R, Parashuraman S, D'Angelo G and
Luini A: GOLPH3 and oncogenesis: What is the molecular link? Tissue
Cell. 49:170–174. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Farber-Katz SE, Dippold HC, Buschman MD,
Peterman MC, Xing M, Noakes CJ, Tat J, Ng MM, Rahajeng J, Cowan DM,
et al: DNA damage triggers Golgi dispersal via DNA-PK and GOLPH3.
Cell. 156:413–427. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Scott KL, Kabbarah O, Liang MC, Ivanova E,
Anagnostou V, Wu J, Dhakal S, Wu M, Chen S, Feinberg T, et al:
GOLPH3 modulates mTOR signalling and rapamycin sensitivity in
cancer. Nature. 459:1085–1090. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Xing M, Peterman MC, Davis RL, Oegema K,
Shiau AK and Field SJ: GOLPH3 drives cell migration by promoting
Golgi reorientation and directional trafficking to the leading
edge. Mol Biol Cell. 27:3828–3840. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chang SH, Hong SH, Jiang HL, Minai-Tehrani
A, Yu KN, Lee JH, Kim JE, Shin JY, Kang B, Park S, et al:
GOLGA2/GM130, cis-Golgi matrix protein, is a novel target of
anticancer gene therapy. Mol Ther. 20:2052–2063. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sehgal PB, Mukhopadhyay S, Patel K, Xu F,
Almodóvar S, Tuder RM and Flores SC: Golgi dysfunction is a common
feature in idiopathic human pulmonary hypertension and vascular
lesions in SHIV-nef-infected macaques. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 297:L729–L737. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sehgal PB and Lee JE: Protein trafficking
dysfunctions: Role in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Pulm Circ. 1:17–32. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Muhammad E, Levitas A, Singh SR, Braiman
A, Ofir R, Etzion S, Sheffield VC, Etzion Y, Carrier L and Parvari
R: PLEKHM2 mutation leads to abnormal localization of lysosomes,
impaired autophagy flux and associates with recessive dilated
cardiomyopathy and left ventricular noncompaction. Hum Mol Genet.
24:7227–7240. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hatt PY: Cellular changes and damage in
mechanically over-loaded hearts. Recent Adv Stud Cardiac Struct
Metab. 6:325–333. 1975.
|
|
63
|
Satoh H: Sino-atrial nodal cells of
mammalian hearts: Ionic currents and gene expression of pacemaker
ionic channels. J Smooth Muscle Res. 39:175–193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Jungk L, Franke H, Salameh A and Dhein S:
Golgi fragmentation in human patients with chronic atrial
fibrillation: A new aspect of remodeling. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
67:98–106. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Prasad K and Singal PK: Ultrastructure of
failing myocardium due to induced chronic mitral insufficiency in
dogs. Br J Exp Pathol. 58:289–300. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Rambourg A, Clermont Y and Hermo L:
Three-dimensional architecture of the golgi apparatus in sertoli
cells of the rat. Am J Anat. 154:455–476. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Xiang Y and Wang Y: New components of the
Golgi matrix. Cell Tissue Res. 344:365–379. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kooy J, Toh BH, Pettitt JM, Erlich R and
Gleeson PA: Human autoantibodies as reagents to conserved Golgi
components. Characterization of a peripheral, 230-kDa
compartment-specific Golgi protein. J Biol Chem. 267:20255–20263.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Fritzler MJ, Hamel JC, Ochs RL and Chan
EK: Molecular characterization of two human autoantigens: Unique
cDNAs encoding 95- and 160-kD proteins of a putative family in the
Golgi complex. J Exp Med. 178:49–62. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wong M and Munro S: Membrane trafficking.
The specificity of vesicle traffic to the Golgi is encoded in the
golgin coiled-coil proteins. Science. 346:12568982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Barr FA, Puype M, Vandekerckhove J and
Warren G: GRASP65, a protein involved in the stacking of Golgi
cisternae. Cell. 91:253–262. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Shorter J and Warren G: A role for the
vesicle tethering protein, p115, in the post-mitotic stacking of
reassembling Golgi cisternae in a cell-free system. J Cell Biol.
146:57–70. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Vinke FP, Grieve AG and Rabouille C: The
multiple facets of the Golgi reassembly stacking proteins. Biochem
J. 433:423–433. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Bergen DJM, Stevenson NL, Skinner REH,
Stephens DJ and Hammond CL: The Golgi matrix protein giantin is
required for normal cilia function in zebrafish. Biol Open.
6:1180–1189. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hennies HC, Kornak U, Zhang H, Egerer J,
Zhang X, Seifert W, Kühnisch J, Budde B, Nätebus M, Brancati F, et
al: Gerodermia osteodysplastica is caused by mutations in SCYL1BP1,
a Rab-6 interacting golgin. Nat Genet. 40:1410–1412. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Nakamura N, Rabouille C, Watson R, Nilsson
T, Hui N, Slusarewicz P, Kreis TE and Warren G: Characterization of
a cis-Golgi matrix protein, GM130. J Cell Biol. 131:1715–1726.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Alvarez C, Garcia-Mata R, Hauri HP and
Sztul E: The p115-inter- active proteins GM130 and giantin
participate in endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi traffic. J Biol Chem.
276:2693–2700. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Huang W, She L, Chang XY, Yang RR, Wang L,
Ji HB, Jiao JW and Poo MM: Protein kinase LKB1 regulates polarized
dendrite formation of adult hippocampal newborn neurons. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 111:469–474. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Liu C, Mei M, Li Q, Roboti P, Pang Q, Ying
Z, Gao F, Lowe M and Bao S: Loss of the golgin GM130 causes Golgi
disruption, Purkinje neuron loss, and ataxia in mice. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 114:346–351. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Matanis T, Akhmanova A, Wulf P, Del Nery
E, Weide T, Stepanova T, Galjart N, Grosveld F, Goud B, De Zeeuw
CI, et al: Bicaudal-D regulates COPI-independent Golgi-ER transport
by recruiting the dynein-dynactin motor complex. Nat Cell Biol.
4:986–992. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Hoogenraad CC, Akhmanova A, Howell SA,
Dortland BR, De Zeeuw CI, Willemsen R, Visser P, Grosveld F and
Galjart N: Mammalian Golgi-associated Bicaudal-D2 functions in the
dynein-dynactin pathway by interacting with these complexes. EMBO
J. 20:4041–4054. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Jaarsma D, van den Berg R, Wulf PS, van
Erp S, Keijzer N, Schlager MA, de Graaff E, De Zeeuw CI, Pasterkamp
RJ, Akhmanova A and Hoogenraad CC: A role for bicaudal-D2 in radial
cerebellar granule cell migration. Nat Commun. 5:34112014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Will L, Portegies S, van Schelt J, van
Luyk M, Jaarsma D and Hoogenraad CC: Dynein activating adaptor
BICD2 controls radial migration of upper-layer cortical neurons in
vivo. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 7:1622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Storbeck M, Horsberg Eriksen B, Unger A,
Hölker I, Aukrust I, Martínez-Carrera LA, Linke WA, Ferbert A,
Heller R, Vorgerd M, et al: Phenotypic extremes of BICD2-opathies:
From lethal, congenital muscular atrophy with arthrogryposis to
asymptomatic with subclinical features. Eur J Hum Genet.
25:1040–1048. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Neveling K, Martinez-Carrera LA, Hölker I,
Heister A, Verrips A, Hosseini-Barkooie SM, Gilissen C, Vermeer S,
Pennings M, Meijer R, et al: Mutations in BICD2, which encodes a
golgin and important motor adaptor, cause congenital
autosomal-dominant spinal muscular atrophy. Am J Hum Genet.
92:946–954. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Oates EC, Rossor AM, Hafezparast M,
Gonzalez M, Speziani F, MacArthur DG, Lek M, Cottenie E, Scoto M,
Foley AR, et al: Mutations in BICD2 cause dominant congenital
spinal muscular atrophy and hereditary spastic paraplegia. Am J Hum
Genet. 92:965–973. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Sonnichsen B, Lowe M, Levine T, Jämsä E,
Dirac-Svejstrup B and Warren G: A role for giantin in docking COPI
vesicles to Golgi membranes. J Cell Biol. 140:1013–1021. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Katayama K, Kuriki M, Kamiya T, Tochigi Y
and Suzuki H: Giantin is required for coordinated production of
aggrecan, link protein and type XI collagen during chondrogenesis.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 499:459–465. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Stevenson NL, Bergen DJM, Skinner REH,
Kague E, Martin-Silverstone E, Robson Brown KA, Hammond CL and
Stephens DJ: Giantin-knockout models reveal a feedback loop between
Golgi function and glycosyltransferase expression. J Cell Sci.
130:4132–4143. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Witkos TM, Chan WL, Joensuu M, Rhiel M,
Pallister E, Thomas-Oates J, Mould AP, Mironov AA, Biot C,
Guerardel Y, et al: GORAB scaffolds COPI at the trans-Golgi for
efficient enzyme recycling and correct protein glycosylation. Nat
Commun. 10:1272019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Sato K, Roboti P, Mironov AA and Lowe M:
Coupling of vesicle tethering and Rab binding is required for in
vivo functionality of the golgin GMAP-210. Mol Biol Cell.
26:537–553. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
92
|
Smits P, Bolton AD, Funari V, Hong M,
Boyden ED, Lu L, Manning DK, Dwyer ND, Moran JL, Prysak M, et al:
Lethal skeletal dysplasia in mice and humans lacking the golgin
GMAP-210. N Engl J Med. 362:206–216. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Wehrle A, Witkos TM, Unger S, Schneider J,
Follit JA, Hermann J, Welting T, Fano V, Hietala M, Vatanavicharn
N, et al: Hypomorphic mutations of TRIP11 cause
odontochondrodysplasia. JCI Insight. 4:e1247012019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
94
|
West DW: Energy-dependent calcium
sequestration activity in a Golgi apparatus fraction derived from
lactating rat mammary glands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 673:374–386.
1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Shull GE, Miller ML and Prasad V:
Secretory pathway stress responses as possible mechanisms of
disease involving Golgi Ca2+ pump dysfunction.
Biofactors. 37:150–158. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Sudbrak R, Brown J, Dobson-Stone C, Carter
S, Ramser J, White J, Healy E, Dissanayake M, Larrègue M, Perrussel
M, et al: Hailey-Hailey disease is caused by mutations in ATP2C1
encoding a novel Ca(2+) pump. Hum Mol Genet. 9:1131–1140. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Hu Z, Bonifas JM, Beech J, Bench G,
Shigihara T, Ogawa H, Ikeda S, Mauro T and Epstein EH Jr: Mutations
in ATP2C1, encoding a calcium pump, cause Hailey-Hailey disease.
Nat Genet. 24:61–65. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Okunade GW, Miller ML, Azhar M, Andringa
A, Sanford LP, Doetschman T, Prasad V and Shull GE: Loss of the
Atp2c1 secretory pathway Ca(2+)-ATPase (SPCA1) in mice causes Golgi
stress, apoptosis, and midgestational death in homozygous embryos
and squamous cell tumors in adult heterozygotes. J Biol Chem.
282:26517–26527. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Lázaro-Diéguez F, Jiménez N, Barth H,
Koster AJ, Renau-Piqueras J, Llopis JL, Burger KN and Egea G: Actin
filaments are involved in the maintenance of Golgi cisternae
morphology and intra-Golgi pH. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 63:778–791.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Huang C and Chang A: pH-dependent cargo
sorting from the Golgi. J Biol Chem. 286:10058–10065. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Rivinoja A, Pujol FM, Hassinen A and
Kellokumpu S: Golgi pH, its regulation and roles in human disease.
Ann Med. 44:542–554. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Drory O and Nelson N: The emerging
structure of vacuolar ATPases. Physiology (Bethesda). 21. pp.
317–325. 2006
|
|
103
|
Maeda Y, Ide T, Koike M, Uchiyama Y and
Kinoshita T: GPHR is a novel anion channel critical for
acidification and functions of the Golgi apparatus. Nat Cell Biol.
10:1135–1145. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Banerjee S and Kane PM: Regulation of
V-ATPase activity and organelle pH by phosphatidylinositol
phosphate lipids. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:5102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Morava E, Guillard M, Lefeber DJ and
Wevers RA: Autosomal recessive cutis laxa syndrome revisited. Eur J
Hum Genet. 17:1099–1110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Van Damme T, Gardeitchik T, Mohamed M,
Guerrero-Castillo S, Freisinger P, Guillemyn B, Kariminejad A,
Dalloyaux D, van Kraaij S, Lefeber DJ, et al: Mutations in ATP6V1E1
or ATP6V1A cause autosomal-recessive cutis laxa. Am J Hum Genet.
100:216–227. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Kariminejad A, Afroozan F, Bozorgmehr B,
Ghanadan A, Akbaroghli S, Khorram Khorshid HR, Mojahedi F, Setoodeh
A, Loh A, Tan YX, et al: Discriminative features in three autosomal
recessive cutis laxa syndromes: Cutis laxa IIA, cutis laxa IIB, and
geroderma osteoplastica. Int J Mol Sci. 18:6352017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
108
|
Kornak U, Reynders E, Dimopoulou A, van
Reeuwijk J, Fischer B, Rajab A, Budde B, Nürnberg P, Foulquier F;
ARCL Debré-type Study Group; et al: Impaired glycosylation and
cutis laxa caused by mutations in the vesicular H+-ATPase subunit
ATP6V0A2. Nat Genet. 40:32–34. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Tümer Z: An overview and update of ATP7A
mutations leading to Menkes disease and occipital horn syndrome.
Hum Mutat. 34:417–429. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Huster D, Hoppert M, Lutsenko S, Zinke J,
Lehmann C, Mössner J, Berr F and Caca K: Defective cellular
localization of mutant ATP7B in Wilson's disease patients and
hepatoma cell lines. Gastroenterology. 124:335–345. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Guan JL, Machamer CE and Rose JK:
Glycosylation allows cell-surface transport of an anchored
secretory protein. Cell. 42:489–496. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Roth J: Protein N-glycosylation along the
secretory pathway: Relationship to organelle topography and
function, protein quality control, and cell interactions. Chem Rev.
102:285–303. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Rosnoblet C, Peanne R, Legrand D and
Foulquier F: Glycosylation disorders of membrane trafficking.
Glycoconj J. 30:23–31. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Grewal PK, McLaughlan JM, Moore CJ,
Browning CA and Hewitt JE: Characterization of the LARGE family of
putative glycosyltransferases associated with dystroglycanopathies.
Glycobiology. 15:912–923. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Kobayashi K, Nakahori Y, Miyake M,
Matsumura K, Kondo-Iida E, Nomura Y, Segawa M, Yoshioka M, Saito K,
Osawa M, et al: An ancient retrotransposal insertion causes
Fukuyama-type congenital muscular dystrophy. Nature. 394:388–392.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Brockington M, Blake DJ, Prandini P, Brown
SC, Torelli S, Benson MA, Ponting CP, Estournet B, Romero NB,
Mercuri E, et al: Mutations in the fukutin-related protein gene
(FKRP) cause a form of congenital muscular dystrophy with secondary
laminin alpha2 deficiency and abnormal glycosylation of
alpha-dystroglycan. Am J Hum Genet. 69:1198–1209. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Desplats PA, Denny CA, Kass KE, Gilmartin
T, Head SR, Sutcliffe JG, Seyfried TN and Thomas EA: Glycolipid and
ganglioside metabolism imbalances in Huntington's disease.
Neurobiol Dis. 27:265–277. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Cooper-Knock J, Moll T, Ramesh T, Castelli
L, Beer A, Robins H, Fox I, Niedermoser I, Van Damme P, Moisse M,
et al: Mutations in the glycosyltransferase domain of GLT8D1 are
associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cell Rep.
26:2298–2306.e5. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Li W, Liu Z, Sun W, Yuan Y, Hu Y, Ni J,
Jiao B, Fang L, Li J, Shen L, et al: Mutation analysis of GLT8D1
and ARPP21 genes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients from
mainland China. Neurobiol Aging. 85:156.e1–156.e4. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Liu S and Storrie B: Are Rab proteins the
link between Golgi organization and membrane trafficking? Cell Mol
Life Sci. 69:4093–4106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Salian S, Cho TJ, Phadke SR, Gowrishankar
K, Bhavani GS, Shukla A, Jagadeesh S, Kim OH, Nishimura G and
Girisha KM: Additional three patients with Smith-McCort dysplasia
due to novel RAB33B mutations. Am J Med Genet A. 173:588–595. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Giannandrea M, Bianchi V, Mignogna ML,
Sirri A, Carrabino S, D'Elia E, Vecellio M, Russo S, Cogliati F,
Larizza L, et al: Mutations in the small GTPase gene RAB39B are
responsible for X-linked mental retardation associated with autism,
epilepsy, and macrocephaly. Am J Hum Genet. 86:185–195. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Bock JB, Matern HT, Peden AA and Scheller
RH: A genomic perspective on membrane compartment organization.
Nature. 409:839–841. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Corbett MA, Schwake M, Bahlo M, Dibbens
LM, Lin M, Gandolfo LC, Vears DF, O'Sullivan JD, Robertson T, Bayly
MA, et al: A mutation in the Golgi Qb-SNARE gene GOSR2 causes
progressive myoclonus epilepsy with early ataxia. Am J Hum Genet.
88:657–663. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Lowe SL, Peter F, Subramaniam VN, Wong SH
and Hong W: A SNARE involved in protein transport through the Golgi
apparatus. Nature. 389:881–884. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Malsam J and Söllner TH: Organization of
SNAREs within the Golgi stack. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
3:a0052492011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Gedeon AK, Colley A, Jamieson R, Thompson
EM, Rogers J, Sillence D, Tiller GE, Mulley JC and Gécz J:
Identification of the gene (SEDL) causing X-linked
spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda. Nat Genet. 22:400–404. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Willett R, Ungar D and Lupashin V: The
Golgi puppet master: COG complex at center stage of membrane
trafficking interactions. Histochem Cell Biol. 140:271–283. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Climer LK, Dobretsov M and Lupashin V:
Defects in the COG complex and COG-related trafficking regulators
affect neuronal Golgi function. Front Neurosci. 9:4052015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Miller VJ and Ungar D: Re'COG'nition at
the Golgi. Traffic. 13:891–897. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Egorov MV, Capestrano M, Vorontsova OA, Di
Pentima A, Egorova AV, Mariggiò S, Ayala MI, Tetè S, Gorski JL,
Luini A, et al: Faciogenital dysplasia protein (FGD1) regulates
export of cargo proteins from the golgi complex via Cdc42
activation. Mol Biol Cell. 20:2413–2427. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Roboti P, Sato K and Lowe M: The golgin
GMAP-210 is required for efficient membrane trafficking in the
early secretory pathway. J Cell Sci. 128:1595–1606. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Zhang H, Winckler B and Cai Q:
Introduction to the special issue on membrane trafficking in
neurons. Dev Neurobiol. 78:167–169. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Rosnoblet C, Legrand D, Demaegd D,
Hacine-Gherbi H, de Bettignies G, Bammens R, Borrego C, Duvet S,
Morsomme P, Matthijs G and Foulquier F: Impact of disease-causing
mutations on TMEM165 subcellular localization, a recently
identified protein involved in CDG-II. Hum Mol Genet. 22:2914–2928.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Larson AA, Baker PR II, Milev MP, Press
CA, Sokol RJ, Cox MO, Lekostaj JK, Stence AA, Bossler AD, Mueller
JM, et al: TRAPPC11 and GOSR2 mutations associate with
hypoglycosylation of α-dystroglycan and muscular dystrophy. Skelet
Muscle. 8:172018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Davis EE, Savage JH, Willer JR, Jiang YH,
Angrist M, Androutsopoulos A and Katsanis N: Whole exome sequencing
and functional studies identify an intronic mutation in TRAPPC2
that causes SEDT. Clin Genet. 85:359–364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Riener MO: Diagnosis of tumours of the
liver and the biliary tract: New tissue and serum markers.
Pathologe. 32(Suppl 2): S304–S309. 2011.In German. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Xu Z, Liu L, Pan X, Wei K, Wei M, Liu L,
Yang H and Liu Q: Serum Golgi protein 73 (GP73) is a diagnostic and
prognostic marker of chronic HBV liver disease. Medicine
(Baltimore). 94:e6592015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Liu Y, Zou Z, Zhu B, Hu Z and Zeng P:
CXCL10 decreases GP73 expression in hepatoma cells at the early
stage of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Int J Mol Sci.
14:24230–24241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Zheng KI, Liu WY, Pan XY, Ma HL, Zhu PW,
Wu XX, Targher G, Byrne C, Wang XD, Chen YP, et al: Combined and
sequential non-invasive approach to diagnosing non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
and persistently normal alanine aminotransferase levels. BMJ Open
Diabetes Res Care. 8:e0011742020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Hou SC, Xiao MB, Ni RZ, Ni WK, Jiang F, Li
XY, Lu CH and Chen BY: Serum GP73 is complementary to AFP and
GGT-II for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
6:1152–1158. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Zhao J, Guo LY, Yang JM and Jia JW:
Sublingual vein parameters, AFP, AFP-L3, and GP73 in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Genet Mol Res. 14:7062–7067. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Liu X, Wan X, Li Z, Lin C, Zhan Y and Lu
X: Golgi protein 73(GP73), a useful serum marker in liver diseases.
Clin Chem Lab Med. 49:1311–1316. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Morota K, Nakagawa M, Sekiya R, Hemken PM,
Sokoll LJ, Elliott D, Chan DW and Dowell BL: A comparative
evaluation of Golgi protein-73, fucosylated hemopexin,
α-fetoprotein, and PIVKA-II in the serum of patients with chronic
hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Chem Lab
Med. 49:711–718. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Gu Y, Chen W, Zhao Y, Chen L and Peng T:
Quantitative analysis of elevated serum Golgi protein-73 expression
in patients with liver diseases. Ann Clin Biochem. 46:38–43. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Tian L, Wang Y, Xu D, Gui J, Jia X, Tong
H, Wen X, Dong Z and Tian Y: Serological AFP/Golgi protein 73 could
be a new diagnostic parameter of hepatic diseases. Int J Cancer.
129:1923–1931. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Ye JZ, Yan SM, Yuan CL, Wu HN, Zhang JY,
Liu ZH, Li YQ, Luo XL, Lin Y and Liang R: GP73 level determines
chemo-therapeutic resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. J Cancer. 9:415–423. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
148
|
Lebredonchel E, Houdou M, Potelle S, de
Bettignies G, Schulz C, Krzewinski Recchi MA, Lupashin V, Legrand
D, Klein A and Foulquier F: Dissection of TMEM165 function in Golgi
glycosylation and its Mn2+ sensitivity. Biochimie.
165:123–130. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Lee JS, Kim MY, Park ER, Shen YN, Jeon JY,
Cho EH, Park SH, Han CJ, Choi DW, Jang JJ, et al: TMEM165, a Golgi
transmembrane protein, is a novel marker for hepatocellular
carcinoma and its depletion impairs invasion activity. Oncol Rep.
40:1297–1306. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Lee SH, Yoo HJ, Rim DE, Cui Y, Lee A, Jung
ES, Oh ST, Kim JG, Kwon OJ, Kim SY and Jeong SW: Nuclear expression
of GS28 protein: A novel biomarker that predicts prognosis in
colorectal cancers. Int J Med Sci. 14:515–522. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Cho U, Kim HM, Park HS, Kwon OJ, Lee A and
Jeong SW: Nuclear expression of GS28 protein: A novel biomarker
that predicts worse prognosis in cervical cancers. PLoS One.
11:e01626232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Rodriguez JL, Gelpi C, Thomson TM, Real FJ
and Fernández J: Anti-golgi complex autoantibodies in a patient
with Sjögren syndrome and lymphoma. Clin Exp Immunol. 49:579–586.
1982.
|
|
153
|
Fritzler MJ, Etherington J, Sokoluk C,
Kinsella TD and Valencia DW: Antibodies from patients with
autoimmune disease react with a cytoplasmic antigen in the Golgi
apparatus. J Immunol. 132:2904–2908. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Hong HS, Morshed SA, Tanaka S, Fujiwara T,
Ikehara Y and Nishioka M: Anti-Golgi antibody in rheumatoid
arthritis patients recognizes a novel antigen of 79 kDa (doublet)
by western blot. Scand J Immunol. 36:785–792. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Gentric A, Blaschek M, Julien C, Jouquan
J, Pennec Y, Berthelot JM, Mottier D, Casburn-Budd R and Youinou P:
Nonorgan-specific autoantibodies in individuals infected with type
1 human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol.
59:487–494. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Griffith KJ, Chan EK, Lung CC, Hamel JC,
Guo X, Miyachi K and Fritzler MJ: Molecular cloning of a novel
97-kd Golgi complex autoantigen associated with Sjögren's syndrome.
Arthritis Rheum. 40:1693–1702. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Gaspar ML, Marcos MA, Gutierrez C, Martin
MJ, Bonifacino JS and Sandoval IV: Presence of an autoantibody
against a Golgi cisternal membrane protein in the serum and
cerebrospinal fluid from a patient with idiopathic late onset
cerebellar ataxia. J Neuroimmunol. 17:287–299. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Huidbüchel E, Blaschek M, Seigneurin JM,
Lamour A, Berthelot JM and Youinou P: Anti-organelle and
anti-cytoskeletal autoantibodies in the serum of Epstein-Barr
virus-infected patients. Ann Med Interne (Paris). 142:343–346.
1991.
|
|
159
|
Paraná R, Schinoni MI, de Freitas LA,
Codes L, Cruz M, Andrade Z and Trepo C: Anti-Golgi complex
antibodies during pegylated-interferon therapy for hepatitis C.
Liver Int. 26:1148–1154. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Mozo L, Simó A, Suarez A, Rodrigo L and
Gutiérrez C: Autoantibodies to Golgi proteins in hepatocellular
carcinoma: Case report and literature review. Eur J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 14:771–774. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Fritzler MJ, Hudson M, Choi MY, Mahler M,
Wang M, Bentow C, Milo J and Baron M; Canadian Scleroderma Research
Group: Bicaudal D2 is a novel autoantibody target in systemic
sclerosis that shares a key epitope with CENP-A but has a distinct
clinical phenotype. Autoimmun Rev. 17:267–275. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Xue F, Wen Y, Wei P, Gao Y, Zhou Z, Xiao S
and Yi T: A smart drug: A pH-responsive photothermal ablation agent
for Golgi apparatus activated cancer therapy. Chem Commun (Camb).
53:6424–6427. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Li H, Zhang P, Luo J, Hu D, Huang Y, Zhang
ZR, Fu Y and Gong T: Chondroitin sulfate-linked prodrug
nanoparticles target the Golgi apparatus for cancer metastasis
treatment. ACS Nano. 13:9386–9396. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Zappa F, Failli M and De Matteis MA: The
Golgi complex in disease and therapy. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
50:102–116. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Borck G, Mollà-Herman A, Boddaert N,
Encha-Razavi F, Philippe A, Robel L, Desguerre I, Brunelle F,
Benmerah A, Munnich A and Colleaux L: Clinical, cellular, and
neuropathological consequences of AP1S2 mutations: Further
delineation of a recognizable X-linked mental retardation syndrome.
Hum Mutat. 29:966–974. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Ammann S, Schulz A, Krägeloh-Mann I,
Dieckmann NM, Niethammer K, Fuchs S, Eckl KM, Plank R, Werner R,
Altmüller J, et al: Mutations in AP3D1 associated with
immunodeficiency and seizures define a new type of Hermansky-Pudlak
syndrome. Blood. 127:997–1006. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Lu J, Tiao G, Folkerth R, Hecht J, Walsh C
and Sheen V: Overlapping expression of ARFGEF2 and Filamin A in the
neuroependymal lining of the lateral ventricles: Insights into the
cause of periventricular heterotopia. J Comp Neurol. 494:476–484.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Vogt G, El Choubassi N, Herczegfalvi Á,
Kölbel H, Lekaj A, Schara U, Holtgrewe M, Krause S, Horvath R,
Schuelke M, et al: Expanding the clinical and molecular spectrum of
ATP6V1A related metabolic cutis laxa. J Inherit Metab Dis. Dec
15–2020.Online ahead of print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Pflieger LT, Dansithong W, Paul S, Scoles
DR, Figueroa KP, Meera P, Otis TS, Facelli JC and Pulst SM: Gene
co-expression network analysis for identifying modules and
functionally enriched pathways in SCA2. Hum Mol Genet.
26:3069–3080. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Shestakova A, Zolov S and Lupashin V: COG
complex-mediated recycling of Golgi glycosyltransferases is
essential for normal protein glycosylation. Traffic. 7:191–204.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Jensson BO, Hansdottir S, Arnadottir GA,
Sulem G, Kristjansson RP, Oddsson A, Benonisdottir S, Jonsson H,
Helgason A, Saemundsdottir J, et al: COPA syndrome in an Icelandic
family caused by a recurrent missense mutation in COPA. BMC Med
Genet. 18:1292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Han C, Alkhater R, Froukh T, Minassian AG,
Galati M, Liu RH, Fotouhi M, Sommerfeld J, Alfrook AJ, Marshall C,
et al: Epileptic encephalopathy caused by mutations in the guanine
nucleotide exchange factor DENND5A. Am J Hum Genet. 99:1359–1367.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Dupuis N, Fafouri A, Bayot A, Kumar M,
Lecharpentier T, Ball G, Edwards D, Bernard V, Dournaud P, Drunat
S, et al: Dymeclin deficiency causes postnatal microcephaly,
hypomyelination and reticulum-to-Golgi trafficking defects in mice
and humans. Hum Mol Genet. 24:2771–2783. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Utine GE, Taşkıran EZ, Koşukcu C,
Karaosmanoğlu B, Güleray N, Doğan ÖA, Kiper PÖ, Boduroğlu K and
Alikaşifoğlu M: HERC1 mutations in idiopathic intellectual
disability. Eur J Med Genet. 60:279–283. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Xing G, Yao J, Wu B, Liu T, Wei Q, Liu C,
Lu Y, Chen Z, Zheng H, Yang X and Cao X: Identification of OSBPL2
as a novel candidate gene for progressive nonsyndromic hearing loss
by whole-exome sequencing. Genet Med. 17:210–218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Dupuis N, Lebon S, Kumar M, Drunat S,
Graul-Neumann LM, Gressens P and El Ghouzzi V: A novel RAB33B
mutation in Smith-McCort dysplasia. Hum Mutat. 34:283–286. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
Kondo Y, Fu J, Wang H, Hoover C, McDaniel
JM, Steet R, Patra D, Song J, Pollard L, Cathey S, et al: Site-1
protease deficiency causes human skeletal dysplasia due to
defective inter-organelle protein trafficking. JCI Insight.
3:e1215962018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
178
|
Carvalho DR, Speck-Martins CE, Brum JM,
Ferreira CR and Sobreira NLM: Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia with
elevated plasma lysosomal enzymes caused by homozygous variant in
MBTPS1. Am J Med Genet A. 182:1796–1800. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Ng BG, Asteggiano CG, Kircher M,
Buckingham KJ, Raymond K, Nickerson DA, Shendure J, Bamshad MJ;
University of Washington Center for Mendelian Genomics; Ensslen M
and Freeze HH: Encephalopathy caused by novel mutations in the
CMP-sialic acid transporter, SLC35A1. Am J Med Genet A.
173:2906–2911. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Dörre K, Olczak M, Wada Y, Sosicka P,
Grüneberg M, Reunert J, Kurlemann G, Fiedler B, Biskup S, Hörtnagel
K, et al: A new case of UDP-galactose transporter deficiency
(SLC35A2-CDG): Molecular basis, clinical phenotype, and therapeutic
approach. J Inherit Metab Dis. 38:931–940. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Wei J, Zhang YY, Luo J, Wang JQ, Zhou YX,
Miao HH, Shi XJ, Qu YX, Xu J, Li BL and Song BL: The GARP complex
is involved in intracellular cholesterol transport via targeting
NPC2 to lysosomes. Cell Rep. 19:2823–2835. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|